木材中英文名对照教学提纲
- 格式:doc
- 大小:167.00 KB
- 文档页数:9

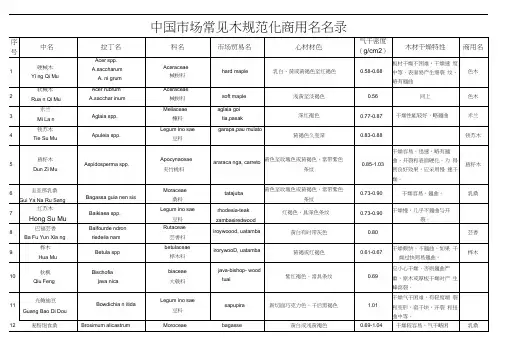

北美木材知识介绍中文英文拉丁文白云杉White Spruce Picea Glauch红云杉Red Spruce Picea Rubens黑云杉Black Spruce Picea Mariana恩氏云杉Engelmann Spruce Picea engelmannii 屋柱松Lodgepole Pine Pinus contorta短叶松Jack Pine Pinus banksiana高山冷杉Alpine Fir Abies Lasiocarpa冷杉Balsam Fir Abies Balsamea铁杉/冷杉群(Hemlock/Fir)中文英文拉丁文加西铁杉Western Hemlock Tsuga heterophylla 便冷杉Amabilis Fir Abies amabilis大冷杉Grand Fir Abies grandis花旗松/ 北美黄杉Douglas fir Pseudotsuga menziesii白松木树种群(Spruce/Pine/Fir)【产品简介】SPF(云杉Spruce-松树Pine-冷杉Fir)俗称加松,是一种针叶木规格材的名称,由云杉、松树和冷杉树种组合而成。
这些树种的性质相近,广泛分布于加拿大的森林中。
SPF规格材的纤维强度高,重量轻并且易加工,是建造木结构房屋和桁架的优良材料。
SPF规格材经过窑炉干燥,使木材线条平直、尺寸稳定。
其洁净、偏白色并带有小树节的优美外观使其也适合用于室内装饰。
用途:建筑工地口料、木方,装修龙骨,托盘面板,包装箱板,家具板材,楼梯踏板、扶手,木结构房屋墙体和桁架等。
产品等级:SE A级J级二级三级四级欧洲云杉/赤松室内墙面板百叶窗一般而言,云杉木颜色浅。
大多白色到浅黄色,边材和心材区别很小。
生长轮形状较淡,通常纹路垂直、非渗水、质地细微到中等。
用途由于容易成型和粘合,云杉用于造船。
由于共鸣品质优良,它也用作大钢琴、声学吉他和其它弦乐器的共鸣板。
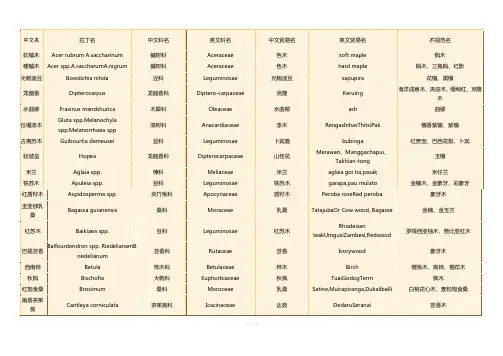
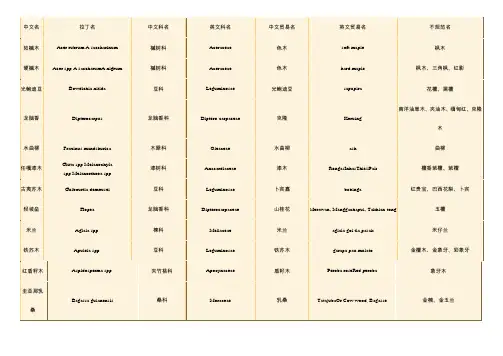

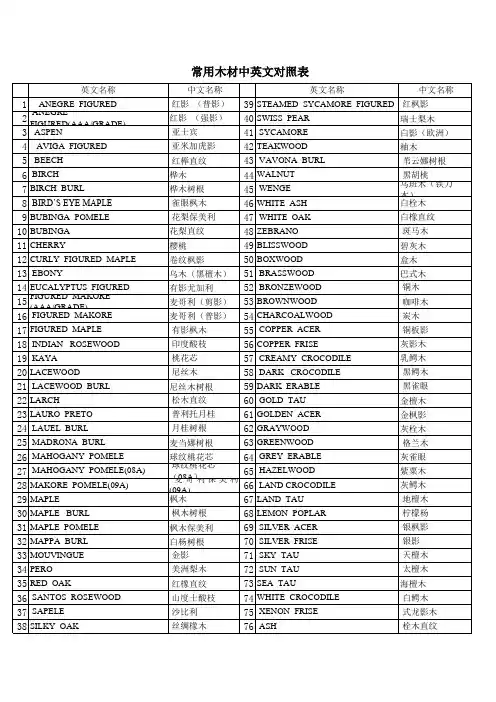
常用木材中英文及拉丁文对照表(按英文字母顺序)非洲桃花芯树叉,卡雅楝树叉African Mahogany Crotch KHAYA IVORENSIS紫檀木,非洲珊瑚木,非洲紫檀木African Padouk PTEROCARPUS SOYAUXII非洲红豆树,高美木豆,西非红豆树,金柚木Afrormosia PERICOPSIS ELATA米仔兰Aglaia AGLAIA SPP桤木Alder ALNUS GLUTINOSA黄柏木(青龙木)树榴,纳拉Amboyna Burl PTEROCARPUS INDICUS樱桃,美洲樱桃,黑樱桃American Black Cherry PRUNUS SEROTINA胡桃木,黑胡桃,美洲黑胡桃American Black Walnut JUGLANS NIGRA美洲桃花心木树杈,桃花心木American Mahogany Crotch SWIETENIA MACROPHYLIA白橡,美洲白橡American White Oak QUERCUS ALBA阿摩楝Amoora AMOORA CUCULLATA安利格Anegre ANINGERIA ROBUSTA苹果树Apple MALUS SYLVESTRIS卷纹白栓,白栓树杈,欧洲白栓Ash Burl FRAXINUS EXCELSIOR非洲杜花楝Avodire TURRAEANTHUS AFRICANA 巴伊亚红木,红木Bahia Rosewood DALBERGIA VARIABILIS菩提树,欧椴树,酸橙树,椴木Basswood TILIA CORDATA, TILIA PLATYPHYLLA 榉木Beech FAGUS SYLVATICA红厚壳木、冰糖果Bintangor CALOPHYLLUM SPP桦木Birch BETULA ALBA雀眼枫木,卷纹枫木,小提琴状枫木Birdseye Maple ACER SACCHARUM有影黑榄仁树Black Figured Limba TERMINALIA SUPERBA沼泽橡,黑橡Bog Oak QUERCUS SSP(红变)热美(山)龙眼木,巴西银桦树Brazilian Lacewood ROUPOLA SSP. (BRASILIENSIS, MONTANA)棕橡,英国棕橡,糠橡Brown Oak QUERCUS SSP.花梨Bubinga GUIBURTIA TESSMANII/DEMEUSII七叶树树榴Buckeye Burl AESCULUS SSP巴林蔷薇木 Busu plum PARINARI CORYMBOSA黑胡桃树榴,加利福尼亚黑胡桃树榴Californian Walnut Bur JUGLANS NIGRA GRAFTED ON JUGLANS REGIA花樟Camphor CINNAMOMUM CAMPHORA樟脑树榴Camphor Burl CINNAMOMUM CAMPHORA雪松Cedar CEDRUS SSP瑞士五针松,瑞士松木Cembra Pine PINUS CEMBRA良木豆树杈Cerejeira Crotch TORRESEA ACREANA, TORRESEA CEARENSIS陈陈,箭毒木Chen Chen ANTIARIS TOXICARIA,ANTIARIS AFRICANA栗子树榴Chestnut Burl CASTANEA SATIVA黄檀,黑酸枝Cocobolo DALBERGIA RETUSA红槭、白桂Cryptocarya CRYPOCARYA SPP卷纹枫木,有影美洲枫木Curly Maple ACER SACCHARUM南美桃花心木(柯鲁派) Curupixa MICROPHOLIS第伦桃、桠果木Dillenia DILLENIA SPP韶子木、毛荔枝、麝香锚果Duian DURIO SPP米瓦桃花心木、大蒜树、葱臭木Dysox DYSOXYLUM SPP紫檀,东印度紫檀East Indian Rosewood DALBERGIA LATIFOLIA榆木树榴Elm Burl ULMUS CARPINIFOLIA, ULMUS GLABRA昆士兰胡桃木 Endiandra ENDIANDRA SPP悬铃木团聚榴,硬木团聚榴English Plane Cluster PLATANUS ACERIROLIA 臭酸仔、白芸香木Erima OCTOMELES SUMATRANA柚加利树榴Eucalyptus Burl EUCALYPTUS SSP柚加利Eucalyptus EUCALYPTUS GLOBULUS,EUCALYPTUS SSP樱桃树,欧洲樱桃European Cherry PRUNUS AVIUM, CERASUS AVIUM荷兰榆木,欧洲榆木European Elm ULMUS CARPINIFOLIA, ULMUS GLABRA 尼斯,欧洲尼斯European Lacewood PLATANUS ACERIFOLIA欧洲的枫木European Maple ACER PLATANOIDES欧洲橡木European Oak QUERCUS ROBUR, QUERCUS PETRAEA A.O欧洲悬铃木树榴European Plane Burl PLATANUS ACERIFOLIA法国胡桃木,欧洲胡桃木European Walnut JUGLANS REGIA巴新无花果、巴新孔雀木Fig FICUS SPP有影安利格(红影)Figured Anegre ANINGERIA SSP有影破布木Figured Etimoe COPAIFERA SALIKOUNDA有影柚加利Figured Eucalyptus EUCALYPTUS GLOBULUS,EUCALYPTUS SSP 有影麦哥利,有影猴子果Figured Macore TIEGHEMELLA AFRICANA有影枫木,白影Figured Sycamore ACER PSEUDOPLATANUS银枞,白枞,冷杉Fir ABIES ALBA桶木、红桐木Geronggang CRATOXYLUM SPP黄檀,黄山榄,黄金檀Goiabao POUTERIA PACHYCARPA灰乳木 Grey milkwood CERBERA FLORIBUNDA硬乳木Hard Alstonia ALSTONIA SPP.爪哇木、重阳木、牛血树Java cedar BISCHOFIA JAVANICA南洋桐、南洋夹竹桃、日罗冬Jelutong DYERA COSTULATA钟康木Jongkong DACTYLOLLADUS STENOSTACHYS剥皮桉Kamarere EUCALYPTUS DEGLUPTA山竹子Kandis GARCINIA SPP木菠萝、面包,马来橡皮树Kapiak ARTOCARPUS SPP山樟、婆罗洲柚木Kapur DRYOBALANOPS南洋红檀、柚木王Keraji DIALIUM SPP克隆Keruing D.GRANDIFLORUS克桫木 Kiso CHISOCHETON SPP山道楝Klampu SANDORICUM SPP木姜子Litsea LITSEA SPP东卫予Lophopetalum LOPHOPETALUM SPP桃花心木Mahogany SWIETENIA MACROPHYLLA马尼尔豆Maniltoa MANILTOA PSYLOGYNE白杨树榴Mapa Burl POPULUS NIGRA枫木树榴Maple Burl ACER MACROPHYLLUM巴西西柚木,帕州饱食桑木Marfim BALFOURODENDRON RIEDELIANUM菠萝格、南洋木宝、铁梨木、太平洋格木Merbau INTSIA SPP山桂花Mersawa AMARGINATA KORTH球纹莫阿比Moabi Pommele BAILLONELLA白梧桐/尼日利亚两蕊苏木Movingui DISTEMONANTHUS BENTHAMIANUS桃金娘树榴,椒木,月桂Myrtle Burl UMBELLULARIA CALIFORNICA牛伯尔Neuburgia NEUBURGIA CORYNOCARPA肉豆蔻Nutmeg MYRISTICA SPP橡木树榴Oak Burl QUERCUS ROBUR, QUERCUS PETRAEA卷纹橡木,橡木树杈Oak Curl QUERCUS SSP奥克美Okoume AUCOUMA PIERRE橄榄白蜡木树榴Olive Ash Burl FRAXINUS EXCELSIOR橄榄白栓Olive Ash FRAXINUS SSP橄榄树Olivetree OLEA EUROPEA杜英Ouandong ELAEOCARPUS SPP潘济木Pangium PANGIUM EDULE拟桂木Parartocarpus PARARTOCARPUS VENENOSUS松木,普通松木Pine PINUS SSP粉椴木、山样木、红椴木Pink satinwood BUCHANANIA SPP枫木,欧洲枫木Plain Sycamore ACER PSEUDOPLATANUS普朗木Planchonia PLANCHONIA PAPUANA洋李树Plumtree PRUNUS DOMESTICA黄花梨、南洋红木、凤眼木、肯帕斯Png kempas KOOMPASSIA GRANDIFLORA 巴新胡桃木Png walnut DRACONTOMELON SPP云状枫木,贝状枫木Quilted Maple ACER MACROPHYLLUM拉明木、白木 ramin GONYSTYLUS SPP大假水青冈木,南方假山毛榉Rauli NOTHOFAGUS ROCERA红桤木,俄勒冈桤木Red Alder ALNUS RUBRA红杉、红雪松Red cedar TOONA CILIATA VAR.SURENI红榆,白榆,滑榆Red Elm ULMUS RUBRA, ULMUS AMERICANA红橡胶,缎纹胡桃木Red Gum LIQUIDAMBAR STYRACIFLUA红橡Red Oak QUERCUS RUBRA美洲衫,海岸红衫Redwood SEQUOIA SEMPERVIRENS红心漆、漆木、南洋漆、印尼花梨Rengas GLUTA SPP巴西黑黄檀,里约热内卢红木,紫薇Rio Rosewood DALBERGIA NIGRA刺槐Robinia ROBINIA PSEUDOACACIA酸枝Santos Rosewood MACHAERIUM SCLEROXYLON球纹沙贝利Sapele Pommele ENTANDOPHRAGMA CYLINDRICUM沙贝利Sapele ENTANDOPHRAGMA CYLINDRICUM黄樟,美洲檫木Sassafras SASSAFRAS ALBIDUM水曲柳Sen ACANTHOPANAX RICINIFOLIUS黄漆树、印缅漆Sepul PARISHIA SPP银桦树,单球悬铃木Silky Oak CARDUELLIA银橡树Silver Oak GREVILLEA ROBUSTA破布木,虎木Special Etimoe COPAIFERA SALICOUNDA酸枣木Spondias SPONDIAS SPP云杉Spruce PICEA ABIES椴绿木,佛手Stainwood CHLOROXYLON SWIETENIA鲍迪豆(柚檀),光鲍迪豆Sucupira BOWDICHIA SSP栗树,甜栗Sweet Chestnut CASTANEA SATIVA瑞士梨木,普通梨木,野生花楸树,山梨树Swiss Pear PYRUS COMMUNIS, SORBUS DOMESTICA欧枫团聚榴Sycamore Cluste ACER SSP欧枫树杈,英国枫木树杈Sycamore Curl ACER PSEUDOPLATANUS洋桐槭,英国悬铃木,美国小无花果木Sycamore Plane PLATANUS ACERIFOLIA花曲柳Tamo FRAXINUS MANDSCHURICA柚木Teak TECTONA GRANDIS榄仁树Terminalia TERMINALIA SPP印尼漆 Ternetang CAMPNOSPERMA SPP黄芸香木 Tetrameles TETRAMELES NUDIFLORA金钟柏树榴Thuya Burl TETRACLINIS ARTICULATA菲律宾特里卡木 Trichadenia TRICHADENIA PHILIPPINENSIS鹅掌楸,美国白木,黄杨Tuliptree LIRIODENDRON TULIPIFERA番樱桃Ubah EUGENIA坤甸Ulin EUSIDEROXYLON ZWAGERI琥珀木树榴,红木树榴Vavona Burl SEQUOIA SEMPERVIRENS黑胡桃团聚榴Walnut Cluster JUGLANS SSP黑胡桃树叉Walnut Crotch JUGLANS NIGRA铁刀Wenge MILLETIA LAURENTII白合欢White albizia ALBIZIA FALCATARIA欧洲白栓,白栓树榴White Ash Burl FRAXINUS EXCELSIOR白栓White Ash FRAXINUS EXCELSIOR白档木、乳松、鸭脚树White cheesewood ALSTONIA SCHOLARIS白柳安、白把麻White meranti SHOREA SPP黄桦木,美国桦木,刨切桦木Yellow Birch BETULA ALLEGHANIENSIS, BETULA LUTEA紫杉树,紫杉Yewtree TAXUS BACCATA斑马Zebrawood MICROBERLINIA BRAZZAVILLEENSIS十二雄破布木Ziricote CORDIA DODECANDRA 高考是我们人生中重要的阶段,我们要学会给高三的自己加油打气。

木材及地板英语词汇一.木材词汇黑胡桃walnut樱桃木cherry山核桃hickory红橡/柞木oak欧枫maple黑胡桃Walnut杨木poplar桦木birchAfrican blackwood 非洲黑木黄檀African ebony 非洲乌木African mabogany 非洲桃花心木African padauk 非洲紫檀Alaska fir 阿拉斯加冷杉木Beech 山毛榉木Beech parquet 山毛榉拼花地板Alaska yellow cedar 阿拉斯加柏木Block floor 拼花地板Blockboard 细工木板Alder 赤杨类American ash 美国白蜡木American beech 美国山毛榉American eim 美国榆,白榆American plane 美国悬铃木American tulipwood美国鹅掌揪Artificial slabs人造板Artificial timber 人造木材Brazilian mahogany 巴西桃花心木Cedar 雪松,杉木Ceylon ebony乌木Chile pine 智利松Chinese chi (中国)漆树Chip 木屑coniferous species 针叶树种cork 软木cypress针叶树Deciduous species 阔叶树种Eastern cottonwood (美国)东部杨木Eastern hemlock (加拿大)铁杉Eastern larch 落叶松Eastern white pine (美国)白松Ebony 乌木Elm burl 榆木树瘤薄木板End cutting 截头English plane 英国悬铃木Eucalyptus 桉木,桉树(类)Eucalyptus pom 柠檬铁皮桉木板Europe cherry 欧洲樱桃木板Eropean ash 欧洲白蜡木European beech 欧洲桦木European birch 欧洲桦木European chestnut 欧洲栗木European hop-hornbeam 欧洲穗子榆European horse-chestnut 欧洲七叶树European larch 欧洲落叶松European lime 欧洲椴木European spruce 欧洲云杉European yew 欧洲紫杉Excelsior-board 木丝板Exotics 外来木Exterior plywood 室外用胶合板Hickory 山核桃木Indian camphor 印度樟木Indian chestnut 印度栗木Indian cinnamon印度肉桂Indian ebony 印度乌木Indian “laurel” 印度“月桂树” Khaya 非洲桃花心木Kiln dried pine 窑干松木plywood 夹板(三合板)softwood 软木poplar 白杨alder 赤杨maple 枫木rubber wood 橡胶木pine 松木pecan 大胡桃木(皮康木) sandalwood 白檀木.檀香木beech 山毛榉ebony 黑檀木(乌木)linden 菩提树(椴木)elm tree 榆木peach 桃树eaglewood 沉香木二、地板词汇木材wood实木柞木地板solid flooring in oak复合柞木地板engineered flooring in oak拉丝brushed上油oil白油white oil黑纹理antique手刮擦handscraped倒角bevel破坏distressed烟熏smoke本色natural规格specification尺寸dimension等级grade指接finger joint地脚线skirting线条moulding门框doorframe托盘pallet隼舌隼槽T&G边缘倒角edge bevel端头倒角end bevel上UV漆UV lacquered含水率moisture处理方式treatment误差tolerance平均长度average length亚光度pre-varnished gloss level厚度thick长度length宽度width样品sample老化,陈化Aging年轮Annual ring树疤,树瘤Burl(knot)人工窑干燥Kiln drying集成材即胶合木(Glued Laminated Timber 简称Glulam)活结running knot(未确定)死结fixed knot(未确定)live knot, dead knot sound knot仿古刷是" antique brushing柜子: cabinet 衣柜: wardrobe食柜: cupboard书柜: bookcase煤气: gas煤气表:gas meter煤气管:gaspipe煤气灶:gas range四、家居种类AAdjustable bed 可调床Air bed 气床Anti-slip strip for stairs (儿童床)防滑楼梯打击扶手Antique furniture 古式家具Antique reproduction furniture 仿古家具Armchair 扶手椅BBaby crib 婴儿床Backless wall-unit 不设背板的壁橱Bamboo furniture 竹家具Banqueting chair 宴会椅Barstool 吧椅Bathroom accessories 浴室配套装置Bathroom combination 浴室组合柜Bathroom consoles 浴室多用架Bathroom furniture 浴室家具Bathroom vanity 浴室盥洗台Batten door 板条门Bed base床架,床套Bed base set 成套床架Bedroom suite 卧室系列家具Bedstead 床架Bentwood furniture 曲木家具Beside table 床头柜Birch door 桦木门Board-room and conference table会议桌Bookcase 书柜Bookshelf 书架Built-in kitchen 配套厨房家具Bunk 双层床Bunk bed 双层床CCabin bed 儿童多功能床Cabin furniture for ships 船用家具Canopy bed 带天篷的床,四柱床CD-video storage cabinet边音响组合柜Chair with castors 脚轮椅Changing table 可调桌Chest of drawers 多屉橱柜Child cot 童床Chi ldren’s bed 儿童床Children’s bedroom suite 儿童卧房系列家具Children’s chair 儿童椅CKD(complete knock down) 整体拆装式家具Clothes rail 挂衣杆Cocktail cabinet 吧柜,酒柜Cocktail table 鸡尾酒桌Coffee table 茶几,咖啡桌Combine-unit 组合柜Composite furniture 复合家具Console 小桌Console table (装在墙上的)蜗形腿台桌Contract furniture 订做家具,承建家具Contract programmers 订做家具Corner sofa suite 拐角扶杆Cot 童床(婴儿床)Couch 长沙发椅Cupboard 橱柜Cupboard wall unit for flat 套房衣柜Curtain 窗帘,挂帘Customized furniture 订做家具DDecorative lighting 装饰灯具Dining room furniture 餐厅家具Dining room set 起居室配套家具Dining table 餐桌Divan 长沙发,沙发床Dividing wall and fitted wall unit 隔墙板及系列DIY furniture 自装式家具Double-bed 双人床Double function sofa-bed 双人沙发床Double sided mirror 双面镜Draughtman chair 吧椅Drawer 抽屉Dressing table 梳妆台EEasy chair 轻便椅End table 茶几Entrance hall furniture 门厅家具Exterior door户外门FFiling cabinet 文件柜Fireplace壁炉Fitment 固定家具Fitting 家居用品Flap 翻门Flower stand 花架Flush door 平面门,全板门Folding chair 折叠椅Folding furniture 折叠家具Folk furniture 民间家具Foot-stool 踏脚凳Framed mirror 带框镜子French-type furniture 模式家具French cabinet 法式桌椅弯脚French door 玻璃门Function sofa多功能沙发椅Furniture for bedrooms 卧室家具Furniture for public premises 公共场所家具GGame table 玩具桌Gate-leg table折叠桌Glass cabinet 玻璃陈设柜Glass case玻璃陈设柜Glass unit and container 玻璃容器制品Glazed door 玻璃门HHall furniture 厅房家具Hat and coat stand 衣帽架Headboard 床头Heirloom quality furniture 祖传家具High bed 儿童高脚床(不带屉柜)High chair 高脚椅High-back executive chair 高背办公椅Home furniture 家庭家具,民用家具Home office furniture 家庭办公家具Hotel furniture 酒店家具Household furniture 家庭家具Hutch碗架IInstitutional furniture 风俗家具,公用家具JJunior desk chair 学生书桌椅KKitchen block /kitchen rock 厨房地砖Kitchen cabinet 餐具柜Kitchen chair, stool and bench 厨房椅、圆凳及条椅Kitchen fitment 厨房固定家具Kitchen table 厨房餐桌Kitchen unit 厨房成套家具LLamp table 灯桌Lath grid 板条格Ledged door 直板门Link chair 写字板椅Living room furniture 起居室家具Locker 衣帽柜Lounge furniture 客厅家具Louvered door 百叶窗柜门Low-back executive chair 低背办公椅Low-back guest chair 低背来宾椅Low-back visitor chair 低背接待椅MManagerial medium-back chair 中背经理椅Margined flush door 镶边平板门Mattress 床垫,席梦思Medium-back executive chair 中背办公椅Metal furniture金属家具Mirror door 玻璃门Mirror for chest of drawers 多屉柜梳妆镜Multi-purpose sofa 多用沙发Multi-purpose table 多用桌NNest 茶几OOccasional furniture 配套家具,休闲家具Occasional table 休闲桌Office furniture 办公家具Office seating 办公座椅Office table 办公桌PPartition wall 隔断Pembroke table 折面桌Planters chair 园艺工用椅Plastic furniture 塑料家具Play furniture 娱乐家具Presidential high-back chair 高背办公椅Pull-out table 伸缩餐具RRattan furniture 藤家具Recliner 躺椅Refectory table长餐桌Rocking chair 摇摆椅Rotary chair 转椅Rustic style furniture 乡村风格家具rectangular table 长方桌red-lacquered chest 红漆木箱round bed 圆床round stool 圆凳round table 圆桌round-backed armchair 圈椅SSchool table 课桌screen 屏风Seat 座椅secretaire 写字桌(尤指有抽屉及分类格者) Secretarial chair 秘书椅sectional sofa 拼合沙发semi-CKD 半拆装家具separate wine cabinet 独立厨柜serving table 送餐桌settee; chaise longue 长靠椅shelving combination 组合架shoe rack 鞋架side table 小桌sideboard 餐具柜simmous bed 席梦思床single bed 单人床slat stool 板条凳sleeper sofa 可睡沙发sofa 沙发sofa bed 沙发床sofa table 沙发桌soft chair 软椅spring bed; steel cot 钢丝床;弹簧床spring-seat chair 弹簧座椅square stool 方凳square table 方桌steel chair 扶手椅steel desk 钢制写字台steel safe 保险柜step stool 梯凳stool 凳子;搁脚凳storage for umbrellas 伞架straight back chair 直背椅strong box; safe 保险箱studio couch 单人沙发床suitcase; trunk 衣箱;小型旅行箱swivel armchair 帆布折叠躺椅swivel-top stool 转动凳五、家具风格Aa generation of chairs办公椅的改进型a proven program 一个已经落实的新项目a relaxed posture in every seating position 适应各种从姿,令人倍感舒适aesthetic design 美学设计allow an ambience to be harmoniously created 营造和谐温馨的气氛appealing design 造型优美artisan craftsmanship 手工工艺BBaroco style 巴洛克风格CColonial plantation furniture 殖民种植风格家具Contemporary design 现代风格设计Copy 复制,模仿,仿冒DDesign studio 设计事务所Design trend 设计趋势Designer 设计师Distinct grain pattern 清晰的木纹图案EEconomical, versatile and efficient 经济实惠,用途多,效率高Emphasize the magnificent features of the range 更烘托出豪华气氛Energy and comfort 方便舒适Essential, functional design 基本功能设计Ethnic African style 非洲民族风格FFocus on the essential 注重本质Freelance 自由职业者Functional, ergonomic, long-lasting 功能齐全,人体工艺,经久耐用Functionality, quality and appealing design 功能全,质量优,造型佳GGraphic design 图片(装帧)设计HHigh quality 优质的IIdeal combination between 两者完美的结合Imitate 模仿In a Italian walnut finish 意大利胡桃木效果Innovative 创新的Intelligent design 理智的设计Interior decorator 室内美术师Interior design室内设计Interior designer室内装饰师Italian style意大利风格LLight color浅色,淡色MMarbled effect 大理石效果Meet the standards of all areas of the modern world of work可满足现代化办公要求Ming Dynasty 明朝NNatural feeling of warmth and texture 质感温暖自然Neoclassic style 新古典式风格PPerfect in shape and function 造型优美,功能完善Product image development 产品形象推广Product industrialization 产品工业化(设计)QQing Dynasty 清朝RRectangular 矩形Rococo style洛可可风格TTerra-cotta granulated paint finish 陶式沙砾漆效果The strength of the company 公司工作重点Traditional design传统风格设计WWith a classic trend 带有古典风格With the experience of specialist 由专家设计制作Without compromise 面面俱到六、油漆涂料词汇AAccelerate 促进剂Accelerator硬化剂,接触剂Acetic acid 醋酸Acetone 丙酮Achromatic color 无彩色Acid stain 丙烯酸树脂Acrylic丙烯酸Acrylics acid resin 丙烯酸(类)树脂Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene resin ABS树脂,丙烯腈-丁二烯-苯乙烯树脂Active agent 活性剂Additive 添加剂Additive mixture 加色混合Adhesive 胶粘剂Adhesive solvent 胶(料)溶剂Adjacent color 类似色Advancing color 进出色Aerosol spraying 简易喷涂After image 残象Air drying 常温干燥Airless spraying 无气喷涂Alcohol stain 酒精着色剂Alert color警戒色Alkyd resin 醇酸树脂Alligatoring 漆膜龟裂Amount of spread 涂胶量Anticorrosive paint 防锈涂料Antifouling paint 防污涂料Antique finish 古式涂料Automatic spraying 自动喷涂BBaking finish 烤漆喷涂Base boat 底漆Blistering 小泡Blushing 白化Body varnish 磨光漆Brilliant 鲜艳的Brushing 刷涂Brushing mark/streak 刷痕Bubbling 气泡Button lac 精致虫胶C咖啡色Carbamide resin adhesive 尿素树脂胶Catalyst 催化剂,触媒,接触剂Chalking 粉化Cherry 樱桃色Chipping 剥落Chromatic color 有彩色Chromaticity 色度Chromaticity coordinates 色度坐标Chromaticity diagram色度圆Clssing 补漆Clear coating 透明涂层Clear lacquer 透明喷漆Clear paint 透明涂料Coarse particle 粗粒Coating 涂料Cobwebbing 裂痕Cocos 可可色Cold water paint 水性涂料Color blindness 色盲Color conditioning 色彩调节Color harmony 色彩调和Color in oil 片种特(调色用)Color matching 调色Color number 色号(色之编号或代号)Color paint 有色涂料Color reaction 显色反应Color reproduction 色重现Color tolerance 色容许差Compatibility 相容性Complimentary color 补色Consistency 稠厚度Contractive color 收缩色Col color 寒色,冷色Cooling agent 冷却剂Covering power 覆盖力Cracking 龟裂,裂纹Cresol resin adhesive 甲酚树脂胶Crimping 皱纹Cure 硬化Curing agent 固化剂Curing temperature 固化温度DDark 暗Deep 深Degumming 脱胶Dewaxed shellac 胶蜡虫胶Diluent 稀释剂,冲淡剂Dilution ratio 稀释比例Dingy 浊色Dipping 浸渍涂层Dipping treatment 变色Discoloring 变色Discord 不调和色Drier 干燥剂Dry rubbing 干磨Drying time 干燥时间Dulling 失光Dusting 粉化EEgg-shell 埴孔亚光,显孔亚光electrostatic spraying 静电涂装emulsion adhesive 乳化胶emulsion paint 乳化涂料enamel 色漆,磁漆end-coating 端面涂层end-gluing 端面胶合epoxy finish环氧效果epoxy resin glue环氧树脂胶ethyl cellulose lacquer乙基纤维素喷漆FFading退色Filler 腻子,埴料,填充剂Finish code 涂料编号Finshing 涂饰Flaking 剥落Flat paint 消光涂料Flatness 消光Floor paint 地板涂料Foam glue 泡沫胶GGelatin 明胶,凝胶Glare 眩目Glue 胶粘剂,胶,胶料Glue and filler bond 动物胶及填料胶结Glue mixer 调胶机Glue spreader 涂胶机Gum 树胶,胶树HHardener 硬化剂Hide 皮胶High solid lacquer 高固体分漆Honey color 蜂蜜色IIlluminant color 光源色JJelly strength 胶质强度Joint strength 胶接强度LLac 虫胶Lac varnish 光漆Lacquer 漆Latex 乳胶Latex paint 合成树脂乳化型涂料Leveling agent 均化剂Light 光亮的Liquid glue 液态胶Long oil varnish 长性清漆Love formaldehyde 低甲醛MMake up paint 调和漆Medium oil varnish 中油度清漆Melamine resin adhesive 三聚氯胺树脂胶,蜜胺树脂胶Melamine resin sheet 三聚氯胺树脂(片)Methyl alcohol 甲醛Multi-color 多彩漆NNatural clear lacquer 清漆N.C lacquer 硝化棉喷漆N.C lacquer enamel 硝色棉色漆N.C lacquer sealer硝化棉底涂料N.C lacquer surfacer 梢化棉中涂整面涂料Nitro-cellulose lacquer 硝化纤维漆,硝基榉Nitro-lacquer 硝基漆Nitrocellulose lacquer 硝化纤维(喷)漆Non toxix finishes无毒喷漆Novolac (线型)酚醛清漆OOff- color 变色的,退色的,不标准的颜色Oil paint 油性漆Oil putty 油性腻子Oil solvent 油溶剂Oil stain 油性着色剂Oil staining 油着色Oil stone 油石Oil varnish 油性清漆,上清漆Opacity 不透明度Opaque paint 不透明涂料PPaint 涂料,油漆Paint film 涂膜Paint nozzle 涂料喷头Penetrant 渗透剂Phenol aldehyde resin 酚醛树脂胶Polishing varish 擦光(亮)清漆Poly Urethane Resin 聚氨酯(PU)Poly ester 聚酯Polyester resin lacquer 聚酯树脂涂料Polypropylene 聚丙烯Polystyrene聚苯乙烯Polyurethane 聚氨酯Polyvinyl acetate adhesive 聚醋酸乙烯(树脂)胶Polyvinyl adhesive 聚乙烯树脂胶Polyvinyl chloride resin 聚乙烯树脂涂层Pre-coating 预涂Procuring 预固化Preservative 防腐剂Primer 底漆(下涂涂料)Putty 腻子Pyroxylin lacquer 硝基漆QQuick drying paint 速干漆RReady mixed paint 调和漆Refined shellac 精制虫胶Resin adhesive 树脂胶Reverse coater 反向涂料器Roller brush 滚筒刷SSample board 样板Sand blast 喷砂七、家具木材词汇AAbele银白杨Abnormal wood 异常(木)材Acoustic acid board 吸音纤维板Acoustical board 吸(隔)音板Adjustable template 可调节的样板Adult wood 成年材African blackwood 非洲黑木黄檀African ebony 非洲乌木African mabogany 非洲桃花心木African padauk 非洲紫檀Aging 老化,陈化Air drying 大气干燥Air seasoning 天然干燥Alaska fir 阿拉斯加冷杉木Alaska yellow cedar 阿拉斯加柏木Alder 赤杨类American ash 美国白蜡木American beech 美国山毛榉American eim 美国榆,白榆American plane 美国悬铃木American tulipwood美国鹅掌揪Annual ring 年轮Apron 望板Armor-plywood 金属贴面板Arris 棱Artificial slabs人造板Artificial timber 人造木材Ash 白蜡木Aspen 白杨类BBabool 阿拉伯胶树Back 背板Back board背板Back veneer 衬板Bald cypress 落羽杉Bamboo 竹子Basswood 椴木,美国椴木Batten board 条板心细木工板Beech parquet 山毛榉拼花地板Bent wood (弯)曲木Birch 白桦,Birdseye maple雀眼枫木板Block 塞角Block floor 拼花地板Blockboard 细工木板Board 板材Bottom 底板Bowing 顺弯Branch wood 枝条材Brazilian mahogany 巴西桃花心木Bright sap 净面边材,无皮边材Broad leaf wood 阔叶材,硬材Brown ash 美国深色白蜡木Burl 树疤,树瘤CCaul 垫板,衬板Cedar 雪松,杉木Ceylon ebony乌木Cherry 樱桃木Chile pine 智利松Chinese chi (中国)漆树Chip 木屑# 1 common 普一级#2 common 普二级compreg 胶压木compressed wood 压缩木coniferous species 针叶树种continuous layer board 多层板cork 软木cottonwood 三角叶杨,杨木(毛白杨类)crok 弯曲木cross rail 拉档crotch 丫权cupping 翘弯curly birch 皱纹桦木板curved laminated wood 弯曲层积材curved plywood曲型合板cypress针叶树DDado 护墙板,墙裙Damp room panel 防潮镶板Decay 初腐Deciduous species 阔叶树种镶板,装饰板Delta wood 多层木Densified wood 强化木材Density of wood 木材密度Dent啃头Depth of cut 切削量(深度)Diffuse porous wood 散孔材Dimension 规格Dimension stock规格材Dimple djohar 波纹Door frame 鸡翅木Door lining 门框Dovetail 门衬板Dowel 燕尾榫Drawer front 圆榫Drawer side 屉旁板Dressed timber净材EEastern cottonwood (美国)东部杨木Eastern hemlock (加拿大)铁杉Eastern larch 落叶松Eastern white pine (美国)白松Ebony 乌木Edge cutting 封边Elm 榆木Elm burl 榆木树瘤薄木板End cutting 截头English plane 英国悬铃木Eucalyptus 桉木,桉树(类)Eucalyptus pom 柠檬铁皮桉木板Europe cherry 欧洲樱桃木板Eropean ash 欧洲白蜡木European beech 欧洲桦木European birch 欧洲桦木European chestnut 欧洲栗木European hop-hornbeam 欧洲穗子榆European horse-chestnut 欧洲七叶树European larch 欧洲落叶松European lime 欧洲椴木European spruce 欧洲云杉European yew 欧洲紫杉Excelsior-board 木丝板Exotics 外来木Exterior plywood 室外用胶合板FFace veneer 表面单板FAS 一级和二级FAX 1F 单面一级Fibre board纤维板Fiddle back提琴背(板)Fiddle butt 乐器用材Figured 影木Figured sycomore 梧桐影木Fine wood board 纤维板Flakeboard 碎料板Flakes 薄片刨花Flame-retardant fibre building board 耐火纤维板Flat-grain lumber 平切纹板材Flooring 地板Flush panel 平(光)镶板Formed plywood 模压(成型)胶合板Frame core flush panel 中空合板From sustainable forests 来自可持续发展的森林Furniture dimension stock 家具规格材Furniture plywood家具胶合板Furniture veneer制作家具用的薄片GGap 离缝Giant cedar (美国)侧柏Gloss 光泽度Grade 等级Grade of lumber 成材等级Graded分等级Grain 纹理HHackberry 朴树Band selected 手工挑选Hard board 硬质纤维板Hard maple 硬枫木,械树Hardy catapa (美国)梓树Heat board 心板Hickory 山核桃木High-density plywood 压缩胶合板,高密度胶合板High gloss 超光泽度High moisture resistant(HMR) 高强度抗湿Hipboard 细木工板Hole drilling 打眼Honey-comb core plywood 蜂窝心胶合板Huanghauli wood 黄花梨木IIdentification of timbers 木材识别Imitation wood 仿制材Imported timber 进口材Impregnated wood (合成树脂)浸渍木Indian camphor 印度樟木Indian chestnut 印度栗木Indian cinnamon印度肉桂Indian ebony 印度乌木Indian “laurel” 印度“月桂树”Insect attack虫眼Inserting panel 装板Install wood strip flooring 安装地板条JJapanese beech 日本山毛榉Japanese larch 日本落叶松Japanese(red)pine 日本赤松Japanese thuja 罗汉柏Japanese white pine 日本五须松Joint flooring 企口地板Jointless flooring 无缝地板KKarelian birch克若利安桦木板Kerf width 锯路宽度Khaya 非洲桃花心木Kiln dried pine 窑干松木Kiln drying 人工窑干燥Kind of timber 材种Kirl 紫花泡桐Knob 节子Knock-down carcass 可随时拆卸的框架Knot 木节,节疤LLaminate 层压Laminated wood 层积材,多层胶合木Leg 腿,脚Liquid cutting of wood 木材水力切割Log 原木MDF/FB(medium density fiberboard) 中纤板plywood 夹板(三合板)softwood 软木poplar 白杨chinese oak 柞木alder 赤杨maple 枫木rubber wood 橡胶木pine 松木pecan 大胡桃木(皮康木) sandalwood 白檀木.檀香木beech 三毛榉ebony 黑檀木(乌木)linden 菩提树(椴木)elm tree 榆木peach 桃树eaglewood 沉香木air spray gun 喷枪finish department 涂装部roller coating 滚筒涂装法finish sanding line 面漆砂光线spray stain 喷底色padding 修色base coat 底漆1st lacquer 一次面漆red copper powder 红口铜粉rust preventive paint 防锈漆glaze 釉alcohol 酒精water powder 水性碳putty 原子灰steel wool 钢丝棉sand paper 砂纸writing brush 毛笔drawknife 刮刀bubble 气泡fisheye 鱼眼orange peel 桔皮blushing 白化yellowing 黄变coat 涂层sample board 样板oil stain 油色sags 下垂cracking 龟裂sealing poor adhesion peeling flaking 剥落color darker 色深bumping 碰伤scratches 刮伤finger print 指印corrosion 腐蚀waxed 打蜡bare spots 斑点finished interior 油漆过的内部accumulation of dust.dirt.stains & smudges under the finish 油漆下灰尘.垃圾.颜料.污点.堆积distressing 破坏处理specking /spatter 喷点bear-tracking 敲边shading 修色crushing 压扁rust removing 除锈pores filling 填孔dyeing 染色color matching 调整色差curing 涂层干燥sloppy sanding 湿砂磨remedying 整修tamponing 揩涂curtaining 淋涂knif-coating or doctor-coating 刮涂sinking 穿心眼stain bleeding 渗花discoloration 变色brushing-mark 刷痕发白.油白.汽白wrinkling 皱皮.皱纹lifting 咬底hib 粒子.油疙瘩.数粒pitting 缩孔.发点.麻点pinbioling 针孔sadning through the finish 磨白greasy gloss 油白loss of gloss 失光scaling 层间剥离gloss 光泽diluent 稀释剂tool marks 工具痕slag build-up 焊渣块sand scratches 砂纸伤痕drit gritiness seed 粒状涂膜paint chipped out 油漆缺口dirt in topcoat 面漆灰尘uneven gloss 光泽不均poor wipping 擦拭不良blemish surface 表面污渍the gel of marred 面板涂膜dirt & trash 灰尘垃圾overspray 喷涂过量poor highlighting 明暗不良even & smooth to touch 手感平滑rub marks 磨损痕迹polishing 抛光打蜡finish blemish or smudges 油漆污点burn-in repairs 氧化修补wrinkling 油漆皱纹runs 垂流(挂流)bulges 凸起.膨胀glaze pattern skips 格丽斯遗漏color mismatched 颜色不搭配glue mark at joint 接合处胶印roughly sanded exterior 表面砂光粗糙open grain or hungry look 油漆裂纹及枯瘦blemish on interior or bottom surface 底部油漆未擦干净embedded sawdust 油漆夹层木屑(锯灰) clear paint 透明涂料simulated grair or wood grain printing 模拟木纹air drying or curing 自然干燥uv-curing 紫外固化hard dry 实际干燥flwability 流平性muddy stain 颜色混浊uniform color 颜色均匀viscosity 粘度skim 桔皮raised grain removing 除木毛smcars removing 除污渍pitch pocket or gum pocket 树脂襄cardboard 纸板carton 纸箱misprints 版书错误cube feet 材积bar codes 条码foam 泡沫wood skids 栈板side pad 边垫tape 胶带hardware packs 五金包outer pack 外包装country of origin 原产地pearl wool 珍珠棉clear sticker sealing tape 打箱胶bubble pack 气泡袋unit pads 组合套角nylon strap 尼龙带子customer's tag 客户标签box print 纸箱印刷description 产品名称right angle foam 直角泡沫polyester plastic 保利塑料crocket 纸箱图样EPS block 保丽龙块crown molding pad 顶饰保护块corner /edge pad 角.边套角support eps block 支撑保丽龙块metal component rough rusting 五金粗糙.生锈.碰伤painted hardware 上色五金caster 轮子polarized plugs 电极插头retain button 玻璃钮扣corrugated fasteners 浪形钉self-drilling screw 自玫螺丝brads 无头钉backplate (拉手)后金属板drilled or pierced holes for attaching hardware or fasteners 五金或扣件孔(钻孔或穿孔)hinge 活页scerw 螺丝screw point 木螺丝尖butt hinge 蝶形活页(连接)special screw 特殊螺丝metal-to-wood guide system 金属与木组成的滑轨系统wood side-guide 侧滑轨prop 支柱.支撑物buttress 支撑物.扶壁center support 床中板支撑glass inserts 嵌玻cane 藤部份wattage label 功力标签filling materials 填充物pitch pockets 不平凹洞cross band 横纹板back 背面glass top.shelves.inserts 玻璃面板.层板.嵌板float glass 浮动玻璃glass door inserts 门玻simulated slate.marble.stone 仿古板.大理石nail or staple & glue 钉与胶mortise & tenon joints 公母榫结合parting 部件corner blocks 三角木clcats 加强条leg blocks 脚加强块dowels ends 木榫两端头octagon 八角形.八边形overlays 镶边driven flush 直进non-decorative fasteners 无装饰钉countersunk & filled 隐埋填充beveled edge 斜边nog 木钉end grain 端头木纹center back support 后中支撑cut-out 通气孔panel span 柜子宽内径(两侧板之距离) felt(pad)on the bottom panel span 毛护垫radius 半径rhombus /lozenge 菱形.斜方形side view 侧视base molding 底饰条return moldings 侧饰insert panel 嵌板manufactured article /goods /product 制成品border 镶边rorted or embossed line 雕刻沟槽线dock cabinet 有蹄子柜子cases using panel on frame 柜子框板solid wood door 实木门raised-panel door 高实木门板light barrier strip 门挡片clearance 间隙chair parts 椅子部件spindle 背枳arrow back 箭背back post /leg (rear leg) 后脚front rail 前框seat cushion /shelf 座框arm post 扶手枳halves & leaves 面板及中板base (pedestal) 下座TV armoire parts 电视柜部件rack 挂衣杆door 门end panel 侧板drop lid support 连杆laminated kraft 牛皮纸hot melt glue 热融胶top edgs & end of dawers 抽前板上边及两端tray interior 抽屉隔底匣english dovettirl (more than one dowel) 英式燕尾fitted drawer 合适的抽屉lipped drawer 镶边的抽屉all drawer guide system 所有抽屉滑轨系统stool leg 吧椅脚ladder 椅背板条back-corner block 后三角块rocker runner 摇椅摇杆arm stump 扶手支柱spline 止转楔frame back 靠背框air vent hole 空气孔strip nail trim tables 细图钉状装饰adjoining aprons 相邻立水pedestal table top (脚筒)桌面chair guard molding 桌镶边MDF/FB(medium density fiberboard) 中纤板PB(particleboard) 塑合板(粒片板) plywood 夹板(三合板)hardwood 硬木(杂木)softwood 软木basswood/linden 椴木poplar 白杨桦木chinese oak 柞木ash 水曲柳alder 赤杨abele 银白杨rubber wood 橡胶木pine 松木pear 梨树pecan 大胡桃木(皮康木)walnut 核桃木(胡桃木) sandalwood 白檀木.檀香木mahogany 桃花芯木(红木)peafowl wood 孔雀木ebony 黑檀木(乌木)chestnut 栗木linden 菩提树(椴木)hickory 山核桃木elm tree 榆木fir 枞树(冷杉木)peach 桃树camphyor tree 樟木eaglewood 沉香木interfere 妨碍high carbon wire 高含量碳精金属线modulus of rupture 抗裂系数proper balance 适当平衡polyester 聚脂.多元脂polystyrene 聚本.烯fiber 纤维coil spring units 螺旋弹簧extension wires 伸展线coil links 线夹子clinch 螺旋固定器tie wire 绳索带spring distortion 弹簧歪斜coil spring edging 螺旋弹簧边饰burlap 粗麻布sinuous wire spring unit 迂回线弹簧withdrawal 收回.撤退maximize 扩大到最大极限maximum 最大值pull-out 拉出back springs 背弹簧sinuous wire clips 回形金属夹tie wires 联结线puncture 刺伤tie wire bent flat 联结线水平弯曲frame uprights 框架垂直modulus of elasticity 弹力系数resiliency 弹性isolate/insulate 绝缘polymer 聚合物vinyl 烯基polyester fiber 多元纤维suspension bars 支撑杆wire clip 边线coil stabilizer 螺旋链环tie strap 敲弯.钉牢spring noise 索柱线spring clip 弹簧夹edging /fringe /trimming 缘饰边饰folded double & stapled 折成双层用钉钉住insulated clip 隔离夹spring crimp 弹簧卷钩minimize 减少到最少minimum 最小tight clips 固定夹seat springs 座弹簧uniform look 整体外观spring rails 弹簧杆strip webbing 细边带。

Wood anatomyIntroductionA Development of wood science1.Concept of wood science2.History of this subject3.Trends of wood science developmentB Characteristic properties of wood1.All wood is cellular in structure with cell walls composed of a characteristic mixture ofpolymers of cellulose, noncellulosic carbohydrates, and lignin, organized as a reinforced matrix.2.Wood is anisotropic in nature.3.Wood is a hygroscopic substance.4.Wood is biodegradable.5.Wood a combustible.6.Wood is remarkably inert to the action of most chemicals.7.Wood is surprisingly durable when used under conditions which are not deliberatelyfavorable to the wood-destroying agencies.8.Because of its fibrous structure and the quantity of entrapped air, wood has excellentinsulating properties; ie., thermal insulation, poor conductor of electricity.C. Variability of wood propertiesWood properties are subject to wide variation brought about by the physiology of the trees and the external factors affecting its growths. Therefore, wood characteristic may vary in different parts of the same trees as well as from tree to tree.D Wood as an industrial raw material1.An outstanding industrial construction materialWood maybe cut and worked into various shapes with the aid of simple hand tools or with power-driven machineryFlexural rigidity in relation to the weight of the material, traceable to the nature of the cell wall material and its distribution as a system of thin-walled tubes, is one of the outstanding mechanical properties of wood.Wood structures can be designed to carry impact loads that are twice as great as those they can sustain under static loading.Dimensional changes that may take place as a result of rise in temperature are less significant in wood construction than they are in construction utilizing metal structural members.2. A raw material for pulp and paper3. A potential source of chemicalsE Knowledge of wood and better useCertain characteristics of wood are sometimes cited as detrimental to its use for particular use. But many of these disadvantages, real or implied, could be overcome by intelligent use of wood, based on comprehensive knowledge of its properties.The tree stemI The plant origin of woodWood is of plant origin. The following criteria serve to distinguish woody from nonwoody plants:1.Wood plants must be vascular plants2.They must be perennial plants3.Posses s stem that persists from year to year4.Exhibit secondary thickeningA kinds of woody plantsTrees: at least 20 feetShrubs: seldom exceeds 20 feetWoody lianas: is a climbing woody vineAmong which no hard and fast lines can be drawnB factors controlling the designation of a wood as commercially important1.The size of the tree species producing wood.2.The quality of the wood3.The accessibility and volume of the stands of a given kind of timber4.The status of technological development of consuming industries5.prevailing economic conditions.Lack of adequate transportation of facilities;Because wood of a number of botanically closely related species can not be distinguished with any certainty after a tree is cut and a log converted in to lumberDepend on such considerations as local scarcity of better woods, improvements in manufacture, development of new products, and a better knowledge of technical properties of wood.C softwoods and hardwoodsSoftwoods: conifers, evergreens.Hardwoods: deciduous, broad-leaved trees.Few coniferous species occupy a unique position in the timber economyHardwoods are composed of a large number of tree species with wood of vastly variable characteristics that determine its suitability for specific, diversified uses.II The stemThe body of all vascular consists of a cylindrical axis and appendages.The stem(trunk, bole): limb, branch and branchletThe root(root system): lateral branch root, rootletAppendages: leaves, thorns containing vascular tissue, prickles of rose formed by the outmost layers and hairs arising as extensions of epidermisThe majority subscribe to the idea that flowers are modified forms of shoots or leaves. The central core called the stele is composed of phloem, cambium and xylem (pith , primary xylem and secondary xylem)A formation of the stemThe axis of a tree is formed through the process of elongation and through growth in diameter. Elongation of tree stems is traceable to the primary growth (apical growing points)Growth in diameter is due to the activities of the vascular wood cambium.Several concepts:The plant tissues arising from the apical growing points are called the primary tissuesPlant tissues originating through cell formation in the vascular cambium are known as secondary tissuesA growth ring or annual ring: a single growth increment is formed in a year ( or one growing season). In transverse, it appears as concentric rings, in longitudinal section, it appears as cone-shaped or paraboloid zones.B stem formStem form refers to the taper of the bole from the base to the top of the tree.The basic form is presumed to be genetically controlled and be strongly modified by the environmental influences and cultural practices which affect the vigor, size and shape of the tree crown.The mechanistic and hormonal theories appear to provide the most plausible explanation.1.Mechanistic theories: this theory assumes that the tree stem must be strong enough not onlyto support the weight of the stem and crown of the tree and the additional weight of snow and ice, but also to be able to resist the forces of wind exerted on the crown. As a consequence of these requirements a cylindrical stem would require a higher proportion of denser and stronger late wood in the lower part of the bole than a tapering stem.2.Hormonal theories:Auxin gradient →govern the distribution of radial growth → determine the stem form3The overall of effect of the tree crown on the shape of the stem:Favorable growth condition →long-crowned trees →maximum ring width is formed in the lower part of the trunk. The stem within the crown is generally strongly tapered because of the downward increase in the number and cumulative effect of branches on formatin of wood in the upper stem.C Gross characteristics of the stem wood1 growth incrementsa/ Early wood (Spring wood): The portion formed in the early part of the growing season has larger cells and is relatively low in density.Late wood (Summer wood): The denser and usually darker-colored wood formed in the last part of growing season.Transition between the early and late wood maybe:Abrupt transition: hard pines, ring-porousGradual transition: soft pines, diffuse-porous.b/Variation in width of growth incrementsFast-growing species: poplar (Populus spp.), Slashpine (Pinus elliottii Engelm.)Shade-tolerant speciesLight-demanding speciesSite effect: better-drained sites, Swamps, dry limestone outcropsc/ Discontinuous and false ringsIn very old or suppressed trees, some of the growth increments may be interrupted.Discontinuous rings: The growth increments do not completely surround the stem but are present only in part of it.False ring: False rings are wholly included within the boundaries of true rings. A band of what appears to be late wood is formed which simulates normal late wood in appearance and density; this is followed by tissue resembling early wood, after which true late wood is producedDouble rings: If only one false ring is included in the true rings, the latter is designated as a double rings;Multiple rings: If more than one of such false rings occur within the boundaries of the true ring, the latter is said to be a multiple ring.2 Planes of reference in the stemTransverse surfaces (x): Cross sectionRadial surface (r)Tangential surface (t)3 Sapwood and heartwoodThat part of the woody core in the tree in which some xylem cells are living and hence physiologically active is called sapwood.Secondary changes that take place as a result of death of the protoplasm of the living cells in the xylem lead to formation of a physiologically dead part of the xylem, called heartwood Intermediate zone: between the sapwood and the heartwooda/ Classify all trees on the basis of distinctiveness of heartwood ;Sapwood trees (Alnus spp)Ripewood trees (Abies spp)Trees with regularly formed heartwood (exs. Oak, walnut, cherry)Trees with irregular heartwood (ex. Fraxinus spp)b/ Bosshard’s Classification of heartwood formationTrees with retarded formation of heartwoodTrees with light heartwoodTrees with obligatory colored heartwoodTrees with facultatively colored heartwoodc/There are two hypotheses of heartwood formationThe older advocates that heartwood formation of air in the closed cell system → this brings about secondary changes in the protoplasm of the parenchyma cells → leading to formation if extraneous substances and causing the death of the parenchyma cells.Rudman’s hypotheses,In late summer, height growth terminates and cambium growth slows → large crown function continue →sugars is likely to exceed the tree’s needs (unneeded sugars move inward by bark ray and unneeded sugars begin to accumulate near the center of stem) → converted into new compounds, decomposition of sugars →leads to formation of various polyphenolic compounds → other food material concentration → kill cells → heartwood formation.d/ Extractive substance is formed while heartwood formationHeartwood is often more durable; reduces the permeability of the heartwood; heartwood is somewhat heavier than sapwood at the same moisture content.Interfere with bleaching of the pulp; is more beautiful.e/ The width of the sapwood expressed as a linear measure or in terms of numbers of growth increments varies in different trees of the same species and at different heights in the same tree. The tree requires a fairly constant volume of sapwood at all levels in the stem; on geometrical considerations it is evident that the sapwood shell in a tree can decrease in width as the tree diameter increases, and still maintain a constant cross-sectional area.f/ wound heartwood: the abnormal tissue of the heartwood, which was caused by wounding of the tree.False heartwood: often forms in trees which do not normally have colored heartwood. False heartwood is known to occur in beech, birch, maple, poplar, aspen, and pine4 Color in woodcolor in wood is due mainly to extractives or may also contribute to the color of exposed wood surface thought oxidation.In general, color of sapwood, it may be gray or pale shade of yellow, white, pink, or red. Color of heartwood, it striking or unusual enough, can be important in identification of wood; it may also be responsible for perferential uses, but precise description of wood color is seldom possible, which must be supplemented with other structural criteria. Measurement of color is obtained with spectrophotometer.Russel effect: A photographic image of a varying degree of intensity for heartwood and sapwood is obtained when a photographic film is placed in contact with a wood specimen and then developed in the usual manner.5 Luster (sheen)Luster is the property of wood that enables it to reflect light, in other words, the property of exhibiting sheen.6 Odor and tasteA number of woods have a distinctive odor, which may be caused by inflitration products in the heartwood or by the action of fungi, bacteria, or molds.7 Grain and textureGrain refers to the longitudinal alignment of cells. It can be determined by the type of cleavage produced when wood is split.Grain includes straight grain, cross-grained, curly or wavy-grained, spiral grain, interlocked grain.Texture refers to the relative differences in appearance of the growth increments in the size, and kinds of cells between early and late wood.Coarse texture: large, open elements in ring-porous hardwood or large lumen from uniformly distribution cells.Even texture: even medium-textured8 WeightThe weight of wood varies according to:Amount of wood substance present per unit volume;The amount of infiltration;Moisture contents.9 HardnessHardness is a useful indicator of its physical characteristics.In general, it can be roughly tested with a knife and thumbnail.10 Anatomical features of wood of importance in identification.a/ According to the size and distribution of vessels or pores in early wood and late wood, the hardwood can be designated as:Ring-porous: The vessels in the early wood are much larger than those in the late wood of the same growth ring. The transition from one size of pores to another may be quite abrupt; such woods then are described as ring-porous. Ex., oak,Diffuse-porous: When transition in size of pores from the early to late wood is gradual, or when the pores do not appreciably vary in size throughout the ring, the woods are said to be diffuse-porous. Ex., birch, poplar, mapleSemi-ring porous: wood with the pore transition between ring-porous and diffuse-porous.b/ resin canals: are tubular intercellular spaces surrounded by secreting cells,mainly formed in pines, spruces, larch and tamarack, doughlas-firit appears as small openings or white spots in the transverse section and inconspicuous in longitudinal sectionc/ rayOn the transverse section: lines of varying widthOn the radial section: flecksIn the tangential plane: short staggered linesd/ wood parenchymaray parenchyma: constitute the bulk of ray tissue.Epithelial parenchymaAxial or longitudinal parenchyma: it may be massed in lines or in bands running along the growth ring or may encircle the pores, making them appear thick-walled on transverse section. It is an important feature in identification of woods with a hand lens.11 Figure in wooda/ Growth increments and figure in woodPlain, flat-saw lumber: it consists of nested, angular parabolic, irregularly concentric patterns Flat-cut veneerQuartered veneer: veneer produced by radial slicing or sawing. It is also called edge-grained or vertical-grained and is often used for flooring because of the more even wearing quality and the reduced transverse shrinkage.sewQuarter-sewn: in Oak, it called rift-sawn. Lumber in which growth rings from an angle of 45 or more with the wide surface of the board is classified commercially.Half-round veneerBack-cut veneer,Cone-cutting: as pencil cuttingb/ Figure caused by grain orientation in woodRibbon or stripe figure caused by interlocked grainCurly or wavy-grain figrueBroken stripeBlister and quilted figrueBird’s eye and dimplesCrotch and stump figuresBurl figuresc/ figure caused by color distributionIII BarkEpidermisPeriderm consists of three layers: the phellogen, the phellem and the phellodermThe number of successive periderms persisting outside the living bark is variable and is not necessarily indicative of the thickness of the dead bark.The bark on a mature tree is formed through the activity of the vascular cambium and the bark cambium, it is never so thick as the wood. There are three reasons for this:1 the layer of xylem formed during a given year usually consists of many rows of cells and therefore is much thicker and the corresponding layer of phloem2 The old phloem tissue is compressed radially and hence no longer occupies so much space as formerly.3 outside layers of bark formed in the later years consist of old phloem tissues; the yare shed from time to time through the process of periderm formation already described.Uses of barkBottle of stopper frp, cork oakTanning leatherBroken or shredded bark are s fuel, insulation, mulching for plants, soil conditioner, animal bedding, packing material, oil-spill absorbent, and plastic and adhesive fillers and for heavy metal ion scavenging and filtering.Also extracted as a source of oil-well drilling mud additives and as a source of waxes.Origin and development of woody cellsAll plants are composed of basic structural and physiological units called cells.Aggregations of the secondary xylem wood cells of similar type or with similar function are knows as tissues.I Apical meristemThe elongation of tree stems (branches and roots) is traceable to primary meristems (apical meristem and growing).Schematic drawing portraying the ontogeny of young tree stem (figure 2-3)II Vascular cambiumA Cell organization in the vascular cambiumThe vascular cambium is composed of fusiform initials and cambial ray initials.the fusiform initials,In conifers, length < 2000um to 9000um; diameter > 30 umIn primitive hardwood, length is 1000um to 2000umIn highly developed hardwoods, length is 300um to 600umB The process of cell division in the vascular cambiumMitosis:C Formation of new cambial initialsCambial initials devide in two ways.PeridinallyPseudotransversely or anticlinallyCause of increase in the circumference of the vascular cambium:The formation of new cambial initials of call types;Increase in length of the fusiform initials;Increase in tangential diameter;Number of fusiform initials in life form 724 to 23100 and the ray initials form 70 to 87961/ Formation of new fusiform initialsstratified cambialThe survival of the newly formed fusiform initials in depends largely on the length of the new initial and the extent of contact with the rays.2/ Formation of ray initials in the vascular cambiumthrough reduction of short fusiform initials to a single ray cell;by separation of the entire such initial into a number of ray cells;formed at the side of a fusiform initial or arise by pinching of the tips of the fusiform initials. Ways of multiseriate rays:✧By addition of more ray initials at the side of the existing initials.✧By division of ray initials themselves✧By fusion of two or more proximate rays3/ Variations in length of fusiform initialsThe variations in the average length of fusiform initials are reflected in corresponding differences in length of the derived xylem cells.a/ variation in length in the radial direction .A negative correlation that exists between the frequency of pseudotransverse division of the cambial initials and the length of the newly formed initials;The extent of preferential loss of shorter, less-efficient fusiform cambial initials by transformation into ray initials or by direct maturation into xylem and phloem cells without further subdivision.b/ Variation along the length of the tree trunkc/ Effect of growth rate on length of cambial initialsD Formation of new xylem and phloem cellsSee figure 2-16E Seasonal activity of the vascular cambiumIII Postcambial xylem cell enlargementMany types of cells increase in their overall dimensions before maturation.The enlargement can be arbitrarily divided into increase in diameter and elongation of the developing cell.In the softwoods, diameter increase is almost entirely in the radial direction, and almost no tangential enlargement takes place.In hardwoods, the vessel elements in early wood of ring-porous woods, exhibit a major increase in tangential diameters, followed by that in the radial direction.Intrusive growth:The Woody cell wallI Chemical components of the plant cell wallSee table 3-1A Polysaccharide fractions of the cell wall(holocellulose)1 cellulose2 hemicelluloseB LigninLignin is formed only in the walls of living plants in the spermatophytes, the pteridophytes, and the mosses.C Secondary cell wall components1 Extraneous materials2 Ash contentD Analytical dataII Basic structure of the woody cell wallA Microfibrillar organizationMicrofibrils: the polysaccharides in woody plant cell walls are physically aggregated into very long strands.Crystallites: the crystalline core of the microfibril can be broken by the action of chemicals into units.B Aggregations of microfibrilsReinforced theory: These microfibrils consist of a core of crystalline cellulose surrounded by short-chain hemicelluloses that are partly linked to the cellulose core. Deposition of lignin and extractives, after the microfibrils are formed, encases them and binds them into a rigid structure, living a network of microcapillary voids which allow water to penetrate into the cell walls.C Density of the cell wallD Summary of organization of cell wall materialsIII The primary cell wallMultinet theoryMcirotubuleAppositionPlasmodesmataIV The normal secondary cell wallA Secondary-wall structure of tracheids and fibersSee figure 3-5, 3-6Pr, S1, S2, S3, WB Wall structure of xylem parenchyma cellsThe major difference in cell wall structure between parenchyma cells and those in tracheids and fibers is that parenchyma, cells posses special wall organization called protective layers.C Distribution of chemical constituents in the cell wallSee figure 3-10V Modification of the cell wallA pitting of the cell wallA pit is defined as a recess in the secondary wall of the cell , open to the lumen on one side and including the membrane closing the recess on the other side.Pit aperture (included, extended)Pit chamberPit borderPit torus(turi)MargoA pit pairComplementary pitsBlind pitsPit cavityPit membraneCell lumenA simple pitBordered pit parsA half-bordered pit pairLinear pittingScalariform pittingOpposite pittingAlternate pittingTwo other mechanisms for reduction of flow through bordered pits of conifers have been proposed in addition to pit aspiration:1/ Occlusion of the pit membrane with heartwood extractives;e.g., extraction of incense cedar wood with ethanol can increase permeability of the heartwood as much as 10,000 times;2/ incrustation of the pit membrane with insoluble lignin-like materialsB perforation of the cell wallSimple perforation plateMultiple perforation plateScalariform perforation plateBarsC Thickenings of the cell wall1 Spiral thickingsspiral thickings are ridges of microfibrils which form on the surface of the S3 layer in varying degrees of prominence2 DentationsD Wart structures and vestured pitting1 warts2 vestured pittingin the angiosperms a development of the warty structure into large simple or branched forms associated with the pits is knows as vestured pittingVI Special forms of cell wallsA Septa(septum)B TylosesVII intercellular spacesThe minute structure of coniferous woods (Softwoods)Table 4-1 illustrate the types of cells (elements) in Coniferous woodsI Longitudinal coniferous tracheidsA Tracheid volume90 to 94 percentB Arrangement and shape of tracheids with growth ringsAbrupt transition in diameter and wall thickness between early and late wood (hard pines)The tangential diameter of longitudinal tracheids remains quite constant within the growth ring or with the age of tree.C Size of longitudianal tracheidsLarge > 3.0 – 5.0Short <3.0Average 3.0- 5.0D Marking of longitudinal tracheidsPitsSpiral thickenTrabeculaeCallitrisoid1 pitsa/ intertrachealb/ those betweeen the longitudinal tracheid and ray parenchymac/ those between the longitudinal tracheid and ray tracheids.Bars of sanio or crassulaeFigure 4-4Crassulae are confined to the radial walls of tracheids2 spiral thickenings on the wall of longitudinal tracheids3 callitresoid4trabeculae: due to fungal hypha5longitudinal resinous tracheidsE Longitudinal strand tracheidsLongitudinal strand tracheids may be regarded as transitional elements between longitudinaltracheids and epithelial or longitudinal parenchymaII Parenchyma in coniferous woodsA Longitudinal ( axial) parenchymaParenchyma usually appears as a strand thinner-walled than neighboring tracheids and frequently contains extraneous materialsDiffuseBandedTerminalMarginalB Ray parenchymaC Epithelial parenchyma and resin canalsThe resin canal as such is therefore not a wood element but a cavity surrounded by thin walled, parenchymatous cells ( epithelial cells)1 Formation of resin canalsAn intercellular cavityNormal resin canalsTraumatic2 Normal resin canalsThe resin canal occurs in pinus, Picea, Larix and Pseudotsuga3 Traumatic resin canalsThey are much larger than the normal canalsIII Transversely oriented cellsA Types of transverse cells in softwoodsRay parenchymaRay tracheidsEpithelial cellsa/ Ray parenchymaCross fields: the common-wall areas between cells of the ray parenchyma and the longitudinal tracheids. (Shape, size and arrangement are different)Window-like ( fenestriform) ( soft pine)Pinoid pits (hard Pine)Piceoid pits (picea, larix and pseudotsuga)Taxodioid pitsCupressoid pits2 ray tracheidsdentate thicknessthe inner wall of ray tracheids in hard pines possesses irregular tooth like projections or reticulatedthe har d pines with dentate ray tracheids also have ―warts‖B Rays in softwoods1 rays without resin canals (uniseriate rays)homocellularheterocellular2 fusiform raysfusiform rays, so-called because of their spinkle- like shapefusiform rays occur in four genera of the pinaceace: Pinus, Picea, Larix and Pseudotsuga.IV Crystalliferous wood elements in softwoodsCrystal-bearing cells are apparently restricted to the pinaceae ( in Abies)Ray tracheidsEpithelial cellsThe minute structure of hardwoodsDistinguished features between coniferous woods and hardwoods:a/ hardwoods possess vessel elements( porous woods, nonporous woods)b/The radial alignment of the longitudinal cells is wanting or more or less obscured in hardwoods because of vessel enlargement and vessel element failing to divide.c/hardwood are much more complex in structure than softwoods because more cells enter in to their composition.d/ the rays of hardwoods are more variable in width than those of conifers.I Development of the elements of porous woods from cambial initialsFigure 5-3 serves to emphasize the fact that the longitudinal elements of wood are all derived from the same type of cambial initial.The way of differentiation of the various types of cells derived from the fusiform initials in the cambium proceeds along three principal lines;1 Elongation2 Increase in daimeter3 Division into a vertical row of cells by means of transverse walls.II Comparative anatomy of the hardwoodsA Longitudinal elements1 vessel elements2 trachiedsa vasicentric tracheidsb vascular tracheids3 fibersa fiber tracheidsb libriform fibers4 longitudinal (axial) parenchymaa cells of axial (strand) parenchymab fusiform parenchyma cellsc epithelial cells; excreting cells encircling the cavities of longitudinal gum canalsB Transverse elements1 cells of ray parenchymaa procumbent or upright ray cell exclusively—homocellular raysb procumbent and upright ray cells – heterocellular rays2 epithelial cells; excreting cells encircling the cavities of transverse gum canalsA Longitudinal elements of porous woods1 vessel elementsvessels do not exist in isolation, but, in fact, numerous areas of communication exist between vessels over their surfaces.a formation of component vessel elementsFusiform cambial initial—enlarges transverselyb shape of size of vessel elementsFigure 5-4c arrangement of vessel elementsRing porousDiffuse porousSemi-ring-porousSolitary porePore multipled sculpturing of vessel elements1/ nature of the opening between vessel elementsperforation plateperforation (simple, scalariform, reticulate)2/ Nature and extent of pitting on he walls of vessel elementspit pairs: bordered , half-bordered and simple pit pairsalternate pittingopposite pittingscalariform pittingvestural pit3/ Spiral thickening in vessel elementse Inclusions in vessel elementstylosis and various amorphous exudiations that are gummy, resinous, or chalky in nature. Raraly, starch grains and crystals are also in evidence.f trabeculae in vessel elementsg vessel volume2 trachiedsa vasicentric tracheids: contain numerous bordered pits, pisses conspicuous spiral thickenings.b vascular tracheidsvesicentric tracheids differ from vascular tracheids in having tapering or around ends and in not being arranged in define longitudinal raws.。

木材进出口方面专业词汇AAbele 银白杨Abnormal wood 异常(木)材Acoustic acid board 吸音纤维板Acoustical board 吸(隔)音板Adjustable template 可调节的样板Adult wood 成年材African blackwood 非洲黑木黄檀African ebonyxxxx African mabogany 非洲桃花心木African padaukxxxx Aging 老化,xx Air drying 大气干燥Air seasoning 天然干燥Alaska fir 阿拉斯加xxAlaska yellow cedar阿拉斯加柏木Alderxx 类America n ashxx 白蜡木American beechxxxxAmerican eimxxxx,xxAmerica n pla nexx 悬铃木American tulipwood 美国鹅掌揪Annual ring 年轮Apron 望板Armor-plywood 金属贴面板Arris 棱Artificial slabs 人造板Artificial timber 人造木材Ash 白蜡木Aspen 白杨类BBabool 阿拉伯胶树Back背板Back board 背板Back veneer 衬板Bald cypress 落羽杉Bamboo 竹子Basswood椴木,xx椴木Batten board 条板心细木工板Beechxx木Beech parquet 山毛榉拼花地板Bent wood (弯)xxBirchxx,Birdseye maple雀眼xx 木板BlockxxBlock floor 拼花地板Blockboard 细工木板Board 板材Bottom 底板Bowing 顺弯Branch wood 枝条材Brazilian mahogany 巴西桃花心木Bright sap 净面边材,无皮边材Broad leaf wood 阔叶材,硬材Brown ashxx 深色白蜡木Burl树疤,树瘤CCaul垫板,衬板Cedarxx 杉木Ceylon ebonyxxCherry 樱桃木Chile pinexxxxChinese chi (xx)漆树Chip木屑coni ferous species 针叶树种continuous layer board 多层板cork 软木cottonwood 三角叶杨,杨木(毛白杨类)crook 弯曲木cross rail 拉档crotch 丫权cupping 翘弯curly birch 皱纹桦木板curved laminated wood 弯曲层积材curved plywood 曲型合板cypress针叶树DDado护墙板,墙裙Damp room panel 防潮镶板Decay初腐Deciduous species 阔叶树种D e cor pane镶板,装饰板Delta wood 多层木Densified wood 强化木材Density of wood 木材密度Dent 啃头Depth of cut 切削量(xx)Diffuse porous wood 散孔材Dimension 规格Dimension stock 规格材Dimple djohar 波纹Door frame 鸡翅木Door ling 门框Dovetail 门衬板Dowelxx 榫Drawer front 圆榫Drawer side 屉旁板Dressed timber 净材EEaster n cott on wood (美国)东部杨木Eastern hemlock (加拿大)铁杉Eastern larch 落叶松Eastern white pine (美国)白松EbonyxxEdge cuttingxxElmxxElm burlxx 瘤薄木板End cutting 截头En glish pla nexx悬铃木Eucalyptus桉木,桉树(类)Eucalyptus pom柠檬铁皮桉木板Europe cherryxx 樱桃木板Eropea n ashxx 白蜡木Europea n beechxx 桦木Europea n birchxx 桦木European chestnut 欧洲栗木European hop-hornbeam 欧洲穗子榆European horse-chestnut 欧洲七叶树Europea n larchxx 落叶松Europea n limexx 椴木European sprucexxxxEuropean yewxxxxExcelsior-board 木丝板Exotics外来木Exterior plywood 室外用胶合板HFace ven eer表面单板FAS—级和二级FAX 1F单面一级Fibre board 纤维板Fiddle back提琴背(板)Fiddle butt 乐器用材Figured 影木Fine wood board 纤维板Flakeboard 碎料板Flakes薄片刨花Flame-retardant fibre building board 耐火纤维板Flat-grain lumber 平切纹板材Flooring 地板Flush panel平(光)镶板Formed plywood 模压(成型)胶合板Frame core flush panel 中空合板From sustai nable forests来自可持续发展的森林Furniture dimension stock 家具规格材Furniture plywood 家具胶合板Furniture veneer制作家具用的薄片GGap离缝Gia nt cedar(xx)侧柏Gloss光泽度Grade 等级Grade of lumber 成材等级Graded 分等级Grain 纹理HHackberryxxBand selected手工挑选Hard board 硬质纤维板Hard maple 硬xx, 械树Hardy catapa (xx) 梓树Heat board 心板Hickory 山核桃木High-density plywood 压缩胶合板,高密度胶合板High gloss超光泽度High moisture resista nt(HMR)高强度抗湿Hipboard 细木工板Hole drilling 打眼Huanghauli wood 黄花梨木IIdentification of timbers 木材识别Imitation wood 仿制材Imported timber 进口材Impregnated wood (合成树脂)浸渍木In dia n camphorxx 樟木Indian chestnutxxxxIndian cinnamonxx 肉桂Indian ebonyxxxxIndian “ laU印度”桂树”In sect attack 虫眼Inserting panel 装板In stall wood strip floori ng 安装地板条JJapa nese beech B 本山毛榉Japa nese larchxx落叶松Japa nese (red )pi ne 日本赤松Japanese thujaxxxxJapa nese white pi ne 日本五须松Joint flooring 企口地板Jointless flooring无缝地板KKarelian birch克若利安桦木板Kerf width 锯路宽度Khayaxx桃花心木Kiln dried pine 窑干xxKiln drying 人工窑干燥Kind of timber 材种Kirl 紫花泡桐Knob 节子Knock-dow n carcass可随时拆卸的框架Knot木节,节疤LLaminate层压Laminated wood 层积材,多层胶合木Leg腿,脚Liquid cutting of wood 木材水力切割Log 原木Log grade原木等级。
林业木材词汇一、基本术语木材防腐:wood preservation 木材防腐剂:wood preservative木材防腐处理:wood preservative treatment 木材保管:wood protection in storage原木保管:log protection in storage 锯材保管:sawntimber protection in storage木材防火:wood fire prevention 木材败坏:wood deterioration生物败坏:biodeterioration 物理和化学损害:physical and chemical degradation 真菌:fungus 细菌:bacterium昆虫:insect 海生钻孔动物:marine borer腐朽:decay/rot 变色:stain蛀孔:bore hole 天然耐久性:natural durability天然耐腐性:natural decay resistance 含水率:moisture content自由水:free moisture /free water 结合水:bound moisture/bound water纤维饱和点:fibre saturation point 平衡含水率:equilibrium moisture content木材吸湿性:hydroscopicity of wood 木材吸水性:water-absorbing capacity of wood 木材透水性:water permeability of wood 细胞壁:cell wall纹孔:pit 木材密度:density of wood木材硬度:hardness of wood 木材强度:strength of wood生材:green wood 湿材:wet timber气干材:air-dried timber 裂纹:check干裂:seasoning check 环裂:shake轮裂:ringe shake 弧裂:cup shake劈裂:split 生长轮:growth ring年轮:annual ring 早材:early wood晚材:late wood 边材:sap wood心材:heart wood 熟材:ripe wood针叶树材:coniferous wood/soft wood 阔叶树材:broadleaves wood/hard wood健康材:sound wood 腐朽材:decayed wood/rotted wood变色材:stained wood 素材:untreated wood二、木材败坏菌害:attack by fungi and bacteria 木材腐朽菌:wood destroying fungi担子菌纲:basidiomycetes 子囊菌纲:ascomycetes半知菌类:fungi-imperfecti/deuteromyetes 结合菌类:Zygomycetes多孔菌目:polyprales/polyporaceae 变色菌:stain fungi霉菌:mould 菌丝:hyphae菌丝体:mycelium 子实体:fruit body孢子:spore 酶:enzyme蓝变blue stain 边材变色:sap stain边材腐朽: sap rot 心材腐朽:heart rot干基腐朽:butt rot 白腐:white rot褐腐:brown rot 干腐:dry rot湿腐:wet rot 软腐:soft rot带线:zone line 虫害:attack by insects木材钻孔虫:wood-boring insects 虫孔:insects hole小虫眼:shothole/small insect-hole 大虫眼:grub hole针孔虫眼:pin hole 表面虫眼和虫沟:surface insect holes and galleries蛀屑:frass/bore dust 蛸翅目:Coleoptera天牛科:Cerambycidae 小蠹科:Scolytidae长小蠹科:Platypodidae 窃蠹科:Anobiidae长蠹科:Bostrychidae 粉蠹科:Lyctidae粉蠹甲虫:powder-post beetles 食菌小蠹:ambrosia beetles象鼻虫科:Curculionidae 吉丁虫科:Buprestidae等翅目:Isoptera 家白蚁:Coptotermes formosanus散白蚁:Reticulitermes spp 堆沙白蚁:Cryptotermes spp膜翅目:Hymenoptera 木蚁:carpenter ant木蜂:carpenter bee 树蜂:wood wasp海生钻孔动物的危害:attack by Marine borers 软体钻孔动物:Molluscan borers甲壳钻孔动物:Crustacean borers 船蛆:Teredo navalis木材耐火性:fire resistance of wood 风化:weathering机械磨损:mechanical wear 化学损坏(降解):chemical degradation三、木材防腐剂焦油类防腐剂:tar-oil type preservative木材防腐油:coal-tar-creosote for the preservation of timber乳化煤焦杂酚油:pigment emulsified creosote(PEC)水煤气焦杂酚油:water-gas tar creosote防腐油石油混合液:creosote-petroleum solution石油分馏物:petroleum distillates 蒽油:anthrancene oil有机溶剂型防腐剂:organic solvent type preservative 五氯苯酚:pentachlorphenol环烷酸铜:copper naphthenate 8羟基喹啉酮:copper 8-hydroxyquinolate(Cu-8)有机锡化合物:organotin compounds 林丹:lindane氯丹:chlordane 辛硫磷:phoxim水载型防腐剂:water-borne preservative 酸性铬酸铜:acid copper chromate氨溶砷酸铜:ammonical copper arsenite 铜铬砷防腐剂:CCA preservative专利性防腐剂:proprietary preservative 水载五氯酚制剂:water-borne penta formulations防水防腐剂:water-repellent preservative 乳化防腐浆膏:emulsion paste阻燃剂:fire retardant 阻燃防腐剂:fire-retardant preservative多硼防腐剂:polybor 防霉剂:antimold chemicals防变色剂:antisapstain chemicals 五氯酚钠—硼砂合剂:pentabor烷基胺化合物:alkyl ammonium compounds 试验方法:test methods分馏试验:fractional distillation test 琼脂木块法:agar-block test土壤木块法:soil-block test 呼吸法:fungal respiration method毒性极限:toxic limit 流失试验:leaching test残余毒性:residual toxicity 菌窑试验:fungus cellar test野外试验:field test 致死中量:median lethal dose垛式支架试验:crib test 火管试验:fire-tube test极限氧指数:limiting oxygen index四、木材防腐处理处理的准备:preparation for treatment 剥皮:debarking预加工:prefabrication 刻痕:incising刻痕机:incising machine 预加热:preheating木芯:core 生长锥:increment borer调湿:conditioning 真空油煮法:boiling under vacuum常压处理:non-pressure treatments 浸渍处理:immersion treatment冷浸处理:cold soaking 长时浸渍:steeping瞬时浸渍:dipping 涂刷:brush treatment炙焦喷涂处理:charring and spraying treatment 干基处理:butt treatment套(车内胎)管法:tyre-tube process 喷射处理:spray treatment隧道式喷淋处理:tunnel spraying 树液置换处理:sap displacement扩散处理:diffusion treatment 双扩散处理:double diffusion treatment绷带处理:bandage treatment 钻孔扩散处理:bore-hole treatment钻孔处理器:bolt-hole treater 地际线处理:ground-line treatment枪注法:gun injection 热冷槽法:hot and cold bath process喷蒸和淬冷处理:steam and quench treatment 修补处理:remedial treatment毒化土壤:soil poisoning 熏蒸:fumigation阻燃处理:fire retarding treatment 木材机械保护法:mechanical protection of wood 加压处理:pressure treatment 真空加压法:vacuum/pressure process定量浸注法:empty-cell process 半定量浸注法:lowry process完全浸注法:full-cell process 循环浸注法:cycle vacuum/pressure process复式处理:dural treatment 频压法:alternating-pressure process加压真空交替法:oscillating-pressure process 后期喷蒸处理:final steaming膨胀浴:expansion bath 真空处理法:vacuum process双真空处理法:double vacuum process 溶剂回收法:solvent recovery process干真空法:dry-vacuum process 前真空:initial vacuum后真空:final vacuum 流动木材防腐装置:mobile timber treating plant处理罐:treating cylinder 机动罐:rueping cylinder混合罐:mixing tank 计量罐:measuring tank余液槽:drain tank 跑锅:surging回出量:kick-back 拒受点:refusal point毛吸收量:gross absorption 初吸收量:inicial absorption净吸收量:net absorption 处理压力:treating pressure处理材的性质:properties of treated wood 处理性:treatability浸注性:impregnability 难注性:refractory渗透性:permeability 透入性:penetration固着:fixation 流失:leaching溢油:bleeding 起霜:blooming保持量的测定:retention by assay 净干盐保持量:net dry salt retention飞机播种造林技术规程Technical guidelines for afforestation by aerial seeding封山(沙)育林技术规程Technical guidelines for setting apart hills (sand area)for tree growing 工业糠醇 Technical furfurylalcohol工业糠醇试验方法Technical furfurylalcohol test methods工业糠醛 Technical furfural工业糠醛试验方法Technical furfural test methods罐道木Sawn timber for shaft lifting guide合成樟脑 Synthetic camphor黑荆树栲胶单宁快速测定方法Quick test method for determination of tannin in wattle bark extracts混凝土模板用胶合板Plywood for concrete form集约经营用材林基地造林总体设计规程Forestation overall design regulations for intensively managed timber-forest base胶合板测试胶合板的抽取方法Plywood--Sampling of test plywood panels胶合板分类 Plywood--Classification胶合板含水率的测定Plywood--Determination of moisture content胶合板胶合强度的测定Plywood--Determination of glue bond strength胶合板普通胶合板标志、包装、运输和贮存Plywood--Marking, packaging,transportation and storage of plywood for general use胶合板普通胶合板尺寸和公差技术条件Plywood--Specification for dimensions and tolerances of plywood for general use胶合板普通胶合板检验规则Plywood--Inspection codes for plywood for general use胶合板普通胶合板通用技术条件 Plywood--General specification for plywood for general use 胶合板普通胶合板外观分等技术条件Plywood--Specification for classification by appearance of plywood for general use胶合板试件尺寸的测量Plywood--Determination of dimensions of test specimens胶合板试件的锯割Plywood--cutting of test specimens胶合板术语和定义Plywood--Terms and definitions浸渍胶膜纸饰面人造板Surface decorated wood-based panels with paper impregnated thermosetting resins锯材材积表Sawn timber volume table锯材干燥质量Drying quality of sawn timber锯材检验Swan timber inspection锯材缺陷Defects in sawn timber锯切用原木树种、主要用途Ripping logs--Species--Main application军用紫胶片Shellac used for arms颗粒紫胶 Seed lac-Specification阔叶树锯材Broad leaves sawn timber阔叶树锯切用原木尺寸、公差、分等Broad leaves ripping logs-Dimensioms--tolerances and grade classification林木良种审定规范The standard of examination and approval of improved varieties of forest tree林木引种Introduction of exotic forest trees林木种质资源保存原则与方法Conservation principle and method of germplasm resources of forest trees林木种子 Forest seed林木种子检验方法Inspection method of tree seeds林木种子贮藏 Tree seed storage林业资源分类与代码林木害虫Classification and codes for forestry resources--Injurioustree-insects林业资源分类与代码森林类型Classification and codes for forestry resources--Forest types 林业资源分类与代码自然保护区Classification and codes for forestry resources--Natural reserves马来松香 Maleated rosin模压刨花制品家具类Molding articles from wood particle for furniture木材PH值测定方法Method for determination of PH of wood木材冲击韧性试验方法Method of testing in toughness of wood木材防腐术语Glossary of terms used in wood preservation木材干缩性测定方法Method for determination of the shrinkage of wood木材干燥术语Terminology in wood drying木材工业胶粘剂用脲醛、酚醛、三聚氰胺甲醛树脂 Woodadhesives--urea-formaldehyde,phenol-formaldehyde and melamine-formaldehyde resins木材含水率测定方法Method for determination of the moisture content of wood木材横纹抗拉强度试验方法Method of testing in tensile strength perpendicular to grain of wood木材横纹抗压弹性模量测定方法Method for determination of the modulus of elasticity in compression perpendicular to grain of wood木材横纹抗压试验方法Method of testing in compression perpendicular to grain of wood木材缓冲容量测定方法Method for determination the buffering capacity of wood木材胶粘剂及其树脂检验方法 pH值测定法Testing methods for wood adhesives and their resins--Method for determination of pH木材胶粘剂及其树脂检验方法沉析温度测定法Testing methods for wood adhesives and their resins--Method for determination of precipitation temperature木材胶粘剂及其树脂检验方法固化时间测定法Testing methods for wood adhesives and their resins--Method for determination of gelation time木材胶粘剂及其树脂检验方法固体含量测定法Testing methods for wood adhesives and their resins--Method for determination of solid content木材胶粘剂及其树脂检验方法含水率测定法Testing methods for wood adhesives and their resins--Method for determination of moisture content木材胶粘剂及其树脂检验方法碱量测定法Testing methods for wood adhesives and their resins--Method for determination of alkali content木材胶粘剂及其树脂检验方法聚合时间测定法Testing methods for wood adhesives and their resins--Method for determination of curing speed木材胶粘剂及其树脂检验方法可被溴化物测定法Testing methods for wood adhesives and their resins--Method for determination of brominable ubstance木材胶粘剂及其树脂检验方法密度测定法Testing methods for wood adhesives and their resins--Method for determination of density木材胶粘剂及其树脂检验方法木材胶合强度测定法Testing methods for wood adhesives and their resins--Method for determination of wood glue bond strength木材胶粘剂及其树脂检验方法适用期测定法Testing methods for wood adhesives and their resins--Method for determination of pot life木材胶粘剂及其树脂检验方法水混和性测定法Testing methods for wood adhesives and their resins--Method for determination of miscibility with water木材胶粘剂及其树脂检验方法外观测定法Testing methods for wood adhesives and their resins--Method for determination of appearance木材胶粘剂及其树脂检验方法游离苯酚含量测定法Testing methods for wood adhesives and their resins--Method for determination of free phenol content木材胶粘剂及其树脂检验方法游离甲醛含量测定法Testing methods for wood adhesives and their resins--Method for determination of free formaldehyde content木材胶粘剂及其树脂检验方法粘度测定法Testing methods for wood adhesives and their resins--Method for determination of viscosity木材胶粘剂及其树脂检验方法贮存稳定性测定法Testing methods for wood adhesives and their resins--Method for determination of storage stability木材胶粘剂及其树脂检验方法羟甲基含量测定法Testing methods for wood adhesives and their resins--Method for determination of methylol content木材抗劈力试验方法Method of testing in cleavage stregth of wood木材抗弯弹性模量测定方法Method for determination of the modulus of elasticity in static bending of wood木材抗弯强度试验方法Method of testing in bending strength of wood木材密度测定方法Method for determination of the density of wood木材年轮宽度和晚材率测定方法Method for determination of the annual rings width and latewood rate of wood木材湿胀性测定方法Method for determination of the swelling of wood木材顺纹抗剪强度试验方法Method of testing in shearing stength parallel to grain of wood木材顺纹抗拉强度试验方法Method of testing in tensile strength parallel to grain of wood木材顺纹抗压弹性模量测定方法Method for determination of the modulus of elasticity in compressive parallel to grain of wood木材顺纹抗压强度试验方法Method of testing in compressive strength parallel to grain of wood木材天然耐久性试验方法木材天然耐腐性实验室试验方法Method for laboratory test of natural decay resistance of woods木材天然耐久性试验方法木材天然耐久性野外试验方法Method for field test of natural durability of wood木材握钉力试验方法Method of testing nail holding power of wood木材物理力学试材采集方法Method of sample tree collection for physical and mechanical tests of wood木材物理力学试材锯解及试样截取方法Method of sample logs sawing and test specimens selection for physical and mechanical tests of wood木材物理力学试验方法总则General requiements for physical and mechnical tests of wood 木材吸水性测定方法Method for determination of the water absorption of wood木材硬度试验方法Method of testing in hardness of wood木炭和木炭试验方法Wood charcoal and test methods of wood charcoal木质净水用活性炭Wooden activated carbon for water purification木质颗粒活性炭对四氯化碳蒸气吸附试验方法Test method of wooden granular activated carbon adsorption to CCl vapor木质味精精制用颗粒活性炭Wooden granular activated carbon for refining of sodium glutamate浓缩天然胶乳硫化胶乳Natural rubber latex concentrate--Prevulcanized rubber latex浓缩天然胶乳硫化胶乳溶胀度的测定Natural rubber latex concentrate--Prevulcanized rubber latex--Determination of swelling capacity浓缩天然胶乳硫化胶乳粘度的测定Natural rubber latex concentrate--Prevulcanized rubber latex--Determination of viscosity刨花板 Particle board刨切单板 Sliced veneer刨切单板用原木Log of sliced veneer漂白紫胶 Bleached lac漆蜡 Lacquer wax氢化松香 Hydrogenated rosin热带阔叶树材普通胶合板General use plywood of tropical broadleaved species热固性树脂装饰层压板表面耐磨性能的测定Decorative laminated sheets based on thermosetting resins--Determination of resistance to surface wear热固性树脂装饰层压板表面耐污染性能的测定Decorative laminated sheets based on thermosetting resins--Determination of resistance to surface staining热固性树脂装饰层压板尺寸稳定性性能的测定Decorative laminated sheets based on thermosetting resins--Determination of dimensional stability热固性树脂装饰层压板技术条件Decorative laminated sheets based on thermosetting resins--Specification热固性树脂装饰层压板抗拉强度的测定Decorative laminated sheets based on thermosetting resins--Determination of tension strengths热固性树脂装饰层压板耐冲击性能的测定Decorative laminated sheets based on thermosetting resins--Determination of resistance to impact热固性树脂装饰层压板耐沸水煮性能的测定Decorative laminated sheets based on thermosetting resins--Determination of resistance to immersion boiling water热固性树脂装饰层压板耐干热性能的测定Decorative laminated sheets based on thermosetting resins--Determination of resistance to dry heat热固性树脂装饰层压板耐开裂性能的测定Decorative laminated sheets based on thermosetting resins--Determination of resistance to cracking热固性树脂装饰层压板耐老化性能的测定Decorative laminated sheets based on thermosetting resins--Determination of resistance to weathering热固性树脂装饰层压板耐香烟灼烧性能的测定Decorative laminated sheets based on thermosetting resins--Determination of resistane to cigarette burns热固性树脂装饰层压板试件尺寸的规定Decorative laminated sheets based on thermosetting resins--Determination of dimensions of test pieces热固性树脂装饰层压板滞燃性能的测定Decorative laminated sheets based on thermosetting resins--Determination of reaction to fire人造板及饰面人造板理化性能试验方法Test methods of evaluating the properties ofwood-based panels and surface decorated wood-based panels森林抚育规程Regulations for tending of forest杉原条Chinese firtree poles杉原条材积表Volume table of chinese firtree poles生漆 Raw lacquer实木地板块检验及试验方法Solid wood blocks--Examination and test methods for physical and mechanical characteristics实木地板块平接地板块技术条件 Solid wood blocks--Flate join specifications实木地板块竖木地板块技术条件Solid wood blocks--Vertical paving block specifications实木地板块镶嵌地板块技术条件Solid wood blocks--Mosaic parquet specifications实木地板块一般规定Solid wood blocks--Greneral rules实木地板块榫接地板块技术条件 Solid wood blocks--Mortise join specifications松节油分析方法Analytical methods of turpentine松香试验方法Test methods of rosin糖液脱色用活性炭Activated carbon for refining of suger特级原木Logs of super grade天然胶乳锰含量的测定(高碘酸钾光度测定法) Natural rubber latex--Determination of manganese content--Potassium periodate photometric method天然胶乳铜含量的测定Natural rubber latex--Determination of copper content天然浓缩胶乳氨保存离心胶乳的规格Natural rubber latex concentrate--Centrifuged ammonia preserved type-Specification天然浓缩胶乳残渣含量的测定Natural rubber latex concentrate--Determination of sludge content天然浓缩胶乳干胶含量的测定Natural rubber latex concentrate--Determination of dry rubber content天然浓缩胶乳挥发脂肪酸值的测定Natural rubber latex concentrate--Determination of volatile fatty acid number天然浓缩胶乳机械稳定度的测定Natural rubber latex concentrate--Determination of mechanical stability天然浓缩胶乳碱度的测定Natural rubber latex concentrate--Determination of alkalinity天然浓缩胶乳凝块含量的测定Natural rubber latex concentrate--Determination of coagulum content天然浓缩胶乳硼酸含量的测定Natural rubber latex concentrate--Determination of boric acid content天然浓缩胶乳氢氧化钾值的测定Natural rubber latex concentrate--Determination of KOH number天然浓缩胶乳取样Natural rubber latex concentrate--Sampling天然浓缩胶乳总固体含量的测定Natural rubber latex concentrate--Determination of total solids content天然生胶白绉胶片和浅色绉胶片Raw natural rubber--White crepes and pale crepes天然生胶标准橡胶包装、标志、贮存和运输Raw natural rubber--Standard rubber--Packing, marks, storage and transportion天然生胶标准橡胶规格Raw natural rubber--Standard rubber--Specifications天然生胶标准橡胶取样Raw natural rubber--Standard rubber--Sampling天然生胶氮含量测定法Raw natural rubber--Determination of nitrogen天然生胶挥发物含量测定法Raw natural rubber--Determination of volatile matter content天然生胶烟胶片Raw natural rubber--Smoked sheets天然生胶颜色指数测定法Raw natural rubber--Colour index test天然生胶样品的制备Raw natural rubber--Sample preparation天然生胶杂质含量测定法Raw natural rubber--Determination of dirt天然生胶术语Terminology of raw natural rubber桐油 Tung oil脱蜡紫胶片, 脱色紫胶片和脱色脱蜡紫胶片Dewaxed shellac, Decolorized shellac and decolorized dewaxed shellac细木工板 Blockboard小径原木Logs of small diameter旋切单板用原木Log of peeled veneer腰状杆螺柱连接副螺母、受力套管Connections with waisted stud--Nuts, extension sleeves 腰状杆螺柱连接副螺柱Connections with waisted stud--Studs硬质纤维板产品的标志、包装、运输和贮存 Hard fibreboard—Marking, packaing, transportation and reservation of the products硬质纤维板含水率的测定Hard fibreboard—Determination of moisture content硬质纤维板技术要求Hard fibreboard—Technical requirement硬质纤维板检验规则 Hard fibreboard—Test code硬质纤维板静曲强度的测定 Hard fibreboard—Defermination of bending strength硬质纤维板密度的测定 Hard fibreboard—Determination of density硬质纤维板试件取样及测量Hard fibreboard—Samping and measurement of test pieces 硬质纤维板术语和分类Hard fibreboard—Terms and classfication硬质纤维板吸水率的测定Hard fibreboard—Determination of water absorption育苗技术规程Technical regulations for cultivation of tree seedlings原木材积表Log volume table原木检验 Log inspection原木检验术语Terms in log inspection原木锯材批量检查抽样、判定方法第部分:锯材批量检查抽样、判定方法 Sampling and judging methods for lot inspection of logs and sawn timbers Part : Sampling and judging methods for lot inspection of sawn timbers原木锯材批量检查抽样、判定方法第部分:原木批量检查抽样、判定方法 Sampling and judging methods for lot inspection of logs and sawn timbers Part : Sampling and judging methods for lot inspection of logs原木缺陷Defects in logs原木缺陷术语符号The symbol of the logs defect terms造林技术规程Technical regulations for afforestation造纸木片Wood chips for the pulp造纸用原木 Pulp logs针叶树锯材Coniferous sawn timber针叶树锯切用原木尺寸、公差、分等 Coniferous rippinglogs--Dimensions--Tolerancesand-grade classification枕木 Sleeper脂松节油 Gum turpentine脂松香 Gum rosin直接用原木坑木Logs for direct--Pit-props制材工艺术语Terms in lumber technology中国林木种子区白榆种子区Seed zones of Chinese forest trees--Seed zones of Ulmuspumila L.中国林木种子区侧柏种子区Seed zones of Chinese forest trees--Seed zones of Platycladus orientalis (Linn) Franco.中国林木种子区长白落叶松种子区Seed zones of Chinese forest trees--Seed zones of Larix olgensis Henry.中国林木种子区红松种子区Seed zones of Chinese forest trees--Seed zones of Pinus koraiensis Sieb.et zucc.中国林木种子区华北落叶松种子区Seed zones of Chinese forest trees--Seed zones of Larix principis-rupprechtii Mayr.中国林木种子区华山松种子区Seed zones of Chinese forest trees--Seed zones of Pinus armandii Franch.中国林木种子区马尾松种子区Seed zones of Chinese forest trees--Seed zones of Pinus massoniana Lamb.中国林木种子区杉木种子区Seed zones of Chinese forest trees--Seed zones of Cunning hamia lanceolata (Lamb.) Hook.中国林木种子区兴安落叶松种子区Seed zones of Chinese forest trees--Seed zones of Larix gmelinii Rupr.中国林木种子区油松种子区Seed zones of Chinese forest trees--Seed zones of Pinus tabulaeformis Carr中国林木种子区云南松种子区seed zones of Chinese forest trees--Seed zones of Pinus yunnanensis Franch.中国林木种子区云杉种子区Seed zones of Chinese forest trees--Seed zones of Picea asperata Mast.中国林木种子区樟子松种子区Seed zones of Chinese forest trees--Seed zones of Pinus sylvestris var.mongolica Litvin.中国主要木材名称Names of Chinese main woods中密度纤维板定义和分类Medium density fiberboard—Defination and classification中密度纤维板含水率的测定Medium density fiberboard—Determination of moisture content 中密度纤维板技术要求和检验规则Medium density fiberboard—Technical requirement and test code中密度纤维板甲醛释放量的测定Medium density fiberboard—Determination of formaldehyde released中密度纤维板静曲强度和弹性模量的测定Medium density fiberboard—Determination of static bending strength and elastic modulus中密度纤维板密度的测定Medium density fiberboard—Determination of density中密度纤维板平面抗拉强度的测定Medium density fiberboard—Determination of flush tensile strength中密度纤维板试件的制备Medium density fiberboard—Cutting and measurement of test pieces中密度纤维板握螺钉力的测定Medium density fiberboard—Determination of screw holding capability中密度纤维板吸水厚度膨胀率的测定Medium density fiberboard—Determination of thickness swelling rate of water absorption竹编胶合板 Bamboo-mat plywood竹编胶合板试验方法Methods of testing bamboo-mat plywood竹材物理力学性质试验方法Testing methods for physical and mechanical properties of bamboos主要商品木材树种代号Code name of the main commercial timber主要造林阔叶林树种良种选育程序与要求Selection and breeding of procedure and request of the main broadleaf trees improved variety主要造林树种林地化学除草技术规程The state technical standard of chemical weed control in main plantation trees主要造林树种苗木Tree seedlings of major species for afforestation装饰单板贴面人造板Decorative veneered wood-based panel紫胶产品检验方法Methods of testing lac products紫胶产品取样方法Methods of sampling lac products紫胶片 Shellac紫胶原胶 Sticklac阻燃木材燃烧性能试验火传播试验方法The test of burning behaviour for flame retardant treated wood--method of test for fire propagation。