专八翻译及人文知识语言学
- 格式:doc
- 大小:99.50 KB
- 文档页数:17

语言学* 现代语言学理论和学派1. Ferdinand de Saussure(1857-1913 瑞士):Father of modern linguistics 现代结构主义语言学创始人Course in General Linguistics《普通语言学教程》:由其学生- C. Bally & A. Sechehaye整理,现代语言学开端,19163 lines: linguistics, sociology and psychology 符号任意性理论;语言单位间的关系;语言和言语区分;共时和历时区分。
语言是符号系统。
符号是形式和意义的联合,即能指signifier和所指signified。
2. The Prague School布拉格学派:synchronic linguistics; Function1) 对语言的共时研究由于可得到全面可控的语言材料以供参考而被充分强调,同时,也没有严格理论;界限被竖立起来将之与历时语言研究相分离。
2) 强调语言的系统性这一本质属性。
3) 在某种意义上,把语言看作是一种功能,是一种有某一语言社团使用的,用来完成一系列基本职责和任务的工具。
~ Phonology and Phonological Oppositions(音位对位):Trubetzkoy–Phonetics belonged to parole whereas phonology belonged to langue. – phoneme~ Functional Sentence Perspective(FSP 句子功能前景):语言学分析理论用信息论原理来分析话语或篇章。
其基本原则就是一句话中各部分的作用取决于它对全局意义的贡献。
捷克语言学家- The point of departure is equally present to the speaker and to the hearer, which is their rallying point, the Theme.The goal of discourse presents the very information that is to be imparted to the hearer and is called the Rheme.3.The London School伦敦学派–systemic linguistics and functional linguistics Sociological approach1) J.R. Firth(1890-1960 英国):伦敦学派创始人; 学生-Malinowski & Halliday语言学的研究对象是实际使用中的语言。

英语专八参考答案英语专业八级考试(TEM-8)是中国英语专业学生的一项重要考试,它涵盖了听力、阅读、写作、翻译和人文知识等多个方面。
以下是一份模拟的参考答案,供参考:一、听力理解1. 短对话理解:这部分测试学生对日常英语对话的理解能力。
考生需仔细聆听对话内容,并从四个选项中选择最合适的答案。
2. 长对话理解:长对话通常涉及更复杂的情境和更多的信息点。
考生需要集中注意力,理解对话的主旨和细节。
3. 新闻听力:这部分要求考生能够理解英语新闻报道,把握新闻的主要内容和关键信息。
4. 讲座听力:考生需聆听一段英语讲座,并回答相关问题,测试学生对讲座内容的理解和分析能力。
二、阅读理解1. 快速阅读:考生需要在限定时间内快速浏览文章,抓住文章的主旨大意。
2. 深度阅读:这部分要求考生仔细阅读文章,理解文章的细节信息,并能对文章进行推理和判断。
3. 词汇理解:考生需要根据上下文推断生词或短语的含义。
三、写作1. 图表作文:考生需根据所给图表信息,撰写一篇描述性或论证性的文章。
2. 议论文写作:考生需就某一话题表达自己的观点,并提供支持性的论据。
四、翻译1. 英译汉:考生需将英语文本翻译成中文,注意语言的准确性和流畅性。
2. 汉译英:考生需将中文文本翻译成英文,同样要注意语言的准确性和地道性。
五、人文知识1. 英美文学:考生需对英美文学的重要作品和作者有所了解。
2. 英美文化:这部分测试考生对英美文化常识的掌握。
3. 语言学基础:考生需要了解基本的语言学概念和理论。
六、完形填空考生需在理解文章大意的基础上,根据上下文逻辑和语境,选择最合适的选项填空。
七、改错考生需识别并纠正文章中的语法、用词等错误。
八、词汇和语法这部分测试考生对英语词汇和语法知识的掌握程度。
九、总结考生需根据所给材料,撰写一篇总结性的文章,概括材料的主要内容。
请注意,以上内容仅为模拟参考答案的示例,实际的TEM-8考试内容和形式可能会有所不同。

第一章概述一、什么是语言?1.Definition of language (语言的定义)Language is a system of arbitrary vocal symbols used for human communication.(语言是人类用来交流的一套具有任意性的声音符号系统。
)2.Design/distinctive feature of language(语言的定义/本质特征)1)2)3)4)(移位性指语言可以让使用者谈论不在说话之时、说话之地存在的物体、事件和观点)例如:我们在中国可以谈论美国的物体和事件。
5)Cultural transmission(文化传播/文化传递性)Language is passed on from generation to generation through teaching and learning rather than instinct.(文化传播指语言是靠文化传播的,而不是靠父母遗传。
虽然人类的语言能力是天生的,但是语言系统的细节不是靠遗传传递,而是靠学习掌握的。
)二、什么是语言学?Linguistics is a scientific study of language.(语言学是对语言的科学研究)语言学的研究对象不是某特定的语种,而是人类所有的语言,在考察分析大量语言现象的基础上总结语言规律。
语言学家想要回答的基本问题是:什么是语言?语言的机制是什么?人们是如何使用语言实现各种目的的。
三、语言学的重要概念1.descriptive vs. prescriptive(描述性与规定性)描述性研究是现代语言学家采取的基本立场,注重观察分析语言中的事实,目的通常是描述人们一般是怎么说话、写作的。
规定性研究注意总结语言中的标准,目的通常是规定人们应该如何说话、写作。
例如:规定只能用单数、复数2.synchronic vs. diachronic(共时性与历时性)synchronic: the study of a language through the course of its history(共时研究以某个特定时期的语言为研究对象)例如:莎士比亚时代语言研究diachronic: takes a fixed instant as its point of observation(历时研究则研究语言各个阶段的发展变化,研究语言的历史发展规律)ngue vs. parole(语言与言语)该区分是现代语言学鼻祖Saussure提出的。

专八加油↖(^ω^)↗语言学(缩略版)1 语言的四个特征:任意性(Arbitrariness),二重性(Duality),创造性(Creativity),移位性(Displacement)2 语言的七个功能:信息功能(Informative),人际功能(Interpersonal Function),施为功能(Performative),感情功能(Emotive Function),寒暄功能(Phatic Communion),娱乐功能(Recreation Function)元语言功能(Metalingual Function)3 语言学的主要分支:语音学(Phonetics),音系学(Phonology)形态学(Morphology),句法学(Syntax),语义学(Semantics),语用学(Pragmatics),4 宏观语言学(Macrolinguistics)的分支:心理语言学(Psycholinguistics),社会语言学(Sociolinguistics),人类语言学(Anthropological Linguistics,计算机语言学(Computational linguistics)5 规定式(Prescriptive)---描述事情应该是怎样的(describe how things ought to be)描写式(Descriptive)---描述事情本是怎样的(describe how thing are)6 共时研究(Synchronic)---以某个特定时期的语言为研究对象(takes a fixed instant as its point of observation)历时研究(Diachronic)---研究语言各个阶段的发展变化(Study of a language through the course of its history)7 语言(Langue)---说话者的语言能力(the linguistic competence of the speaker)言语(Parole)---语言的实际现象或语料(the actual phenomena or data of linguistic)----索绪尔(Saussure)区分8 语言能力(Competence)---理想语言使用者关于语言的知识储备(underlying knowledge)语言运用(Performance)---真实的语言使用者在实际场景中语言的使用(Actual use ofLanguage)----乔姆斯基(Chomsk)区分9 语音学主要分支:发音语言学(Articulatory Phonetics),声学语言学(Acoustic Phonetics)。


英语专业八级 - - 人文及语言学知识归纳人文一、语言和语言学1、语言的区别性特征:Design of features of language 任意性arbitrariness 指语言符号和它代表的意义没有天然的联系二重性 duality 指语言由两层结构组成创造性 creativity 指语言可以被创造移位性 displacement 指语言可以代表时间和空间上不可及的物体、时间、观点2、语言的功能(不是很重要)信息功能 informative 人际功能interpersonal 施为功能 performative 感情功能 emotive function 寒暄功能 phatic communication 娱乐功能 recreational function 元语言功能metalingual function3、语言学主要分支语音学 phonetics 研究语音的产生、传播、接受过程,考查人类语言中的声音音位学 phonology 研究语音和音节结构、分布和序列形态学 morphology 研究词的内部结构和构词规则句法学 syntax 研究句子结构,词、短语组合的规则语义学 semantics 不仅关心字词作为词汇的意义,还有语言中词之上和之下的意义。
如语素和句子的意义语用学 pragmatics 在语境中研究意义 4、宏观语言学 macrolingustics心理语言学 psycholinguistics 社会语言学 sociolinguistics 人类语言学anthropological linguistics 计算机语言学 computational linguistics 5 语言学中的重要区别规定式和描写式:规定式:prescriptive说明事情应该是怎么样的描写式:descriptive 说明事情本来是怎么样的共时研究和历时研究:共时:synchronic 研究某个特定时期语言历时:diachronic 研究语言发展规律语言和言语:语言:langue指语言系统的整体言语:parole指具体实际运用的语言语言能力和语言运用:乔姆斯基(chomsky提出)能力:competence用语言的人的语言知识储备运用:performance 真实的语言使用者在实际中的语言使用二、语音学1、语音学分支发音语音学articulatory phonetics研究语言的产生声学语言学acoustic phonetics 研究语音的物理属性听觉语音学 auditory phonetics 研究语言怎样被感知 2 IPA(国际音标)是由daniel Jones琼斯提出的三、音位学1、最小对立体minimal pairs2、音位 phoneme 3 音位变体 allophones4 互补分布 complementary distribution5 自由变体 free variation6 区别特征 distinctive features7 超音段特征 suprasegmental feature音节 syllable 重音stress 语调tone 声调intonation 四形态学 1 词的构成语素morpheme 自由语素free morpheme 粘着语素bound morphemeRoot 词根词缀affix 词干stem屈折词汇和派生词汇 inflectional affix and derivational affix2 特有的词汇变化lexical change proper新创词语invention 混拼词blending 缩写词abbreviation首字母缩写词 acronym 逆构词汇back-formation例:editor―edit类推构词analogiacal creation 例:work-worked,,slay-slayed外来词 borrowing 五句法学1 范畴category 数number 性gender 格case 时tense 体aspect一致关系concord 支配关系govenrment 2 结构主义学派the structure approach组合关系 syntagmatic relation词和词组合在一起聚合关系 paradigmatic 具有共同的语法作用的词聚在一起结构和成分 construction and constituents :句子不仅是线性结构liner structure还是层级结构hierarchical structure (句子或短语被称为结构体,而构成句子或短语即结构体的称为成分)3 直接成分分析法 immediate constitutional analysis 指把句子分成直接成分-短语,再把这些短语依次切分,得到下一集直接成分,这样层层切分,直到不能再分4 向心结构和离心结构endocentric and exocentric constructions向心:指一个结构中有中心词,例an old man ,中心为man 离心:指结构中没有明显的中心词。


练习题:1、T he traditional dividing line in America between "east” and "west” is the Mississippi River.密西西比河是美国传统的东方和西方的分界线。
2、T he earliest part in America to be found and taken over by early settlers is The Atlantic and Gulf Coastal Plain. 最早被早期定居者发现和占领的地方是大西洋及其沿岸平原。
3、T he largest racial group in the whole population of U.S.A is Non-hispanics white.非西班牙裔的白人是美国最大的种族群体。
4、B efore 2000, the largest minority group in the United States is African Americans. 2000 年以前非裔美国人是美国最大的少数民族群体。
2000年以后,拉丁裔美国人的人数超过了非裔美国人的人数,成为美国第一大少数民族群体。
5、A merica has the world’s oldest written constitution and political party.美国拥有世界上最古老的宪法和政党。
6、T he economic problem caused by the depression in 1929 was eventually solved by World War II.第二次世界大战的爆发帮助美国走出了经济困境。
7、I n the United States, primary education requires Six years years.美国的小学要花费大约六年的时间。


全国翻译专业八级考试解析翻译专业八级考试是全国性考试,考察考生对于翻译理论和实践的掌握能力,从而评估考生的翻译实践能力和综合素质。
本文对于翻译专业八级考试进行解析,帮助考生更好地理解考试内容和提高考试能力。
一、考试科目和内容翻译专业八级考试由笔试和口试两部分组成。
笔试包括翻译理论和实践、语言知识、修辞学和文化常识四个部分,每个部分分值均为72分,总分为288分。
口试包括实际翻译能力的测试和专业能力的考查两个部分,每个部分分值均为36分,总分为72分。
考试主要内容如下:1.翻译理论和实践本部分主要测试考生对于翻译理论的理解和应用以及翻译实践的能力。
考试内容包括翻译方法、翻译技巧、翻译基本概念和理论以及翻译实践等。
重点考查考生的翻译思维和翻译能力。
2.语言知识本部分主要测试考生对于语言知识的掌握能力,包括词汇、语法、语用、修辞学等方面。
考试内容主要涉及英汉两种语言的基本词汇、语法以及常用修辞手法等。
3.修辞学本部分主要测试考生对于修辞学的理解能力,包括修辞学的基本概念、修辞手法的分类和应用以及修辞分析能力等。
4.文化常识本部分主要测试考生对于中西方文化的认识和了解程度,包括文学、历史、哲学、宗教等方面的知识。
考试内容主要涉及西方文化和中西方文化的比较。
二、考试难度和要求翻译专业八级考试难度较大,需要考生具有较高的语言水平和翻译实践能力。
考试要求考生熟练掌握英汉两种语言的基本词汇、语法和修辞手法,具有一定的翻译思维和逻辑能力,能够理解和运用翻译理论和方法,灵活运用语言,准确表达意思。
考试要求考生具有中西方文化的一定了解和认识,能够理性分析翻译中出现的文化差异和难点。
三、备考建议备考翻译专业八级考试,需要考生具有一定的语言功底和翻译经验。
以下为考生备考建议:1.重视语言能力的提升,注重词汇和语法的巩固和提高,增强语音语调的准确性和流利度。
2.熟悉翻译理论和方法,掌握翻译技巧和翻译实践经验,积累翻译课程或者实践经验。
专八考试人文知识考试内容的总结涉及到三个方面的内容:英美文学,英语语言学和英语国家概况。
其中英美文学包括英国文学和美国文学。
英国文学主要分为六个时期:1. Old and Medieval English Literature(中古英国文学)。
2. The Renaissance Period(文艺复兴时期)。
3. The Neoclassical Period(新古典主义时期)。
4. The Romantic Period(维多利亚时期)。
5. The Victorian Period(维多利亚时期)。
6. The Modern Period(现代时期)。
美国文学主要分为四个时期:1. The Literature Around the Revolution of Independence(独立革命前后的文学)。
2. American Romanticism(美国浪漫主义文学)。
3. American Realism(美国现实主义文学)。
4. American Modernism(美国现代主义文学)。
语言学,考生不光要知道语言的本质还要掌握语音学,音位学,形态学,句法学,语义学和语言学的知识。
关于英语国家概况,英语专业的学生都会开设英美概况这门课程,但是专八考试的中需要考生了解的是英语国家概况,不光包括英国和美国,还有其他一些说英语的地区,包括爱尔兰概况,加拿大概况,澳大利亚概况和新西兰概况。
了解了专业八级考试人文知识的内容以后,下一步我们要做的就是好好学习,抓紧时间去掌握这些必需的知识了。
祝愿大家都能适应新的考试题型,都能考出理想的成绩。
1. A Tale of Two Cities was written by Charles Dickens.2. Phonology: The study of speech sounds in language or a language with reference to their distribution and patterning and to tacit rules governing pronunciation. 音位学;在语言或一门语言中,对有关其分类和模式以及为大家所默认的发音规则的研究音韵学,音系学3. Syntax: The study of the rules whereby words or other elements of sentence structure are combined to form grammatical sentences. 句法,研究词或其它句子成分如何联合起来形成合乎语法的句子规则的学科4. Semantics: The study or science of meaning in language forms.语义学,以语言形式表示意思的研究或科学5. acronym :首字母组合词,首字母缩略词,比如,NA TO, UNESCO, BASIC,它们可以连拼,但VOA是Initialism。
一.古英语时期(Old English Literature 公元499—1066 年)古英语时期(—英国文学开山之作:头韵体诗歌(《贝奥武甫》(Beowulf)头韵体诗歌(alliteration))开德蒙(Caedmon):《赞美诗》(Anthem)琴涅武甫(Cynewulf):《十字架之梦》(Dream of the Rood)比德(Bede):《英吉利人教会史》(Historia Ecclesiastica Gentis Anglorum)阿尔弗雷德大帝(King Alfred):《盎格鲁—撒克逊编年史》(Anglo-Saxon Chronicle),被誉为“英国散文之父”Father “英国散文之父”(of English Prose))世纪)二.中古英语时期(Medieval English Literature 公元1066 年—15 世纪)中古英语时期(头韵体诗歌:《高文爵士和绿衣骑士》(Sir Gawain and the Green Knight)英国名谣:《罗宾汉名谣集》(The Robin Hood Ballads)威廉·兰格伦(William Langland):《农夫皮尔斯的幻想》(The Vision Concerning piers the Plowman)杰弗里·乔叟(Geoffrey Chaucer):英国中世纪最伟大的诗人诗人,享有“英国诗歌之父英国诗歌之父”的美誉(Father of English Poetry)。
诗人英国诗歌之父()代表作:八音节(octosyllabic)英雄双韵体(heroic couplet)诗歌八音节((The 八音节)英雄双韵体()诗歌《坎特布雷故事集》Canterbury Tales)。
托马斯·马洛礼(Sir Thomas Malory):英国15 世纪优秀的散文家,代表作为《亚瑟王之死》散文家(Le Morte d’Arthur)散文世纪末—世纪)三.文艺复兴时期(Renaissance 15 世纪末—17 世纪)文艺复兴时期(托马斯·莫尔(Thomas More):伟大的人文主义者人文主义者,代表作:《乌托邦》(Utopia)《国王爱德华五世悲戚的一生》,(The 人文主义者painful Life of Edward Ⅴ). 托马斯·魏厄特(Thomas Wyatt)和亨利·霍华德(Henry Howard)的十四行诗(Sonnet)。
复习专八的同志们注意啦,个人潜心整理--人文知识之语言学部分,希望能帮上点儿忙,一起加油!作者:張旭BEYONDTEM-8 语言学知识复习总结重要概念梳理CNU 张旭ZX第一节语言的本质一、语言的普遍特征(Design Features)1任意性Arbitratriness:shu 和Tree都能表示“树”这一概念;同样的声音,各国不同的表达方式2双层结构Duality:语言由声音结构和意义结构组成(the structure of sounds and meaning)3多产性productive:语言可以理解并创造无限数量的新句子,是由双层结构造成的结果(Understand and create unlimited number with sentences)4移位性Displacemennt:可以表达许多不在场的东西,如过去的经历、将来可能发生的事情,或者表达根本不存在的东西等5文化传播性Cultural Transmission:语言需要后天在特定文化环境中掌握二、语言的功能(Functions of Language)6 1. 传达信息功能Informative:最主要功能The main function7 2. 人际功能Interpersonal:人类在社会中建立并维持各自地位的功能establish and maintain their identity8 3. 行事功能performative:现实应用——判刑、咒语、为船命名等Judge,naming,and curses9 4. 表情功能Emotive:表达强烈情感的语言,如感叹词/句exclamatoryexpressions10 5. 寒暄功能Phatic:应酬话phatic language,比如“吃了没?”“天儿真好啊!”等等11 6. 元语言功能Metalingual:用语言来谈论、改变语言本身,如book可以指现实中的书也可以用“book这个词来表达作为语言单位的“书”三、语言学的分支1. 核心语言学Core linguisticl 语音学Phonetics:关注语音的产生、传播和接受过程,着重考察人类语言中的单音。
人文知识讲义2004年2月全国英语考试专业教学指导委员会修订专八考试大纲,2005年正式实施,开始新增人文知识的内容。
主要包括:英语国家概括、英语语言文学知识、和英语语言学知识。
专业八级人文知识题型:英语国家概况(4分或5分)英语国家地理、历史、文化、教育等等。
主要考察英国、美国必有(地理、历史、文化和政治),加拿大、澳大利亚和新西兰概括,爱尔兰没有出现。
英语语言文学知识(3分或4分)文学部分英美文学作家作品,作家、作品、年代、流派和概念英语语言学知识。
(3分或2分)语言学基本概念,代表理论、代表著作及运用。
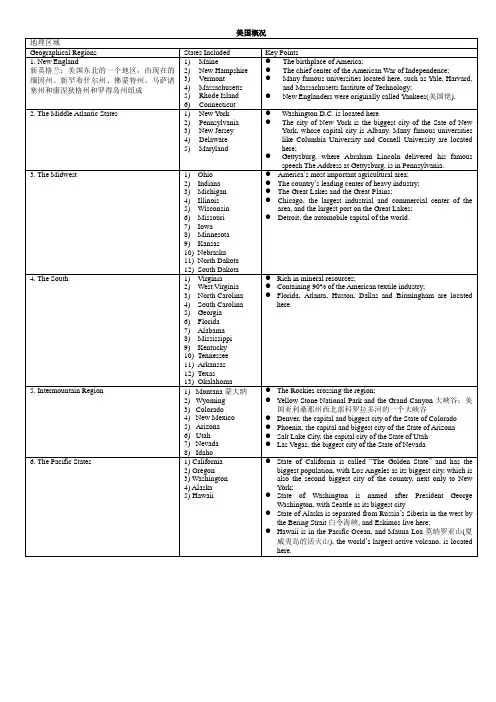
注意:人文一般不会考很偏的知识第一章英语国家概况第一节美国美国概况:东南西北地理位置、人口3亿,最新统计数字3亿4千多万,980万平方公里。
(人口最多的是加州、德州、纽约州、佛罗里达州等,主要为印第安人,首先移民到此是英国人和荷兰人)、星条旗为国旗(13和50)、国徽白头鹰、国歌《星条旗永不落》(1931年通过)、首都华盛顿哥伦比亚特区,属于中央政府管理。
美国又称为Uncle Sam(1961年美国国会正式承认),国花为玫瑰Rose。
美国地理:美国本土共分为6大地区:50州,最大阿拉斯加州,最小罗得岛州,美国本土最大德克萨斯州。
New England:6州,美国政治、经济、文化的发源地。
1其中最重要为马萨诸塞州(又称麻省),因为:美国诞生地和独立战争的主要战场。
波士顿美国最古老的城市,教育的发源地,有麻省理工学院和哈佛和波士顿大学。
波士顿的龙虾很有名。
2最小的是罗德岛州有布朗大学3新罕布什尔州–是美国大选的第一个州4新英格兰人又称为yankees.the Middle Atlantic States: 7州、最重要的为纽约州、宾州、新泽西州和马里兰州。
1纽约州:(注意:根据授课老师可自己画图或对照地图更为容易记忆)纽约是美国最大的城市,联合国大厦等等著名建筑在此。
共有5个区:分别是曼哈顿、皇后、布鲁克林、布朗克斯和斯塔滕岛。
英语专业八级考试人文知识Introduction:The English Major Level 8 Examination, also known as the TEM-8, is a crucial test for English language learners, especially for those majoring in English. Besides language proficiency, one essential aspect of this examination is the knowledge of humanities. In this article, we will explore various topics related to humanities that are frequently tested in the TEM-8.I. Literature:A. Literary Movements:Literary movements encompass various styles and trends that emerged throughout history. Understanding these movements is vital for comprehending literary texts and analyzing their themes, techniques, and societal implications. Some significant literary movements include:1. Romanticism: Originating in the late 18th century, Romanticism emphasized individualism, emotions, and nature. Poets such as William Wordsworth and Lord Byron were key figures in this movement.2. Realism: Arising in the mid-19th century, Realism focused on portraying everyday life, often addressing social issues. Famous Realist authors include Leo Tolstoy and Gustave Flaubert.3. Modernism: Emerging in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, Modernism rejected traditional forms and experimented with new narrative techniques. Prominent Modernist writers are T.S. Eliot and Virginia Woolf.B. Literary Devices:Literary devices are tools employed by writers to enhance the meaning and impact of their works. Familiarity with these devices is necessary to analyze and interpret literary texts. Some common literary devices are:1. Metaphor: A figure of speech that compares two unrelated things, highlighting their similarities.Example: "Life is a journey."2. Symbolism: The use of symbols to represent ideas or qualities beyond their literal meaning.Example: In "The Great Gatsby," the green light symbolizes Jay Gatsby's aspirations and dreams.3. Irony: A literary technique that conveys a meaning opposite to what is expected.Example: In Orwell's "Animal Farm," the pigs proclaim the equality of all animals while subjugating them.II. Art and Architecture:A. Art Movements:Art movements reflect changing trends and styles in visual art. Recognizing various art movements helps interpret artworks and understand their historical and cultural contexts. Some notable art movements include:1. Renaissance: This period, spanning the 14th to 17th centuries, witnessed a renewed interest in classical art and literature. Artists like Leonardo da Vinci and Michelangelo thrived during this time.2. Impressionism: Originating in the 19th century, Impressionism focused on capturing a moment's fleeting impression through light and color. Claude Monet and Edgar Degas were prominent Impressionist painters.3. Cubism: Developed by Pablo Picasso and Georges Braque in the early 20th century, Cubism presented objects from multiple viewpoints, fragmenting and reassembling them in abstract forms.B. Architectural Styles:Architecture reflects the cultural, social, and historical background of a society. Familiarity with different architectural styles aids in understanding their purpose and significance. Some well-known architectural styles include:1. Gothic Architecture: Prominent in medieval Europe, Gothic architecture is characterized by pointed arches, ribbed vaults, and intricate details found in cathedrals such as Notre-Dame in Paris.2. Renaissance Architecture: Inspired by ancient Greek and Roman styles, Renaissance architecture is characterized by symmetry, harmonious proportions, and domes. Examples include St. Peter's Basilica and the Florence Cathedral.3. Modernist Architecture: Appearing in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, Modernism emphasized functionality, simplicity, and the use of new materials such as glass and steel. Architects like Le Corbusier and Ludwig Mies van der Rohe were prominent figures in this movement.III. Philosophy:Philosophy encompasses the study of fundamental questions about existence, knowledge, ethics, and more. Some influential philosophers and their areas of focus are:1. René Descartes: Descartes delved into epistemology and metaphysics, famously stating, "I think, therefore I am."2. Immanuel Kant: Kant explored ethics and developed the categorical imperative, emphasizing moral duties based on reason.3. Friedrich Nietzsche: Nietzsche questioned traditional values and morality, advocating for the affirmation of life and the individual's pursuit of power.Conclusion:Having a solid understanding of humanities is crucial for success in the English Major Level 8 Examination. Literature, art, architecture, and philosophy are all integral aspects of humanities, and familiarity with their various elements and movements allows for a comprehensive understanding of English literature and culture. By delving into these topics, English majors can enhance their knowledge and appreciation of the humanities, ultimately improving their performance in the TEM-8.。
TEM-8翻译必备,英语专业的顶起来哦~作者:邱妍(1)把握大局:grasp the overall situation (2) 摆谱儿:put on airs;keep up appearances(3)白手起家:start from scratch (4)拜年:pay New Year call (5)班门弄斧:teach one's grand ma to suck eggs (5)保质期:guarantee period(6)报销:apply for reimbursement(7)爆冷门:produce an unexpected answer(8)曝光:make public(9)奔小康:strive for a relatively comforta ble life(10)闭门羹:given cold-shoulder(11)比上不足,比下有余:fall short of the best,but be better than the best(12)逼上梁山:be driven to drastic alternatives(13)变相涨价:dis guised inflation(14)边远贫困地区:outlying poverty-stricken areas(15)边缘知识人:Marginal intellectuals(16)表面文章:Lip service;surface formality(17) 博导:Ph.D supervisor(18)补发拖欠的养脑筋:Clear up pension payments in arrears(19)不眠之夜:white night(20)菜鸟:green hand(21)产品科技含量techn oligical element of a product(22)长江三角洲:Yangtze River de lta(23)长江中下游:the middle and lower reaches of Changjian g River(24)超前消费:pre-mature consumption(25)城镇居民最低生活保障:a minimum standard of living for residents(26)城镇职工医疗保险制度:the system of medical insurance for urban w orkers(27)重复建设:buiding redundant project;duplication of similar projects(28)充值卡:rechargeable card(29)春运:pas senger transport around the Chinese lunar new year(30)打破僵局:break the deadlock/stalemate(31)电脑盲:computer illiter ate(32)点球:penalty kick(33)电视会议:video conference(34)电视直销:TV home shopping(35)定向培训:training for specifi c posts(36)动感电影:multidimensional movie(37)豆腐渣工程:jerry-built projects(38)对...毫无顾忌:make no bones about(39)夺冠:take the crown(40)政治多元化:political pluralis m(41)服务行业:catering industry(42)复合型人才:inter-disci plinary talent(43)岗位培训:on-the-job training(44)高等教育自学考试:self-study higher education examination(45)高新技术产业开发区:high and new technological industrial develop ment zone(46)各大菜系:major styles of cooking(47)各行各业:every walk of life(48)功夫不负有心人:Everything comes t o him who waits(49)各尽其能:let each person do his best(50)公益活动:public welfare activities(51)工薪阶层:state emplo yee;salaried person(52)过犹不及:going too far ia as bad asnot going far enough(53)函授大学:correspondence university(54)好莱坞大片:Hollywood blockbuster(55)核心竞争力:core competitiveness(56)虎父无犬子:A wise goose never lays a tam e leg(57)基本国情:fundamental realities of the country(58)激烈竞争:cut-throat competition(59)极限运动:maximal exerci se/X-games(60)集中精力把经济建设搞上去:go all out for econom ic development(61)加班:work extra shifts(62)嘉宾:distingui shed/honored guest(63)加快市场步伐:quicken the pace of mark etization(64)假冒伪劣产品:counterfeit and shoddy products(65)减负:alleviate burdens on sb(66)江南水乡:the south o f the lower reaches of the Yangtze River(67)教书育人:impart knowledge and educate people(68)脚踏实地:be down-to-earth(69)解除劳动关系:sever labor relations(70)扩大内需:expan d domestic demand(71)拉拉队:cheering squad(72)论文答辩:(t hesis)oral defence(73)马到成功:achieve immediate victory(7 4)三维电影/动画片:three-dimensional movie/animation(75)森林覆盖率:forest coverage(76)社会保险机构:social security ins titutions(77)社会热点问题:hot spots of society(78)社会治安情况:law-and-order situation(79)申办城市:the bidding citie s(80):身体素质:physical constitution(81)生计问题:bread-and-butter issue(82)生意兴隆:business flourishes(82)市场疲软:sluggish market(83)市政工程:municipal works/engineeri ng(84)事业单位:public institution(85)试用期:probationar y period(86)首创精神:pioneering spirit(87)手机充值:cellul ar phone replenishing(88)台湾同胞:Taiwan compatriots(89)脱贫致富:cast off poverty and set out on a road to prosperity(90)西部大开发:Development of the West Regions(91)新秀:u p-and-coming star(92)学生处:students' affairs division(9 3)舆论导向:direction of public opinion(94)招生就业指导办公事:enrolment and vocation guidance office(95)支柱产业:pill ar conerstone industry(96)中专生:secondary specialized or t echnical school student(97)专题报道:special coverage(98)《阿Q正传》:The True Story of Ah Q(99)《春秋》:Spring and A utumn Annals(100)知识产权:intellectual property rights重要概念梳理CNU 张旭 ZX第一节语言的本质一、语言的普遍特征(Design Features)1.任意性 Arbitratriness:shu 和Tree都能表示“树”这一概念;同样的声音,各国不同的表达方式2.双层结构Duality:语言由声音结构和意义结构组成(the structure of sounds andmeaning)3.多产性productive:语言可以理解并创造无限数量的新句子,是由双层结构造成的结果(Understand and create unlimited number with sentences)4.移位性 Displacemennt:可以表达许多不在场的东西,如过去的经历、将来可能发生的事情,或者表达根本不存在的东西等5.文化传播性 Cultural Transmission:语言需要后天在特定文化环境中掌握二、语言的功能(Functions of Language)1. 1. 传达信息功能 Informative:最主要功能The main function2. 2. 人际功能 Interpersonal:人类在社会中建立并维持各自地位的功能establishand maintain their identity3. 3. 行事功能 performative:现实应用——判刑、咒语、为船命名等Judge,naming,and curses4. 4. 表情功能 Emotive:表达强烈情感的语言,如感叹词/句exclamatory expressions5. 5. 寒暄功能 Phatic:应酬话phatic language,比如“吃了没?”“天儿真好啊!” 等等6. 6. 元语言功能 Metalingual:用语言来谈论、改变语言本身,如book可以指现实中的书也可以用“book这个词来表达作为语言单位的“书”三、语言学的分支1. 核心语言学 Core linguisticl 语音学 Phonetics:关注语音的产生、传播和接受过程,着重考察人类语言中的单音。