2020090 光纤光学(中英文)(2011)
- 格式:doc
- 大小:72.50 KB
- 文档页数:6

光学专业词汇大全Iris – aperture stop虹膜孔俓光珊retina视网膜Color Blind 色盲weak color 色弱Myopia – near-sighted 近视Sensitivity to Light感光灵敏度boost推进lag behind落后于Hyperopic – far-sighted 远视Dynamic Range 动态范围critical fusion frequency 临界融合频率CFF临界闪变频率visual sensation视觉Chromaticity Diagram色度图Color Temperature色温HSV Model色彩模型(hue色度saturation饱和度value纯度CIE Model 相干红外能量模式Complementary Colors补色Bar Pattern条状图形Heat body 热稠化approximate近似violet紫罗兰Body Curve人体曲线Color Gamut色阶adjacent邻近的normal illumination法线照明Primary colors红黄蓝三原色Color saturation色饱和度Color Triangle颜色三角Color Notation颜色数标法Color Difference色差TV Signal Processing电视信号处理Gamma Correction图像灰度校正Conversion Tables换算表out of balance失衡wobble摇晃back and forth前后clear (white) panel 白光板vibrant震动fuzzy失真quantum leap量子越迁SVGA (800x600)derive from起源自culprit犯人render呈递inhibit抑制,约束stride大幅前进blemish污点obstruction障碍物scratch刮伤substance物质实质主旨residue杂质criteria标准parameter参数adjacent邻近的接近的asynchrony异步cluster串群mutually互助得algorithm运算法则Chromatic Aberrations色差Fovea小凹Visual Acuity视觉灵敏度Contrast Sensitivity对比灵敏度Temporal (time) Response反应时间rendition表演,翻译animation活泼又生气ghost重影Parallax视差deficient缺乏的不足的Display panel显示板NG.( Narrow Gauge)窄轨距dichroic mirror二色性的双色性的Brewster Angle布鲁斯特角Polarized Light极化光Internal reflection 内反射Birefringence 双折射Extinction Ratio 消光系数Misalignment 未对准Quarter Waveplates四分之一波片blemish污点瑕疵Geometric几何学的ripple波纹capacitor电容器parallel平行的他tantalum钽(金属元素) exsiccate使干燥exsiccate油管,软膏furnace炉子镕炉electrolytic电解的,由电解产生的module 模数analog类似物out of the way不恰当pincushion针垫拉lateral侧面得rectangle长方形fixture固定设备control kit工具箱DVI connector DVI数局线Vertical垂直的horizontal 水平的interlace隔行扫描mullion竖框直楞sawtooth锯齿toggle套索钉keypad数字按键键盘tangential切线diagnostic tool诊断工具sagittal direction径向的cursor position光标位置3Yw'/#p3`ray aberration光线相差weighting factor权种因子variables变量for now暂时,目前.眼下check box复选框Airy disk艾里斑exit pupil出[射光]瞳optical path difference光称差with respect to关于diffraction limited 衍射极限wavefront aberration波阵面相差spherical aberration球面象差paraxial focus傍轴焦点chromatic aberration象差local coordinate system局部坐标系统coordinate system坐标系orthogonal直角得,正交的conic sections圆锥截面account for解决,得分parabolic reflector拋物面反射镜radius ofcurvature曲率半径spherical mirror球面镜geometrical aberration几何相差incident radiation入射辐射global coordinate总体坐标in terms of根据按照reflected beam反射束FYI=for your information供参考Constructive interference相长干涉phase difference相差achromatic singlet消色差透镜Interferometer 干涉仪boundary constraint边界约束,池壁效应radii半径Zoom lenses变焦透镜Beam splitters分束器discrete不连续的,分离的objective/eye lens物镜/目镜mainframe主机rudimentary根本的,未发展的photographic照相得摄影得taxing繁重的,费力得algebra代数学trigonometry三角学geometry几何学calculus微积分学philosophy哲学lagrange invariant拉格朗日不变量spherical球的field information场信息Standard Lens标准透镜Refracting Surface折射面astigmatism散光HDTV高清晰度电视DLV ( Digital Light Valve)数码光路真空管,简称数字光阀diffraction grating衍射光珊field angle张角paraxial ray trace equations近轴光线轨迹方称back focal length后焦距principal plane主平面vertex顶点,最高点astigmatism散光,因偏差而造成的曲解或错判medial中间的,平均的variance不一致conic圆锥的,二次曲线field of view视野collimator瞄准仪convolution回旋.盘旋,卷积fuzzy失真,模糊aberrated异常的asymmetry不对称得indicative可表示得parabolic拋物线得suffice足够,使满足specification规格,说明书straightforward易懂的,直接了当的,solidify凝固,巩固. Constraints 约束,限制metrology度量衡field coverage视场,视野dictate口述, 口授, 使听写, 指令, 指示, 命令, 规定irradiance发光, 光辉,辐照度aerial空气得,空中得halide卤化物的monochromatic单色的,单频的polychromatic多色的aspherical非球面的spherical球面的alignment列队,结盟power(透镜)放大率equiconvergence 同等收敛EFL(effective focal length)有效焦距workhorse广为应用的设备biconvex两面凸的global optimization整体最优化concave凹得,凹面得cylindrical圆柱得solid model实体模型Modulation Transfer Function调制传递函数in the heat of在最激烈的时候protocol协议,规定triplet三重态sanity心智健全zinc锌,涂锌的selenide 硒化物,硒醚miscellaneous各色各样混在一起, 混杂的, 多才多艺的versus与...相对polynomial多项式的coefficient系数explicit function显函数" wYgi%distinct清楚的,截然不同的emanate散发, 发出, 发源rudimentary根本的,未发展的intersection角差点PRTE=paraxial ray trace equation旁轴光线轨迹方程achromats 消色差透镜cardinal points基本方位separations分色片dashed虚线blow up放大overlay覆盖,覆盖图multiplayer 多层的humidity 湿度float glass浮法玻璃square one 出发点,端点square up to 准备开打,坚决地面对reflecting telescope 反射式望远镜diagnostic tools诊断工具Layout plots规划图Modulation transfer function调制转换功能FFT快速傅里叶变换Point spread function点传播功能wavelength波长angle角度absorption吸收system aperture 系统孔径lens units透镜单位wavelength range波长范围singlet lens单业透镜spectrum光谱diffraction grating衍射光栅asphere半球的LDE=Lens data editor Surface radius of curvature表面曲率半径surfacethickness表面厚度material type材料种类semi-diameter半径focal length焦距aperture type孔径类型aperture value孔径值field of view视场microns微米F, d, and C= blue hydrogen, yellow helium, red hydrogen lines, primary wavelength主波长sequential mode连续模式object surface物表面The front surface of the lens透镜的前表面stop光阑The back surface of the lens透镜的后表面The image surface 像表面symmetric相对称的biconvex两面凸的The curvature is positive if the center of curvature of the surface is to the right of the vertex. It is negative if the center of curvature is to the left of the vertex.如果曲率中心在最高点的右边,曲率值为正,如果曲率中心在最高点的左边,则曲率为负image plane像平面Ray Aberration光线相差tangential direction切线方向sagittal direction径向paraxial focus旁轴的Marginal 边缘的spherical aberration球面像差Optimization Setup最优化调整variable变量mathematical sense 数学角度MFE= Merit Function Editor, Adding constraints增加约束focal length焦矩长度operand操作数the effective focal length有效焦矩primary wavelength主波长initiate开始spot diagram位图表Airy disk 艾里斑axial chromatic aberration轴向色差with respect to关于至于exit pupil出射光瞳OPD=optical path difference光学路径差diffraction limited衍射极限chromatic aberration色差chromatic focal shift色焦距变换paraxial focus傍轴焦点axial spherical aberration轴向球差(longitudinal spherical aberration 纵向球差:沿光轴方向度量的球差)lateral spherical aberration垂轴球差(在过近轴光线像点A‵的垂轴平面内度量的球差)coma、comatic aberration彗差meridional coma子午彗差sagittal coma弧矢彗差astigmatism像散local coordinate system本地坐标系统meridional curvature of field子午场曲sagittal curvature of field弧矢场曲decentered lens偏轴透镜orthogonal直角的垂直的conic section圆锥截面account for说明,占有,得分stigmatic optical system无散光的光学系统Newtonian telescope牛顿望远镜parabolic reflector抛物面镜foci焦距chromatic aberration,色差superpose重迭parabola抛物线spherical mirror球面镜RMS=Root Mean Square均方根wavefront波阵面spot size光点直径Gaussian quadrature高斯积分rectangular array矩阵列grid size磨粒度PSF=Point Spread Function点扩散函数FFT=Fast Fourier Transform Algorithm快速傅里叶变换Cross Section横截面Obscurations昏暗local coordinates局部坐标系统vignette把…印为虚光照Arrow key键盘上的箭头键refractive折射reflective反射in phase同相的协调的Ray tracing光线追迹diffraction principles衍射原理order effect式样提出的顺序效果energy distribution能量分配Constructive interference相长干涉dispersive色散的Binary optics二元光学phase advance相位提前achromatic single消色差单透镜diffractive parameter衍射参数Zoom lenses变焦透镜Athermalized lenses绝热透镜Interferometers干涉计Beam splitter分束器Switchable component systems可开关组件系统common application通用symmetry对称boundary constraint边界约束multi-configuration (MC) MC Editor (MCE) perturbation动乱,动摇index accuracy折射率准确性indexhomogeneity折射率同种性index distribution折射率分配abbe number离差数Residual剩余的Establishing tolerances建立容差figure of merit质量因子tolerance criteria公差标准Modulation Transfer Function (MTF)调制传递函数boresight视轴,瞄准线Monte Carlo蒙特卡洛Tolerance operands误差操作数conic constant ]MC1"{_qT圆锥常数astigmatic aberration像散误差Mechanical tilt机械倾斜,机械倾角Tolerance Data Editor (TDE)公差资料编辑器compensator补偿棱镜estimated system performance预估了的系统性能iteratively反复的,重迭的statistical dependence统计相关性sequential ray trace model连续光线追迹模型imbed埋葬,埋入multiple多样的,多重的,若干的Non-Sequential Components不连续的组件Corner cube角隅棱镜,三面直角透镜Sensitivity Analysis灵敏度分析Faceted reflector有小面的反射镜emit发射,发出nest嵌套overlap交迭outer lens外透镜brute force强力seidel像差系数aspect ratio长宽比MRA边缘光线角MRH边缘光线高度asynchronous不同时的,异步Apodization factor变迹因子hexapolar六角形dithered 高频脉冲衍射调制传递函数(DMTF),衍射实部传递函数(DRTF),衍射虚部传递函数(DITF),衍射相位传递函数(DPTF),方波传递函数(DSWM)logarithmic对数的parity奇偶% Uc,I elongitudinal aberrations 纵向像差赛得系数: 球差(SPHA,SI),彗差(COMA,S2),像散(ASTI,S3),场曲(FCUR,S4),畸变(DIST,S5),轴向色差(CLA,CL)和横向色差(CTR,CT).横向像差系数:横向球差(TSPH),横向弧矢彗差(TSCO),横向子午彗差(TTCO),横向弧矢场曲(TSFC),横向子午场曲(TTFC),横向畸变(TDIS)横向轴上色差(TLAC)。


光纤英语单词单词:fiber(光纤)1. 定义与释义1.1词性:名词1.2释义:一种细长的、可用于传输光信号的纤维材料,是现代通信等领域的重要组成部分。
1.3英文解释:A long, thin, flexible thread - like structure, especially one made of glass or plastic, which can be used for transmitting light signals.1.4相关词汇:fibre(英式拼写,同义词),optical fiber(同指光纤,完整表述),fiber - optic(形容词形式,光纤的)。
2. 起源与背景2.1词源:“fiber”源自拉丁语“fibra”,原意为“纤维、细丝”。
随着科技发展,这种材料在光学通信领域的应用日益广泛,逐渐特指用于传输光信号的光纤。
2.2趣闻:最初研究光纤时,科学家们面临着如何在细长的玻璃纤维中实现光的高效传输且减少损耗的难题。
经过无数次的试验和改进,才使得光纤能够广泛应用于现代通信,就像从一根简单的玻璃丝发展成为信息高速公路的基石。
3. 常用搭配与短语3.1短语:(1) fiber optics:光纤技术例句:The development of fiber optics has revolutionized themunication industry.翻译:光纤技术的发展使通信行业发生了革命性的变化。
(2) fiber cable:光纤电缆例句:The fiber cable is being laid underground for the new network.翻译:为了新的网络正在地下铺设光纤电缆。
(3) single - mode fiber:单模光纤例句:Single - mode fiber is often used in long - distancemunication.翻译:单模光纤常用于长距离通信。

激光、光电、光学词汇中英文对照1. 激光(Laser)2. 光电效应(Photoelectric Effect)3. 光学(Optics)4. 光纤(Fiber Optic)5. 光谱(Spectrum)6. 折射率(Refractive Index)7. 透镜(Lens)8. 反射(Reflection)9. 干涉(Interference)10. 衍射(Diffraction)11. 偏振(Polarization)12. 激光切割(Laser Cutting)13. 激光焊接(Laser Welding)14. 光电探测器(Photoelectric Detector)15. 光电传感器(Photoelectric Sensor)16. 光学显微镜(Optical Microscope)17. 光学望远镜(Optical Telescope)18. 光学镜头(Optical Lens)19. 光学滤波器(Optical Filter)20. 光学编码器(Optical Enr)21. 光学通信(Optical Communication)22. 光学存储(Optical Storage)24. 光学子系统(Optical Subsystem)25. 光学设计(Optical Design)26. 光学加工(Optical Fabrication)27. 光学镀膜(Optical Coating)28. 光学检测(Optical Inspection)29. 光学成像(Optical Imaging)30. 光学治疗(Optical Therapy)31. 光学材料(Optical Materials)32. 光学元件(Optical Elements)33. 光学路径(Optical Path)34. 光学平台(Optical Platform)35. 光学子件(Optical Component)36. 光学连接器(Optical Connector)37. 光学开关(Optical Switch)38. 光学调制器(Optical Modulator)39. 光学衰减器(Optical Attenuator)40. 光学放大器(Optical Amplifier)41. 光学显示器(Optical Display)42. 光学子午线(Optical Meridian)43. 光学分辨率(Optical Resolution)44. 光学畸变(Optical Distortion)45. 光学厚度(Optical Thickness)46. 光学密度(Optical Density)48. 光学干涉仪(Optical Interferometer)49. 光学相干断层扫描(Optical Coherence Tomography)50. 光学扫描器(Optical Scanner)51. 光学跟踪(Optical Tracking)52. 光学遥感(Optical Remote Sensing)53. 光学成像系统(Optical Imaging System)54. 光学跟踪系统(Optical Tracking System)55. 光学定位系统(Optical Positioning System)56. 光学子午仪(Optical Meridian Instrument)57. 光学补偿器(Optical Compensator)58. 光学补偿器(Optical Corrector)59. 光学基准(Optical Reference)60. 光学基准面(Optical Reference Plane)这些词汇涵盖了激光、光电和光学领域的基本概念、技术和设备。

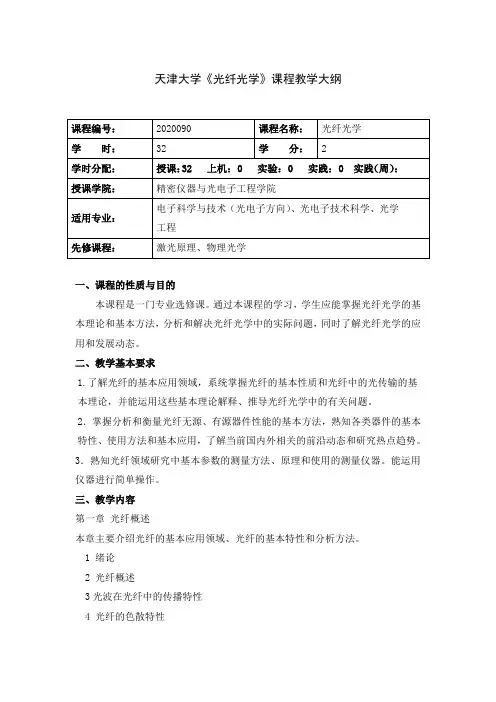
天津大学《光纤光学》课程教学大纲课程编号:2020090 课程名称:光纤光学学时:32 学分: 2学时分配:授课:32 上机: 0 实验: 0 实践: 0 实践(周):授课学院:精密仪器与光电子工程学院适用专业:电子科学与技术(光电子方向)、光电子技术科学、光学工程先修课程:激光原理、物理光学一、课程的性质与目的本课程是一门专业选修课。
通过本课程的学习,学生应能掌握光纤光学的基本理论和基本方法,分析和解决光纤光学中的实际问题,同时了解光纤光学的应用和发展动态。
二、教学基本要求1.了解光纤的基本应用领域,系统掌握光纤的基本性质和光纤中的光传输的基本理论,并能运用这些基本理论解释、推导光纤光学中的有关问题。
2.掌握分析和衡量光纤无源、有源器件性能的基本方法,熟知各类器件的基本特性、使用方法和基本应用,了解当前国内外相关的前沿动态和研究热点趋势。
3.熟知光纤领域研究中基本参数的测量方法、原理和使用的测量仪器。
能运用仪器进行简单操作。
三、教学内容第一章光纤概述本章主要介绍光纤的基本应用领域、光纤的基本特性和分析方法。
1 绪论2 光纤概述3光波在光纤中的传播特性4 光纤的色散特性5 光纤的损耗6单模光纤中的非线性效应第二章光无源器件本章主要介绍光纤光学中常用的光无源器件,分析各类器件的基本原理和特性、衡量指标以及典型应用。
1光纤连接器2光纤耦合器3 偏振控制器4光隔离器)5 光滤波器/复用器第三章光有源器件本章主要介绍光纤光学中基本的光有源器件及其典型应用,分析各类器件的原理、特性。
1 光调制器2光放大器3 光纤激光器第四章故障诊断和测试设备简介本章主要介绍光纤光学中常见参数的测量方法和常用的测量仪器。
1 光功率测量2 波长和频率测量3 时间测量4 信号质量测量5 光时域反射计四、学时分配五、评价与考核方式平时成绩10%,期末成绩90%六、教材与主要参考资料1.《光纤光学》,廖延彪编著,清华大学出版社,19992.《光纤光学》,Jeff. Hecht 著,贾东方等译,人民邮电出版社, 20043.《光无源器件》,林学煌等编著,人民邮电出版社,19984.《光通信器件与系统》,J. H. Franz 著,徐宏杰等译,北京电子工业出版社,20025.Fiber-Optic Communication Systems, G. P. Agrawal,A John wiley & Sons, Inc.Publication,2002TU Syllabus for Fiber OpticsCode: 2020090Title: Fiber Optics Semester Hours: 32 Credits: 2Semester Hour Structure Lecture:32 Computer Lab:Experiment:Practice:Practice (Week):Offered by:College of precision instrument and opto-electronicsengineeringfor: Electronic science and technology (optoelectronics); opto-electronic technology science; information engineeringPrerequisite: Laser principle, physical optics1. ObjectiveWe start by covering the basics of fiber optics theories, fiber structures and characteristics. Light propagation through multi-mode and single-mode optical fibers is studied, including the effects of dispersion, attenuation and nonlinear effects. The passive and active optical fiber components are also covered extensively, including the basic principles, parameters and applications. The last part of the course focused on instruments usually used in fiber systems.2. Course DescriptionThis course is a specialized optional course. This course covers the fundamentals of fiber optics. Its goal is to help students develop a thorough understanding of the underlying physical principles and possess analytical ability to deal with problems of fiber systems. Students are also expected to know applications and developmental tendency of fiber optics.3. TopicsChapter 1 Introduction1 Introduction of fiber2 Light propagation in fibers3 Group-velocity dispersion4 Fiber losses5 Nonlinear effects in fibersChapter 2 Passive fiber devices1 Fiber connectors2 Fiber couplers3 Polarization controllers4 Optical isolators5 Optical filtersChapter 3 Active fiber devices1 Optical modulators2 Optical Amplifiers3 Optical fiber lasersChapter 4 Instruments in fiber systems1 Optical power measurements2 Wavelength and frequency measurements3 Time measurements4 Signal quality measurements5 OTDR4. Semester Hour StructureHomework 10%, Final exam 90%6. Text-Book & Additional Readings1. Fiber optics, Liao Yanbiao, Tsinghua University Press, 19992. Fiber optics, Jeff. Hecht, People postal Press, 20043. Passive fiber devices, Lin Xuehuang, People postal Press, 19984. Optical communications components and systems, J. H. Franz, Beijing electronic industry Press, 20025.Fiber-Optic Communication Systems, G. P. Agrawal,A John wiley & Sons, Inc.Publication,2002。

光通信中英文比照通过整理的光通信中英文比照相关文档,渴望对大家有所扶植,感谢观看!光纤:optical fiber; fibergrat ing:光栅OFC :光缆GIF :渐变型光纤SIF:阶越型光纤DSF:色散位移光纤DCF:色散补偿光纤DFF:色散平坦光纤POF:塑料光纤(Plastic Optical Fiber)PCF:光子晶体光纤PANDA光纤:偏振保持光纤HNLF :高非线性光纤HCF:密封涂层光纤CCF:碳涂层光纤MCF :金属涂层光纤ECF:偏心光纤光纤阵列:fiber array; FA; FABU;BFA 光纤阵列模块:Fiber Array Block (FAB) AWG :阵列波导光栅FBT :熔融拉锥Coupler:耦合器平面波导型光分路器:PLC splitter熔融拉锥光纤分路器:Fused Fiber SplitterCW :连续Pump :泵浦Power :电源laser crystal:激光晶体PD:光电二极管LD :半导体激光器、激光二极管ILD :注入型半导体激光器LED :发光二极管Light Emitting DiodeDBR :分布式布拉格反射DFB :分布反馈DFB-LD :分布反馈式半导体激光器FP-LD:法布里-珀罗半导体激光器DSM-LD :动态单模半导体激光器SC:超连续光源(Super continuum)PA:前置放大器LA :线路放大器BA、PA:功率放大器OA :光放大器LNA :低噪声放大器OFA :光纤放大器SOA :半导体光放大器SRS:受激拉曼散射SRA(RFA):拉曼光纤放大器SBS:受激布里渊散射SBA :受激布里渊散射光纤放大器BRA(BFA):布里渊光纤放大器TDFA :掺铥光纤放大器(属掺杂稀土离子) EDFA :掺饵光纤放大器PDFA :掺错光纤放大器NDFA :掺铌光纤放大器IL :插入损耗RL :回波损耗EL :附加损耗TL :传输损耗PDL :偏振相关损耗BIL :弯曲附加损耗CR:分光比ER:消光比FL :匀整性PMD :偏振模色散、单模光纤中偏振色散EMB :有效模式带宽OFL :满注入带宽OM :光模式Optical ModeMFD :模场直径Isolator :隔离器Coupler:耦合器Connector:连接器Splitter :分路器Collimator :准直器Optical switch :光开关Attenuator :衰减器Modulator :调制器Filter :滤波器Receive :接收器OC :光载体、光纤载波CW :载波carrier waveOLT :光缆终端设备、局端机房设备ODN :光配线网络ONU :光节点、光网络单元ONT:光网络终端OTN :光传送网OTM :光终端复用器OUT:光转发器OTU :波长转换器OSU:光用户单元OXC :光交换节点ODF :光纤配线架DDF:数字配线架OT:输出终端PCM:电端机CO:中心局3U :超高速、超大容量、超长距离OAN :光纤接入网LAN :局域网MAN :城域网高速短距离的光纤通信系统WAN :广域网Metro networks :地下网路Ethernet:以太网Network :网络CUN :可持续网络NGN :下一代网络NPN :新公众网UN :一体化网ASON :自动交换光网络OAN :光接入网PON:无源光网络WDMPON :波分复用型无源光网络CDMA PON :码分多址型无源光网络PSPON:功率分割型无源光网络APON :BPON :宽带无源光网络Broadba nd PON EPON:以太无源光网络Ethernet PON GPO N:吉比特无源光网络Gigabit PONTDM :时分复用OTDM :光时分复用OADM :光分插复用(Optical Add-DropMultiplexer)CDM :码分复用FDM :频分复用WDM :波分复用Wavelength :波长Division :分开Multiplexer :多路(复用)器DWDM :密集波分复用CWDM :粗波分复用FWDM :滤波片式波分复用器HWDM :高隔离度波分复用器CDMA :码分多址(Code-division multiple access) SDMA :空分多址MUX :多路复用(multiplex)DEMUX :解复用(de-multiplex)GFF:增益平坦滤波器(gain flattening filter)bit :二进制位、比特Byte:字节、8位元组1字节=8比特ban dwidth :带宽、频宽baud:波特率bps (bit per second) : bit/sDFG :差频3R再生:再放大、再整形、再定时2R再生:再整形、再定时1R再生:再放大REG:再生器XGM :交叉增益调制XPM :交叉相位调制FWM :四波混频TOBPF:带通滤波器SPN::节点共享式SPL:链路共享式RZ:归零码NRZ :不归零码ASK :幅移键控FSK:频移键控PSK:相移键控IM-DD :强度调制-干脆检测PC:偏振限制器OC:光环形器PBS:偏振分束器GEQ :增益平坦器MTBF :平均无故障时间match gel:匹配液CamSplice:光纤接续子OTDR :光时域反射器ESA :激发态吸取DGD :微分群时延FTTH :光纤至U户Fiber To The Home FTTB :光纤到大楼FTTC :光纤到路边VOD :视频点播IPTV :即交互式网络电视CATV :有线电视网(接受模拟传输方式)Adapter:适配器connector:连接器Atte nu ator:衰减器Isolator:隔离器Transceive:收发器Coupler:耦合器光耦合器(OC)FIC :快速连接头field in stallable connector V-groove: V 型槽Source:源lamp-house:(仪器上的)光源Power Meter:功率计Photoelectric detector:光电探测器optical switch:光开关FVW :电子显微镜Adhesive:胶粘剂Optical Adhesive:光学胶黏剂Sett ing:测试I/O:开/关Bare:赤裸Bare Fiber :裸纤Ribbon Fiber :带状光纤Loose :宽松Tube:管Loose Tube : 松套管Tight :紧的Buffer :缓冲层Tight Buffer :紧缓冲层sin gle :单dual :双Multi- mode 多模Standard :标准storage:储存temperature 温度loss :损耗Fan-Out:输出端In put :输入Output:输出Special :特殊的Other :其他TLC :泰尔认证ITU-T :国际电信联盟远程通信标准化组织IEC :国际电工委员会ISO :国际标准化组织GB/T :举荐性国家标准Package :包装Dimension :尺寸Port :端口Type :类型Length :长度None :没有Six-axes stage六维微调架Backstop :支架Fixi ng :固定Precision:精密optical part :光学零件Side Pull :侧拉LSZH :聚烯烃PE :聚乙烯PVC :聚氯乙烯Metal : 属Steel :钢铁Stai nless Steel :不锈钢Plastic :塑胶PMMA :亚克力或者亚加力、有机玻璃。

光纤光学字母-回复什么是光纤光学?光纤光学是一种光信号传输技术,利用光纤作为光信号的传输介质。
光纤由光导纤维构成,光信号通过光波的传播来实现信息的传输。
光纤光学是光学通信领域的关键技术之一,已广泛应用于电话通信、互联网、电视等领域。
一、光纤光学的发展历程光纤光学的发展可以追溯到19世纪末,当时科学家开始研究光的传播性质。
然而,直到20世纪60年代,光纤光学技术才逐渐成熟并开始应用于通信领域。
1970年,发明了第一根低损耗光纤。
1980年代,光纤光学通信技术得到了迅速发展,高品质、高速率的光纤通信网络开始广泛部署。
二、光纤光学的工作原理光纤光学的工作原理可以简单概括为光信号的传输和调制解调。
光信号通过光纤传输时,会发生光波的折射和反射。
光波的传输过程中,会受到多种因素的影响,如色散、衰减等。
因此,光纤的设计和制造需要考虑这些因素,以提高信号传输的质量和效率。
在光纤光学通信系统中,光信号通过发光二极管(LED)或半导体激光器产生。
光信号经过调制器调制成数字信号,然后通过光纤传输到接收端。
接收端通过接收器将光信号解调成原始的数字信号,然后再进行处理和解码。
三、光纤光学的优点光纤光学比传统的铜质电缆有许多优点。
首先,光纤光学传输的带宽更大,传输速度更快。
其次,光纤光学的信号传输不受电磁干扰的影响,更稳定可靠。
此外,光纤光学的传输距离更远,可以覆盖更大的范围。
最后,光纤光学的体积较小,更便于布线和安装。
这些优点使得光纤光学在现代通信技术中得到广泛应用。
崇尚高速和稳定的互联网、高清晰度的数字电视、高品质的电话通信等,都离不开光纤光学的支持。
四、光纤光学的应用领域光纤光学广泛应用于不同领域。
在通信领域,光纤光学用于光纤通信网络的构建,实现高速和稳定的数据传输。
在医疗领域,光纤光学被用于内窥镜和激光手术等医疗设备中,实现无创伤的检查和治疗。
在工业领域,光纤光学被用于检测设备和传感器中,实时监测温度、压力、湿度等参数。

光纤光学知识总结1. 引言光纤光学是一门研究光传输和操控的学科,它是现代通信、医学和工业等领域中不可或缺的关键技术。
光纤光学利用光纤作为传输介质,通过光的折射和全反射实现信号传输。
本文将对光纤光学的基本原理、传输性能和应用领域进行总结和介绍。
2. 光纤的基本原理光纤是一种通过内部光的全反射实现光信号传输的介质。
它由一个中心芯和一个外包层组成。
中心芯是光信号传输的主要部分,通常由高折射率的玻璃或塑料材料构成。
外包层则是低折射率的材料,用于包裹和保护中心芯。
光纤通过光的折射和全反射,实现将光信号沿着光纤传输的目的。
3. 光纤的传输性能3.1 传输带宽光纤的传输带宽是指光纤能够传输的最大频率信号的能力。
它受到光纤的材料特性、设计和制造工艺等因素的影响。
高质量的光纤能够支持更高的传输带宽,从而实现更高速率、更大容量的数据传输。
3.2 传输损耗传输损耗是光信号在光纤中传输过程中的能量损失。
它由散射、吸收和弯曲等因素引起。
传输损耗通常以每单位长度的衰减值(dB/km)来表示。
光纤的传输损耗越低,传输距离就越长,信号质量就越好。
3.3 色散色散是指光信号在光纤中传输过程中,不同频率的光信号由于折射率的差异而传播速度不同的现象。
色散会导致光脉冲的展宽和失真,限制了光信号的传输距离和速率。
4. 光纤光学的应用领域4.1 光通信光通信是光纤光学的主要应用之一。
光纤光学的高带宽和低损耗特性使得光纤成为主流的长距离通信传输介质。
光纤通信系统通过调制光信号来传输数据,实现了高速率、大容量的信息传输。
4.2 医学影像光纤光学在医学影像领域有广泛的应用。
通过光纤的灵活性和小尺寸,可以将光信号传输到人体内部,实现光学成像和激光手术等应用。
例如,内窥镜和激光手术器械中都使用了光纤。
4.3 工业检测光纤光学在工业检测领域也具有重要的应用价值。
光纤传感器可以通过测量光的强度、相位和波长等参数,实现对温度、压力、液位等物理量的测量。
光纤传感器具有高精度、抗干扰和耐腐蚀等特点,被广泛应用于工业自动化和安全监测等领域。

A01光学材料:A01-001 光学材料Optical MaterialsA01-002 光学玻璃Optical GlassA01-003 激光玻璃Laser GlassA01-004 声光玻璃Acousto-Optic GlassA01-005 红外线玻璃Infrared GlassA01-006 红外线材料Infrared MaterialsA01-007 紫外线材料Ultraviolet MaterialsA01-008 石英镜片Fused Silica GlassA01-009 光学陶瓷CeramicsA01-010 矽半导体材料Silicon Semiconductor MaterialsA01-011 化合物半导体材料Compound Semiconductor Materials A01-012 光纤材料Fiber Optic MaterialsA01-013 光纤预型体Fiber Optic PreformsA01-014 PLZT晶圆,钛酸锆酸铅晶圆PLZT WafersA01-015 环氧树脂EpoxiesA01-016 声光光学晶体Acousto-Optic CrystalsA01-017 双折射/偏光晶体Birefringent and Polarizing Crystals A01-018 电光光学晶体Electro-Optic CrystalsA01-019 红外线晶体Infrared CrystalsA01-020 激光晶体(YAG) YAG Laser CrystalsA01-021 激光晶体(亚历山大) Alexandrite Laser CrystalsA01-022 激光晶体(GGG) GGG Laser CrystalsA01-023 激光晶体(GSGG,GSAG) GSGG GSAG Laser Crystals A01-024 激光晶体(YLF) YLF Laser CrystalsA01-025 激光晶体(其他) Other Laser CrystalsA01-026 非线性光学晶体Nonlinear CrystalsA01-027 有机光学材料Organic Optical MaterialsA01-028 萤光放射晶体Fluorescent Emission CrystalsA01-029 结晶育成材料Crystals Growing MaterialsA01-030 镀膜材料Coating MaterialsA01-031 光罩材料Photomask MaterialsA01-032 真空蒸镀化学药品Vaccum Evaporation ChemicalsA01-033 感光剂SensitizersA01-034 影像用材料Materials for ImagingA01-035 热色材料Thermochromic MaterialsA01-036 光色材料Photochromic MaterialsA01-037 稀土族材料Rare Earth MaterialsA01-038 光碟基板,基板材料Optical Disk Substrate Materials A01-039 光碟记录材料Optical Disk Data Storage MaterialsA02加工用其他材料:A02 加工用其他材料MATERIALS FOR PROCESSINGA02-001 光学用胶合剂/接著剂Optical Cements and Adhesives A02-002 光学用气体Gases for Optical ApplicationA02-003 激光用气体Gases for LasersA02-004 光学研磨材料(研磨布纸) Optical-Coated AbrasiveA02-005 光学研磨材料(砥粒) Optical-Powder or Grin Abrasive A02-006 光学研磨材料(砥石) Optical-Wheel AbrasiveA02-007 研磨化合物Polishing CompoundsA02-008 研磨衬垫及布Polishing Pads and ClothA02-009 全像底片及感光板Holographic Films and PlatesA02-010 红外线底片及感光板Infrared Films and PlatesA02-011 相片用化学药品Photographic Chemicals激光产品网A02-012 折射率液Refractive Index LiquidsA02-013 显微镜浸液Microscope Immerison LiquidsA02-014 显微镜埋置用材料Microscope Imbedding MediaA02-015 激光用染料Laser DyesA02-016 冷媒CoolantsA02-017 拭镜纸Lens TissueA03 显示器用材料:A03 显示器用材料MATERIALS FOR DISPLAYA03-001 液晶Liquid CrystalsA03-002 导电膜玻璃基板ITO Glass SubstrateA03-003 彩色滤光片Color FilterA03-004 偏光板/相位差板Polarizer/ Phase Shift LayerA03-005 显示面板用驱动IC Driver ICA03-006 背光源BacklightA03-007 配向膜Alignment FilmA03-008 间隔物SpacerB01 透镜:B01 透镜LENSESB01-001 单透镜Simple (Single) LensesB01-002 球透镜Ball LensesB01-003 歪像透镜Anamorphic LensesB01-004 圆锥透镜Conical LensesB01-005 柱状透镜,环形透镜Cylindrical & Toroidal LensesB01-006 非球面透镜Aspheric LensesB01-007 反射折射透镜Catadioptric LensesB01-008 绕射极限透镜Diffraction-Limited LensesB01-009 GRIN透镜GRIN Lenses (Graduated Refractive Index Rod)B01-010 微小透镜阵列Micro Lens ArraysB01-011 准直透镜Collimator LensesB01-012 聚光透镜Condenser LensesB01-013 多影像透镜Multiple Image LensesB01-014 傅利叶透镜Fourier Lenses B01-015 菲涅尔透镜Fresnel Lenses B01-016 替续透镜Relay LensesB01-017 大口径透镜(直径150mm以上) Large Aperture Lenses (150mm) B01-018 复合透镜Complex LensesB01-019 红外线透镜Infrared LensesB01-020 紫外线透镜Ultraviolet LensesB01-021 激光透镜Laser LensesB01-022 望远镜对物镜Telescope Objectives LensesB01-023 显微镜对物镜Microscope Objectives LensesB01-024 接目镜Eyepieces LensesB01-025 向场透镜Field LensesB01-026 望远镜头Telephoto LensesB01-027 广角镜头Wide Angle LensesB01-028 可变焦伸缩镜头Variable Focal Length Zoom LensesB01-029 CCTV镜头CCTV LensesB01-030 影印机镜头Copy Machine LensesB01-031 传真机镜头Facsimile LensesB01-032 条码扫描器镜头Bar Code Scanner LensesB01-033 影像扫描器镜头Image Scanner LensesB01-034 光碟机读取头透镜Pick-up Head LensesB01-035 APS相机镜头APS Camera LensesB01-036 数位相机镜头Digital Still Camera Lenses激光产品网B01-037 液晶投影机镜头Liquid Crystal Projector LensesB02 镜面:B02 镜面MIRRORB02-001 平面镜Flat MirrorsB02-002 球面凹面镜,球面凸面镜Spherical Concave and Convex Mirrors B02-003 抛物面镜,椭圆面镜Off-Axis Paraboloids and Ellipsoids Mirrors B02-004 非球面镜Aspheric MirrorsB02-005 多面镜Polygonal MirrorsB02-006 热镜Hot MirrorsB02-007 冷镜Cold MirrorsB02-008 玻璃,玻璃/陶瓷面镜Glass and Glass-Ceramic MirrorsB02-009 双色向面镜Dichroic MirrorB02-010 金属面镜Metal MirrorsB02-011 多层面镜Multilayer MirrorsB02-012 半涂银面镜Half-Silvered MirrorsB02-013 激光面镜Laser MirrorsB02-014 天文用面镜Astronomical MirrorsB02-099 其他面镜Other MirrorsB03 棱镜:B03 棱镜PRISMB03-001 Nicol棱镜Nicol PrismsB03-002 Glan-Thomson棱镜Glan-Thomson PrismsB03-003 Wollaston棱镜Wollaston PrismsB03-004 Rochon棱镜Rochon PrismsB03-005 直角棱镜Right-Angle; Rectangular PrismsB03-006 五面棱镜Pentagonal PrismsB03-007 脊角棱镜Roof PrismsB03-008 双棱镜BiprismsB03-009 直视棱镜Direct Vision PrismsB03-010 微小棱镜Micro PrismsB03-099 其他棱镜Other PrismsB04 滤光镜:B04 滤光镜FILTERB04-001 尖锐滤光镜Sharp Cut (off) FiltersB04-002 色温变换滤光镜,日光滤光镜Colour Conversion/Daylight Filters B04-003 干涉滤光镜Interference FiltersB04-004 中性密度滤光镜Neutral Density FiltersB04-005 空间/光学匹配滤光镜Spatial/Optical Matched FiltersB04-006 双色向滤光镜Dichroic FiltersB04-007 偏光滤光镜Polarizing FiltersB04-008 排除频带滤光镜Rejection Band FiltersB04-009 可调式滤光镜Turnable FilterB04-010 超窄频滤光镜Ultra Narrowband FiltersB04-011 色吸收滤光镜Absorption FiltersB04-012 红外吸收/反射滤光镜Infrared Absorbing/Reflecting FiltersB04-013 红外透过滤光镜Infrared Transmitting FiltersB04-014 紫外吸收滤光镜Ultraviolet Absorbing FiltersB04-015 紫外透过滤光镜Ultraviolet Transmitting FiltersB04-016 针孔滤光镜Pinhole FiltersB04-017 有色玻璃滤光镜Colored-Glass FiltersB04-018 塑胶滤光镜Plastic FiltersB04-019 照像用滤光镜Photographic Filters激光产品网B04-020 全像滤光镜Holographic FiltersB04-021 微小干涉滤光镜Micro Interference FiltersB06 激光:LASERS B06 激光LASERSB06-100 气体激光GAS LASERSB06-101 氦氖激光He-Ne LasersB06-102 金属蒸气激光Metal Vapor LasersB06-103 氩离子激光Argon LasersB06-104 氪离子激光Krypton LasersB06-105 二氧化碳激光(气流型) CO2 (Gas Flow type) LasersB06-106 二氧化碳激光(脉冲,TEA型) CO2 (Pulsed,TEA) LasersB06-107 二氧化碳激光(密封型) CO2 (Sealed tube) LasersB06-108 二氧化碳激光(波导型) CO2 (Wave guide) LasersB06-109 一氧化碳激光CO LasersB06-110 氦镉激光He-Cd LasersB06-111 氮分子激光Nitrogen LasersB06-112 准分子激光Excimer LasersB06-113 氙分子激光Xenon LasersB06-200 固体激光SOLID STATE LASERSB06-201 红宝石激光Ruby LasersB06-202 玻璃激光Glass LasersB06-203 Nd:YAG激光(脉冲式) Nd:YAG (Pulsed) LasersB06-204 Nd:YAG激光(连续式) Nd:YAG Laser (CW) LasersB06-205 Nd:YAG激光(半导体激光激发) Nd:YAG (LD Pumped) LasersB06-206 YLF激光YLF LasersB06-207 亚历山大激光Alexanderite LasersB06-208 铒固体激光Erbium LasersB06-209 半导体激光激发式固态激光Solid State(LD pumped)LaserB06-210 其他固态激光OthersB06-300 染料激光DYE LASERSB06-301 染料激光(闪光灯激发) Dye (Flash lamp Pumped) LasersB06-302 染料激光(激光激发) Dye (Laser Pumped) LasersB06-400 半导体激光SEMICONDUCTOR LASERSB06-401 半导体激光(1.55μm带) Semiconductor (1.55μm) LasersB06-402 半导体激光(1.30μm带) Semiconductor (1.30μm) LasersB06-403 半导体激光(0.85μm带) Semiconductor (0.85μm) LasersB06-404 半导体激光(0.78μm带) Semiconductor (0.78μm) LasersB06-405 半导体激光(0.60μm带) Semiconductor (0.60μm) LasersB06-406 半导体激光(其他波长带) Other Semiconductor LasersB06-407 半导体激光模组(长波长) Semiconductor (Long Wavelength) Laser Modules B06-408 半导体激光模组(短波长) Semiconductor (Short Wavelength) Laser Modules B06-409 半导体激光模组(可见光) Semiconductor (Visible) Laser ModulesB06-501 铁离子中心激光F-Center LasersB06-502 化学激光(HF-DF) Chemical (HF-DF) LasersB06-503 平板激光Slab LasersB06-504 远红外线激光Far-Infrared LasersB06-505 真空紫外线激光Vacuum Ultraviolet LasersB06-506 多色激光Multi Colour LasersB06-507 稳频激光Frequency Stabilized LasersB06-508 自由电子激光Free Electron LasersB07 激光用元件:B07 激光用元件LASER COMPONENTSB07-001 Q 开关Laser Q-Switches激光产品网B07-002 激光管Laser Tubes and BoresB07-003 激光棒Laser RodsB07-004 激光板Laser SlabsB07-005 气体再生设备,气体填充设备Gas Recyclers and Gas Handling EquipmentB07-006 激光控制设备Laser Control EquipmentB07-007 激光用盒Laser CellsB07-008 参数振汤器Parametric OscillatorsB07-009 光脉冲产生设备Optical Pulse GeneratorsB07-010 激光用共振腔Resonators for LasersB07-011 磁铁MagnetsB07-012 激光用冷却设备Cooling Systems for LasersB07-013 激光护眼镜Safty Equipment; Goggles Glasses and FilmsB07-014 激光光吸收体Safty Equipment; Laser AbsorbersB07-015 激光用安全设备Safty Equipment; Protective HousingsB08 发光二极体:B08 发光二极体LIGHT-EMITTING DIODES; LEDB08-001 通信用1.55μm发光二极体1.55μm LEDs for CommunicationB08-002 通信用1.30μm发光二极体1.30μm LEDs for CommunicationB08-003 通信用0.85μm发光二极体0.85μm LEDs for CommunicationB08-004 通信用长波长发光二极体模组Long Wavelength LED Modules for Communication B08-005 通信用短波长发光二极体模组Short Wavelength LED Modules for Communication B08-006 可见光发光二极体(红色) Visible (Red) LEDsB08-007 可见光发光二极体(黄色) Visible (Yellow,Orange) LEDsB08-008 可见光发光二极体(绿色,多色) Visible (Green,Multi-Color) LEDsB08-009 可见光发光二极体(蓝色) Visible (Blue) LEDsB08-010 红外线二极体(非通信用) Infrared (not for Communication) LEDsB08-011 文数字表示用发光二极体Alpha-Numeric LEDsB08-012 发光二极体晶圆(通信用) LED Wafers for CommunicationB08-013 发光二极体晶圆(非通信用) LED Wafers not for CommunicationB08-014 发光二极体晶片、晶粒(通信用) LED Chips for CommunicationB08-015 发光二极体晶片、晶粒(非通信用) LED Chips not for CommunicationB09 光源设备:B09 光源设备LIGHT SOURCESB09-001 标准光源Standard Light SourcesB09-002 安定化光源Stabilized Light SourcesB09-003 弧光灯Arc Light SourcesB09-004 氪灯Krypton Light SourcesB09-005 卤素灯Halogen Light SourcesB09-006 氙灯Xenon /Xenon Flashlamps Light SourcesB09-007 紫外线光源Ultraviolet Light SourcesB09-008 真空紫外线光源VUV Light SourcesB09-009 红外线光源Infrared Light SourcesB09-010 闪光光源Stroboscopic Light SourcesB09-011 小型光源Miniature Light SourcesB09-012 光纤光源Fiber Optic IlluminatorsB10 显示器元件:B10 显示器元件DISPLAY PANELB10-001 发光二极体显示器LED DisplaysB10-002 液晶显示器Liquid Crystal Display (LCD)B10-003 电浆显示器Plasma Display Panels(PDP)B10-004 电激发光显示器Electroluminescence Display (ELD)B10-005 电铬显示器Electrochromic Display (ECD)B10-006 真空萤光显示器Vacuum Fluorescent Display (VFD)激光产品网B10-007 平面阴极射线管Flat CRTsB10-008 场发射显示器Field Emitter Display(FED)B10-099 其他平面显示元件Other Flat Panel DisplaysB11 检光元件及光纤混成元件:B11 检光元件及光纤混成元件DETECTORS & FIBEROPTIC HYBRID DEVICESB11-001 通信用PIN光二极体PIN Photodiodes for CommunicationB11-002 通信用崩溃光二极体Avalanche Photodiodes for CommunicationB11-003 通信用(长波长)Ge和III-V族检光元件Long-wavelength Detectors for CommunicationB11-004 通信用PIN光二极体模组PIN Photodiode Modules for CommunicationB11-005 通信用崩溃光二极体模组Avalanche Photodiode Modules for CommunicationB11-006 通信用(长波长)Ge和III-V族检光模组Long-wavelength Decector Modules for CommunicationB11-007 光二极体(近红外光) Near-infrafed PhotodiodesB11-008 光二极体(可见光) Visible PhotodiodesB11-009 光二极体(紫外光) Ultraviolet PhotodiodesB11-010 光电晶体PhototransistorsB11-011 光电管PhototubesB11-012 光电子增倍管(PMT) PhotomultipliersB11-013 光导电池Photoconductive CellsB11-014 热电偶检测器Thermocouple DetectorsB11-015 热堆检测器Thermopile DetectorsB11-016 微道板Microchannel PlatesB11-017 热电检测器Pyroelectroic DetectorsB11-018 辐射热测定器BolometersB11-019 其他红外线检测器Infrared DetectorsB11-020 摄像管Camera TubesB11-021 线型检光元件One Dimension Detector ArraysB11-022 面型检光元件Two Dimension Detector ArraysB11-023 光电耦合器Photo CouplerB11-024 光断续器Photo InterrupterB11-025 光反射器Photo ReflectorB11-026 光闸流晶体管PhotocyristorsB11-027 光感测元件Photosensing UnitsB11-028 内藏电路之光感测器Detectors with CircuitB11-029 民用用太阳电池Solar Cells for Consumer UseB11-030 产业用太阳电池Solar Cells for Power & Space UseB12 光纤及光缆:B12 光纤及光缆FIBER OPTIC FIBERS & CABLEB12-100 光纤FIBER OPTIC FIBERSB12-101 石英系多模态步阶式折射率型光纤Fiber Optic Fibers, Silica, Multimode, Step IndexB12-102 石英系多模态渐近式折射率型光纤(50/125) Fiber Optic Fibers, Silica, Multimode, Graded Index,50/125B12-103 石英系多模态渐近式折射率型光纤(62.5/125) Fiber Optic Fibers, Silica, Multimode,Graded Index ,62.5/125 B12-104 石英系多模态渐近式折射率型光纤(100/140) Fiber Optic Fibers, Silica, Multimode,Graded Index ,100/140 B12-105 石英系单模态标准型光纤Fiber Optic Fibers, Silica, Single Mode,StandardB12-106 色散位移光纤Fiber Optic Fibers, Dispersion – ShiftedB12-107 偏振恒持光纤Fiber Optic Fibers, Polarization – MaintainingB12-108 其他单模态光纤Other Single Mode Optic FibersB12-109 石英系塑胶包覆光纤Fiber Optic Fibers, Plastic - Clad SilicaB12-110 塑胶光纤Fiber Optic Fibers, PlasticB12-111 石英系影像光纤Fiber Optic Bundles, Silica, ImagingB12-112 多成分影像光纤Fiber Optic Bundles, Non-silica, ImagingB12-113 光导管Fiber Optic LightguidesB12-199 其他集束光纤Other Fiber Optic BundlesB12-200 光缆FIBER OPTIC CABLE激光产品网B12-201 单模态标准型松包悬空式光缆Fiber Optic Cable, Single Mode, Standard, Loosely Buffered, AerialB12-202 单模态标准型松包管路式光缆Fiber Optic Cable, Single Mode, Standard, Loosely Buffered, DuctB12-203 单模态标准型松包直埋式光缆Fiber Optic Cable, Single Mode, Standard, Loosely Buffered, Direct BuriedB12-204 单模态标准型紧包单心式光缆Fiber Optic Cable, Single Mode, Standard, Tightly Buffered, Single FiberB12-205 单模态标准型紧包多心式光缆Fiber Optic Cable, Single Mode, Standard, Tightly Buffered, MultifiberB12-206 光纤带RibbonB12-207 色散位移光缆Fiber Optic Cable, Dispersion-ShiftedB12-208 偏振恒持光缆Fiber Optic Cable, Polarization – MaintainingB12-209 其他单模态光缆Other Single Mode Fiber Optic CableB12-210 多模态石英系(50/125)光缆Fiber Optic Cable, Multimode, Silica, 50/125B12-211 多模态石英系(62.5/125)光缆Fiber Optic Cable, Multimode, Silica, 62.5/125B12-212 多模态石英系(100/140)光缆Fiber Optic Cable, Multimode, Silica, 100/140B12-213 塑胶光缆Fiber Optic Cable, PlasticB12-214 石英系塑胶包覆光缆Fiber Optic Cable, Plastic-Clad SilicaB12-215 其他多模态光缆Other Multimode Fiber Optic CableB12-216 光纤保护用管Protect Tubes for Fiber Optic FiberB13 光被动元件/光控制元件:B13 光被动元件/光控制元件OPTICAL PASSIVE DEVICES/CONTROL DEVICESB13-001 单模态ST光纤连接器Fiber Optic Connectors, Single Mode, STB13-002 单模态Biconic光纤连接器Fiber Optic Connectors, Single Mode, BiconicB13-003 单模态FC/PC光纤连接器Fiber Optic Connectors, Single Mode, FC/PCB13-004 单模态APC光纤连接器Fiber Optic Connectors, Single Mode, APCB13-005 单模态FDDI光纤连接器Fiber Optic Connectors, Single Mode, FDDIB13-006 单模态SC光纤连接器Fiber Optic Connectors, Single Mode, SCB13-007 单模态D4光纤连接器Fiber Optic Connectors, Single Mode, D4B13-008 单模态光纤连接器插座(ST,FC/PC,SC,Biconic) Fiber Optic Connectors, Single Mode, Adapter(ST,FC/PC,SC,Biconic) B13-009 单模态多心光纤连接器(MT) Fiber Optic Connectors, Single Mode,Multi-Channel/MTB13-010 其他单模态光纤连接器Other Single Mode Fiber Optic ConnectorsB13-011 多模态ST光纤连接器Fiber Optic Connectors, Multimode, STB13-012 多模态FC/PC相容光纤连接器Fiber Optic Connectors, Multimode, FC/PCB13-013 多模态SMA光纤连接器Fiber Optic Connectors, Multimode, SMAB13-014 多模态FDDI光纤连接器Fiber Optic Connectors, Multimode, FDDIB13-015 多模态SC光纤连接器Fiber Optic Connectors, Multimode, SCB13-016 多模态D4光纤连接器Fiber Optic Connectors, Multimode, D4B13-017 多模态光纤连接器插座(ST,SMA,FC/PC) Fiber Optic Connectors, Multimode,Adapter(ST,SMA,FC/PC)B13-018 多模态多心光纤连接器Fiber Optic Connectors, Multimode, Multi-ChannelB13-019 其他多模态光纤连接器Other Multimode Fiber Optic ConnectorsB13-020 套筒SleevesB13-021 金属箍(套管) Metal FerrulesB13-022 塑胶箍(套管) Plastic FerrulesB13-023 陶瓷箍(套管) Ceramic FerrulesB13-024 插座ReceptaclesB13-025 插头PlugsB13-026 光连接器(含光纤线) Optical Connectors with FiberB13-027 光纤耦合器(两分支) Optical Couplers, Tap/SplitterB13-028 光纤耦合器(树状分支) Optical Couplers, TreeB13-029 星状光纤耦合器(穿透形) Transmission Type Star Optical CouplersB13-030 星状光纤耦合器(反射形) Reflection Type Star Optical CouplersB13-031 其他光纤耦合器Other Optical CouplersB13-032 光分波合波器(两波长) Optical Couplers, WDM, Dual-WavelengthB13-033 光分波合波器(多波长) Optical Couplers, WDM, Over Two WavelengthB13-034 其他光分波合波器Other Optical WDM CouplersB13-035 光衰减器(固定) Fixed Optical Attenuators激光产品网B13-036 光衰减器(可变) Adjustable Optical AttenuatorsB13-037 光隔离器(通信用) Optical Isolators for CommunicationB13-038 光隔离器(非通信用) Optical Isolators for Non-CommunicationB13-039 光环流器Optical CirculatorsB13-040 光开关(机械式) Mechanical Optical SwitchesB13-041 光开关(非机械式) Non-mechanical Optical SwitchesB13-042 光纤光栅Fiber Bragg GratingB13-043 光移相器Optical Phase ShiftersB13-044 光共振器Optical ResonatorsB13-045 空间调变元件Spatial Light ModulatorsB13-046 光影像转换元件(ITC) Incoherent to Coherent Devices(ITC)B13-047 光截波器,机械式光调变器Optical Choppers, Mechanical ModulatorsB13-048 磁光调变器Maganeto-Optic ModulatorsB13-049 声光调变器Acousto-Optic ModulatorsB13-050 电光调变器Electro-Optic ModulatorsB13-051 波导形调变器,行波形调变器Optical Waveguide,Travelling-wave ModulatorsB13-052 类比/强度调变器Analog/Intensity ModulatorsB13-053 数位调变器Digital ModulatorsB13-054 其他调变器Other ModulatorsB13-055 光弹性调变器Photoelastic ModulatorsB13-056 机械式偏折/扫瞄器(Galvanometer方式) Mechanical Optical Deflectors/Scanners(Galvanometer Mirror)B13-057 声光偏折/扫瞄器Acousto-Optic Optical Deflectors/ScannersB13-058 电光偏折/扫瞄器Electro-Optic Optical Deflectors/ScannersB13-059 机械式扫瞄器(回转多面镜方式) Mechanical Optical Scanners(Polygonal Mirrors)B13-060 机械式扫瞄器(全像方式) Mechanical Optical Scanners(Holographic)B13-061 光纤跳接线Fiber Optic Patchcord PigtailB13-062 光纤终端箱Fiber Optic Distribution BoxB13-063 光纤接续盒Fiber Optic ClosureB13-099 其他光被动元件/控制元件Other Optical Passive Devices/Control DevicesB14 积体光元件:B14 积体光元件INTEGRATED OPTICAL DEVICESB14-001 光IC Optical ICB14-002 OEIC Optoelectronic ICB14-099 其他光电元件Other DevicesC01 光通讯设备:C01 光通讯设备OPTICAL COMMUNICATION EQUIPMENTC01-100 电信用光通讯设备OPTICAL COMMUNICATION EQUIPEMNT(TELECOMMUNICATION)C01-101 同步光纤网路光波传输系统及多工机设备Lightwave/Transimission System and Multiplexer Equipment (SONET-Based) C01-102 同步光纤网路光数位回路载波机设备Optical/Digital Loop Carrier Equipment (SONET-Based)C01-103 同步光纤网路数位交换连接系统设备Digital Cross Connect System Equipment (SONET-based)C01-104 同步数位阶层光波传输系统及多工机设备Lightwave/Transmission System and Multiplexer Equipment (SDH-Based)C01-105 同步数位阶层光数位回路载波机设备Optical/Digital Loop Carrier Equipment (SDH-Based)C01-106 同步数位阶层数位交换连接系统设备Digital Cross Connect System Equipment (SDH-Based)C01-107 光纤网路单体ONU(Optical Network Unit)C01-108 非同步光通讯设备Asynchronous Optical Communication EquipmentC01-199 其他公众用光通讯设备Other Optical Communication Equipment (Telecommunication)C01-200 数据通讯光纤网路设备OPTICAL DATA COMMUNICATION NETWORK EQUIPMENT (PREMISES)C01-201 光纤分散式资料介面网路设备FDDI Network EquipmentC01-202 非同步传输模式网路设备ATM Network EquipmentC01-203 高速乙太网路设备Fast Ethernet Network EquipmentC01-204 光纤通道Fiber ChannelC01-299 其他用户光数据通讯设备Other Optical Data Communication Network Equipment (Premises)C01-300 特殊用途光传输设备OPTICAL TRANSMISSION EQUIPMENT(SPECIAL PURPOSE)激光产品网C01-301 有线电视光传输设备Optical Transmission Equipment, CATVC01-302 视讯/闭路监视光传输设备Optical Transmission Equipment, Video/CCTVC01-303 量测/控制信号光传输设备Optical Transmission Equipment, Measure/ControlC01-304 空间(无线)光传输设备Optical Transmission Equipment, Spatial (Wireless)C01-305 光放大器Optical AmplifierC01-399 其他特殊用途光传输设备Other Optical Transmission Equipment (Special Purpose)C02 光测仪器设备:C02 光测仪器设备OPTICAL MEASURING EQUIPMENTC02-001 量测用标准光源Standard/Stabilized Light SourcesC02-002 光功率计(热转换型) Thermal Conversion Type Optical Power MetersC02-003 光功率计(光电转换型) Photoelectric Conversion Type Optical Power MetersC02-004 光谱分析仪Optical Spectrum AnalyzersC02-005 光波长计Optical Wavelength MetersC02-006 光谱幅宽量测器Spectral Width Measuring EquipmentC02-007 光时域反射计(OTDR) Optical Time-Domain Reflectometers(OTDR)C02-008 基频传输特性检测器Baseband Frequency Characteristics Evaluation EquipmentC02-009 波长色散量测器Wavelength Dispersion Measuring EquipmentC02-010 光纤测试设备Optical Fiber Test EquipmentC02-011 激光光束波形量测器Laser Beam Profile Measuring EquipmentC02-012 光纤尺寸量测器Optical Fiber Sizes Measuring EquipmentC02-013 光纤模态参数测试器Optical Fiber Mode Field Parameters Test EquipmentC02-014 光纤强度测试器Optical Fiber Strength Test EquipmentC02-015 其他光纤相关量测设备Other Optical Fiber Measurement EquipmentC02-016 光连接器尺寸量测器Optical Connector Sizes Measuring EquipmentC02-017 光碟测定检查设备(装置用) Optical Disk Drive Inspection EquipmentC02-018 光碟测定检查设备(碟片用) Optical Disk Inspection EquipmentC02-019 光度计PhotometersC02-020 复光束光度计,复光束量测器Double Beam PhotometersC02-021 测微光度计MicrophotometersC02-022 感光密度计DensitometersC02-023 光泽度计GrossmetersC02-024 照度计Illuminance MetersC02-025 测距仪RangefindersC02-026 曝光计Exposure MetersC02-027 辉度计Luminance MetersC02-028 比色计Comparison ColorimetersC02-029 色彩计(分光型) Spectral ColorimetersC02-030 色彩计(光电型) Photoelectric ColorimetersC02-031 积分球Integrating SpheresC02-032 折射计RefractometersC02-033 椭圆计EllipsometersC02-034 偏振光镜PolariscopesC02-035 偏振计PolarimetersC02-036 比较量测器ComparatorsC02-037 焦距仪FocometersC02-038 球径计SpheremetersC02-039 OTF(光学转换函数)设备Optical Transfer Function InstrumentationC02-040 MTF分析/量测装置Modulation Transfer Function(MTF) Analysis/Measurement Equipment C02-041 投影检查器Profile ProjectorsC02-042 自动准直仪AutocollimatorsC02-043 光弹性机器Photoelastic InstrumentsC02-099 其他光(学)量测器Other Optical Measurement Equipment激光产品网C03 分光镜、干涉仪:C03 分光镜、干涉仪SPECTROSCOPES, INTERFEROMETERSC03-001 分光计SpectrometersC03-002 单色器MonochromatorsC03-003 分光镜,干涉分光镜,摄谱仪Spectroscopes, Interference Spectroscopes,SpectrographsC03-004 分光光度计,分光测光器SpectrophotometerC03-005 Michelson干涉仪Michelson InterferometersC03-006 Tywman Green干涉仪Tywman Green InterferometersC03-007 Mach-Zehnder干涉仪Mach-Zehnder InterferometersC03-008 Fizeau干涉仪Fizeau InterferometersC03-009 Fabry-Perot干涉仪Fabry-Perot InterferometersC04 显微镜,望远镜,照像机:C04 显微镜,望远镜,照像机MICROSCOPES, TELESCOPES, CAMERASC04-001 放大镜MagnifiersC04-002 单接物镜双眼显微镜Binocular MicroscopesC04-003 双眼实体显微镜,立体显微镜Stereo MicroscopesC04-004 金属显微镜Metallurgical MicroscopesC04-005 偏光显微镜Polarizing MicroscopesC04-006 相位差显微镜Phase-Contrast MicroscpoesC04-007 干涉显微镜,微分干涉对比显微镜Interferences/Differential Interference Contrast Microscopes C04-008 萤光显微镜Fluorescence MicroscopesC04-009 激光显微镜Laser MicroscopesC04-010 量测用显微镜,工具显微镜Measurement MicroscopesC04-011 显微镜光度计Microscope PhotometersC04-012 折射望远镜,Galilean望远镜Galilean Refracting TelescopesC04-013 反射望远镜Reflecting TelescopesC04-014 反射折射望远镜Catadioptric TelescopesC04-015 35mm焦平面自动对焦相机35mm AF Focal Plane CamerasC04-016 35mm焦平面手动对焦相机35mm NON-AF Focal Plane CamerasC04-017 35mm镜头快门多焦点相机35mm Multi Focal Points Lens Shutter CamerasC04-018 35mm镜头快门单焦点相机35mm Single Focal Point Lens Shutter CamerasC04-019 中,大型照相机Medium and Large Size CamerasC04-020 VTR摄影机VTR CamerasC04-021 电视摄影机TV CamerasC04-022 高画质电视摄影机High Definition(HDTV) CamerasC04-023 CCTV摄影机CCTV CamerasC04-024 全像照像机Holographic CamerasC04-025 眼镜EyeglassesC04-026 夜视设备Night Vision EquipmentC04-027 照像机用之日期显示模组Date moduleC04-028 照像机用之底片计数器Film counterC04-029 APS相机APS CamerasC05 光感测器:C05 光感测器OPTICAL SENSORSC05-001 光电开关,光电感测器Photo Switches, Photo SensorsC05-002 标记感测器Mark Photo SensorsC05-003 色彩标记感测器Color Mark Photo SensorsC05-004 色彩感测器Color Photo SensorsC05-005 光学式编码器,角度感测器Optical Encoders, Angle SensorsC05-006 光遥控器Optical Remote Control EquipmentC05-007 影像感测器式量测设备Image Sensor Type Measurement InstrumentsC05-008 显微镜式量测设备Microscope Type Measurement InstrumentsC05-009 精密长度干涉仪Precise Length Interferometers激光产品网C05-010 光波测距装置Electronic Distance MetersC05-011 三角测量法距离感测器Triangulation Distance MetersC05-012 激光调变测距方式距离感测器Laser Modulation Distance MetersC05-013 脉冲测距方式距离感测器Pulse Distance MetersC05-014 激光外径测定器Laser Outer Diameter Measuring SensorsC05-015 激光厚度计Laser Thickness GaugesC05-016 激光拉伸计Laser Extension MeterC05-017 红外线厚度计Infrared Thickness GaugesC05-018 水平仪LevelsC05-019 激光水平仪Laser LevelsC05-020 经纬仪Theodlites/TransitsC05-021 激光经纬仪Laser Theodlites/TransitsC05-022 激光标线设备Laser Marking-off EquipmentC05-023 位置光电感测器Position Sensors, Pattern Edge SensorsC05-024 半导体位置感测器Position Sensitive Devices(PSDs)C05-025 激光指示器Laser PointersC05-026 激光都卜勒测速计Laser Doppler VelocimetersC05-027 环形激光流速计,光纤陀螺仪Ring Laser Velocimeters, Optical Fiber Laser GyrosC05-028 转速仪Rotational Speed MetersC05-029 激光都卜勒转速仪Laser Doppler Rotational Speed MetersC05-030 全像方式图样量测设备Holographic Method Pattern Measurement EquipmentsC05-031 激光移位计Laser Displacement MetersC05-032 激光指纹检测器Laser Fingerprint DetectorsC05-033 光学水质污染检测设备Optical Water Pollution Measurement and Detection Equipment C05-034 光学大气污染检测设备Optical Air Pollution Measurement and Detection EquipmentC05-035 红外线气体浓度感测器Infrared Gas Density MetersC05-036 光电式烟检知器Photo Smoke DetectorsC05-037 激光粉尘监视器,粒径量测器Laser Dust MonitorsC05-038 距离测定用激光雷达Rang-finding Lidar SystemsC05-039 环境监测用激光雷达Environment Monitoring Lidar SystemsC05-040 激光表面检查设备Laser Surface Inspection EquipmentC05-041 平面度测定系统Flatness TestersC05-042 斑点图形量测设备Speckle Method Pattern Measurement EquipmentC05-043 云纹图形量测设备Moire Method Pattern Measurement EquipmentC05-044 影像分析仪Image AnalyzersC05-045 激光缺陷检查设备Laser Defect Inspection EquipmentC05-046 红外线辐射温度感测器Infrared ThermometersC05-047 人体检知感测器,激光保全设备Laser Security/Surveillance EquipmentsC05-048 光计数器Photo CountersC05-049 激光公害检测设备Laser Pollution Detective DevicesC05-050 激光热常数量测设备Laser Thermal Constants Measurement EquipmentC05-051 全像非破坏检查设备Holographic Nondestructive Testing EquipmentC06 光纤感测器:C06 光纤感测器FIBER OPTIC SENSORSC06-001 光纤光电开关/感测器Fiber Optic Photo Switches/ SensorsC06-002 光纤式标记感测器Fiber Optic Mark Photo SensorsC06-003 光纤式色彩标记感测器Fiber Optic Color Mark Photo SensorsC06-004 光纤温度感测器Fiber Optic Temperature SensorsC06-005 光纤压力感测器Fiber Optic Pressure SensorsC06-006 光纤声波感测器Fiber Optic Acoustic SensorsC06-007 光纤变形感测器Fiber Optic Strain SensorsC06-008 光纤振动感测器Fiber Optic Vibration SensorsC06-009 光纤移位感测器Fiber Optic Displacement Sensors激光产品网C06-010 光纤陀螺仪感测器Fiber Optic Gyro SensorsC06-011 光纤速度感测器Fiber Optic Velocity SensorsC06-012 光纤磁通量感测器Fiber Optic Magnetic Flux SensorsC06-013 光纤磁场感测器Fiber Optic Magnetic Field SensorsC06-014 光纤电流感测器Fiber Optic Current SensorsC06-015 光纤电场感测器Fiber Optic Electric Field SensorsC06-016 光纤浓度、成份感测器Fiber Optic Density,Constituent SensorsC06-017 光纤油膜感测器Fiber Optic Oil Film SensorsC06-018 光纤液位感测器Fiber Optic Liquid Surface Level SensorsC06-019 光纤光分布/放射线感测器Fiber Optic Light Distribution/Radiation SensorsC06-020 光纤显微镜Fiber Optic FiberscopesC06-021 光纤光栅应变感测器Fiber Grating Strain SensorC07 光储存装置:C07 光储存装置OPTICAL STORAGE PRODUCTC07-100 消费性光碟机CONSUMER OPTICAL DISC PLAYERSC07-101 激光唱盘Compact Disc (CD) PlayersC07-102 激光音响组合Products Incorporated CD(CD-Radio-Cassette Tape Recorders)C07-103 LD 影碟机Laser Disc (LD) PlayersC07-104 影音光碟机Video CD PlayersC07-105 DVD DVD 影碟机Digital Versatile Disc (DVD) PlayersC07-106 迷你音碟机Mini Disc (MD) PlayersC07-200 资讯用仅读型光碟机READ-ONLY OPTICAL DISC DRI597VESC07-201 CD-ROMCD-ROM光碟机CD-ROM DrivesC07-202 DVD-ROM DVD-ROM 光碟机DVD-ROM DrivesC07-300 资讯用仅写一次型光碟机RECORDABLE OPTICAL DISC DRIVESC07-301 CD-R CD-R 光碟机CD-R DrivesC07-399 其他仅写一次型光碟机Other Recordable Optical Disc DrivesC07-400 资讯用可覆写型光碟机REWRITABLE OPTICAL DISC DRIVESC07-401 3.5" MO 光碟机3.5" MO Disc DrivesC07-402 5.25" MO 光碟机5.25" MO Disc DrivesC07-403 PD 光碟机PD DrivesC07-404 CD-RW光碟机CD-RW DrivesC07-499 其他可覆写型光碟机Other Rewritable Optical Disc DrivesC07-500 光碟机零组件DEVICES OF OPTICAL DISC DRIVESC07-501 光学头,光学读取头Optical Heads , Pick-up HeadsC07-502 光学头伺服装置,伺服用IC模组Optical Head Controllers, Control ICs/Modules C07-503 光学头驱动装置Optical Head ServomotorsC07-504 光碟匣Optical Disc CartridgesC07-505 主轴马达Spindle MotorC07-600 光碟片OPTICAL DISCSC07-601 CD 音碟片Compact DiscsC07-602 LD 影碟片Laser DiscsC07-603 影音光碟片Video CDsC07-604 DVD光碟片Digital Versatile Discs : DVDsC07-605 迷你音碟片Mini Discs : MDsC07-606 CD-ROM 光碟片CD-ROMsC07-607 DVD-ROM光碟片DVD-ROMsC07-608 CD-R 光碟片CD-RsC07-609 其他可写仅读型光碟片Other Recordable Optical DiscsC07-610 3.5" MO 光碟片3.5" MO DiscsC07-011 5.25" MO 光碟片5.25" MO DiscsC07-612 PD 光碟片PD DiscsC07-613 CD-RW 光碟片CD-RW Discs激光产品网。

光学工程英语专业词汇光学工程涉及到许多专业词汇,下面我将从不同方面列举一些相关术语。
1. 基本光学术语:光学 (Optics)。
折射 (Refraction)。
反射 (Reflection)。
透镜 (Lens)。
凸透镜 (Convex Lens)。
凹透镜 (Concave Lens)。
焦距 (Focal Length)。
焦点 (Focus)。
光谱 (Spectrum)。
波长 (Wavelength)。
折射率 (Refractive Index)。
2. 光学元件和设备:激光器 (Laser)。
光纤 (Optical Fiber)。
光栅 (Grating)。
透镜组 (Lens Assembly)。
光学薄膜 (Optical Coating)。
光学仪器 (Optical Instrumentation)。
光学检测设备 (Optical Detection Equipment)。
光学显微镜 (Optical Microscope)。
光学测量设备 (Optical Measurement Equipment)。
3. 光学工程中的技术和方法:光学设计 (Optical Design)。
光学仿真 (Optical Simulation)。
光学加工 (Optical Fabrication)。
光学测试 (Optical Testing)。
光学薄膜沉积 (Optical Thin Film Deposition)。
光学成像 (Optical Imaging)。
光学通信 (Optical Communication)。
光学传感 (Optical Sensing)。
4. 相关学科交叉专业术语:光电子学 (Optoelectronics)。
光学工程学 (Optical Engineering)。
光学材料 (Optical Materials)。
光学信号处理 (Optical Signal Processing)。
光学计算机视觉 (Optical Computer Vision)。
光纤通信系统Optical Fiber Communications英文资料及中文翻译Communication may be broadly defined as the transfer of information from one point to another .When the information is to be conveyed over any distance a communication system is usually required .Within a communication system the information transfer is frequently achieved by superimposing or modulating the information on to an electromagnetic wave which acts as a carrier for the information signal .This modulated carrier is then transmitted to the required destination where it is received and the original information signal is obtained by demodulation .Sophisticated techniques have been developed for this process by using electromagnetic carrier waves operating at radio requites as well as microwave and millimeter wave frequencies.The carrier maybe modulated by using either optical an analog digital information signal.. Analog modulation involves the variation of the light emitted from the optical source in a continuous manner. With digital modulation, however, discrete changes in the length intensity are obtained (i.e. on-off pulses). Although often simpler to implement, analog modulation with an optical fiber communication system is less efficient, requiring a far higher signal to noise ratio at the receiver than digital modulation. Also, the linearity needed for analog modulation is mot always provided by semiconductor optical source, especially at high modulation frequencies .For these reasons ,analog optical fiber communications link are generally limited to shorter distances and lower bandwidths than digital links .Initially, the input digital signal from the information source is suitably encoded for optical transmission .The laser drive circuit directly modulates the intensity of the semiconductor last with the encoded digital signal. Hence a digital optical signal is launched into the optical fiber cable .The avalanche photodiode detector (APD) is followed by a front-end amplifier and equalizer or filter to provide gain as well as linear signal processing and noise bandwidth reduction. Finally ,the signal obtained isdecoded to give the original digital information .Generating a Serial SignalAlthough a parallel input-output scheme can provide fast data transfer and is simple in operation, it has the disadvantage of requiring a large number of interconnections. As an example typical 8 bit parallel data port uses 8 data lines, plus one or two handshake lines and one or more ground return lines. It is fairly common practice to provide a separate ground return line for each signal line, so an 8 bit port could typically use a 20 core interconnection cable. Whilst such a multi way cable is quite acceptable for short distance links, up to perhaps a few meters, it becomes too expensive for long distance links where, in addition to the cost of the multiword cable, separate driver and receiver circuits may be required on each of the 10 signal lines. Where part of the link is to be made via a radio link, perhaps through a space satellite, separate radio frequency channels would be required for each data bit and this becomes unacceptable.An alternative to the parallel transfer of data is a serial in which the states of the individual data bits are transmitted in sequence over a single wire link. Each bit is allocated a fixed time slot. At the receiving end the individual bit states are detected and stored in separate flip-flop stages, so that the data may be reassembled to produce a parallel data word. The advantage of this serial method of transmission is that it requires only one signal wire and a ground return, irrespective of the number of bits in the data word being transmitted. The main disadvantage is that the rate at which data can be transferred is reduced in comparison with a parallel data transfer, since the bits are dealt with in sequence and the larger the number of bits in the word, the slower the maximum transfer speed becomes. For most applications however, a serial data stream can provide a perfectly adequate data transfer rate . This type of communication system is well suited for radio or telephone line links, since only one communication channel is required to carry the data.We have seen that in the CPU system data is normally transferred in parallel across the main data bus, so if the input -output data is to be in serial form, then a parallel to serial data conversion process is required between the CPU data bus andthe external I/O line. The conversion from parallel data to the serial form could be achieved by simply using a multiplexed switch, which selects each data bit in turn and connects it to the output line for a fixed time period. A more practical technique makes use of a shift register to convert the parallel data into serial form.A shift register consists of a series of D type flip-flops connected in a chain, with the Q output of one flip-flop driving the D input of the next in the chain. All of the flip-flops ate clocked simultaneously by a common clock pulse, when the clock pulse occurs the data stored in each flip-flop is transferred to the next flip-flop to the right in the chain. Thus for each clock pulse the data word is effectively stepped along the shift register by one stage, At the end of the chain the state of the output flip-flop will sequence through the states of the data bits originally stored in the register. The result is a serial stream of data pulses from the end of the shift register.In a typical parallel to serial conversion arrangement the flip-flops making up the shift register have their D input switchable. Initially the D inputs are set up in a way so that data can be transferred in parallel from the CPU data bus into the register stages. Once the data word has been loaded into the register the D inputs are switched so that the flip-flops from a shift register .Now for each successive clock pulse the data pattern is shifted through the register and comes out in serial form at the right hand end of the register.At the receiving end the serial data will usually have to be converted back into the parallel form before it can be used. The serial to parallel conversion process can also be achieved by using a shift register .In this case the serial signal is applied to the D input of the stage at the left hand end of the register. As each serial bit is clocked into the register the data word again moves step by step to the right, and after the last bit has been shifted in the complete data word will be assembled within the register .At this point the parallel data may be retrieved by simply reading out the data from individual register stages in parallel It is important that the number of stages in the shift register should match the number of bits in the data word, if the data is to be properly converted into parallel form.To achieve proper operation of the receiving end of a serial data link, it isimportant that the clock pulse is applied to the receive shift register at a time when the data level on the serial line is stable. It is possible to have the clock generated at either end of the link, but a convenient scheme is to generate the clock signal at the transmitting end (parallel-serial conversion )as the master timing signal. To allow for settling time and delays along the line, the active edge of the clock pulse at the receive end is delayed relative to that which operates the transmit register. If the clock is a square wave the simples approach might be to arrange that the transmit register operates on the rising edge of the clock wave, and the receive register on the falling edge, so that the receiver operates half a clock period behind the transmitter .If both registers operate on arising edge, the clock signal from the transmitter could be inverted before being used to drive the receive shifty register.For an 8 bit system a sequence of 8 clock pulses would be needed to send the serial data word .At the receiving end the clock pulses could be counted and when the eighth pulse is reached it might be assumed that the data in the receive register is correctly positioned, and may be read out as parallel data word .One problem here is that, if for some reason the receive register missed a clock pulse ,its data pattern would get out of step with the transmitted data and errors would result. To overcome this problem a further signal is required which defines the time at which the received word is correctly positioned in the receive shift register and ready for parallel transfer from the register .One possibility is to add a further signal wire along which a pulse is sent when the last data bit is being transmitted, so that the receiver knows when the data word is correctly set up in its shift register. Another scheme might be to send clock pulses only when data bits are being sent and to leave a timing gap between the groups of bits for successive data words. The lack of the clock signal could then be detected and used to reset the bit counter, so that it always starts at zero at the beginning of each new data word.Serial and Parallel Data lion is processed. Serial indicates that the information is handled sequentially, similar to a group of soldiers marching in single file. In parallel transmission the info The terms serial and parallel are often used in descriptions of data transmission techniques. Both refer to the method by which information isdivided in to characters, words, or blocks which are transmitted simultaneously. This could be compared to a platoon of soldiers marching in ranks.The output of a common type of business machine is on eight—level punched paper tape, or eight bits of data at a time on eight separate outputs. Each parallel set of eight bits comprises a character, and the output is referred to as parallel by bit, serial by character. The choice of cither serial or parallel data transmission speed requirements.Business machines with parallel outputs, how—ever, can use either parallel outputs, how—ever, can use either direct parallel data trans—mission or serial transmission, with the addition of a parallel—to—serial converter at the interface point of the business machine and the serial data transmitter. Similarly, another converter at the receiving terminal must change the serial data back to the parallel format.Both serial and parallel data transmission systems have inherent advantages which are some—what different. Parallel transmission requires that parts of the available bandwidth be used as guard bands for separating each of the parallel channels, whereas serial transmission systems can use the entire linear portion of the available band to transmit data, On the other hand, parallel systems are convenient to use because many business machines have parallel inputs and outputs. Though a serial data set has the added converters for parallel interface, the parallel transmitter re—quires several oscillators and filters to generate the frequencies for multiplexing each of the side—by—side channels and, hence, is more susceptible to frequency error.StandardsBecause of the wide variety of data communications and computer equipment available, industrial standards have been established to provide operating compatibility. These standards have evolved as a result of the coordination between manufacturers of communication equipment and the manufacturers of data processing equipment. Of course, it is to a manufacturer’s advantage to provide equipment that isuniversally acceptable. It is also certainly apparent that without standardization intersystem compatibility would be al—most impossible.Organizations currently involved in uniting the data communications and computer fields are the CCITT, Electronic Industries Association (EIA), American Standards Association (ASA), and IEEE.A generally accepted standard issued by the EIA, RS—232—B, defines the characteristics of binary data signals, and provides a standard inter—face for control signals between data processing terminal equipment and data communications equipment. As more and more data communications systems are developed, and additional ways are found to use them, the importance ways are found to use them, the importance of standards will become even more significant.Of the most important considerations in transmitting data over communication systems is accuracy. Data signals consist of a train of pulses arranged in some sort of code. In a typical binary system, for example, digits 1 and 0 are represented by two different pulse amplitudes. If the amplitude of a pulse changes beyond certain limits during transmission, the detector at the receiving end may produce the wrong digit, thus causing an error.It is very difficult in most transmission systems to completely avoid. This is especially true when transmission system designed for speech signals. Many of the inherent electrical characteristics of telephone circuits have an adverse effect on digital signals.Making the circuits unsatisfactory for data transmission—especially treated before they can be used to handle data at speeds above 2000 bits per second.V oice channels on the switched (dial—up) telephone network exhibit certain characteristics which tend to distort typical data signal waveforms. Since there is random selection of a particular route for the data signal with each dialed connection, transmission parameters will generally change, sometimes upsetting the effect of built—in compensationNetworks. In addition, the switched network cannot be used of for large multipleaddress data systems using time sharing. Because of these considerations, specially treated voice bandwidth circuits are made available for data use. The characteristics and costs of these point—to—point private lines are published in document called tariffs, which are merely regulatory agreements reached by the FCC, state public utilities commissions, and operating telephone companies regarding charges for particular types of telephone circuits. The main advantage of private or dedicated facilities is that transmission characteristics are fixed and remain so for all data communications operations.Correlative TechniqueCorrelative data transmission techniques, particularly the Duobinary principle, have aroused considerable interest because of the method of converting a binary signal into three equidistant levels. This correlative scheme is accomplished in such a manner that the predetermined level depends on past signal history, forming the signal so that it never goes from one level extreme to another in one bit interval.The most significant property of the Duobinary process is that it affords a two—to—one bandwidth compression relative to binary signaling, or equivalently twice the speed capability in bits per second for a fixed bandwidth. The same speed capability for a multilevel code would normally require four levels, each of which would represent two binary digits.The FutureIt is universally recognized that communication is essential at every level of organization. The United States Government utilizes vast communications network for voice as well as data transmission. Likewise, business need communications to carry on their daily operations.The communications industry has been hard at work to develop systems that will transmit data economically and reliably over both private—line and dial up telephone circuits. The most ardent trend in data transmission today is toward higher speeds over voice—grade telephone channels. New transmission and equalization techniques now being investigated will soon permit transmitting digital data over telephone channels at speeds of 4800 bits per second or higher.To summarize: The major demand placed on telecommunications systems is for more information-carrying capacity because the volume of information produced increases rapidly. In addition, we have to use digital technology for the high reliability and high quality it provides in the signal transmission. However, this technology carries a price: the need for higher information-carrying capacity.The Need for Fiber-Optic Communications Systems The major characteristic of a telecommunications system is unquestionably its information-carrying capacity, but there are many other important characteristics. For instance, for a bank network, security is probably more important than capacity. For a brokerage house, speed of transmission is the most crucial feature of a network. In general, though, capacity is priority one for most system users. And there’s the rub. We cannot increase link capacity as much as we would like. The major limit is shown by the Shannon-Hartley theorem,Where C is the information-carrying capacity(bits/sec), BW is the link bandwidth (Hz=cycles/sec), and SNR is the signal-to-noise power ratio.Formula 1.1 reveals a limit to capacity C; thus, it is often referred to as the “ Shannon limit.” The formula, which comes from information theory, is true regardless of specific technology. It was first promulgated in 1948 by Claude Shannon, a scientist who worked at Bell Laboratories. R. V. L. Hartley, who also worked at Bell Laboratories, published a fundamental paper 20 years earlier, a paper that laid important groundwork in information theory, which is why his name is associated with Shannon’s formula.The Shannon-Hartley theorem states that information-carrying capacity is proportional to channel bandwidth, the range of frequencies within which the signals can be transmitted without substantial attenuation.What limits channel bandwidth? The frequency of the signal carrier. The higher the carrier’s frequency, the greater the channel bandwidth and the higher the information-carrying capacity of the system. The rule of thumb for estimating possible order of values is this: Bandwidth is approximately 10 percent of the carrier-signal frequency. Hence, if a microwave channel uses a 10-GHz carrier signal.Then its bandwidth is about 100 MHz.A copper wire can carry a signal up to 1 MHz over a short distance. A coaxial cable can propagate a signal up to 100 MHz. Radio frequencies are in the range of 500 KHz to 100 MHz. Microwaves, including satellite channels, operate up to 100 GHz. Fiber-optic communications systems use light as the signal carrier; light frequency is between 100 and 1000 THz; therefore, one can expect much more capacity from optical systems. Using the rule of thumb mentioned above, we can estimate the bandwidth of a single fiber-optic communication link as 50 THz.To illustrate this point, consider these transmission media in terms of their capacity to carry, simultaneously, a specific number of one-way voice channels. Keep in mind that the following precise value. A single coaxial cable can carry up to 13,000 channels, a microwave terrestrial link up to 20,000 channels, and a satellite link up to 100,000 channels. However, one fiber-optic communications link, such as the transatlantic cable TAT-13, can carry 300,000 two-way voice channels simultaneously. That’s impressive and explains why fiber-optic communications systems form the backbone of modern telecommunications and will most certainly shape its future.To summarize: The information-carrying capacity of a telecommunications system is proportional to its bandwidth, which in turn is proportional to the frequency of the carrier. Fiber-optic communications systems use light-a carrier with the highest frequency among all the practical signals. This is why fiber-optic communications systems have the highest information-carrying capacity and this is what makes these systems the linchpin of modern telecommunications.To put into perspective just how important a role fiber-optic communications will be playing in information delivery in the years ahead, consider the following statement from a leading telecommunications provider: “ The explosive growth of Internet traffic, deregulation and the increasing demand of users are putting pressure on our customers to increase the capacity of their network. Only optical networks can deliver the required capacity, and bandwidth-on-demand is now synonymous with wavelength-on-demand.” Th is statement is true not only for a specific telecommunications company. With a word change here and there perhaps, but withthe same exact meaning, you will find telecommunications companies throughout the world voicing the same refrain.A modern fiber-optic communications system consists of many components whose functions and technological implementations vary. This is overall topic of this book. In this section we introduce the main idea underlying a fiber-optic communications system.Basic Block DiagramA fiber-optic communications system is a particular type of telecommunications system. The features of a fiber-optic communications system can be seen in Figure 1.4, which displays its basic block diagram.Information to be conveyed enters an electronic transmitter, where it is prepared for transmission very much in the conventional manner-that is, it is converted into electrical form, modulated, and multiplexed. The signal then moves to the optical transmitter, where it is converted into optical detector converts the light back into an electrical signal, which is processed by the electronic receiver to extract the information and present it in a usable form (audio, video, or data output).Let’s take a simple example that involves Figures 1.1, 1.3, and 1.4 Suppose we need to transmit a voice signal. The acoustic signal (the information) is converted into electrical form by a microphone and the analog signal is converted into binary formby the PCM circuitry. This electrical digital signal modulates a light source and the latter transmits the signal as a series of light pulses over optical fiber. If we were able to look into an optical fiber, we would see light vary between off and on in accordance with the binary number to be transmitted. The optical detector converts the optical signal it receives into a set of electrical pulses that are processed by an electronic receiver. Finally, a speaker converts the analog electrical signal into acoustic waves and we can hear sound-delivered information.Figure 1.4 shows that this telecommunications system includes electronic components and optical devices. The electronic components deal with information in its original and electrical forms. The optical devices prepare and transmit the light signal. The optical devices constitute a fiber-optic communications system.TransmitterThe heart of the transmitter is a light source. The major function of a light source is to convert an information signal from its electrical form into light. Today’sfiber-optic communications systems use, as a light source, either light-emitting diodes (LEDs) or laser diodes (LDs). Both are miniature semiconductor devices that effectively convert electrical signals are usually fabricated in one integrated package. In Figure 1.4, this package is denoted as an optical transmitter. Figure 1.5 displays the physical make-up of an LED, an LD, and integrated packages.Optical fiberThe transmission medium in fiber-optic communications systems is an optical fiber. The optical fiber is the transparent flexible filament that guides light from a transmitter to a receiver. An optical information signal entered at the transmitter end of a fiber-optic communications system is delivered to the receiver end by the optical fiber. So, as with any communication link, the optical fiber provides the connection between a transmitter and a receiver and, very much the way copper wire and coaxial cable conduct an electrical signal, optical fiber “ conducts” light.The optical fiber is generally made from a type of glass called silica or, less commonly nowadays, from plastic. It is about a human hair in thickness. To protect very fragile optical fiber from hostile environments and mechanical damage, it is usually enclosed in a specific structure. Bare optical fiber, shielded by its protective coating, is encapsulated use in a host of applications, many of which will be covered in subsequent chaptersReceiver The key component of an optical receiver is its photodetector. The major function of a photodetector is to convert an optical information signal back into an electrical signal (photocurrent). The photodetector in today's fiver-optic communications systems is a semiconductor photodiode (PD). This miniature device is usually fabricated together with its electrical circyitry to form an integrated package that provides power-supply connections and signal amplification. Such an integrated package is shown in Figure 1.4 as an optical receiver. Figure 1.7 shows samples of a photodiode and an integrated package.The basic diagram shown in Figure 1.4 gives us the first idea of what a fiber-optic communications system is and how it works. All the components of this point-to-point system are discussed in detail in this book. Particular attention is given to the study of networks based on fiber-optic communications systems.The role of Fiber-Optic Communications Technology has not only already changed the landscape of telecommunications but it is still doing so and at a mind-boggling pace. In fact, because of the telecommunications industry's insatiable appetite for capacity, in recent years the bandwidth of commercial systems has increased more than a hundredfold. The potential information-carrying capacity of a single fiber-optic channel is estimated at 50 terabits a second (Tbit/s) but, from apractical standpoint, commercial links have transmitted far fewer than 100 Gbps, an astoundingamount of data in itself that cannot be achieved with any other transmission medium. Researchers and engineers are working feverishly to develop new techniques that approach the potential capacity limit.Two recent major technological advances--wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) anderbium-doped optical-fiber amplifiers (EDFA)--have boosted the capacity of existing system sand have brought about dramatic improvements in the capacity of systems now in development. In fact,' WDM is fast becoming the technology of choice in achieving smooth, manageable capacity expansion.The point to bear in mind is this: Telecommunications is growing at a furious pace, and fiber-optic communications is one of its most dynamically moving sectors. While this book refleets the current situation in fiber-optic communications technology, to keep yourself updated, you have to follow the latest news in this field by reading the industry's trade journals, attending technical conferences and expositions, and finding the time to evaluate the reams of literature that cross your desk every day from companies in the field.光纤通信系统一般的通信系统由下列部分组成:(1) 信息源。
海外销售离不开英语,要成为行业的海外销售精英更离不开行业的专业英语。
初入光缆行业时,由于对光纤光缆的专业英语不是很清楚,所以经常看不懂客户提供的规格书,不知道如何介绍自己的产品,以至于报价不及时,不准确,从而导致客户流失。
每一个外贸新手都希望入行时能够第一时间掌握到自己行业的专业英语,以下是本人在工作中总结出来的部分光纤光缆专业英语,希望能对广大的客户朋友和光缆行业的外贸新手们有帮助。
也希望大家一起来补充完善,共同进步。
一、光纤专业英语光纤Optical Fiber/Optic fiber单模光纤Single-mode fiber / monomode fiber多模光纤multimode fibe突变型光纤Step index fiber渐变型光纤graded index fiber紧套光纤Tight buffered fiber光纤包层Cladding of Fiber /Fiber Cladding包层直径Cladding diameter一次被覆层(预涂层)primary coating /procoated衰减Attenuation带宽Bandwidth色散Dispersion数值孔径Numerical Aperture截止波长Cut-off Wavelength模场直径Mode field diameter模场同心度Mode field concertricity包层不圆度Cladding non-circularity同芯度误差Concertricity error偏振模色散,极化模色散PMD(polarization mode dispersion)色度色散chromatic dispersion二、光缆专业术语光缆Ooptical Fiber Cable /Fiber Optic Cable纤芯fiber core束管式光缆Unitube cable层绞式光缆Stranded loose tube cable8字缆Figure 8 Cable光电混合缆Optical Power Composite Cable全介质自承式光缆All Dielectric Self-supporting Aerial Cable铠装光缆:Armored cable非金属加强芯FRP/Fiberglass reinforce with plasticcentral strength menber填充绳Filler剥离绳Ripcord允许拉伸力Tensile Strength允许压扁力Crush Resistance弯曲半径Bending Radius芳纶纱Aramid yarn阻水凝胶Hydrophobic gel光缆油膏Fiber filling gel悬缆线, 承力吊索, 吊线(8字缆用)Messenger wire (supporting strand)三、其他光纤光缆英语光纤跳线Optical Fiber Patch Cord光纤适配器Optical Fiber Adapter光缆终端盒Optical Fiber Termination Box光缆接续盒Optical Fiber Splice Closure光纤到办公室Fiber To The Office FTTO光纤到大楼Fiber To The Building FTTB光纤到服务区Fiber To The Service Area FSA光纤到家Fiber To The Home FTTH光纤到路边Fiber To The Curb FTTC光纤到远端Fiber to the Remote FTTR光纤的Fiber-optic光纤放大器Optical Fiber Amplifier光纤分布式数据接口Fiber Distributed Data Interface FDDI光纤固定衰减器Optical Fixed Attenuator光纤管道Fiber Conduit光纤光缆Optical fiber cable光纤光栅Fiber Grating光纤基带快速以太网FastEthernet, 100baseX光纤接口Fiber Interface FBI光纤连接器Fiber Connector FC光纤耦合器Fiber Coupler光纤熔接盒Fiber splice tray光纤衰减器Fiber Attenuator光纤同轴混合网Hybrid Fiber and Coax Network HFC光纤尾纤Fiber Pigtail光纤引入线Fiber Optic Drop光纤用户环路Fiber In The Loop光纤载波等级3 OC-3 OC-3光线路Optical Line OL光线路板Optical Line Board OL光线路放大器Optical Line Amplifier OLA光线路收发板Optical Line Transceiver Board OLT 光线路终端Optical line terminal OLT光信号Optical Signal光学器件Optics光学字符识别Optical Character Recognition OCR 光载波第1级Optical Carrier Level 1 OC-1光载波第N级Optical Carrier Level N OC-N光栅(fiber) grating光支路接口optical tributary interface光支路接口单元optical interface units高密度分波多任务DWDM。
了解高功率光纤激光光束传输提交的原稿是由一个美国政府在承包商的合同号W - 31 - 109 -英格- 38。
因此,美国政府保留一个排他性的、免版税许可公布或者复制发表的贡献, 或出于美国政府的目的让别人来这么做。
Boyd V. Hunter and Keng H. Leong阿贡国家实验室技术开发部激光应用试验室南Cass大道、建筑207Argonne, Illinois 60439Carl B. Miller, James F. Golden, Robert D. Glesias and Patrick J. LavertyU. S. Laser Corporation825 Windham Court NorthP. O. Box 609Wyckoff, New Jersey 074811996年3月25日摘要光纤束传输常用在工业激光系统。
本文主要考察了优化传播条件高功率光纤光束传输。
光束质量的影响是一步一步地,也会考虑到梯度折射率纤维有多种不同的长度。
纤维束的分离、光束的聚集和纤维面的差异会被阐明。
最糟糕质量的光束纤维,这种估计也会被假设。
指南还提供选择的传输组件基于光束的局限性光学系统和任务来进行。
关键词:激光器、光纤、梁交货,光束质量,YAG、二氧化碳、波导、模式、镜片。
介绍激光的普及应用和波长不同的功率水平已经移除了基于激光材料加工从实验室的好奇心去经济重要制造技术。
然而,利用高功率激光的力量要求,要博学而审慎的选择激光器及其梁输送系统。
本文着重于研究相关问题的理解和指定光纤束交货系统。
我们来复习物理支撑这一操作的光纤提供的一些方针规定一个系统。
对高功率YAG激光器进行数据分析来作为实例说明。
因为许多在理解梁价款不依赖于交货波长的激光,在随后的讨论中普遍适用,尤其当限制波长400纳米、2000纳米之间,在相同的光学材料都可以使用。
采用激光光束产生传输工件有两种不同的方式:freespace传播(1)或(2)光纤。
A01光学材料:A01-001 光学材料Optical MaterialsA01-002 光学玻璃Optical GlassA01-003 激光玻璃Laser GlassA01-004 声光玻璃Acousto-Optic GlassA01-005 红外线玻璃Infrared GlassA01-006 红外线材料Infrared MaterialsA01-007 紫外线材料Ultraviolet MaterialsA01-008 石英镜片Fused Silica GlassA01-009 光学陶瓷CeramicsA01-010 矽半导体材料Silicon Semiconductor MaterialsA01-011 化合物半导体材料Compound Semiconductor Materials A01-012 光纤材料Fiber Optic MaterialsA01-013 光纤预型体Fiber Optic PreformsA01-014 PLZT晶圆,钛酸锆酸铅晶圆PLZT WafersA01-015 环氧树脂EpoxiesA01-016 声光光学晶体Acousto-Optic CrystalsA01-017 双折射/偏光晶体Birefringent and Polarizing Crystals A01-018 电光光学晶体Electro-Optic CrystalsA01-019 红外线晶体Infrared CrystalsA01-020 激光晶体(YAG) YAG Laser CrystalsA01-021 激光晶体(亚历山大) Alexandrite Laser CrystalsA01-022 激光晶体(GGG) GGG Laser CrystalsA01-023 激光晶体(GSGG,GSAG) GSGG GSAG Laser Crystals A01-024 激光晶体(YLF) YLF Laser CrystalsA01-025 激光晶体(其他) Other Laser CrystalsA01-026 非线性光学晶体Nonlinear CrystalsA01-027 有机光学材料Organic Optical MaterialsA01-028 萤光放射晶体Fluorescent Emission CrystalsA01-029 结晶育成材料Crystals Growing MaterialsA01-030 镀膜材料Coating MaterialsA01-031 光罩材料Photomask MaterialsA01-032 真空蒸镀化学药品Vaccum Evaporation ChemicalsA01-033 感光剂SensitizersA01-034 影像用材料Materials for ImagingA01-035 热色材料Thermochromic MaterialsA01-036 光色材料Photochromic MaterialsA01-037 稀土族材料Rare Earth MaterialsA01-038 光碟基板,基板材料Optical Disk Substrate Materials A01-039 光碟记录材料Optical Disk Data Storage MaterialsA02加工用其他材料:A02 加工用其他材料MATERIALS FOR PROCESSINGA02-001 光学用胶合剂/接著剂Optical Cements and Adhesives A02-002 光学用气体Gases for Optical ApplicationA02-003 激光用气体Gases for LasersA02-004 光学研磨材料(研磨布纸) Optical-Coated AbrasiveA02-005 光学研磨材料(砥粒) Optical-Powder or Grin Abrasive A02-006 光学研磨材料(砥石) Optical-Wheel AbrasiveA02-007 研磨化合物Polishing CompoundsA02-008 研磨衬垫及布Polishing Pads and ClothA02-009 全像底片及感光板Holographic Films and PlatesA02-010 红外线底片及感光板Infrared Films and PlatesA02-011 相片用化学药品Photographic ChemicalsA02-012 折射率液Refractive Index LiquidsA02-013 显微镜浸液Microscope Immerison LiquidsA02-014 显微镜埋置用材料Microscope Imbedding MediaA02-015 激光用染料Laser DyesA02-016 冷媒CoolantsA02-017 拭镜纸Lens TissueA03 显示器用材料:A03 显示器用材料MATERIALS FOR DISPLAYA03-001 液晶Liquid CrystalsA03-002 导电膜玻璃基板ITO Glass SubstrateA03-003 彩色滤光片Color FilterA03-004 偏光板/相位差板Polarizer/ Phase Shift LayerA03-005 显示面板用驱动IC Driver ICA03-006 背光源BacklightA03-007 配向膜Alignment FilmA03-008 间隔物SpacerB01 透镜:B01 透镜LENSESB01-001 单透镜Simple (Single) LensesB01-002 球透镜Ball LensesB01-003 歪像透镜Anamorphic LensesB01-004 圆锥透镜Conical LensesB01-005 柱状透镜,环形透镜Cylindrical & Toroidal LensesB01-006 非球面透镜Aspheric LensesB01-007 反射折射透镜Catadioptric LensesB01-008 绕射极限透镜Diffraction-Limited LensesB01-009 GRIN透镜GRIN Lenses (Graduated Refractive Index Rod)B01-010 微小透镜阵列Micro Lens ArraysB01-011 准直透镜Collimator LensesB01-012 聚光透镜Condenser LensesB01-013 多影像透镜Multiple Image LensesB01-014 傅利叶透镜Fourier Lenses B01-015 菲涅尔透镜Fresnel Lenses B01-016 替续透镜Relay LensesB01-017 大口径透镜(直径150mm以上) Large Aperture Lenses (150mm) B01-018 复合透镜Complex LensesB01-019 红外线透镜Infrared LensesB01-020 紫外线透镜Ultraviolet LensesB01-021 激光透镜Laser LensesB01-022 望远镜对物镜Telescope Objectives LensesB01-023 显微镜对物镜Microscope Objectives LensesB01-024 接目镜Eyepieces LensesB01-025 向场透镜Field LensesB01-026 望远镜头Telephoto LensesB01-027 广角镜头Wide Angle LensesB01-028 可变焦伸缩镜头Variable Focal Length Zoom LensesB01-029 CCTV镜头CCTV LensesB01-030 影印机镜头Copy Machine LensesB01-031 传真机镜头Facsimile LensesB01-032 条码扫描器镜头Bar Code Scanner LensesB01-033 影像扫描器镜头Image Scanner LensesB01-034 光碟机读取头透镜Pick-up Head LensesB01-035 APS相机镜头APS Camera LensesB01-036 数位相机镜头Digital Still Camera LensesB01-037 液晶投影机镜头Liquid Crystal Projector LensesB02 镜面:B02 镜面MIRRORB02-001 平面镜Flat MirrorsB02-002 球面凹面镜,球面凸面镜Spherical Concave and Convex Mirrors B02-003 抛物面镜,椭圆面镜Off-Axis Paraboloids and Ellipsoids Mirrors B02-004 非球面镜Aspheric MirrorsB02-005 多面镜Polygonal MirrorsB02-006 热镜Hot MirrorsB02-007 冷镜Cold MirrorsB02-008 玻璃,玻璃/陶瓷面镜Glass and Glass-Ceramic MirrorsB02-009 双色向面镜Dichroic MirrorB02-010 金属面镜Metal MirrorsB02-011 多层面镜Multilayer MirrorsB02-012 半涂银面镜Half-Silvered MirrorsB02-013 激光面镜Laser MirrorsB02-014 天文用面镜Astronomical MirrorsB02-099 其他面镜Other MirrorsB03 棱镜:B03 棱镜PRISMB03-001 Nicol棱镜Nicol PrismsB03-002 Glan-Thomson棱镜Glan-Thomson PrismsB03-003 Wollaston棱镜Wollaston PrismsB03-004 Rochon棱镜Rochon PrismsB03-005 直角棱镜Right-Angle; Rectangular PrismsB03-006 五面棱镜Pentagonal PrismsB03-007 脊角棱镜Roof PrismsB03-008 双棱镜BiprismsB03-009 直视棱镜Direct Vision PrismsB03-010 微小棱镜Micro PrismsB03-099 其他棱镜Other PrismsB04 滤光镜:B04 滤光镜FILTERB04-001 尖锐滤光镜Sharp Cut (off) FiltersB04-002 色温变换滤光镜,日光滤光镜Colour Conversion/Daylight Filters B04-003 干涉滤光镜Interference FiltersB04-004 中性密度滤光镜Neutral Density FiltersB04-005 空间/光学匹配滤光镜Spatial/Optical Matched FiltersB04-006 双色向滤光镜Dichroic FiltersB04-007 偏光滤光镜Polarizing FiltersB04-008 排除频带滤光镜Rejection Band FiltersB04-009 可调式滤光镜Turnable FilterB04-010 超窄频滤光镜Ultra Narrowband FiltersB04-011 色吸收滤光镜Absorption FiltersB04-012 红外吸收/反射滤光镜Infrared Absorbing/Reflecting FiltersB04-013 红外透过滤光镜Infrared Transmitting FiltersB04-014 紫外吸收滤光镜Ultraviolet Absorbing FiltersB04-015 紫外透过滤光镜Ultraviolet Transmitting FiltersB04-016 针孔滤光镜Pinhole FiltersB04-017 有色玻璃滤光镜Colored-Glass FiltersB04-018 塑胶滤光镜Plastic FiltersB04-019 照像用滤光镜Photographic FiltersB04-020 全像滤光镜Holographic FiltersB04-021 微小干涉滤光镜Micro Interference FiltersB06 激光:LASERS B06 激光LASERSB06-100 气体激光GAS LASERSB06-101 氦氖激光He-Ne LasersB06-102 金属蒸气激光Metal Vapor LasersB06-103 氩离子激光Argon LasersB06-104 氪离子激光Krypton LasersB06-105 二氧化碳激光(气流型) CO2 (Gas Flow type) LasersB06-106 二氧化碳激光(脉冲,TEA型) CO2 (Pulsed,TEA) LasersB06-107 二氧化碳激光(密封型) CO2 (Sealed tube) LasersB06-108 二氧化碳激光(波导型) CO2 (Wave guide) LasersB06-109 一氧化碳激光CO LasersB06-110 氦镉激光He-Cd LasersB06-111 氮分子激光Nitrogen LasersB06-112 准分子激光Excimer LasersB06-113 氙分子激光Xenon LasersB06-200 固体激光SOLID STATE LASERSB06-201 红宝石激光Ruby LasersB06-202 玻璃激光Glass LasersB06-203 Nd:YAG激光(脉冲式) Nd:YAG (Pulsed) LasersB06-204 Nd:YAG激光(连续式) Nd:YAG Laser (CW) LasersB06-205 Nd:YAG激光(半导体激光激发) Nd:YAG (LD Pumped) LasersB06-206 YLF激光YLF LasersB06-207 亚历山大激光Alexanderite LasersB06-208 铒固体激光Erbium LasersB06-209 半导体激光激发式固态激光Solid State(LD pumped)LaserB06-210 其他固态激光OthersB06-300 染料激光DYE LASERSB06-301 染料激光(闪光灯激发) Dye (Flash lamp Pumped) LasersB06-302 染料激光(激光激发) Dye (Laser Pumped) LasersB06-400 半导体激光SEMICONDUCTOR LASERSB06-401 半导体激光(1.55μm带) Semiconductor (1.55μm) LasersB06-402 半导体激光(1.30μm带) Semiconductor (1.30μm) LasersB06-403 半导体激光(0.85μm带) Semiconductor (0.85μm) LasersB06-404 半导体激光(0.78μm带) Semiconductor (0.78μm) LasersB06-405 半导体激光(0.60μm带) Semiconductor (0.60μm) LasersB06-406 半导体激光(其他波长带) Other Semiconductor LasersB06-407 半导体激光模组(长波长) Semiconductor (Long Wavelength) Laser ModulesB06-408 半导体激光模组(短波长) Semiconductor (Short Wavelength) Laser ModulesB06-409 半导体激光模组(可见光) Semiconductor (Visible) Laser ModulesB06-501 铁离子中心激光F-Center LasersB06-502 化学激光(HF-DF) Chemical (HF-DF) LasersB06-503 平板激光Slab LasersB06-504 远红外线激光Far-Infrared LasersB06-505 真空紫外线激光Vacuum Ultraviolet LasersB06-506 多色激光Multi Colour LasersB06-507 稳频激光Frequency Stabilized LasersB06-508 自由电子激光Free Electron LasersB07 激光用元件:B07 激光用元件LASER COMPONENTSB07-001 Q 开关Laser Q-SwitchesB07-002 激光管Laser Tubes and BoresB07-003 激光棒Laser RodsB07-004 激光板Laser SlabsB07-005 气体再生设备,气体填充设备Gas Recyclers and Gas Handling EquipmentB07-006 激光控制设备Laser Control EquipmentB07-007 激光用盒Laser CellsB07-008 参数振汤器Parametric OscillatorsB07-009 光脉冲产生设备Optical Pulse GeneratorsB07-010 激光用共振腔Resonators for LasersB07-011 磁铁MagnetsB07-012 激光用冷却设备Cooling Systems for LasersB07-013 激光护眼镜Safty Equipment; Goggles Glasses and FilmsB07-014 激光光吸收体Safty Equipment; Laser AbsorbersB07-015 激光用安全设备Safty Equipment; Protective HousingsB08 发光二极体:B08 发光二极体LIGHT-EMITTING DIODES; LEDB08-001 通信用1.55μm发光二极体1.55μm LEDs for CommunicationB08-002 通信用1.30μm发光二极体1.30μm LEDs for CommunicationB08-003 通信用0.85μm发光二极体0.85μm LEDs for CommunicationB08-004 通信用长波长发光二极体模组Long Wavelength LED Modules for Communication B08-005 通信用短波长发光二极体模组Short Wavelength LED Modules for Communication B08-006 可见光发光二极体(红色) Visible (Red) LEDsB08-007 可见光发光二极体(黄色) Visible (Yellow,Orange) LEDsB08-008 可见光发光二极体(绿色,多色) Visible (Green,Multi-Color) LEDsB08-009 可见光发光二极体(蓝色) Visible (Blue) LEDsB08-010 红外线二极体(非通信用) Infrared (not for Communication) LEDsB08-011 文数字表示用发光二极体Alpha-Numeric LEDsB08-012 发光二极体晶圆(通信用) LED Wafers for CommunicationB08-013 发光二极体晶圆(非通信用) LED Wafers not for CommunicationB08-014 发光二极体晶片、晶粒(通信用) LED Chips for CommunicationB08-015 发光二极体晶片、晶粒(非通信用) LED Chips not for CommunicationB09 光源设备:B09 光源设备LIGHT SOURCESB09-001 标准光源Standard Light SourcesB09-002 安定化光源Stabilized Light SourcesB09-003 弧光灯Arc Light SourcesB09-004 氪灯Krypton Light SourcesB09-005 卤素灯Halogen Light SourcesB09-006 氙灯Xenon /Xenon Flashlamps Light SourcesB09-007 紫外线光源Ultraviolet Light SourcesB09-008 真空紫外线光源VUV Light SourcesB09-009 红外线光源Infrared Light SourcesB09-010 闪光光源Stroboscopic Light SourcesB09-011 小型光源Miniature Light SourcesB09-012 光纤光源Fiber Optic IlluminatorsB10 显示器元件:B10 显示器元件DISPLAY PANELB10-001 发光二极体显示器LED DisplaysB10-002 液晶显示器Liquid Crystal Display (LCD)B10-003 电浆显示器Plasma Display Panels(PDP)B10-004 电激发光显示器Electroluminescence Display (ELD)B10-005 电铬显示器Electrochromic Display (ECD)B10-006 真空萤光显示器Vacuum Fluorescent Display (VFD)B10-007 平面阴极射线管Flat CRTsB10-008 场发射显示器Field Emitter Display(FED)B10-099 其他平面显示元件Other Flat Panel DisplaysB11 检光元件及光纤混成元件:B11 检光元件及光纤混成元件DETECTORS & FIBEROPTIC HYBRID DEVICESB11-001 通信用PIN光二极体PIN Photodiodes for CommunicationB11-002 通信用崩溃光二极体Avalanche Photodiodes for CommunicationB11-003 通信用(长波长)Ge和III-V族检光元件Long-wavelength Detectors for CommunicationB11-004 通信用PIN光二极体模组PIN Photodiode Modules for CommunicationB11-005 通信用崩溃光二极体模组Avalanche Photodiode Modules for CommunicationB11-006 通信用(长波长)Ge和III-V族检光模组Long-wavelength Decector Modules for Communication B11-007 光二极体(近红外光) Near-infrafed PhotodiodesB11-008 光二极体(可见光) Visible PhotodiodesB11-009 光二极体(紫外光) Ultraviolet PhotodiodesB11-010 光电晶体PhototransistorsB11-011 光电管PhototubesB11-012 光电子增倍管(PMT) PhotomultipliersB11-013 光导电池Photoconductive CellsB11-014 热电偶检测器Thermocouple DetectorsB11-015 热堆检测器Thermopile DetectorsB11-016 微道板Microchannel PlatesB11-017 热电检测器Pyroelectroic DetectorsB11-018 辐射热测定器BolometersB11-019 其他红外线检测器Infrared DetectorsB11-020 摄像管Camera TubesB11-021 线型检光元件One Dimension Detector ArraysB11-022 面型检光元件Two Dimension Detector ArraysB11-023 光电耦合器Photo CouplerB11-024 光断续器Photo InterrupterB11-025 光反射器Photo ReflectorB11-026 光闸流晶体管PhotocyristorsB11-027 光感测元件Photosensing UnitsB11-028 内藏电路之光感测器Detectors with CircuitB11-029 民用用太阳电池Solar Cells for Consumer UseB11-030 产业用太阳电池Solar Cells for Power & Space UseB12 光纤及光缆:B12 光纤及光缆FIBER OPTIC FIBERS & CABLEB12-100 光纤FIBER OPTIC FIBERSB12-101 石英系多模态步阶式折射率型光纤Fiber Optic Fibers, Silica, Multimode, Step IndexB12-102 石英系多模态渐近式折射率型光纤(50/125) Fiber Optic Fibers, Silica, Multimode, Graded Index,50/125B12-103 石英系多模态渐近式折射率型光纤(62.5/125) Fiber Optic Fibers, Silica, Multimode,Graded Index ,62.5/125B12-104 石英系多模态渐近式折射率型光纤(100/140) Fiber Optic Fibers, Silica, Multimode,Graded Index ,100/140B12-105 石英系单模态标准型光纤Fiber Optic Fibers, Silica, Single Mode,StandardB12-106 色散位移光纤Fiber Optic Fibers, Dispersion – ShiftedB12-107 偏振恒持光纤Fiber Optic Fibers, Polarization – MaintainingB12-108 其他单模态光纤Other Single Mode Optic FibersB12-109 石英系塑胶包覆光纤Fiber Optic Fibers, Plastic - Clad SilicaB12-110 塑胶光纤Fiber Optic Fibers, PlasticB12-111 石英系影像光纤Fiber Optic Bundles, Silica, ImagingB12-112 多成分影像光纤Fiber Optic Bundles, Non-silica, ImagingB12-113 光导管Fiber Optic LightguidesB12-199 其他集束光纤Other Fiber Optic BundlesB12-200 光缆FIBER OPTIC CABLEB12-201 单模态标准型松包悬空式光缆Fiber Optic Cable, Single Mode, Standard, Loosely Buffered, AerialB12-202 单模态标准型松包管路式光缆Fiber Optic Cable, Single Mode, Standard, Loosely Buffered, DuctB12-203 单模态标准型松包直埋式光缆Fiber Optic Cable, Single Mode, Standard, Loosely Buffered, Direct BuriedB12-204 单模态标准型紧包单心式光缆Fiber Optic Cable, Single Mode, Standard, Tightly Buffered, Single FiberB12-205 单模态标准型紧包多心式光缆Fiber Optic Cable, Single Mode, Standard, Tightly Buffered, MultifiberB12-206 光纤带RibbonB12-207 色散位移光缆Fiber Optic Cable, Dispersion-ShiftedB12-208 偏振恒持光缆Fiber Optic Cable, Polarization – MaintainingB12-209 其他单模态光缆Other Single Mode Fiber Optic CableB12-210 多模态石英系(50/125)光缆Fiber Optic Cable, Multimode, Silica, 50/125B12-211 多模态石英系(62.5/125)光缆Fiber Optic Cable, Multimode, Silica, 62.5/125B12-212 多模态石英系(100/140)光缆Fiber Optic Cable, Multimode, Silica, 100/140B12-213 塑胶光缆Fiber Optic Cable, PlasticB12-214 石英系塑胶包覆光缆Fiber Optic Cable, Plastic-Clad SilicaB12-215 其他多模态光缆Other Multimode Fiber Optic CableB12-216 光纤保护用管Protect Tubes for Fiber Optic FiberB13 光被动元件/光控制元件:B13 光被动元件/光控制元件OPTICAL PASSIVE DEVICES/CONTROL DEVICESB13-001 单模态ST光纤连接器Fiber Optic Connectors, Single Mode, STB13-002 单模态Biconic光纤连接器Fiber Optic Connectors, Single Mode, BiconicB13-003 单模态FC/PC光纤连接器Fiber Optic Connectors, Single Mode, FC/PCB13-004 单模态APC光纤连接器Fiber Optic Connectors, Single Mode, APCB13-005 单模态FDDI光纤连接器Fiber Optic Connectors, Single Mode, FDDIB13-006 单模态SC光纤连接器Fiber Optic Connectors, Single Mode, SCB13-007 单模态D4光纤连接器Fiber Optic Connectors, Single Mode, D4B13-008 单模态光纤连接器插座(ST,FC/PC,SC,Biconic) Fiber Optic Connectors, Single Mode, Adapter(ST,FC/PC,SC,Biconic) B13-009 单模态多心光纤连接器(MT) Fiber Optic Connectors, Single Mode,Multi-Channel/MTB13-010 其他单模态光纤连接器Other Single Mode Fiber Optic ConnectorsB13-011 多模态ST光纤连接器Fiber Optic Connectors, Multimode, STB13-012 多模态FC/PC相容光纤连接器Fiber Optic Connectors, Multimode, FC/PCB13-013 多模态SMA光纤连接器Fiber Optic Connectors, Multimode, SMAB13-014 多模态FDDI光纤连接器Fiber Optic Connectors, Multimode, FDDIB13-015 多模态SC光纤连接器Fiber Optic Connectors, Multimode, SCB13-016 多模态D4光纤连接器Fiber Optic Connectors, Multimode, D4B13-017 多模态光纤连接器插座(ST,SMA,FC/PC) Fiber Optic Connectors, Multimode,Adapter(ST,SMA,FC/PC)B13-018 多模态多心光纤连接器Fiber Optic Connectors, Multimode, Multi-ChannelB13-019 其他多模态光纤连接器Other Multimode Fiber Optic ConnectorsB13-020 套筒SleevesB13-021 金属箍(套管) Metal FerrulesB13-022 塑胶箍(套管) Plastic FerrulesB13-023 陶瓷箍(套管) Ceramic FerrulesB13-024 插座ReceptaclesB13-025 插头PlugsB13-026 光连接器(含光纤线) Optical Connectors with FiberB13-027 光纤耦合器(两分支) Optical Couplers, Tap/SplitterB13-028 光纤耦合器(树状分支) Optical Couplers, TreeB13-029 星状光纤耦合器(穿透形) Transmission Type Star Optical CouplersB13-030 星状光纤耦合器(反射形) Reflection Type Star Optical CouplersB13-031 其他光纤耦合器Other Optical CouplersB13-032 光分波合波器(两波长) Optical Couplers, WDM, Dual-WavelengthB13-033 光分波合波器(多波长) Optical Couplers, WDM, Over Two WavelengthB13-034 其他光分波合波器Other Optical WDM CouplersB13-035 光衰减器(固定) Fixed Optical AttenuatorsB13-036 光衰减器(可变) Adjustable Optical AttenuatorsB13-037 光隔离器(通信用) Optical Isolators for CommunicationB13-038 光隔离器(非通信用) Optical Isolators for Non-CommunicationB13-039 光环流器Optical CirculatorsB13-040 光开关(机械式) Mechanical Optical SwitchesB13-041 光开关(非机械式) Non-mechanical Optical SwitchesB13-042 光纤光栅Fiber Bragg GratingB13-043 光移相器Optical Phase ShiftersB13-044 光共振器Optical ResonatorsB13-045 空间调变元件Spatial Light ModulatorsB13-046 光影像转换元件(ITC) Incoherent to Coherent Devices(ITC)B13-047 光截波器,机械式光调变器Optical Choppers, Mechanical ModulatorsB13-048 磁光调变器Maganeto-Optic ModulatorsB13-049 声光调变器Acousto-Optic ModulatorsB13-050 电光调变器Electro-Optic ModulatorsB13-051 波导形调变器,行波形调变器Optical Waveguide,Travelling-wave ModulatorsB13-052 类比/强度调变器Analog/Intensity ModulatorsB13-053 数位调变器Digital ModulatorsB13-054 其他调变器Other ModulatorsB13-055 光弹性调变器Photoelastic ModulatorsB13-056 机械式偏折/扫瞄器(Galvanometer方式) Mechanical Optical Deflectors/Scanners(Galvanometer Mirror)B13-057 声光偏折/扫瞄器Acousto-Optic Optical Deflectors/ScannersB13-058 电光偏折/扫瞄器Electro-Optic Optical Deflectors/ScannersB13-059 机械式扫瞄器(回转多面镜方式) Mechanical Optical Scanners(Polygonal Mirrors)B13-060 机械式扫瞄器(全像方式) Mechanical Optical Scanners(Holographic)B13-061 光纤跳接线Fiber Optic Patchcord PigtailB13-062 光纤终端箱Fiber Optic Distribution BoxB13-063 光纤接续盒Fiber Optic ClosureB13-099 其他光被动元件/控制元件Other Optical Passive Devices/Control DevicesB14 积体光元件:B14 积体光元件INTEGRATED OPTICAL DEVICESB14-001 光IC Optical ICB14-002 OEIC Optoelectronic ICB14-099 其他光电元件Other DevicesC01 光通讯设备:C01 光通讯设备OPTICAL COMMUNICATION EQUIPMENTC01-100 电信用光通讯设备OPTICAL COMMUNICATION EQUIPEMNT(TELECOMMUNICATION)C01-101 同步光纤网路光波传输系统及多工机设备Lightwave/Transimission System and Multiplexer Equipment (SONET-Based) C01-102 同步光纤网路光数位回路载波机设备Optical/Digital Loop Carrier Equipment (SONET-Based)C01-103 同步光纤网路数位交换连接系统设备Digital Cross Connect System Equipment (SONET-based)C01-104 同步数位阶层光波传输系统及多工机设备Lightwave/Transmission System and Multiplexer Equipment (SDH-Based)C01-105 同步数位阶层光数位回路载波机设备Optical/Digital Loop Carrier Equipment (SDH-Based)C01-106 同步数位阶层数位交换连接系统设备Digital Cross Connect System Equipment (SDH-Based)C01-107 光纤网路单体ONU(Optical Network Unit)C01-108 非同步光通讯设备Asynchronous Optical Communication EquipmentC01-199 其他公众用光通讯设备Other Optical Communication Equipment (Telecommunication)C01-200 数据通讯光纤网路设备OPTICAL DATA COMMUNICATION NETWORK EQUIPMENT (PREMISES) C01-201 光纤分散式资料介面网路设备FDDI Network EquipmentC01-202 非同步传输模式网路设备ATM Network EquipmentC01-203 高速乙太网路设备Fast Ethernet Network EquipmentC01-204 光纤通道Fiber ChannelC01-299 其他用户光数据通讯设备Other Optical Data Communication Network Equipment (Premises)C01-300 特殊用途光传输设备OPTICAL TRANSMISSION EQUIPMENT(SPECIAL PURPOSE)C01-301 有线电视光传输设备Optical Transmission Equipment, CATVC01-302 视讯/闭路监视光传输设备Optical Transmission Equipment, Video/CCTVC01-303 量测/控制信号光传输设备Optical Transmission Equipment, Measure/ControlC01-304 空间(无线)光传输设备Optical Transmission Equipment, Spatial (Wireless)C01-305 光放大器Optical AmplifierC01-399 其他特殊用途光传输设备Other Optical Transmission Equipment (Special Purpose)C02 光测仪器设备:C02 光测仪器设备OPTICAL MEASURING EQUIPMENTC02-001 量测用标准光源Standard/Stabilized Light SourcesC02-002 光功率计(热转换型) Thermal Conversion Type Optical Power MetersC02-003 光功率计(光电转换型) Photoelectric Conversion Type Optical Power MetersC02-004 光谱分析仪Optical Spectrum AnalyzersC02-005 光波长计Optical Wavelength MetersC02-006 光谱幅宽量测器Spectral Width Measuring EquipmentC02-007 光时域反射计(OTDR) Optical Time-Domain Reflectometers(OTDR)C02-008 基频传输特性检测器Baseband Frequency Characteristics Evaluation EquipmentC02-009 波长色散量测器Wavelength Dispersion Measuring EquipmentC02-010 光纤测试设备Optical Fiber Test EquipmentC02-011 激光光束波形量测器Laser Beam Profile Measuring EquipmentC02-012 光纤尺寸量测器Optical Fiber Sizes Measuring EquipmentC02-013 光纤模态参数测试器Optical Fiber Mode Field Parameters Test EquipmentC02-014 光纤强度测试器Optical Fiber Strength Test EquipmentC02-015 其他光纤相关量测设备Other Optical Fiber Measurement EquipmentC02-016 光连接器尺寸量测器Optical Connector Sizes Measuring EquipmentC02-017 光碟测定检查设备(装置用) Optical Disk Drive Inspection EquipmentC02-018 光碟测定检查设备(碟片用) Optical Disk Inspection EquipmentC02-019 光度计PhotometersC02-020 复光束光度计,复光束量测器Double Beam PhotometersC02-021 测微光度计MicrophotometersC02-022 感光密度计DensitometersC02-023 光泽度计GrossmetersC02-024 照度计Illuminance MetersC02-025 测距仪RangefindersC02-026 曝光计Exposure MetersC02-027 辉度计Luminance MetersC02-028 比色计Comparison ColorimetersC02-029 色彩计(分光型) Spectral ColorimetersC02-030 色彩计(光电型) Photoelectric ColorimetersC02-031 积分球Integrating SpheresC02-032 折射计RefractometersC02-033 椭圆计EllipsometersC02-034 偏振光镜PolariscopesC02-035 偏振计PolarimetersC02-036 比较量测器ComparatorsC02-037 焦距仪FocometersC02-038 球径计SpheremetersC02-039 OTF(光学转换函数)设备Optical Transfer Function InstrumentationC02-040 MTF分析/量测装置Modulation Transfer Function(MTF) Analysis/Measurement EquipmentC02-041 投影检查器Profile ProjectorsC02-042 自动准直仪AutocollimatorsC02-043 光弹性机器Photoelastic InstrumentsC02-099 其他光(学)量测器Other Optical Measurement EquipmentC03 分光镜、干涉仪:C03 分光镜、干涉仪SPECTROSCOPES, INTERFEROMETERSC03-001 分光计SpectrometersC03-002 单色器MonochromatorsC03-003 分光镜,干涉分光镜,摄谱仪Spectroscopes, Interference Spectroscopes,SpectrographsC03-004 分光光度计,分光测光器SpectrophotometerC03-005 Michelson干涉仪Michelson InterferometersC03-006 Tywman Green干涉仪Tywman Green InterferometersC03-007 Mach-Zehnder干涉仪Mach-Zehnder InterferometersC03-008 Fizeau干涉仪Fizeau InterferometersC03-009 Fabry-Perot干涉仪Fabry-Perot InterferometersC04 显微镜,望远镜,照像机:C04 显微镜,望远镜,照像机MICROSCOPES, TELESCOPES, CAMERASC04-001 放大镜MagnifiersC04-002 单接物镜双眼显微镜Binocular MicroscopesC04-003 双眼实体显微镜,立体显微镜Stereo MicroscopesC04-004 金属显微镜Metallurgical MicroscopesC04-005 偏光显微镜Polarizing MicroscopesC04-006 相位差显微镜Phase-Contrast MicroscpoesC04-007 干涉显微镜,微分干涉对比显微镜Interferences/Differential Interference Contrast Microscopes C04-008 萤光显微镜Fluorescence MicroscopesC04-009 激光显微镜Laser MicroscopesC04-010 量测用显微镜,工具显微镜Measurement MicroscopesC04-011 显微镜光度计Microscope PhotometersC04-012 折射望远镜,Galilean望远镜Galilean Refracting TelescopesC04-013 反射望远镜Reflecting TelescopesC04-014 反射折射望远镜Catadioptric TelescopesC04-015 35mm焦平面自动对焦相机35mm AF Focal Plane CamerasC04-016 35mm焦平面手动对焦相机35mm NON-AF Focal Plane CamerasC04-017 35mm镜头快门多焦点相机35mm Multi Focal Points Lens Shutter CamerasC04-018 35mm镜头快门单焦点相机35mm Single Focal Point Lens Shutter CamerasC04-019 中,大型照相机Medium and Large Size CamerasC04-020 VTR摄影机VTR CamerasC04-021 电视摄影机TV CamerasC04-022 高画质电视摄影机High Definition(HDTV) CamerasC04-023 CCTV摄影机CCTV CamerasC04-024 全像照像机Holographic CamerasC04-025 眼镜EyeglassesC04-026 夜视设备Night Vision EquipmentC04-027 照像机用之日期显示模组Date moduleC04-028 照像机用之底片计数器Film counterC04-029 APS相机APS CamerasC05 光感测器:C05 光感测器OPTICAL SENSORSC05-001 光电开关,光电感测器Photo Switches, Photo SensorsC05-002 标记感测器Mark Photo SensorsC05-003 色彩标记感测器Color Mark Photo SensorsC05-004 色彩感测器Color Photo SensorsC05-005 光学式编码器,角度感测器Optical Encoders, Angle SensorsC05-006 光遥控器Optical Remote Control EquipmentC05-007 影像感测器式量测设备Image Sensor Type Measurement InstrumentsC05-008 显微镜式量测设备Microscope Type Measurement InstrumentsC05-009 精密长度干涉仪Precise Length InterferometersC05-010 光波测距装置Electronic Distance MetersC05-011 三角测量法距离感测器Triangulation Distance MetersC05-012 激光调变测距方式距离感测器Laser Modulation Distance MetersC05-013 脉冲测距方式距离感测器Pulse Distance MetersC05-014 激光外径测定器Laser Outer Diameter Measuring SensorsC05-015 激光厚度计Laser Thickness GaugesC05-016 激光拉伸计Laser Extension MeterC05-017 红外线厚度计Infrared Thickness GaugesC05-018 水平仪LevelsC05-019 激光水平仪Laser LevelsC05-020 经纬仪Theodlites/TransitsC05-021 激光经纬仪Laser Theodlites/TransitsC05-022 激光标线设备Laser Marking-off EquipmentC05-023 位置光电感测器Position Sensors, Pattern Edge SensorsC05-024 半导体位置感测器Position Sensitive Devices(PSDs)C05-025 激光指示器Laser PointersC05-026 激光都卜勒测速计Laser Doppler VelocimetersC05-027 环形激光流速计,光纤陀螺仪Ring Laser Velocimeters, Optical Fiber Laser GyrosC05-028 转速仪Rotational Speed MetersC05-029 激光都卜勒转速仪Laser Doppler Rotational Speed MetersC05-030 全像方式图样量测设备Holographic Method Pattern Measurement EquipmentsC05-031 激光移位计Laser Displacement MetersC05-032 激光指纹检测器Laser Fingerprint DetectorsC05-033 光学水质污染检测设备Optical Water Pollution Measurement and Detection Equipment C05-034 光学大气污染检测设备Optical Air Pollution Measurement and Detection EquipmentC05-035 红外线气体浓度感测器Infrared Gas Density MetersC05-036 光电式烟检知器Photo Smoke DetectorsC05-037 激光粉尘监视器,粒径量测器Laser Dust MonitorsC05-038 距离测定用激光雷达Rang-finding Lidar SystemsC05-039 环境监测用激光雷达Environment Monitoring Lidar SystemsC05-040 激光表面检查设备Laser Surface Inspection EquipmentC05-041 平面度测定系统Flatness TestersC05-042 斑点图形量测设备Speckle Method Pattern Measurement EquipmentC05-043 云纹图形量测设备Moire Method Pattern Measurement EquipmentC05-044 影像分析仪Image AnalyzersC05-045 激光缺陷检查设备Laser Defect Inspection EquipmentC05-046 红外线辐射温度感测器Infrared ThermometersC05-047 人体检知感测器,激光保全设备Laser Security/Surveillance EquipmentsC05-048 光计数器Photo CountersC05-049 激光公害检测设备Laser Pollution Detective DevicesC05-050 激光热常数量测设备Laser Thermal Constants Measurement EquipmentC05-051 全像非破坏检查设备Holographic Nondestructive Testing EquipmentC06 光纤感测器:C06 光纤感测器FIBER OPTIC SENSORSC06-001 光纤光电开关/感测器Fiber Optic Photo Switches/ SensorsC06-002 光纤式标记感测器Fiber Optic Mark Photo SensorsC06-003 光纤式色彩标记感测器Fiber Optic Color Mark Photo SensorsC06-004 光纤温度感测器Fiber Optic Temperature SensorsC06-005 光纤压力感测器Fiber Optic Pressure SensorsC06-006 光纤声波感测器Fiber Optic Acoustic SensorsC06-007 光纤变形感测器Fiber Optic Strain SensorsC06-008 光纤振动感测器Fiber Optic Vibration SensorsC06-009 光纤移位感测器Fiber Optic Displacement SensorsC06-010 光纤陀螺仪感测器Fiber Optic Gyro SensorsC06-011 光纤速度感测器Fiber Optic Velocity SensorsC06-012 光纤磁通量感测器Fiber Optic Magnetic Flux SensorsC06-013 光纤磁场感测器Fiber Optic Magnetic Field SensorsC06-014 光纤电流感测器Fiber Optic Current SensorsC06-015 光纤电场感测器Fiber Optic Electric Field SensorsC06-016 光纤浓度、成份感测器Fiber Optic Density,Constituent SensorsC06-017 光纤油膜感测器Fiber Optic Oil Film SensorsC06-018 光纤液位感测器Fiber Optic Liquid Surface Level SensorsC06-019 光纤光分布/放射线感测器Fiber Optic Light Distribution/Radiation SensorsC06-020 光纤显微镜Fiber Optic FiberscopesC06-021 光纤光栅应变感测器Fiber Grating Strain SensorC07 光储存装置:C07 光储存装置OPTICAL STORAGE PRODUCTC07-100 消费性光碟机CONSUMER OPTICAL DISC PLAYERSC07-101 激光唱盘Compact Disc (CD) PlayersC07-102 激光音响组合Products Incorporated CD(CD-Radio-Cassette Tape Recorders)C07-103 LD 影碟机Laser Disc (LD) PlayersC07-104 影音光碟机Video CD PlayersC07-105 DVD DVD 影碟机Digital Versatile Disc (DVD) PlayersC07-106 迷你音碟机Mini Disc (MD) PlayersC07-200 资讯用仅读型光碟机READ-ONLY OPTICAL DISC DRI597VESC07-201 CD-ROMCD-ROM光碟机CD-ROM DrivesC07-202 DVD-ROM DVD-ROM 光碟机DVD-ROM DrivesC07-300 资讯用仅写一次型光碟机RECORDABLE OPTICAL DISC DRIVESC07-301 CD-R CD-R 光碟机CD-R DrivesC07-399 其他仅写一次型光碟机Other Recordable Optical Disc DrivesC07-400 资讯用可覆写型光碟机REWRITABLE OPTICAL DISC DRIVESC07-401 3.5" MO 光碟机3.5" MO Disc DrivesC07-402 5.25" MO 光碟机5.25" MO Disc DrivesC07-403 PD 光碟机PD DrivesC07-404 CD-RW光碟机CD-RW DrivesC07-499 其他可覆写型光碟机Other Rewritable Optical Disc DrivesC07-500 光碟机零组件DEVICES OF OPTICAL DISC DRIVESC07-501 光学头,光学读取头Optical Heads , Pick-up HeadsC07-502 光学头伺服装置,伺服用IC模组Optical Head Controllers, Control ICs/Modules C07-503 光学头驱动装置Optical Head ServomotorsC07-504 光碟匣Optical Disc CartridgesC07-505 主轴马达Spindle MotorC07-600 光碟片OPTICAL DISCSC07-601 CD 音碟片Compact DiscsC07-602 LD 影碟片Laser DiscsC07-603 影音光碟片Video CDsC07-604 DVD光碟片Digital Versatile Discs : DVDsC07-605 迷你音碟片Mini Discs : MDsC07-606 CD-ROM 光碟片CD-ROMsC07-607 DVD-ROM光碟片DVD-ROMsC07-608 CD-R 光碟片CD-RsC07-609 其他可写仅读型光碟片Other Recordable Optical DiscsC07-610 3.5" MO 光碟片3.5" MO DiscsC07-011 5.25" MO 光碟片5.25" MO DiscsC07-612 PD 光碟片PD DiscsC07-613 CD-RW 光碟片CD-RW DiscsC07-699 其他可复写型光碟片Other Rewritable Optical DiscsC08 光输出入装置:C08 光输出入装置OPTICAL INPUT &OUTPUT DEVICESC08-100 数位相机Digital Still CameraC08-200 光学印表机OPTICAL PRINTERSC08-201 彩色激光印表机Laser Color PrintersC08-202 单色激光印表机Laser Monochrome PrintersC08-203 彩色LED印表机LED Color PrintersC08-204 单色LED印表机LED Monochrome PrintersC08-299 其他光学式印表机Other Optical PrintersC08-300 影印机COPY MACHINESC08-301 彩色激光数位影印机Laser Digital Color Copy MachinesC08-302 单色激光数位影印机Laser Digital Monochrome Copy MachinesC08-400 传真机FACSIMILESC08-401 热感纸传真机Termal Paper Facsimiles。
天津大学《工程光学Ⅰ》课程教学大纲课程代码:2020015课程名称:工程光学Ⅰ学时:48学分:3授课:48 上机:实验:实践:实践学时分配:(周):授课学院:精仪学院更新时间:2011年12月适用专业:生物医学工程先修课程:高等数学,大学物理一、课程的性质与目的本课程是一门基础课,主要讲授几何光学、物理光学和现代光学方面的基本理论、基本方法和典型光学元件、系统实例及应用。
通过本课程的学习,学生应能理解光的本质特性,了解各种光学现象及对应的基本原理,熟悉常见光学元件和典型系统,为学习生物光子学、医用光学仪器和从事光学研究打下坚实的基础。
二、教学基本要求任课教师应尽可能充分利用多媒体课件、课程网站等现有教学资源,根据实际条件开展不同程度的双语教学实践;课堂教学后,要留一定数量的作业题,并坚持批改1/3,以利掌握学生的学习情况;学生应按要求参加全部的课堂教学活动,按要求完成作业;参加期末考试,获得该课程学分。
通过本课程的学习,要求达到:1.系统掌握几何光学的基础理论,包括基本定律、成像相关表述、理想光学系统理论。
2.掌握典型的光学系统,包括放大系统、显微系统和望远系统。
3.掌握光的电磁理论及光波叠加的相关知识。
4.掌握光的干涉、衍射、偏振的理论和计算。
5.了解现代光学系统。
三、教学内容绪论1.学习《工程光学》的意义和重要性(光学发展的历史,对国民经济发展的重要作用,光学在生物医学工程领域的应用)2.本课程的性质、任务和内容3.学习的基本要求、教学环节和学习方法第1章几何光学基本定律与成像概念1.几何光学基本定律:1)光的直线传播定律 2)光的独立传播定律 3)反射定律和折射定律(全反射及其应用) 4)光路的可逆性 5)费马原理(最短光程原理) 6)马吕斯定律:2.完善成像条件的概念和相关表述3.应用光学中的符号规则,单个折射球面的光线光路计算公式(近轴、远轴)4.单个折射面的成像公式,包括垂轴放大率、轴向放大率、角放大率γ、拉赫不变量等公式。
天津大学《光纤光学》课程教学大纲
课程编号:2020090 课程名称:光纤光学
学时:32 学分: 2
学时分配:授课:32 上机: 0 实验: 0 实践: 0 实践(周):授课学院:精密仪器与光电子工程学院
适用专业:电子科学与技术(光电子方向)、光电子技术科学、光学工程
先修课程:激光原理、物理光学
一、课程的性质与目的
本课程是一门专业选修课。
通过本课程的学习,学生应能掌握光纤光学的基本理论和基本方法,分析和解决光纤光学中的实际问题,同时了解光纤光学的应用和发展动态。
二、教学基本要求
1.了解光纤的基本应用领域,系统掌握光纤的基本性质和光纤中的光传输的基本理论,并能运用这些基本理论解释、推导光纤光学中的有关问题。
2.掌握分析和衡量光纤无源、有源器件性能的基本方法,熟知各类器件的基本特性、使用方法和基本应用,了解当前国内外相关的前沿动态和研究热点趋势。
3.熟知光纤领域研究中基本参数的测量方法、原理和使用的测量仪器。
能运用仪器进行简单操作。
三、教学内容
第一章光纤概述
本章主要介绍光纤的基本应用领域、光纤的基本特性和分析方法。
1 绪论
2 光纤概述
3光波在光纤中的传播特性
4 光纤的色散特性
5 光纤的损耗
6单模光纤中的非线性效应
第二章光无源器件
本章主要介绍光纤光学中常用的光无源器件,分析各类器件的基本原理和特性、衡量指标以及典型应用。
1光纤连接器
2光纤耦合器
3 偏振控制器
4光隔离器)
5 光滤波器/复用器
第三章光有源器件
本章主要介绍光纤光学中基本的光有源器件及其典型应用,分析各类器件的原理、特性。
1 光调制器
2光放大器
3 光纤激光器
第四章故障诊断和测试设备简介
本章主要介绍光纤光学中常见参数的测量方法和常用的测量仪器。
1 光功率测量
2 波长和频率测量
3 时间测量
4 信号质量测量
5 光时域反射计
四、学时分配
五、评价与考核方式
平时成绩10%,期末成绩90%
六、教材与主要参考资料
1.《光纤光学》,廖延彪编著,清华大学出版社,1999
2.《光纤光学》,Jeff. Hecht 著,贾东方等译,人民邮电出版社, 2004
3.《光无源器件》,林学煌等编著,人民邮电出版社,1998
4.《光通信器件与系统》,J. H. Franz 著,徐宏杰等译,北京电子工业出版社,2002
5.Fiber-Optic Communication Systems, G. P. Agrawal,A John wiley & Sons, Inc.
Publication,2002
TU Syllabus for Fiber Optics
Code: 2020090Title: Fiber Optics Semester Hours: 32 Credits: 2
Semester Hour Structure Lecture:32 Computer Lab:Experiment:Practice:
Practice (Week):
Offered by:
College of precision instrument and opto-electronics
engineering
for: Electronic science and technology (optoelectronics); opto-electronic technology science; information engineering
Prerequisite: Laser principle, physical optics
1. Objective
We start by covering the basics of fiber optics theories, fiber structures and characteristics. Light propagation through multi-mode and single-mode optical fibers is studied, including the effects of dispersion, attenuation and nonlinear effects. The passive and active optical fiber components are also covered extensively, including the basic principles, parameters and applications. The last part of the course focused on instruments usually used in fiber systems.
2. Course Description
This course is a specialized optional course. This course covers the fundamentals of fiber optics. Its goal is to help students develop a thorough understanding of the underlying physical principles and possess analytical ability to deal with problems of fiber systems. Students are also expected to know applications and developmental tendency of fiber optics.
3. Topics
Chapter 1 Introduction
1 Introduction of fiber
2 Light propagation in fibers
3 Group-velocity dispersion
4 Fiber losses
5 Nonlinear effects in fibers
Chapter 2 Passive fiber devices
1 Fiber connectors
2 Fiber couplers
3 Polarization controllers
4 Optical isolators
5 Optical filters
Chapter 3 Active fiber devices
1 Optical modulators
2 Optical Amplifiers
3 Optical fiber lasers
Chapter 4 Instruments in fiber systems
1 Optical power measurements
2 Wavelength and frequency measurements
3 Time measurements
4 Signal quality measurements
5 OTDR
4. Semester Hour Structure
Homework 10%, Final exam 90%
6. Text-Book & Additional Readings
1. Fiber optics, Liao Yanbiao, Tsinghua University Press, 1999
2. Fiber optics, Jeff. Hecht, People postal Press, 2004
3. Passive fiber devices, Lin Xuehuang, People postal Press, 1998
4. Optical communications components and systems, J. H. Franz, Beijing electronic industry Press, 2002
5.Fiber-Optic Communication Systems, G. P. Agrawal,A John wiley & Sons, Inc.
Publication,2002。