(1) 词法分析与有穷自动机.
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:4.37 MB
- 文档页数:44







第3章词法分析习题答案1.判断下面的陈述是否正确。
(1)有穷自动机接受的语言是正规语言。
(√)(2)若r1和r2是Σ上的正规式,则r1|r2也是Σ上的正规式。
(√)(3)设M是一个NFA,并且L(M)={x,y,z},则M的状态数至少为4个。
(× )(4)设Σ={a,b},则Σ上所有以b为首的符号串构成的正规集的正规式为b*(a|b)*。
(× )(5)对任何一个NFA M,都存在一个DFA M',使得L(M')=L(M)。
(√)(6)对一个右线性文法G,必存在一个左线性文法G',使得L(G)=L(G'),反之亦然。
(√) (7)一个DFA,可以通过多条路识别一个符号串。
(× )(8)一个NFA,可以通过多条路识别一个符号串。
(√)(9)如果一个有穷自动机可以接受空符号串,则它的状态图一定含有 边。
(× )(10)DFA具有翻译单词的能力。
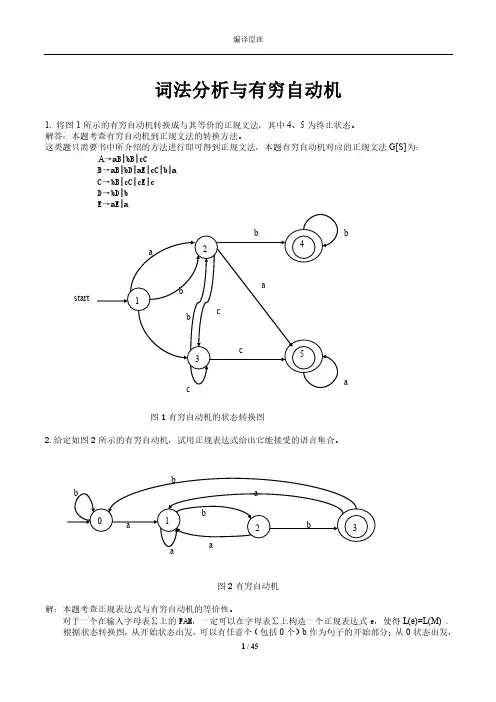
(× )2.指与出正规式匹配的串.(1)(ab|b)*c 与后面的那些串匹配?ababbc abab c babc aaabc(2)ab*c*(a|b)c 与后面的那些串匹配? acac acbbc abbcac abc acc(3)(a|b)a*(ba)* 与后面的那些串匹配? ba bba aa baa ababa答案(1) ababbc c babc(2) acac abbcac abc(3) ba bba aa baa ababa3. 为下边所描述的串写正规式,字母表是{0, 1}.(1)以01 结尾的所有串(2)只包含一个0的所有串(3) 包含偶数个1但不含0的所有串(4)包含偶数个1且含任意数目0的所有串(5)包含01子串的所有串(6)不包含01子串的所有串答案注意 正规式不唯一(1)(0|1)*01(2)1*01*(3)(11)*(4)(0*10*10*)*(5)(0|1)*01(0|1)*(6)1*0*4.请描述下面正规式定义的串. 字母表{x, y}.(1) x(x|y)*x(2)x*(yx)*x*(3) (x|y)*(xx|yy) (x|y)*答案(1)必须以 x 开头和x结尾的串(2)每个 y 至少有一个 x 跟在后边的串 (3)所有含两个相继的x或两个相继的y的串5.处于/* 和 */之间的串构成注解,注解中间没有*/。


实验三词法分析——有穷自动机的应用一、实验目的:一:输入正则文法二:FA1.生成FA(DFA或NFA)2.运行FA,DFA(自动);NFA(交互)3.**NFA→DFA二、实验设想:对输入的文法存储并判断是确定的有穷状态自动机还是不确定是有穷状态自动机,并给出标准的表示形式,若是DFA,可直接测试一个符号串是否是文法的句子,即能否被有穷状态机接受,给出过程及结果;若是NFA,首先将其转化为DFA,再测试一个符号串是否是文法的句子,亦即是否能被DFA接受。
例如:输入文法规则的数目:7输入开始状态: S输入文法Z::=Za Z::=Bb Z::=Aa B::=Ab B::=b A::=Ba A::=a此为确定有穷状态自动机!DFA D=({Z,A,B},{a,b},M,S,{Z})其中M:M(Z,a)=ZM(B,b)=ZM(B,a)=AM(A,a)=ZM(A,b)=BM(S,b)=BM(S,a)=A输入要推导的符号串:ababaaM(S,ababaa)=M(M(S,a),babaa)=M(A,babaa)=M(M(A,b),abaa)=M(B,abaa)=M(M(B,a),baa)=M(A,baa)=M(M(A,b),aa)=M(B,aa)=M(M(B,a),a)=M(A,a)=Z该符号串能被有穷状态所接受!输入文法规则的数目:7输入开始状态: S输入规则:Z::=Ab Z::=Ba Z::=Zc A::=Ba A::=a B::=Ab B::=b 文法规则存储完毕!此为非确定有穷状态自动机!NFA N=({Z,B,A},{b,a,c},M,{S},{Z})其中M:M(A,a)=$M(A,b)={Z,B}M(A,c)=$M(B,a)={Z,A}M(B,b)=$M(B,c)=$M(Z,a)=$M(Z,b)=$M(Z,c)={Z}M(S,a)={A}M(S,b)={B}M(S,c)=$将NFA转化为DFA!DFA N'=({[S],[B],[A],[AZ],[BZ],[Z]},{[b],[a],[c]}, M',[S],F')其中M':M'([S],b)=[B]M'([S],a)=[A]M'([B],a)=[AZ]M'([A],b)=[BZ]M'([AZ],b)=[BZ]M'([AZ],c)=[Z]M'([BZ],a)=[AZ]M'([BZ],c)=[Z]M'([Z],c)=[Z]其中F'={[AZ],[BZ],[Z]}输入要推导的字符串:ababcM'([S],ababc)=M'(M'([S],a),babc)=M'([A],babc)=M'(M'([A],b),abc)=M'([BZ],abc)=M'(M'([BZ],a),bc)=M'([AZ],bc)=M'(M'([AZ],b),c)=M'([BZ],c)=[Z][Z]属于终止状态集合!该字符串能被有穷状态所接受!三、参考程序#include<iostream.h>#include<String.h>struct LeftItem;struct RightNode //存储状态转换关系中弧与终止状态结点结构{char tran;char nextstate;RightNode* nextsibling;RightNode(char x,char y){tran=x; nextstate=y; nextsibling=NULL;}};struct LeftItem //存储状态转换关系中初始状态结点结构{char state;RightNode* link;};struct StateItem //存放确定化的NFA状态结点结构{char newstates[10];StateItem(){newstates[0]='\0';}};////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// int CheckState(LeftItem Array[],int size){RightNode* p;RightNode* q;for(int i=0;i<size;i++){p=Array[i].link;q=p->nextsibling;if(q==NULL) return 1;while(q!=NULL){if(p->tran==q->tran) return 0;q=q->nextsibling;}}return 1;}int CheckExist(StateItem SArray[],int& length,char temp[])//将NFA确定化创建二维矩阵时判别新产生的状态是否在状态数组中存储过{int i=0,k,m;while(i<=length){if(strlen(SArray[i].newstates)==strlen(temp)){if(strcmp(SArray[i].newstates,temp)==0){k=i;break;}}i++;}if(i>length){length++;m=length;return m;}elsereturn k;}int getcount1(LeftItem Array[],int size) //取得FA中状态的个数{char temp[20];int len=0,count=0;int i,j;RightNode* pNode;for(i=0;i<size;i++){pNode=Array[i].link;while(pNode){for(j=0;j<len;j++)if(pNode->nextstate==temp[j]) break;if(j==len){count++;temp[len]=pNode->nextstate;len++;}pNode=pNode->nextsibling;}}return count;}int getcount2(LeftItem Array[],int size) //取得FA中输入字母的个数{char temp[20];int len=0,count=0;int i,j;RightNode* pNode;for(i=0;i<size;i++){pNode=Array[i].link;while(pNode){for(j=0;j<len;j++)if(pNode->tran==temp[j]) break;if(j==len){count++;temp[len]=pNode->tran;len++;}pNode=pNode->nextsibling;}}return count;}int getstate(RightNode* pNode,char arc) //判定一个状态是否能通过一条弧进入下一状态{while(pNode){if(pNode->tran==arc) return 1;pNode=pNode->nextsibling;}return 0;}void Sort(char A[],int n) //将取得的新状态进行排序{for(int i=n-1;i>0;i--)for(int j=0;j<i;j++){if(A[j+1]<A[j]){char temp=A[j+1];A[j+1]=A[j];A[j]=temp;}}}void Bianli1(LeftItem Array[],int size) //输出FA中有穷非空的状态集合{char temp[20];int len=0;int i,j;RightNode* pNode;for(i=0;i<size;i++){pNode=Array[i].link;while(pNode){for(j=0;j<len;j++)if(pNode->nextstate==temp[j]) break;if(j==len){if(len==0) cout<<pNode->nextstate;elsecout<<","<<pNode->nextstate;temp[len]=pNode->nextstate;len++;}pNode=pNode->nextsibling;}}}void Bianli2(LeftItem Array[],int size)//输出FA中有穷的输入字母表{char temp[20];int len=0;int i,j;RightNode* pNode;for(i=0;i<size;i++){pNode=Array[i].link;while(pNode){for(j=0;j<len;j++)if(pNode->tran==temp[j]) break;if(j==len){if(len==0) cout<<pNode->tran;elsecout<<","<<pNode->tran;temp[len]=pNode->tran;len++;}pNode=pNode->nextsibling;}}}void Bianli31(LeftItem Array[],int size)//输出DFA状态转换关系的集合M{int i;RightNode* pNode;for(i=0;i<size;i++){pNode=Array[i].link;while(pNode!=NULL){cout<<" M("<<Array[i].state<<","<<pNode->tran<<")="<<pNode->nextstate<<endl;pNode=pNode->nextsibling;}}}void Bianli32(LeftItem Array[],int size) //输出NFA状态转换关系集合M {char K[20];int len=0;int i,j;RightNode* pNode;RightNode* qNode;for(i=0;i<size;i++){pNode=Array[i].link;while(pNode){for(j=0;j<len;j++)if(pNode->tran==K[j]) break;if(j==len){K[len]=pNode->tran;len++;}pNode=pNode->nextsibling;}}Sort(K,len);for(i=0;i<size;i++){for(j=0;j<len;j++){pNode=Array[i].link;cout<<" M("<<Array[i].state<<","<<K[j]<<")=";if(getstate(pNode,K[j])){cout<<"{";while(pNode){if(pNode->tran==K[j]){qNode=pNode->nextsibling;cout<<pNode->nextstate;break;}pNode=pNode->nextsibling;}while(qNode){if(qNode->tran==K[j])cout<<","<<qNode->nextstate;qNode=qNode->nextsibling;}cout<<"}"<<endl;}elsecout<<"$"<<endl;}}}void Initiate(LeftItem Array[],int size,char TArray[]) //将FA中的输入字母表存入数组TArray[] {int len=0;int i,j;RightNode* pNode;for(i=0;i<size;i++){pNode=Array[i].link;while(pNode){for(j=0;j<len;j++)if(pNode->tran==TArray[j]) break;if(j==len){TArray[len]=pNode->tran;len++;}pNode=pNode->nextsibling;}}}void GetState(LeftItem Array[],int size,char nstate[],char arc,char temp[])//将NFA确定化创建二维矩阵时取得新状态{int i=0;while(nstate[i]!='\0'){for(int j=0;j<size;j++){if(Array[j].state==nstate[i]){RightNode* p=Array[j].link;while(p!=NULL){if(p->tran==arc){int k=0;while(temp[k]!='\0'){if(p->nextstate==temp[k]) break;k++;}if(temp[k]=='\0'){temp[k]=p->nextstate;temp[k+1]='\0';}}p=p->nextsibling;}}}i++;}}void Change(StateItem SArray[],char temp[],int& length,int MArray[][20],int index,int i) //取得新状态后对状态数组以及状态转换矩阵进行对应变化{int k;if(temp[0]!='\0'){k=CheckExist(SArray,length,temp);MArray[index][i]=k;if(k==length)strcpy(SArray[length].newstates,temp);}}char FindNewState(LeftItem Array[],int size,char S,char arc) //得到当前状态的下一状态{int i;for(i=0;i<size;i++){if(Array[i].state==S){RightNode* p=Array[i].link;while(p!=NULL){if(p->tran==arc) return p->nextstate;p=p->nextsibling;}}}return NULL;}int Findy(char TArray[],char s) //取得输入字母在字母表中的下表{int i=0;while(TArray[i]!='\0'){if(TArray[i]==s) return i;i++;}}void CreateFA1(LeftItem Array[],int size,char start,char end)//根据输入文法创建FA{if(CheckState(Array,size)){cout<<"此为确定有穷状态自动机!"<<endl;cout<<"DFA D=(";}else{cout<<"此为非确定有穷状态自动机!"<<endl;cout<<"NFA N=(";cout<<"{";Bianli1(Array,size);cout<<"},{";Bianli2(Array,size);cout<<"},M,";if(CheckState(Array,size)) cout<<start;else cout<<"{"<<start<<"}";cout<<","<<"{"<<end<<"})"<<endl;cout<<"其中M:"<<endl;if(CheckState(Array,size))Bianli31(Array,size);elseBianli32(Array,size);}void CreateFA2(LeftItem Array[],int size,char start,char end,StateItem SArray[],char TArray[],int& length,int MArray[][20])//将NFA转换为DFA{char temp[20];int index=0;int i;do{i=0;while(TArray[i]!='\0'){temp[0]='\0';GetState(Array,size,SArray[index].newstates,TArray[i],temp);Sort(temp,strlen(temp));Change(SArray,temp,length,MArray,index,i);i++;}index++;}while(index<=length);}void Display(StateItem SArray[],char TArray[],int MArray[][20],int x,int y,char start,char end)//输出确定化的NFA{int i,j,k;cout<<"将NFA转化为DFA!"<<endl;cout<<"DFA N'=({";for(i=0;i<x;i++)if(i==0) cout<<"["<<SArray[i].newstates<<"]";else cout<<",["<<SArray[i].newstates<<"]";}cout<<"},{";for(i=0;i<y;i++){if(i==0) cout<<"["<<TArray[i]<<"]";elsecout<<",["<<TArray[i]<<"]";}cout<<"}, M',["<<start<<"],F')"<<endl;cout<<"其中M':"<<endl;for(i=0;i<x;i++)for(j=0;j<y;j++){if(MArray[i][j]!=-1){k=MArray[i][j];cout<<"M'(["<<SArray[i].newstates<<"],"<<TArray[j]<<")=["<<SArray[k].newstates<<"]"<<endl;}}cout<<"其中F'={";k=0;for(i=0;i<x;i++){j=0;while(SArray[i].newstates[j]!='\0'){if(SArray[i].newstates[j]==end) break;j++;}if(SArray[i].newstates[j]!='\0'){if(k==0) cout<<"["<<SArray[i].newstates<<"]";elsecout<<",["<<SArray[i].newstates<<"]";k++;}}cout<<"}"<<endl;}void RunFA1(LeftItem Array[],int size,char start,char end){char TD[20];int i=0,j;char s=start;cout<<"请输入要推导的符号串:";cin>>TD;cout<<" M("<<s<<",";for(j=0;TD[j]!='\0';j++)cout<<TD[j];cout<<")"<<endl;while(TD[i]!='\0'){if(TD[i+1]!='\0'){cout<<"=M(M("<<s<<","<<TD[i]<<"),";for(j=i+1;TD[j]!='\0';j++)cout<<TD[j];cout<<")"<<endl;}s=FindNewState(Array,size,s,TD[i]);if(s==NULL) break;if(TD[i+1]=='\0')cout<<"="<<s<<endl;else{cout<<"=M("<<s<<",";for(j=i+1;TD[j]!='\0';j++)cout<<TD[j];cout<<")"<<endl;}i++;}if(TD[i]=='\0'){if(s==end)cout<<"该符号串能被有穷状态所接受!"<<endl<<endl;elsecout<<"该符号串不能被有穷状态所接受!"<<endl<<endl;}elsecout<<"该符号串不能被有穷状态所接受!"<<endl<<endl;void RunFA2(StateItem SArray[],char TArray[],int start,int end,int MArray[][20]){char TD[20];int i,j,k,x,y;char s=start;cout<<"请输入要推导的字符串:";cin>>TD;cout<<" M'(["<<s<<"],";for(i=0;TD[i]!='\0';i++)cout<<TD[i];cout<<")"<<endl;x=0;i=0;while(TD[i]!='\0'){if(TD[i+1]!='\0'){cout<<"=M'(M'([";cout<<SArray[x].newstates;cout<<"]";cout<<","<<TD[i]<<"),";for(j=i+1;TD[j]!='\0';j++)cout<<TD[j];cout<<")"<<endl;}y=Findy(TArray,TD[i]);x=MArray[x][y];if(x==-1) break;if(TD[i+1]=='\0'){cout<<"=";cout<<"["<<SArray[x].newstates<<"]"<<endl;}else{cout<<"=M'(";cout<<"["<<SArray[x].newstates<<"],";for(j=i+1;TD[j]!='\0';j++)cout<<TD[j];cout<<")"<<endl;}i++;}if(TD[i]=='\0'){for(k=0;SArray[x].newstates[k]!='\0';k++)if(SArray[x].newstates[k]==end) break;if(SArray[x].newstates[k]!='\0'){cout<<"["<<SArray[x].newstates<<"]"<<"属于终止状态集合!"<<endl;cout<<"该字符串能被有穷状态所接受!"<<endl<<endl;}elsecout<<"该字符串不能被有穷状态所接受!"<<endl<<endl;}elsecout<<"该字符串不能被有穷状态所接受!"<<endl<<endl;}////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// void main(){int size=0,sign=0;int i,j,n,sel;int count1,count2;int length=0;char start;char end;char temp[10];int MArray[20][20];RightNode* p;cout<<"请输入文法规则的数目:";cin>>n;cout<<"请输入开始状态: ";cin>>start; //得到初始状态LeftItem* Array=new LeftItem[n];for(i=0;i<n;i++){do{cout<<"请输入第"<<i+1<<"条规则:";cin>>temp;}while(strlen(temp)>6);if(strlen(temp)==6){for(j=0;j<size;j++)if(Array[j].state==temp[4]) break;if(j==size){Array[size].state=temp[4];Array[size].link=new RightNode(temp[5],temp[0]);size++;}else{for(p=Array[j].link;p->nextsibling!=NULL;p=p->nextsibling) {}p->nextsibling=new RightNode(temp[5],temp[0]);}}else{for(j=0;j<size;j++)if(Array[j].state==start) break;if(j==size){Array[size].state=start;Array[size].link=new RightNode(temp[4],temp[0]);size++;}else{for(p=Array[j].link;p->nextsibling!=NULL;p=p->nextsibling) {}p->nextsibling=new RightNode(temp[4],temp[0]);}}}end=Array[0].link->nextstate; //得到终止状态cout<<endl<<"文法规则存储完毕!"<<endl<<endl;count1=getcount1(Array,size);count2=getcount2(Array,size);StateItem* SArray=new StateItem[100];char* TArray=new char[count2+1];SArray[0].newstates[0]=start;SArray[0].newstates[1]='\0';Initiate(Array,size,TArray);TArray[count2]='\0';for(i=0;i<20;i++)for(j=0;j<20;j++)MArray[i][j]=-1;cout<<endl;aaa:cout<<"-----生成FA请按1-----"<<endl;cout<<"-----运行FA请按2-----"<<endl;cout<<"-----退出请按3-------"<<endl;do{cin>>sel;}while(sel!=1&&sel!=2&&sel!=3);switch(sel){case 1:CreateFA1(Array,size,start,end); //根据输入文法建立FAif(!CheckState(Array,size)) //将NFA确定化{CreateFA2(Array,size,start,end,SArray,TArray,length,MArray);Display(SArray,TArray,MArray,length+1,count2,start,end);}sign++;break;case 2:if(sign==0){cout<<"请先生成FA!"<<endl;goto aaa;}if(CheckState(Array,size))RunFA1(Array,size,start,end); //运行DFA elseRunFA2(SArray,TArray,start,end,MArray); //运行确定化的NFAbreak;case 3:break;}if(sel!=3) goto aaa;}四、实验截图1、DFA2、NFA- 21 -- 21 -。
有穷自动机在词法分析中的应用郝亮11北京林业大学,北京100083(heroleo@)The application of finite automaton in lexical analysis of compiling principleLiang Hao11(Beijing Forestry University , Beijing 100083)AbstractLexical analysis is a sequence of characters in the computer science convert word sequence process, lexical analysis is the first stage of t he compilation process, and its task is left to right, a character, a character read into the source code or documentation of the constitutioncharacter stream source or document scanning and decomposition, thereby identifying words and sent a grammar program. Lexical anal yzer output but the system is often expressed as a binary notation style forms, such as (the word species do not, the property value of word symbols). The finite automata (FA) is divided into a deterministic finite automaton (DFA) and non-deterministic finite automata (NF A), which is used to describe a specific type of algorithm of mathematical methods. In particular, a finite automaton can be used as descr ibed in the identification process in the input string, using analytical methods can process more intuitive understanding of lexical analysis of finite automata. Finite state machine diagram indicates also simplifies our lexical analysis of state transitions of understanding. Finite Automata Lexical analysis is widely used.Key words Lexical analysis; finite automata; DFA; NFA; regular expression摘要词法分析是计算机科学中将字符序列转换为单词序列的过程,词法分析是编译过程的第一个阶段,它的任务是从左到右一个字符,一个字符地读入源程序或文档,对构成源程序或文档的字符流进行扫描和分解,从而识别出一个个单词并发送给语法程序。