西方国家概况课后英国key
- 格式:docx
- 大小:26.44 KB
- 文档页数:17


英语国家概况课后questions答案第⼀单元;1. "British history has been a history of invasion". Please illustrate this point with the examples from the text. How did each of the invasions influence English culture ?British history has been a history of invasions. Before the first century AD Britain was made up of many tribal kingdoms of Celtic people: a powerful culture originating in central Europe. Then in 43AD Britain was invaded by the Roman empire, and England and Wales (though not Scotland or Ireland) became a part of the Roman empire for nearly 400 years.Two more groups of invaders were to come after the English: from the late 8th century on, raiders from Scandinavia, the ferocious V ikings, threatened Britain's shores….2. Are there any differences between England and W ales in terms of cultural tradition ?Y es, there are. The close long-standing relationship means that modern Wales lacks some of the outward signs of difference which Scotland possesses—its legal system and its education system are exactly the same as in England. Often official statistics are given for "England and Wales". However, Wales is different, and one of the key markers of that difference is the Welsh language—the old British Celtic tongue which is still in daily use.第⼆单元;3、what do you think should be the right solution to the political problem in Northern Ireland?(Margaret Thatcher's government did not give in to this demand for political status and 11 prisoners starved to death. This event revitalised the political campaign of Sinn Fein, the legal political party which supports the IRA's right to fight. Its leaders spoke of a twin campaign for union with Ireland, both political and military, which they called the policy of "The Bullet and the Ballot Box".)The problem lay in the "commitment to peaceful methods" aspect of the possible talks. Province-wide elections are planned under a complex formula to ensure a wide range of representation on the body which will carry out these talks, in an attempt to give them legit imacy. Without the participation of Sinn Fein and the IRA it is hard to see them succeeding. Northern Ireland is poised on the brink—a new peaceful future, or a return to the violence that has claimed 3150 lives so far.第三单元;4、What are some of the characteristics of the British constitutional monarchy? How has the English monarchy evolved gradually to the present constitutional monarchy?There are some characters in the Britain Constitutional Monarchy:1. The monarch is primarily to symbolize the traditional and unity of the British state. The Queen reigns but does not rule. And she is legally head of the executive and judiciary branches, an integral part of the legislature, the commander-in-chief of all armed forces and “supreme governor” of the Church of England2. Parliament becomes the country authority centre, which have right to pass laws, bills and acts of Parliament, to vote for taxation, to scrutinize, criticize and restrain the actions of the government and so on.3. The king must believe in Established Church (being that person succeeds tothe throne not to be that Prod), catholic or same catholic get married.Until the end of the 17th century, British monarchs were an executive monarch, which means that they had he right make and pass legislation. But even in early time there were occasions when the Sovereign had to act in accordance with the law and take into account the will of the paper. With the signing Magna Charta i n 1215, for example, the leading noblemen of England succeeded in forcing King John to accept that they and other freemen had rights against the Crown.In 17th century,the Stuart kings propagated the theory of the divine right of kings, claiming that the Sovereign was subject only to God and not to the law. Widespread unrest against their rule led to civil war in the second half of the 17th century. In 1688-1689 Parliamentarians drew up the Bill of Rights, which established basic tenets such as the supremacy of Parliament. The constitutional monarchy we know today really developed in the 18th and 19th centuries,as day-to-day power came to be exercised by Ministers in Cabinet, and by Parliaments elected by a steadily-widening electorate.第四单元:5、How are people in the UK divided into different classes? What are some of the main features in the division? Is the classsystem similar with the United States?(1)The British people are divided into classes economically, culturally, educationally and etc. The different idea of class is related to the group or class. Upper class , middle class, lower class. People in the UK divided into different classes also according to their jobs.(2) The British people are divided into classes economically, culturally, educationally and etc. The people of different classes have different levels of income, the education they get is totally different.(3)The answer to the last question is “no”. British class system is not so similar to the U.S. Which marks British class system different from the American, is that it has also retained a hereditary aristocracy.第五单元:6.What are the three main areas in national ecnomies?Describe the development of each of the three areas in the UK economy.(1)National economies can be broken down into three main areas:primary industries, such as agriculture, fishing, and mining,Second-ary industries, which manufacture complex goods from those primary produets;And tertiary industuies often described as services, such as banking, insuranc, tourism, and the selling of goods.(2)Britan’s agricultural sector is small(producing 1.4%of the national wealth)but efficient, producing 58% of the UK’s food needs with only 2%of its workforce. Three quarters of Britain’s land is used for agriculture. with about a quarter of that under crops-wheat and barley are the two commmnests. The rest is grazing for animals, including cattle.The fishing industy provides 55%of the UK demand for fish.In the secondary sector of the economy. manufacturing industry remains important, producing 22% of national wealth.British companies are are active in all major fields of manufacturing industry, but are particulary strong in pharmaceuticals, chemicals, aerospace and food drink.第六单元:7、What are some of the features of Romantic Literature?Roughly the first third of the 19th century makes up English literature's romantic period. Writers of romantic literature are more concerned with imagination and feeling than with the power of reason, which marked the 18th century. Perhaps the rather violent and ugly world about them drove 19th-century writers to a literary refuge.第七单元:8、What are the purposes of the British education system? What are the main purpose of the Chinese education system? Are there any differences or similarities in the education of the two nations?British;To develop students creativity and imaginationTo have better communication skills to getting along with different peopleTo have various knowledge about life and nature which is out of textbooksTo be not so good at controlling knowledge—— especially the accounting ability aboutfiguresChina;To pass the examsTo let everyone accepts education, have knowledge and skills to make lifeTo get a good job and make moneyTo be able to cope with life on the wholeTo improve students qualityCompulsory ——(1)Both the UK and China have compulsory education.(2)The general education systems in two countries are quite similar. They bothhave primary schooling, secondary and university education.(3)Both countries have vocational schools providing study and training for thosewho want to follow a certain career instead of seeking university education. differences——Chinese Education System and Western Education System have their own advantages and disadvantages. Chinese emphasizes foundational knowledge whereas Western thinks highly of creativeness.T eaching Philosophy (1)the main concept of education(2)In Britain,education aims to develop individual abilities.But in China, we always kill students? ability of creationand imagination to some degree.T eaching Method(1)In Britain, thei r homework doesn?t have a unified rightanswer. If the answers given by students are reasonable,marks will be given. while in China, the knowledge welearn most have little relationship with our own life, they…remore basic courses .第⼋单元8、Why does the author think that Britain has the "special relationship" with the United States? Does this relationship still exist?Another major factor which influences British foreign policy is its relationship with the United States. This was quite natural, as the two were closely allied during World War II, and continued to work together closely in the post war years because they shared many of the sameworries about the Soviet Union.Even today, in many respects British and American policy-makers agree generally on, for example, how the global economy should be managed, how a warlike state should be dealt with, issues about arms control and so on.第九单元9、The author says that "the media are central to British leisure culture", why does the author say so?Comparison between British Media and Chinese Media(1)On an average day, 90 per cent of Britons over the age of 15 read a national or local paper. And in the evening, most Britons settle down to watch some television: 96 percent of the population watch TV at least once a week, making it Britain's most popular leisure activity. The third most popular pastime, after watching telly and reading newspapers, is listening to the radio, an activity in which 73 per cent of the population engages in on a weekly basis. It is obvious, then, that the media are central to British leisure culture.(2) similarities: Firstly, like British Media, the role that Chinese Media plays has becomemore and more important.Secondly, both the two media have some organizations which aredominant and influential.Thirdly, British Media and Chinese Media are accelerating integration ofthe traditional media and IT.Differences: Paper media in the UK is still a huge industry no matter at present or infuture. But in China, more and more people begin to rely on Internetand hanging around online even with nothing at all to do.In addition, British Media has more freedom than their Chinesecolleagues to criticize politic.第⼗单元10、How do the British celebrate this holiday? In what way does thisholiday and the ways of celebration in British reflect W estern culturaltradition in general and British traditions in particular?(1)Nowadays, Christmas is celebrated by most Britons by exchanging gifts andChristmas cards, preparing holiday foods, and decorating homes and workplaceswith coloured lights, Christmas trees and ornaments.(2)第⼗⼀单元11、Discuss the features of the Celts and their influence on Ireland.Tribe: Celts consisted of a patchwork of tribal areas , each with its own king .Classifications of Celtic language:Proto-Celtic divided into foursub-families .Gaulish ,Hispano-Celtic ,Brythonic ,Goidelic Religion :The Celts believed in many gods and goddesses After LifeThe Celts believed that the human soul had an afterlife, so when aperson died they were buried with many things they would need for theafter life.●House :They lived in round houses with thatched roofs of straw or heather .Cloth:'The way they dress is astonishingThe influence on Ireland:Irish culture came from Celtics culture, including languages, costumes, dancing , instruments and so onIrish dress mainly is lattice costumes(格⼦服装), for women, is linen skirt(⿇布裙⼦), which is made by Irish traditional manual cloth.As forman, their folk dress is skirt.Languages:All the legacies of the Celts, it is their language thathas proved the most lastingIrish is the first official language of the Republic of Ireland (thesecond being English)With the language, the Celts brought an instrument of social andcultural unity to the island, which transcended political and social divisionIrish tap dance(踢踏舞)is enthusiastic and jazzy, and its melody is very beautifulwhat are the unique features of the Australian continentIsolated from other major land masses, Australia?s distinctive flora and fauna evolved through its long period as an island continent.。

英语国家概况(课后问答题)第一部分英国概况1 What are the differences between Britain and the British Isles, Great Britain, England, the UnitedKingdom and the British Commonwealth?Britain is the shortened form of the United kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland while the British Isles is a geographical name.2 What are the three political divisions on the island of Great Britain?They are England, Scotland and Wales3.What is the official name ofGreat Britain ?The United Kingdom of Great Britainand Northern Ireland4. Where did the King Harold defeatTostig and Harold Hardrada?( At Stanford Bridge)5.What did William do after hesuppressed镇压the Saxon risings in the north?(He built a string of defense 防卫castles to ensure his military control ofthe whole country.)6.How long was Britain under the Roman occupation?( For nearly 400 years)7 What was the peculiar features ofthe feudal system of England?(All landowners, whether the tenants-in-chief or subtenants, took the oath ofallegiance for the land they held, notonly to their immediate lord, but also tothe king.)8 What did Willliam I leave to hissons after he died?( He left Normandy to his eldest son,Robert, and England to his second sonWilliam, and a large sum of money tohis third son, Henry.)9 What was William I ’ spolicytowards the church?(He wanted to keep it completely underhis control, but at the same time toupload its power.)10 When was the Domesday Bookcompleted?( In 1086)11 What was the consequence of theHundred Years ’ War?(The French drove the English out oftheir land. By 1453, Calais was the onlypart of France that was still in the handsof English)12 What did the Lollards preach?(The Lollards preached the equality ofmen before God)13 What were the twocountriesElizabeth I successfully played offagainst each other for nearly30years?( France and Spain were the twocountries that Elizabeth I successfullyplayed off against each other for nearly30 years)14 What was the outcome 结果ofthe English Civil War?(It not only overthrew feudal system inEngland but also shook the foundationof the feudal rule in Europe. It isgenerally regarded as the beginning ofmodern world history.)15 What were the three main causesof Henry VIII’religious reform ofthe Church?( The three main causes were: a desirefor change and reform in the Churchhad been growing for many years andnow, encouraged by the success ofMarin Luther, many people believed itstime had come; the privilege and wealthof the clergy were also resented; andHenry needed money)16 Which party did MargaretThatcher represent in the 1970s?(She represented the ConservativeParty)17 What did the Whigs stand for inthe early 19 th century?Whigs stood for a reduction in Crownpatronage,sympathy towardsNonconformists, and care for theinterests of merchants and bankers.18 Why did changes in farmingmethods改变耕作方式 affect lives ofmillions in the 18th century?(Because village and agriculture werethe backbone of England at that time.)19 When did Britain finally becomea full member of the EuropeanEconomic Community?(Britain finally became a full memberof the European Economic Communityin January, 1973)没背20 Why was Mrs. Thatcherremoved from office in 1990?(It was because of her opposition toEuropean Union and her imposition of anextremely unpopular flatrate ‘ polltax ’in place of property taxes to pay forlocal government service.21 What were the two groups of theChartiests?What was theirdifference?(The Chartists could be divided intotwo groups: the Moral Force Chartistsand the Physical Force Chartists. Theformer wanted to realize their aims bypeaceful means while the latter wantedto achieve their purpose by violence)22 What was the goal of the LondonWorking Men’ s Association in itsstruggle?(It aimed to ‘to seek by every legalmeans to place all classes of society inpossession of equal political and socialrights)精品文库23 Why was Britain known as the (ThethreemainChristianfestivalsin 是 后 果 , 英 爱 条约 1921 (Violentfactory of the world in the mid-19 thBritain are Christmas. Easter,oppositionandtoWhite treatyby century?Sunday.) ultranationalists led to a civil w(BecausethBritisheconomywas没背42 What was the result ofamong the strongest in the world)33 Who is directly responsible for the24 Who has the power to declare war and make peace in the UK?(TheQueen) 25 How many members ofParliament does the House ofCommons in the UK consist of ?NHS in Britain?谁直接负责国民保growing Irish nationalism in the early decades of the 20thcentury?健制度在英国(Irish nationalism became stron(Centralgovernmentisdirectly even more violent in the early d responsible for the NHS inof Britain)the20century and climaxed in 34 What are the two established EasternUprisingof1916inwhichan Irish Republic was proclaimed. 26 What does the British Parliament没背43Wht happened aftertheEnglish king was declared the headconsist of ?in Scotland)(It consists of the Sovereign, the Houseof the Church of Irelandreplaceing35 Howmany provinces does theof Lords and the House of Commons)the Pope? 英国国王宣布爱尔兰教会Church of England have?领袖代替教皇27Whatdidtheterm ‘parliament ’(Therefollowedcenturiesofreligiousoriginally mean?(TheChurchof Englandhastwo政治迫( It originallymeantmeetingforprovinces: Canterbury and York)parley or discussion)36What is the National Day in害, whichhelpedtostrengthenanddeepen Ireland ’sCatholic spirit.)Britain?第二部美分国部分28 WheredoestheSovereign ’scoronation take place?(The birthday of the British Monarch isa National Day in Britain)1What are the two novels giving a威vivid description of the miserable life斯敏斯特教堂 in London)Great Britain?of the black slaves?(Uncle ’TomsCabin and Roots)29Wheredoesthe Queen ’s (It refers to the Universities of Oxfordand Cambridge)2 What is the reason for the growth expenditure arising from 支出所产生38 What kind of schools are theof population in Florida?的 public duties come from?没背(Florida ’populationsgrowthowesindependent schools in Britain?( The Queen ’sexpenditure arising from(Theindependentschoolsarethose muchtoitsattractivenessbothapublic duties comes from the Civil Listsupportedentirelybfeesandprivateplaceto retireandasa convenientand government departments)placeforbusinesswithandtraveltofuns)30 How is the British House of 39What are the three groups ofCentral and South America)Commons elected?3 When did the higher birth ratenation newspapers?TheHouseofCommonsiselectedby(Theyare quality,popularnd appear in the United States? universal adult suffrage. mid-market papers.) (Thebirthrateappearedduring ‘the影子baby boom ’[1946-1964])?? 31Whatisa ‘shadowcabinet ’ 40 Which religion in Ireland is the内阁 in Britain?4 When was the Declaration of( Thepartywhichwinsthesecond largest non-Catholic denomination?Independence adopted?largestnumberofseatsinparliament圣 公 会of (It was adopted on July4,1776)(TheAnglicanChurch5Please write any three of thebecomes the Official Opposition and it没背formsits own ‘cabinetknown ’as Irelandis thelargestnon-Catholicdenomination.)13 colonies the British established ‘shadow cabinet ’along the east coast of North32 What are the three main41 What was the consequence ofAmerica between 1607 and没背1733.(Virginia,Maine, Newchurches in Britain?(651Members of Parliament)(TheyaretheChurchofEnglandthe Church of Scotland什么Christian festivals in Britain?the Anglo-Irish Treaty of 1921?欢迎下载2Hampshire)6What are the implications of the‘ Manifest Destiny’?The implications of‘ manifest Destiny’ are three fold(1)the inevitability of the founding of the United States of America; 是必然的(2)the legitimacy合法的 of the expansion of America Territory美国领土; (3) the spread of American democracy 美国民主being the task 任务of American people who were chosen to do the Lord’ s work.没背7 What were the two seriousweaknesses of the Articles of Confederation? 邦联条款They were:(1)There was no national executive or law-enforcing branch;没有执行或执法部门(2)Congress 国会was too large a body to function 功能as government. And Congress had no power to raise taxes.国会无权征税8What agreement did America and Britain sign in 1783 by which Britain recognized the independence of the United States? The Treaty of Paris9 What were the features in the colonial period which had influence on later American development?They were representive form of government, rule of law, respect of individual rights, religious tolerance and a strong spirit of individual enterprise.。

英语国家概况课后题摘要:一、英语国家概况概述1.英美两国的历史背景2.地理位置及气候特点3.政治体制及社会制度二、英国概况1.历史发展简述2.地理位置及气候特点3.政治体制及社会制度4.经济状况及产业结构5.文化教育及著名旅游景点三、美国概况1.历史发展简述2.地理位置及气候特点3.政治体制及社会制度4.经济状况及产业结构5.文化教育及著名旅游景点正文:一、英语国家概况概述英语国家概况主要涉及英国和美国两个国家。
这两个国家具有深厚的历史背景,独特的地理位置和气候特点,以及各自的政治体制和社会制度。
在这部分,我们将对这两个国家进行简要的概述。
二、英国概况英国,全名“大不列颠及北爱尔兰联合王国”,位于欧洲西北部,由英格兰、苏格兰、威尔士和北爱尔兰四个部分组成。
英国是一个具有君主立宪制政体的国家,现任君主是伊丽莎白二世女王。
英国气候多样,但总体上属于海洋性气候,四季分明。
英国的经济以服务业为主,特别是金融、教育、旅游等产业具有较高地位。
在文化教育方面,英国拥有世界一流的大学,如牛津、剑桥等,吸引了全球众多学子前来求学。
著名旅游景点包括白金汉宫、大本钟、伦敦塔桥等。
三、美国概况美国,全名“美利坚合众国”,位于北美洲,东临大西洋,西濒太平洋。
美国是一个民主共和制国家,实行总统制。
美国的气候同样多样,但大部分地区属于温带大陆性气候。
美国是全球最大的经济体,拥有高度发达的工业、农业和服务业。
美国在科技、金融、航空航天等领域具有领先地位。
在文化教育方面,美国拥有众多世界顶级大学,如哈佛、耶鲁、斯坦福等。
著名旅游景点包括自由女神像、大峡谷、黄石国家公园等。
以上就是对英国和美国这两个英语国家的概况介绍。

英语国家概况P171.Britain is now a multiracial society which produces a population ofwhich 1 in 20 are of non-European ethnicity.2.Britain is a country with a history of invasions. In 43 AD Britain wasinvaded by the Roman Empire in the 11th century they suffered invasions from Normans.3.Charles the first, king of Britain, was executed, because he attemptedto overthrow parliament in the English Revolution. two Scottish cities which have ancient and internationallyrespected universities: Edinburgh and Glasgow.5.Both the Scottish and Welsh people elect their members ofparliaments to the London Parliament and each holds 72 and 38 seats respectively.P476.The doctrine of the “divine right of kings”held that the sovereignderived his authority from God not from his subjects.7.During the civil war in the 17th century, those who represented theinterests of Parliament aare called roundheads, and those who supported the King were called loyalists.8.In 1215, some feudal barons and the Church forced King John to signthe Magna Carta to place some limits on the King’s power.9.In medical times, kings would summon a group of wealthy barons andrepresentatives of countries, towns and cities—called the Great Council to raise money.10.I n 1689, Parliament passed the Bill of Rights to ensure that the kingwould never be able to ignore Parliament.11.I n Britain, the official head of state is the Queen while the real centreof political life is in the House of Commons.12.S trictly speaking, the Parliament today consist of the Queen, theHouse of Lords and the House of Commons.13.L ife peers should be nominated by Prime minister and appointed bythe sovereign.P6714.T he UK is divided into 650constituencies with each of themrepresented by a member in the parliament.15.T he party which wins the majority seats in parliament forms thegovernment and its party leader becomes the Prime Minister.16.N ormally, a government can be in power for 5 years, and then it hasresign and hold a general election.17.N ational Health Service was established by the Labour government in1948, providing health care for all the people.18.O ne distinctive feature about the class system in British is that it stillretains a hereditary aristocracy.P11719.T wo famous public schools mentioned in the text are Eton andWinchester.20.C hildren in Britain must receive a full-time education legally from theage of five to sixteen.21.P upils from the age of 5 to11mainly attend state-run primaryschools.22.S tudents attend secondary schools from the age of 11 up to aroundthe age of 19.23.C omprehensive schools provide a general education, teachingstudents everything from academic subjects like literature and science to more practical subjects like cooking and carpentry.24.N ame two of the four Scottish Universities dating from the 14th and15th centuries St. Andrews and Glasgow.25.I n Britain, people can go to the Open University without having anyformal educational qualifications.26.G CSE stands for General Certificate of secondary Education27.G CEA stands for General Certificate of Education-Advanced28.G NVQs stands for General National Vocational Qualifications名词解释1.The Anglo-SaxonsThey were two groups of Germanic peoples who settled down inEngland from the 5th century. They were regarded as the ancestors of th English and the founders of England.2.The Bill of Rights of 1689In 1688, King James II’s daughter Mary and her husband William were invited by the politicians and church authorities to take the throne, on condition that they would respect the rights of parliament. The Bill of Rights was passed in 1689 to ensure that the King would never be able to ignore Parliament.3.The ConstitutionBritain has no written Constitution. The foundations of the British state are laid out in statute law, which are laws established through common practice in the courts; and conventions.4.The functions of ParliamentThe function of Parliament are: to pass laws, to vote for taxation, to scrutinize government policy, administration and expenditure and to debate the major of the day.5.The House of LordsThe House of Lords consists of the Lords Spiritual, who are the Archbishops and most prominent bishops of the Church of the England; and the Lords Temporl, which refers to those lords who either have inherited the seat from their forefathers or they have been appointed. The Lords mainly represented themselves instead ofthe interests of the public.6.The House of CommonsThe House of Commons is the real center of British political life because it is the place where about 650 elected representatives (Members of Parliament) make and debate policy. These MPs are elected in the General Elections and should represent the interests of the people who vote for them.prehensive schoolsComprehensive schools are the most popular secondary schools in Britain today. Such schools admit children without reference to their academic abilities and provide a general education. Pupils can study everything from academic subjects like literature to more practical subjects like cooking.8.Grammar schoolsIt is a type of secondary schools in Britain .Grammar schools select children at the age 11, through an examination called “the 1-plus”.Those children with the highest marks go to grammar schools. These schools lay emphasis on advanced academic subjects rather than the more general curriculum of the comprehensive schools and expect many of their pupils to go on to universities.9.Independent schoolsIndependent schools are commonly called public schools which are actually private schools that receive thir funding through the private sector and tuition rates, with some government assistance.Independent schools are not part of national education systm, but the quality of institution and standards are maintained through visits from Her Majesty’s Inspectors of Schools. These schools are restricted to the students whose parents are comparatively rich.10.T he Open UniversityThe Open University was founded in Britain in the 1960s for people who might not get the opportunity for higher education for economic and social reasons. It’s open to everybody and does not demand the same formal educational qualification as the other universities.Universities courses are followed through TV, radio, correspondence, videos and a net work of study centers. At the end of their studies at the Open University, successful students are awarded a university degree.。


英语国家概况复习笔记TheUKThe UKUnit 11.The official name:The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland (Since 1927)national flag:The Union Flag OR popularly known as the Union Jacknational anthem(国歌):GOD SAVE THE QUEENnational capital of the country :London:Greater London⼤伦敦都市区: the City of London + 32 boroughs[?b?r?](⾃治的市镇)The City of London伦敦城: at the center of the metropolitan-the financial center of thecountryInner London: the City of London + its 12 boroughsOuter London: 20 boroughs [?b?r?](⾃治的市镇)surrounding Inner London2. The location and size of the country (了解)3. The terrain [t??re?n](地形), rivers and mountains of the countryRoughly two kinds of terrain---highland and lowland.The highland area --- in the northern part of the country, comprising the mountainousregions of Scotland, Northern Ireland, northern England and north Wales.The lowland area --- especially in the Midland, southern and eastern England.The longest river in the UK is River Severn(塞⽂河).Among the most important rivers is the Thames(泰晤⼠河), which is second longest but is the deepest river in the county. Ben Nevis(本·尼维斯)is the highest peak of the UK.(⼤不列颠境内的最⾼⼭峰,海拔1,343.8⽶,位于苏格兰西部的格兰扁⼭脉)Lough Neagh (396km2)(內伊湖): the largest lake in the whole country4. The natural resources of the countryCoal 煤●Britain has a rich deposit of coal with major coal mines in central and southwest of England.●For the last decades, there has been a steady decline in both coal production and number of coal mines.Petroleum [p??tr?uli?m] ⽯油●1965 saw discovery of big oil and oil fields under the North Sea, east of Britain.5. The climate of the countryTemperate maritime climate(温带海洋性⽓候)What are the characteristics of the climate in Great Britain?FoggyRainyUncertain and changeable6. Major citiesLondon ;Edinburgh [?edn?b?:r?] 爱丁堡;Cardiff [?kɑ:d?f] 加地夫(威尔⼠的主要海港);Belfast [?bel?f?st] 贝尔法斯特(北爱尔兰⾸府);Birmingham ['b?:mh?m] 伯明翰市(英国中部城市,第⼆⼤城市)Manchester: the Guardian(卫报)Glasgow:[?ɡlɑ:sɡ?u] 格拉斯哥(苏格兰最⼤城市,第三⼤城市)7. Population Density and Population DistributionPopulation density: 248 persons per square kilometer.The Population of the UK is the 3rd largest in Europe.Population distribution: high urbanization (7 conurbations)7 conurbations:Greater London⼤伦敦区, W. Midlands西密德兰都市郡, South Yorkshire 南约克都市郡, W. Yorkshire西约克郡都市郡, Greater Manchester⼤曼切斯特都市郡, Merseyside默西赛德都市郡(England), Tyne& Wear泰恩及威尔都市郡(Scotland) (了解)8. Nations and the Languages Spoken1) Nations: English, Scottish, Welsh and IrishEnglish (80%): descendants [d?'send?nts] 后裔of Anglo-SaxonsWelsh, Irish & Scottish::descendants of Celts2)Languages:A) English (official language):B) Gaelic [?g?l?k] 盖尔语: Scotland & Northern IrelandC) Welsh [wel?] 威尔⼠语: Wales [we?lz]3) T he history and development of the English language(p.7)Old English (450AD-1100 AD) influenced by Old Norse (古斯堪的纳维亚语) spoken by Vikings (北欧海盗) and was closely related to the German and Dutch (荷兰) languages. The introduction of Christianity added the first wave of Latin and Greek words to the language and ended with the Norman Conquest.Middle English (1100AD-1500AD) French replaced English as the official language in England. Numerous French words came into the English vocabulary and ended with the Black Death (⿊死病).Modern English (1500AD- present) Assimilating(吸收) words from Latin and Greek words throughout the Renaissance (⽂艺复兴) such as William Shakespeare and the King James Bible.Standard English= the Queen’s Englis h= BBC EnglishExplanation of Standard EnglishStandard English is based on the speech of the upper class of the southeastern England.It is preferred by the educated andit is widely used in media and taught at schools. Is has developed and has been promoted as a model for the correct British English. It is also the norm(标准)carried overseas. Today, Standard English is codified to the extent that the grammar and vocabulary are much the same everywhere in the world where English is taught and used.9. Religion1. Britain is a multi-faith society in which everyone has the right to religious freedom.2. Christianity is the dominant religion of the country. Most of citizens are eitherProtestant ['pr?t?st?nt]新教徒or Catholic.3. English nation: The church of England(英格兰圣公会)is the established church of theEnglish nation.4. The major non-Christian communities in Britain are the Jews, the Moslems and theBuddhists.10. Character and manners of British peopleConservatismTalking about the WeatherPunctuality11. Traditions and custom●Trooping the Color英国皇家军队阅兵仪式around the Bucking Place in London(P.62)to celebrate the Queen’s Birthday Parade. (The Changing Guard ceremony)●Religious FestivalsChristmas ( Three Christmas Traditions )①Christmas pantomime [?p?nt?ma?m] (童话剧)②Queen's Christmas message③Boxing Day(节礼⽇)Easter纪念耶稣复活Halloween12. MediaNewspaperTraditionally British newspapers have been divided into "quality", serious-minded newspapers (usually referred to as "broadsheets宽幅印刷品" because of their large size) and the more populist ['p?pj?l?st] 平民化, "tabloid" varieties.Quality Press: The Times(泰晤⼠报), The Guardian(卫报), The Daily Telegraph(每⽇电讯报)Tabloid [?t?bl??d] 通俗⼩报: The Sun on SundayTelevision and BroadcastBBC(the British Broadcasting Corporation), ITV(Independent Television) 英国独⽴电视台, BSkyB(the British Sky Broadcasting Group PLC)英国天空⼴播集团TV programs done well by the BBC (P.60)Unit 4. British Economy1. The Relative Decline of British Economy (Why?)1) The country suffered a great loss in the two World Wars.2) The era[r]时代of the British Empire was over.3) Britain was still forced to maintain a substantial and expensive military presence.4) Britain failed to invest in industry after WWII.However, the decline is not an absolute one. The UK is not poorer than before. In fact, it iswealthier and more productive than before. The only thing is that other countries develop faster than the UK. So, the UK has experienced a relative decline.2. Recent History of British Economy1970 - high Inflation rate, strikes1979 - Reformation Program(改⾰⽅案)by Thatcher government→去国有化privatization [?pra?v?ta?'ze??n]What was the content of the programThatcherism [?θ?t??(r)z?m] 撒切尔主义:Throughout the 1980s an extensive program of privatization was carried out.---Denationalization [?di:?n??n?la?'ze??n] ⾮国有化①Government expenditure [?k?spend?t??(r)] 花费was reduced;②Taxation reformed;③Foreign exchange controls lifted外汇管制解除④Rules governing banks loosened;⑤Worker strikes restricted.What was the long-term results①Inflation(通货膨胀) has been controlled②Unemployment rate falling③Encouraged by low interest rates, investment has increased. It is second only to the US as a destination for international direct investment. It is also itself a major source of international investment --- it is the second biggest international investor in the world.Policies of Blair Government & Results (P.45)Policies: ①Blair made the Bank of England independent.②In social policy, the Blair government changed the old Labor Party’s practice of usingtax system, public expenditure[?k?spend?t??(r)] 花费and price controls to reduce inequality and put an emphasis on the minimum wage and supplementing low incomes. It also emphasized individual responsibility.Results:①limit government spending②keep inflation under control③reduce unemploymentBy the end of the 20th century, British economic growth surpassed that of other major European countries.3. The Current British Economy1) Primary IndustriesAgricultureA. Features: small population, high mechanization[?mek?na?'ze??n]机械化and highefficiency; but can not satisfy its domestic needsB. Chief agricultural products:wheat(⼩麦),barley [?bɑ:li]⼤麦,sugar beet(甜菜) and potatoesEnergy production (5% of national wealth).Main energy resources: coal (Rio Tinto Group⼒拓集团),oil (Shell 壳牌, British Petroleum and British Gas)2) Secondary Industries:P .473) Tertiary Industries: 65% of national wealth1. (P .50)Foreign Trade ---- Lifeline. Britain is both an importer and exporter in the world.2. FinanceThe position of London in the world economyCentral Bank----Bank of EnglandThe Big Four: Lloyds 劳埃德, Barclays 巴克莱银⾏, Midland ⽶德兰,the National Westminster Bank Group 国民西敏寺银⾏3. Currency :Pound Sterling [paund ?st ?:li ?] 英镑Unit 3 Political System1. Political System : Constitutional Monarchy [ ?k ?nst ??tu:??n ?l ?m ?n ?ki ] 君主⽴宪制What does it mean by Constitutional Monarchy?The King or Queen reigns [re n]君主统治and is the head of the country, but dose notrule the country. The country is governed, in the name the Sovereign [ ?s ?vr ?n ] 君主, but by His or Her Majesty ’s [ ?m?d ?? sti ]陛下government---- a body of ministers who are responsible to Parliament [ ?p ɑ:l?m ?nt ]议会.2. Parliament议会(最⾼⽴法机关)、⽴法政府、⾏政部门司法机关 [ d ?u?d ri ]上议院下议院君主Parliament:The UK is a unitary [ ju:ntri ]中央集权country.The British Parliament is often referred to assupreme legislative authority(最⾼⽴法机关)of the UK.The Main functions are making laws and supervising(监督)government and finance.The life of Parliament is fixed at five years.Sovereign: Theoretically[ ?θ??'ret?kl? ]理论上, the Queen has all the power. In reality, she does everything on the advice of the Prime Minister.The significance of the Queen? P.32It represents the continuity and adaptability of the whole political system and is a symbol of British unity, an indissoluble [ ?? nd??s?lj?bl ] (牢不可破的) bond among people who retain many regional and cultural difference.( 它代表了整个政治体系的连续性和适应性,是英国团结的象征,⼈们保留了许多地区和⽂化差异的不解之缘。

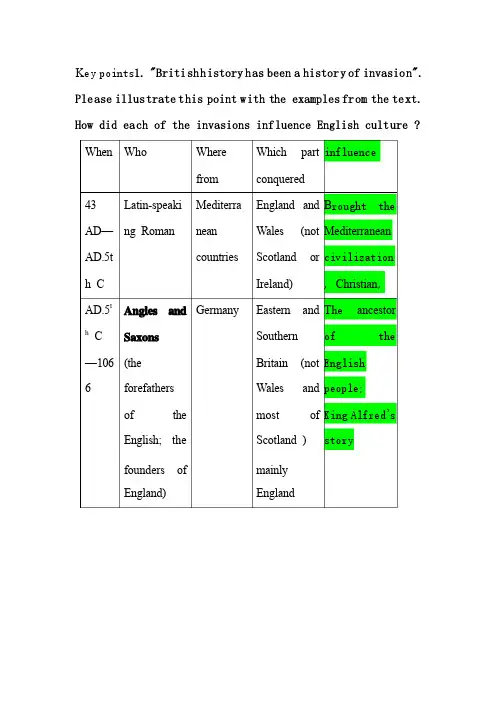
K ey points1. "British history has been a history of invasion". Please illustrate this point with the examples from the text. How did each of the invasions influence English culture ?When Who Where from Which part conquered influence 43 AD AD——AD.5th C Latin-speaking Roman Mediterranean countries England and Wales (not Scotland or Ireland) B rought theMediterraneancivilization, Christian,AD.5t h C —106 6 Angles andSaxons(the forefathers of the English; the founders of England) Germany Eastern and Southern Britain (not Wales and most of Scotland ) mainly England T he ancestorof theEnglishpeople;King Alfred’sstoryLate AD.8t h C –AD 10th C. the the ferocious ferocious Vikings Scandinavia (北欧:北欧:瑞典、挪威一带。
丹麦、芬兰、冰岛等) Northern Northern and and Eastern England, Scotland T he process offorming aunitedBritain(EnglishKings unitedmean, so didthe ScottishCrown),1707, theunited Britaincame intobeingAD 11th C (1066 ) Norman French (William (William the the Conqueror defeated King Harold at at the the the Battle Battle of Hastings, and and built built built the the Normandy (northern France) The next few hundred years, joining various various parts parts of the British Isles under English rule (England, I mport aruling classTower of London) Wales, Scotland, Ireland) 1. What are some of the factors in Irish and English history that affect the situation in Northern Ireland today? K eys:1. racial, racial,2. 2. 2. religious religious3. immigration immigration in in in 1717th c.4. 4. the the British solders ’ station in 19691. How did the doctrine of the ―divine right of kings ǁ, according to the author, lead to the English Civil War? What do you know about the causes of the English Revolution in the 17th century?K ing James I believed the divine right of kings, so did his descent---Charles I.Charles Charles I I I called called called his his his t t t Parliament Parliament only when he needed to collect money.T he Civil War was caused caused by by by a a a dispute dispute dispute over over over the the the power power power of of of the the the king king against Parliament in the 17th C. The Republican ―roundheadsǁ, led by Oliver Oliver Cromwell, Cromwell, Cromwell, wanted wanted wanted to to to abolish abolish abolish the the the monarchy monarchy monarchy and and and to to to reassert reassert reassert the the rights rights of of of Parliament. Parliament. In In 1642, 1642, 1642, the the the royalists royalists were were defeated defeated and and King King Charles I was executed in 1649.The The English English English Civil Civil Civil War War War not not not only only only overthrew overthrew overthrew feudal feudal feudal in in in England England England but but but also also shook the foundation of the feudal rule in Europe. It is generally regarded as as the the the beginning beginning of of modern modern world world history. history. T he Civil War was in essence a capitalist revolution because capitalism paved its way of development after the war.1. What are three big parties in the UK? W hat are some of the similarities and dissimilarities between the three parties? There are three m ajor national parties: The Conservative party and the major national parties: The Conservative party and the Labour party are the two biggest, and any general election is really about which of those two is going to govern. But there is a third important party, the Liberal Democrats, who usually receive up to about 20% of the votes: not enough to form a government, but enough to have a big impact on which which of of of the the the other other other two two two parties parties parties does does does so. so. so. The The The Conservative Conservative Conservative Party Party Party spent spent most time in power T hey are the Labor party, the Conservative party and the Liberal Democratic party.the Labour party--- one of the 2 biggest parties in the UK. It is also the newest party, created by the trade union movement at the end of the 19th century. It is a socialist party, believing that a society should be relatively equal in economic terms, and that the government should redistribute the wealth between the rich and the poor. It also thinks that the government should provide a range of public services for all the people. the the Conservative Conservative Conservative party party party --- --- --- one one one of of of the the the 2 biggest 2 biggest parties parties in in in the the the UK. UK. UK. It It It is is basically the party of the individual, protectin g the individual’ s right to acquire acquire wealth wealth wealth and and and to spend to spend it it as as as he/she he/she he/she wants. wants. wants. It It It advocates advocates advocates economic economic policies which are favourable to businessmen, such as low taxes. From 1979 1979 to to to 1997, 1997, 1997, the the the Conservative Conservative Conservative party party party won won won 4 4 4 consecutive consecutive consecutive elections elections elections and and was in power for quite a long period of time. the Liberal Democrats--- the 3rd biggest party and often seen as a party of the the ―middleǁ, ―middleǁ, o ccupying occupying occupying the the the ideological ideological ideological ground ground ground between between between the the the two two two major major parties. They are comparatively flexible and pragmatic in their balance of the the individual individual individual and and and the the the social. social. social. They They They emphasize emphasize emphasize the the the need need need to to to change change change the the Britain’s constitutional arrangements to make the government more democratic and accountable. S imilarities:1. they all support the capitalist system2. generally speaking, they all are the active participants and supporters of representative democracy3. they share some similar beliefs in their political and socioeconomic ideology D issimilarities:1. they represent the interests of different social groups2. they have different opinions on the government’s role in social economy and they each take different economic policies duringtheir administration51. What are the foundations of Britain's foreign policy?51. The contemporary foreign policy of the UK is greatly influenced by its imperial history and also by its geopolitical traits. Perhaps the most important single factor which influences British policy-makers is its history. 。


Chapter One1.Blank fillings:1)England;2)Ben Nevis;3)North Sea;4)Britain;5)British;6)cotton;7)agricultural;8)Iberians;9)Birmingham;10)Liverpool2.Questions:1)To other Europeans, the best known quality of the British, and of the English in particular, is"reserve".2)The reluctance to communicate with others tends to give the impression of coldness, and it istrue that the English (except perhaps in the North) are nor noted for their generosity and hospitality. On the other hand, they are perfectly human behind their barrier of reserve, and may be quite pleased when a friendly stranger or foreigner succeeds for a time in breaking the barrier down.3)The English self-deprecation, mixed with their reserve, often produces a sort of general air ofindifference which appears to foreigners as a pose, difficult to understand and irritating.4)Along with the political campaign for home-rule there were groups who followed a moredirect method of pursuing Irish independence, engaging in guerilla or terrorist activities against British institutions and the British military forces. During the First World War and immediately after, this activity increased, sometimes brutally suppressed by British forces. 5)Y es, there are. The close long-standing relationship means that modern Wales lacks some ofthe outward signs of difference which Scotland possesses—its legal system and its education system are exactly the same as in England. Often official statistics are given for "England and Wales". However, Wales is different, and one of the key markers of that difference is the Welsh language—the old British Celtic tongue which is still in daily use.3. T erms for explanation:1) Union Jack: flag of United Kingdom: the flag of the United Kingdom, which combines the flags of England, Scotland, and Ireland.2) Lake District: region of mountains and lakes in Cumbria, northwestern England. The district extends about 50 km/30 mi from north to south and 40 km/25 mi from east to west.3) The Bible: also called the Holy Bible, the sacred book or Scriptures of Judaism and of Christianity.4) The Puritans: members of a group of Protestants in 16th- and 17th-century England and 17th-century America who believed in strict religious discipline and called for the simplification of acts of worship.5) Great Charter: document sealed by King John of England on June 15, 1215, in which he made a series of promises to his subjects that he would govern England and deal with his vassals according to the customs of feudal law (see Feudalism). Over the course of centuries, these promises have required governments in England (and in countries influenced by English tradition) to follow the law in dealing with their citizens.4. Analysis and comments:1) In the United Kingdom, the upper classes are the aristocracy and royalty, with wealth playing a less important role in class status. Many aristocratic peerages or titles have …seats‟ attached to them, with the holder of the title (e.g. Earl of Bristol) and his family being the custodians of the house, but not the owners. Many of these require high expenditures, so wealth is typically needed. Many aristocratic peerages and their homes are parts of estates, owned and run by the title holder with moneys generated by the land, rents, or other sources wealth. The middle class is the most contested of the three categories, the broad group of people in contemporary society who fall socio-economically between the lower and upper classes. Lower class are those employed in low-paying wage jobs with very little economic security.2) It was sealed under oath by King John at Runnymede, on the bank of the River Thames near Windsor, England. Magna Carta was the first document forced onto a King of England by a group of his subjects, the feudal barons, in an attempt to limit his powers by law and protect their rights. The charter is widely known throughout the English speaking world as an important part of the protracted historical process that led to the rule of constitutional law in England and beyond.Chapter T wo1.Blank fillings:1)parliamentary democracy;2)the House of Commons, the House of Lords;3)the House of Commons;4)the Queen;5)executive;6)constitution;7)European Union (EU);8)military equipment;9)The Lord Chancellor;10)proven guilty2.Questions:1)The contemporary foreign policy of the UK is greatly influenced by its imperial history andalso by its geopolitical traits. Perhaps the most important single factor which influences British policy-makers is its history.2)The word "parliament" comes from the verb "to parley", that is, to discuss or talk. The termwas first used officially in 1236 to describe the gathering of feudal barons and representatives from counties and towns which the king occasionally summoned if he wanted to raise money.3)There are three major national parties: The Conservative party and the Labour party are thetwo biggest, and any general election is really about which of those two is going to govern.But there is a third important party, the Liberal Democrats, who usually receive up to about 20% of the votes: not enough to form a government, but enough to have a big impact on which of the other two parties does so. The Conservative Party spent most time in power4)The House of Commons.5)The party that wins most votes in general election and the leader of this winning party wouldbecome Prime Minister.3.T erms for explanation:1)Britain‟s legislature is made up of the House of Commons, the House of Lords and the kingin his constitutional role. The House of Commons has 651 elected Members of Parliament (MPs), who represent local constituencies. The center of parliamentary power is the House of Commons.2)The nonelected upper house of Parliament in the United Kingdom, made up of life peers,some hereditary peers, and some bishops.3)In British criminal trials the accused is presumed innocent until proven guilty. Trials are inopen court and the accused is represented by a lawyer. Most cases are tried before layjustices sitting without a jury. The more serious cases are tried in the higher courts before a jury of 12 (15 in Scotland) which decides guilt or innocence.4)Actions brought to court are usually tried without a jury. Higher courts deal with morecomplicated civil cases. Most judgments are for sums of money, and the costs of an action are generally paid by the losing party.5)The Lord Chancellor is the head of the judiciary branch of government.4. Analysis and comments:1) Constitutional monarchy is a form of democratic government in which a nonpolitical monarch acts as head of state within the boundaries of a constitution, whether written or unwritten.[1] While the monarch may hold formal reserve powers and while government officially takes place in the monarch‟s name, they do not set public policy or choose political leaders. Political scientist V ernon Bogdanor, paraphrasing Thomas Macaulay, has defined a constitutional monarch as "a sovereign who reigns but does not rule." This form of government differs from absolute monarchy, in which the monarch controls political decision-making and is not effectively bound by a constitutional order.2) Debates can be witnessed very commonly in House of Commons. They take place sometimes in harmony, but more times in a very heated situation. Think about if the debates necessary in House of Commons.Chapter Three1.Blank fillings:1)Banking;2)Insurance;3)service;4)manufacturing;5)North Sea;6)Margaret Thatcher;7)military;8)1970s;9)London;10)service;11)electronics2.Questions:1)By the 1880s the British economy was dominant in the world, producing one third of theworld‟s manufactured goods, half its coal and iron, half its cotton.2)But even by 1900 this was no longer the case, the UK having been overtaken by both theUnited States and Germany; and certainly from 1945 until the present, the story of the UK economy is usually thought of as one of decline.3)India, popularly known as "The Jewel in the Crown" of the British Empire, gained itsindependence in 1947.4)This has a number of consequences for British society, mainly positive, though with someindirect negative effects. On the positive side such immigrant groups bring their culture with them, which increases the variety and interest within British culture: for example, the UK, which used to have a bad reputation for food, now has a cuisine as varied as any, with Indian and Chinese restaurants in every community, as well as many other varieties in bigger cities.This variety in restaurant food has resulted in more experimentation at home, so that shops now carry a much wider variety of goods to supply the demand, and there are many TV programmes and books devoted to all kinds of different cooking. The negative side of things lies largely in the attitude of some of their white neighbours.5)While there is a growing ethnic minority middle-class, and many individual success stories,by most measures the immigrant population is worse-off economically speaking than the white population as a whole. Individuals from ethnic minorities are more likely to be unemployed; and they are under-represented in politics too, though there are now a number of black and Asian MPs. But there are also a number of small political parties in the UK with overtly racist policies.3.T erms for explanation:1)Conservative Party (Britain), oldest political party in the United Kingdom. The ConservativeParty evolved as the successor to the Tory Party in the 1830s. It is known in full as the Conservative and Unionist Party. The party‟s tenets of conservatism inclu de the continuance of monarchical parliamentary government. Until after the end of World War II in 1945 imperialism was also a major force in British conservatism. For decades Northern Ireland‟s major political party, the Ulster Unionist Organization, was an integral part of Britain‟s Conservative Party, but that relationship has eroded considerably. The Scottish Conservative and Unionist Association also is related to the larger unit but has a separate existence.2)Margaret Thatcher, born in 1925, British politician and the first woman to hold the office ofprime minister of the United Kingdom. The winner of three consecutive general elections, Thatcher served as prime minister from 1979 to 1990. She was the longest-serving British prime minister of the 20th century.3)The London Stock Exchange, one of the largest exchanges in the world, has always been afocus of international trade. In 1986 it was substantially deregulated, an event known as the Big Bang in financial circles. This led to the rapid expansion of products, markets, and numbers of employees, a movement that slowed in the early 1990s but has since rebounded.4)HSBC:HSBC Holdings plc is a British multinational banking and financial servicescompany headquartered in London, England, United Kingdom. It is one of the world‟s largest banks.5)Second Industrial Revolution: The Second Industrial Revolution, also known as theTechnological Revolution, was a phase of the larger Industrial Revolution corresponding to the latter half of the 19th century until World War I. It is considered to have begun around the time of the introduction of Bessemer steel in the 1860s and culminated in early factory electrification, mass production and the production line.4. Analysis and comments:1) Town and country planning in the United Kingdom is the part of English land law which concerns land use planning. Its goal is to ensure sustainable economic development and a better environment. Each country of the United Kingdom has its own planning system that is responsible for town and country planning devolved to the Northern Ireland Assembly, the Scottish Parliament and the Welsh Assembly.2) Based on the collection of history of two countries‟ economic development, a summary can be made.Chapter Four1.Blank fillings:1)owner occupation,2)semi-detached,3)Detached houses,4)Class,5)Christmas,6)Boxing Day,7)Easter egg,8)The Guardian,9)1400,10)The Broadcasting Act2.Questions:1)There are, broadly speaking, four main types of home. The first kind are "flats" (orapartments), of varying size, often in modern multi-storey purpose-built buildings, though sometimes made by sub-dividing big old houses. Flats are often publicly owned. The second kind are "terraced" houses: that is, individual two-storey houses built joining on to each other at each side in a terrace or row. The second kind are "terraced" houses: that is, individual two-storey houses built joining on to each other at each side in a terrace or row; the fourth one is “detached.”2)(Open ended)3)On an average day, 90 per cent of Britons over the age of 15 read a national or local paper.And in the evening, most Britons settle down to watch some television: 96 percent of the population watch TV at least once a week, making it Britain‟s most popular leisure activity.The third most popular pastime, after watching telly and reading newspapers, is listening to the radio, an activity in which 73 per cent of the population engages in on a weekly basis. It is obvious, then, that the media are central to British leisure culture.4)British newspaper culture is unusual in the extent to which class and educational differencesare reflected in the newspapers people read. In other developed countries like Japan and the United States, newspaper reading is a mainly middle-class habit, but in Britain the "lower classes" are also regular readers.5)While officially speaking the British press is "free" from government control and censorshipand can print what it likes, there are limits to what will appear in the daily paper.3.T erms for explanation:1)Terraced houses: refer to those individual two-storey houses built joining on to each other ateach side in a terrace or row. They often have two rooms downstairs and two bedrooms upstairs, plus a small kitchen and bathroom in a projection(突出部分) at the back. These kinds of houses are most common in inner-city areas.2)Detached houses: the most desirable houses for the British people to live in. They usuallystand alone with garden on all sides separating them a little from their neighbours. It might be one-storey house, called bungalow or two. These houses are usually built in the suburban areas.3)The Christmas Pantomime: a typical British Christmas tradition. It is a comical musical playusually based on a popular traditional children‟s story. There are two ma in characters in the play: “the principal boy”, played by a young woman, and “the Dame”(滑稽老太婆角色), played by a man. It is a play with songs and jokes which can be enjoyed by both adults and children.4)Boxing Day: a typical British tradition celebrated on the day after Christmas. People used togive Christmas gifts or money to their staff or servants on this day. And now they mostly do shopping, pay visits, enjoy eating or just relax.5)The Financial Times: The Financial Times (FT) is a British English-language internationaldaily newspaper with a special emphasis on business and economic news internationally. The paper, published by Pearson PLC in London, was founded in 1888 by James Sheridan and Horatio Bottomley, and merged with its closest rival, the Financial News (which had been founded in 1884) in 1945.4.Analysis and comments:1) The United Kingdom has one of the world‟s oldest established newspaper industries. In the late eighteenth and early nineteenth century, as the British economy began to industrialise, as the democratic franchise was extended to larger segments of the population, and as literacy levels rose through the introduction of mass education, more and more newspapers began to appear. They began to influence British society and people‟s life. T ry to gather different types of newspaper and their functions as a further study.2) In cultural studies, media culture refers to the current western capitalist society that emerged and developed from the 20th century, under the influence of mass media. The term alludes to the overall impact and intellectual guidance exerted by the media (primarily TV, but also the press, radio and cinema), not only on public opinion but also on tastes and values.Chapter Five1. Blank fillings:1)Reading, Writing, Arithmetic2)A-level3)Flexibility4)Oxbridge5)glorious wit6)church7)math, physics, computer science and economics8)12th and 13th centuries9)Forty10)tutorial2.Questions:1)In the UK, the amount of funding each university receives is based on its size, the number ofstudents it teaches, and the research it conducts. So far, the UK has only one privately funded university, the University of Buckingham.2)The British education system is run by the state.3)Cambridge University and Oxford University.4)The goal of British education is to socialize children.5)(Open ended)3.T erms for explanation:1) middle-class man: The middle class is a class of people in the middle of a societal hierarchy. In Weberian socio-economic terms, the middle class is the broad group of people in contemporary society who fall socio-economically between the working class and upper class. The common measures of what constitutes middle class vary significantly among cultures.2) “A-level”: A-level—is an academic qualification offered by educational bodies in the United Kingdom and the British Crown dependencies to students completing secondary or pre-university education.3) “Oxbridge”: Oxbridge is a portmanteau of the University of Oxford and the University of Cambridge in the United Kingdom, and the term is used to refer to them collectively, often with implications of perceived superior social status. "Oxbridge" can be used as a noun referring to either or both universities or as an adjective describing them or their students.4) working-class: The working class (or lower class, labouring class, sometimes proletariat) are those employed in lower tier, subordinate jobs. These typically include blue-collar jobs, but also include large amounts of white collar and service work.5) tutorial system: At Cambridge University and Oxford University, undergraduates are taught in the tutorial system. Students are taught by faculty fellows in groups of one to three on a weekly basis. At Cambridge, these are called "supervisions" and at Oxford they are called "tutorials." One benefit of the tutorial system is that students receive direct feedback on their weekly essays or work in a small discussion setting.4.Analysis and comments:1) There are advantages in attending schools abroad. Students who have studied abroad can act as mediators between people of different cultures. Students can learn much more advanced knowledge of science and technology from foreign countries. Students can learn foreign languages more quickly. However, there some disadvantages. Most of the students are too young to live by themselves without any living experience. Besides, being far away from their home country, they may feel lonely and homesick. Of course the costs are much.2) Knowledge/ Discipline/ hardworking/ creativity/ imagination/…。
英语国家概况(课后问答题)第一部分英国概况1 What are the differences between Britain and the British Isles, Great Britain, England, the United Kingdom and the British Commonwealth?Britain is the shortened form of the United kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland while the British Isles is a geographical name.2 What are the three political divisions on the island of Great Britain?They are England, Scotland and Wales 3. What is the official name of Great Britain?The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland4. Where did the King Harold defeat Tostig and Harold Hardrada?( At Stanford Bridge)5.What did William do after he suppressed镇压the Saxon risings in the north?(He built a string of defense防卫castles to ensure his military control of the whole country.)6. How long was Britain under the Roman occupation?( For nearly 400 years)7 What was the peculiar features of the feudal system of England?(All landowners, whether the tenants-in-chief or subtenants, took the oath of allegiance for the land they held, not only to their immediate lord, but also to the king.)8 What did Willliam I leave to his sons after he died?( He left Normandy to his eldest son, Robert, and England to his second son William, and a large sum of money to his third son, Henry.) 9 What was William I’s policytowards the church?(He wanted to keep it completely underhis control, but at the same time toupload its power.)10 When was the Domesday Bookcompleted?( In 1086)11 What was the consequence of theHundred Years’ War?(The French drove the English out oftheir land. By 1453, Calais was theonly part of France that was still in thehands of English)12 What did the Lollards preach?(The Lollards preached the equality ofmen before God)13 What were the two countriesElizabeth I successfully played offagainst each other for nearly 30years?( France and Spain were the twocountries that Elizabeth I successfullyplayed off against each other for nearly30 years)14 What was the outcome结果ofthe English Civil War?(It not only overthrew feudal system inEngland but also shook the foundationof the feudal rule in Europe. It isgenerally regarded as the beginning ofmodern world history.)15 What were the three main causesof Henry VIII’s religious reform ofthe Church?( The three main causes were: a desirefor change and reform in the Churchhad been growing for many years andnow, encouraged by the success ofMarin Luther, many people believed itstime had come; the privilege andwealth of the clergy were also resented;and Henry needed money)16 Which party did MargaretThatcher represent in the 1970s?(She represented the ConservativeParty)17 What did the Whigs stand for inthe early 19th century?Whigs stood for a reduction in Crownpatronage, sympathy towardsNonconformists, and care for theinterests of merchants and bankers.18 Why did changes in farmingmethods改变耕作方式affect lives ofmillions in the 18th century?(Because village and agriculture werethe backbone of England at that time.)19 When did Britain finally becomea full member of the EuropeanEconomic Community?(Britain finally became a full memberof the European Economic Communityin January, 1973)没背20 Why was Mrs. Thatcherremoved from office in 1990?(It was because of her opposition toEuropean Union and her imposition ofan extremely unpopular flatrate ‘polltax’ in place of property taxes to payfor local government service.21 What were the two groups of theChartiests? What was theirdifference?(The Chartists could be divided intotwo groups: the Moral Force Chartistsand the Physical Force Chartists. Theformer wanted to realize their aims bypeaceful means while the latter wantedto achieve their purpose by violence)22 What was the goal of the LondonWorking Men’s Association in itsstruggle?(It aimed to ‘ to seek by every legalmeans to place all classes of society inpossession of equal political and socialrights)23 Why was Britain known as the factory of the world in the mid-19th century?(Because the British economy was among the strongest in the world)24 Who has the power to declare war and make peace in the UK?(The Queen)25 How many members of Parliament does the House of Commons in the UK consist of ? (651Members of Parliament)26 What does the British Parliament consist of ?(It consists of the Sovereign, the House of Lords and the House of Commons) 27 What did the term ‘parliament’ originally mean?( It originally meant a meeting for parley or discussion)28 Where does the Sovereign’s coronation take place?(It takes place at Westminster Abbey威斯敏斯特教堂in London)29Where does the Queen’s expenditure arising from支出所产生的public duties come from?( The Queen’s expenditure arising from public duties comes from the Civil List and government departments)30 How is the British House of Commons elected?The House of Commons is elected by universal adult suffrage.31 What is a ‘shadow cabinet’ 影子内阁in Britain?( The party which wins the second largest number of seats in parliament becomes the Official Opposition and it forms its own ‘cabinet’ known as ‘shadow cabinet’32 What are the three main Christian festivals in Britain? (The three main Christian festivals inBritain are Christmas. Easter, and WhitSunday.)33 Who is directly responsible for theNHS in Britain?谁直接负责国民保健制度在英国(Central government is directlyresponsible for the NHS in Britain)34 What are the two establishedchurches in Britain?(They are the Church of England andthe Church of Scotland in Scotland)35 How many provinces does theChurch of England have?(The Church of England has twoprovinces: Canterbury and York)36What is the National Day inBritain?(The birthday of the British Monarch isa National Day in Britain)37 What does ‘Oxbridge’ refer to inGreat Britain?(It refers to the Universities of Oxfordand Cambridge)没背38 What kind of schools are theindependent schools in Britain?(The independent schools are thosesupported entirely by fees and privatefuns)39What are the three groups ofnation newspapers?(They are quality, popular andmid-market papers.)40 Which religion in Ireland is thelargest non-Catholic denomination?(The Anglican Church圣公会ofIreland is the largest non-Catholicdenomination.)没背41 What was the consequence ofthe Anglo-Irish Treaty of 1921?什么是后果,英爱条约1921?(Violentopposition to the treaty byultranationalists led to a civil war.)没背42 What was the result ofgrowing Irish nationalism in theearly decades of the 20th century?(Irish nationalism became stronger andeven more violent in the early decadesof the 20th century and climaxed in theEastern Uprising of 1916 in which anIrish Republic was proclaimed.)没背43 Wht happened after theEnglish king was declared the headof the Church of Ireland replaceingthe Pope?英国国王宣布爱尔兰教会领袖代替教皇(There followed centuries of religiousas well as political persecution政治迫害, which helped to strengthen anddeepen Ireland’s Catholic spirit.)第二部分美国部分1What are the two novels giving avivid description of the miserable lifeof the black slaves?(Uncle Tom’s Cabin and Roots)2 What is the reason for the growthof population in Florida?(Florida’s population growth owesmuch to its attractiveness both as aplace to retire and as a convenientplace for business with and travel toCentral and South America)3 When did the higher birth rateappear in the United States?(The birth rate appeared during ‘thebaby boom’[1946-1964]) ??4 When was the Declaration ofIndependence adopted?(It was adopted on July4,1776)没背5Please write any three of the13 colonies the British establishedalong the east coast of NorthAmerica between 1607 and1733.(Virginia, Maine, NewHampshire)6What are the implications of the ‘Manifest Destiny’?The implications of ‘manifest Destiny’ are three fold(1)the inevitability of the founding of the United States of America;是必然的(2)the legitimacy 合法的of the expansion of America Territory美国领土; (3) the spread of American democracy美国民主being the task任务of American people who were cho sen to do the Lord’s work.没背7 What were the two serious weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation?邦联条款They were:(1)There was no national executive or law-enforcing branch;没有执行或执法部门(2)Congress国会was too large a body to function功能as government. And Congress had no power to raise taxes.国会无权征税8What agreement did America and Britain sign in 1783 by which Britain recognized the independence of the United States? The Treaty of Paris9 What were the features in the colonial period which had influence on later American development?They were representive form of government, rule of law, respect of individual rights, religious tolerance and a strong spirit of individual enterprise.。
英语国家概况英国--课后问答题[1]英语国家概况课后问答题Book 1Chapter 1 Questions for Thought:1.What was the British Empire? What do you know about it? In what way is the ―Empire‖ still felt in Britainand in the international field?Key points:1. Before the end of WWII, the British Empire was one of the most powerful empires; it enjoyed the name of ―an empire on which the sun never set‖ due to its overseas colonies on the world.2. People of the British Empire are descendents of the Anglo-Saxons.3. A system of monarchy was observed still on today’s Britain, which went through the history. The Queen is still the Head of the Commonwealth.4. the ―Empire‖ still can be felt in the following ways:a. there are still close relationships between the UK and the fifty or more countries which used to be its former colonies, and which maintain links through a loose organization called the Commonwealth of Nations.b. it became one member of the European Union since 1973.c. the effect also lies in the makeup of the British population itself. Newly immigrants mainly came from the former colonies, specially from India and Caribbean area.d. today the Monarch represents the country in many occasions.e. class exists and lords and peers are obvious evident of the imperial past.2.Why does the author say that it is not possible to sum up the British people with a few simple phrases?Key points:Reasons: 1. regional differences---England, Scotland, Wales, Northern Ireland 2. racial differences 3. class differences 4. cultural differences---Highland vs Lowland 5. religious differences---protestants vs Catholics (main in Northern Ireland) 3.―British history has been a history of invasion‖. Please illustrate this point with the examples from the text.How did each of the invasions influence English culture?Key points:4.What are some general characteristics of Scotland? How did Scotland become part of the union of GreatBritain?Key points:1.The Celts originally lived on Scotland, they kept their own culture and language—the Gealic.2.Around the AD 6th C, people from Northern Ireland invaded the South-west --- the lowland zone. They were called Scots and gave the modern country of Scotland its name.3.The Scottish people have a strong sense of nationality and desire for cultural independence. They observed some old customs and tradition, like the Highland tradition. Today, bagpipe, and tartan are considered as the souvenir of the Scottish history.4.The division between highland and lowland Scotland remains a cultural divide today, in much the same way as north and south England see themselves as different from each other.5.Scotland has a great tradition of innovation in the arts, philosophy and science.Robert Louis Stevenson’s famous novel Dr Jekyll and Mr Hyde 《吉基尔医⽣与海德先⽣》shows that: Scotland was superficially fully integrated into the UK, but concealed beneath this is a still-strong Scottish identity.Union with England in 17071. In 1603, Queen Elizabeth I of England died. James the 6th of Scotland took the throne, called James the First of England; uniting the two thrones2. Scotland maintained its separate political identity.3. In 1707, Scotland joined the Union by agreement of the English and Scottish Parliaments4. Scotland sends 72 representatives to the London Parliament.5.Describe characteristics of Wales and Wales’ unification with Great Britain.Characteristics:1. capital: Cardiff, on the south coast2. rich coal deposits3. attract foreign investment from Japan and U.S, etc.-- new industries to replace coal and steel4. smallest on the British mainland; close to central England; hilly and rugged5. retains a powerful sense of difference from England6. retains its own language; 19% population speaking GaelicUnification with Great Britain1. 1267, Llywelyn ap Gruffudd(卢埃林·阿普·格鲁菲德), forced the English toacknowledge him as Prince of Wales by a military campaign, and unified Wales as an independent nation.2. 1282, he was killed. The English King Edward I named his son the Prince of Wales, trying to bring Wales into the British nation.3. 1400, Owain Glyndwr(欧⽂·格林道⽡尔) led an unsuccessful rising against the English.4. 1536, Wales was brought legally into the UK by an act of the British Parliament.5. Wales sends 38 representatives to the London Parliament. 4 are from the Nationalist Party.6.Are there any differences between England, Scotland and Wales in terms of cultural tradition?Chapter 2 Northern Ireland Questions for Thought:1.Why is Northern Ireland so significant in the UK? What is the political problem there?Keys:1. it is significant because of the political troubles there.2. the political troubleOriginal inhabitants were mainly descents of Celts; they believed in Catholics. The immigrants from Scotland and north England in the 17th c, sent by the English king for the sake of better control over Ireland, were mainly Protestants. Their arrival aroused local people’s hostility. They were pressured.In 1921 the Ireland got independence while in Northern Ireland, the majority was Protestant and loyalists to the British government, wanted to be separated from the rest parts of Ireland.Now in Northern Ireland, the minority—the Catholics found it difficult for them to find job. The conflicts between Protestants and Catholics got increased.To protect the local Catholics, the British soldiers stationed Northern Ireland in 1969, which later accelerated the conflicts between the local people and the British government.2.What are some of the factors in Irish and English history that affect the situation in Northern Ireland today? Keys:1. racial,2. religious3. immigration in 17th c.4. the British solders’ station in 1969Chapter 3 The Government of the United KingdomQuestions for Thought:1.What are some of the characteristics of the British constitutional monarchy? How has the English monarchyevolved gradually to the present constitutional monarchy?1. the oldest institution of government2. King Egbert (埃格伯特国王): the ancestor of the present Queen Elizabeth II. United England under his rule in 829.3. divine right of kings (君权神授)---The ancient doctrine held that the sovereign derived his authority from God, not from his subjects. This was used by the kings as an excuse for abusing power. And the dispute over the p ower of the king and the parliament led to the civil war.4. the Civil war set the rights of the Parliament. The monarch was kept but his power was limited. The constitution was set up to guarantee rights of people. Monarch became a symbol of the country.2.How did the doctrine of the ―divine right of kings‖, according to the author, lead to the English Civil War?What do you know about the causes of the English Revolution in the 17th century?King James I believed the divine right of kings, so did his descent---Charles I.Charles I called his t Parliament only when he needed to collect money.The Civil War was caused by a dispute over the power of the king against Parliament in the 17th C. The Republican―roundheads‖, led by Oliver Cromwell, wanted to abo lish the monarchy and to reassert the rights of Parliament. In 1642, the royalists were defeated and King Charles I was executed in 1649.The English Civil War not only overthrew feudal in England but also shook the foundation of the feudal rule in Europe. It is generally regarded as the beginning of modern world history. The Civil War was in essence a capitalist revolution because capitalism paved its way of development after the war.3. What is the history of English parliament? What role did the parliament play in the Civil War?In medieval times, a group of leading, wealthy barons who were summoned by the king several times a year to give the king some extra money. This was the Great Council. By the 13th C., representatives of counties, towns and cities were also included in order to raise more money. This was the beginning of what we know as Parliament today.In the Civil War, the parliament was opposite to the monarchy in their dispute over the power. The Republican―roundheads‖, led by Oliver Cromwel l, wanted to abolish the monarchy and to reassert the rights of Parliament.4. Discuss the major characteristics and the main content of the British constitution.Britain, like Israel, has no written Constitution. The foundations of the British State are laid out in statute law(成⽂法), which are laws passed by Parliament; the common laws(普通法,判例法), which are laws established through common practice in the courts; and conventions(习惯法), which are rules and practices not existing legally, but regarded as vital to the workings of government.5. Why the parliament is supreme in the British sate? What function does parliament have? What role does the Queen and the Prime Minister play in British government?Parliament is supreme in the British state because it alone had the power to change the terms of the Constitution. There are no legal restraints upon Parliament. It can make or change laws,functions:1) passes laws2) provides the means of carrying on the work of government by voting for taxation3) scrutinize government policy, administration and expenditure and to debate the major issues of the day.the roles of the Queen/King1. symbolize the tradition and unity of the British State2. legally head of the executive, (⾏政部)3. an integral part of the legislature(⽴法机关)4. head of the judiciary(司法部)5. commander in chief of the armed forces6. ―supreme governor‖ of the Church of England--- most Britons felt the Queen’s important jobs were:1. represent Britain at home and abroad2. set standards of good citizenship and family life3. a confidante(知⼰的⼥友) to the Prime Minister, offering valuable observations on the running of governmentRole of the Prime MinisterKing George I was ―imported‖ from Germany in 1714 and was not interested in politics, so he left the job of chairing cabinet meetings to one of his cabinet ministers, called the prime minister. Later in 1832, elections replaced appointment. The party with the most supporters in the Commons forms the government and the leader of that party becomes Prime Minister.Today Prime Minister and his cabinet compose of the entity of the government.6. What kind of institution is the House of Lords? What role does it play in British government?It’s one house of the Parliament, but the power of making law and collecting taxes mainly resides on the House of Commons. The House of Lords consists of the Lords Spiritual(上议院的神职议员), who are the Archbishops and most prominent bishops of the Church of England; and the Lords Temp oral(上议院的世俗议员), which refers to those lords who either have inherited the seat from their forefathers(called hereditary peers) or they have been appointed(by the sovereign, at the suggestion of the Prime Minister and were called life peers(终⾝贵族). The lords mainly represent themselves instead of the interests of the publicChapter 4 PoliticsQuestions for Thought:1.Who can stand for election as an MP in the UK? Why are small parties and independent candidates powerlessin the election campaign for the formation of a government?Anyone who is eligible to vote can stand as an MP. It is necessary only to make a deposit of 500 pounds which is lost if the candidate does not receive at least 5% of the vote.Because even they were to win the seat they would be powerless in parliament against the big parties’representatives (p54, para1)2.What are three big parties in the UK? What are some of the similarities and dissimilarities between the threeparties?They are the Labor party, the Conservative party and the Liberal Democratic party.the Labour party--- one of the 2 biggest parties in the UK. It is also the newest party, created by the trade union movement at the end of the 19th century. It is a socialist party, believing that a society should be relatively equal in economic terms, and that the government should redistribute the wealth between the rich and the poor. It also thinks that the government should provide a range of public services for all the people.the Conservative party --- one of the 2 biggest parties in the UK. It is basically the party of the individual, protecting the individual’ s right to acquire wealth and to spend it as he/she wants. It advocates economic policies which are favourable to businessmen, such as low taxes. From 1979 to 1997, the Conservative party won 4 consecutive elections and was in power for quite a long period of time.the Liberal Democrats--- the 3rd biggest party and often seen as a party of the ―middle‖, occupying the ideological ground between the two major parties. They are comparatively flexible and pragmatic in their balance of the individual and the social. They emphasize the need to change the Britain’s constitutional arrangements to make the government more democratic and accountable.Similarities:1. they all support the capitalist system2. generally speaking, they all are the active participants and supporters of representative democracy3. they share some similar beliefs in their political and socioeconomic ideologyDissimilarities:1. they represent the interests of different social groups2. they have different opinions on the government’s role in social economy and they each take different economic policies during their administration3.What are some of the recent political trends in the UK? Are these trends more democratic or undemocratic?What is the author’s opinion?recent political trends--- The 1970s were a decade of problems in the UK. The economy did badly, with high inflation and low growth. Big private companies started to go bankrupt, and the nationalized industries were seen as inefficient.--- In 1979, the Labour government faced a vote of no confidence, which it lost, causing a general election. This was won by the Conservative under their leader Margaret Thatcher, who became the UK’s first woman Prime Minister--- the policies of the Conservative:1. privatise nationalized industry (successful, companies become efficient and profitable * negative consequences of the policy: 1) Unemployment went up2) Poverty increased 3) Government welfare payments have become less generous. So the society became less equal---a time of ―private affluence and public squalor‖⼀部分个⼈富裕起来,⽽⼤部分百姓的⽣活却贫困化, 公众福利制度也处于困境)2. cut tax rates (a less re-distributive taxation system削弱再分配性质的税收制度)Summary of the political trend in the 1980s:British politics move to the ―right‖, away from the ―public‖ and toward the ―private‖; away from the ―social‖, and toward the ―individual‖.Chapter 5 The UK EconomyQuestions for Thought:1. Define ―absolute decline and relative decline‖ in the UK economy. How does the author explain the reason for absolute decline and relative decline?To be brief, absolute decline refers to all kinds of the indexes indicate economy declines, for example, the GDP and GNP declines, the currency devalued, unemployment increased, the economy retrogresses, the country’s economic status ranks behind its former rank. People’s living standard become lowered, and the comprehensive national strength falls behind others’. While relative decline refers to economy develops in a relatively low speed. Compared to its former economic strength and the index of GNP,GDP, the present economic development is relatively slower.Absolute and relative decline of the British Economy1. By the 1880s, dominant in the world--- 1/3 of the world’s manufactured goods; 1/2 of the world’s coal, iron and cotton; shipping greater than the sum of the rest of the world2. By 1900, overtaken by the U.S and Germany3. From 1945(the year when WWII ended) until present, thought of as relative decline because of steady economic growth and rapidly increasing living standards and still remaining one of the Group of Seven industrial economies(七⼤⼯业国:US, UK. Germany, France, Japan, Italy and Canada), but other countries developed more rapidly, so it slip from being the 2nd largest economy to being the 6th.4. causes for the relative decline1) gone into heavy debt to finance the war(selling many accumulated overseas assets, borrowing large amounts from the US and Canada)2) British colonies which used to provide raw materials and big markets gained independence —the end of the era of empire *Supplementary note: In the 17th C., trade between Britain and India started, which was undertaken by a trading company called the East India Company. In 1813, Britain took over the company. At that time, the company controlled nearly all the official and administrative work in the whole sub-continent of India. Then the British Empire’s rule began. In 1947, India,―The Jewel in the Crown‖ of the Briti sh Empire, gained its independence. So the UK lost the largest resource of raw materials and a big market for its goods.3) Britain was heavily burdened with the huge military expenditure during the process of decolonisation. [It was still forced to maintain a substantial and expensive military presence in many overseas locations until the process was completed (mostly by the end of the 1960s). And as one of the shapers of the post-war world required substantial military contributions (member of NA TO and UN Security Council).]4) lacked the investment in modern equipment and new products (Britain’s industry survived comparatively unaffected. It continued with its older factories and pre-war products. While the main losers in the war, Germany and Japan, had to startfrom nothing, so they could invest in the most modern equipment and new products, which was sufficient.)* low rates of domestic industrial investment; high rate of overseas investment* lack of a close relationship between industry and banks because the UK was the 1st economy to industrialise, and industrial firms grew used to financing their own development, without need to borrow from banks. So banks looked overseas for investment opportunities.Summary of the decline:---The UK has experienced an economic decline since 1945. but this is a relative decline rather than an absolute one. Britain is wealthier and more productive than it was in 1945, but since other countries developed more rapidly, it has slid from being the 2nd largest economy to being the 6th.2. What did the Conservative party under Margret Thatcher promise to do to the UK national economy in 1979? What was her radical reform programmer? Was the program successful?the Conservative party under Margret Thatcher promise to launch a radical program of reform.Thatcher’s radical reform:1. Reduce bureaucracy---limited government2. privatizationThe British economy went through a particularly bad period in the 1970s, with high rates of inflation and devaluation of he currency.(forced the Labour government to borrow money from IMF) Therefore, in the 1980s, when the Conservative party under Margaret Thatcher was in power, an extensive programme of privatization was carried out. Many state-owned businesses(such as steel, telecom, gas, aerospace) were turned into private companies. The author thinks that privatization was successful in controlling inflation but at the same time unemployment rate increased rapidly.* After the recession 1990-1992, the economy had a steady growth. The UK is the 2nd only to the U.S as a destination for international direct investment.3. what are the three main areas of national economies? Describe the development of each of the three areas in the UK economy.1. primary industries, such as agriculture (crop and grazing)(small in relation to national health—1.4%, but efficient—producing 58% of the food need with 2% of the workforce; 3/4 of the land for agriculture—1/4 of that for crops, the rest for grazing animals of which sheep are the most numerous livestock), fishing(渔业), and mining [energy production: oil, gas, nuclear energy, coal mining etc. *3 of the 10 biggest companies in Britain: Shell(half Dutch), British Petroleum (BP), and British Gas英国三⼤能源公司:壳牌公司(与荷兰合资),英国⽯油公司,英国煤⽓天然⽓公司]; the world’s largest mining company, RTZ, is a UK company]2. secondary industries, which manufacture complex goods from those primary products (producing 22% of the national wealth, particularly strong in pharmaceuticals药品—the British company Glaxo-Wellcome is the biggest drug company in the world; chemicals化⼯产品—ICI is the 2n largest paint manufacturer in the world; aerospace—the 3rd largest in the world inferior to the U.S and Russia, producing the full range of aerospace products from civil and military aircrafts to missiles, satellites and jet engines, producing 2% of UK national output, accounting for 8% of manufactured export goods; when an Englishman Frank Whittle developed the world’s first practical jet engine in 1937, the foundations had been laid for the 3 major branches of the aviation industry: aircraft, engines and aviation electronics, with British companies prominent in each field; The Comet was the world’s first jet- powered civil airliner; Lynx holds the world speed record for helicopters; and food and drink. Big electronics industry: the 4th largest in the world, but foreign-owned like car industry. High-technology engineering industry. British Steel is the world’s 4th largest steel company)3. tertiary industries (or service, producing 65% of the national health), such as banking, insurance, tourism, advertising and the selling of goods (financial sector is important with London as one of the top 3 financial centers in the world; the world’s largest foreign exchange market; one of the busiest share-dealing centers股票交易中⼼in the world— the London Stock Exchange )Chapter 7 British Education SystemQuestions for Thought:1.What are the purposes of the British education system? Please comment on these purp oses. What are the mainpurposes of the Chinese education system? Are there any differences or similarities in the education of the two nations?---―the three R’s‖ (―reading, ’riting and ’rithmetic‖) — to provide children with literacy and the other basic skills they will need to become active members of society and also to socilise children, teaching them rules and values needed to become good citizens, to participate in the community, an to contribute to the economic prosperity of an advanced industrial economy.2. How does the British education system reflect social class?Class inequality can be erased or continued according to educational policy.Children from the lower-class families may have less chance of receiving education than those from middle-class or upper-class families. They may leave school for their families could not afford their tuition fees or for they have to work to support their families. They could not enjoy as excellent education as those from middle-class families, either. The unequal chances of education brought by social class may further influence one’s social bonds and opportunities of finding good jobs or getting rapid promotion on the social ladder.3. What are the major changes that have taken place since WWII? Is British education moving towards more progress or more equality? Rick up some examples from the text to support your points.Major changes---to raise enrollment and ensure more equal opportunities of education(p105)1. 1944 education act2. 1960 comprehensive school---entrance examination abolished3. great education debate---1989 national curriculum established5. what is the open university in Britain? What do you think of this system?Keys (p115)。
Understanding UK & IrelandKey to Chapter 9 A General Survey of UKI. 1.T 2. F 3. F 4. TII. 5. C 6. D 7. BIII. 8.C 9. B 10. AIV.11. What are the four regions of Britain?The four regions of Britain are England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. England is the largest of the four with an area of 130,000 square kilometers,making up the south and east, which takes up nearly 60% of the British Isles. It is the most populous and richest section of the country.12. What kind of geographical position does Britain have?Britain is an island country. It lies in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north coast of Europe. It is separated from the rest of Europe by the English Channel in the south and the North Sea in the east.13. Which places in Great Britain are mostlyhighland and lowland?The north and west of Britain are mainly highland,while the south and south-east are mostly lowlands.14. Does Britain have a favorable climate? Yes,it has a favorable climate,because it has a maritime type of climate ——winters are mild,not too cold and summers are cool,not too hot. It has a steady reliable rainfall throughout the whole year. It has a smallrange of temperature,too.15. What are the factors which influence the climate in Britain? Which part of Britain hasthe most rainfall and which part is the driest? The factors which influence the climate in Britain are the following three:1) The surrounding waters balance the seasonal differences;2) The prevailing south-west winds bringwarm and wet air in winter and keep the temperatures moderate;3) The North Atlantic Drift ,a warmcurrent,passes the western coast of the British Isles and warms them.The northwestern part has the most rainfall,while the south-eastern corner is the driest. Key to Chapter 10Geography & History of UK◆Key to Section ExercisesSection A. GeographyI. 1.F 2.F 3.TII. 4.A 5.B 6.A 7.D 8.A 9.C 10.ASection B.HistoryI. 1.T 2.T 3.T 4.F 5.TII. 6.D 7.B 8.B 9.B 10.C◆Key to Chapter ExercisesI. 1. T 2. F 3.F 4.T 5.FII. 6. A 7. D 8.D 9.D 10.BIII.11. The total area of Britain is about244,110 square kilometers.12. Britain is separated from the European continent by North Sea, Strait of Doverand English Channel.13. The capital of the Scotland is 1) Edinburgh, the capital of Wales is2) Cardiff and the capital of Northern Ireland is 3) Belfast.14.England is the largest and most populous of the three political divisions on the island of Great Britain.15. The first steam engine was devised by Thomas Newcomer at the end of the 17th century, and the Scottish inventor James Watt modified and improved the design in 1765.IV.16. The Hundred Years' War: it refers to the war between England and France that lasted intermittently from 1337 to 1453. The causes of the war were partly territorial and partly economic. The territorial causes were related with the possession by the English kings of the large duchy in France. The economic causes were connected with cloth manufacturing towns in Flanders. Besides, England's desireto stop France from giving aid to Scots and a growing sense of nationalism were the other causes.17. The Lowland Zone: the island of Great Britain can be divided into two major natural regions—the lowland area and the highland area. The north and west of Britain are mainly highlands; and the east and southeast are mostly lowlands. The lowland zone has a milder climate and better soils for farming. Historically, most people in Britain have lived in the lowland zone rather than in the harsher highland zone. The lowland area comprises Midland, southern and eastern England. 18. Norman Conquest of 1066: In January 1066, King Edward, the last Saxon king, died childless. He had promised to leave the English throne to his cousin William, but he chose Harold, his wife’s brother as king. So William led his army to invade England. In October 1066, during the important battle of Hastings, William defeated Harold and killedhim. One Christmas Day, William was crowned king of England, thus beginning the Norman Conquest of England. The Norman Conquest of 1066 is perhaps the best-known event in English history.19. Industrial Revolution: The industrial Revolution refers to the mechanization of industry and the consequent changes in social and economic organization in Britain in the late 18th and early 19th centuries.The Industrial Revolution forever transformed the way people live and work in most parts of the world. It changed the world so much that people called it a revolution.Typical inventions during the Industrial Revolution:John Kay’s flying shuttle in 1733;James Hargreaves’ Spinning Jenny in 1766; Richard Arkwright’s water frame in 1769; Edmund Cartwright’s power looms in 1784; James Watt’s steam engine in 1765.20. The Chartist Movement: Chartism was oneof the major popular reform movements of the Victorian era. The Chartists sponsored a People’s Charter demanding suffrage for all male citizens over age 21, a secret ballot, and other rights. Chartist leaders are shown here addressing a large crowd in 1848. Most of their demands eventually became law.The Reform Bill of 1832 was the first successful attempt to correct these inequities. In 1836, a group of skilled workers and small shopkeepers formed the London Working Men’s Association. They drew up a charter of political demands (a People’s Charter) in 1838, with the intention of presenting it to Parliament. It had six points: 1)the vote for all adult males; 2)voting by secret ballot;3)equal electoral districts; 4)abolition of property qualifications for members of Parliament; 5)payment of members of Parliament; 6)annual Parliaments, with a General Election every June.Key to Chapter 11Political System & National Economy of UK ◆Key to Section ExercisesA.Political SystemI. 1.F 2.F 3.T 4.F 5.TII. 6.A 7.B 8.D 9.BIII. 10.1)-e 2)-a 3)-dB.National EconomyI. 1.T 2.F 3.TII. 4.A 5.D 6.B 7.B 8.B 9.AIII. 10.1)-b2)- d 3)- e◆Key to Chapter ExercisesI.1. The British were the first in the world to enter the Industrial Revolution.2. The main textile producing regions of Britain are the East Midlands, Yorkshire, Humberside, and Northern Ireland.3. An industrial complex in suburban Glasgow dubbed "Silicon Glen" is the center of Scotland’s thriving technology industry.4. Historically, the financial services industry has been based in the city of London in an area called the Square Mile.5. The Bank of England, chartered in 1694, was nationalized in 1946 and is the only bank that issues banknotes in England and Wales.6. The predecessor of the English parliament is the Great council.7. There are three political divisions on the island of Great Britain.8. In the UK, the party which wins the second largest number of seats in the House becomes the Opposition, with is one leader, and forms a Shadow cabinet.9. The Tories were the forerunners of the Conservative Party.10. In the United Kingdom, the party which wins the second number of seats in the House of Commons becomes the official Opposition. II.11. Constitutional monarchy:Constitutional monarchy means that the power of the monarch is limited by the country’s constitution, the legal authority is given to Parliament, and the executive authority to thegovernment. Theoretically, the Queen has the power,but in reality , she has no power at all. The Sovereign reigns, but does not rule; the country is governed, in the name of the Sovereign, by His or Her Majesty’s Government, who is responsible to the Parliament.12. Primogeniture: Primogeniture refers tothe passing of the throne to the eldest son when a monarch dies, has been the rule of succession, and when there are no sons, the eldest daughter ascends the throne.13. First past the post:The current voting system in UK is called “first pa st the post.” This means that the party and candidates receiving the most votes win the election and become the party in power even if they do not receive more than 50 percent of the vote.14. The Conservative Party and the Labor Party: The Conservative Party developed outof the Tory Party(托利党). It supports privateenterprise and is opposed to nationalization (国有化)and extending social services. It openly helps the monopolists to getsuper-profits.The Labor Party was founded in 1900 by a union between the Trade Union, the Independent party and the Fabian Society. It practices social democracy or bourgeois reformism.15. High Street Banks: High Street Banks are the main banks, such as Royal Bank of Scotland, HSBC, NatWest, Citibank, and Barclays.III.16. What is a general election?The election of all Members of Parliament (MPs) for each constituency (local area) is called a General Election. In the US it is like voting fora Congressman or Senator. However, unlikethe US, the voters do not choose the Prime Minister (PM). He/she is voted for within their party.17. What is the supreme legislative authorityin Britain? What does it consists of?British Parliament is the supreme legislative authority in the realm. It consists of the Sovereign, the House of Lords(上院)and the House of Commons(下院). Most of the power of Parliament is in the House of Commons. The Parliament was called in 1264 and is generally considered the beginning of “parliament”.18. What are the three areas in Britain which have seen some high-tech industrial growth? The three areas in Britain which have seen some high-tech industrial growth are:1)the area between London and South Wales,2)the Cambridge area of East Anglia and 3)the area between Glasgow and Edinburgh in Scotland. The third area is the most spectacular of the three and is now often referred to as the “Silicon Glen”.19. What is the British government’s role inthe economy?Like many modern developed countries, theUnited Kingdom has a mixed economy. This means that some sectors of the economy are operated by the government and some are operated by private businesses.After World War II, the government nationalized a number of large and troubled industries including coal, electricity, transport, gas, oil, steel, certain car and truck manufacturing, shipbuilding, and aircraft building. Since the 1950s, the government has privatized a number of these industries. The Conservative governments between 1979 and 1996 denationalized oil companies, telecommunications, car and truck production, gas, airlines and aircraft building, electricity, water, railways, and nuclear power. The government also seeks to encourage competition in the economy and increase productivity by sponsoring and subsidizing training and educational programs.20. How did the structure of British industry change in the last half of the 20th century?The coal mining and cotton textile industries declined sharply. As coal production declined, oil production replaced it as a major industry. Motor vehicle production became a significant part of the industrial base but was subject to severe foreign competition. As incomes increased, consumer demand rose for durable goods such as cars and kitchen appliances. British industrial production also expanded into communications equipment, including fiber optics, computers, computer-controlled machine tools, and robots.Key to Chapter 12Society & Culture of UK◆Key to Section ExercisesSection 1 British People & Their Ways of Life I. 1.T 2.T 3.F 4.FII. 5.A 6.D 7.B 8.-c 9.-a) 10.-dSection 2 Holidays and Special DaysI. 1.T 2.F 3.TII. 4. C 5. B 6.C 7.-c 8.-d 9.-a 10.-bSection 3 EducationI. 1.T 2.F 3.T 4.FII. 5.C 6.A 7.AII. 8.-f 9.-e 10.-aSection 4 English LiteratureI. 1.F 2.T 3.T 4.FII. 5.C 6.D 7.AIII. 8. 1)-b 2)-a 3)-dIV. Gap-filling9. Romance is the most popular literary form in the medieval period.10. The Romantic Movement appeared on the literary arena of England from the publication of Lyrical Ballads by Wordsworth and Samuel Coleridge in 1798 to the deathof Sir Walter Scott in 1832. The literary form which is the most flourishing during the Romantic Period is poetry.11. Samuel Richardson was the master of writing epistolary novels and the first novelist of sentimentalism tradition. His novels have a moral purpose, trying to inculcate virtue and good deportment.Pamela was his best novel.12. W. M. Thackeray was another representative of critical realism in 19th England. In 1847 he published his masterpiece Vanity Fair with a subtitle “a Novel without a Hero”.13.Hamlet, Othello, King Lear, and Macbeth are considered as Shakespeare's fourgreatest tragedies.V.1. Spenserian stanzaA nine-line verse stanza originated byEdmund Spenser is known as the Spenserian stanza. In the nine-line Spenserian stanzathe first eight lines are iambic pentameterand the ninth, iambic hexameter, with the rhyme scheme being ababbcbcc. This formof stanza creates a special musical effectand contributes greatly to the technique of poetry composition.2. Stream of ConsciousnessIt is a literary technique in which acharacter’s thoughts are presented in the confusing, jumbled, and inconsequential manner of real life without any clarification by the author. The aim of the technique is to provide a textual equivalent to the stream of a fictional character’s consciousness. It creates the impression that the reader is eavesdropping on the flow of conscious experience in the character’s mind, gaining intimate access to their private “thoughts”. James Joyce and Virginia Woolf are masters of this literary technique.。