1-2#制图基本知识
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:10.85 MB
- 文档页数:93



1、英语:有条件1-2岁就开始亲近英语,3岁后就可以正规的学习了。
因为孩子再大的话,母语习惯已形成,再学外语就有语音干扰了。
2、画画:一般四岁开始正规学习比较好,这时候孩子上了一年幼儿园也能坐的住了。
不过要注意这么小的孩子学画画就是涂鸦探索,锻炼孩子的想象力和创造力,父母千万不要让孩子学习简笔画,会毁了孩子的创造力的。
3、书法:孩子学习书法的最佳年龄是小学三年级,因为书法毕竟是一种技巧性很高的艺术,太小的孩子学习是有难度的,孩子三年级后汉字已经学了很多,也基本适应了文化学习,所以这个时候最合适。
4、游泳:考虑到安全因素,一般都建议孩子在4-5岁之间开始学习比较好。
5、舞蹈:3-4岁可以上舞蹈兴趣班,5岁后可以学一些基本功,5-7岁就可以学一些高难度的动作,比如做劈腿、下弯腰等。
猫爸女儿基本也是按这个顺序学的。

森吉米尔二十辊冷轧机介绍森吉米尔冷轧机与四辊轧机或其他类型轧机的本质区别是轧制力的传递方向不同。
森吉米尔冷轧机轧制力从工作辊通过中间辊传到支撑辊装置,并最终传到坚固的整体机架上。
这种设计保证了工作辊在整个长度方向的支撑。
这样辊系变形极小,可以在轧制的整个宽度方向获得非常精确的厚度偏差。
森吉米尔轧机在结构性能上有如下主要特点:(1)具有整体铸造(或锻造)的机架,刚度大,并且轧制力呈放射状作用在机架的各个断面上。
(2)工作辊径小,道次压下率大,最大达60%。
有些材料不需中间退火,就可以轧成很薄的带材。
(3)具有轴向、径向辊形调整,辊径尺寸补偿,轧制线调整等机构,并采用液压压下及液压AGC系统,因此产品板形好,尺寸精度高。
(4)设备质量轻,轧机质量仅为同规格的四辊轧机的三分之一。
轧机外形尺寸小,所需基建投资少。
森吉米尔冷轧机基本上是单机架可逆式布置,灵活性大,产品范围广。
但是亦有极个别呈连续布置的森吉米尔轧机,如日本森吉米尔公司1969年为日本日新制钢公司周南厂设计制造的一套1270mm四机架全连续式二十辊森吉米尔轧机。
该轧机第一架为ZR22-50"型轧机,其余三架均为,ZR21-50"型轧机,轧制规格为O.3mm×1270mm不锈钢,卷重22t,轧制速度600m/min。
森吉米尔冷轧机的形式及命名法介绍如下:最常用的森吉米尔冷轧机形式是1-2-3-4型二十辊轧机。
例如ZR33-18″,“Z"是波兰语Zimna的第一个字母,意思是“冷”;“R”表示“可逆的”;“33”表示轧机的型号;“18″”是轧制带材宽度的英寸数。
森吉米尔冷轧机还有1-2-3型十二辊轧机,但是1-2-3型森吉米尔冷轧机在1964年以后就不再生产制造了。
森吉米尔冷轧机1-2型六辊轧机,由2个传动的工作辊和4个背衬轴承辊装置组成,如ZS06型,“S”表示“板材”,用来轧制宽的板材,但是它同样可以轧制带材,并且有一些还用在连续加工线上。



实验一 拉伸和压缩实验拉伸和压缩实验是测定材料在静载荷作用下力学性能的一个最基本的实验。
工矿企业、研究所一般都用此类方法对材料进行出厂检验或进厂复检,通过拉伸和压缩实验所测得的力学性能指标,可用于评定材质和进行强度、刚度计算,因此,对材料进行轴向拉伸和压缩试验具有工程实际意义。
不同材料在拉伸和压缩过程中表现出不同的力学性质和现象。
低碳钢和铸铁分别是典型的塑性材料和脆性材料,因此,本次实验将选用低碳钢和铸铁分别做拉伸实验和压缩实验。
低碳钢具有良好的塑性,在拉伸试验中弹性、屈服、强化和颈缩四个阶段尤为明显和清楚。
低碳钢在压缩试验中的弹性阶段、屈服阶段与拉伸试验基本相同,但最后只能被压扁而不能被压断,无法测定其压缩强度极限bc σ值。
因此,一般只对低碳钢材料进行拉伸试验而不进行压缩试验。
铸铁材料受拉时处于脆性状态,其破坏是拉应力拉断。
铸铁压缩时有明显的塑性变形,其破坏是由切应力引起的,破坏面是沿45︒~55︒的斜面。
铸铁材料的抗压强度bc σ远远大于抗拉强度b σ。
通过铸铁压缩试验观察脆性材料的变形过程和破坏方式,并与拉伸结果进行比较,可以分析不同应力状态对材料强度、塑性的影响。
一、 实验目的1.测定低碳钢的屈服极限s σ(包括sm σ、sl σ),强度极限b σ,断后伸长率δ和截面收缩率ψ;测定铸铁拉伸和压缩过程中的强度极限b σ和bc σ。
2.观察低碳纲的拉伸过程和铸铁的拉伸、压缩过程中所出现的各种变形现象,分析力与变形之间的关系,即P —L ∆曲线的特征。
3.掌握材料试验机等实验设备和工具的使用方法。
二、 实验设备和工具1. 液压摆式万能材料试验机。
2. 游标卡尺(0.02mm)。
三、 拉伸和压缩试件材料的力学性能sm s σσ(、sl σ)、b σ、δ和ψ是通过拉伸和压缩试验来确定的,因此,必须把所测试的材料加工成能被拉伸或压缩的试件。
试验表明,试件的尺寸和形状对试验结果有一定影响。
为了减少这种影响和便于使各种材料力学性能的测试结果可进行比较,国家标准对试件的尺寸和形状作了统一的规定,拉伸试件应按国标GB /T6397—1986《金属拉伸试验试样》进行加工,压缩试件应按国标GB /T7314—1987《金属压缩试验方法》进行加工。
短串联重复序列(short tandem repeats,STR)是人类的一类重要遗传标记,因其多态性丰富,扩增片断长度短,广泛地应用于亲子鉴定中。
但是,STR 基因座在遗传的过程中发生突变的概率较高,因此在鉴定过程中是个不容忽视的问题,要值得注意。
笔者在工作中遇一例较罕见的母亲发生二步突变的羊水检材鉴定,现报道如下。
1 案例资料1.1 案情简介李某(孕17周+),自然受孕,未确定腹中胎儿父亲是否为其老公,特委托本鉴定所鉴定是否存在亲子关系。
1.2 检验方法胎儿羊水5m l 、男方带毛囊毛发2根、女方血样备用。
采用Chelex-100 法分别提取DNA。
经PowerPlex R21 (普洛麦格生物技术有限公司)、AGCU EX22(无锡中德美联生物技术有限公司)复合扩增系统以及Investigator Argus RX-12(德国QIAGEN公司)扩增系统进行扩增,扩增产物在ABI3500型DNA测序仪上电泳,由GeneMapper ID X1.3软件进行结果分析。
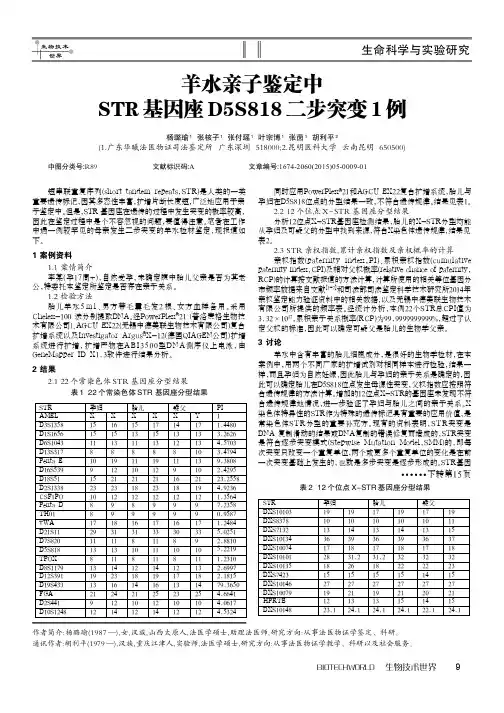
2 结果2.1 22个常染色体STR 基因座分型结果同时应用PowerPlex R21和AGCU EX22复合扩增系统,胎儿与孕妇在D5S818位点的分型结果一致,不符合遗传规律。
结果见表1。
2.2 12个位点X-STR 基因座分型结果分析12位点X-STR基因座检测结果,胎儿的X-STR分型均能从孕妇及可疑父的分型中找到来源,符合X染色体遗传规律,结果见表2。
2.3 STR 亲权指数,累计亲权指数及亲权概率的计算亲权指数(paternity index,PI)、累积亲权指数(cumulative paternity index,CPI)及相对父权概率(relative chance of paternity,RCP)的计算按文献报道的方法计算,计算所使用的相关等位基因分布频率数据来自文献[1-2]和司法部司法鉴定科学技术研究所2014年亲权鉴定能力验证资料中的相关数据,以及无锡中德美联生物技术有限公司所提供的频率表。

一二的写法
“一”的写法:
1. 笔划从左下向右上运笔,在田字格左半格书写,在竖中线偏左一点的位置起笔,向左下方画直线,到下边线收笔,收笔处在左边线偏右一点的位置。
2. 用直直的线连起来,一笔写成数字1。
“二”的写法:
1. 第一个点在左边线上半格的中间,第二个点在上边线左半格的中间,第三个点在竖中线上半格的中间,第四个点在左边线与下边线的交点处,第五个点在竖中线与下边线的交点处。
2. 前三个点用弧线画出一个半圆,第三个点和第四个点用直直的线连接,第四个点和第五个点用直直的线连接。
一笔写成数字2。
本文将为各位教育工作者提供一份从入门到精通,2的减法中班数学教案全方位指导。
这份教案将包含适合中班阶段学生的2的减法课程,以及针对不同学习层次的教学方法,以确保每个学生都能理解并掌握这一知识点。
第一部分:教学目标在开始教学前,我们需要明确学生需要达到什么样的学习目标。
以下是适用于中班阶段学生的2的减法目标:1.能够理解什么是减法,能够与加法区分出来。
2.能够理解“减去”以及“等于”这两个概念。
3.能够通过手动计算方式来解决2的减法问题。
4.能够独立完成基础的2的减法练习,如2-1、2-2、2-0等。
5.能够通过日常生活中的示例来看待2的减法问题,如:“我有2个饼干,我吃掉了1个,还剩下几个”?第二部分:教学内容1.引入讲师应该首先明确减法与加法的区别,此外还应该举出几个例子解释“减去”和“等于”这两个概念。
教师需要问学生一个问题:“如果我手里有两个糖果,我吃掉了一个,我还有一个,这种情况是减法还是加法呢?”2.定义减法在明确学生理解了减法与加法的区别后,教师可以开始解释减法的定义。
教师可以用一个具体例子来解释减法的定义,比如:“如果在大脑中将2个糖果减去1个糖果,那我们得到了1个糖果。
”3.2的减法接下来,教师可以从最简单的2的减法开始讲解,如2-1、2-2、2-0等。
需要注意的是,老师需要通过具体的模型,如糖果、扑克牌等,来教授2的减法概念。
4.练习教师可以设计一些简单的2的减法练习,如2-1、2-2、2-0等,以测试学生是否掌握了学习内容。
5.动手计算除了通过图形、模型等手段来说明2的减法,老师还需要让学生自己动手做题。
老师可以向学生提供纸和笔,让他们自己算出2的减法的答案。
6.例子老师还可以教授一些生活中的例子来帮助学生理解2的减法。
例如,洗碗时,如果我们降低了盘子的数量,我们的堆积就会减少;糖果的数量减少了,剩余的糖果数量就会变少。
第三部分:教学方法对于不同的学生来说,教师还需使用不同的教学方法来提高他们的学习效率。
Unit 1 ParentsPassage 1Ex. 11-3 c a bEx. 21. her husband spend more time with his mother. //Life is too short, you need to spend time with the people you love, Y ou probably won’t believe me, but I know you love her and I think that if the two of you spend more time together, it will make us closer.2. 1) she was waiting by the door with her coat on and she had her hair curled.2) She had told her lady friends about this.Passage 2Ex. 1 1-3 c d dEx. 2 1. took// out to dinner// neighborhood2. nicer than he expected.3. A couple of times.4. the importance of slowing down//his marriagePart C 1-5 b c b d dUnit 2 CoincidencePassage 1Ex 1 1-4 b a d cEx 2 1984 // son // medical school // tuition // afford it // realize // newspaper ads // extra business // advertisement //succeeded // agent // changed // phone call // put aside // doing // immediately familiar // his father-in-law’s // visited // father-in-law // alive //coincidencePassage 21. The house was decorated exactly the same as Mr. Stewartremembered it2. Mr. Stewart happened to be in the house when a postman cameto deliver a letter to his father-in-law who had died 15 years ago.3. The old postman had called in sick that day, and the postmanwho came in his place was not familiar with the neighborhood.Other wise the letter would have been returned to its sender.Ex. 21. He was intrigued.2. A bank statement.3. His father-in-law had put an amount of money in the bank for hisgrandchildren’s education.4. A little over $ 15,0005. He could use the money to cover the tuition of his first year at amedical college.6. He is a doctor in Illinois.Part C1) collections 2) shot 3)presence 4)justice5)Theater 6) occur 7) victim8) officers had only managed to identify the first victim minutes before the second accident9) They married on the same day, had worn identical wedding dresses and carried the same flowers.10) How can we explain the above similarities?Unit 3 CourageEx 1 1-2 c c Ex 2 1-8 T F F F F T T FPassage 21-2 d bEx. 21. Because she was afraid Krimali might not be able to catch thebaby.2. Because she thought the bed sheets could somehow protect thebaby form being hurt if she failed to catch her.3. Because they were afraid of the swaying ceiling.4. To make it easier and safer for the baby’s mother to get down.5. About two dozen.Part C1-4 a b d dUnit 4 MarriageConversation 1Ex. 1 1-3 b c aEx. 21. understand each other’s expectations // could be avoided //livehappily2. Cleaning up // cleaned up and put away before going to bed3. Sleeping //11 p.m. // 6:30 a.m. // on weekendsConversation 2Ex. 1 1-3 c c aEx. 21. get lost// five minutes // driving // stop // directions2. breaking rules // break a rule // apologize and do something nicefor the other person to make it up3. reviewing the contents of the agreement // review thisagreement once a year // make necessary changesPart C 1-3 a d bUnit 5 Y outhPassage 1Ex. 1 1-2 d cEx. 2 Testing //river // if there were antibiotics // resistant // 350 water samples // the samples // Low levels // three // Water Prize // 5000 / Sweden’sPassage 2Ex. 11. reaching //everybody //exposing //lies2. advertising campaign // youth // against tobacco companies3. the message // teenagers // their advertisementsEx. 2 1-5 c a d c bPart C1-4 a c d cUnit 6 StressConversation 11-3 d c aEx. 2 police officer // 30 // patrol // undercover // detective //supervising investigations // being a police officer // assignment // patrol // the fear of the unknownConversation 2Ex 1 1-5 T F T F TEx. 21. an exercise program // a psychological program // counselingfor officers // several discussion groups //2. baseball // get some sort of exercise // his personalrelationships // relationship with his wifePart C 1-5 d d d b cUnit 7 The Business WorldConversation 1Ex. 11. In Mr. Andrew Song’s office2. Boss and secretary3. To see Mr. Andrew Song on businessEx. 2 1-5 d b a b cConversation 2Ex. 1 1-2 b cEx 2. to discuss the causes of the decline in profits // 10 :00a.m. // Chief Sales Executive1. Sales are down but not by too much2. The budget for sales hasn’t increased even with inflation3. The products are oldPart C1-4 d b d bUnit 8 The EnvironmentPassage 1Ex. 1 1-3 c a dEx. 2 15 million // at the beaches // and in local waters // serious pollution // $ 70 // burning // cancer-causing chemicals// the number of plastic bags used // the public’s overall awareness of environmental problems // the public’s overall awareness of environmental problems //1500 // customers //10 // marketsPassage 2Ex. 1 1-3 d c bEx. 21. Western Europe 、、waterway2. seriously polluted// Fish // dangerous to swim in it3. A fire broke out // tons of pesticides to leak into the Rhine4. The countries //realized // clean it up // keep it clean5. Every six // 24 hoursPart C 1-4 c b d dUnit 9 The Single CurrencyPassage 1 1-3 b b dEx. 21. midnight // 31 // 2001 // the new notes / new currency2. 300 million // 15 billion // 52 billion // 646 billion // 568 billion3. greater Europe // stronger // wealthier4. championed // peace and securityPassage 21-3 d c cEx. 21. When economic conditions are right2. The polls show that many Britons oppose the euro and see it asharming Britain’s sovereignty3. Because as very small retail outlets they don’t have the facilitiesfor changing currencies4. More than 6.55 billion eurosPart C1)symbols 2)ancient 3) grief 4) rebirth5)stable 6) reputation 7) abolishing8)such a conservative people did not express greater sorrow for the loss of their familiar francs9) The name franc was first used in 1360, to celebrate and help to pay for the release of the King of France10) On February 17th, 2002, the French franc disappeared completely from the financial scene.Unit 10 The CinemaPassage 1 Ex. 1 1-2 c dEx. 2 popcorn // successful // 20 million // soft drinks // ice cream // three // four // box office // half the moeny // 69 percent // 89 percent // a little over 90p // 4 // 3.95 Passage 2Ex. 1 1-3 b c dEx. 21. falling2. swimming3. driving4. setting fire5. fights6. flying // exploding helicopter // back of a speeding trian bbcd这是partC的。