中元音central vowels
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:61.50 KB
- 文档页数:4

语音实践之中元音Central V owels/?:/ /?/ /?//?:/字母和字母组合ir er or ur ear our yr1. fur sir her shirt hurt bird third word heard birth worth nursesearch church term fir girl curl first worst2. early journey certain person service purchase furnish earnest perfectcourtesy myrtle (番樱桃)3. the first year the first term the German expert learn the word a dirty shirt a firm girla nervous nurse an early bird the third word the third world an earnest personperfect service4. First come, first served.Workers of the world, unite!Perfect service deserves an earnest and worthy return.The girls learn world history in the first and third terms at the university.It’s the early bird that ca tches the worm.5.Worms squirm in the earthWhen first is heardThe murmur and chirpOf the early bird.6.Turn purple serve a customer at first give birth to a daughter on earth learn the list of words be at work make a long journey7.My shirt is dirty. I should clean it.I work as a nurse.I will begin my work on Thursday.I will travel around the world.Have a good journey.It’s my turn to speak.I got the third place in the competition. Mary got the first place.8.The early bird catches the worm. 早鸟先得食。

前元音中元音和后元音 GE GROUP system office room 【GEIHUA16H-GEIHUA GEIHUA8Q8-元音分类1:前元音、中元音和后元音根据元音发音过程中舌头在口腔中抬起的部位不同,我们可以把元音分为前元音、中元音和后元音。
(1) Front(前元音)4The front vowels in English are the vowels that are articulated near the front of the oral cavity, such as:发前元音时,发音部位靠近口腔前部。
例如:1./i:/ 前、高、不圆唇、长元音;2. /i/ 前、半高、不圆唇、短元音;3./e/ 前、半高、不圆唇、短元音;4. /æ/ 前、低、不圆唇、短元音.(2) Central(中元音)2The central vowels in English are the vowels that are articulated near the center of the vocal cavity, such as:发央元音时,发音部位靠近口腔中ә部。
例如:1./ә/ 中、半高、不圆唇、长元音;2. /ә:/ 中、半低、不圆唇、短元音.(3) Back(后元音)6The back vowels in English are the vowels that are articulated near the rear of the vocal cavity, such as:发后元音时,发音部位靠近口前后部。
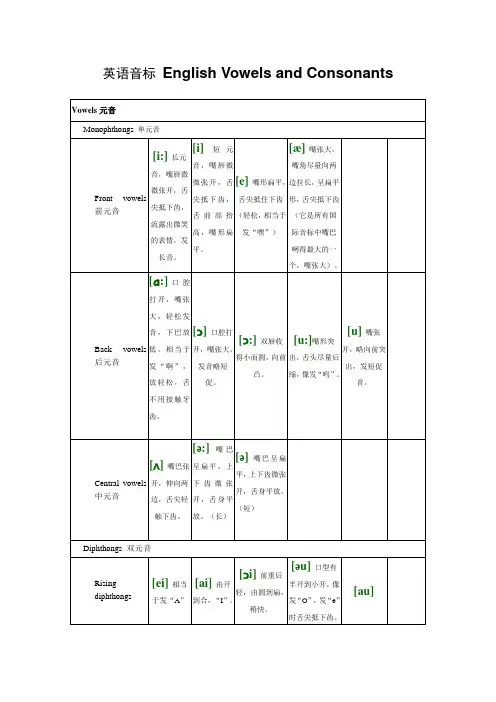
例如:1./u/ 后、高、圆唇、短元音;2. /u:/ 后、高、圆唇、长元音;3./ɔ/ 后、低、圆唇、短元音;4./ɔ:/后、半低、圆唇、长元音;5./Λ/后、半低、不圆唇、短元音;6./a:/ 后、低、不圆唇、长元音.单元音和双元音根据元音的构成要素,我们可以把元音分为12个单元音(monophthongs)和8个双元音(Diphthongs)。
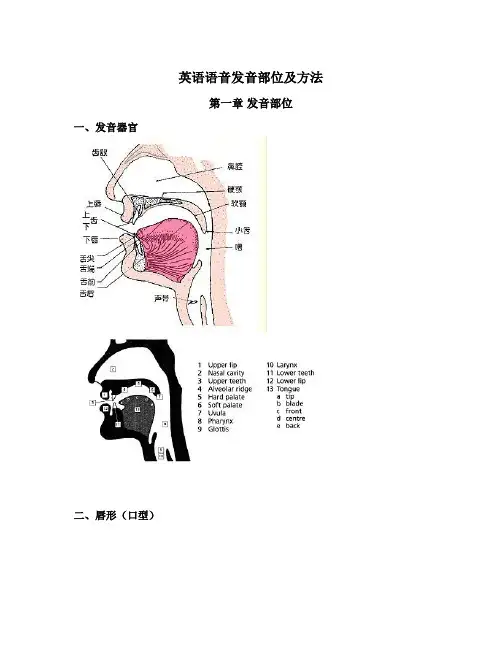
英语语音发音部位及方法第一章发音部位一、发音器官二、唇形(口型)(1)双唇紧闭(2)自然开口(3)扁唇:微笑(4)大圆唇:尽量张大口(5)小圆唇:口型渐渐变小第二章元音(Vowel)发音方法一、单元音(Monophthong)1.前元音(4 Front Vowels)1)/i:/——舌尖抵下齿龈,但不要抵得太紧。
略略扁唇,像微笑的口型。
发音时间略长。
(Open your mouth just a little for the sound. Spread your lips into a smile. Push your tongue forward in your mouth. It’s a long sound. Move your tongue up a little as you say it.)2) /I/(/i/)——先发/i:/,在此基础上,嘴角稍微收小一点,开口略大一点,舌尖靠近,但不要紧贴下齿龈,发音时间相对较短。
(Open your mouth just a little more for this sound. Don’t spread your lips into a smile. The sound is shorter, more relaxed than /i:/.)3)/e/(ε)——舌尖抵下齿龈,不要抵得太紧。
口略开,约可放入一个指尖。
不扁唇,口型自然放松,发音时间相对较短。
(Practice the sound /I/, then open your mouth a little more for this sound. It is a short and relaxed sound.)4)/æ/——舌尖抵下齿龈,双唇尽量向两边张开,嘴角肌肉感到紧张。
开口程度大,约可放入食指和中指交叠。
不扁唇。
(Practice the sound / e /, then open your mouth a little more for this sound.)2.后元音(5 Back Vowels)1)/a:/——松弛自然,口张到最大,不要撅嘴,舌尖离开下齿龈,长元音。

英语语音知识【音素phoneme】The phoneme is the smallest unit of speech sound in a language that is capable of conveying a distinction in meaning,音素是构成音节的最小单位或最小的语音片段。
Front vowels(前元音):/i:/, /I/, /e/, /æ/Pure V owels/Monophthongs(单元音) Central vowels(中元音):/ə:/, /ə/V owels(元音) Back vowels(后元音):/ɔ/, /ɔ:/, /u/, /u:/, /ʌ/, /a:/(20) Falling diphthongs(合口双元音):/ei/ , /əu/, ai/, /au/, /ɔi/Diphthongs(双元音)Phoneme Rising diphthongs(集中双元音):/iə/, /ε/, /ə/, /uə/Stops(爆破音):/p/, /b/. /d/, /t/, /k/, /g/Fricatives(摩擦音):/f/, /v/, /θ/, /ð/, /s/, /z/, /ʃ/, /ʒ/, /h/Consonants(辅音) Affricates(塞擦音):/ts/, /dz/, /tr/, /dr/(28) Lateral(边音):/l/Nasals(鼻音):/m/, /n/, /ŋ/Approximants(半元音):/w/, /r/, /j/语言学知识Morpheme that occur “unattached” are called free morpheme.Inquiry and discovery learning is to involve learners in investing energy and attention in order to discoversomething about the language for themselves.Sapir-Whorf hypothesis is also known ad linguistic relativity.Pragmatic competence requires teacher to help learners to learn the relationship between grammatical formsand function.Phonetics is the study of the phonic medium of language; it is concerned with all the sounds that occur in theworld’s languages.Correct perception of sounds is vital for listening comprehension.Different stress and intonation indicate different meanings.The dialect which is caused by social status is socialect.The famous line “My love is a red, red rose”, stirs up vividly the imagination of a beautiful lady. This is theiconic meaning of “rose”.Linguistics is generally defined as the scientific study of language.The reasons for teaching writing to students of English as a foreign language include reinforcement, languagedevelopment, learning style and, most importantly, writing as a skill in its own right.The different phones which can represent a phoneme in different phonetic environment are called theallophones of that phoneme.Semantics is generally considered to be the study of meaning in language.。



音标专业术语1.元音vowels2.前元音front vowels3.中元音central vowels4.后元音back vowels5.双元音diphthongs6.辅音consonants7.清辅音(有声辅音)voiceless8.浊辅音(无声辅音)voiced9.音节syllable10.重读音节stressed syllables11.单音节monosyllabic12.双音节disyllabic13.多音节polysyllabic14.重读闭音节stressed close syllables15.重读开音节stressed open syllables16.绝对开音节17.相对开音节18.弱读reduced forms19.单词重音word stress20.语调intonation21.辅音连缀consonant clusters22.S后清音浊化23.节奏rhythm24.连读linking of sounds25.音标phonics26.音素phoneme27.音标框phonics frame28.半元音semi-vowels29.缩读contractions30.字母组合compound letters31.升调rising tone32.降调falling tone33.元音字母34.辅音字母35.请找出以下单词的相同点(发音上的,写法上的)Please find out thesimilarity in the pronunciation\spelling among these words.36.写上单词划线部分的音标Please write the phonics of the lettersunderlined.37.让我们来比较一下[ I ]和[ e ]的发音Let’s compare the sound of[ I ] with [ e ]. Please find out the differences among the sounds of these words.38.[ i ]有那些字母组合What compound letters are pronounced[ i ]?39.cat中的a发音…The letter “a” in “cat” makes the sound\is pronounced…40.看谁做得又好又快Let me see that who is better.。



前中后双元音音标的分类
前元音、中元音和后元音是根据舌位的不同来划分的。
前元音(front vowel)发音时舌位最高点都在舌前部,舌端靠近下齿,舌前部抬高。
在英语中,/iː/、/ɪ/、/e/和/æ/都属于前元音。
中元音(central vowel)发音时舌位最高点都在舌中部,发音时舌中部向硬腭抬起。
在英语中,/ɜː/、/ə/和/ʌ/属于中元音。
后元音(back vowel)发音时舌后部向软腭抬起,舌头后缩,舌尖向下,舌面后部对着软腭抬起。
在英语中,/uː/、/ʊ/、/ɔː/、/ɒ/和/ɑː/属于后元音。
此外,根据唇形还可以分为扁唇元音、中唇元音和圆唇元音;按音的长短还可以分为短元音和长元音。
在英语中还有一些双元音,例如合口双元音和集中双元音,根据发音器官的滑动方向进行分类。
英语元音发音要领单元音the pure vowels单元音的发音要领是准确掌握其舌位的前、中、后及高、中、低。
单元音发音的共性:舌位不移动;发音过程中没有任何摩擦;不受发音器官的任何阻碍。
单元音发音的特性:单元音因舌位抬高部位的差异而分成三大类:前元音(the front vowels)、中元音(the central vowels)、后元音(the back vowels)。
前元音发音时,舌尖靠近下齿,舌前部抬高;中元音发音时,舌尖离开下齿,舌中部抬高;后元音发音时,舌尖离开下齿,舌后部抬高。
(一)前元音1. /♓i:/ 前元音、高元音发音特性:舌尖靠近下齿;舌前部抬高,但不接触上齿龈;唇形扁平;口形很小,接近闭合。
有些学生容易把元音/♓:/读成汉语中的“衣”音,主要原因是舌位抬高,与上颚发生摩擦。
纠正的方法是舌前部压低,从而不接触上颚,不发生任何摩擦。
2. /✋/ 前元音、高元音发音特性:舌尖靠近下齿;舍前部抬高,略低于/♓:/的舌位;唇形扁平;开口比/♓:/略大,接近半闭。
3. /♏/ 前元音、中高元音发音特性:舌尖靠近下齿;舍前部抬高,但略低于/✋/的舌位;口形介于半开半合之间,比/✋/的口形略大;唇形扁平。
有些学生在读/♏/音时,往往开口过大,须控制口形。
4. /✌/ 前元音、低元音发音特性:舌尖靠近下齿;舌前部抬高,但其舌位是四个前元音中最低的;开口比/♏/大,是四个前元音中开口最大的音,介于半开和开之间;唇形扁平自然。
有些学生,尤其是北方学生容易把/✌/读成普通话中的“爱”,问题在于发/✌/音时,舌位移动了。
纠正的方法是控制舌位,不要移动。
(二)后元音5. / :/ 后元音、低元音发音特点:舌端离开下齿,舌后略抬高,舌位较低;唇形自然略成圆形;牙床打开。
中国学生有把/ :/读成“啊”的倾向。
纠正方法是注意前舌放低而后舌抬起,舌后部要感觉紧张。
6. / / 后元音、低元音发音特点:舌端离开下齿,舌后抬高,略高于/ :/;双唇自然成圆形,口形略小于/ :/;牙床近于开,但略小于/ :/7. / :/ 后元音、中低元音发音特点:舌端离开下齿,后舌抬高,明显高于/ /;唇形较圆,比/ /更圆;牙床半开,较/ /的开口程度小。
语音的基本概念Ⅰ字母是语言的书写形式。
1、元音字母:又叫母音字母,是指语言里起着发声作用的字母。
英语26个字母中,有5个元音字母a, e, i, o, u。
字母y后无元音字母时,充当元音字母,发音与i相同,称为半元音字母;作为辅音发/j/,作为元音发/i/。
元音字母在重读开音节中发长音,在重读闭音节中发短音。
一般说来,元音字母发元音,但有时也不发音(e),而两个元音字母组合在一起时常常发一个元音,所以,音节的个数以音标中的元音个数来判断。
2、辅音字母:除元音字母外其余的都是辅音字母,辅音字母在单词中发音比较单一,不随音节变化而变化。
a. 元音字母组合:aar, ae, ai, air, aor, ar, are, au, aw, ay, ea, ear, eau, ee, eer, ei, eir, eo, er, ere, eu, eur, ew, ey, ia, iar, ie, ier, iew, io, ior, iou, ir, ire, iu, oa, oar, oe, oi, oir, oo, oor, ore, ou, ough, our, ow, oy, ua, uar, ue, uer, ui, uou, ur, ure, uu, uy, ya, ye, yer, yi, yo, yr, yreb. 辅音字母组合:bb, cc, ch, ck, d, dge, dj, ff, gg, gh, gu, ll, mm, nn, ph, pp, qu, rr, sc, sch, sci, sh, si, ss, tch, ti, th, tt, sh, xc, zzb. 混合字母组合:sion, sure, tion, tureⅡ音素是语音的最小的单位。
音素分为元音和辅音,英语中有48个音素,元音音素20个,辅音音素28个。
Ⅲ每一个单词都有语音形式和书写形式。
音标就是语言的语音标记,是词的语音形式。
发音概述--英语发音类别基本分类及常识语音分元音和辅音两大类,每一个语音必定属于这两者之一。
元音元音是一种有声音,发音时用舌头和嘴唇使口腔定形,声带振动。
同时气流从咽腔和口腔不断流出,不受阻碍,也没有变狭窄,因而听不出摩擦。
辅音(在正常言语中)除元音外所有的其它音都叫辅音。
一部分辅音发音时,气流不通过口腔,如[m];另一部分辅音发音时,气流在通过口腔时,受到这样或那样的阻碍,或在口腔中的某个点受到摩擦。
元音分类A根据发音时舌头在口腔中抬起的部位不同,我们把单素元音分为前元音、中元音和后元音。
例如:[1] 前元音,口型舒展[u:] 后元音,口型收拢前元音舌前部向硬颚抬起时发出的元音叫前元音。
前元音(Front Vowels)主要有:英式英语:[i:] [i] [e] [1]美式英语:[i] [I] [A] [1]Practice these four sounds in phrases.eat the meat make a wish very wella mad man keep the seat sit downget ready a jazz band three treesbest friend a black bag Peter’s secreta small fish ten men a plastic bagthe Chinese people a bit chilly Teddy Bearhand in hand a piece of cheese bit by bitwet with sweat a happy marriage a friend in needfit as a fiddle best seller on behalf of our class中元音舌中部向硬颚抬起时发出的元音叫中元音。
中元音(Central Vowels)主要有:英式英语:[4:] [4] [8]美式英语:没有[4:],多为[4r];[4]与[8]相同。
26个英语字母音素归类【原创实用版】目录1.26 个英语字母的音素分类概述2.辅音音素的分类3.元音音素的分类4.音素归类的重要性正文英语字母是英语语言的基础,它们构成了英语单词。
然而,这些字母并非孤立存在,它们可以通过音素组合形成音节,进而组成单词。
了解英语字母的音素归类有助于我们更好地掌握英语发音和语言运用。
下面,我们将对 26 个英语字母的音素归类进行详细分析。
首先,我们来看辅音音素的分类。
辅音音素是指在发音过程中,气流受到口腔、鼻腔等部位的阻碍而产生的声音。
英语中有 21 个辅音音素,它们可以分为以下几类:1.塞音(Stops):发音时,气流被口腔内的某个部位阻碍,然后突然释放。
例如字母“b”、“p”、“d”等。
2.摩擦音(Frictives):发音时,气流在口腔或鼻腔中受到摩擦而产生的声音。
例如字母“f”、“s”、“z”等。
3.破擦音(Affricates):发音时,气流先受到一定程度的阻碍,然后迅速释放。
例如字母“t”、“d”、“tr”等。
4.鼻音(Nasals):发音时,气流从口腔进入鼻腔,并产生声音。
例如字母“m”、“n”等。
5.边音(Laterals):发音时,气流从口腔的一侧流出,产生声音。
例如字母“l”等。
接下来,我们来看元音音素的分类。
元音音素是指发音时,气流通过口腔不受阻碍,产生的声音。
英语中有 5 个元音音素,它们可以分为以下几类:1.前元音(Front vowels):发音时,舌头位于口腔前部,例如字母“a”、“e”、“i”等。
2.中元音(Central vowels):发音时,舌头位于口腔中部,例如字母“o”、“u”等。
3.后元音(Back vowels):发音时,舌头位于口腔后部,例如字母“ou”、“ie”、“ue”等。
音素归类的重要性在于,它能帮助我们更好地理解和记忆英语发音。
通过对 26 个英语字母的音素归类,我们可以发现它们在发音上的规律,从而提高我们的英语听说能力。