英语句法基本知识
- 格式:doc
- 大小:62.00 KB
- 文档页数:5

英语语法知识:
英语语法是英语语言的基础,它涉及到词法、句法、时态、语态等多个方面。
以下是一些常见的英语语法知识:
1.词法:词法研究的是单词的构成和变化,包括名词、动词、形容词、副词、介词等。
2.句法:句法研究的是句子的构成和结构,包括主语、谓语、宾语、定语、状语等。
3.时态:时态是表示动作或状态发生时间的方式,包括现在时、过去时、将来时等。
4.语态:语态是表示动作和承受者的关系的方式,包括主动语态和被动语态。
5.句子结构:英语句子结构可以分为简单句、并列句和复合句。
简单句只有一个主语和一个谓语,并列句由两个或多个
简单句组成,复合句由一个主句和一个或多个从句组成。
6.虚拟语气:虚拟语气是一种表示假设或不可能的情况的语气,包括条件句和虚拟语气从句。
7.直接引语和间接引语:直接引语是直接引用别人的话,而间接引语则是用自己的话来转述别人的意思。
8.强调句型:强调句型是一种用来强调某个成分的句型,通常用“It is/was...that...”的结构。

英语句子成分及简单句5种基本句型一、英语句子成分根据英语词汇在英语句子中的地位和作用, 英语句子的成分可分为主语、谓语、宾语、宾语补足语、表语、定语、状语、同位语及独立成分等。
其中,主语和谓语是句子的主要成分,一般情况下,一个句子不能缺少这两种成分。
现将不同句子成分的用法列举如下:1. 主语:表示句子所要说明或描述的人或事物,一般由名词、代词或相当于名词的词组或句子充当,置于句首。
如:It's getting cold. 天冷起来了。
Now everything is ready. 现在一切都准备好了。
The teacher is very kind to us. 老师对我们很好。
2. 谓语:说明或描述主语的动作、状态或特征,由动词或动词短语充当,位于主语之后。
如:Mother bought me a birthday present. 妈给我买了个生日礼物。
We have finished our work already. 我们已经完成了工作。
3. 表语:表示主语的身份、性质、状态和特征,一般由名词、形容词、或相当于名词、形容词的词、短语或句子充当,位于系动词之后,形成英语独有的主系表结构。
如:Be careful! 小心!All the students are lovely. 所有的学生都很可爱。
He looks very angry. 他看上去很生气。
4. 宾语:指动作所涉及的人或事物,一般由名词、代词或相当于名词的词组或句子充当,位于动词之后。
如:He wrote many plays. 他写了许多剧本。
She loves swimming. 她喜欢游泳。
5. 宾语补足语:用来对宾语进行补充和说明,一般由名词、形容词、副词、介词短语或非谓语动词充当。
如:He told us to stay. 他叫我们留下。
I've never seen her dancing. 我从未看见过她跳舞。
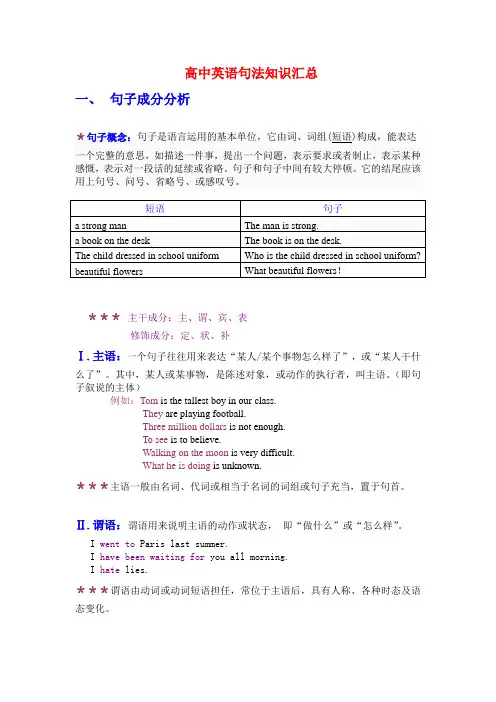
高中英语句法知识汇总一、句子成分分析*句子概念:句子是语言运用的基本单位,它由词、词组(短语)构成,能表达一个完整的意思,如描述一件事,提出一个问题,表示要求或者制止,表示某种感慨,表示对一段话的延续或省略。
句子和句子中间有较大停顿。
它的结尾应该用上句号、问号、省略号、或感叹号。
***主干成分:主、谓、宾、表修饰成分:定、状、补Ⅰ.主语:一个句子往往用来表达“某人/某个事物怎么样了”,或“某人干什么了”。
其中,某人或某事物,是陈述对象,或动作的执行者,叫主语。
(即句子叙说的主体)例如:Tom is the tallest boy in our class.They are playing football.Three million dollars is not enough.To see is to believe.Walking on the moon is very difficult.What he is doing is unknown.***主语一般由名词、代词或相当于名词的词组或句子充当,置于句首。
Ⅱ.谓语:谓语用来说明主语的动作或状态,即“做什么”或“怎么样”。
I went to Paris last summer.I have been waiting for you all morning.I hate lies.***谓语由动词或动词短语担任,常位于主语后,具有人称、各种时态及语态变化。
III.宾语:谓语动词的动作的承受者,即动作的对象或内容。
I love you.I study Chinese.He wrote many plays.I taught him a lesson yesterday.Can you show me your photo?***许多及物动词后可以有两个宾语(双宾语):直接宾语和间接宾语。
直接宾语表示动作的承受者,通常是物;间接宾语表示动作对谁或为谁而做,通常是人。

专升本英语核心语法(一)句法知识点汇总第一章:英语复合句第一节:主语从句主语从句指的是在主语的位置出现的不是词或者词组,而是一个句子,这样的句子就称为主语从句。
例如:what he said is true .That he did so much made everyone puzzled.1)引导主语从句的词有:that,whether,who,what,which,when,where,how,why 等。
例句:1.When and where we have this meeting has not beendecided .2.Whether he will come or not was not very clear .3.Who had stolen the gun has not been known .4.Which one will be our teacher is a secret .5.How we solve this problem is very serious .6.Why he didn’t kill her has not been known2)有些时候由于主语太长,可以用it作为形式主语来代替主句。
很多考生对于it作形式主语代替主语从句存在一个误区,即所有的主语从句都能用it代替,这样太绝对了,应当说that,whether 引导的主语从句都可以用it作形式主语,其余的尤其是what ,whatever,whoever引导的主语从句,基本上都不用it代替。
如:It is said that there are 300 people killed in the accident at least .据说至少有300人死于这场事故。
1.It is estimated that in some of the biggest cities of the Third World , more than half of the water entering the system is lost through leaks in pipes .据估计,在第三世界的一些大城市中,有一半以上的水由于水管漏水而流失。

语法基础知识目录一、字母与语音 (1)二、词法 (3)三、句法 (12)四、时态 (16)语法基础知识一、字母与语音ɔ 主要字母组合的发音字母组合发音例词aralcar,bar,far,star small [a:][ɔ:]ayea play [ei][i :][ei]tea,beat,read,eat break,great bread [e]eeei[i :][ei]bee,see,Lee,jeep eight oo[u ]cook,foot,look,classroom boot,food,gooes,room coat,boat,goat oil [u :]oaoiu [ə ]ɔ[ i ]ir:[ə ]bird ooroyow[ :]door ɔɔ[ i ]boy [au ][ əu ][au ]how Know ouor house [ə:][ə]work,world,worse doctor,visitor,tractor morning [ɔ:]er[ə]sister,brother,mother,father her,term [ə:]irəbird,shirt,third,girl beer,deer,cheer turn [ :][ ə]eeruri [ə:][e ə]eirereeartheir [εə][i ə]there,where hear,fear [εə][εə][θ][ð]pear,bear,wear chair,hair airththree,thirty,thin,thousand this,those,these,they chick,click,cock,clockck [k ]0给大家推荐一个英语微信群Empty Your Cup英语微信群是目前学习英语最有效的方法,群里都是说英语,没有半个中文,而且规则非常严格,是一个超级不错的英语学习环境,群里有好多英语超好的超牛逼的人,还有鬼佬和外国美眉。

句子的种类(一)按使用目的可分为陈述句、疑问句、祈使句和感叹句。
1)陈述句(Declarative Sentences):说明一个事实或陈述一种看法。
Light travels faster than sound.光比声速度快。
(说明事实)The film is rather boring.这部电影很乏味。
(说明看法)2)疑问句(Interrogative Sentences):提出问题。
有以下四种:a.一般疑问句(General Questions):Can you finish the work in time?你能按时完成工作吗?b.特殊疑问句(W Questions; H Questions):Where do you live?你住那儿?How do you know that? 你怎么知道那件事?c.选择疑问句(Alternative Questions):Do you want tea or coffee?你是要茶还是要咖啡?d.反意疑问句(Tag-Questions):He doesn't know her, does he?他不认识她,对不对?3)祈使句(Imperative Sentences):提出请求,建议或发出命令,例如:Sit down, please.请坐。
Don't be nervous!别紧张!4)感叹句(Exclamatory Sentences):表示说话人惊奇、喜悦、愤怒等情绪,例如:What good news it is!多好的消息啊!(二)句子按其结构可以分为以下三类:1)简单句(Simple Sentences):只包含一个主谓结构句子叫简单句,例如:She is fond of collecting stamps.她喜欢集邮。
(主)(谓)2)并列句(Compound Sentences):包含两个或两个以上主谓结构的句子叫并列句,句与句之间通常用并列连词或分号来连接,例如:The food was good, but he had little appetite.(主)(谓)(主)(谓)食物很精美,但他却没什么胃口。

英语常用句法介绍:陈述句,疑问句1.陈述句(1)肯定句:是指用肯定的语气来陈述的句子,如:I’m a student. She is a doctor. He works in a hospital.There are four fans in our classroom. He will eat lunch at 12:00. I watched TV yesterday evening.(2)、否定句:含有否定词或表示否定意义词的句子,如:I’m not a student. She is not (isn’t) a doctor.He does not (doesn’t) work in a hospital. There are not (aren’t) four fans in our classroom.He will not (won’t) eat lunch at 12:00. I did not (didn’t) watch TV yesterday evening.2. 疑问句一般疑问句:是指询问事实的句子,此类句子必须用“yes”,或“no”来回答。
特殊疑问句:以特殊疑问词(what , where , who , which , when , whose , why , how等)开头引导的句子。
此类句子应该问什么就答什么,不能用“yes 、no”来回答。
3.There be句型There be 句型与have, has的区别1、There be 句型表示:在某地有某物(或人)2、在there be 句型中,主语是单数,be 动词用is ; 主语是复数,be 动词用are ; 如有几件物品,be 动词根据最*近be 动词的那个名词决定。
3、there be 句型的否定句在be 动词后加not , 一般疑问句把be 动词调到句首。
4、there be句型与have(has) 的区别:there be 表示在某地有某物(或人);have(has) 表示某人拥有某物。

英语句法一、句子成分组成句子的各个部分叫做句子成分。
英语中的句子成分主要有主语、谓语、宾语定语、状语、补语、同位语等1.主语(subject)表示句子主要说明的人或物,通常由名词、人称代词等担任。
He reads English every day.Is this seat occupied?2.谓语(predicate)说明主语的动作、状态或特征,由动词担任。
画出下面句子中的谓语:They live in a small fishing village.That job involves travelling a lot.He took up drama while he was at college.3.宾语(object)宾语肯定跟在动词或介词之后,通常称为动宾结构或介宾结构,由名词、代词、数词等担任。
有时候动词后可以带两个宾语称为双宾语. 其中一个指人,一个指物,指人的叫间接宾语,指物的叫直接宾语。
画出下面句子中的宾语:He offered me a suggestion.4.定语(attribute)定语往往起修饰名词或代词的作用,通常由形容词、分词、动词不定式、介词短语等来充当。
画出下面句子中的定语:The boy standing by the door is a new student.Social workers reported that 85 percent of the youths were out of work in that city.5.状语(adverbial)修饰动词、形容词、副词或全句的词等请找出下面句子中的状语,并说出是什么担任了状语Generally speaking, he speaks English fluently. 分词做状语If we are given more chances, we’ll succeed. 条件状语He has lived in the city for five years. 时间状语He is proud to have passed the national college entrance examination. 目的状语We will have a meeting in Room 5 tomorrow. 地点状语6.表语(predicative)出是由什么来充当表语的:My mother is a nurse. 名词充当表语The weather has turned cold. 形容词充当表语The machine must be out of order. 名词短语充当表语That red bike is mine. 人称代词充当表语7.补足语(complement)位于宾语之后,补充说明主语或宾语特征,通常由形容词、名词、分词、动词不定式等充当。

英语语法大全知识树一、词法篇1. 名词(Noun)可数名词与不可数名词名词的数、格、性名词修饰语及名词短语2. 代词(Pronoun)人称代词、物主代词、指示代词反身代词、相互代词、疑问代词不定代词、关系代词3. 形容词(Adjective)定语形容词与表语形容词形容词的比较级和最高级形容词的顺序4. 副词(Adverb)状语副词、连接副词、程度副词副词的比较级和最高级副词的位置与排列顺序5. 动词(Verb)动词的分类与形式动词的时态、语态、语气系动词、助动词、情态动词6. 数词(Numeral)基数词、序数词分数、小数、百分数数词的用法7. 介词(Preposition)介词的分类与用法介词短语介词与其他词类的搭配8. 连词(Conjunction)并列连词与从属连词连词的用法与辨析常见连词短语9. 冠词(Article)不定冠词与定冠词零冠词的用法冠词的辨析与注意事项二、句法篇1. 句子成分主语、谓语、宾语定语、状语、补语独立成分与插入语2. 句子类型简单句、并列句、复合句主从句、并列句、倒装句祈使句、感叹句、疑问句3. 句子结构主谓结构、主谓宾结构主系表结构、主谓双宾结构并列结构与从属结构4. 句子时态一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时现在进行时、过去进行时、将来进行时现在完成时、过去完成时、将来完成时5. 句子语态被动语态的构成与用法被动语态与主动语态的转换被动语态的注意事项6. 句子语气陈述句、疑问句、祈使句感叹句、虚拟语气语气词的用法与辨析三、章法篇1. 段落结构主题句、支撑句、结论句段落的展开与衔接段落的一致性与连贯性2. 文章结构引言、、结尾文章的层次与过渡文章的连贯性与逻辑性3. 标点符号句号、问号、感叹号逗号、分号、冒号引号、括号、破折号4. 英语书写规范字母大小写词与词之间的空格标点符号与单词的间距通过这棵英语语法大全知识树,我们可以系统地学习和掌握英语语法知识,为英语学习和日常应用打下坚实基础。

英语语法基础知识大全可打印英语语法基础知识大全可打印英语语法是学习英语必不可少的一部分,它包括了词法、句法和语义等方面的内容。
掌握英语语法的基础知识对于正确理解和使用英语至关重要。
下面是一份英语语法基础知识大全,可以打印下来供学习参考。
1. 词类(Parts of Speech):英语单词可以分为名词(Nouns)、代词(Pronouns)、形容词(Adjectives)、动词(Verbs)、副词(Adverbs)、介词(Prepositions)、连词(Conjunctions)和感叹词(Interjections)等八种基本词类。
了解每种词类的用法和特点,对于正确使用单词起到关键作用。
2. 句子结构(Sentence Structure):英语句子通常由主语(Subject)、谓语(Predicate)和宾语(Object)构成。
了解主谓宾的基本概念,以及不同类型的句子结构(陈述句、疑问句、祈使句等)对于构建正确的句子非常重要。
3. 时态(Tense):英语中的时态用来表示动作发生的时间。
常见的时态包括一般现在时(Simple Present)、一般过去时(Simple Past)、一般将来时(Simple Future)等。
了解各种时态的构成和用法,可以帮助准确描述动作发生的时间。
4. 语态(Voice):英语中的语态用来表示动作的主语与宾语之间的关系。
常见的语态包括主动语态(Active Voice)和被动语态(Passive Voice)。
了解不同语态的构成和用法,可以帮助准确描述动作的执行者和受动者。
5. 主谓一致(Subject-Verb Agreement):英语中的主语和谓语动词在人称和数方面需要保持一致。
了解主谓一致的规则和常见的例外情况,可以有效避免主谓不一致的错误。
6. 修饰语的位置(Placement of Modifiers):形容词和副词在句子中起到修饰名词或动词的作用。

导言:同一个词类可以在句中充当不同的成分,同一个句子成分也可以由不同的词类来担任。
现代汉语里一般的句子成分有六种,即主语、谓语、宾语、定语、状语和补语。
英语的基本成分有七种:主语(subject)、谓语(predicate)、表语(predicative)、宾语(object)、定语(attribute)状语(adverbial)和补语(complement)。
把句子的各个成分搞清楚,也就是把句子各部分的关系搞清楚。
做到这一点,才可以准确地理解句子的意思或造出结构正确、意思明白的句子。
有一点要注意,在分析句子结构时,应该抓住主要成分。
我们分析句子结构,划分句子成分无非是为了理解,或者是为了造句。
各种语言有各自的规则、各自的习惯,而且语言是很灵活的东西,发展过程也很复杂,很难把语法的现象都做出明确、统一的解释来。
在使用一种语言时,语法应让位于习惯。
符合习惯的,有时尽管不符合语法,也是正确的。
英语句子有长在短,有简有繁,从现象看,似乎千变万化,难以捉摸,但从实质看,可以发现其内在联系,找出其共同规律。
英语句子的基本结构可以归纳成五种基本句型及其扩大、组合、省略或倒装。
掌握这五种基本句型,是掌握各种英语句子结构的基础。
英语十大词类:实词—名词,代词,动词,形容词,副词,数词,虚词—-冠词,介词,连词,感叹词句子基本结构:(定语)主+谓(主补)+(定语)宾(宾补)(定语)+(状语)注意:主语和谓语是句子成立的充分且必要的条件,两者缺一不可。
第一部分:句子成分1. 主语是句子要说明的人或物,一般在句首。
一. 名词作主语(要注意名词单数形式常和冠词不分家!)David arrived last night. 大卫昨晚到达。
Pride goes before a fall. 骄必败。
二. 代词作主语Who is speaking, please? (在电话中)请问您是谁?That's OK. 这没问题。
英语语法词法句法简介★清华大学★英语系测试:为中学英语量身定做.官方网站:/清华大学英语教授50年研究成果词法句法基本知识1词类(parts of speech)词类英语名称作用所作句子成分例词名词Noun(n.)表示人或事物名称主语/宾语/表语/定语/状语/同位语/补语man, car, China,Beijing, desk,advice(建议),代词Pronoun(pron.)代替名词等主语/宾语/表语/定语I, it, them, that,his, who, any,数词Numeral(num.)表示数目或顺序主语/宾语/表语/定语one, two, first,second动词Verb (v.)表示动作或状态谓语is, am, are, have,study,work,want, like实词形容Adjective(adj.)修饰人、事物的特表语/定语/补语big,small,long,short, boring,词征new, sad, funny副词Adverb(adv.)修饰动词/形容词/副词状语/表语also, too, very,often, here,there, not冠词Article(art.)用在名词前,限制名词的意义a, an, the介词Preposition(prep.)表示名词或代词与他词关系of,in,on, for,at,about,with,over,连词Conjunction(conj.)用来连接词与短语/从句/句子的词/从句/句子and,but,or,because,when,where虚词感叹Interjection(interj.)表示说话的感情不作句子成分oh,aha,hi,hello,词2句子成分(members of sentences)(1)句子成分:组成句子的各个部分。
(2)英语句子成分有主语,谓语,宾语,表语,状语,同位语,补语定语等。
如何读懂、写出正确的句子?一、句子成分(主谓宾定状补)二、时态:1.一般现在时(描述惯常发生的事情)注意:主语若是第三人称单数,动词需要加s/es ;其他情况下,动词用原型We start our work at 7 o’clock every morning.He leaves the work site at 5 o’clock every afternoon.He does his work very well.2.现在进行时(描述此刻正在发生的事情)注意:进行时需要用系动词(am, is , are)+ (动词+ing )The workers are working on the work site.The electrician is dealing with an electric problem.3.一般过去时(描述过去发生的事情)注:过去时中,动词需要用过去式(即动词+ed)We signed a contract last week.The project started a month ago.4.过去进行时(描述过去发生的事情)注意:系动词(was, were)+ (动词ing)They were planning to go abroad for vocation two months ago.5.一般将来时(描述未来将要发生的事情)注:将来时,需要在动词前加will,be going to。
We will have a meeting with the supplier.We are going to construct a new bridge in Bengal.The project will be complete soon.6.现在完成时(描述到目前为止已经发生的事情)注:完成时的基本结构为 have/has + 动词的过去分词(动词+ed)的形式We have run out of food.We have spent 5000 dollars on the car.The meal has been finished.7.过去完成时(描述到过去为止已经发生的事情)注:过去完成时的基本结构为had + 动词的过去分词(动词+ed)的形式The professor had finished his job when his students came to see him.三、英语五种基本句型基本句型一:(主+谓)The workers arrived. 工人们已经到了。
英文的句法结构英语是一门结构性语言.一个学英语之人在使用英语时必须具备三个意识,即词形变化意识,时态和语态意识和句子结构意识。
如果我们具备以上三意识,在平时有意识地进行必要的训练,在短短几个月中完全可以大幅度地提高自己的英语水平的.英文的句子结构可分两大类:基本结构和特殊结构。
英文句子的基本结构1.简单句的五大基本句型。
英文句子是以简单句为主体。
并列句是由并列连接词连接的两个简单句;主从复合句是由一个从属连接词连接的从句和一个独立的简单句构成的.英文简单句的五种基本句型。
(1)主语+ 谓语。
此句型的谓语动词是不及物动词,常带状语。
例如:The fruit shop has closed.They have been singing and dancing for two hours.The plane will take off soon.They will fly to London.(2)主语+ 系动词+ 表语.此句型结构中的谓语动词是系动词,后接表语。
常用的系动词除be外,还有become, look,seem,appear, get,feel, grow,turn,remain, come, hold,keep, stand,stay(保持),smell,sound, taste等等。
例如:The motor is out of order。
Her mother has fallen ill.The weather is getting quite hot.The roses smell sweet.Silk feels soft and smooth。
The plan sound perfect.(3)主语+ 谓语+ 宾语此句型中的谓语动词是及物动词,后面跟宾语。
例如:He studies English。
The teacher corrected her poor pronunciation more than once。
英语句法基本知识 一. 英语基本句型 I. 主语+系动词(linking verb)+表语 ◆⑴表示主语的状态、特征合身份的系动词be,look,seem,appear ,feel,smell,taste,sound; ★常见的系动词有 ◆⑵表示主语从一种状态到另一种状态,但侧重于转变后的结果的系动词become,turn ,come。go,get,grow,fall,prove; ◆⑶表示主语继续或保持某种身份、特征或状态的系动词keep,remain,stay,stand,lie, hold;
★常用作表语的词有:名词, 形容词, 非谓语动词, 介词短语, 从句等。如: 1.Seeing is believing. (_______ 充当主语和表语) 2.To see is to believe. (_______ 充当主语和表语) 3.She is disappointed at the disappointing news. 4.It doesn’t look as if we’ll be moving after all. 看起来我们还是不能搬迁。 5.The classroom looks amazing. 6.That looks like an amazing classroom. That looks an amazing classroom. 7. brilliant. It sounded /seemed like a brilliant idea. a brilliant idea. 8.It always seemed /sounded as though they would get married. 9.I seem to have left my book at home. 10.It seems that we still have a long way to go to catch up with the developed countries.要赶上发达国家我们似乎还有好长一段路要走。 11.There seems no need to be nervous about the first day at Senior High. 12.She didn’t appear embarrassed at the embarrassing moment.. 13.The retired worker appears an enthusiastic person. 那个退休工人似乎是个热心肠。 14.She appears to be in her late thirties. 15.It appears (that) there has been some misunderstanding between us. There appears to have been some misunderstanding between us. 看来我们之间一直有误会 16.You’ll feel better after a good night’s sleep. 17.Foreign guests feel amazed at the rapid development of China. 外宾对中国的快速发展感到惊叹。 18.Luckily, I was feeling in a good mood. 19.Standing there on the stage I felt a complete fool. 站在台上我感觉自己是十足的傻瓜。 20.I felt like a complete fool. 21.Her head felt as if / though it would burst. 22.This wallet feels (to me) like leather. 我觉得这钱包是皮的。 23.It will be difficult for him to become a doctor. It will be difficult for him to turn doctor. 24.She turns 21 in June. 25.His dream of becoming President has come true. 26.Something has gone wrong with our TV. 27.You’ll soon get used to the climate here. 28.We ought to go; it’s getting late. 29.They plan to get married in the summer. get angry/bored/hungry/fat/dressed/undressed 30.As time went on he grew more and more patient. 31.Mother had fallen asleep on the sofa before I got home. 32.At the teacher’s entry everyone fell silent. 33.This book will prove (to be) of great use to you in your studies. 这本书将来会证明对你的学习很有用。
34.It is also bad manners to keep silent when teachers ask you questions. 35.Train fares are likely to remain unchanged. 火车票价很可能保持不变。 36.In spite of their quarrel, they remain the best of friends. 尽管他们争吵过,他们仍是好朋友。 remain silent/standing/seated/untouched 37.He never stays angry for long. 38.The store stays open until late on Thursday. 39.The house stood empty for a long time. 40.My hometown lies on the coast. 41.The same argument doesn’t hold good in all cases. 同一论点并非对所有情况都适用。 42.What he said about you also holds true for the other comrades.
II. 主语+动词(intransitive verb) 这种句型中的谓语动词是不及物动词,没有直接宾语,但常带有状语。如:
1. The smell disappeared quite quickly. 2. He behaves in a serious and polite manner in his maths lessons. 他在数学课上表现得严肃而有礼貌。
III. 主语+动词(transitive verb)+宾语 这一句型中的谓语动词是及物动词,它必须带有自己的宾语。在英文中,当一个动词(包括单个动词和动词短语)作及物动词用时,它必须要有自己的宾语(除非宾语在上下 文里很明确地提到过,为避免不必要的重复,才会省去),否则会视为“句子不完整”。如:
1. She has the biggest smile in the world. 2. We’ are studying Chinese, maths, English and so on this term. IV. 主语+动词+间接宾语+直接宾语 A:接双宾语~ sb. sth.的动词,可转换为~ sth. to sb. 的:give, bring , take , send , pass ,hand , show , leave , lend , rent , offer , pay , owe , return , read , tell , write , promise , recommend B:接双宾语~ sb. sth.的动词,可转换为~ sth. for sb. 的:get , buy , cook , order , make , find , draw , spare , do sb. a favordo a favor for sb. 注:do sb. good/harmdo good/harm to sb. eg: 1. Will you rent me this television? Will you rent this television to me? 2. The company offered me a job. The company offered a job to me. 3. You haven’t paid me the money you owe me. You haven’t paid the money you owe me to me. 4. He owes his father £50. He owes £50 to his father. 5. Please return me my $100. Please return my $100 to me. 6. Please read us a story. Please read a story to us. 7. The firm promised. The workers a wage increase. The firm promised a wage increase to the workers 8. I have promised my wife a trip to Hongkong. I have promised a trip to Hongkong to my wife. 9. Can you recommend me a good novel? Can you recommend a good novel to me? 你能推荐一本好小说给我吗?
10. Can I get you a drink? Can I get a drink for you? 11. He bought me a gift on my birthday. He bought a gift for me on my birthday. 12. Mother cooks me my dinner every day. Mother cooks my dinner for me every day. 13. He ordered himself three shirts. He ordered three shirts for himself. 14. I made myself a cup of coffee. I made a cup of coffee for myself. 15. Will you please spare me a few minutes? Will you please spare a few minutes for me? 15. Will you please do me a favor? Will you please do a favor for me?