机械工程专业英语讲课教案
- 格式:doc
- 大小:51.50 KB
- 文档页数:11

汽车制造与装配技术专业《机械工程英语》课程标准课程基本信息一、制订课程标准的依据本标准依据《汽车制造与装配技术专业教学标准》中的人才培养规格要求和对《机械工程英语》课程教学目标要求而制订。
根据学生毕业后从事的生产技术岗位,经过深入研究,设计接近生产实际的教学项目,满足企业对汽车制造与装配人员的需求;该标准用于指导《机械工程英语》课程教学与课程建设。
二、课程的性质本课程是汽车制造与装配技术专业的专业拓展课,是理论实践一体化(B 类)课程,主要介绍汽车构造与汽车制造与装配方面的专业英语,本课程以工作过程为导向,以本专业的英文资料为载体,为学生在需要英语基础的汽车企业的工作打下基础,并培养学生职业素养,是一门理论与实践一体、教学做一体的专业拓展课程。
三、本课程与其它课程的关系四、课程的教育目标(一)知识目标1)掌握本专业的常用英语词汇及用法。
2)了解汽车领域英语文章结构及体裁。
3)通过对英语资料的阅读、理解及翻译,掌握发动机、底盘和变速器等汽车组成部件的组成、结构、工作原理及零部件装配作业方法。
4)通过对英语资料的阅读、理解及翻译,掌握汽车制造四大工艺的流程与交流方式。
5)通过对英语资料的阅读、理解及翻译,掌握装配线常用英语词汇。
6)培养学生的英语阅读和翻译能力,以便更好地直接从国外资料中获取新的知识和信息。
(二)能力目标1)具备本专业的英语阅读和听说能力。
2)具备本专业的英语翻译能力。
3)具备从英语网站和原版英语装配资料中获取汽车制造及维修信息的能力,能从英文装配手册中获取信息,指导进行零部件装配工作。
4)具备通过过英文资料掌握汽车装配工具使用方法和工作原理的能力。
5)具备通过原版英语资料了解汽车行业的发展潮流和业界主流技术的能力。
(三)素质目标1)沟通能力及团队协作精神。
2)培养学生分析问题、解决问题的能力。
3)自主学习、查阅资料并解决问题的能力。
五、课程的教学内容与建议六、教学基本条件1.教学团队的基本要求1)从事本课程教学的教师,应具备以下相关知识、能力和资质:a.具有机械工程、发动机、汽车底盘、变速器、汽车电器、汽车电控技术、汽车空调等课程的理论知识,具备对汽车整车及零部件进行装配和调试的综合能力。

主要教学步骤和教学内容课程回顾:回顾Machines Using NC相关方面的内容新课讲授:Early machines tools were operated by craftsmen who decided many variables such as speeds. feeds, and depth of out, etc. With the development of science and technology, a new term, numerical control (NC) appeared. Controlling a machine tol using a punched tape or stored program is known as numerical control (NC). NC has been defined by the Electronic Industries Association (EIA) as “A system in which actions are controlled by the direct insertion of numerical data at some point. The system must automatically interpret at least some portion some portion of this datadj.”老式机床通常是由工人操作并由他们决定机床的速度、进给量、切屑深度等。
随着科学技术的发展,一个新的术语——数字控制(NC)诞生了。
数字控制就是利用穿孔纸带或储存的程序来控制机床。
每个电子工业协会把数控定义为"采用在某些点直接插入数字数据来控制操作的系统,此系统必须能够自动解释翻译这些信息中的一部分。
”1. Single-Spindle Drilling MachineOne of the simplest numerically controlled machine tools is the single-spindle drilling machine. Most drilling machines are programmed on three axes:a. The X-axis controls the table movement to the right and left.b. The Y-axis controls the table movement toward or away from the column.c. The Z-axis controls the up or down movement of the spindle to drill holes todepth.1.单轴钻床单轴钻床是最简单的数控机床之一。


主要教学步骤和教学内容课程回顾:回顾Hydraulics相关方面的内容新课讲授:Machine tools are machines for cutting metals.The most importantmachine tools used in industry are lathes,drilling machines. Other kinds of metal working machines are not so widely used in machine metals as these three kinds.机床是用来切削金属的机器。
工业上最重要的机床有车床、钻床和铣床。
其他种类的机床没有这三种使用范围如此广泛。
A lathe is a machine tool for cutting metai form the surface of a round work fastened between the two lathe centers and turning around its axis . In turning the work a cutter moves in the direction paraiiel to the axis of rotation of the work or at an angel to this axis,cutting off the metai from the surface of the work . This movement of the cutter is called the feed. The cutter is clamped in thetool post that is mounted on the carriage. The carriage is the mechanism feeding the cutter in the needed direction . The lathe may feed the cutter by hand or may make it be fed automatically by means of special gears.车床是一种机床,它用来切削装夹在车床两顶尖之间并且围绕轴线旋转的圆形工作表面的金属。

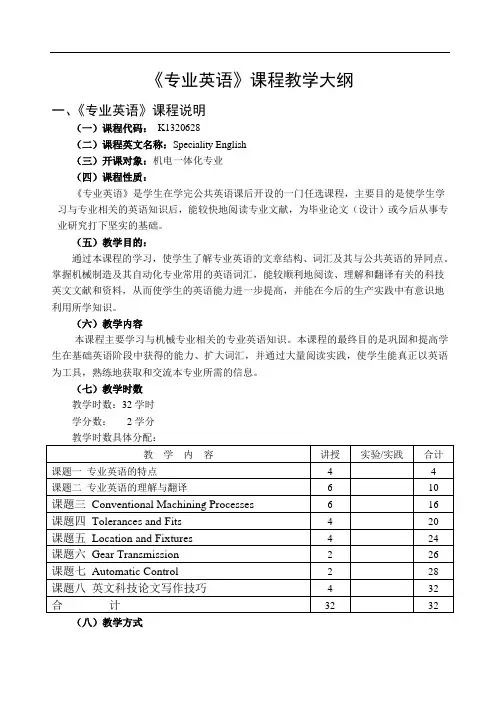
《专业英语》课程教学大纲一、《专业英语》课程说明(一)课程代码:K1320628(二)课程英文名称:Speciality English(三)开课对象:机电一体化专业(四)课程性质:《专业英语》是学生在学完公共英语课后开设的一门任选课程,主要目的是使学生学习与专业相关的英语知识后,能较快地阅读专业文献,为毕业论文(设计)或今后从事专业研究打下坚实的基础。
(五)教学目的:通过本课程的学习,使学生了解专业英语的文章结构、词汇及其与公共英语的异同点。
掌握机械制造及其自动化专业常用的英语词汇,能较顺利地阅读、理解和翻译有关的科技英文文献和资料,从而使学生的英语能力进一步提高,并能在今后的生产实践中有意识地利用所学知识。
(六)教学内容本课程主要学习与机械专业相关的专业英语知识。
本课程的最终目的是巩固和提高学生在基础英语阶段中获得的能力、扩大词汇,并通过大量阅读实践,使学生能真正以英语为工具,熟练地获取和交流本专业所需的信息。
(七)教学时数教学时数:32学时学分数:2学分(八)教学方式以黑板+多媒体教学手段为主,以学生自学、讨论、练习为辅的教学方式。
(九)考核方式和成绩记载说明考核方式为开卷考试。
严格考核学生出勤情况,达到学籍管理规定的旷课量取消考试资格。
综合成绩根据平时成绩和期末成绩评定。
二、讲授大纲与各章的基本要求课题一专业英语的特点教学要点:通过本课题内容的教学,使学生了解并熟悉机械工程专业英语的词汇特点、语法特点以及修辞特点等相关知识,为专业英语材料的阅读理解打下基础。
教学时数:4学时教学内容:1. 专业英语的意义与功用2. 专业英语的常见词汇特点3. 专业英语的常见语法特点4. 专业英语的修辞特点考核要求:1、了解专业英语的意义与功用(熟悉);2、了解专业英语词汇的组成特点(领会)3、认识专业英语的语法及修辞特征(领会)课题二专业英语的理解与翻译教学要点:通过本课题内容的教学,使学生了解翻译的基本方式,熟悉典型语法现象的翻译技巧,初步熟悉机械工程专业英语的词汇及语法翻译技巧。

机械工程专业英语Lesson11、the branch of scientific analysis, which deals with motions, time, and forces, is called mechanics and is made up of two parts, statics and dynamics. Statics deals with the analysis of stationary systems, i.e., those in which time is not a factor, and dynamics deals with systems, which change with time.对运动时间和作用力作出科学分析的分支成为力学。
他由静力学和动力学两部分组成。
静力学对静止系统进行分析,即在其中不考虑时间这个引述,动力学对事件而变化的系统进行分析。
2、Any two such forces acting on a body constitutea couple. The arm of the couple is the perpendicular distance between their lines of action, and the plane of the couple is the plane containing the two lines of action.作用在一个刚体上的两个这样的的里构成一个力偶。
力偶臂是这两个条作用线之间的垂直距离,力偶面是包含着两条作用线的平面。
3、Mechanics deal with two kinds of quantities: scalars and vectors. Scalar quantities are those with which a magnitude alone is associated. Examples of scalar quantities in mechanics are time, volume, density, speed, energy, and mass. Vector quantities, on the other hand, possess direction as well as magnitude. Examples of vectors are displacement, velocity, acceleration, force, moment, and momentum.力学涉及两种类型的量,标量和矢量。




Unitl Engineering Drawing一> New Words:Coordi nate system :The basic of all in put AutoCAD is the Cartesia n coordinate system, and the various method of input(absolute or relative) rely on this system.Coordinate value : 坐标值Cartesian coordinate axes : 笛卡尔坐标轴Perpendicularly:垂肓地Projection:投影Orthographic projection: ih投影1.1coordinate systemCAD = computer-aided designFixed: firmly in position ; stationaryLocate: vt. To determine the position ofPositive and negative :Illustrate : to explainDrafting : n.制图1.2Types of ViewsAuxiliary:辅助视图Detail: n.详图;局部Derived :取得;由来Scali ng :en large scaleClarification :to make clearPlanar: tow-D drawingCross-section: 横截而Datum plane:基准面Fig. 1-3:Brush with spring: F带弹簧的电刷Handle:手柄Needle bearing:滚针轴承Retaining ring:挡圈Chuck spacer:夹头衬片Key:销Symmetrical:对称的Configuration::结*勾1.3Multiview drawingengineering drawing is an abstract universal language used to represent a designer's idea to other Home work:Page 9:Exercise:fill the blanks with a proper word according to the text.The following diagram shows what happens in a displacer type Stirling engine during one working cycle.A . The power piston is in its lowest and the displacer in its highest position. All the working gas is inthe cold space.B . The displacer is still in its highest position. But the power piston has gone up and compressed thegas in the cold space・C . The power piston is now in its upper position and the displacer has pushed the gas through thecooler, the regenerator; and the heating pipes into the hot space.D . The hot gas is being expanded, and hest energy is being transformed into mechanical energy as thedisplacer and the power piston are pushed down into their lowest positions. The piston will stay there while the displacer rises and pushes the gas through the heating pipes, regenerator and cooler into the cold space_and we are back where we started.Words:Diagram:图表Position:位置Stirling: 斯特林(音译)Displacer:置换器Piston: 活塞Regenerator:蓄热器Cooler:冷却器Expand:膨胀As:随之hest energy:热能mechanical energy:机械能译文:置换器型斯特林发动机工作循环如下所示:A.置换器在最高位,动力活塞在最低位。
---Course Title: Mechanical BasisCourse Code: [Enter Course Code]Department: [Enter Department Name]Instructor: [Enter Instructor's Name]Class Duration: [Enter Class Duration, e.g., 1 hour, 2 hours]Class Date: [Enter Date]Classroom: [Enter Classroom Number]---Objective:To provide students with a comprehensive understanding of the fundamental principles and concepts of mechanical engineering. This lesson aims to enhance students' knowledge of mechanical systems, components, and their applications in real-world scenarios.---Lesson Outline:1. Introduction (10 minutes)- Briefly introduce the topic and its relevance to mechanical engineering.- State the learning objectives and outline the structure of the lesson.2. Mechanical Systems and Components (20 minutes)- Discuss the basic components of mechanical systems (e.g., gears, bearings, shafts).- Explain the function and operation of each component.- Use diagrams and illustrations to enhance understanding.3. Practical Applications (15 minutes)- Present real-world examples of mechanical systems and components in action.- Discuss the advantages and limitations of different mechanical systems.- Encourage students to think critically about the applications of mechanical engineering.4. Hands-on Activity (20 minutes)- Organize a group activity where students can disassemble and reassemble a simple mechanical device.- Guide students through the process, emphasizing the importance of safety and proper technique.5. Discussion and Q&A (15 minutes)- Facilitate a class discussion on the topic covered in the lesson.- Address any questions or concerns raised by students.6. Conclusion and Homework Assignment (10 minutes)- Summarize the key points discussed during the lesson.- Assign a homework assignment that reinforces the lesson's objectives.---Materials Needed:- Projector and screen- Handouts or printed materials- Diagrams and illustrations of mechanical systems and components- Simple mechanical device for hands-on activity- Safety equipment (e.g., gloves, goggles)---Assessment:- Participation: Students will be evaluated on their participation in class discussions and hands-on activities.- Homework: Students will be required to complete a homework assignment related to the lesson's topic.- Quiz: A short quiz may be administered to assess students' understanding of the material covered in the lesson.---Lesson Notes:- Ensure that the language used in the lesson is clear and concise, making it accessible to students from diverse linguistic backgrounds.- Encourage students to engage actively in the learning process, fostering a collaborative and interactive classroom environment.- Be prepared to adapt the lesson plan based on students' needs and feedback.- Provide additional resources, such as online articles, videos, and textbooks, for students who wish to delve deeper into the subject matter.---Homework Assignment:- Research and write a short essay on the application of mechanical systems in a modern-day industry of your choice. Discuss the benefits and challenges associated with the use of these systems.---Expected Outcomes:By the end of this lesson, students should be able to:- Identify and describe the basic components of mechanical systems.- Explain the function and operation of various mechanical components.- Analyze real-world applications of mechanical systems.- Demonstrate a basic understanding of the principles of mechanical engineering.---Note: This template can be customized and adapted to fit the specific needs and requirements of your course and students.。
---Subject: Mechanical BasisCourse Level: (e.g., Freshman, Sophomore)Course Duration: (e.g., 12 weeks)Instructor: [Instructor's Name]Objective:To provide students with a foundational understanding of mechanical principles, including mechanics, materials, and design, enabling them to apply these principles in practical problem-solving and to further their studies in mechanical engineering.---Week 1: Introduction to Mechanical EngineeringLesson Title: Introduction to Mechanical EngineeringObjective:- Introduce the field of mechanical engineering.- Discuss the importance of mechanical principles in daily life and various industries.Materials:- PowerPoint presentation- Handouts- Mechanical engineering examplesActivities:1. Introduction (10 minutes): Briefly introduce the course structure, objectives, and grading criteria.2. Lecture (30 minutes): Discuss the definition of mechanical engineering, its historical development, and its applications in various fields.3. Group Discussion (20 minutes): Divide students into small groups to discuss mechanical engineering applications in their daily lives or specific industries.4. Summary and Q&A (10 minutes): Summarize the key points of the lesson and answer any questions from students.---Week 2: Basic MechanicsLesson Title: Basic MechanicsObjective:- Understand the fundamental concepts of mechanics, including forces, motion, and equilibrium.Materials:- Textbook chapters- Online tutorials- CalculatorActivities:1. Review of prerequisite knowledge (10 minutes): Review basic mathematical concepts such as algebra and trigonometry.2. Lecture (30 minutes): Explain the laws of motion, forces, and equilibrium.3. In-class exercise (20 minutes): Solve simple mechanics problems to reinforce understanding.4. Homework assignment (10 minutes): Assign problems from the textbook for students to work on independently.---Week 3: StaticsLesson Title: StaticsObjective:- Learn the principles of statics, including forces acting on objects, equilibrium, and moments.Materials:- Textbook chapters- Handouts- Drawing toolsActivities:1. Review of the previous lesson (10 minutes): Review the basic concepts of mechanics.2. Lecture (30 minutes): Introduce the concept of statics, including forces in two and three dimensions, equilibrium conditions, and the calculation of moments.3. In-class activity (20 minutes): Conduct a group activity where students analyze static forces in simple structures.4. Homework assignment (10 minutes): Assign problems that involve the application of statics principles.---Week 4: DynamicsLesson Title: DynamicsObjective:- Understand the fundamental concepts of dynamics, including motion, forces, and energy.Materials:- Textbook chapters- Online simulations- CalculatorActivities:1. Review of the previous lessons (10 minutes): Review the concepts of statics and mechanics.2. Lecture (30 minutes): Introduce the concept of dynamics, including acceleration, velocity, and the equations of motion.3. In-class demonstration (20 minutes): Demonstrate the principles of dynamics using a simple pendulum or other physical setup.4. Homework assignment (10 minutes): Assign problems that involve the application of dynamics principles.---Continuation of the Course:Each subsequent week will follow a similar structure, focusing on different topics within mechanical engineering, such as materials science, design principles, and mechanical systems. The activities will include a mix of lectures, group work, in-class exercises, and homework assignments to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the subject matter.---Assessment:-。
机械基础教案英语初中Objective: The objective of this lesson is to introduce students to the basic concepts and principles of mechanical systems. Students will learn about forces, motion, and energy, and how they relate to real-world examples.Materials:- Whiteboard or blackboard- Markers or chalk- Visual aids (e.g., diagrams, models)- Handouts with practice problemsProcedure:1. Introduction (5 minutes)- Begin the lesson by asking students what they already know about mechanical systems. - Introduce the key terms and concepts that will be covered in the lesson (forces, motion, energy).2. Theory (15 minutes)- Explain the basic principles of mechanical systems, including Newton's laws of motion and the law of conservation of energy.- Use visual aids to illustrate these concepts and provide examples of real-world applications.3. Example problems (15 minutes)- Provide students with a few example problems that involve forces, motion, and energy. - Work through these problems step by step, explaining the reasoning behind each solution.4. Group work (15 minutes)- Divide students into small groups and give each group a few practice problems to solve. - Encourage students to work together and discuss their solutions.5. whole-class discussion (10 minutes)- Bring the class back together and discuss the solutions to the group work problems.- Encourage students to ask questions and clarify any misunderstandings.6. Conclusion (5 minutes)- Summarize the main concepts covered in the lesson and emphasize their importance in everyday life.- Assign a homework assignment that allows students to apply what they learned in class to real-world scenarios.Assessment:- Participation in class discussions- Completion of example problems- Homework assignmentExtensions:- For advanced students, introduce more complex mechanical systems and equations.- For students who need additional support, provide additional practice problems and resources.Note: This lesson plan is just one possible way to teach the topic of mechanical basics. The teacher should adapt the plan to meet the specific needs and abilities of their students.。
机械专业外语教案第一章:机械专业外语基础知识1.1 机械专业外语的重要性1.2 机械专业外语的基本词汇与术语1.3 机械专业外语的语法与句型1.4 机械专业外语的翻译技巧第二章:机械工程图样阅读2.1 机械工程图样的基本概念2.2 机械工程图样的阅读方法与步骤2.3 机械工程图样中的常见符号与标注2.4 机械工程图样阅读实践第三章:机械设计基础3.1 机械设计的基本原则与方法3.2 机械零件的设计与计算3.3 机械传动系统的设计与分析3.4 机械设计实例解析第四章:机械制造工艺4.1 机械制造工艺的基本概念与流程4.2 机械加工方法与设备4.3 机械制造工艺参数的计算与选择4.4 机械制造工艺案例分析第五章:机械设备管理与维护5.1 机械设备管理的基本内容与方法5.2 机械设备的维护与保养5.3 机械设备的故障诊断与维修5.4 机械设备管理的实例分析第六章:机械制造自动化技术6.1 机械制造自动化技术的基本概念6.2 数控技术与数控机床6.3 自动化装配线与技术6.4 机械制造自动化技术的应用案例第七章:机械电子技术7.1 机械电子技术的基本原理7.2 传感器与信号处理7.3 执行器与控制原理7.4 机械电子技术应用实例第八章:机械强度与材料8.1 机械强度计算的基本理论8.2 常用工程材料的基本性能8.3 机械零件的材料选择与热处理8.4 机械强度计算实例分析第九章:机械动力学9.1 机械动力学的基本方程9.2 机器运动的分析与计算9.3 机械系统的平衡与稳定9.4 机械动力学在工程中的应用第十章:机械创新设计与实践10.1 机械创新设计的基本理念10.2 机械创新设计的方法与步骤10.3 机械创新设计实践案例10.4 机械创新设计的评价与展望重点和难点解析一、机械专业外语基础知识重点和难点解析:机械专业外语基础知识是整个教案的基础,学生需要掌握专业词汇和术语,理解语法和句型,以及翻译技巧。
这一部分的学习对于后续章节的理解和应用至关重要。
主要教学步骤和教学内容课程回顾:回顾Lathe相关方面的内容新课讲授:A CAD system is basically a design tool in which the computer is used to analyze various aspects of a designed product1 .The CAD system supports the design process at all levels—conceptual,preliminary,and final design. The designer can then test the product in various environmental conditions, such as temperature changes, orunder different mechanical stresses.计算机辅助设计系统基本上是一种设计工具,计算机是用来分析所设计的产品的各个方面的。
CAD系统支持各种阶段的设计过程-------设计构想,初步设计以及最终设计。
然后设计者可在各种环境条件下,比如温度的变化不同机械压力下检验插屏的状况。
Although CAD systems do not necessarily involve computer graphice ,the display of the designed object on a screen is one of the most valuable features of CAD systems. The picture of the object is usually displayed on the surface of a cathode-ray tube (CRT).Computer graphics enables the designer to study the object by rotating it on the computer screen , separating it into segments, enlarging a specific portion of the object in order to observe it in detail , and studying the motion of mechanisms with the aid of kinematic programs.尽管CAD系统并非一定要包含计算机绘图,但能将设计的产品显示在屏幕上是CAD 系统的最有价值的特性之一。
机械工程专业英语Lesson11、the branch of scientific analysis, which deals with motions, time, and forces, is called mechanics and is made up of two parts, statics and dynamics. Statics deals with the analysis of stationary systems, i.e., those in which time is not a factor, and dynamics deals with systems, which change with time.对运动时间和作用力作出科学分析的分支成为力学。
他由静力学和动力学两部分组成。
静力学对静止系统进行分析,即在其中不考虑时间这个引述,动力学对事件而变化的系统进行分析。
2、Any two such forces acting on a body constitutea couple. The arm of the couple is the perpendicular distance between their lines of action, and the plane of the couple is the plane containing the two lines of action.作用在一个刚体上的两个这样的的里构成一个力偶。
力偶臂是这两个条作用线之间的垂直距离,力偶面是包含着两条作用线的平面。
3、Mechanics deal with two kinds of quantities: scalars and vectors. Scalar quantities are those with which a magnitude alone is associated. Examples of scalar quantities in mechanics are time, volume, density, speed, energy, and mass. Vector quantities, on the other hand, possess direction as well as magnitude. Examples of vectors are displacement, velocity, acceleration, force, moment, and momentum.力学涉及两种类型的量,标量和矢量。
标量是那些只有大小的量。
在力学中标量的例子有时间、体积、密度、速率、、能量和质量。
另一方面,矢量既有大小又有大小又有方向。
矢量的例子有位移、速度、加速度、力、力矩、动量。
Lesson2(此课后面没翻译,翻译的不太准确谅解)1 、The turning of a part in a lathe is another example of several forces in action.(as shown in figure1)车床车削是一些力在起作用的另一个例子。
figure1(如图)。
2 、If this workpiece is held between the centers of the lathe, the centers exert a compressive force against the work.如果这个工件在放在车床中心之间,中心车床对工作产生压力。
3、 Rotary motion is required to drill holes, turn parts in a lathe, mill surfaces, or drive a generator or fan belt.扶轮运动需要去钻孔,在车床上转换两件,表面,或驱动发电机或风扇皮带4 、Harmonic and Intermittent Motion(谐和运动和间歇运动): Any simple vibration, such as the regular back, and forth movement of the end of a pendulum, is simple harmonic motion.Lesson41 、Virtually all machines contain shafts. The most common shape for shafts is circular and the cross section can be either solid or hollow.仅供学习与交流,如有侵权请联系网站删除谢谢2实际上,几乎所有的机器中都装有轴。
轴的最常见的形状是圆形,其截面可以是实心的,也可以是空心的(空心轴可以减轻重量)。
有时也采用矩形轴,例如,螺丝起子的头部.套筒扳手和控制旋钮的杆。
2、 A shaft must have adequate torisonal strength to transmit torque and not be over stressed it must also be torsional stiff enough so that one mounted component does not deviate excessively from its original angular position relative to a second component mounted on the same shaft.为了在传递扭矩时不发生过载,轴应该有适当的抗扭强度。
轴还应该具有足够的抗扭强度,以使在同一轴上的两个传动零件之间的相对转角不会过大。
3 、Components such as gears and pulleys are mounted on shafts by means of key. The design of the key and the corresponding keyway in the shaft must be properly evaluated. For example, stress concentrations occur in shafts due to keyways, and the material removed to from the keyway further weakens the shaft.齿轮和皮带轮等零件通过键连接在轴上。
在键及轴上与之相对应的键槽的设计中,必须进行认真的计算。
例如,轴上的键槽会引起应力集中,由于键槽的存在会使轴的横截面积减小,会进一步减弱轴的强度。
4、Another important aspect of shaft design is the method of directly connecting one shaft to another. Devices such as rigid and flexible couplings accomplish this.轴的设计工作中的另一个重要方面是一根轴与另一根轴之间的直接连接方法。
这是由刚性或者弹性联轴器来实现的。
Lesson51、The term shaft usually refers to a relatively long member of round cross section that rotates and transmits power. One or more members such as gears ,sprockers,pullys,and cams are usually attached to the shaft by means of pins,keys,splines,snap rings,and other devices . These latter members are among the "associated parts" consedered in this text,as ate couplings and universal joints , which serve to connect the shaft to the source of power or load.2、It is apparent that shafts can be subjected to various combinations of axial,bending,and torsional loads,and that these loads may be static or fluctuating.3、Torsional defection can affect the accuracy of a cam or gear driven mechanism .Furthermore,the greater the flexibility -either lateral or torsional-the lower the corresponding critical speed.4、A gear can be gripped axially between a shoulder on the shaft and a spacer ,with torque being transmitted through a keyways.Lesson71、Fasteners are devices which permit one part to be joined to a second part and ,hence,they are involved in almost all designs . The acceptability of any product depends not only on the selected components , but also on the means by which they are fastened together. The principal purposes of fasteners are to provide the following design features;仅供学习与交流,如有侵权请联系网站删除谢谢3紧固件是将一个零件与另一个零件进行连接的零件。
因此,几乎在所有的设计中都要用到紧固件。
人们对于任何产品的满意程度不仅取决于其组成部件,还取决于其连接方式。