长沙学院《大学英语》专升本考试大纲.
- 格式:doc
- 大小:110.50 KB
- 文档页数:12

一、考核目标《大学英语》的考核目的是培养学生具有较强的阅读能力,以及初步的写作能力,主要考核学生运用语言的能力和对语法结构和词语用法的掌握程度。
二、考核内容本考试包括四个部分:阅读理解、词语用法与语法结构、完形填空和短文写作。
第一部分:阅读理解(Reading Comprehension)测试学生通过阅读获取信息的能力。
包括掌握所读材料的主旨和大意;了解说明主旨和大意的事实和细节;既理解字面的意思,也能根据所读材料进行一定的判断和推论;既理解个别句子的意义,也理解上下文的逻辑关系,理解文章的深层含义。
阅读理解不但要求准确,而且要有一定的速度。
要求考生阅读若干篇短文,总阅读量约1000词。
阅读材料的选材原则是:(1)题材广泛,可以包括人物传记、社会、文化、日常知识、科普常识等,但是所涉及的背景知识应能为学生所理解;(2)体裁多样,可以包括叙述文、说明文、议论文等;(3) 语言难度及词汇量约相当于三级水平(3000词汇量左右)第二部分:词语用法与语法结构(Vocabulary and Structure)词语用法部分主要测试学生对词和短语的意义、搭配和用法的掌握程度,语法结构部分则主要测试正确使用语法结构的能力。
第三部分:完形填空(Cloze)测试学生综合运用语言的能力。
完形填空部分的选材原则与阅读理解部分相同,要求学生在全面理解内容的基础上答题。
在一篇题材熟悉、难度适中的短文中留有多个空白,填空的词项包括结构词和实义词。
三、考核方式闭卷四、教材《大学英语Ⅰ》修订版。
上海外语教育出版社。
《大学英语Ⅱ》修订版。
上海外语教育出版社。
一.考核目标:1.了解函数, 极限, 连续, 导数, 微分, 不定积分, 定积分等基本概念及基本理论.2.熟练掌握极限, 导数, 积分等基本运算, 并能应用于实际问题.二.考试内容:(一)函数1.函数的概念: 函数定义, 分段函数2.函数的简单性质:单调性, 奇偶性, 有界性, 周期性.3.反函数4.函数的四则运算与复合运算5.基本初等函数及初等函数(二)极限1.数列极限的概念2.数列极限的性质:唯一性, 有界性, 四则运算定理,夹逼定理,单调有界数列极限存在定理.3.函数极限的概念4.函数极限的定理: 唯一性, 夹逼定理, 四则运算定理.5.无穷小量和无穷大量6.两个重要极限(三)连续1.函数连续的概念, 函数的间断点.2.函数在一点处连续的性质.3.闭区间上连续函数的性质.4.初等函数的连续性(四)导数与微分1.导数的概念: 导数定义, 左导数与右导数, 导数的几何意义,导数与连续的关系.2.导数的四则运算法则与导数的基本公式.3.求导法则, 复合函数的求导法, 隐函数的求导法, 对数求导法.4.高阶导数的概念: 高阶导数的定义, 二阶导数的计算.5.微分: 微分的定义, 微分与导数的关系, 微分法则(五)中值定理及导数的应用1.中值定理: 罗尔中值定理, 拉格朗日中值定理.2.洛比达法则3.函数增减性的判定法4.函数极值及极值点, 最大值与最小值5.曲线的凸凹性, 拐点(六)不定积分1.不定积分的概念, 原函数与不定积分的定义,不定积分的性质.2.基本积分公式3.换元积分法, 第一类换元法, 第二类换元法4.分部积分法5.一些简单有理函数的积分(七)定积分1.定积分的概念: 定积分的定义及几何意义, 可积条件.2.定积分的性质3.定积分的计算, 变上限的定积分, 牛顿--莱布尼兹公式,换元积分法, 分部积分法4.定积分的应用: 平面图形的面积, 旋转体的体积.三.考试方法: 闭卷笔试四.参考书目1.高等数学基础与应用(陶铁胜主编陆履亨编著上海三联书店2000年11月第1 版)2. 高职高专专用书籍<<高等数学上册>> 2001. 6上海高等数学组编写, 上海科学技术出版社计算机应用基础考试大纲基本要求1. 掌握计算机基础知识。

长沙学院专升本英语真题1、—How’s your tour around the North Lake? Is it beautiful?—It ________ be, but it is now heavily polluted.A. willB. wouldC. shouldD. must【答案】C。
【解析】考查情态动词表推测。
句意:—你在北海周围的旅行怎么样?它漂亮吗?—它本应该是漂亮的,但是现在被严重污染了。
Should在此处表示推测,意为“本应该”,故选C。
2.Which do you enjoy ________ your holiday, going abroad or staying at home?A. spendingB. to spendC. being spentD. spend【答案】B。
【解析】考查目的状语。
句意:出国或者在家,你更喜欢以哪种方式度过假期呢?此题极易受enjoy后接动词-ing形式的干扰,从而错选A或C。
其实,enjoy的宾语是which,即在going abroad与staying at home作出选择。
to spend your holiday是作目的状语的,故选B。
3. —Where is Bob?—He ________ to Harbin for a meeting.A. wentB. has beenC. has goneD. go【答案】C。
【解析】考查动词时态。
句意:—鲍勃去了哪里?—他去了北京开会。
have been to指“去过(已经回来)”;have gone to指“去了(未回来)”。
根据句意,故选C。
4、This washing machine is environmentally friendly because it uses ________ water and electricity than ________ models.A. less; olderB. less; elderC. fewer; olderD. fewer; elder【答案】A。
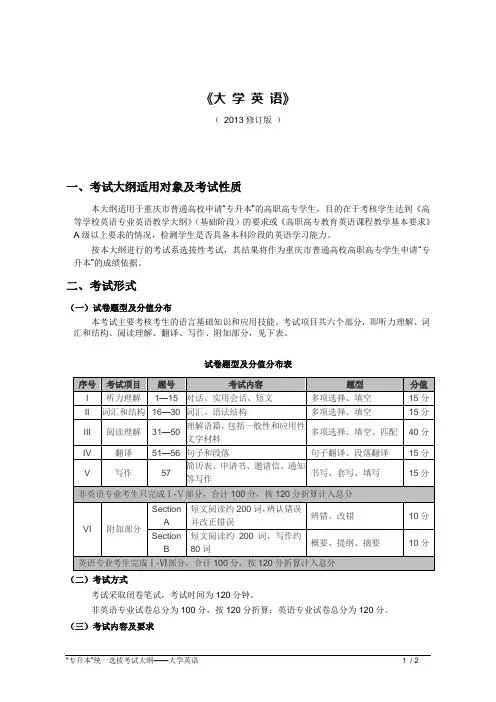
《大学英语》(2013修订版)一、考试大纲适用对象及考试性质本大纲适用于重庆市普通高校申请“专升本”的高职高专学生,目的在于考核学生达到《高等学校英语专业英语教学大纲》(基础阶段)的要求或《高职高专教育英语课程教学基本要求》A级以上要求的情况,检测学生是否具备本科阶段的英语学习能力。
按本大纲进行的考试系选拔性考试,其结果将作为重庆市普通高校高职高专学生申请“专升本”的成绩依据。
二、考试形式(一)试卷题型及分值分布本考试主要考核考生的语言基础知识和应用技能。
考试项目共六个部分,即听力理解、词汇和结构、阅读理解、翻译、写作、附加部分,见下表。
试卷题型及分值分布表(二)考试方式考试采取闭卷笔试,考试时间为120分钟。
非英语专业试卷总分为100分,按120分折算;英语专业试卷总分为120分。
(三)考试内容及要求(一)听力理解(Part ⅠListening Comprehension)考核考生理解所听对话、会话和短文的能力。
听力材料语速为每分钟130词。
听力材料为一般语言材料和实用交流材料。
本部分共15小题,分值15分,题型为多项选择题和填空题。
(二)词汇和结构(Part Ⅱ Vocabulary & Structure)考核考生词汇和语法结构的运用能力。
本部分共15小题,分值15分,题型为多项选择题和填空题。
(三)阅读理解(Part Ⅲ Reading Comprehension)考核考生通过阅读获取信息的能力。
阅读内容为一般阅读材料和常见实用性文字材料。
本部分共4篇短文,总词汇量约1300词,共20小题,分值40分,题型为多项选择题,填空题和匹配题。
其中前2篇阅读材料共10小题,分值20分,题型为多项选择题; 第三篇阅读材料共5小题,分值10分,题型为填空题; 第四篇阅读材料共5小题,分值10分,题型为匹配题。
(四)翻译(Part Ⅳ Translation)考核学生英汉互译能力。
本部分由汉译英和英译汉两部分组成。

专升本大学英语教学大纲第一篇:专升本大学英语教学大纲专升本大学英语教学大纲一、教学对象教学对象是我校专升本非英语专业的学生。
学生在听、说、读、写、译等方面受过专门训练。
二、教学目的大学英语教学是高等教育的一个有机组成部分,大学英语课程是大学生的一门必修的基础课程。
大学英语教学是以英语语言知识与应用技能、学习策略和跨文化交际为主要内容,以外语教学理论为指导,并集多种教学模式和教学手段为一体的教学体系。
大学英语的教学目标是培养学生英语综合应用能力,特别是听说能力,使他们在今后工作和社会交往中能用英语有效地进行口头和书面的信息交流,同时增强其自主学习能力、提高综合文化素养,以适应我国经济发展和国际交流的需要。
大学英语课程要开拓思路,拓展教学方向,满足我校的特色人才培养的需求,实现培养应用型创新型和复合型高级人才的目标。
三、教学要求我校的本科生通过2学年4个学期的大学英语教学,应达到《大学英语课程教学要求》规定的较高要求的英语能力。
较高要求的英语能力要求如下:1.听力理解能力:能够基本听懂来自英语国家人士的谈话和讲座,能听懂题材熟悉、篇幅较长的国内英语广播或电视节目,语速为每分钟150词左右。
能基本听懂外国专家用英语讲授的专业课程。
能掌握其中心大意,抓住要点。
2.口语表达能力:能够和来自英语国家的人士进行比较流利的会话,较好地掌握会话策略,能基本表达个人意见、情感、观点等,能基本陈述事实、事件、理由等,表达思想清楚,语音、语调基本正确。
3.阅读理解能力:能基本阅读英语国家报刊杂志的一般性题材的文章,阅读速度为每分钟80词,在快速阅读篇幅较长的材料时,阅读速度达到每分钟120词,能就阅读材料进行略读或寻读。
能够基本读懂自己专业方面的综述性文献,并能正确理解中心大意,抓住主要事实和有关细节。
4.书面表达能力:能写日常应用文,能写自己专业论文的英语摘要,能借助参考资料写出与专业相关、结构基本清晰、内容较为丰富的报告和论文,能描写各种图表,能就一定的话题在半小时内写出160词的短文,内容完整,条理清楚,文理通顺。

湖南工程学院2017年“专升本”选拔考试《大学英语1》考试大纲(满分150分,时限120分钟)一、考试对象本大纲适用于修完《基本要求》所规定的全部内容的高等职业教育和普通高等专科教育非英语专业的理工科学生。
二、考试性质本考试的目的是考核考生的语言知识、语言技能和使用英语处理有关一般业务和涉外交际的基本能力,其性质是考核学生英语水平。
三、考试方式与内容考试方式为笔试,包括五个部分:阅读理解、词汇和语法结构、完型填空、翻译(英译汉和汉译英)和写作。
考试范围为《基本要求》对A级所规定的全部内容。
第一部分:阅读理解(Reading Comprehension)测试考生从书面文字材料获取信息的能力。
总阅读量约1000词。
本部分测试的文字材料包括一般性阅读材料(文化、社会、常识、科普、经贸、人物等)和应用性文字,其内容能为理工科各专业学生所理解。
阅读材料涉及的语言技能和词汇限于《基本要求》中的“阅读技能表”所列全部技能范围和“词汇表”中3,400词的范围。
主要测试以下阅读技能:1.了解语篇和段落的主旨和大意。
2.掌握语篇中的事实和主要细节。
3.理解语篇上下文的逻辑关系。
4.对句子和段落进行推理。
5.了解作者的目的、态度和观点。
6.根据上下文正确理解生词的意思。
7.了解语篇的结论。
8.进行信息转换。
本部分的得分占总分的40%。
测试时间是35分钟。
第二部分:词汇与语法结构(Vocabulary and Structure)测试考生运用词汇和语法知识的能力。
测试范围包括《基本要求》中“词汇表”所涉及的词汇和“语法结构表”所规定的全部内容。
本部分的得分占总分的15%。
测试时间为20分钟。
第三部分:完型填空(Cloze)测试考生综合运用语言的能力。
测试范围包括词语搭配、句型结构和语篇理解。
要求考生在全面理解内容的基础上选择一个最佳答案,使短文意思清楚,结构完整。
本部分的得分占总分的10%。
测试时间为15分钟。
第四部分:翻译---英译汉和汉译英(Translation--English to Chinese and Chinese to English)测试考生是否掌握一定的翻译技巧和具备初步的翻译能力。

2024年湖南专升本考试大纲已经正式公布,考试时间为2024年3月18-19日,考试科目分为公共课和专业课两大类。
公共课包括语文、数学、英语三科,专业课根据不同专业而有所不同。
考生需要根据自己的专业选择相应的专业课考试科目。
一、公共课考试大纲1.语文:考试内容包括现代文阅读、古文阅读、写作三部分。
现代文阅读主要考查考生对文章的理解和分析能力,古文阅读主要考查考生对古文的理解和翻译能力,写作主要考查考生的写作能力。
2.数学:考试内容包括高等数学、线性代数、概率论与数理统计三部分。
高等数学主要考查考生对微积分、线性代数、多元函数等内容的理解和应用能力,线性代数主要考查考生对矩阵、行列式、向量空间等内容的理解和应用能力,概率论与数理统计主要考查考生对概率论、数理统计等内容的理解和应用能力。
3.英语:考试内容包括英语阅读、英语写作、英语翻译三部分。
英语阅读主要考查考生对英语文章的理解和分析能力,英语写作主要考查考生的英语写作能力,英语翻译主要考查考生将汉语翻译成英语或将英语翻译成汉语的能力。
二、专业课考试大纲专业课考试科目根据不同专业而有所不同,具体考试科目请查看湖南省教育考试院发布的《2024年湖南专升本考试专业目录》。
专业课考试内容主要包括以下几个方面:1.专业基础知识:主要考查考生对本专业基础理论、基本概念、基本原理的掌握情况。
2.专业应用能力:主要考查考生运用专业知识解决实际问题的能力。
3.专业实践能力:主要考查考生在专业实践中所具备的操作技能、实验技能等。
三、备考建议1.制定合理的复习计划:考生应根据自己的实际情况,制定合理的复习计划,并严格按照计划执行。
2.强化基础知识:考生应夯实基础知识,熟练掌握基本概念、基本原理和基本方法。
3.注重综合应用能力:考生应注重综合应用能力的培养,学会将所学知识综合运用到实际问题中去解决问题。
4.加强实战训练:考生应多做历年试题和模拟试题,熟悉考试题型和考试难易程度,以便在考试中更好地发挥自己的水平。

专升本英语考试大纲专升本英语考试大纲那可是很多同学关心的事儿!咱今天就好好唠唠。
先来说说词汇吧,这就像是盖房子的砖头,没砖头可盖不了结实的房子。
大纲要求掌握的词汇量可不少,得有 3500 左右呢。
别被这个数字吓到,其实每天积累一点,就像每天吃一口饭,慢慢也就吃饱了。
我记得之前有个同学,他把单词写在小纸条上,上厕所都拿出来瞅两眼,嘿,还真有效!语法也是个重点。
时态、语态、从句等等,可别觉得头疼。
就说那个虚拟语气,好多同学迷糊,其实你就把它想象成一种假设的情况。
比如说“要是我会飞,那该多好啊”,这就是虚拟语气。
阅读理解在考试中占比很大。
做阅读理解可不能像没头的苍蝇乱撞,得有技巧。
先快速浏览题目,带着问题去读文章,边读边标记关键信息。
我曾经观察过一个学霸,他读文章的时候,手里的笔不停地动,把重点都划出来了,这样做题的时候就能很快找到答案。
写作也是不能忽视的。
平时得多练,各种体裁都要熟悉。
有一次考试,题目是让写一封感谢信,有个同学居然写成了投诉信,这分数能高吗?所以,一定要看清题目要求。
听力部分呢,要多听多练。
可以听听英语新闻、电影原声,培养语感。
有个同学每天早上起来就放英语听力,刷牙洗脸都听着,时间长了,听力水平明显提高。
翻译题考查的是语言的综合运用能力。
不仅要翻译准确,还要符合英语的表达习惯。
这就需要我们平时多积累一些常用的短语和句型。
总之,专升本英语考试大纲虽然有一定的难度,但只要我们一步一个脚印,认真学习,就一定能取得好成绩。
就像爬山一样,虽然过程辛苦,但当你爬到山顶,看到美丽的风景时,一切都值得了!加油吧,同学们!。

湖南专升本考试大纲的详细内容如下:考试性质:湖南专升本考试是中国湖南省教育系统的一项重大考试,旨在为专科应届毕业生提供继续提升学历的机会,也是评价本科院校招生录取的重要依据。
考试范围广,涉及学科众多,考察知识面广泛,旨在全面评估考生的综合素质。
考试科目及内容:1. 公共课:英语,总分为100分。
内容涵盖词汇、语法、阅读理解、翻译、写作等方面,考试时间为90分钟。
2. 专业课一:大学语文,总分为150分。
考试内容涉及文学、历史、哲学、文化、教育等多个领域,考试时间为120分钟。
3. 专业课二:专业综合知识,总分为200分。
考试内容根据考生所报专业而异,考试时间为150分钟。
其中,专业知识占比约80%,基础知识占比约20%。
题型及难度:题型主要包括选择题、简答题、论述题、分析题等。
难度适中,符合专科应届毕业生水平。
评分标准:根据答案的准确程度、语言的规范程度和卷面的整洁程度等因素进行评分。
对于专业课,将设立参考书籍、知识点和重点进行分析和说明,以便考生能够更好地准备。
考试形式:考试形式为闭卷,笔试。
试卷由统一命题、统一制卷、统一阅卷,考试过程中禁止考生抄袭和作弊。
时间安排:考试时间为每年的某一周末,具体时间会根据实际情况进行调整。
考试大纲的重要性:湖南专升本考试大纲为考生提供了明确的复习方向和重点,有助于考生有针对性地进行备考,提高备考效率。
同时,大纲也为教师提供了教学指导,有助于提高教学质量。
建议:建议考生在备考过程中,要全面掌握考试内容,注重基础知识的理解和应用,关注时事新闻和社会热点问题,提高自己的综合素质和能力。
同时,要合理安排时间,注重真题练习,掌握答题技巧和方法,提高自己的应试能力。
此外,考生还应注重自己的心理素质和身体素质的培养,以保持良好的心态和状态,迎接即将到来的考试。
希望以上回答对您有所帮助。

工学院专升本“大学英语”考试纲领一、考试对象本纲领合用于修完大学英语专科阶段的容,参加工学院“专升本”考试的学生。
二、考试性质科学、公正、正确、规地测试考生的英语阅读、表达、运用能力以及逻辑思想能力。
考生应掌握英语的语音知识,读音正确;掌握英语的基础词汇;能较好地掌握和运用英语的语法例则;拥有必定的综合应用英语语言的能力。
三、考试方式与容考试形式为笔试、闭卷。
考试时间为120 分钟。
考试容主要包含以下几个方面:1)词汇构造(Vocabulary & Structure)测试考生运用词汇与语法知识的能力。
测试围包含《基本要求》中的“ 语法构造表”所规定的所有容和一部分大学英语四级要求的容。
包含多项选择和词形变换等题型。
本部分的得分占总分的 25%。
测试时间为 25 分钟。
2)完型填空( Cloze )测试考生运用词汇与语法知识的能力。
测试围包含《基本要求》中的“语法构造表”所规定的所有容和一部分大学英语四级要求的容。
本部分的得分占总分的 10%。
测试时间为 10 分钟。
3)阅读理解( Reading Comprehension)测试考生从书面文字资料获守信息的能力。
本部分测试的文字资料包含一般性阅读资料(文化、社会、知识、科普、经贸、人物等)和应用性文字,其容能为各专业学生所理解。
包含多项选择 (Multiple Choice)、选词填空 (Banked Cloze) 、简答题 (Short Answer Questions) 等题型。
主要测试以下阅读技术:①认识语篇和段落的要旨和粗心。
②掌握语篇中的事实和主要情节。
③理解语篇上下文的逻辑关系。
④对句子和段落进行推理。
⑤认识作者的目的、态度和看法。
⑥依据上下文正确理解生词的意思。
⑦认识语篇的结论。
⑧进行信息变换。
本部分的得分占总分的 40%。
测试时间是 45 分钟。
4)翻译(Translation)翻译部分为英汉互译。
汉译英部分:句中的一部分已用英文给出,要求考生依据全句意思将汉语部分译成英语。

2024专升本湖南英语大纲English:The 2024 Hunan Provincial Adult College Entrance Examination English syllabus covers a range of topics aimed at assessing candidates' English language proficiency and communication skills. The syllabus includes sections on reading comprehension, listening comprehension, writing, and translation. The reading comprehension section comprises passages of varying lengths and difficulty levels, requiring candidates to demonstrate their ability to understand and interpret written English. The listening comprehension section presents audio recordings of conversations, lectures, or announcements, followed by questions that assess candidates' ability to comprehend spoken English and extract relevant information. The writing section assesses candidates' ability to express ideas clearly and coherently in written English, with tasks ranging from short essays to longer compositions. Finally, the translation section tests candidates' proficiency in translating between English and Chinese, evaluating their understanding of both languages' grammar, vocabulary, and idiomatic expressions. Overall, the syllabus aims to comprehensively evaluate candidates' English language skills invarious contexts, preparing them for academic pursuits and professional endeavors.中文翻译:2024年湖南省成人高考英语大纲涵盖了多个主题,旨在评估考生的英语语言能力和沟通技巧。

《英语》专升本考试大纲(2019年)一、考试方式:闭卷考试二、考试时间:120分钟三、考试总分:100分四、考试范围1.英语基础知识运用考查考生对英语语法、词汇知识和较为简单表达方式的掌握情况。
2.阅读理解能力考查考生理解主旨要义、理解文中具体信息、作出简单判断和推理、理解作者的意图和态度、根据上下文推测生词词义以及理解文章的基本结构的能力。
3.翻译能力能恰当地运用参考书目中所学的单词、词组和句型翻译句子。
4.应用文写作能力掌握感谢信、邀请信、祝贺信、道歉信、投诉信、求职信、推荐信等英语应用文的基本写作格式、结构和常用句型,注重词汇和语法的使用准确性,文章要求有连贯性和逻辑性。
五、考试题型选择题、填空题、阅读理解题、翻译题、作文题等。
六、参考教材:1.《大学英语综合教程I》,宋乃康主编,陕西人民教育出版社,2009年3月第1版。
2.《大学英语综合教程Ⅱ》,宋乃康主编,陕西人民教育出版社,2010年。
《计算机基础》专升本考试大纲(2019年)一、考试方式:闭卷考试二、考试时间:100分钟三、考试总分:100分四、考试范围:1.计算机基础知识(1)计算机的发展、类型及其应用领域。
(2)计算机系统的组成;微型计算机硬件系统的组成及主要技术指标;中央处理器的组成及功能;存储器功能和分类;常见输入输出设备的功能和使用方法;软件系统的组成;系统软件和应用软件的基本概念。
(3)计算机语言的分类;计算机中数据的表示、存储与处理;进制的概念及数制间的相互转换。
(4)多媒体技术概念与应用。
(5)计算机安全,病毒的预防与消除使用知识。
2.操作系统的功能和使用(1)操作系统的基本概念、功能和分类。
(2)Windows7操作系统的基本概念和常用术语:文件、文件夹、库等。
(3)Windows7操作系统文件及文件夹的相关操作(新建、复制、移动、删除、查找、重命名、更改属性、隐藏等操作)。
(4)Windows7操作系统桌面外观的设置:任务栏、桌面背景、分辨率、屏幕保护等相关操作及设置。
工学院专升本“大学英语”考试大纲一、考试对象本大纲适用于修完大学英语专科阶段的容,参加工学院“专升本”考试的学生。
二、考试性质科学、公平、准确、规地测试考生的英语阅读、表达、运用能力以及逻辑思维能力。
考生应掌握英语的语音知识,读音正确;掌握英语的基础词汇;能较好地掌握和运用英语的语法规则;具有一定的综合应用英语语言的能力。
三、考试方式与容考试形式为笔试、闭卷。
考试时间为120分钟。
考试容主要包括以下几个方面:1)词汇结构(Vocabulary & Structure)测试考生运用词汇与语法知识的能力。
测试围包括《基本要求》中的“语法结构表”所规定的全部容和一部分大学英语四级要求的容。
包含多项选择和词形变换等题型。
本部分的得分占总分的25%。
测试时间为25分钟。
2)完型填空(Cloze)测试考生运用词汇与语法知识的能力。
测试围包括《基本要求》中的“语法结构表”所规定的全部容和一部分大学英语四级要求的容。
本部分的得分占总分的10%。
测试时间为10分钟。
3)阅读理解(Reading Comprehension)测试考生从书面文字材料获取信息的能力。
本部分测试的文字材料包括一般性阅读材料(文化、社会、常识、科普、经贸、人物等)和应用性文字,其容能为各专业学生所理解。
包括多项选择(Multiple Choice)、选词填空(Banked Cloze)、简答题(Short Answer Questions)等题型。
主要测试以下阅读技能:①了解语篇和段落的主旨和大意。
②掌握语篇中的事实和主要情节。
③理解语篇上下文的逻辑关系。
④对句子和段落进行推理。
⑤了解作者的目的、态度和观点。
⑥根据上下文正确理解生词的意思。
⑦了解语篇的结论。
⑧进行信息转换。
本部分的得分占总分的40%。
测试时间是45分钟。
4)翻译(Translation)翻译部分为英汉互译。
汉译英部分:句中的一部分已用英文给出,要求考生根据全句意思将汉语部分译成英语。
专升本英语大纲英文回答:In terms of the general requirements for the English section of the undergraduate entrance exam, candidates are expected to possess a comprehensive understanding of the English language and its various aspects. This includes a strong command of grammar, vocabulary, and reading comprehension. Additionally, test-takers should be able to effectively express themselves in English both verbally and in writing. The exam format typically consists of multiple-choice questions covering grammar, vocabulary, reading comprehension, and writing. To excel in this section, candidates should familiarize themselves with the exam structure and practice answering different types of questions. Moreover, they should allocate sufficient time for preparation and review to enhance their chances of achieving a desirable score.Specific requirements outlined for the English sectioninclude:1. Vocabulary: Candidates should have a vast knowledge of English vocabulary, including idioms, phrasal verbs, and specialized terms. This aspect tests the depth and breadth of their vocabulary, which is crucial for successful communication.2. Grammar: A thorough understanding of English grammar is essential, encompassing topics such as parts of speech, sentence structure, tenses, and punctuation. This section assesses the candidate's ability to construct grammatically correct sentences and comprehend complex sentence structures.3. Reading Comprehension: Candidates are evaluated on their ability to comprehend and analyze written texts. This includes passages from various sources, such as news articles, academic papers, and literary works. Test-takers should be able to identify main ideas, supporting details, and inferential meanings.4. Writing: The writing section tests the candidate's ability to express themselves coherently and effectively in English. It typically involves tasks such as essay writing, letter writing, or other forms of written communication. Candidates should demonstrate their proficiency in organizing their thoughts, using appropriate vocabulary and grammar, and adhering to the prescribed word count.5. Translation: In some cases, the English section may include a translation component, where candidates are required to translate passages from their native language into English or vice versa. This aspect assesses their ability to bridge linguistic gaps and convey meanings accurately.中文回答:专升本英语大纲要求解析:1. 词汇,要求考生掌握丰富的英语词汇量,包括习语、短语动词和专业术语。
【大学英语】湖南工学院专升本大学英语考试大纲(可编辑)湖南工学院专升本大学英语考试大纲科学、公平、准确、规范地测试考生的英语阅读、表达、运用能力以及逻辑思维能力。
考生应掌握英语的语音知识,读音正确;掌握英语的基础词汇;能较好地掌握和运用英语的语法规则;具有一定的综合应用英语语言的能力。
考试形式为笔试、闭卷。
考试时间为120分钟。
考试内容主要包括以下几个方面:)多项选择选词填空(Banked Cloze)简答题(Short Answer Questions)?了解语篇和段落的主旨和大意。
掌握语篇中的事实和主要情节。
理解语篇上下文的逻辑关系。
对句子和段落进行推理。
了解作者的目的、态度和观点。
根据上下文正确理解生词的意思。
了解语篇的结论。
进行信息转换。
本部分的得分占总分的40%。
测试时间是45分钟。
4)翻译 (Translation) 翻译部分为英汉译。
句中的一部分已用英文给出,要求考生根据全句意思将汉语部分译成英语。
翻译须符合英语的语法结构和表达习惯,要求用词准确。
写作选用考生所熟悉的题材。
考生根据规定的题目和所提供的提纲、情景、图片或图表等,写出一篇词的短文。
写作要求是思想表达准确、意义连贯、无严重语法错误试卷为客观题、主观题混合型,共100分试卷共分五部分,题型结构如下:I(。
共分。
每题II(。
每题0.5分,共10分。
III(阅读理解。
题,共分。
要求考生阅读篇短文,两篇为多项选择题型的短文理解测试,一篇为选词填空(Banked Cloze)一篇为简答题(Short Answer Questions)。
共计5题。
考生应根据短文内容所给最佳选择答案。
IV(翻译。
小题,共0分。
题目分两内容准确、完整,语言明白V(短文写作。
1题,1分。
考生应根据题目以及写作提纲或规定情景、图表等写出100词的短文。
要求内容切题,表达清楚,意义连贯,语言比较规范。
语言技能及要求词汇和词汇掌握约300个基础英语单词和相应的常用词组。
长沙学院《大学英语》“专升本”考试大纲一、考试形式及适用对象本考试采用客观试题与主观试题相结合、单项技能测试与综合技能测试相结合的形式。
考试对象为参加选拔考试的所有考生,主要考查听力、阅读、写作等语言技能。
二、题型及比例本考试由五个部分组成:听力理解、阅读理解、词汇语法、完形填空和短文写作,其中:听力理解30分(占20%)、阅读理解60分(占40%)、词汇语法20分(占13.33%)、完形填空20分(占13.33%)和短文写作20分(占13.33%)。
三、考试时间和分数本课程考试满分为150分,考试时限为120分钟。
四、考试大纲第一部分听力理解(Listening Comprehension)1.考核题型(1)本部分分为两节:对话题与短篇题。
第一节为对话题,共10组对话,每组对话后有一个问句,每个问句为一题。
第二节为短篇题,共三篇短文,每篇后有3 - 4个题目,每题有一个问句。
每篇短文及问题只读一遍。
(2)本部分每个问题提供四个选择项。
2.考核要求(1)能听懂由一个语轮组成的涉及日常生活的简短对话。
(2)能听懂短篇听力中题材,熟悉、表达不太复杂的简短故事,讲话或叙述等。
(3)能理解听力部分中用教学大纲中常见高频词所表达的一般信息。
第二部分阅读理解(Reading Comprehension)1.考核题型(1)本部分由四篇短文组成,每篇短文250个词左右。
(2)每篇短文后有5个问题,考生根据短文内容从每个问题后的四个选择中选出最佳答案。
2.考核要求(1)能读懂题材熟悉、难度适中(相当于应用英语能力考试A级)、体裁多样的英文短文。
(2)能掌握所读材料的主旨和大意。
(3)能了解和辨认说明主旨大意的事实与细节。
(4)能根据具体句子的意义理解上下文的逻辑关系及所指关系。
(5)能根据所读材料的事实进行归纳和逻辑推理。
第三部分词汇语法(Vocabulary and Structure)1.考核题型(1)本部分由词汇用法题和语法结构题组成,共30题,其中词汇用法题约占70% -80%,语法结构题约占20% - 30% 。
(2)考试题型为多项选择题,每题有四个选择项,要求学生根据题中提供的语境,从中选出一个最佳答案。
2.考核要求(1)具有对覆盖专科教学大纲中的全部词汇进行准确识词和辨词的能力。
(2)能正确运用常用词汇、短语及基本语法和句型。
(3)能根据语境对高频词进行搭配运用。
第四部分完形填空(Cloze)1.考核题型本部分由一篇题材熟悉,难度适当,约150个词的短文构成。
文中留有20个单词空白,每个空白为一题,每题提供四个选择词项。
填空词项一般为结构词和实义词。
2.测试考核要求(1)考生能在全面理解内容的基础上,选择一个最佳答案,使短文的意思和结构恢复完整。
(2)本部分主要测试学生整体运用语言的能力。
第五部分短文写作(Writing)1.考核题型本部分由题目、作题要求及提示三部分组成。
提示既可以是英文,也可以是中文。
2.考核要求(1)考生能在规定时间内,根据所给题目和要求,撰写一篇约120字的英文短文。
(2)考生能读懂所给的做题要求与提示,按题撰文。
(3)考生能就日常生活、学习、社会或文化教育中一般常识性题材进行英文写作。
文体包括记叙文、说明文、议论文、书信等。
(4)考生作文应文体正确,语言通顺,用词恰当,结构合理,具有一定的说服力。
五、样题College English ExaminationPaper (A)Listening Comprehension (30′ Section A 1′×10=10′; Section B 2′×10=20′)Section A ConversationDirections:In this section, you will hear 10 short conversations. At the end of each conversation,a question will be asked about what was said. Both the conversation and the questionwill be spoken only once. After each question there will be a pause. During the pause,you must read the four choices marked (A), (B), (C) and (D), and decide which is thebest answer. Then mark the corresponding letter on the ANSWER SHEET with asingle line through the center.1. (A) Not knowing what he wants. (B) The weather that he doesn’t like.(C) The plane. (D) Flying to the north.2. (A) Steve looks good in anything. (B) He knew someone who looked like Steve.(C) He wishes he had a tie like Steve’s. (D) Steve should wear the old tie.3. (A) At the hotel. (B) At the airport. (C) On the train. (D) In the plane.4. (A) In a restaurant. (B) At the post office. (C) In a school. (D) In a hospital.5. (A) She hasn’t gone traveling for several weeks. (B) She likes to take long trips.(C) She prefers not to go outing on weekends. (D) She spends a long time in planning her trips.6. (A) The woman will ask Frank to come home earlier. (B) Frank will come home earlier.(C) She will have a quarrel with Frank. (D) She is tired of waiting for him there.7. (A) Bob is too tired to study any more. (B) He told Bob not to study late at night.(C) He had often advised Bob to prepare earlier. (D) Bob didn’t hear the warning.8. (A) It’s not important how he dances. (B) It’s too crowded to dance.(C) If he is careful, no one will notice. (D) No one knows how to dance.9. (A) 4 dollars. (B) 5 dollars. (C) 6 dollars. (D) 15 dollars.10. (A) 20 minutes (B) 30 minutes (C) 45 minutes (D) 15 minutesSection B PassageDirections: In this section you will hear 3 short passages. At the end of each passage, you will hear some questions. Both the passage and the questions will be spoken only once.After you hear a question, you must choose the best answer from the four choicesmarked (A), (B), (C) and (D). Then mark the corresponding letter on the ANSWERSHEET with a single line through the center.Passage OneQuestions 11 and 12 are based on the passage you have just heard.Passage OneQuestions 11 and 12 are based on the passage you have just heard.11. (A) Plants (B) Sun (C) Animals (D) Human beings12. (A) Breaking up (B) Dying out (C) Stopping (D) DisappearingPassage TwoQuestions 13 to 15 are based on the passage you have just heard.13. (A) They went to the theater. (B) They stayed at home talking.(C) They went to the cinema. (D) They washed the dishes at home.14. (A) A woman (B) A man (C) A driver (D) An actress15. (A) They were having a joke.(B) They were washing the dishes.(C) They were running for the first who will not wash the dishes.(D) They were running for the first who will wash the dishes.Passage ThreeQuestions 16 to 20 are based on the passage you have just heard.16. (A) Not rich but kind (B) Rich and kind(C) Neither rich nor kind (D) Rich but mean17. (A) He lost them. (B) He gave them to pay for his taxi home.(C) He used them to pay for his lunch (D) He gave them to a beggar.18. (A) The artist (B) The beggar(C) Neither of them paid (D) Each paid his own bill.19. (A) He invited the beggar to another lunch.(B) He invited the beggar to spend the night in his home.(C) He took the beggar home and gave him back the money.(D) He gave the beggar more money.20. (A) He didn’t want to pay for the taxi too. (B) He had no money to pay for the taxi.(C) He didn’t want the artist to pay for the taxi. (D) He had something else to do.Reading Comprehension (3′×20=60′)Directions:There are 4 passages in this part. Each passage is followed by some questions or unfinished statements. For each of them there are four choices marked (A), (B), (C)and (D). You should decide on the best choice and mark the corresponding letter onthe Answer Sheet with a single line through the center.Passage OneQuestions 21 to 25 are based on the following passage:A few years ago it was common to speak of a generation gap between young people and their elders. Parents said that children didn’t respect and listen to them, while children said that their parents did not understand them at all. What had gone wrong? Why had the generation gap suddenly appeared? Actually, the generation gap has been around for a long time. Many people argue that it is built into every part of our society.One important cause of the generation gap is the opportunity that young people have to choose their ways of life. In a more traditional (传统的) society, when children grow up, they are expected to live in the same area as their parents, to marry people that their parents know and like, and often to continue the family jobs. In our society, young people often travel great distances for their education, move out of the family at an early age, marry or live with people whom theirparents have never met, and choose jobs different from those of their parents.In our society, parents often expect their children to do better than they did, to find better jobs, to make more money and to do all the things that they were unable to do. Often, that is another cause of the gap between them. Often they discover that they have very little in common with each other.Finally, the speed at which changes take place in our society is the third cause of the gap between the generations. In a traditional culture, senior people are valued for their knowledge, but in our society the knowledge of a life time may become out of date. The young and the old seem to live in two different worlds, separated by different skills and abilities. No doubt, the generation gap will continue in American life for some time to come.21.The first paragraph tells us that ________.(A) the problem of the generation gap draws much attention from people.(B)it is out of date to talk about the generation gap.(C)children and parents are trying to understand each other.(D)it is very important for people to frequently communicate with each other.22.In a more traditional society, old people ________.(A) have their children respect and listen to them. (B) do not care for their children at all.(C)expect their children to rebel against them. (D) do not live together with theirchildren.23.In American society young people ________.(A) do not need to find jobs (B) marry people younger than them(C)have better education than their parents (D) leave home at an early age24.Which of the following is NOT the cause of the generation gap?(A) Young people like to depend more on themselves. (B) Parents do not love their children dearly.(C)American society changes rapidly. (D) Parents expect too much oftheir children.25.The main idea of the passage is _________.(A) that the generation gap needs considering(B)when the generation gap is necessary in American society(C)why the generation gap exists(D) how we can reduce the generation gap.Passage TwoQuestions 26 to 30 are based on the following passage:Agnes Miller was one of the earliest leaders of the women's liberation movement in the United States. She was born on a farm in Missouri in 1892.Strangely enough she had a very happy life as a child. She was the only daughter and the youngest child of five. Her parents and her brothers always treated her as their favorite.In 1896 the family moved to Chicago. Three years later they moved back to St. Louis where Agnes spent the rest of her childhood. She enjoyed her years in school and was an excellentstudent of mathematics. She also was quite skillful as a painter.It was when Agnes went off to college that she first learned that women were not treated as equals. She didn't like being treated unequally but she tried not to notice it. After graduating from college she tried to get a job in her major field——physics. She soon found it was almost impossible for a woman.Agnes spent a full year looking for a job. Finally she gave up in anger. She began writing letters of anger to various newspapers. An editor in New York liked her ideas very much. He specially liked her style(风格).He asked her to do a series of stories on the difficulties that women had in finding a job. And there she began her great fight for equal rights for women.26. How many children did Mr. Miller and Mrs. Miller have?(A) 1 (B) 3 (C) 4 (D) 527. Where did Agnes spend her childhood?(A) Missouri (B) Chicago (C) New York (D) St. Louis and Chicago28. At school,Agnes was good at ________.(A) physics and painting (B) maths and painting(C) writing and maths (D) physics and writing29. What is her major in college?(A) Physics (B) Mathematics (C) Chemistry (D) English30. What happened in Agnes's life when she was in college?(A) She learned to accept the fact that men and women were unequal.(B) She learned that it was impossible for a woman to be a scientist.(C) She came to know of the inequality between men and women.(D) She developed her personal way of writing.Passage ThreeQuestions 31 to 35 are based on the following passage:People often say that the Englishman's home is his castle. They mean that the home is very important and personal. Most people in Britain live in houses rather than flats(公寓),and many people own their homes. This means that they can make them personal, and change them in any way they like.Most houses have a garden, even if it is a small one, and the garden is usually loved. The house and the garden are the private space of a person. In a crowded city a person knows that he or she has a private space which is only for him or herself and for invited friends.People usually like to mark their space. If you are on the beach you may have spread(铺开)your towels(浴巾)around you; on the train you may have put your coat or small bag on the seat beside you; in a library you may spread your books around you.Once I was travelling on a train to London. I was in a section for four people and there was a table between us. The man opposite to me had his briefcase(公文包)on the table. There was no space on my side of the table at all. I was unhappy. I thought he thought that he owned the whole table. I had been reading a book about nonverbal(非言语的)communication(交流)so I took various papers out of my bag and put them on his case!When I did this he suddenly becameangry and his eyes nearly popped out(突出)of his head. I had taken up his space!A few minutes later I took my papers off in order to read them. He immediately(立即)moved his case to his side of the table.31. What does the first sentence in Paragraph 1 mean?(A) The home matters greatly to Englishmen.(B) The castle is more important than the home.(C) The home is more important than the castle.(D) Englishmen usually live in homes instead of castles.32. Which of the following is NOT the reason for most British to live in houses?(A) They can make changes in the houses in which they live.(B) They love houses more than gardens.(C) They can own private space like the house and the garden.(D) They can keep the private space to themselves and friends.33. According to Paragraph 2, if you spread your books around you in a library, it means ________.(A) you want to spread your towels around you further (B) you want to put your coat on the table(C) you find no space for your books on the seat (D) you want to tell others the space belongs to you34. How did the man opposite the writer show he owned the whole table?(A) He sat in a section for four people. (B) He placed his briefcase on the table.(C) He was travelling on a train to London. (D) He was reading a book.35. The writer tried to get back his space by ________.(A) moving the case off the table (B) taking all his papers out(C) taking up the space of the man opposite (D) showing the books concerned tothe manPassage FourQuestions 36 to 40 are based on the following passage:For a long time women with HIV (艾滋病毒) were ignored because the focus was totally on HIV men. The gay community (同性恋团体) was very much in sight and vocal and successfully got support for its cause. Now we are rapidly approaching the point where one half of all AIDS cases in the world are women. But no one is taking this dangerously high level of infection (感染) among women seriously enough.Women usually have a worse time dealing with HIV than men do. In most cases, the woman is taking care of children as well as her sick partner. She may not even have time to take care of herself. The HIV-positive (HIV阳性) women ends up shouldering the family as well as her own personal problems. Men, however, are usually the ones who have insurance (保险), income, andaccess to doctors. They get care. Women often do not.The discrimination(歧视) against women HIV-positive women is simply terrible. They are likely to be more inactive than men in the home and workplace because too many people think that women are the cause of the disease .This is not at all true. They get it from a man. They don’t just simply have HIV. Of course, there’s a social discrimination against all peop le with HIV. They are scared that other people will know they are HIV-positive and that they will, therefore, be discriminated against. For example, it’s very difficult for people with HIV to travel. They are not allowed to enter many countries, including the United States, China and Russia.The biggest difficulty an HIV-positive woman must face is the isolation(孤立). Once the woman knows she’s HIV-positive, she lives in fear that other people will find out. She’s so frightened she will go into hiding, into an isolated place (与世隔绝的地方) by herself. It’s not at all uncommon to meet a woman who has been HIV-positive for nearly 10 years and has never told anyone, except the doctor. And the resulting stress(压力)is enough to make her sick. But HIV-positive women who got support, who can discuss their trouble and then do something about it---whether that means taking better care of themselves or going to the United Nations to struggle for their rights.--- are likely to live longer. Active women don’t die out of shame in a corner. This happens to too many HIV-positive women.36.Women with HIV were ignored because________.(A) their effort to attract attention was not as successful as the HIV men’s(B)they often lived in a community that was hardly noticed by others.(C)HIV men were the only concern over a long time(D)they failed to get support.37.Which of the following statements is NOT true?(A) HIV-positive women make up nearly half of all AIDS cases in the world.(B)The gay community succeeded in getting support.(C)The high level of infection (感染) among women has been taken seriously.(D)There is social discrimination against all people with HIV.38.According to the passage, it’s difficult for women to deal with HIV but not because________.(A) they often lose their jobs after other people find out they are HIV-positive(B)they usually have the family problem(C)they often have no access to doctors(D)they have little time to take care of themselves39.Countries such as the United States and China are mentioned in the article in order to showthat ________.(A) there are more AIDS cases in those countries(B)it is convenient for HIV-positive people to travel(C)HIV-positive people are usually discriminated against(D)People who are HIV-positive are afraid that these countries will find out40.Which of the fol lowing does the passage show to us that active women don’t do?(A) Get support from others. (B) Discuss their trouble with their doctorsonly.(C) Struggle for their rights. (D)Take better care of themselves.Vocabulary and Structure (41-60 0.5′×20=10′; 61-70 1′×10=10′)Directions:There are 30 incomplete sentences in this part. For each sentence there are four choices marked (A), (B), (C) and (D). Choose the ONE that best completes thesentence. Then mark the corresponding letter on the Answer Sheet with a single linethrough the center.41. We are looking forward _____ the respected professor soon.(A)to see (B)to seeing (C)for seeing (D)seeing42. I saw Bob ______in the library when I was there last night.(A) to read (B) is reading (C) reading (D) was reading43. The classrooms in Building One are ______ Building Two.(A) larger than that of (B) larger than in (C) larger than those (D) larger than those in44. It is necessary that a graduate student _______ a gra de point average of “B” in his major field.(A) maintain (B) maintains (C) will maintain (D) shall maintain45. He is capable of _______ several foreign languages.(A) speaking (B) talking (C) saying (D) telling46. Look, the trees are fallen. There ___________ a strong wind.(A) must be (B) should have been (C) must have been (D) could be47. _______ those pictures, he couldn’t help thinking of those memorable days in Yun nan.(A) To see (B) Seeing (C) See (D) Seen48. Evidence came up ______ specific speech sounds are recognized by babies as young as sixmonths old.(A) that (B) which (C) what (D) whose49. There are so many dresses there that I really don’t know ______ to choose.(A) whether (B) when (C) why (D) which50. It was in China _______ the agreement was signed.(A) what (B) that (C) where (D) which51. I can’t carry this box. Will you _________ me a favor, please?(A) make (B) give (C) do (D) show52. They talked as if they __________ each other for years.(A) know (B) had known (C) have known (D) know53. Not until the game had began ________ at the sports ground.(A) he arrived (B) did he arrive (C) he didn’t arrive(D) would he arrive54. I do wish you ____________ so much.(A) don’t smoke(B) are not smoking (C) didn’t smoke(D) to have smoked55. __________ his wealth, he is not happy.(A) In spite of (B) Because of (C) Besides (D) Except for56. Reagan used to be known ________ everyone ________ a famous actor.(A) to….as(B) to … for (C) with … as (D) for … with57.Certainly _________ we leave this dangerous place the better.(A) the soon (B) soon (C) sooner (D) the sooner58. They said the house was _________ large ________ bright so they don’t rent it.(A) neither, and (B) neither, or (C) neither, nor (D) either, or59. _________is known to the world, Mark Twain is a great American writer.(A) That (B) Which (C) It (D) As60. New York is the city ________ she is going to visit.(A) where (B) what (C) that (D) in which61. ________ surprised me most was ________ he could speak English so fluently.(A) That, that (B) What, that (C) That, what (D) What, if62. The general manager was busy to see visitors.(A) too much (B) much (C) very much (D) much too 63. The ancient Egyptians believed all illnesses were related to _______ was eaten.(A) which (B) it (C) that (D) what64. How many times have I told you _______ football in the street?(A) do not play (B) not to have played (C) not to play (D) not your playing65. If I _________ you, I would do it in a different way.(A) am (B) was (C) were (D) would be66. Air isn’t so clean here as it used to _________.(A) was (B) is (C) be (D) being67. My father has been out on business for _______ and he will come back________ next week.(A) sometime, some time (B) some time, sometime(C) sometimes, sometime (D) sometime, sometimes68. Would you please lend me a ________? The box is too heavy for me.(A) favor (B) hand (C) help (D) lift69. It’s no use _______ to her about the importance of the document.(A) talking (B) talked (C) to talk (D) talk70. Don’t worry about your brother’s illness; what he needs is nothing else _______ a good rest.(A) but (B) besides (C) including (D) lessCloze (1′×20=20′)Directions:There are 20 blanks in the following passage. For each blank there are four choices marked (A), (B), (C) and (D). Choose the ONE that best fits into the passage. Thenmark the corresponding letter on the Answer Sheet with a single line through thecenter.One day a police officer managed to get some fresh mushrooms. He was so 71 what he had bought that he offered to 72 the mushrooms with his fellow officers. When their breakfast arrived the next day, each officer found some mushrooms on his plate.“Let the dog 73 a piece first.” suggested one74 officer who was afraid that the mushrooms might be poisonous. The dog seemed to 75 his mushrooms, and theofficers then began to eat their meal saying that the mushrooms had a very strange 76 quite pleasant taste.An hour later, however, they were all 77 when the gardener rushed in and said 78 the dog was dead. 79 the officers jumped into their cars and rushed into the nearest hospital. Pumps (泵) were used and the officers had a very 80 time getting rid of the mushrooms that 81 in their stomachs. When they 82 to the police station, they sat down and started to 83 the mushroom poisoning. Each man explained the 84 that he had felt and they agreed that these had grown worse 85 their way to the hospital. The gardener was called to tell the way 86 the poor dog had died. “Did it 87 much before death?”asked one of the officers, 88 very pleased that he had escaped a 89 death himself. “No,” answered the gardener, looking rather 90 . “It was killed the moment a car hit it.”71. (A) sure of (B) careless about (C) pleased with (D) disappointed at72. (A) share (B) grow (C) wash (D) cook73. (A) check (B) smell (C) try (D) examine74. (A) frightened (B) shy (C) cheerful (D) careful75. (A) refuse (B) hate (C) want (D) enjoy76. (A) besides (B) but (C) and (D) or77. (A) astonished (B) exhausted (C) puzzled (D) fainted78. (A) cruelly (B) curiously (C) seriously (D) finally79. (A) Immediately (B) Carefully (C) Suddenly (D) Slowly80. (A) hard (B) busy (C) exciting (D) unforgettable81. (A) kept (B) dropped (C) settled (D) remained82. (A) hurried (B) drove (C) went (D) returned83. (A) study (B) discuss (C) record (D) remember84. (A) panic (B) pains (C) dangers (D) worry85. (A) in (B) along (C) on (D) with86. (A) how (B) in that (C) where (D) in which87. (A) suffer (B) eat (C) harm (D) bite88. (A) to feel (B) feeling (C) felt (D) having felt89. (A) strange (B) painful (C) peaceful (D) natural90. (A) alarmed (B) interested (C) surprised (D) excited Writing (20′)Directions:For this part, you are allowed 30 minutes to write a composition on the topic: My Favorite Sport. You should write at least 120 words, and base your composition onthe outline given in Chinese below.You should write this composition on the Composition Sheet.(1) 你最喜欢的体育运动是什么?(2) 喜欢的原因及它能带来的益处。