小学英语语法句法
- 格式:doc
- 大小:16.00 KB
- 文档页数:2

小学英语语法大全16句法1、陈述句说明事实或陈述说话人观点的句子。
基本结构:主语+谓语+其他1)肯定陈述句We all like pandas very much.2)否定陈述句He doesn’t do housework at weekends3)肯定陈述句改否定陈述句①一般是在be动词或情态动词后加not。
Mary was at school yesterday. —> Mary was not at school yesterday.I can make a model plane. —>I can not make a model plane.②不含be动词或情态动词的,行为动词前要用助动词的否定式(don’t,doesn’t,didn’t),后面跟动词的原形。
He likes drawing pictures.—>He doesn’t like drawing pictures.I went to the park yesterday. —>I didn’t go to the park yesterday.4)陈述句改一般疑问句①有be动词或情态动词的,把be动词或情态动词提前。
Mary was at school yesterday. —> Was Mary at school yesterday?I can make a model plane. —> Can you make a model plane?②不含be动词或情态动词的句子,借助助动词开头,动词还原成原形。

小学英语:1~6年级语法知识大全,一篇帮你搞定6大句型,孩子6年学习必备!
小学阶段,除了记忆一些简单的英语单词,还要学习一些基本的英语句型,也就是我们语法知识中常说的句法知识。
这是一个很重要的部分,很多孩子在表达上常常出现错误,就是句法这一块没有掌握好。
句法是一个语法复杂知识点,但是小学阶段需要掌握的只是一些基本的句型,如陈述句、疑问句、祈使句等。
今天,小编老师要讲解的就是小学阶段必会的6大句型:陈述句、疑问句、祈使句、感叹句、There be句型、has got/have got句型。
很多孩子会问老师,为什么没有否定句和肯定句呀?这是因为肯定句和否定句是陈述句的两个分支,它们完整的名字是陈述句的肯定式和陈述句的否定式。
这一点有些孩子还没有弄清楚。
下面就跟着老师来学习这6大句型,掌握好这项语法知识。
第一大句型:陈述句
第二大句型:疑问句
第三大句型:祈使句
第四大句型:There be句型
第五大句型:have got/has got 句型
第六大句型:感叹句。

小学英语语法句法句法主要研究句子的成分,语序以及句子的种类,类型等的内容。
一,句子成分组成句子的各个部分叫句子成分。
根据词汇在句子中的不同作用,英语句子主要含有以下六个成分:主语,谓语,表语,宾语,定语,状语。
句子主要由主语和谓语两部分组成。
1.主语主语是句子的主体,表示所说的是谁一或是什么。
主语的位置一般放在句首,有时在特殊句型中主语放在句末。
I go to school by bike every day.2.谓语用来说明主语的动作,特征或状态等。
谓语主要有两种形式:动词谓语(包括动词短语)和复合谓语(系动词+表语)。
This happened in 1990. (动词谓语)He must take good care of his little sister at home today. (动词短语)The young man became a doctor . (系动词+表语)(Trees turn green in spring. (系动词+表语)3.表语用来说明评语的身份,特征和状态等。
它通常位于系动词的后面,可作表语的有名词,代词,数词,形容词等。
Is this pencil yours She is not at home.4.宾语是动作的承受者。
及物动词和相当于及物动词的短语都必须有宾语,可作宾语的有名词,代词,数词等。
句子作宾语和叫宾语从句。
有些及物动词可以有两个宾语:一个指人,一个指物。
W e are waiting for Lily. He knows he should work hard.5.宾语补足语用来说明补充宾语,与宾语一起构成复合宾语。
可作宾语补足语的有名词,形容词,副词等。
Let me do it . We must keep the classroom clean every day.6.定语用来修饰名词或代词的句子成份。
形容词作定语时,一般放在名词前面,副词或副词短语作定语时,放在名词后面。

小学英语语法句型归纳总结英语作为一门国际语言,学习英语语法对于小学生来说是至关重要的。
掌握英语语法句型,不仅能够帮助学生更好地理解英语的用法,还能够提高他们的英语表达能力。
下面是对小学英语语法句型的归纳总结:一、简单句型1. 主语 + 动词(及物或不及物)例如:- I eat an apple.(我吃一个苹果。
)- They run in the park.(他们在公园里跑。
)2. 主语 + 动词 + 宾语例如:- She reads a book.(她读一本书。
)- Tom throws a ball.(汤姆扔一个球。
)3. 主语 + 系动词(be动词)+ 表语例如:- I am a student.(我是一个学生。
)- The flower is beautiful.(这朵花很漂亮。
)4. 主语 + 系动词(be动词)+ 地点例如:- The book is on the table.(书在桌子上。
)- The cat is under the chair.(猫在椅子下面。
)二、疑问句1. 一般疑问句使用助动词do、does或did加在句子的主语前,然后再加上动词原形。
例如:- Do you like ice cream?(你喜欢冰淇淋吗?)- Does he play basketball?(他打篮球吗?)2. 特殊疑问句特殊疑问句是用来询问特定信息或细节的问句,通常以疑问代词开头。
例如:- What is your name?(你叫什么名字?)- When is your birthday?(你的生日是什么时候?)- Where do you live?(你住在哪里?)在句子前面加上否定词,通常为don't、doesn't或didn't。
例如:- I don't like pizza.(我不喜欢披萨。
)- He doesn't have a pet.(他没有宠物。

句法讲解一、句子成分句子成分大体可分为主语、谓语、表语、宾语、定语、状语、补足语、同位语、独立成分等。
1、主语:主语是句子叙述的主体,是全局述说的对象。
表明这句话描述的是什么,常有名词、代词充当。
例:We are students.2、谓语:谓语主要是对主语加以陈述,表示主语的动作或状态,由动词或动词词组担任。
放在主语的后面。
例:We are students. I like cats.3、宾语:宾语表示及物动词动作的对象,放在及物动词或者介词之后,常用名词、代词充当。
例:Mike do the job. I like cats.4、表语:用来说明主语的性质或状态。
表语放在连系动词(如be)之后表示主语的身份或特征,常用名词、代词、形容词充当。
例:The apple is red. Her voice sounds sweet.5、定语:用来说明或者限制名词的成分,常用形容词或者相当于形容词的短语或从句担任。
例:This is a red sun. He is a tall boy.6、状语:用来说明动词、形容词、副词或整个句子的成分。
常有副词担任。
修饰动词时可以放在动词之前,也可以放在动词之后;修饰形容词或副词时放在它们之前。
例:The students study hard. I often write to him. The bag is too heavy.7、补足语:用于补充说明主语或宾语的性质、状态的句子成分。
由名词、形容词、副词、介词短语、不定式等充当。
例:We call him Monkey. The tiger was caught alive.8、同位语:同位语是对前面的名词或代词作进一步的解释,通常是由名词、数词、代词或从句等担任。
例:This is Mr.Li, our teacher.二、句子种类英语句子按照目的分为:陈述句,祈使句,感叹句,疑问句(一般疑问句,特殊疑问句,反意疑问句)。

句子的种类(一)按使用目的可分为陈述句、疑问句、祈使句和感叹句。
1)陈述句(Declarative Sentences):说明一个事实或陈述一种看法。
Light travels faster than sound.光比声速度快。
(说明事实)The film is rather boring.这部电影很乏味。
(说明看法)2)疑问句(Interrogative Sentences):提出问题。
有以下四种:a.一般疑问句(General Questions):Can you finish the work in time?你能按时完成工作吗?b.特殊疑问句(W Questions; H Questions):Where do you live?你住那儿?How do you know that? 你怎么知道那件事?c.选择疑问句(Alternative Questions):Do you want tea or coffee?你是要茶还是要咖啡?d.反意疑问句(Tag-Questions):He doesn't know her, does he?他不认识她,对不对?3)祈使句(Imperative Sentences):提出请求,建议或发出命令,例如:Sit down, please.请坐。
Don't be nervous!别紧张!4)感叹句(Exclamatory Sentences):表示说话人惊奇、喜悦、愤怒等情绪,例如:What good news it is!多好的消息啊!(二)句子按其结构可以分为以下三类:1)简单句(Simple Sentences):只包含一个主谓结构句子叫简单句,例如:She is fond of collecting stamps.她喜欢集邮。
(主)(谓)2)并列句(Compound Sentences):包含两个或两个以上主谓结构的句子叫并列句,句与句之间通常用并列连词或分号来连接,例如:The food was good, but he had little appetite.(主)(谓)(主)(谓)食物很精美,但他却没什么胃口。

英语语法体系-9大词法,10大句法九大词法:1. 名词(Nouns):表示人、事物、地点或抽象概念的词汇。
2. 代词(Pronouns):用来代替名词的词汇,如I, you, he, she, it 等。
3. 形容词(Adjectives):描述或修饰名词的词汇,如beautiful, smart, happy 等。
4. 副词(Adverbs):修饰动词、形容词或其他副词的词汇,如quickly, very, extremely 等。
5. 动词(Verbs):表示动作或状态的词汇,如run, eat, be 等。
6. 数词(Numerals):表示数量或顺序的词汇,如one, two, first, second 等。
7. 冠词(Articles):包括定冠词the 和不定冠词a/an,用于特指或泛指名词。
8. 介词(Prepositions):表示位置、时间、方向等关系的词汇,如in, on, at, under 等。
9. 连词(Conjunctions):连接句子或词语的词汇,如and, but, or, so 等。
十大句法:1. 句子(Sentences):包含一个完整的表达和独立意思的语言单位。
2. 主语(Subjects):句子中执行动作或被描述的主体。
3. 谓语(Predicates):描述主语的动作、状态或性质。
4. 宾语(Objects):动作的接受者或受影响的对象。
5. 状语(Adverbials):修饰动词、形容词、副词或整个句子的成分。
6. 定语(Attributives):修饰名词或代词的成分。
7. 同位语(Appositives):对名词或代词进行进一步解释或说明的成分。
8. 从句(Clauses):作为句子的一个组成部分,如定语从句、状语从句等。
9. 倒装句(Inversion):句子成分的语序颠倒,以强调或特殊语法结构。
10. 省略(Ellipsis):有意省略句子中的某些成分,但不影响理解。
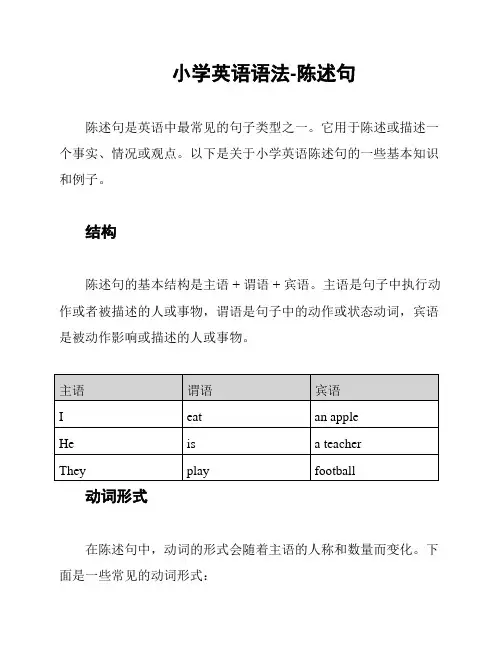
小学英语语法-陈述句
陈述句是英语中最常见的句子类型之一。
它用于陈述或描述一个事实、情况或观点。
以下是关于小学英语陈述句的一些基本知识和例子。
结构
陈述句的基本结构是主语 + 谓语 + 宾语。
主语是句子中执行动作或者被描述的人或事物,谓语是句子中的动作或状态动词,宾语是被动作影响或描述的人或事物。
动词形式
在陈述句中,动词的形式会随着主语的人称和数量而变化。
下面是一些常见的动词形式:
- 第三人称单数主语(如:he, she, it)在动词后面加上-s或-es。
例如:He eats an apple.
- 除了第三人称单数外,其他人称和复数主语动词保持原形不变。
例如:I eat an apple. They eat apples.
示例
以下是一些关于陈述句的例子:
1. I have a dog.
2. She likes to dance.
3. The sky is blue.
4. We play soccer on the weekends.
5. They are happy.
注意事项
- 陈述句通常以句号(.)结束。
- 主语、谓语和宾语的顺序可以变化,但句子的意思必须保持一致。
希望这份小学英语语法-陈述句的文档能够对您有所帮助!在写陈述句时,请记得遵循正确的主谓宾结构和动词形式。
祝您学习愉快!。

小学英语中的基本句型与语法结构小学英语中的基本句型与语法结构英语是小学学生必修的一门课程,掌握基本句型和语法结构是建立英语语言能力的基础。
本文将介绍小学英语中常见的基本句型和语法结构。
一. 简单句型1. 主语 + 动词例如:I eat an apple.(我吃一个苹果。
)2. 主语 + 动词 + 宾语例如:She reads a book.(她读一本书。
)3. 主语 + 动词 + 地点例如:They play football in the park.(他们在公园踢足球。
)4. 主语 + 动词 + 时间例如:He goes to school every morning.(他每天早上去学校。
)二. 疑问句1. 助动词 + 主语 + 动词例如:Do you like ice cream?(你喜欢冰淇淋吗?)2. 疑问词 + 助动词 + 主语 + 动词例如:What do you do on weekends?(你周末做什么?)3. 特殊疑问句(疑问词 + 助动词 + 主语 + 动词)例如:Where did you go last summer?(你去哪里过去暑假?)三. 否定句1. 主语 + 助动词 + not + 动词例如:He does not like carrots.(他不喜欢胡萝卜。
)2. 主语 + do/does not + 动词例如:I do not play tennis.(我不打网球。
)四. 复合句1. 主从句主从句结构由一个主句和一个或多个从句组成。
从句可以是名词从句、形容词从句或副词从句。
例如:I know that she is a teacher.(我知道她是一名老师。
)I like the book which is on the table.(我喜欢桌上的那本书。
)2. 并列句并列句由两个或多个主句组成,它们之间用逗号或连词连接。
例如:I like apples, but my sister likes oranges.(我喜欢苹果,但是我妹妹喜欢橙子。


小学英语句式梳理汇总一、否定句:表示某一否定意思。
句中一定有not。
有三种可能:be动词(am、is、are、was、were)+not、情态动词(can、must、should)+not、助动词(do、does、did)+not 如何将一个肯定的陈述句改为否定句:1、看句中有无be动词,如有,直接在be动词后+not。
2、看句中有无情态动词,如有,直接在情态动词后+not。
3、如上述二者都没有,就应用助动词+not。
分四个步骤:(1)肯定陈述句中本来是没有助动词的,要加上去,位置在主语(某人或某物)后,动词前。
(2)确定助动词用do、does还是did,根据句中动词,动词是原形的助动词就用do,动词是第三人称单数的助动词就用does,动词用过去式的助动词就有did。
(3)在助动词后加not。
(4)原句中动词假如发生变化就要恢复成原形。
强调一点,有some的要考虑是否要用any。
二、一般疑问句。
表示疑问,一般回答只有两种可能Yes,……或No,……句中没有疑问词。
如何将一个肯定的陈述句改为否定句:1、看句中有无be动词,如有,把be动词提到句首即可。
2、看句中有无情态动词,如有,把情态动词提到句首即可。
3、如上述二者都没有,就应把助动提到句首。
分四个步骤:(1)肯定陈述句中本来是没有助动词的,要加上去,位置在主语(某人或某物)后,动词前。
(2)确定助动词用do、does还是did,根据句中动词,动词是原形的助动词就用do,动词是第三人称单数的助动词就用does,动词用过去式的助动词就有did。
(3)把助动词后提到句首。
(4)原句中动词假如发生变化就要恢复成原形。
强调一点,有some的要考虑是否要用any。
三、特殊疑问句。
表示疑问,有疑问词(在开头),回答有很多种可能。
常用疑问词:What、When、Which、Who、Whose、Why、How如何对划线部分提问:1、将原问句翻译为汉语(在读中要将划线部分重读)。
小学英语句型结构一、什么是句型结构句型结构指的是句子的基本组成方式,它由主语、谓语和宾语组成,用来表达完整的意思。
在研究英语的过程中,掌握句型结构是非常重要的,因为它直接影响到句子的准确性和流畅性。
二、常见的句型结构1. 主语+谓语这是最简单的句型结构,主语是句子中的主要执行者,谓语表示主语的动作、状态或特征。
例句:- Cats sleep.(猫睡觉。
)- I study.(我研究。
)2. 主语+谓语+宾语这是一个更加完整的句型结构,宾语是动作的承受者或影响者。
例句:- She eats an apple.(她吃了一个苹果。
)- We love our parents.(我们爱我们的父母。
)3. 主语+谓语+宾语+宾补宾补用来进一步说明宾语,通常是形容词、名词、代词等。
例句:- They made him the captain.(他们让他成为队长。
)- The teacher declared the student the winner.(老师宣布学生是胜利者。
)4. 主语+谓语+间宾+直宾间宾是动作发生的“对象”,而直宾是动作的“承受者”。
例句:- He bought me a book.(他给我买了一本书。
)- She cooked her family a delicious meal.(她给她的家人煮了一顿美味的饭菜。
)5. 主语+谓语+宾语+宾补+间宾这是较为复杂的句型结构,同时包含了宾补和间宾。
例句:- He made his sister the monitor of their class.(他让他的妹妹成为他们班的班长。
)6. 主语+谓语+宾语+宾补+直宾这是句型结构中最复杂的一种形式,同时包含了宾补和直宾。
例句:- We consider her a good teacher.(我们认为她是一位好老师。
)需要注意的是,以上仅为常见句型结构的介绍,实际上英语中还存在许多其他的句型结构,如倒装句、感叹句等,需要通过不断研究和练来掌握。
第一部分:语法知识(词类)一.名词:名词单复数,名词的格式(一)名词单复数1.一般情况,直接加-s,如:book-books, bag-bags, cat-cats, bed-beds2.以s. x. sh. ch结尾,加-es,如:bus-buses, box-boxes, brush-brushes, watch-watches3.以“辅音字母+y”结尾,变y为i, 再加-es,如:family-families, strawberry-strawberries4.以“f或fe”结尾,变f或fe为v, 再加-es,如:knife-knives5.不规则名词复数:man-men, woman-women, policeman-policemen, policewoman-policewomen,mouse-mice,child-children, foot-feet, tooth-teeth, fish-fish, people-people, Chinese-Chinese, Japanese-Japanese不可数名词的复数就是原型:paper, juice, water, milk, rice, tea(二)名词的格(1) 有生命的东西的名词所有格:a) 单数后加’s 如: Lucy’s ruler my father’s shirtb) 以s 结尾的复数名词后加’如: his friends’ bagsc) 不以s 结尾的复数后加’s children’s shoesd)并列名词中,如果把’s加在最后一个名词后,表示共有, 如:Tom and Mike’s car 汤姆和迈克共有的小汽车要表示所有物不是共有的,应分别在并列名词后加’sTom’s and Mike’s cars 汤姆和麦克各自的小汽车(2)表示无生命东西的名词通常用“ of +名词”来表示所有关系:如:a picture of the classroom a map of China二.冠词:不定冠词,定冠词1.种类:(1)不定冠词:a / an a unit / an uncle元音开头的可数名词前用an :an egg / an apple / an orange / an eraser / an answer / an ID card / an alarm clock / an actor / an actress / an e-mail / an address / an event / an example / an opera / an houran old man / an interesting book / an exciting sport / an action movie / an art lesson /(2)定冠词:the the egg the plane2. 用法:定冠词的用法:(1)特指某(些)人或某(些)物:The ruler is on the desk.(2)复述上文提到的人或物:He has a sweater. The sweater is new.(3)谈话双方都知道的人或物:The boys aren’t at school.(4)在序数词前:John’s birthday is February the second.(5)用于固定词组中:in the morning / afternoon / evening不用冠词的情况:(1)专有名词前:China is a big country.(2)名词前有定语:this , that , my , your , some, any , no 等:This is my baseball.(3)复数名词表示一类人和事:Monkeys can’t swim. They are teachers.(4)在节日,日期,月份,季节前:Today is Christmas Day. It’s Sunday.(5)一日三餐前:We have breakfast at 6:30.(6)球类棋类运动前:They often play football after class. He plays chess at home(7)学科名称前:My favorite subject is music.(8)在称呼或头衔的名词前:This is Mr Li.(9)固定词组中:at noon at night by bus三、代词、形容词、副词1.代词:人称代词(主格,宾格),物主代词第一人称单数I(我)me my(我的)复数we(我们)us our(我们的)第二人称单数you(你)you your(你的)复数you(你们)you your(你们的)第三人称单数he(他)him his(他的)she(她)her her(她的)it(它)it its(它的)复数they(他们/她们/它们)them their(他们的/她们的/它们的)2.形容词,副词:比较级,最高级(一)形容词的比较级1、形容词比较级在句子中的运用:两个事物或人的比较用比较级,比较级后面一般带有单词than。
语法总结(一)一.一般疑问句---Do you go to the park on Saturday? ---Yes, I do. /No, I don’t.---Do you like cats? ---Yes, I do. /No, I don’t.---Do you have long arms? ---Yes, I do. /No, I don’t.---Do you like spring? ---Yes, I do. /No, I don’t (like spring).---Do you like summer? ---Yes, I do. /No, I don’t (like summer).---Do you like autumn? ---Yes, I do. /No, I don’t (like autumn).---Do you like winter? ---Yes, I do. /No, I don’t (like winter).---Do you have a lot of snow in winter? ---Yes, we do. /No, w e don’t. ---Do you have a lot of rain in autumn? ---Yes, we do. /No, we don’t. ---Do you have a lot of rain in summer? ---Yes, we do. /No, we don’t. ---Do you have a lot of snow in spring? ---Yes, we do. /No, we don’t. ---Do you want any sweet potatoes? ---Yes, please.---Do you want any biscuits? ---Yes, please.---Do you want chocolates? ---Yes, please.---Do you want a pancake? ---Yes, please.---Do you want to fly my new kite? ---Yes, I do. /Sorry, I can’t.---Do you want to go to the bookstore? ---Yes, I do. /Sorry, I can’t.---Do you want to go to the cinema? ---Yes, I do. /Sorry, I can’t.---Do you want to go for lunch now? ---Yes, I do. /Sorry, I can’t.---Does he come by taxi? ---Yes, he does. /No, he doesn’t.---Does he go to the park by subway? ---Yes, he does. /No, he doesn’t. ---Does he go to the hospital by bus? ---Yes, he does. /No, he doesn’t.---Did you go to see your grandparents? ---Yes, I did. /No, I didn’t.---Did she return the books? --- Yes, I did. /No, I didn’t.---Did they win the football match? --- Yes, I did. /No, I didn’t.---Can I have fish and rice, please? ---Yes, here you are.---Can I have fried rice, please? ---Yes, here you are.---Can I have rice noodles, please? ---Yes, here you are.---Can I have a fried egg, please? ---Yes, here you are.---Can I use the bathroom, please? ---Sure. / Sorry you can’t.---Can I use the towel, please? ---Sure. / Sorry you can’t.---Can I use the soap, please? ---Sure. / Sorry you can’t.---Can I use the shampoo, please? ---Sure. / Sorry you can’t.---Can I use the toothpaste, please? ---Sure. / Sorry you can’t.---Can you play ping-pong with me? ---I’m sorry I can’t. /Yes, let’s go.---Can you play basketball with me? ---I’m sorry I can’t. /Yes, let’s go.---Can you go ice-skating with me? ---I’m sorry I can’t. /Yes, let’s go.---Can you fly a kite with me? ---I’m sorry I can’t. /Yes, let’s go.---Can you tell me more about Halloween? ---Children dress up at night and knock on doors for candy. ---Can you tell me more about The Dragon Boat Festival? ---People have dragon boat races and eat zongzi.---Can you tell me more about Thanksgiving? ---Families get together and eat turkey.---Can you tell me more about Easter? ---Children have an Easter egg hunt.---Can I open the gift now? ---Plea se do. /Please don’t.---Can I have some ice cream now? --- Please do. /Please don’t.---Can I go home now? --- Please do. /Please don’t.---Can I go swimming with Maomao now? ---Please do. /Please don’t. ---Can I borrow your ping-pong bat? ---Yes, of course.---Can I borrow your markers? ---Yes, of course.---Can I borrow your ruler? ---Yes, of course.---Can I borrow your scissors? ---Yes, of course.---Can I borrow your crayons? ---Yes, of course.---Can I borrow your pencil sharpener? ---Yes, of course.---Can I use your computer? ---Sorry. I need to finish my homework first. ---Can I open the gift box? ---Sorry. It’s not for you.---Can I go out and play? ---Sorry. It’s raining outside.---Can I watch the cartoons? ---Sorry. Dad is watching the news.---Would you like to come to my room? ---Yes, we’d love to.---Would you like to read my books? ---Yes, we’d love to.---Would you like to ride my bike? ---Yes, I’d love to.---Would you like to play with my toys? ---Yes, I’d love to.---Would you like to use the glasses? ---No, thank you.---Would you like to use the spoon? ---No, thank you.---Would you like to use the bowl? ---No, thank you.---Would you like to use the chopsticks? ---No, thank you.---Would you please hold these books for me? ---No problem.---Would you please close the window for me? ---No problem.---Would you please turn off the light for me? ---No problem.---Would you please pass me the water for me? ---No problem.---Would you mind opening the door, please? ---Sure. No problem.---Would you mind turning off the radio, please? ---Sure. No problem.---Would you mind turning on the light, please? ---Sure. No problem.---Would you like to come to my house? ---Sorry I can’t. I must stay at home. ---Would you like to walk the dog? ---Sorry I can’t. I must tidy my room.---Is this your jacket? ---Yes, it is. /No, it isn’t.---Is this your watch? ---Yes, it is. /No, it isn’t.---Is this your cap? ---Yes, it is. /No, it isn’t.---Is this your football? ---Yes, it is. /No, it isn’t.---Is the second class Chinese? --- Yes, it is. /No, it isn’t.---Is the sixth class Maths? --- Yes, it is. /No, it isn’t.---Is the fifth class English? --- Yes, it is. /No, it isn’t.---Is the seventh class PE? --- Yes, it is. /No, it isn’t.---Is Guoguo there? ---Sorry, she is not home/here.---Is Sara there? ---Sorry, she is not home/here.---Is Maomao there? ---Sorry, he is not home/here.---Are these your trousers? ---Yes, they are. /No, they are not.---Are these your shorts? ---Yes, they are. /No, they are not.---Are these your socks? ---Yes, they are. /No, they are not.---Are these your shoes? ---Yes, they are. /No, they are not.---Are you going to run a race? ---Yes, I am. /No, I am not.---Are you going to do the high jump? ---Yes, I am. /No, I am not.---Are you going to do the long jump? ---Yes, I am. /No, I am not.---Are you going to jump the rope? ---Yes, I am. /No, I am not.---Are you going to Chengdu by train? ---No, we are going by plane.---Are you going to the Bird’s Nest by car? ---No, we are going by subway.---Are you going to the Summer Palace by bus? ---No, we are going by taxi.---May I borrow your markers, please? ---Here you are.---May I borrow your eraser, please? ---Here you are.---May I borrow your ruler, please? ---Here you are.---May I borrow your books, please? ---Here you are.---May I borrow your pencil, please? ---Here you are.---May I have a cup of milk tea, please? ---Sure.---May I have a cup of black tea, please? ---Sure.---May I have a cup of green tea, please? ---Sure.---May I look at that pair of shoes, please? ---Sure. Here you are.---May I look at that pair of slippers, please? --- Sure. Here you are.---May I look at these boots, please? --- Sure. Here you are.---May I look at these sandals, please? --- Sure. Here you are.---May I look at those sneakers, please? --- Sure. Here you are.---May I take your order now? ---Yes, I’d like/ I’ll have a salad, fish, and mushroom soup.---May I take your order now? ---Yes, I’d like/ I’ll have a pizza, a glass o f juice, and a sandwich. ---Will Dad drive us there? ---Yes, he will.---Will Mike come for dinner? ---Yes, he will.---Will your sister come to see us? ---Yes, she will.---Will you take football lessons? ---Yes, I will. /No, I won’t.---Will you take ballet lessons? ---Yes, I will. /No, I won’t.---Will you take computer lessons? ---Yes, I will. /No, I won’t.---Will you take piano lessons? ---Yes, I will. /No, I won’t.---The windows are dirty. Shall we clean them this afternoon? ---Yes, let’s. ---The bike is broken. Shall we fix it this afternoon? ---Yes, let’s.---The plants are dry. Shall we water them this afternoon? ---Yes, let’s.二.特殊疑问句---What do you do on Saturday? ---I often go to see a film.---What do you do on Sunday? ---I go to the zoo.---What do you collect? ---I collect rulers. I have forty.---What do you collect? ---I collect crayons. I have thirty.---What do you collect? ---I collect cards. I have fifty.---What do you collect? ---I collect stickers. I have sixty.---What do you see in spring? ---The trees turn green.---What do you see in spring? ---The butterflies dance.---What do you see in spring? ---The bears wake up.---What do you want to be? ---I want to be a writer.---What do you want to be? ---I want to be a singer.---What do you want to be? ---I want to be a dancer.---What do you want to be? ---I want to be a football player.---What does your father do? ---He is a teacher.---What does your father do? ---He is a policeman.---What does your mother do? ---She is a dentist.---What does your father do? ---He is a worker.---What does she wear on stage? ---She wears pretty dresses.---What does he wear at work? ---He wears a suit with a tie.---What does she wear at school? ---She wears formal clothes.---What did you do this summer? ---I went back to Canada.---What did you do this summer? ---I wrote a story.---What did you do this summer? ---I made cakes.---What did you say? ---I said you should stop eating too much.---What did your father say? ---He said I should stop playing computer games. ---What did the doctor say? ---He said I should stop smoking.---What is your number? ---My number is twelve.---What is (What’s) this? ---It is (It’s) an elephant.---What is(What’s) for breakfast? ---We have bread, milk, eggs, and fruits. ---What is (What’s) the ninth month in English? ---It’s September.---What is (What’s) the tenth month in English? ---It’s October.---What is (What’s) the eleventh month in English? ---It’s November.---What is (What’s) the twelfth month in English? ---It’s October.---What’s your favourite food? ---It’s jiaozi.---What’s your favourite food? ---It’s noodles.---What’s your favourite food? ---It’s fried fish.---What’s your favourite food? ---It’s meat balls.---What is the date today? ---It’s October the thirteenth.---What is the date today? ---It’s November the seventeenth.---What is the date today? ---It’s November the eighteenth.---What is the date today? ---It’s December the twenty-third.---What is the date today? ---It’s December the twenty-second. ---What is (What’s)the weather like today? ---It’s sunny.---What is (What’s)the weather like today? ---It’s warm.---What is (What’s)the weather like today? ---It’s cool.---What is (What’s)the weather like today? ---It’s cold.---What is (What’s)the weather like today? ---It’s hot.---What is he wearing? ---He is wearing a blue suit with a silver tie. ---What is she wearing? ---She is wearing a denim skirt.---What is she wearing? ---She is wearing jeans.---What is he wearing? ---He is wearing a hoody.---What is she wearing? ---She is wearing pajamas.---What’s your favourite game? ---It’s rugby.---What’s your favourite game? ---It’s tennis.---What’s your favourite game? ---I t’s badminton.---What’s your favourite game? ---It’s ice hockey.---What’s your favourite game? ---It’s basketball.---What’s your favourite game? ---It’s baseball.---What’s your favourite game? ---It’s volleyball.---What’s your watch like? ---It’s square, and It’s black.---What’s your box like? ---It’s round, and it’s red.---What’s your clock like? ---It’s round, and it’s pink.---What’s your eraser like? ---It’s square, and it’s green.---What shapes do you see in the house? ---I see a triangle.---What shapes do you see in the bus? ---I see two circles.---What shapes do you see in the ship? ---I see five rectangles.---What size do you wear? ---I wear a Medium and she wears a Large.---What size do you wear? ---I wear a 34 and he wears a 42.---What size do you wear? ---I wear an XS and she wears a XL.---What are you going to do this afternoon? ---We are going to plant trees.---What are you going to do this morning? ---We are going to make a cake.---What are they going to do today? ---They are going to see the monkeys at the zoo. ---What are they going to do this evening? ---They are going to make a card.---What are you doing? ---I’m making a card.---What are you doing? ---I’m playing a game.---What are you doing? ---I’m listening to music.---What are you good at? ---We are good at ice sports.---What are you good at? ---We are good at table tennis.---What are you good at? ---We are good at diving.---What time are we going to leave? ---We are going to leave at 7:30.---What time are we going to get up? ---We are going to get up at 6:30.---What time are we going to have breakfast? ---We are going to have breakfast at 7:00.---What time are we going to visit the palace? ---We are going to visit the palace at 8:30.---What time are we going to meet at the gate? ---We are going to meet at the gate at 12:00.---What time are we going to have lunch? ---We are going to have lunch at 12:30.---What time are we going to leave for the museum? ---We are going to leave for the museum at 13:30. ---What time are we going to have dinner? ---We are going to have dinner at 17:30.---What time are we going to leave for the show? ---We are going to leave for the show at 18:30.---What time are we going to get back to the hotel? ---We are going to get back to the hotel at 21:30. ---What would you like to eat? ---I’d like some vegetables.---What would you like to eat? ---I’d like some meatballs.---What would you like to have? ---I’d like Peking Duck.---What would you like to have? ---I’d like some ji aozi.---What would you like to drink? ---I’d like a glass of soy milk.---What would you like to drink? ---I’d like a glass of orange juice.---What will you do in Sichuan? ---I will visit Du-jiang-yan.---What will you do in Shandong? ---I will visit Mount Tai.---What will you do in Tibet? ---I will visit the Potala Palace.---What will you do in Gansu? ---I will visit the Mogao Caves.---What happened to you? ---I hurt my right leg.---What happened to you? ---My cat scratched me.---What happened to you? ---I broke my arm.---How many pigs do you have on your farm? ---I have sixteen pigs.---How many girls do you have in your class? ---We have nineteen girls.---How many seasons are there in a year? ---There are four.---How many days are there in a week? ---There are seven.---How many hours are there in a day? ---There are twenty-four.---How many stars are there? ---There are five yellow stars, one big star and four small ones.---How many pencils are there? ---There are five pencils, three long pencils and two short ones.---How many cats are there? ---There are four cats, one big cat and three small ones.---How many monkeys are there? ---There are three monkeys, one old monkey and two young ones.---How many medals did the Chinese athletes win? ---They won 51 gold medals, 21 silver medals, and 28 bronze medals.---How many shirts did he buy? ---He bought three shirts.---How many books did she borrow? ---She borrowed six books.---How much is it? ---It’s sixty-nine yuan. ---Here is the money. ---Here is your change.---How much is it? ---It’s eight yuan. ---Here is the money. ---Here is your change.---How much is it? ---It’s three yuan. ---Here is the money. ---Here is your change.---How much is it? ---It’s twenty yuan. ---Here is the money. ---Here is your change.---How old are you? ---I am(I’m) eight.---How old is your girl? ---She is eight.---How old is he? ---He is eight.---How often does each animal come around? ---Every twelve years.---How often does the girl go to the dentist? ---Every six months.---How often does the boys practice together? ---Every three days.---How is the weather in Sydney? ---Bad. It’s raining.---How is the weather in Kunming? ---Fine. The sun is shining.---How is the weather in Alaska? ---Cold. It’s snowing.---How does your dad go to work? ---He goes to work by car.---How does your mum go to work? ---She goes to work by taxi.---How does Lingling go to see her grandparents? ---She goes to see them by subway. ---How do you go to school? ---I go to school by bus.---How do you go to the cinema? ---I go to the cinema by bike.---How do you go to the zoo? ---I go to the zoo on foot.---How did you go to Hangzhou? ---We went there by air.---How did you go to the Spring Festival Fair? ---We went there on foot.---How did you go to the train station? ---We went there by taxi.---How did you go to Shanghai? ---We went there by train.---I will dance. How about you? ---I will play the piano.---I will play the drum. How about you? ---I will do magic tricks.---When do you go home? ---At five thirty.---When do you get up? ---At sixty thirty.---When do you go to school? ---At seven thirty.---When do you go to bed? ---At nine thirty.---When did you came back? ---I came back last Thursday.---When did he go to the airport? ---He went to the airport last Monday morning.---When did she finish the piano lessons? ---She finished the piano lessons last week. ---When is Teachers’ Day? ---It’s September the tenth.---When is Thanksgiving? ---It’s in November.---When is Halloween? ---It’s in October.---When is Christmas? ---It’s in December.---When is New Year’s Day? ---It’s in January.---When is Kevin’s birthday? ---It’s September the eighth.---When is Susan’s birthday? ---It’s September the ninth.---When is your birthday? ---It’s in March.---When is your birthday? ---It’s in April.---When is your birthday? ---It’s in May.---When is your birthday? ---It’s in June.---When is your birthday? ---It’s in July.---When is your birthday? ---It’s in August.---When is the Mid-Autumn Festival? ---It’s on the fifteenth day of the eighth month in the Chinese calendar.---When is the Double Ninth Festival? ---It’s on the ninth day of the ninth month in the Chinese calendar. ---When is the Lantern Festival? ---It’s on the fi fteenth day of the second month in the Chinese calendar. ---When is the Dragon Boat Festival? ---It’s on the fifth day of the fifth month in the Chinese calendar. ---When was Grandma born? ---She was born on June 15th.---When was Grandpa born? ---He was born on February 9th.---When was mother born? ---She was born on August 14th.---When was father born? ---He was born on July 29th.---When did the ancient Olympic Games begin? ---They began in 776BC.---When did the Qin Dynasty begin? ---It began in 221BC.---When did the Tang Dynasty begin? ---It began in 618AD.---When did people hold the first modern Olympics? ---They held them in 1896 in Athens.---When did people hold the 29th modern Olympics? ---They held them in 2021 in Beijing.---When did people hold the 30th modern Olympics? ---They held them in 2021 in London.---Where is my shirt? ---It’s under the bed.---Where is my coat? ---It’s behind the sofa.---Where is my cap? ---It’s on the desk.---Where is my dress? ---It’s in the box.---Where is the UK? ---It’s in Europe.---Where is China? ---It’s in Asia.---Where is the USA? ---It’s North Am erica.---Where is Australia? ---It’s in Oceania.---Where is Canada? ---It’s in North America.---Where is Russia? ---It’s in Asia.---Where is Ottawa? ---It’s in the east of the country.---Where is Shanghai? --- It’s in the east of the country.---Where is Lhasa? ---It’s in the west of the country.---Where is Hohhot? ---It’s in the north of the country.---Where is Guangzhou? ---It’s in the south of the country. ---Where are you from? ---I’m from New York in the USA. ---Where are you from? ---I’m from Toronto in Canada.---Where are you from? ---I’m from Sydney in the Australia. ---Where does he live? ---He lives on a farm.---Where does he live? ---He lives in the forest.---Where does he live? ---He lives by the lake.---Where does he live? ---He lives on the grassland.---Where does he live? ---He lives in the mountains.---Where did you go last weekend? ---We flew to Hangzhou.---Where did you go yesterday afternoon? ---We drove to Xiangshan.---Where did you go on Friday morning? ---We took the train to Tianjin.---Which season do you like? ---I like spring. I can fly a kite.---Which season do you like? ---I like summer. I can go camping.---Which season do you like? ---I like autumn. I can pick apples.---Which season do you like? ---I like winter. I can play in the snow.---Which kind would you like? ---This one looks nice.---Which colour would you like? ---This one looks nice.---Which shape would you like? ---This one looks nice.---Which animal was the first of the twelve? ---It was the rat.---Which season is the first of the four? ---It is spring.---Which month is the first of the year? ---It is January.---Chicken or fish, which do you like better? ---I like fish better.---Sandwiches or hamburgers, which do you like better? ---I like hamburgers better. ---Donuts or cupcakes, which do you like better? ---I like cupcakes better.---Milk shake or apple juice, which do you like better? ---I like apple juice better.---Which class do you like best? ---I like English best. I do best in English.---Which class do you like best? ---I like English PE. I do best in PE.---Which class do you like best? ---I like Chinese best. I do best in Chinese.---Which class do you like best? ---I like calligraphy best. I do best in calligraphy.---Which class do you like best? ---I like science best. I do best in science.---Which class do you like best? ---I like art best. I do best in art.---Why are you so happy? ---Because we are back at school.---Why are you upset? ---Because my new watch is missing.---Why are you worried? ---Because my English book is missing.---Why are you sad? ---Because my new football is missing.---Why is she so angry? ---Because the room is messy.---Why is he so tired? ---Because he played too hard.---Why do you look so sad? ---Because my dog is missing.---Why does he look so surprised? ---Because the gold is missing.---Why do they look so excited? ---Because they will go to the zoo.---Why did you stand on your head? ---Because I wanted to practice kungfu. ---Why did she cry? ---Because she fell.---Why did you go to hospital? ---Because I cut my finger.---Who invented those vehicles? ---Some smart people did.---Who invented the plane? ---The Wright brothers did.---Who invented the telephone? ---Mr. Bell did.。
三年级至五年级英语语法
(实用版)
目录
1.三年级英语语法概述
2.四年级英语语法概述
3.五年级英语语法概述
4.三至五年级英语语法的共同点和不同点
正文
【三年级英语语法概述】
三年级英语语法主要涉及基础的词法和句法规则,包括名词、动词、形容词、副词、代词、介词等词类的使用,以及简单句子的构成。
此阶段的英语语法学习,重在培养学生对英语语言的基本认知和运用能力。
【四年级英语语法概述】
四年级英语语法在三年级的基础上,增加了时态、被动语态、疑问句和祈使句等语法知识点。
时态方面,主要学习一般现在时、一般过去时和一般将来时。
被动语态则主要涉及 be done 结构。
此外,学生还需学习
如何构成简单的疑问句和祈使句。
【五年级英语语法概述】
五年级英语语法进一步扩展,引入了情态动词、名词从句、状语从句等较复杂的语法知识点。
情态动词表示说话人的可能性、许可、建议等语气,是英语口语和书面语中不可或缺的组成部分。
名词从句和状语从句则涉及从句的构成和使用。
【三至五年级英语语法的共同点和不同点】
三至五年级英语语法的共同点在于,都以基础的词法和句法规则为主,
重在培养学生的语言运用能力。
不同点在于,随着年级的升高,语法知识点逐渐增多,难度逐渐加大。
小学英语语法句法
句法主要研究句子的成分,语序以及句子的种类,类型等的内容。
一,句子成分
组成句子的各个部分叫句子成分。
根据词汇在句子中的不同作用,英语句子主要含有以下六个成分:主语,谓语,表语,宾语,定语,状语。
句子主要由主语和谓语两部分组成。
1.主语主语是句子的主体,表示所说的是谁一或是什么。
主语的位置一般放在句首,有时在特殊句型中主语放在句末。
I go to school by bike every day.
2.谓语用来说明主语的动作,特征或状态等。
谓语主要有两种形式:动词谓语(包括动词短语)和复合谓语(系动词+表语)。
This happened in 1990. (动词谓语)
He must take good care of his little sister at home today. (动词短语)
The young man became a doctor . (系动词+表语)
Trees turn green in spring. (系动词+表语)
3.表语用来说明评语的身份,特征和状态等。
它通常位于系动词的后面,可作表语的有名词,代词,数词,形容词等。
Is this pencil yours She is not at home.
4.宾语是动作的承受者。
及物动词和相当于及物动词的短语都必须有宾语,可作宾语的有名词,代词,数词等。
句子作宾语和叫宾语从句。
有些及物动词可以有两个宾语:一个指人,一个指物。
W e are waiting for Lily. He knows he should work hard.
5.宾语补足语用来说明补充宾语,与宾语一起构成复合宾语。
可作宾语补足语的有名词,形容词,副词等。
Let me do it . We must keep the classroom clean every day.
6.定语用来修饰名词或代词的句子成份。
形容词作定语时,一般放在名词前面,副词或副词短语作定语时,放在名词后面。
可作定语的有名词,代词,数词形容词,副词等。
Spring is the first season of a year. The bike under the tree is mine.
7.状语是修饰动词,形容词,副词等的句子成分,说明时间,地点,目的,结果,条件,原因,方式等。
She studies very hard. They are working in the park.
二.句子的种类
根据英语所表示的不同功用,它们可分为陈述句,疑问句,祈使句,感叹句四种种类。
1.用来说明事实或陈述说话人看法的句子叫陈述句。
陈述句Uncle Wang likes making things.
2.用来提出问题的句子叫作疑问句。
疑问句有三种:一般疑问句,特殊疑问句,选择疑问句。
Was he hete a month ago Whose bike do you want to borrow
Would you like coffee or tea
3.表示请求,命令或劝告等的句子叫祈使句。
它通常省略主语(you)。
根据语气的强弱,句末用感叹号或句号,句子用降调说或读。
祈使句有肯定式祈使句,否定式祈使句和let 开头的祈使句。
Stop playing !Listen to me !
Let’s go together! Let’s not wait for him.
4.用来表示说话人强烈的喜怒哀乐等情绪的句子叫感叹句。
多用how和
What 引起,,how 和what 所修饰的词放在句首,其它部份用陈述语序。
在口语当中为主常常省略,句末用感叹句,句子用降调读或说。
感叹句的表达方式:what作定语修饰名词(名词前有其它定语),单数可数名词前要加不定冠词 a/an. What a good idea! What beautiful flowers (they are)!
How作状语修饰形容词,副词或动词,结构为:how +形容词(副词)+主语+谓语
或“how +主语+谓语”(这时how直接修饰谓语动词)
How hard he works! How fast he is running!
How I wanted to see you!(how修饰谓语动词)
5.there be 结构英语里有一个独特的句型叫there be 句型,这个“there be +.....”结构表示“某地或某时间存在某事物”。
There 是无意义的引导词,be 是谓语动词,它后面的名词是主语,两者在数上必须要一致,句子最后为地点或时间状语。
There are seven days in a week .
There isn;t a/any student in the reading room. Is there anything I can do for you
How many boats are there on the lake
*there be 表示“某地某时存在某物”,而have则表示“某人某地方拥有”,表示“所有,拥有关系”。
There are sis books in her schoolbag.(只表示存在) Our school has a bus.(表示拥有)。