英汉笔译基础教程 第2章 中国翻译史简介
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:1.42 MB
- 文档页数:37


Unit2 HistoryLesson 4 (E—C)Ngland Before the Idndustrial RevolutionThe contry was a place where men worked form dawn to dark, and the labourer lived not in thd sun, but in poverty and karkness. What aids there were to lighten labour were immemorial, like the mill, which was already ancient in Chaucer’s time. The Industrial Revolution began with such machines; the millwrights were the engineers of the coming age. James Brindley of Staffordshire started his self-made career in 1733 by working at mill wheels, at the age of seventeen, having been born poor in a illage.Brindley’s improvements were practical: to sharpen and step up the performance of the water wheel as a machine. It was the first multi-purpose machine for the new industries. Brindley worked, for example, to improve the grinding of flints, which were used in the rising pottery industry.Yet there was a bigger movement in the air by 1750. water had become the engineers’element, and men like Brindley were possessed by it. Water was gushing and fanning out all over the countryside. It was not simply a source of power, it was a new wave of movement. James brindley was a pioneer in the art of building canals or, as it was then called, ‘navigation’.Brindley had begun on his own account, out of interest, to survey the waterways that he travelled as he went about his engineering projects for mills and mines. The Duke of Bridgewater then got him to build a canal to carry coal from the Duke’s pits at Worsley to the rising town of Manchester…. Brindley went on to connect Manchester with Liverpool in an even bolder manner, and in all laid out almost four hundred miles of cannals in a network all over England.Two things are outstanding in the creation of the English system of canals, and they characterise all the Industrial Revolution. One is that the men who made the revolution were practical men. Like Brindley, they often had little education, and in fact school education as it then was could only dull an inventive mind. The grammar schools legally could only teach the classical subjects for which they had been founded. The universities also(there were only two, at Oxford and Cambridge) took little interest in modern or scientific studies; and they were closed to those who did not conform to the Church of England.The other outstanding feature is that the new invetions were for veryday use. The canals were arteries of communication: They were not made to carry pleasure boat, but barges. And the barges were not made to carry luxuries,but pots and pans and bales of cloth, boxes of ribbon, and all the common things that people buy by the pennyworth. These things had been manufactured in villages which were growing into towns now, away from London; it was a country-wide trade.(from J. Bronowski, The Ascent of Man)译文:工业革命前的英国在农村,人们从早到晚都得干活,劳动者并不是沐浴在阳光下,而是生活在贫困和黑暗中,那些帮助减轻劳动的机械都不知从哪个年代起就有了。


【免费下载】新编汉英翻译教程第二版第二章汉英翻译基础知识第二章汉英翻译基础知识1.探春笑道:“只恐又是你的杜撰。
”宝玉笑道:“除《四书》外,杜撰的太多,偏只我是杜撰不成?”“You're making that up, I'm afraid,” teased Tan Chun. “Most works, apart from the FOUR BOOKS, are made up; am I the only one who made things up?” he retorted with a grin. 2.贾母笑道:“你不认得他,他是我们这里有名的一个泼皮破落户儿,南省俗谓作‘辣子’,你只叫他‘凤辣子’就是了。
”“You don't know her, ”said Grandmother Jia merrily. “She's a holy terror this one. What we used to call in Nanking a ‘peppercorn ’. You just call her ‘Peppercorn Feng ’. She'll know who you mean!” (David Hawkes 译)3.贾母笑道:“外客未见,就脱了衣裳,还不去见你妹妹!”With a smile at Pao-yu, the Lady Dowager scolded, “Fancy changing your clothes before greeting our visitor. Hurry up now and pay your re spects to your cousin.”4.贾母笑道:“可又是胡说,你又何曾见过他?”、管路敷设技术通过管线敷设技术,不仅可以解决吊顶层配置不规范问题,而且可保障各类管路习题到位。
在管路敷设过程中,要加强看护关于管路高中资料试卷连接管口处理高中资料试卷弯扁度固定盒位置保护层防腐跨接地线弯曲半径标高等,要求技术交底。



第二章汉英翻译基础知识1.探春笑道:“只恐又是你的杜撰。
”宝玉笑道:“除《四书》外,杜撰的太多,偏只我是杜撰不成?”“You're makingthat up, I'm afraid,” teasedTan Chun. “Most works, apart from the FOUR BOOKS, are made up; am I the only one who made thingsup?” he retorte d with a grin.2.贾母笑道:“你不认得他,他是我们这里有名的一个泼皮破落户儿,南省俗谓作‘辣子’,你只叫他‘凤辣子’就是了。
”“You don't know her, ”said Grandmo ther Jia merrily. “She's a holy terrorthis one. What we used to call in Nanking a ‘pepperc orn’. You just call her ‘Pepperc orn Feng’. She'll know who you mean!” (David Hawkes译)3.贾母笑道:“外客未见,就脱了衣裳,还不去见你妹妹!”With a smile at Pao-yu, the Lady Dowager scolded, “Fancy changin g your clothes beforegreetin g our visitor. Hurry up now and pay your respect s to your cousin.”4.贾母笑道:“可又是胡说,你又何曾见过他?”“You're talking nonsens e again,”said his grandmo ther,laughin g. “How could you possibl y have met her?”5.他是只狡猾的老狐狸。

《英汉翻译教程》第一章:我国翻译史简介我国的翻译事业有约两千多年的光辉历史。
早在公元前六年西汉哀帝时代,伊存到中国口传一些佛教经句,但还谈不上佛教的翻译。
佛经的翻译是在东汉桓帝建和两年(公元148年)开始的,译者是安世高,他是安息人(即波斯),他译了《安般守意经》等三十多部佛经。
过些时候,娄迦谶来中国,因为他是月支人,所以又称支娄迦谶。
他也译了十多部佛经,但文笔生硬,不易看懂,所以从那时起,大概就有直译和意译这个问题了。
他有个学生叫支亮,支亮又有个弟子叫支谦,他们三人号称“三支”,都是当时翻译佛经很有名的人。
就在那时,月支派里出现了一个叫竺法护的大翻译家,他译了175部佛经,对于佛法的流传贡献很大。
但这些翻译活动还只是民间私人事业。
到了符秦时代,释道安设置了“译场”,成了有组织的活动,他本人不懂梵文,惟恐失真,主张严格的直译,在这期间他请来了天竺人(即印度)鸠摩罗什,他全改以前群家的直古风格,主张“意译”,他的译著为我国翻译文学奠定了基础。
到南北朝时,一个叫真谛的印度佛教学者应梁武帝之聘来到中国,他译了49部经论,对中国佛教思想有较大影响。
从隋代(公元590年)起到唐代,是我国翻译事业高度发达的时期,隋代有个释彦琮,梵文造诣很深。
在他以后出现了古代翻译界的巨星玄奘(与上述鸠摩罗什、真谛一起号称我国佛经三大翻译家),他成为第一个把汉文著作向国外介绍的中国人,他自创了“新译”。
从明代万历年间到清代“清学”时期,佛经翻译呈现一片衰落现象,但却出现了以徐光启、林纾(琴南)、严复(又陵)等为代表的介绍西欧各国科学、文学、哲学的翻译家。
徐光启和意大利人利玛窦合作,翻译了欧几里得的《几何原本》、《测量法义》等书。
林纾和他的合伙人以口述笔记的方式译了160多部文学作品,其中最著名的有《巴黎茶花女遗事》、《黑奴吁天录》、《块肉余生记》、《王子复仇记》等。
严复是我国清末新兴资产阶级启蒙思想家(曾担任过北大校长),等到八国联军战役以后,他避居上海,搞翻译工作,他“曾查过汉晋六朝翻译佛经的方法”,破天荒第一次在《天演论·译例言》里正面提出了信达雅作为译事楷模。

英汉翻译教程—张培基编著上海外语教育出版社绪论翻译:是运用一种语言把另一种语言所表达的思维内容准确而完整地重新表达出来的语言活动。
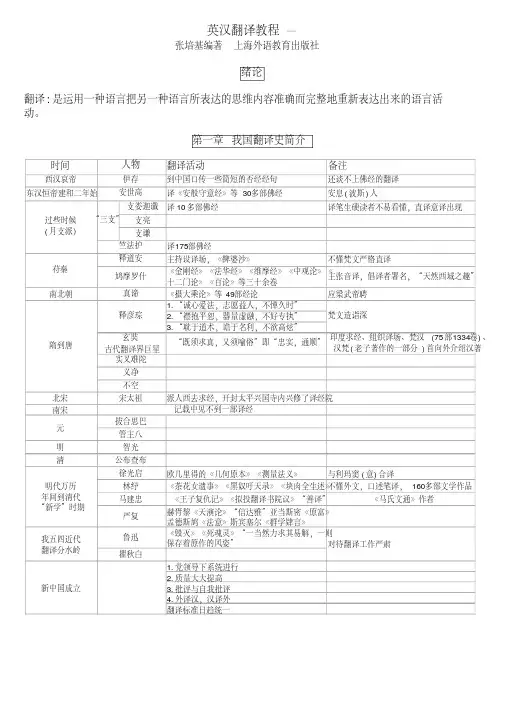
第一章我国翻译史简介时间翻译活动备注西汉哀帝到中国口传一些简短的否经经句还谈不上佛经的翻译东汉恒帝建和二年始译《安般守意经》等30多部佛经安息(波斯)人支娄迦谶译10多部佛经译笔生硬读者不易看懂,直译意译出现支亮支谦译175部佛经主持设译场,《鞞婆沙》不懂梵文严格直译《金刚经》《法华经》《维摩经》《中观论》《十二门论》《百论》等三十余卷主张音译,倡译者署名,“天然西域之趣”南北朝《摄大乘论》等49部经论应梁武帝聘1.“诚心爱法,志愿益人,不惮久时”2.“襟抱平恕,器量虚融,不好专执”3.“耽于道术,谵于名利,不欲高炫”北宋派人西去求经,开封太平兴国寺内兴修了译经院南宋明清欧几里得的《几何原本》《测量法义》与利玛窦(意)合译《茶花女遗事》《黑奴吁天录》《块肉全生述》不懂外文,口述笔译,160多部文学作品《王子复仇记》《拟投翻译书院议》“善译”《马氏文通》作者赫胥黎《天演论》“信达雅”亚当斯密《原富》孟德斯鸠《法意》斯宾塞尔《群学肄言》《毁灭》《死魂灵》“一当然力求其易解,一则保存着原作的风姿”1.党领导下系统进行2.质量大大提高3.批评与自我批评4.外译汉,汉译外翻译标准日趋统一人物伊存安世高明代万历年间到清代“新学”时期严复苻秦鸠摩罗什玄奘古代翻译界巨星马建忠林纾过些时候(月支派)竺法护“三支”“既须求真,又须喻俗”即“忠实,通顺”印度求经、组织译场、梵汉(75部1334卷)、汉梵(老子著作的一部分)首向外介绍汉著新中国成立管主八公布查布徐光启梵文造诣深释道安真谛对待翻译工作严肃我五四近代翻译分水岭实叉难陀义净宋太祖拔合思巴智光鲁迅瞿秋白元不空隋到唐记载中见不到一部译经释彦琮第二章翻译的标准、过程以及对译作的要求第一节翻译的标准忠实:忠于原作内容、保持原作风格通顺:通顺易懂、符合规范语言现象(词汇含义、句法结构、惯用法)理解逻辑关系原文所涉及的事物第二节翻译的过程表达直译:保持内容、形式(比喻、形象等)意译:正确表达原文内容,不拘泥于形式人名、地名、日期、方位、数字段、句、重要的词校核错或不妥的词、句无生僻字、陈腔滥调、标点符号校核两遍:内容、润饰蚊子对照原文通读一遍第二节对翻译工作者的要求1.坚定的无产阶级立场和较高的马克思主义、毛泽东思想的理论水平2.努力提高本族语和外语的水平3.不断吸收和丰富各种基础知识,对有关国家的历史、地理、政治、外交、经济、文化、科学、风俗习惯等。
翻译简史姓名:张静芳学号:201414331 学院:翻译学院指导老师:薄振杰中国翻译简史人类自有语言以来,操不同语言的人们要交流思想,达到相互理解,必须通过翻译作中介手段。
即所谓“洪荒造塔语言殊,从此人间要象胥”。
就中国而言,远在原始社会,各氏族或部落之间就应该有翻译活动,然而没有文献可供考究。
到了夏、商两代,现存的史料也是失之过简。
只有到了周王朝,才留下了关于翻译机构和译员职称的记载。
因此,中国的翻译史,只能从周代开始。
周王朝及其以后的各时代的政权,与周边诸民族(部族)或是国家交往,都设置了配有翻译人员的外事机构。
周朝有大行人下属的象胥,秦有典客和典属国,两汉有大鸿胪和尚书主客曹,魏晋南北朝和隋设有大鸿胪或鸿胪寺和主客司,唐有鸿胪寺、客省和礼部主客郎中,宋朝有鸿胪寺、中书省和礼部主客郎中,元朝有礼部下属的会同馆,明朝有鸿胪寺和礼部下属的主客清吏司,清朝有鸿胪寺、理藩院和礼部下属的会同四译馆以及后来改设的总理各国事务衙门,到光绪27年,将的总理各国事务衙门改为外务部,民国以及现在均称外交部,配有译员。
我国翻译至少已有三千多年历史。
但早期翻译,多属与周边民族(部族)或国家的交往,皆以口译为主。
中国翻译史上最早的口译情况的记录,应当是越裳国来使通过三象重译与周公姬旦的对话。
而我国翻译史上有文本的笔译,当始于东汉桓帝建和二年的印度佛经翻译。
由此可见,到东汉桓帝建和二年是我国历史上的口译阶段,而从东汉桓帝建和二年至今则应是口笔译并行的阶段。
季羡林老先生曾经把中华文化比作一条长河,它之所以永不枯竭,是因为不断有新水注入,历史上最大的有两次,一次是从印度来的水,一次是从西方来的水,而这两次的大注入,依靠的都是翻译(见《中国翻译词典序》)。
注入的印度之水,是指中国翻译史上的第一次翻译(即佛经翻译)高潮;注入的西方之水,是指中国翻译史上的第二次翻译(明末清初的西学翻译)高潮、第三次翻译(鸦片战争到“五四”的西学翻译)高潮以及当前的第四次翻译(改革开放以来的翻译)高潮。