国际经济学作业答案-第三章
- 格式:doc
- 大小:97.50 KB
- 文档页数:14

第三章)Answers to End-of-Chapter Questions1. Use the information in the table on labor productivities in France and Germany toanswer the following questions.使用该信息表上关于法国和德国的劳动生产率,以回答以下问题。
Output per Hour Worked单位工作小时的产出France GermanyCheese 2 kilograms 1 kilogramCars 0.25 0.5a. Which country has an absolute advantage in cheese? In cars?哪个国家有奶酪的绝对优势?汽车呢?b. What is the relative price of cheese in France if it does not trade? In Germany, if itdoes not trade?什么是奶酪在法国的相对价格,如果它不交易?在德国,如果不进行交易?c. What is opportunity cost of cheese in France? In Germany?法国奶酪的机会成本是多少?德国呢?d. Which country has a comparative advantage in cheese? In cars? Show how youknow.在奶酪生产上,那个国家有比较优势?在汽车生产上呢?解释你的结论e. What are the upper and lower bounds for the trade price of cheese?奶酪交易价格的上下边界是什么?f.Draw a hypothetical PPC for France and label its slope. Suppose that France followsits comparative advantage in deciding where to produce on its PPC. Label itsproduction point.画一条假设的法国生产可能性曲线并标出其斜率。
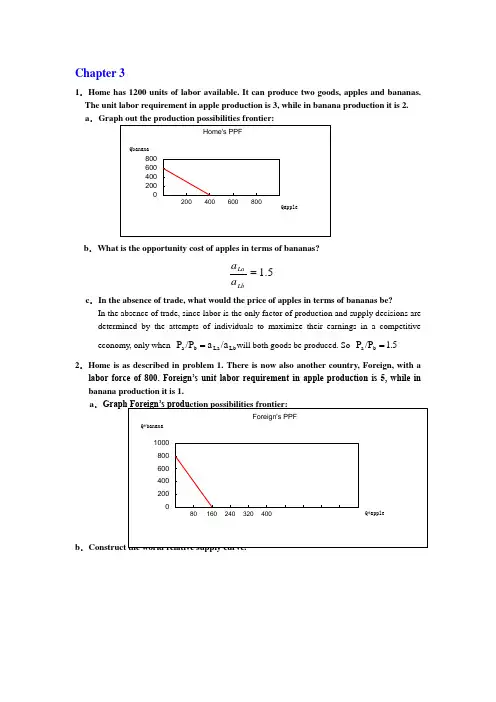
Chapter 31.Home has 1200 units of labor available. It can produce two goods, apples and bananas. The unit labor requirement in apple production is 3, while in banana production it is 2. a .b .What is the opportunity cost of apples in terms of bananas?5.1=LbLa a a c .In the absence of trade, what would the price of apples in terms of bananas be?In the absence of trade, since labor is the only factor of production and supply decisions aredetermined by the attempts of individuals to maximize their earnings in a competitive economy, only when Lb La b a /a a /P P =will both goods be produced. So 1.5 /P P b a =2.Home is as described in problem 1. There is now also another country, Foreign, with alabor force of 800. Foreign’s unit labor requirement in apple production is 5, while in banana production it is 1.a .b .3.Now suppose world relative demand takes the following form: Demand for apples/demand for bananas = price of bananas/price of apples.a .Graph the relative demand curve along with the relative supply curve:a b b a /P P /D D =∵When the market achieves its equilibrium, we have 1b a )(D D -**=++=ba b b a a P P Q Q Q Q ∴RD is a hyperbola xy 1=b .What is the equilibrium relative price of apples?The equilibrium relative price of apples is determined by the intersection of the RD and RScurves.RD: yx 1= RS: 5]5,5.1[5.1],5.0(5.0)5.0,0[=∈=⎪⎩⎪⎨⎧+∞∈=∈y y y x x x ∴25.0==y x∴2/=b P a P e ec .Describe the pattern of trade.∵b a b e a e b a P P P P P P ///>>**∴In this two-country world, Home will specialize in the apple production, export apples and import bananas. Foreign will specialize in the banana production, export bananas and import apples.d .Show that both Home and Foreign gain from trade.International trade allows Home and Foreign to consume anywhere within the coloredlines, which lie outside the countries’ production possibility frontiers. And the indirect method, specializing in producing only one production then trade with other country, is a more efficient method than direct production. In the absence of trade, Home could gain three bananas by foregoing two apples, and Foreign could gain by one foregoing five bananas. Trade allows each country to trade two bananas for one apple. Home could then gain four bananas by foregoing two apples while Foreign could gain one apple by foregoing only two bananas. So both Home and Foreign gain from trade.4.Suppose that instead of 1200 workers, Home had 2400. Find the equilibrium relative price. What can you say about the efficiency of world production and the division of the gains from trade between Home and Foreign in this case? RD: yx 1=RS: 5]5,5.1[5.1],1(1)1,0[=∈=⎪⎩⎪⎨⎧+∞∈=∈y y y x x x ∴5.132==y x∴5.1/=b P a P e eIn this case, Foreign will specialize in the banana production, export bananas and importapples. But Home will produce bananas and apples at the same time. And the opportunity cost of bananas in terms of apples for Home remains the same. So Home neither gains nor loses but Foreign gains from trade.5.Suppose that Home has 2400 workers, but they are only half as production in both industries as we have been assuming, Construct the world relative supply curve and determine the equilibrium relative price. How do the gains from trade compare with those in the case described in problem 4?In this case, the labor is doubled while the productivity of labor is halved, so the "effective labor "remains the same. So the answer is similar to that in 3. And both Home and Foreign can gain from trade. But Foreign gains lesser compare with that in the case4.6.”Korean workers earn only $2.50 an hour; if we allow Korea to export as much as it likes to the United State s, our workers will be forced down to the same level. You can’t import a $5 shirt without importing the $2.50 wage that goes with it.” Discuss.In fact, relative wage rate is determined by comparative productivity and the relative demand for goods. Kore a’s low wage reflects the fact that Korea is less productive than the United States in most industries. Actually, trade with a less productive, low wage country can raise the welfare and standard of living of countries with high productivity, such as United States. So this pauper labor argument is wrong.7.Japanese labor productivity is roughly the same as that of the United States in the manufacturing sector (higher in some industries, lower in others), while the United States, is still considerably more productive in the service sector. But most services are non-traded. Some analysts have argued that this poses a problem for the United States, because our comparative advantage lies in things we cannot sell on world markets. What is wrong with this argument?The competitive advantage of any industry depends on both the relative productivities of the industries and the relative wages across industries. So there are four aspects should be taken into account before we reach conclusion: both the industries and service sectors of Japan and U.S., not just the two service sectors. So this statement does not bade on the reasonable logic. 8.Anyone who has visited Japan knows it is an incredibly expensive place; although Japanese workers earn about the same as their U.S. counterparts, the purchasing power of their incomes is about one-third less. Extend your discussing from question 7 to explain this observation. (Hint: Think about wages and the implied prices of non-trade goods.) The relative higher purchasing power of U.S. is sustained and maintained by its considerably higher productivity in services. Because most of those services are non-traded, Japanese could not benefit from those lower service costs. And U.S. does not have to face a lower international price of services. So the purchasing power of Japanese is just one-third of their U.S. counterparts.9.How does the fact that many goods are non-traded affect the extent of possible gains from trade?Actually the gains from trade depended on the proportion of non-traded goods. The gains will increase as the proportion of non-traded goods decrease.10.We have focused on the case of trade involving only two countries. Suppose that there are many countries capable of producing two goods, and that each country has only one factor of production, labor. What could we say about the pattern of production and in this case? (Hint: Try constructing the world relative supply curve.)Any countries to the left of the intersection of the relative demand and relative supply curves export the good in which they have a comparative advantage relative to any country to the right of the intersection. If the intersection occurs in a horizontal portion then the country with that price ratio produces both goods.。

第一章练习与答案1.为什么说在决定生产和消费时,相对价格比绝对价格更重要?答案提示:当生产处于生产边界线上,资源则得到了充分利用,这时,要想增加某一产品的生产,必须降低另一产品的生产,也就是说,增加某一产品的生产是有机会机本(或社会成本)的。
生产可能性边界上任何一点都表示生产效率和充分就业得以实现,但究竟选择哪一点,则还要看两个商品的相对价格,即它们在市场上的交换比率。
相对价格等于机会成本时,生产点在生产可能性边界上的位置也就确定了。
所以,在决定生产和消费时,相对价格比绝对价格更重要。
2.仿效图1—6和图1—7,试推导出Y商品的国民供给曲线和国民需求曲线。
答案提示:3.在只有两种商品的情况下,当一个商品达到均衡时,另外一个商品是否也同时达到均衡?试解释原因。
答案提示:4.如果生产可能性边界是一条直线,试确定过剩供给(或需求)曲线。
答案提示:5.如果改用Y商品的过剩供给曲线(B国)和过剩需求曲线(A国)来确定国际均衡价格,那么所得出的结果与图1—13中的结果是否一致?答案提示:国际均衡价格将依旧处于贸易前两国相对价格的中间某点。
6.说明贸易条件变化如何影响国际贸易利益在两国间的分配。
答案提示:一国出口产品价格的相对上升意味着此国可以用较少的出口换得较多的进口产品,有利于此国贸易利益的获得,不过,出口价格上升将不利于出口数量的增加,有损于出口国的贸易利益;与此类似,出口商品价格的下降有利于出口商品数量的增加,但是这意味着此国用较多的出口换得较少的进口产品。
对于进口国来讲,贸易条件变化对国际贸易利益的影响是相反的。
7.如果国际贸易发生在一个大国和一个小国之间,那么贸易后,国际相对价格更接近于哪一个国家在封闭下的相对价格水平?答案提示:贸易后,国际相对价格将更接近于大国在封闭下的相对价格水平。
8.根据上一题的答案,你认为哪个国家在国际贸易中福利改善程度更为明显些?答案提示:小国。
9*.为什么说两个部门要素使用比例的不同会导致生产可能性边界曲线向外凸?答案提示:第二章答案1.根据下面两个表中的数据,确定(1)贸易前的相对价格;(2)比较优势型态。

《国际经济学》课后习题参考答案第一章练习与答案1.为什么说在决定生产和消费时,相对价格比绝对价格更重要?答案提示:当生产处于生产边界线上,资源则得到了充分利用,这时,要想增加某一产品的生产,必须降低另一产品的生产,也就是说,增加某一产品的生产是有机会机本(或社会成本)的。
生产可能性边界上任何一点都表示生产效率和充分就业得以实现,但究竟选择哪一点,则还要看两个商品的相对价格,即它们在市场上的交换比率。
相对价格等于机会成本时,生产点在生产可能性边界上的位置也就确定了。
所以,在决定生产和消费时,相对价格比绝对价格更重要。
2.仿效图1—6和图1—7,试推导出Y商品的国民供给曲线和国民需求曲线。
答案提示:3.在只有两种商品的情况下,当一个商品达到均衡时,另外一个商品是否也同时达到均衡?试解释原因。
答案提示:4.如果生产可能性边界是一条直线,试确定过剩供给(或需求)曲线。
答案提示:5.如果改用Y商品的过剩供给曲线(B国)和过剩需求曲线(A国)来确定国际均衡价格,那么所得出的结果与图1—13中的结果是否一致?答案提示:国际均衡价格将依旧处于贸易前两国相对价格的中间某点。
6.说明贸易条件变化如何影响国际贸易利益在两国间的分配。
答案提示:一国出口产品价格的相对上升意味着此国可以用较少的出口换得较多的进口产品,有利于此国贸易利益的获得,不过,出口价格上升将不利于出口数量的增加,有损于出口国的贸易利益;与此类似,出口商品价格的下降有利于出口商品数量的增加,但是这意味着此国用较多的出口换得较少的进口产品。
对于进口国来讲,贸易条件变化对国际贸易利益的影响是相反的。
7.如果国际贸易发生在一个大国和一个小国之间,那么贸易后,国际相对价格更接近于哪一个国家在封闭下的相对价格水平?答案提示:贸易后,国际相对价格将更接近于大国在封闭下的相对价格水平。
8.根据上一题的答案,你认为哪个国家在国际贸易中福利改善程度更为明显些?答案提示:小国。

《国际经济学》第三章习题(一)辨析题(判断正误,并说明原因)1、如果某一商品的价格上升将会导致该商品生产部门的劳动需求曲线向上移动。
2、短期内,如果劳动是可流动要素,那么某一商品上升会导致该部门资本-劳动比上升。
3、短期内,国际贸易一定会造成劳动力实际报酬的上升。
4、动态比较优势理论认为,一国出口模式将随产品生命周期的不同阶段和相对要素禀赋的变化而改变。
5、内部规模经济是指厂商的平均成本随着其自身规模的扩大而下降。
6、如果存在外部规模经济,即使不存在比较优势,也可以导致国际贸易的发生。
(二)问答题1、根据下面的两个表,试判断:(1)哪个国家是资本相对丰富的;(2)哪个国家是劳动相对丰富的;(3)如果X是资本密集型产品,Y是劳动密集型产品,那么两国的比较优势如何?表12、如何根据雷布津斯基定理,来解释要素禀赋不同的两个国家生产可能性边界之间的差别?3、假定在现有要素价格下,棉布生产中每用1英亩的土地就需要投入20小时的劳动,而在生产粮食时,每用1英亩的土地只需要投入5小时的劳动。
(1)假设该经济拥有的总资源量为:600小时的劳动和60英亩的土地。
请画图说明资源应如何分配。
(2)现在假设劳动供给首先上升到800小时,然后是1000小时,再然后是1200小时。
请用图展示出资源分配变化的轨迹。
(3)如果劳动供给继续增加将出现什么样的情形?4、如果一国的资本与劳动同时增加,那么在下列情况下,两种产品的生产以及该国的贸易条件如何变化?(1)资本、劳动同比例增加;(2)资本增加的比例大于劳动增加的比例;(3)资本增加的比例小于劳动增加的比例。
5、日本原本出口制造品,进口原材料如粮食、石油。
分析以下情况下日本贸易条件的变化:(1)中东战争使得石油供应紧缺(2)韩国扩展了汽车的生产能力,并在加拿大和美国进行销售(3)美国的工程师建立了核反应堆以代替石油燃料发电厂(4)俄罗斯农业歉收(5)日本降低牛肉和柑橘的进口关税6、在战后几十年间,日本、韩国等东亚的一些国家或地区的国际贸易商品结构发生了明显变化,主要出口产品由初级产品到劳动密集型产品,再到资本密集型产品。

第二章古典国际贸易理论1.根据重商主义的观点,一国必须保持贸易顺差。
在两国模型中是否可能?为什么?思路:在两国模型中一国的贸易顺差等于另一国的贸易逆差,不可能出现两国都顺差的情况,重商主义贸易顺差的目标必有一国无法实现。
2.在分析中国加入世界贸易组织(WTO)的利弊时,有人说“为了能够打开出口市场,我们不得不降低关税,进口一些外国产品。
这是我们不得不付出的代价”;请分析评论这种说法。
思路:这种说法实际是“重商主义”,认为出口有利,进口受损,实际上降低关税多进口本国不具有比较优势的产品,把资源用在更加有效率的产品生产中去再出口,能大大提高一国的福利水平,对一国来说反而是好事。
3.在古典贸易模型中,假设A国有120名劳动力,B国有50名劳动力,如果生产棉花的话,A国的人均产量是2吨,B国也是2吨;要是生产大米的话,A国的人均产量是10吨,B国则是16吨。
画出两国的生产可能性曲线并分析两国中哪一国拥有生产大米的绝对优势?哪一国拥有生产大米的比较优势?思路:B国由于每人能生产16吨大米,而A国每人仅生产10吨大米,所以B国具有生产大米的绝对优势。
从两国生产可能性曲线看出A国生产大米的机会成本为0.2,而B国为0.125,所以B国生产大米的机会成本或相对成本低于A 国,B 国生产大米具有比较优势。
4.理论,决不是个强权理论,只要按照比较优势进行贸易,专业化生产,充分有效地利用资源,穷国也可以得到好处,这不仅可以从Sachs 和Warner 对78个发展中国家贸易与经济发展的关系研究中的得到证实,单从中国改革开放的实践就可以得到说明。
5. 下表列出了加拿大和中国生产1单位计算机和1单位小麦所需的劳动时间。
假定生产计算机和小麦都只用劳动,加拿大的总劳动为600小时,中国总劳动为800小时。
(1) 计算不发生贸易时各国生产计算机的机会成本。
(2) 哪个国家具有生产计算机的比较优势?哪个国家具有生产小麦的比较优势?800 1200(3)如果给定世界价格是1单位计算机交换22单位的小麦,加拿大参与贸易可以从每单位的进口中节省多少劳动时间?中国可以从每单位进口中节省多少劳动时间?如果给定世界价格是1单位计算机交换24单位的小麦,加拿大和中国分别可以从进口每单位的货物中节省多少劳动时间?(4)在自由贸易的情况下,各国应生产什么产品,数量是多少?整个世界的福利水平是提高还是降低了?试用图分析。

克鲁格曼《国际经济学》中文版·第九版课后习题答案克鲁格曼《国际经济学》中文版·第九版课后习题答案第一章练习与答案1.为什么说在决定生产和消费时,相对价格比绝对价格更重要?答案提示:当生产处于生产边界线上,资源则得到了充分利用,这时,要想增加某一产品的生产,必须降低另一产品的生产,也就是说,增加某一产品的生产是有机会机本(或社会成本)的。
生产可能性边界上任何一点都表示生产效率和充分就业得以实现,但究竟选择哪一点,则还要看两个商品的相对价格,即它们在市场上的交换比率。
相对价格等于机会成本时,生产点在生产可能性边界上的位置也就确定了。
所以,在决定生产和消费时,相对价格比绝对价格更重要。
2.仿效图1—6和图1—7,试推导出Y商品的国民供给曲线和国民需求曲线。
答案提示:3.在只有两种商品的情况下,当一个商品达到均衡时,另外一个商品是否也同时达到均衡?试解释原因。
答案提示:4.如果生产可能性边界是一条直线,试确定过剩供给(或需求)曲线。
答案提示:5.如果改用Y商品的过剩供给曲线(B国)和过剩需求曲线(A 国)来确定国际均衡价格,那么所得出的结果与图1—13中的结果是否一致?答案提示:国际均衡价格将依旧处于贸易前两国相对价格的中间某点。
6.说明贸易条件变化如何影响国际贸易利益在两国间的分配。
答案提示:一国出口产品价格的相对上升意味着此国可以用较少的出口换得较多的进口产品,有利于此国贸易利益的获得,不过,出口价格上升将不利于出口数量的增加,有损于出口国的贸易利益;与此类似,出口商品价格的下降有利于出口商品数量的增加,但是这意味着此国用较多的出口换得较少的进口产品。
对于进口国来讲,贸易条件变化对国际贸易利益的影响是相反的。
7.如果国际贸易发生在一个大国和一个小国之间,那么贸易后,国际相对价格更接近于哪一个国家在封闭下的相对价格水平?答案提示:贸易后,国际相对价格将更接近于大国在封闭下的相对价格水平。

第一章练习与答案1.为什么说在决定生产和消费时,相对价格比绝对价格更重要?答案提示:当生产处于生产边界线上,资源则得到了充分利用,这时,要想增加某一产品的生产,必须降低另一产品的生产,也就是说,增加某一产品的生产是有机会机本(或社会成本)的。
生产可能性边界上任何一点都表示生产效率和充分就业得以实现,但究竟选择哪一点,则还要看两个商品的相对价格,即它们在市场上的交换比率。
相对价格等于机会成本时,生产点在生产可能性边界上的位置也就确定了。
所以,在决定生产和消费时,相对价格比绝对价格更重要。
2.仿效图1—6和图1—7,试推导出Y商品的国民供给曲线和国民需求曲线。
答案提示:3.在只有两种商品的情况下,当一个商品达到均衡时,另外一个商品是否也同时达到均衡?试解释原因。
答案提示:4.如果生产可能性边界是一条直线,试确定过剩供给(或需求)曲线。
答案提示:5.如果改用Y商品的过剩供给曲线(B国)和过剩需求曲线(A 国)来确定国际均衡价格,那么所得出的结果与图1—13中的结果是否一致?答案提示:国际均衡价格将依旧处于贸易前两国相对价格的中间某点。
6.说明贸易条件变化如何影响国际贸易利益在两国间的分配。
答案提示:一国出口产品价格的相对上升意味着此国可以用较少的出口换得较多的进口产品,有利于此国贸易利益的获得,不过,出口价格上升将不利于出口数量的增加,有损于出口国的贸易利益;与此类似,出口商品价格的下降有利于出口商品数量的增加,但是这意味着此国用较多的出口换得较少的进口产品。
对于进口国来讲,贸易条件变化对国际贸易利益的影响是相反的。
7.如果国际贸易发生在一个大国和一个小国之间,那么贸易后,国际相对价格更接近于哪一个国家在封闭下的相对价格水平?答案提示:贸易后,国际相对价格将更接近于大国在封闭下的相对价格水平。
8.根据上一题的答案,你认为哪个国家在国际贸易中福利改善程度更为明显些?答案提示:小国。
9*.为什么说两个部门要素使用比例的不同会导致生产可能性边界曲线向外凸?答案提示:第二章答案1.根据下面两个表中的数据,确定(1)贸易前的相对价格;(2)比较优势型态。
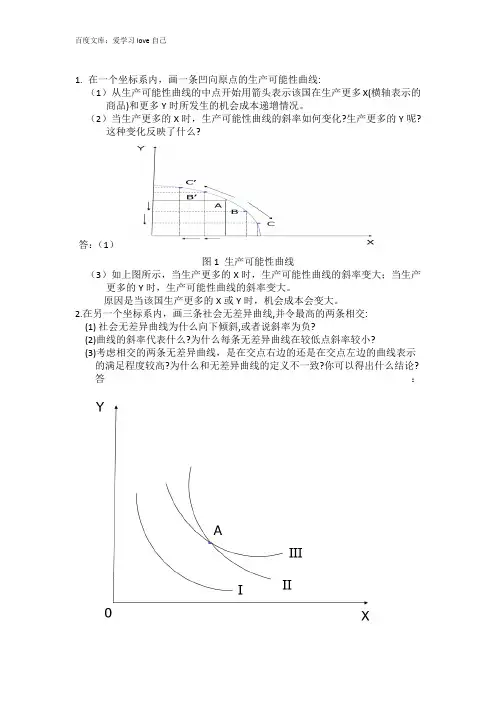
1.在一个坐标系内,画一条凹向原点的生产可能性曲线:(1)从生产可能性曲线的中点开始用箭头表示该国在生产更多X(横轴表示的商品)和更多Y时所发生的机会成本递增情况。
(2)当生产更多的X时,生产可能性曲线的斜率如何变化?生产更多的Y呢?这种变化反映了什么?答:(1)图1 生产可能性曲线(3)如上图所示,当生产更多的X时,生产可能性曲线的斜率变大;当生产更多的Y时,生产可能性曲线的斜率变大。
原因是当该国生产更多的X或Y时,机会成本会变大。
2.在另一个坐标系内,画三条社会无差异曲线,并令最高的两条相交:(1) 社会无差异曲线为什么向下倾斜,或者说斜率为负?(2)曲线的斜率代表什么?为什么每条无差异曲线在较低点斜率较小?(3)考虑相交的两条无差异曲线,是在交点右边的还是在交点左边的曲线表示的满足程度较高?为什么和无差异曲线的定义不一致?你可以得出什么结论?答:图2 社会无差异曲线(1)社会无差异曲线之所以会向下倾斜是因为为了维持社会福利水平不变,随着X商品消费的增加必须减少Y的消费。
(2)曲线的斜率代表一国在保持处在同一条无差异曲线的前提下,多消费一单位x而必须少消费Y的数量。
一国消费X越多,则其消费Y越少。
对该国来说,一单位Y的效用会逐渐增大。
因此,该国每多消费一单位X,只会放弃越来越少的Y商品。
所以,无差异曲线在较低点斜率较小。
(3)无差异曲线的定义表明每条无差异曲线意味着一个给定的满足程度,无差异曲线互不相交。
无差异曲线II显示了比交点右边更高的满足程度,无差异曲线II显示了比交点左边更高的满足程度。
因此,这个图是不合理。
3.在一个坐标系内,画一条生产可能性曲线,再画一条无差异曲线切于生产可能性曲线较平坦的地方,在另一个坐标系内,面另一条生产可能性曲线,再画另一条无差异曲线切于生产可能性曲线较陡直的地方。
(1)画一条表示各国孤立均衡相对价格的直线。
(2)各国具有比较优势的商品分别是什么?(3)在什么(极端)情况下,两国之间不存在比较优势或比较劣势?答:国家1 国家2图3 孤立均衡(1)如图3所示,P A和P A’是两国在孤立均衡情况下的价格。

第一章练习与答案1 . 为什么说在决定生产和消费时,相对价格比绝对价格更重要?答案提示:当生产处于生产边界线上,资源则得到了充分利用,这时,要想增加某一产品的生产,必须降低另一产品的生产,也就是说,增加某一产品的生产是有机会机本(或社会成本)的。
生产可能性边界上任何一点都表示生产效率和充分就业得以实现,但究竟选择哪一点,则还要看两个商品的相对价格,即它们在市场上的交换比率。
相对价格等于机会成本时,生产点在生产可能性边界上的位置也就确定了。
所以,在决定生产和消费时,相对价格比绝对价格更重要。
2. 仿效图1—6和图1—乙试推导出丫商品的国民供给曲线和国民需求曲线。
答案提示:3. 在只有两种商品的情况下,当一个商品达到均衡时,另外一个商品是否也同时达到均衡?试解释原因。
答案提示:4. 如果生产可能性边界是一条直线,试确定过剩供给(或需求)曲线。
答案提示:5. 如果改用丫商品的过剩供给曲线(B国)和过剩需求曲线(A 国)来确定国际均衡价格,那么所得出的结果与图1 —13中的结果是否一致?答案提示:国际均衡价格将依旧处于贸易前两国相对价格的中间某点。
6. 说明贸易条件变化如何影响国际贸易利益在两国间的分配。
答案提示:一国出口产品价格的相对上升意味着此国可以用较少的出口换得较多的进口产品,有利于此国贸易利益的获得,不过,出口价格上升将不利于出口数量的增加,有损于出口国的贸易利益;与此类似,出口商品价格的下降有利于出口商品数量的增加,但是这意味着此国用较多的出口换得较少的进口产品。
对于进口国来讲,贸易条件变化对国际贸易利益的影响是相反的。
7. 如果国际贸易发生在一个大国和一个小国之间,那么贸易后,国际相对价格更接近于哪一个国家在封闭下的相对价格水平?答案提示:贸易后,国际相对价格将更接近于大国在封闭下的相对价格水平。
& 根据上一题的答案,你认为哪个国家在国际贸易中福利改善程度更为明显些?答案提示:小国9* .为什么说两个部门要素使用比例的不同会导致生产可能性边界曲线向外凸?答案提示:第二章答案1.根据下面两个表中的数据,确定(1)贸易前的相对价格;(2)比较优势型态。

第一章练习与答案1.为什么说在决定生产和消费时,相对价格比绝对价格更重要?答案提示:当生产处于生产边界线上,资源则得到了充分利用,这时,要想增加某一产品的生产,必须降低另一产品的生产,也就是说,增加某一产品的生产是有机会机本(或社会成本)的。
生产可能性边界上任何一点都表示生产效率和充分就业得以实现,但究竟选择哪一点,则还要看两个商品的相对价格,即它们在市场上的交换比率。
相对价格等于机会成本时,生产点在生产可能性边界上的位置也就确定了。
所以,在决定生产和消费时,相对价格比绝对价格更重要。
2.仿效图1—6和图1—7,试推导出Y商品的国民供给曲线和国民需求曲线。
答案提示:3.在只有两种商品的情况下,当一个商品达到均衡时,另外一个商品是否也同时达到均衡?试解释原因。
答案提示:4.如果生产可能性边界是一条直线,试确定过剩供给(或需求)曲线。
答案提示:5.如果改用Y商品的过剩供给曲线(B国)和过剩需求曲线(A国)来确定国际均衡价格,那么所得出的结果与图1—13中的结果是否一致?答案提示:国际均衡价格将依旧处于贸易前两国相对价格的中间某点。
6.说明贸易条件变化如何影响国际贸易利益在两国间的分配。
答案提示:一国出口产品价格的相对上升意味着此国可以用较少的出口换得较多的进口产品,有利于此国贸易利益的获得,不过,出口价格上升将不利于出口数量的增加,有损于出口国的贸易利益;与此类似,出口商品价格的下降有利于出口商品数量的增加,但是这意味着此国用较多的出口换得较少的进口产品。
对于进口国来讲,贸易条件变化对国际贸易利益的影响是相反的。
7.如果国际贸易发生在一个大国和一个小国之间,那么贸易后,国际相对价格更接近于哪一个国家在封闭下的相对价格水平?答案提示:贸易后,国际相对价格将更接近于大国在封闭下的相对价格水平。
8.根据上一题的答案,你认为哪个国家在国际贸易中福利改善程度更为明显些?答案提示:小国。
9*.为什么说两个部门要素使用比例的不同会导致生产可能性边界曲线向外凸?答案提示:第二章答案1.根据下面两个表中的数据,确定(1)贸易前的相对价格;(2)比较优势型态。
2.本国共有1200单位的劳动,能生产两种产品:苹果和香蕉。
苹果的单位产品劳动投入是3,香蕉的单位产品劳动投入是 2.a。
画出本国的生产可能性边界。
b.用香蕉衡量的苹果的机会成本是多少?c.贸易前,苹果对香蕉的相对价格是多少?为什么?a.b.c.在贸易前,当劳动是生产的唯一要素,且在竞争日益激烈的经济环境中,供给决策是由个人获得的最大收益决定时,只有当时,这两种货物才能被生产。
所以,教科书问题的答案1. a。
生产可能性曲线是一条直线,截获苹果轴在400(1200/3)和香蕉轴上600(1200/2)。
b。
机会成本的苹果,香蕉是3/2而言。
它需要3个单位的劳动收获一个苹果,但是只有两个单位的劳动收获一根香蕉。
如果一个人foregoes收获一个苹果,这释放3个单位的劳动。
这3个单位的劳动就能够被用来收获1.5香蕉。
c。
劳动力流动,保证了每一个环节上常见的工资和竞争保证了货物的价格等于他们的生产成本。
因此,相对价格的相对成本相等时,它等于倍的工资单位劳动条件为苹果的工资倍除以单位劳动要求香蕉。
由于工资是平等的交叉,价格比率之比相等单位劳动要求,为苹果每2是3个香蕉。
2,3,6,7,11,14]。
生产可能性曲线是线性的,在苹果和拦截800/5相当于160(轴)和拦截踩在香蕉轴等于800(800/1)。
b。
世界相对供给曲线,建立确定供应苹果相对于供应的香蕉在每个相对价格。
最低的相对价格,比如苹果是收获3苹果每2个香蕉。
供给曲线是平的相对这个价钱。
苹果的最大数量的价格提供3/2在家里是400所提供的同时,以这样的价格,外国的丰收,800香蕉和没有苹果给最大相对供应以这个价格的1 / 2。
这种相对供应价格之间3/2适用任何和五日。
的价格是5,两国将在收成苹果。
供给曲线是又相对平坦的5。
因此,相关的供给曲线是一步成型,公寓,租金价格相对而言3/2供应为0到1 / 2,垂直的,从3/2数量相对半上升到5元,然后再从半无限地来讲一个。
克鲁格曼《国际经济学》中文版·第九版课后习题答案第一章练习与答案1.为什么说在决定生产和消费时,相对价格比绝对价格更重要?答案提示:当生产处于生产边界线上,资源则得到了充分利用,这时,要想增加某一产品的生产,必须降低另一产品的生产,也就是说,增加某一产品的生产是有机会机本(或社会成本)的。
生产可能性边界上任何一点都表示生产效率和充分就业得以实现,但究竟选择哪一点,则还要看两个商品的相对价格,即它们在市场上的交换比率。
相对价格等于机会成本时,生产点在生产可能性边界上的位置也就确定了。
所以,在决定生产和消费时,相对价格比绝对价格更重要。
2.仿效图1—6和图1—7,试推导出Y商品的国民供给曲线和国民需求曲线。
答案提示:3.在只有两种商品的情况下,当一个商品达到均衡时,另外一个商品是否也同时达到均衡?试解释原因。
答案提示:4.如果生产可能性边界是一条直线,试确定过剩供给(或需求)曲线。
答案提示:5.如果改用Y商品的过剩供给曲线(B国)和过剩需求曲线(A国)来确定国际均衡价格,那么所得出的结果与图1—13中的结果是否一致?答案提示:国际均衡价格将依旧处于贸易前两国相对价格的中间某点。
6.说明贸易条件变化如何影响国际贸易利益在两国间的分配。
答案提示:一国出口产品价格的相对上升意味着此国可以用较少的出口换得较多的进口产品,有利于此国贸易利益的获得,不过,出口价格上升将不利于出口数量的增加,有损于出口国的贸易利益;与此类似,出口商品价格的下降有利于出口商品数量的增加,但是这意味着此国用较多的出口换得较少的进口产品。
对于进口国来讲,贸易条件变化对国际贸易利益的影响是相反的。
7.如果国际贸易发生在一个大国和一个小国之间,那么贸易后,国际相对价格更接近于哪一个国家在封闭下的相对价格水平?答案提示:贸易后,国际相对价格将更接近于大国在封闭下的相对价格水平。
8.根据上一题的答案,你认为哪个国家在国际贸易中福利改善程度更为明显些?答案提示:小国。
第三章复习题(1),本国共有1200单位的劳动,能生产两种产品:苹果和香蕉。
苹果的单位产品劳动投入是3,香蕉的单位劳动产品投入时2。
a.画出本国的生产可能性边界。
b.用香蕉衡量的苹果的机会成本是多少?c.贸易前,苹果对香蕉的相对价格是多少?为什么?答:a.本国的生产可能性边界曲线是一条直线,在400(1200/3)处与苹果轴相截,在600(1200/2)处与香蕉轴相截,如图2-7所示。
b.用香蕉衡量苹果的机会成本是3/2。
生产1单位苹果需要3单位的劳动,生产1单位香蕉需要2单位的劳动。
如果放弃1单位苹果的生产,这将释放出3单位的劳动。
这2单位的劳动可以被用来生产3/2单位的香蕉。
c.劳动的流动性可以使得各个部门的工资趋同,竞争可以使得商图2-7 本国生产可能性曲品的价格等于它们的生产成本。
这样,相对价格等于相对成本,而相对成本等于工资乘以苹果的单位劳动产品投入。
因为各个部门工资相等,所以价格比率等于单位产品劳动投入的比率,即生产苹果所需的3单位劳动与生产香蕉所需的2单位劳动比率。
(2)假设本国的情况和习题1相同。
外国拥有800单位的劳动,外国苹果的单位劳动投入是5,香蕉的单位产品劳动投入是1。
a.画出外国的生产可能性边界。
b.画出世界相对供给曲线。
答:a.外国的生产可能性边界曲线是一条直线,在160(800/5)处与苹果轴相截,在800(800/1)处与香蕉轴相截。
如图2-8所示。
b.世界相对供给曲线可以由苹果和香蕉的相对价格和相对供给量绘出。
如图2-9。
从图2-9可以看出,苹果对香蕉的最低相对价格是3/2,在这个价格上,苹果的世界相对供给曲线是水平的。
在3/2的相对价格上,本国对苹果的最大供给量是400,外国对香蕉的供给量是800,这时,相对供给量为1/2。
只要相对价格保持在3/2和5之间,相对供给量就不变。
如果相对价格成为5,两个国家都会生产苹果,香蕉的产量为零。
这时,相对供给曲线是水平的。
奥鹏《国际经济学》在线作业三答案一、单选题(共 15 道试题,共 60 分。
)V1. 根据政策配合说,被分派去管理外部均衡的是( B )A. 汇率政策B. 货币政策C. 外汇政策D. 财政政策满分:4 分2. 古典利率平价理论的提出者是经济学家( B )A. 卡塞尔B. 凯恩斯C. 艾因齐格D. 弗里得曼满分:4 分3. 大国实施出口补贴之所以受损失更大,是因为( D )A. 大国的实力不强B. 大国的财政补贴太多C. 大国的进口量太大D. 大国会影响国际市场价格满分:4 分4. 根据孟代尔-弗莱明模型,在浮动汇率制下,财政政策(A )A. 完全失效B. 完全有效C. 同货币政策作用一致D. 无法判断满分:4 分5. 对于小国征收关税,下列说法正确的是( D )A. 消费者可能从中获益B. 生产者会有净损失C. 政府会损失关税收入D. 国家的净福利不可能为正满分:4 分6. 根据相互需求原理,决定两国产品交换实际比例的关键因素是( C )A. 两国的要素禀赋B. 两国的比较优势C. 两国的相对需求强度D. 两国的技术水平满分:4 分7. 赫-俄模型研究的是( C )A. 贸易的作用B. 贸易的利益分配C. 贸易的模式D. 贸易对收入的影响满分:4 分8. 购买力平价理论的基础是( C )A. 利率平价成立B. 铸币平价成立C. 一价定律成立D. 汇兑心理说满分:4 分9. 根据对外贸易乘数理论,在其他条件不变的条件下,边际进口倾向同对外贸易乘数值呈( A )A. 反向关系B. 无关联C. 正向关系D. 无法判断满分:4 分10. 对小国而言,最优关税( B )A. 是最高关税B. 是零关税C. 是禁止性关税D. 介于零关税和禁止性关税之间满分:4 分11. 根据货币主义汇率理论,在其他条件不变的情况下,一国的国民收入增长快于其他国家会导致该国货币汇率( A )A. 上升B. 下跌C. 不变D. 难以判断满分:4 分12. 根据货币主义汇率理论,在其他条件不变的情况下,一国的货币供应量相对于其他国家增加会导致该国货币汇率( B )A. 上升B. 下跌C. 不变D. 难以判断满分:4 分13. 根据IMF对国际收支的定义,"经济体"的含义比国家要( A )A. 广B. 窄C. 二者相同A.B.C.D.E.A.B.C.D. 价格效应E. 贸易条件效应满分:4 分3. 根据H-O-S定理,国际贸易将会(AB )A. 提高劳动力丰裕国家的劳动力价格B. 降低资本丰裕国的劳动力价格C. 提高劳动力丰裕国家的资本价格D. 降低资本丰裕国的资本价格E. 以上说法都对满分:4 分4. 根据吸收分析理论,纠正贸易逆差的政策有(DE)A. 贬值B. 增加货币发行量C. 提高利率D. 增加产量E. 减少支出满分:4 分5. 比较优势理论的贡献在于(AB)A. 打破了绝对优势理论的严格假设B. 肯定了国际贸易同国内贸易的不同特征C. 对国际贸易进行了动态分析D. 探讨了贸易的利益分配问题E. 分析了两国之间的交换比价满分:4 分6. 关境是海关管辖的势力范围,同国境相比,二者(ABC)A. 很可能一致B. 关境有可能大于国境C. 关境有可能小于国境D. 二者无法比较E. 上述说法都不正确满分:4 分7. 按照政府是否干预,浮动汇率制可以分为(BC)A. 单独浮动B. 清洁浮动C. 管理浮动D. 钉住浮动E. 联合浮动满分:4 分8. 浮动汇率制按其浮动方式,可以分为(ADE)A. 单独浮动B. 清洁浮动C. 管理浮动D. 钉住浮动E. 联合浮动满分:4 分9. 赫-俄模型假定(ABCDE)A. 两国的技术水平相同B. 要素在两国间完全不能流动C. 两种产品的生产都具有规模报酬不变的特点D. 没有运输成本E. 两国的资源都得到了充分利用A.B.C.D.E.放心做题好了,只要学科对了,学校对了,肯定100分。
克鲁格曼《国际经济学》中文版·第九版课后习题答案第一章练习与答案1.为什么说在决定生产和消费时,相对价格比绝对价格更重要?答案提示:当生产处于生产边界线上,资源则得到了充分利用,这时,要想增加某一产品的生产,必须降低另一产品的生产,也就是说,增加某一产品的生产是有机会机本(或社会成本)的。
生产可能性边界上任何一点都表示生产效率和充分就业得以实现,但究竟选择哪一点,则还要看两个商品的相对价格,即它们在市场上的交换比率。
相对价格等于机会成本时,生产点在生产可能性边界上的位置也就确定了。
所以,在决定生产和消费时,相对价格比绝对价格更重要。
2.仿效图1—6和图1—7,试推导出Y商品的国民供给曲线和国民需求曲线。
答案提示:3.在只有两种商品的情况下,当一个商品达到均衡时,另外一个商品是否也同时达到均衡?试解释原因。
答案提示:4.如果生产可能性边界是一条直线,试确定过剩供给(或需求)曲线。
答案提示:5.如果改用Y商品的过剩供给曲线(B国)和过剩需求曲线(A国)来确定国际均衡价格,那么所得出的结果与图1—13中的结果是否一致?答案提示:国际均衡价格将依旧处于贸易前两国相对价格的中间某点。
6.说明贸易条件变化如何影响国际贸易利益在两国间的分配。
答案提示:一国出口产品价格的相对上升意味着此国可以用较少的出口换得较多的进口产品,有利于此国贸易利益的获得,不过,出口价格上升将不利于出口数量的增加,有损于出口国的贸易利益;与此类似,出口商品价格的下降有利于出口商品数量的增加,但是这意味着此国用较多的出口换得较少的进口产品。
对于进口国来讲,贸易条件变化对国际贸易利益的影响是相反的。
7.如果国际贸易发生在一个大国和一个小国之间,那么贸易后,国际相对价格更接近于哪一个国家在封闭下的相对价格水平?答案提示:贸易后,国际相对价格将更接近于大国在封闭下的相对价格水平。
8.根据上一题的答案,你认为哪个国家在国际贸易中福利改善程度更为明显些?答案提示:小国。
国际经济学课后题答案集团文件发布号:(9816-UATWW-MWUB-WUNN-INNUL-DQQTY-第3章课后题答案、1、商品的相对要素强度:不同商品的资本/劳动比率的不同,通过比较可判断该商品是资本密集型商品还是劳动力密集型商品。
国家的相对要素丰裕:要素丰裕度是指一国要素拥有的相对状况。
贸易的商品构成:即使技术水平相同,生产要素禀赋不同也可以产生贸易。
一国终将出口密集的使用其相对丰裕(便宜的生产要素)生产的商品,进口那些密集使用其相对稀缺(昂贵的要素)生产的商品。
商品流动和要素流动的相互替代:如果加拿大或者欧洲国家对美国的资本密集型商品设立保护性贸易壁垒,那么,美国企业就可以向这些国家进行投资,建立工厂,在这些国家之内进行生产,绕过贸易壁垒。
(P37)里昂剔夫悖论是否证实了这种解释如果不是,那又是什么里昂惕夫利用计算结果表明得出了与要素禀赋理论完全相悖的结论。
人力资本说、贸易壁垒说、自然资源稀缺说、需求逆转说可以解释这种现象。
2、要素比例理论不是产业内贸易的一个良好的解释。
规模经济理论可以更好的解释。
6、区别产业间贸易与产业内贸易,并分别举例。
请提供有关产业间贸易和产业内贸易的解释。
•产业间贸易:是国家之间完全不同商品的贸易,可以用要素禀赋理论来解释。
•产业内贸易:是国家之间高度相似的商品的贸易,可以用规模经济来解释。
例子:略7、根据垄断竞争和规模经济理论,产业内贸易的利益包括:•对于生产者:规模经济效应,降低了每个种类商品的生产成本•对于消费者:更低的价格和更多的商品种类•生产要素所有者:所有的生产要素都从贸易中获得利益。
第4章课后题答案2:有效保护率是指关税使被保护行业每单位产出的附加值提高的百分率。
a. 对最终商品的有效保护率取决于最终产品的名义税率和投入品的名义税率。
取决于商品国内附加值占商品价格的比例。
为了保护本国的出口企业,提高有效保护率,对进口原材料免税或者低的关税。
b用有效保护率的分析方法解释下列政策问题:发展中国家的生产深化:第一阶段,发展中国家实行保护性的高关税,并对投入品进口免征关税,进而开始建立起总装配厂。
Chapter 3 Labor Productivity and Comparative Advantage —The Ricardian ModelMultiple Choice Questions1. Countries trade with each other because they are _______ and because of ______.(a) different, costs(b) similar, scale economies(c) different, scale economies(d) similar, costs(e) None of the above.Answer: C2. Trade between two countries can benefit both countries if(a) each country exports that good in which it has a comparative advantage.(b) each country enjoys superior terms of trade.(c) each country has a more elastic demand for the imported goods.(d) each country has a more elastic supply for the supplied goods.(e) Both (c) and (d).Answer: A3. The Ricardian theory of comparative advantage states that a country has a comparative advantagein widgets if(a) output per worker of widgets is higher in that country.(b) that country’s exchange rate is low.(c) wage rates in that country are high.(d) the output per worker of widgets as compared to the output of some other product is higher inthat country.(e) Both (b) and (c).Answer: D4. In order to know whether a country has a comparative advantage in the production of one particularproduct we need information on at least ____unit labor requirements(a) one(b) two(c) three(d) four(e) fiveAnswer: DChapter 3 Labor Productivity and Comparative Advantage—The Ricardian Model 19 5. A country engaging in trade according to the principles of comparative advantage gains from tradebecause it(a) is producing exports indirectly more efficiently than it could alternatively.(b) is producing imports indirectly more efficiently than it could domestically.(c) is producing exports using fewer labor units.(d) is producing imports indirectly using fewer labor units.(e) None of the above.Answer: B6. Given the following information:Unit Labor RequirementsCloth WidgetsHome 10 20Foreign 60 30(a) Neither country has a comparative advantage.(b) Home has a comparative advantage in cloth.(c) Foreign has a comparative advantage in cloth.(d) Home has a comparative advantage in widgets.(e) Home has a comparative advantage in both products.Answer: B7. If it is ascertained that Foreign uses prison-slave labor to produce its exports, then home should(a) export cloth.(b) export widgets.(c) export both and import nothing.(d) export and import nothing.(e) All of the above.Answer: A8. If the Home economy suffered a meltdown, and the Unit Labor Requirements in each of theproducts quadrupled (that is, doubled to 30 for cloth and 60 for widgets) then home should(a) export cloth.(b) export widgets.(c) export both and import nothing.(d) export and import nothing.(e) All of the above.Answer: A9. If wages were to double in Home, then Home should:(a) export cloth.(b) export widgets.(c) export both and import nothing.(d) export and import nothing.(e) All of the above.20 Krugman/Obstfeld •Seventh EditionAnswer: A10. If the world equilibrium price of widgets were 4 Cloths, then(a) both countries could benefit from trade with each other.(b) neither country could benefit from trade with each other.(c) each country will want to export the good in which it enjoys comparative advantage.(d) neither country will want to export the good in which it enjoys comparative advantage.(e) both countries will want to specialize in cloth.Answer: A11. Given the following information:Number of Units Produced by one Unit of LaborCloth WidgetsHome 10 20Foreign 60 30(a) Neither country has a comparative advantage.(b) Home has a comparative advantage in cloth.(c) Foreign has a comparative advantage in cloth.(d) Foreign has a comparative advantage in widgets.(e) Home has a comparative advantage in both products.Answer: C12. The opportunity cost of cloth in terms of widgets in Foreign is if it is ascertained that Foreign usesprison-slave labor to produce its exports, then home should(a) export cloth.(b) export widgets.(c) export both and import nothing.(d) export and import nothing.(e) All of the above.Answer: B13. If wages were to double in Home, then Home should(a) export cloth.(b) export widgets.(c) export both and import nothing.(d) export and import nothing.(e) All of the above.Answer: B14. If the world equilibrium price of widgets were 4 Cloths, then(a) both countries could benefit from trade with each other.(b) neither country could benefit from trade with each other.(c) each country will want to export the good in which it enjoys comparative advantage.(d) neither country will want to export the good in which it enjoys comparative advantage.(e) both countries will want to specialize in cloth.Chapter 3 Labor Productivity and Comparative Advantage—The Ricardian Model 21 Answer: A15. If the world equilibrium price of widgets were 40 cloths, then(a) both countries could benefit from trade with each other.(b) neither country could benefit from trade with each other.(c) each country will want to export the good in which it enjoys comparative advantage.(d) neither country will want to export the good in which it enjoys comparative advantage.(e) both countries will want to specialize in cloth.Answer: A16. In a two product two country world, international trade can lead to increases in(a) consumer welfare only if output of both products is increased.(b) output of both products and consumer welfare in both countries.(c) total production of both products but not consumer welfare in both countries.(d) consumer welfare in both countries but not total production of both products.(e) None of the aboveAnswer: B17. As a result of trade, specialization in the Ricardian model tends to be(a) complete with constant costs and with increasing costs.(b) complete with constant costs and incomplete with increasing costs.(c) incomplete with constant costs and complete with increasing costs.(d) incomplete with constant costs and incomplete with increasing costs.(e) None of the above.Answer: B18. As a result of trade between two countries which are of completely different economic sizes,specialization in the Ricardian 2X2 model tends to be(a) incomplete in both countries(b) complete in both countries(c) complete in the small country but incomplete in the large country(d) complete in the large country but incomplete in the small country(e) None of the aboveAnswer: C19. A nation engaging in trade according to the Ricardian model will find its consumption bundle(a) inside its production possibilities frontier.(b) on its production possibilities frontier.(c) outside its production possibilities frontier.(d) inside its trade-partner’s production possibilities frontier.(e) on its trade-partner’s production possibilities frontier.Answer: C22 Krugman/Obstfeld •Seventh Edition20. In the Ricardian model, if a country’s trade is restricted, this will cause all except which?(a) Limit specialization and the division of labor.(b) Reduce the volume of trade and the gains from trade(c) Cause nations to produce inside their production possibilities curves(d) May result in a country producing some of the product of its comparative disadvantage(e) None of the above.Answer: C21. If a very small country trades with a very large country according to the Ricardian model, then(a) the small country will suffer a decrease in economic welfare.(b) the large country will suffer a decrease in economic welfare.(c) the small country only will enjoy gains from trade.(d) the large country will enjoy gains from trade.(e) None of the above.Answer: C22. If the world terms of trade for a country are somewhere between the domestic cost ratio of H andthat of F, then(a) country H but not country F will gain from trade.(b) country H and country F will both gain from trade.(c) neither country H nor F will gain from trade.(d) only the country whose government subsidizes its exports will gain.(e) None of the above.Answer: B23. If the world terms of trade equal those of country F, then(a) country H but not country F will gain from trade.(b) country H and country F will both gain from trade.(c) neither country H nor F will gain from trade.(d) only the country whose government subsidizes its exports will gain.(e) None of the above.Answer: A24. If the world terms of trade equal those of country, F then(a) country H but not country F will gain from trade.(b) country H and country F will both gain from trade.(c) neither country H nor F will gain from trade.(d) only the country whose government subsidizes its exports will gain.(e) None of the above.Answer: EChapter 3 Labor Productivity and Comparative Advantage—The Ricardian Model 23 25. If a production possibilities frontier is bowed out (concave to the origin), then production occursunder conditions of(a) constant opportunity costs.(b) increasing opportunity costs.(c) decreasing opportunity costs.(d) infinite opportunity costs.(e) None of the above.Answer: B26. If the production possibilities frontier of one the trade partners (“Country A”) is bowed out (concaveto the origin), then increased specialization in production by that country will(a) Increase the economic welfare of both countries.(b) Increase the economic welfare of only Country A.(c) Decrease the economic welfare of Country A.(d) Decrease the economic welfare of Country B.(e) None of the above.Answer: A27. If two countries have identical production possibility frontiers, then trade between them is not likely if(a) their supply curves are identical.(b) their cost functions are identical.(c) their demand conditions identical.(d) their incomes are identical.(e) None of the above.Answer: E28. If two countries have identical production possibility frontiers, then trade between them is not likely if(a) their supply curves are identical.(b) their cost functions are identical.(c) their demand functions differ.(d) their incomes are identical.(e) None of the above.Answer: C29. The earliest statement of the principle of comparative advantage is associated with(a) David Hume.(b) David Ricardo.(c) Adam Smith.(d) Eli Heckscher.(e) Bertil Ohlin.Answer: B24 Krugman/Obstfeld •Seventh Edition30. If one country’s wage level is very high relative to the other’s (the relative wage exceeding therelative productivity ratios), then if they both use the same currency(a) neither country has a comparative advantage.(b) only the low wage country has a comparative advantage.(c) only the high wage country has a comparative advantage.(d) consumers will still find trade worth while from their perspective.(e) None of the above.Answer: E31. If one country’s wage level is very high relative to the other’s (the relative wage exceeding therelative productivity ratios), then(a) it is not possible that producers in each will find export markets profitable.(b) it is not possible that consumers in both countries will enhance their respective welfares throughimports.(c) it is not possible that both countries will find gains from trade.(d) it is possible that both will enjoy the conventional gains from trade.(e) None of the above.Answer: D32. If one country’s wage level is very high relative to the other’s (the relative wage exceeding therelative productivity ratios) then it is probable that(a) free trade will improve both countries’ welfare(b) free trade will result in no trade taking place(c) free trade will result in each country exporting the good in which it enjoys comparativeadvantage(d) free trade will result in each country exporting the good in which it suffers the greatestcomparative disadvantage.(e) None of the above.Answer: B33. The Ricardian 2X2 model is based on all of the following except only two nations and two products.(a) no diminishing returns.(b) labor is the only factor of production.(c) product quality varies among nations.(d) None of the above.Answer: D34. Ricardo’s original theory of comparative advantage seemed of limited real-world value because itwas founded on the labor theory of value.(a) capital theory of value.(b) land theory of value.(c) entrepreneur theory of value.(d) None of the above.Answer: AChapter 3 Labor Productivity and Comparative Advantage—The Ricardian Model 2535. According to Ricardo, a country will have a comparative advantage in the product in which its(a) labor productivity is relatively low.(b) labor productivity is relatively high.(c) labor mobility is relatively low.(d) labor mobility is relatively high.(e) None of the above.Answer: B36. In a two-country, two-product world, the statement “Germany enjoys a comparative advantage overFrance in autos relative to ships” is equivalent to(a) France having a comparative advantage over Germany in ships.(b) France having a comparative disadvantage compared to Germany in autos and ships.(c) Germany having a comparative advantage over France in autos and ships.(d) France having no comparative advantage over Germany.(e) None of the above.Answer: A37. Assume that labor is the only factor of production and that wages in the United States equal$20 per hour while wages in Japan are $10 per hour. Production costs would be lower in the United States as compared to Japan if(a) U.S. labor productivity equaled 40 units per hour and Japan’s 15 units per hour.(b) U.S. productivity equaled 30 units per hour whereas Japan’s was 20.(c) U.S. labor productivity equaled 20 and Japan’s 30.(d) U.S. labor productivity equaled 15 and Japan’s 25 units per hour.(e) None of the above.Answer: A38. If the United States’s production possibility frontier was flatter to the widget axis, whereasGermany’s was flatter to the butter axis, we know that(a) the United States has no comparative advantage(b) Germany has a comparative advantage in butter.(c) the U.S. has a comparative advantage in butter.(d) Not enough information is given.(e) None of the above.Answer: B39. Suppose the Uni ted State’s production possibility frontier was flatter to the widget axis, whereasGermany’s was flatter to the butter axis. We now learn that the German mark sharply depreciates against the U.S. dollar. We now know that(a) the United States has no comparative advantage(b) Germany has a comparative advantage in butter.(c) the United States has a comparative advantage in butter.(d) Not enough information is given.(e) None of the above.Answer: B26 Krugman/Obstfeld •Seventh Edition40. Suppose the United State’s production possibility fr ontier was flatter to the widget axis, whereasGermany’s was flatter to the butter axis. We now learn that the German wage doubles, but U.S.wages do not change at all. We now know that(a) the United States has no comparative advantage.(b) Germany has a comparative advantage in butter.(c) the United States has a comparative advantage in butter.(d) Not enough information is given.(e) None of the above.Answer: B41. Which of the following statements is true(a) Free trade is beneficial only if your country is strong enough to stand up to foreign competition(b) Free trade is beneficial only if your competitor does not pay unreasonably low wages(c) Free trade is beneficial only if both countries have access to the same technology.(d) All of the above(e) None of the aboveAnswer: E42. The Gains from Trade associated with the principle of Comparative Advantage depends on(a) The trade partners must differ in technology or tastes.(b) There can be no more goods traded than the number of trade partners.(c) There may be no more trade partners than goods traded.(d) All of the above(e) None of the aboveAnswer: A43. If transportation costs are especially high for Widgets in a Ricardian 2X2 model in which Country Aenjoys a comparative advantage, then(a) Country B must also enjoy a comparative advantage in Widgets(b) Country B may end up exporting Widgets(c) Country A may switch to having a comparative advantage in the other good.(d) All of the above(e) None of the aboveAnswer E44. Mahatma Ghandi exhorted his followers in India to promote economic welfare by decreasingimports. This approach(a) Makes no sense(b) Makes no economic sense(c) Is consistent with the the Ricardian model of comparative advantage.(d) Is not consistent with the Ricardian model of comparative advantage.(e) None of the aboveAnswer: DChapter 3 Labor Productivity and Comparative Advantage—The Ricardian Model 27 45. The Country of Rhozundia is blessed with rich copper deposits. The cost of Copper produced(relative to the cost of Widgets produced) is therefore very low. From this information we know that(a) Rhozundia has a comparative advantage in Copper(b) Rhozundia should export Copper and import Widgets(c) Rhozundia should export Widgets and export Copper(d) Both (a) and (b) are true(e) None of the above.Answer: E46. We know that in antiquity, China exported silk because no-one in any other country knew how toproduce this product. From this information we learn that(a) China enjoyed a comparative advantage in Silk(b) China enjoyed an absolute advantage, but not a comparative advantage in silk.(c) No comparative advantage exists because technology was not diffused(d) China should have exported silk even though it had no comparative advantage(e) None of the above.Answer: A47. If two countries engage in Free Trade following the principles of comparative advantage, then(a) Neither relative prices nor relative marginal costs (marginal rates of transformation—MRTs) inone country will equal those in the other country.(b) Both relative prices and MRTs will become equal in both countries(c) Relative prices but not MRTs will become equal in both countries(d) MRTs but not relative prices will become equal in both countries(e) None of the above.Answer: C48. Let us define the real wage as the purchasing power of one hour of labor. In the Ricardian 2X2 model,if two countries under autarky engage in trade then(a) The real wage will not be affected since this is a financial variable.(b) The real wage will increase only if a country attains full specialization(c) The real wage will increase in one country only if it decreases in the other(d) The real wage will rise in both countries.(e) None of the above.Answer: D49. If two countries in Autarky (not engaged in international trade) begin trading with other in a mannerconsistent with the Ricardian model of comparative advantage, then(a) The amount of labor required to produce one unit of imports will decrease in both countries.(b) The amount of labor required to produce one unit of both products will decrease in bothcountries.(c) The amount of labor required to produce one unit of imports will decrease only in the relativelylabor abundant country(d) The amount of labor required to produce one unit of imports will decrease only in the relativelycapital abundant country.(e) None of the above.Answer: AEssay Questions1. Many countries in Sub-Saharan Africa have very low labor productivities in many sectors, inmanufacturing and agriculture. They often despair of even trying to attempt to build their industries unless it is done in an autarkic context, behind protectionist walls because they do not believe they can compete with more productive industries abroad. Discuss this issue in the context of theRicardian model of comparative advantage.Answer: The Ricardian model of comparative advantage argues that every country must have a comparative advantage in some product (assuming there are more products than countries).However, the Ricardian model is not a growth model, and cannot be used to identifygrowth nodes or linkages.2. In 1975, wage levels in South Korea were roughly 5% of those in the United States. It is obviousthat if the United States had allowed Korean goods to be freely imported into the United States atthat time, this would have caused devastation to the standard of living in the United States, because no producer in this country could possibly compete with such low wages. Discuss this assertion in the context of the Ricardian model of comparative advantage.Answer: Regardless of relative wage levels, the United States would be able to provide its populace with a higher standard of living than would be possible without trade. Also, low wagestend to be associated with low productivities.3. The evidence cited in the chapter using the examples of the East Asia New Industrializing Countriessuggests that as international productivities converge, so do international wage levels. Why do you suppose this happened for the East Asian NICs? In light of your answer, what do you think is likely to happen to the relative wages (relative to those in the United States) of China in the coming decade?Explain your reasoning.Answer: Following the logic of the Ricardian model of comparative advantage, the East Asian countries played to their respective comparative advantages. This allowed the worlddemand to provide excess demands for their relatively abundant labor, which in turntended to raise these wages. If China follows the same pattern, their wages levels shouldalso be expected over time to converge to those in their industrialized country markets.4. When we examine the 2 Good 2 Country version of the Ricardian model of comparative advantage,we note that comparative advantage is totally determined by physical productivity ratios. Changes in wage rates in either country cannot affect these physically determined comparative advantages, and hence cannot affect, which product will be exported by which country. However, when more than2 goods are added to the model (still with 2 countries), changes in wage rates in one or the othercountry can in fact determine which good or goods each of the countries will export. How can you explain this anomaly?Answer: This is not really an anomaly. As long as only two goods exist, then as long as trade takes place, each country must have a comparative advantage in one of them (or none).However, if there are more goods than countries, then the physical productivity definitionof comparative advantage becomes ambiguous. Changes in relative wage rates will shiftthe international competitiveness along the “chain of comparative advantage.”5. An examination of the Ricardian model of comparative advantage yields the clear result that trade is(potentially) beneficial for each of the two trading partners since it allows for an expandedconsumption choice for each. However, for the world as a whole the expansion of production of one product must involve a decrease in the availability of the other, so that it is not clear that trade isbetter for the world as a whole as compared to an initial situation of non-trade (but efficientproduction in each country). Are there in fact gains from trade for the world as a whole? Explain.Answer: If we were to combine the production possibility frontiers of the two countries to create a single world production possibility frontier, then it is true that any change in productionpoints (from autarky to specialization with trade) would involve a tradeoff of one good foranother from the world’s perspective. In other words, the new solution cannot possiblyinvolve the production of more of both goods. However, since we know that each countryis better off at the new solution, it must be true that the original points were not on thetrade contract curve between the two countries, and it was in fact possible to make somepeople better off without making others worse off, so that the new solution does indeedrepresent a welfare improvement from the world’s perspective.6. It is generally claimed that a movement from autarky to free trade consistent with Ricardiancomparative advantage increases the economic welfare of each of the trade partners. However, it may be demonstrated that under certain circumstances, not everyone in each country is made better off. Illustrate such a case.Answers: (a) If inter-generational, or economic growth considerations are taken into account, thena country may end up specializing in a good that has no or few growth linkages withthe rest of the economy (e.g. an “enclave” sector).(b) If some of the residents of a country have tastes biased toward their exportable, thenthey may suffer due to the trade-affected increase in the market price of theexportable good.7. It is generally claimed that state trading, or centrally controlled trading will tend to reach a lowereconomic welfare than would be reached by allowing market forces to determine trade flowdirections and terms of trade. Illustrate a counter-example to this proposition.Answer: In general, if we begin with any suboptimal distortion, the theory of the second best tells us that an additional “distortion” may move a country in the correct direction of a welfareimprovement. For example, If a country has an overvalued exchange rate (that is, itscurrency is overpriced in the foreign exchange markets), it is possible that it will find itselfin an autarkic equili brium (that is, it might “overprice itself out of the internationalmarket”). In such a case it is easy to demonstrate that if the government exports the goodsin which the country enjoys comparative advantage, and imports the other (bypassingmarket price s and mechanisms), the country’s economic welfare will improve.8. The Ricardian proposition that international trade will benefit any country (“gains from trade”) aslong as the world terms of trade do not equal its autarkic relative prices is a straightforward andpowerful concept. Nevertheless, it is impossible to demonstrate empirically. Why?Answer: This is because there is no way of knowing exactly what are, or would have been, the autarky MRTs or MRSs. This is because there is no single example in the world ofa country that is totally unengaged in international trade.Quantitative/Graphing Problems1. Given the following information:Unit Labor RequirementsCloth WidgetsHome 100 200Foreign 60 30What is the opportunity cost of Cloth in terms of Widgets in Foreign?Answer: One half a widget.2. Given the following information:Unit Labor RequirementsCloth WidgetsHome 100 200Foreign 60 30If these two countries trade these two goods in the context of the Ricardian model of comparative advantage, then what is the lower limit of the world equilibrium price of widgets?Answer: 2 Cloths.3. Given the following information:Unit Labor RequirementsCloth WidgetsHome 100 20s0Foreign 60 30If these two countries trade these two goods with each other in according to the Ricardian model of comparative advantage, what is the lower limit for the price of cloth?Answer: One half a widget.4. Given the following information:Unit Produced by One Worker/HourCloth WidgetsHome 100 200Foreign 60 30What is the opportunity cost of cloth in terms of Widgets in Foreign?Answer: 2 widgets.。