
高考英语必须掌握的16种时态用法技巧
首先回归到最初的问题,什么是时态?
时态(Tense)是表示行为、动作和状态在各种时间条件下的动词形式。因此,当我们说时态结构的时候,指的是相应时态下的动词形式。
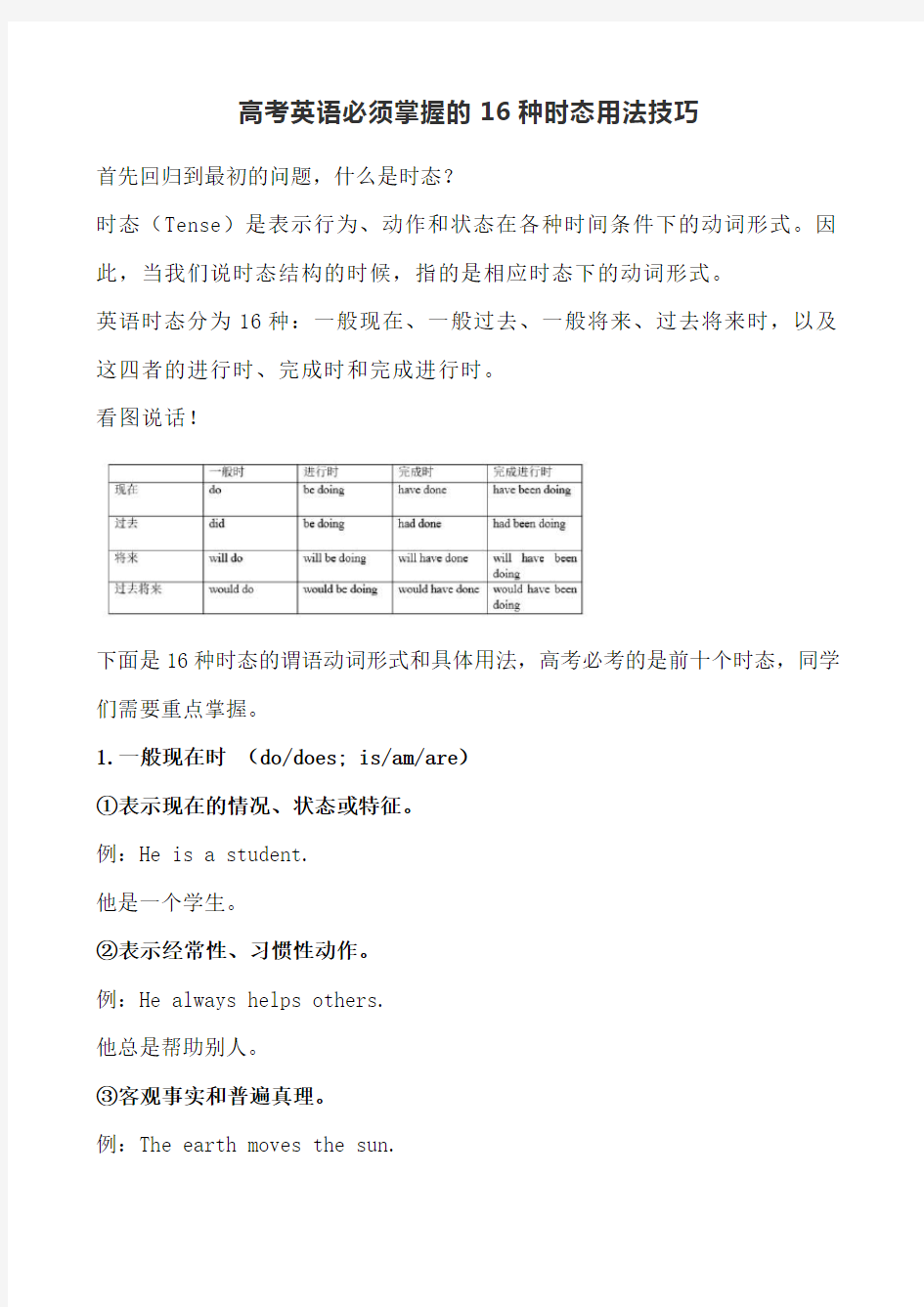
英语时态分为16种:一般现在、一般过去、一般将来、过去将来时,以及这四者的进行时、完成时和完成进行时。
看图说话!
下面是16种时态的谓语动词形式和具体用法,高考必考的是前十个时态,同学们需要重点掌握。
1.一般现在时(do/does; is/am/are)
①表示现在的情况、状态或特征。
例:He is a student.
他是一个学生。
②表示经常性、习惯性动作。
例:He always helps others.
他总是帮助别人。
③客观事实和普遍真理。
例:The earth moves the sun.
地球绕着太阳转。
④表示一个按规定、计划或安排要发生的动作。
仅限于某些表示“来、去、动、停、开始、结束、继续”等的动词,可以与表示未来时间的状语搭配使用。
常见的用法是:飞机、火车、轮船、汽车等定期定点运行的交通方式。
例:The next train leaves at 3 o'clock this afternoon.
下一趟火车今天下午3点开车。
⑤在时间、条件和让步状语从句中经常用一般现在(有时也用现在完成时)表示将的来事情。(即:主将从现原则)
例:I will call you as soon as I arrive at the airport.
我一到机场就会给你打电话。
When you have finished the report, I will have waited for about 3 hours. 等你完成这份报告的时候,我就已经等了将近3个小时了。
2. 现在进行时(am/is/are doing)
①表示此时此刻正在发生的事情。
例:He is listning to the music now.
他现在正在听音乐。
②表示目前一段时间内一直在做的事情,但不一定此时此刻正在做。
例:I am studying computer this term.
这个学期我一直在学习计算机。
③现在进行时可以表示将来的含义。
瞬时动词的进行一定表将来。
例:I am leaving.
我要离开了。
持续动词的进行只有有将来的时间状语或有将来语境中才表将来。
例:I am travelling next month.
下个月我要去旅行。
④现在进行时与频度副词连用,表示说话者或褒义或贬义的感情色彩。
例:He is always helping others.
他总是帮助别人。(褒义)
3. 现在完成时(have/has done)
①表示动作到现在为止已经完成或刚刚完成,强调对现在产生的影响。
例:I bought a new house, but I haven't sold my old one yet, so at the moment I have two houses.
我买了一所新房子,但是还没有卖掉旧的,所以现在我又两所房子。
②表示从过去某时刻开始,持续到现在的动作或情况,并且有可能会继续延续下去。此时经常用延续性动词。
时间状语常用since加一个过去的时间点,或for加一段时间,或by加一个现在时间。
例:Great as Newton was, many of his ideas have been challenged today and are being modified by the work of scientists of our time.
虽然牛顿是个伟大的人物,但他的许多见解直到今天还在受到挑战,并且被现代科学家的工作所修正
4. 现在完成进行时(have/has been doing)
表示某一动作开始于过去某一时间,延续或重复地出现至今,或将继续延续至将来。
例:We have been working on this project for over a month now.
到目前为止,我们一直在处理那个项目,已经花了一个多月时间了。
5. 一般过去时 (did; was/were)
①表示过去某个时间发生的动作或情况。
例:I bought some fruits yesterday.
我昨天买了一些水果。
②表示过去习惯性动作。
例:When I was a boy,I often swam in that river.
would/used to do:表示过去常常......
例:The old man would sit on a bench in the quiet park and look at others for hours without doing anything or talking to anybody.老人过去常常坐在宁静的公园里的一条长椅上,看着其他的人,一坐就是数个小时,什么也不干,也不和任何人交谈。
He used to visit his mother once a week.
他以前总是每周看望一次他的母亲。
6. 过去完成时(had done)
表示在过去的某个时间或动作以前已经发生的动作或已经存在的状态。就是我们常说的"过去的过去"。
Until then, his family hadn't heard from him for six months.
到那时为止,他家里已经有六个月没得到他的消息了。
7. 过去将来时(would do)
表示从过去的某个时间看将要发生的事。
例:I said on Thursday I should see my friend the next day.
我星期四说我将于第二天拜访我的朋友。
8. 过去进行时(was/ were doing)
①表示在过去具体的时间正在发生的动作。
例:Mary was listening to light music 10 minutes ago.
10分钟前,玛丽正在听轻音乐。
②表示过去某个时间段内一直在发生的事情。
例:I was travelling in London last summer vacation.
去年暑假我在伦敦旅行。
③过去进行时可以表示过去将来的含义。
瞬时动词的过去进行时一定表示过去将来的含义。
例:Then she said she was leaving.
然后她说她要离开了。
持续动词的过去进行时只有在有过去将来的时间状语或过去将来的语境下才能表示过去将来。
例:She said that she was travelling the next day.
她说她第二天要去旅行。
④过去进行时和频度副词连用可以表示说话者或褒义或贬义的感情色彩。
9. 一般将来时
(1)will do
①表示主语主观意愿的将来。
例:I will send her a glass hand-made craft as her birthday gift. 我将送给她一个玻璃的手工制品,作为给她的生日礼物。
②表示客观将来。
例:Fish will die without water.
离开水,鱼会死。
③表示临时决定。
例:——Mary has been ill for a week.
——Oh,I didn't know. I will go and see her.
(2)am/is/are going to do
①表示计划、打算做某事。
例:This is just what I am going to say.
这正是我想说的。
②表示根据某种迹象看,很可能或即将发生的事情,表推测。
例:Look at the dark clouds in the sky. It's going to rain.
看天上的乌云,要下雨了。
(3)am/is/are about to do
表示“即将、正要”时,可用。强调近期内或马上要做的事。
例:Don't worry, I am about to make a close examination on you. 别担心,我马上就给你做一次仔细的检查。
(4)be to do
①表示“按计划、安排即将发生某事或打算做某事”。
例:She is to be seen in the lab on Monday.
星期一你准会在实验室见到她。
②该做或不该做的事情(语气上接近于should, must, ought to, have to),表示一种命令、规劝性语气。
例:You are to go to bed and keep quiet, kids. Our guests are arriving in less than 5 minutes.
孩子们,你们必须上床睡觉,不准吵闹。我们的客人5分钟之内就要到了。10. 将来进行时(will be doing)
强调在将来的某个具体时间正在发生的动作或事情。
例:Don't worry, you won't miss her. She will be wearing a red T-shirt and a white skirt at that time.别担心,你不会认不出她的。她到时会穿一件红色的T恤衫和一条白色的短裙。
11. 将来完成时(will have done)
表示从将来的某一时间开始、延续到另一个将来时间的动作或状态,或是在某个将来时间完成,但对其后的另一个将来时间有影响的动作或状态。就好象把现在完成时平移到时间轴的将来时时段一样。
例:The conference will have lasted a full week by the time it ends. 会议从开始到结束将持续整整一个星期。
12.将来完成进行时:(will have been doing)
例:By the end of next month, the project will have been being worked for 3 years.
到下个月底为止,这项工程就已经不停地进行了3年了。
13.过去完成进行时:had been doing
例:The old clock had been being taken apart of and fixed up again for several times by my 10-year old son before I came back home.
我回到家之前,我10岁大的儿子已经把这个旧钟表拆卸并重新组装了好几回了。
14.过去将来进行时:( would be doing )
例:The government promised that a new highway would be being built next July.
政府承诺说第二年7月将有一条新的高速公路正在修建。
15.过去将来完成时:(would have done)
例:I believed by the end of that year an advanced version of that software would have been developed, but I was wrong.
我坚信到那年年底为止,那个软件的新版本将被开发出来。但是我错了。
16.过去将来完成进行时:(would have been doing)
例:They said that by the end of the following month, the project would have been being worked for 3 years.
他们说到第二个月底为止,这项工程就已经不停地进行了3年了。
高考英语必须掌握的八大时态结构 一、一般现在时 1、概念:表示经常发生的情况;有规律出现的情况;总是发生的;事实真理。 2.时间状语: Always, usually, often, sometimes, every week (day, year, month…), once a week (day, year, month…), on Sundays (on Mondays…), etc. 3.基本结构:主语+动词原形(如主语为第三人称单数,动词上要改为第三人称单数形式) 4.否定形式:主语+am / is / are+not+其他;此时态的谓语动词若为行为动词,则在其前加 don't,如主语为第三人称单数,则用 doesn't,同时还原行为动词。 5.一般疑问句:把 be 动词放于句首;用助动词 do 提问,如主语为第三人称单数,则用 does,同时,还原行为动词。 eg: ①It seldom snows here. 这里很少下雪。 ②He is always ready to help others. 他总是乐于帮助别人。 ③Action speaks louder than words. 事实胜雄辩。 二、一般过去时 1.概念:过去某个时间里发生的动作或状态;过去习惯性、经常性的动作、行为。 2.时间状语:ago, yesterday, the day before yesterday, last week, last (year,night,month…), in 1989, just now, at the age of 5, one day, long long ago, once upon a time,etc. 3.基本结构:主语+动词的过去式或 be 的过去式+名词 4.否定形式:主语+was / were+not+其他;在行为动词前加didn't,同时还原行为动词。 5.一般疑问句:was 或 were 放于句首;用助动词 do 的过去式 did 提问,同时还原行为动词。 eg:
各种时态的用法 一、一般现在时 构成:a.主动:动词原形(主语是第三人称单数时,谓语动词要加s/es);be动词要用am,is,are。 b.被动:am / is / are + 过去分词 用法: ①一般现在时表示经常性或习惯性的动作,常用频度副词sometimes, often, always, usually, seldom及时间副词every day, night, week, month, year, in the morning, in the afternoon, in the evening, at night做状语。如: I go to school at 6 every morning. 每天早上我6点去上学。 ②一般现在时表示客观存在及普遍真理。如: Summer follows spring. 春天之后是夏天。 The sun rises in the east. 太阳从东方升起。 注意:此种用法即使出现在过去的语境中,仍用一般现在时。如: I learned that the earth goes around the sun when I was in primary school. 我在小学就学过地球是围绕太阳转的。 ③一般现在时表示格言或警句。如: Pride goes before a fall. 骄兵必败。 ④一般现在时表示目前的情况或状态,常跟时间副词now连用。如: I am a teacher. Peter writes good Chinese but does not speak well. He lives in Beijing now, ⑤以here,there等开始的倒装句,表示动作正在进行。如: Here comes the bus. = The bus is coming. There goes the bell. = The bell is ringing. ⑥习惯性的爱好或行为。如: I like dancing while she likes singing. 我喜欢跳舞,而她喜欢唱歌。 We get up at six. ⑦在某些习惯表达法中,常用一般现在时表示已经发生过的动作或存在的状态。如: They say Wu Dong is ill. 据说吴东病了。 The paper says the disease is under control. 报纸上说这种病已经得到了控制。 The diagram tells us that people’s living is improving. 这份图标告诉我们,人们的生活正在改善。 ⑧在下列情况下表示将来: a.在(时间、条件等)状语从句中用一般现在时代替一般将来时。如: I will give it to him as soon as I see him. 我一看见他就会交给他。 He will come if you invite him. 如果你请他,他会来的。 Suppose he doesn’t agree, what shall we do? 假如他不同意,那怎么办? I shall do as I please. 我高兴怎么做就怎么做。 He will continue the work no matter what happens. 不管发生什么情况他都要继续这项工作。 b.在the more…the more…(越…越…)句型中,前者通常用一般现在时代替一般将
2007高考动词时态和语态 1. The flowers were so lovely that they __________ in no time. [2007 全国卷I] A. sold B. had been sold C. were sold D. would sell 2. I know a little bit about Italy as my wife and I ________ there several years ago. [2007 全国卷 I] A. are going B. had been C. went D. have been 3. —Is there anything wrong, Bob? You look sad. —Oh, nothing much. In fact, I ____ of my friends back home. [2007 全国卷II] A. have just thought B. was just thinking C. would just think D. will just be thinking 4. —Tom, you didn’t come to the party last night? —I ____, but I suddenly remembered I had homework to do. [2007 全国卷II] A. had to B. didn’t C. was going to D. wouldn’t 5. —Did you tidy your room? [2007 上海卷] —No, I was going to tidy my room but I ______ visitors. A. had B. have C. have had D. will have 6. With the help of high technology, more and more new substances ______ in the past years. [2007 上海卷] A. discovered B. have discovered C. had been discovered D. have been discovered never have been able to afford to go. 7. They_____ two free tickets to Canada, otherwise they’d [2007 山东卷] A.had got B.got C.have got D.get 8. —Did Peter fix the computer himself? —He ______, because he doesn't know much about computers. [2007 安徽卷] A. has it fixed B. had fixed it C. had it fixed D. fixed it 9. They became friends again that day. Until then, they _____ to each other for nearly two years. [2007 安徽卷] A. didn't speak B. hadn't spoken C. haven' t spoken D. haven' t been speaking 10. —How can I apply for an online course? —Just fill out this form and we _____ what we can do four you. [2007 北京卷] A.see B.are seeing C. have seen D. will see 11. I got caught in the rain and my suit____.[2007 北京卷] A. has ruined B. had ruined C. has been ruined D. had been ruined 12. —It was really very kind of you to give me a lift home. —Oh, don’t mention it. I _____past your house anyway. [2007 北京卷] A. was coming B. will come C. had come D. have come 13. —I saw Jane and her boyfriend in the park at eight yesterday evening.[2007 福建卷] —Impossible. She TV with me in my home then. A.watched B.had watched C.would watch D.was watching 14. Danny hard for long to realize his dream and now he is popular. [2007 福建卷]
初中英语八大时态结构及用法详解英语八大时态: 1一般现在时 标志:动词原形 1. 表示经常性或习惯性动作,常与表频度的时间状语连用: She often speaks English. I leave home for school at 7 every morning. 2. 表示现在的状态、特征、职业、能力、感觉等: He seems to feel a bit down today. He works as a driver. 3. 表示真理、客观存在、科学事实或用于格言警句中: Shanghai lies in the east of China. Columbus proved that the earth is round. Where there is a will, there is a way. 4. 表示现在瞬间的动作: Here comes the bus! 5. 表示将来 1) 表按规定、计划、安排将要发生的动作(仅限于某些表示“来、去、动、停、开始、结束、继续”等的趋向动词),可以与表示未来的时间状语搭配使用。常见的用法是:飞机、火车、轮船、汽车等定期定点运行的交通状况。如:The next train leaves at 3 o’clock this afternoon.
How often does the shuttle bus run? 2) 在时间和条件状语从句中常使用一般现在时表示将来发生的事情: When Bill comes (不用will come), ask him to wait for me. I shall go there tomorrow unless I’m too busy. 2一般过去时 标志:动词过去式 *闭音节:元音字母a, e, i, o, u如果发字母本来的音则称为开音节,否则称为闭音节。 1. 表示过去某时所发生的动作或存在的状态,常与表示过去的时间状语连用(e.g. yesterday, this morning, just now, a moment ago, in May, last night / year / week, once upon a time, the other day, before …, when …, in the past等)。如: Jim rang you just now. Liu Ying was in America last year. 2. 表示过去经常或反复发生的动作,特别是used to do表达的句型,本身表示 的就是过去常常。如: When I was a kid, I often played football in the street. She used to visit her mother once a week. *注意区分sb. used to do sth.(某人过去常常做某事,此处to是动词不定式 标志符号)和sb. be used to sth./doing sth.(某人习惯于某物/做某事,此处to 是介词)。 3. 代替一般现在时,表示一种婉转、客气、礼貌、商量的语气。此用法仅适用于少数动词(如want, hope, wonder, think, intend等)及情态动词could, would。如:
英语八种时态讲解-CAL-FENGHAI.-(YICAI)-Company One1
英语八大基本时态和被动语态要点指南 英语八大基本时态 一、一般现在时 定义:经常、反复发生的动作、行为及现在的某种状况。 结构:①am(第一人称单数)/is(第三人称单数)/are(其他人称); ②has (第三人称单数)have(其他人称) ③行为动词,除了第三人称单数要由动词原形词尾-s /-es /y变为i,-es; 其他概用动词原形 时间状语:always(“总是,一直”,反义词为never), usually(“通常如此,很少例外”,反义词为unusually), often(“经常、常常,动 作重复,但中有间断”,反义词为never), sometimes(“有时、不 时,动作偶然,常有间断”), seldom(“很少,不常”), never (“从不,未曾”), forever(永远), every week (day, year, month…)(每周,每天,每年,每月…), once a week(一周一次), on Sundays(在每个星期天),now and then(时常) from time to time (不时地),in the morning(afternoon, evening…)(在上午,在下午,在 晚上…) etc. Tips:(频度副词频率由高到低)always> usually > often > sometimes >Seldom > never 通常说来,always表示100%,usually表 示80%,often表示60%,sometimes表示40%,seldom表示20%, never表示0%。 否定式:①am/is/are+ not;②谓语动词若为行为动词,则在动词前加don't,如主语为第三人称单数,则用doesn't,同时还原行为动词。(即后边的行 为动词用原形) 一般疑问句:①把be动词放于句首,且用be动词回答;②用助动词do提问,如主语为第三人称单数,则用does,同时,还原行为动词。 用什么样助动词提问,就用相应助动词回答 用法:A) 表示现在发生的动作、情况或主语具有的状态和特征。 B) 习惯用语。 C) 经常性、习惯性动作。 D) 客观事实和普遍真理。尤其要注意,如果前后文不是一般现在时,则 无法保持主句、从句时态一致。 E) 表示一个按规定、计划或安排要发生的动作,(仅限于某些表示 “come、go、start、leave 、stay、arrive、return、begin、be”等的 动词)可以与表示未来时间的状语搭配使用。常见的用法是:飞 机、火车、轮船、汽车等定期定点运行的交通方式。 例:The next train leaves at 3 o'clock this afternoon. 下一趟火车今天下午3点开车。)
英语的16种时态 英语共有十六种时态,其表现形式如下(以study为例): 1. 一般现在时 He always_______(help)others. The next train _______(leave)at 3 o'clock this afternoon. 2. 现在进行时(be doing) They_______(have)a meeting. I_______(study)at an evening school. Mike _______(come)home on Thursday. They_______(have)a party next week. ■现在进行时在时间和条件状语从句中,代替过去将来时。如: He will promise to buy me a computer if he _______(get )a raise. 3. 现在完成时(have done) A) 表示动作到现在为止已经完成或刚刚完成。 例:I bought a new house, but I _________ my old one yet, so at the moment I have two houses. A) didn't sell B) sold C) haven't sold D) would sell B) 表示从过去某时刻开始,持续到现在的动作或情况,并且有可能会继续延续下去。例:Great as Newton was, many of his ideas ___________ today and are being modified by the work of scientists of our time. A) are to challenge C) have been challenged B) may be challenged D) are challenging 4. 现在完成进行时(have been doing) 用法:表示某一动作开始于过去某一时间,延续或重复地出现至今,或将继续延续至将来。 例:We _______(work)on this project for over a month now. 5. 一般过去时 I _______(want )to ask you if I could borrow your car? _______(will)you mind my sitting here?
初中英语八大时态结构及用法 时态无疑是初中英语最重要的语法内容,学好时态基本就拿下了语法的半壁江山。 英语八大时态: 一、一般现在时 标志:动词原形 1. 表示经常性或习惯性动作,常与表频度的时间状语连用: She often speaks English. I leave home for school at 7 every morning. 2. 表示现在的状态、特征、职业、能力、感觉等: He seems to feel a bit down today. He works as a driver.
3. 表示真理、客观存在、科学事实或用于格言警句中: Shanghai lies in the east of China. Columbus proved that the earth is round. Where there is a will, there is a way. 4. 表示现在瞬间的动作: Here comes the bus! 5. 表示将来: 1)表按规定、计划、安排将要发生的动作(仅限于某些表示“来、去、动、停、开始、结束、继续”等的趋向动词),可以与表示未来的时间状语搭配使用。常见的用法是:飞机、火车、轮船、汽车等定期定点运行的交通状况。如: The next train leaves at 3 o’clock this afternoon. How often does the shuttle bus run? 2)在时间和条件状语从句中常使用一般现在时表示将来发生的事情:When Bill comes(不用will come)ask him to wait for me. I shall go there tomorrow unless I’m too busy. 二、一般过去时 标志:动词过去式
高中英语必备基础句型和时态 必背句型 句型1:There+be +主语+地点状语/ 时间状语 There're three books on the table. 桌子上有三本书。 句型2:What's wrong with+sb./sth.? What's wrong with your telephone? 你的手机有什么毛病? 句型3:How do you like…? How do you like China?你觉得中国怎么样? 句型4:What do you like about…? What do you like about China? 你喜欢中国的什么? 句型5:had better(not)+动词原形 You'd better ask that policeman over there. 你最好去问问那边的那个警察。 句型7:Thank+sb.+for (doing) sth. Thank you for coming to see me. 感谢你来看我。 句型8:So+be/情态动词/助动词+主语 He is a student. So am I. 他是一个学生,我也是。 句型9:not…until… He didn't have supper until his parents came back. 直到他的父母回来他才吃饭。 句型10:比较级十and+比较级 The baby cried harder and harder. 那孩子哭得越来越厉害。 句型11:the+比较级,the+比较级 The more one has,the more one wants. 拥有的越多,想要的越多。 句型12:…as+adj./adv.+as…
人教版英语英语动词的时态用法总结及解析百度文库 一、初中英语动词的时态 1.--- Will you go to America next month? ---Yes. But I promise I will call you as soon as I _________there. A.get to B.will get to C.will get D.get 【答案】D 【解析】 【详解】 句意:——下个月你将要去美国吗?——是的。但是我保证我一到达那里,就给你打电话。as soon as引导的时间状语从句,用一般现在时,主句用一般将来时。there是副词,前面不加介词,get there到达那里。故选D。 2.— Who the classroom tomorrow, Tony? — Our group. A.will clean B.cleans C.cleaned D.clear 【答案】A 【解析】 句意:——托尼,明天谁打扫教室?——我们小组。考查一般将来时。根据提示词tomorrow可知时态用一般将来时,其构成为:will+动词原形;故答案选A。 3.Jenny_______in the kitchen when you called her at 5 o'clock this afternoon. A.is cooking B.was cooking C.cooks D.cooked 【答案】B 【解析】 本题难度适中,考查过去进行时,当你昨天5点打电话给她时,他正在煮饭,答案是was cooking,选B。 4.—Do you know _________ the meeting? —Tomorrow morning. A.when they had B.when they are going to have C.when did they have D.when are they going to have 【答案】B 【解析】 【详解】 句意:——你知道他们什么时候来开会吗?——明天早上。 此题考查宾语从句,宾语从句要用陈述句语序,C和D是疑问句语序,故排除;根据回答Tomorrow morning可知此句时态是一般将来时,A是一般过去时,B是一般将来时;故选
一般将来时时态 1. 一般将来时的定义 一般将来时表示在现在看来即将要发生的动作或存在的状态。常用时间副词tomorrow, soon或短语next year / week / month, in a few days, in the future, sometime 做状语。如:What will you do this afternoon?你今天下午干什么? We will have a meeting tomorrow. 我们明天要开会。 He is going to study abroad(到国外)next year. 明年他要出国学习。 2. 一般将来时的结构及应用 (1) shall / will + 动词原形。表示即将发生的动作或存在的状态。特别是表示客观性的事情或在某条件下要发生的事情,只能用此结构。如: What shall we do if he doesn’t come? 如果他不来,我们该怎么办? Will you be free this evening? 今天晚上有空吗? I think he will tell us the truth(真相)。我想他会告诉我们真实情况的。 (2) be going to + 动词原形。表示已经计划或安排好了的事情,也可表示有迹象表明肯定要发生的事情。如: We are going to have a meeting to discuss (讨论)the matter this evening. 今天晚上开会讨论这件事情。 Look at the black clouds over there. I think it is going to rain soon. 看一看那边的乌云,我想天要下雨了。 There is going to be an English evening this week. 本周要举行一个英语晚会。 (3) be +现在分词。表示即将发生的动作或存在的状态。这个句型中动词主要是瞬间动词:come, go, leave, arrive, begin, start, stop, close, open, die, join, borrow, buy等。如: Go ahead, and I’m coming. 走前面一点吧,我就来。 The dog is dying. 那条狗要死了。 Hurry up. The shop is closing. 快点,商店就要关门了。 (4) 一般现在时。表示一种严格按照计划进行的动作。比方说,上课、飞机起飞、火车离站等。如: Don’t hurry. The meeting starts at a quarter past eight. 不要匆忙,回忆八点过一刻开始。 The bus goes back at four thirty. 汽车四点返回。
高考英语时态,前十种拉开分数差距 1.一般现在时(do/does; is/am/are) ① 表示现在的情况、状态或特征。 例:He is a student.他是一个学生。 ② 表示经常性、习惯性动作。 例:He always helps others. 他总是帮助别人。 ③ 客观事实和普遍真理。 例:The earth moves the sun.地球绕着太阳转。 ④ 表示一个按规定、计划或安排要发生的动作。 仅限于某些表示“来、去、动、停、开始、结束、继续”等的动词,可以与表示未来时间的状语搭配使用。
常见的用法是:飞机、火车、轮船、汽车等定期定点运行的交通方式。 例:The next train leaves at 3 o'clock this afternoon. 下一趟火车今天下午3点开车。 ⑤ 在时间、条件和让步状语从句中经常用一般现在(有时也用现在完成时)表示将的来事情。(即:主将从现原则) 例:I will call you as soon as I arrive at the airport.我一到机场就会给你打电话。 When you have finished the report, I will have waited for about 3 hours.等你完成这份报告的时候,我就已经等了将近3个小时了。 2. 现在进行时(am/is/are doing) ① 表示此时此刻正在发生的事情。 例:He is listning to the music now.他现在正在听音乐。
② 表示目前一段时间内一直在做的事情,但不一定此时此刻正在做。 例:I am studying computer this term.这个学期我一直在学习计算机。 ③ 现在进行时可以表示将来的含义。 a. 瞬时动词的进行一定表将来。 例:I am leaving.我要离开了。 b. 持续动词的进行只有有将来的时间状语或有将来语境中才表将来。 例:I am travelling next month.下个月我要去旅行。 ④ 现在进行时与频度副词连用,表示说话者或褒义或贬义的感情色彩。 例:He is always helping others.他总是帮助别人。(褒义)
本专题为大家讲解了16种英语时态的用法,为大家总结了英语时态表,方便同学们更好的英语时态的结构. 英语的基本时态由三种“时”(时间),四种“态”(状态)交叉构成。 三种“时”:过去现在将来 四种“态”:常态进行态完成态完成进行态 一般时进行 时完成时完成进行时 现在 study be studying have studied have been studying 过去 studied be studying had studied had been studying 将来 will study wil be studying will have studied will have been studying 过去将来would study would be studying would have studied would have been studying
时态(Tense)是表示行为、动作和状态在各种时间条件下的动词形式。因此,当我们说时态结构的时候,指的是相应时态下的动词形式。 Ⅰ现在时态:四种 1.一般现在时态:表示现存的状态(be动词),经常做的动作 I do it. 我(经常)做这件事。 2.现在进行时态:表示正在进行的动作 I am doing it. 我(现在)正在做这件事。 3.现在完成时态:表示现在已经完成,对现在产生影响,形成结果 I have done it. 我(现在)已经做完这件事了。 4.现在完成进行时态:表示一直在进行的动作(字面意思已经在进行) I have been doing it. 我(现在)一直正在做这件事。 Ⅱ过去时态:四种 5.一般过去时态:表示过去存在的状态(be动词),经常做的动作 I did it. 我(过去经常)做这件事。 6.过去进行时态:表示过去正在进行的动作 I was doing it. 我(过去的某个时间)正在做这件事。 7.过去完成时态:表示过去已经完成,对过去的某个时间产生影响,形成结果 I had done it. 我(过去的某个时间)已经做完这件事了。 8.过去完成进行时态:表示一直在进行的动作(字面意思已经在进行) I had been doing it. 我(到过去的某个时间)一直在做这件事。 Ⅲ 将来时态:四种 9.一般将来时态:表示将来存在的状态(be动词),将来经常做的动作
般将来时时态 1. 一般将来时的定义 一般将来时表示在现在看来即将要发生的动作或存在的状态。常用时间副词tomorrow, soon 或短语n ext year / week / mon th, in a few days, in the future, sometime 做状语。如: What will you do this afternoon ? 你今天下午干什么? We will have a meet ing tomorrow. 我们明天要开会。 He is going to study abroad (到国外) next year.明年他要出国学习。 2. 一般将来时的结构及应用 (1) shall / will + 动词原形。表示即将发生的动作或存在的状态。特别是表示客观性的事情 或在某条件下要发生的事情,只能用此结构。如: What shall we do if he doesn '如果他不?来,我们该怎么办? Will you be free this evenin g? 今天晚上有空吗? I think he will tell us the truth (真相)。我想他会告诉我们真实情况的。 (2) be going to +动词原形。表示已经计划或安排好了的事情,也可表示有迹象表明肯定要 发生的事情。如: We are going to have a meeting to discuss (讨论)the matter this evening. 今天晚上开会讨论这件事情。 Look at the black clouds over there. I think it is going to rain soon. 看一看那边的乌云,我想天 要下雨了。 There is going to be an En glish evening this week. 本周要举行一个英语晚会。 (3) be +现在分词。表示即将发生的动作或存在的状态。这个句型中动词主要是瞬间动词:come, go, leave, arrive, begi n, start, stop, close, ope n, die, jo in, borrow, buy 等。如: Go ahead, and I ' m con走前面一点吧,我就来。 The dog is dying.那条狗要死了。 Hurry up. The shop is closi ng.快点,商店就要关门了。 (4) 一般现在时。表示一种严格按照计划进行的动作。比方说,上课、飞机起飞、火车离
高考英语动词时态和语态讲义 动词时态 英语中的时态共有十六种,但是常考的或较常用的有十一种。见下表: (一)一般现在时 1.表示经常或习惯性的动作,多用行为动词,且常与表频率的时间状语连用 We always care for each other and help each other. 2.表示客观事实或普遍真理(不受主句时态的限制) The geography teacher told us the earth moves around the sun. 1.表示一个按规定、计划或安排要发生的动作,只用一般现在时; The plane takes off at 10:00 a.m.飞机上午10点起飞。 2.在时间、条件状语从句中常用一般现在时代替将来时。但要注意由if 引导的条件状语从句中有时可以 用shall或will表“意愿”,不表示时态; I’ll go there after I finis h my work. If you will accept my invitation and come to our party, my family will be pleased. 3.以here, there开头的句子里,go, come等少数动词的一般在时表示正在发生的动作。 There comes the bus.汽车来了。 Here she comes.她来了。
(二)一般过去时 1.过去某一时间内经常发生或反复发生的动作或存在的状态 He lived in Beijing when he was young.他年轻时生活在北京。 2.表达过去发生的动作 We visited the factory last Friday.上周五我们参观了那家工厂。 1.有些动词如:think, want, plan等用在一般过去时中常常译为“原来认为/以为,原来想,原计划”。 I thought the film would be interesting, but it isn't.我原以为这部电影是很有趣的,但是事实并非如此。 2.考生有时用现在完成时代替一般过去时 Hello, I _______you were in London. How long _________here? A. don’t know; were you B. hadn’t known; are you C. haven’t known; are D. didn’t know; have you been 【解析】非常容易误选B。其实答案为D,因为“didn’t know” 强调的是见面前不知道,即指过去不知道。(三)一般将来时 1.表示将来的动作和存在的状态 The first time we’ll sen d you with an experienced reporter.第一次我们要派有经验的记者陪同你一起去。2.表示一种倾向或习惯性动作 Oil will float on water.油会浮在水面上。 Crops will die without water.没有水庄稼会死亡 一般将来时几种特殊表达形式的区别 1.be going to:表示打算做某事或有迹象表明即将发生某事 I am going to visit my friend in hospital.我将去看望住在医院的朋友。 It looks as if it is going to rain.看起来好象要下雨了。 2.be about to:表示即时的将来。一般不与时间状语连用 Now ladies and gentleman, you’re about to hear the most incredible tale. 女士们,先生们,你们马上就要听到一个难以置信的故事。 3.be to:可用来表示计划、安排(通常是正式的安排);指令;(表示可能)会做……,可能;必定会发生 或已发生了某事;发布命令或告之规则 Their daughter is to get married soon.他们的女儿可能不久就要结婚了。
英语中的各种时态及用法 英语的时态(tense)是一种动词形式,不同的时态用以表示不同的时间与方式。是表示行为、动作和状态在各种时间条件下的动词形式。因此,当我们说时态结构的时候,指的是相应时态下的动词形式。英语时态分为16种:一般现在、一般过去、一般将来、过去将来时,以及这四者的进行时、完成时和完成进行时下面就英语中常见的八种基本时态进行阐述,其它的时态都是在这八种时态的基础上结合而成的。 一、一般现在时: 1.概念:经常、反复发生的动作或行为及现在的某种状况。 2.时间状语: always, usually, often, sometimes, every week (day, year, month…), once a week, on Sundays, 3.基本结构:动词原形(如主语为第三人称单数,动词上要改为第三人称单数形式) 4.否定形式:am/is/are+not;此时态的谓语动词若为行为动词,则在其前加don't,如主语为第三人称单数,则用doesn't,同时还原行为动词。 5.一般疑问句:把be动词放于句首;用助动词do提问,如主语为第三人称单数,则用does,同时,还原行为动词。 6.例句:. It seldom snows here. He is always ready to help others. Action speaks louder than words. 二、一般过去时: 1.概念:过去某个时间里发生的动作或状态;过去习惯性、经常性的动作、行为。2.时间状语:ago, yesterday, the day before yesterday, last week,last(year, night, month…), in 1989, just now, at the age of 5, one day, long long ago, once upon a time, etc. 3.基本结构:be动词;行为动词的过去式4.否定形式:was/were+not;在行为动词前加didn't,同时还原行为动词。5.一般疑问句:was或were放于句首;用助动词do的过去式did 提问,同时还原行为动词。 6.例句:She often came to help us in those days. I didn't know you were so busy. 三、现在进行时: 1.概念:表示现阶段或说话时正在进行的动作及行为。2.时间状语:now, at this time, these days, etc. 3.基本结构:am/is/are+doing 4.否定形式:am/is/are+not+doing. 5.一般疑问句:把be动词放于句首。6.例句: How are you feeling today? He is doing well in his lessons. 四、过去进行时: 1.概念:表示过去某段时间或某一时刻正在发生或进行的行为或动作。2.时间状语:at this time yesterday, at that time或以when引导的谓语动词是一般过去时的时间状语等。3.基本结构:was/were+doing 4.否定形式:was/were + not + doing. 5.一般疑问句:把was或were放于句首。6.例句:At