美罗培南与亚胺培南西司他丁比较
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:1.11 MB
- 文档页数:22




美罗培南与亚安培南/西司他丁的区别亚安培南属于碳青霉烯第一代药物,美罗培南属于第二代。
碳青霉烯是ß-内酰胺类抗生素之一,具有超广谱的抗菌活性,覆盖了多数临床常见的需氧及厌氧菌,因而成为治疗严重感染的一线经验性治疗药物,特别是致病菌不明或怀疑为耐药菌株时。
当致病菌对头孢菌素类耐药或治疗困难时,碳青霉烯是非常有效的药物。
此药对产AmpC 酶或ESBL的很多细菌仍保存其抗菌活性。
一、抗菌活性及抗菌谱1.化学结构及作用方式碳青霉烯的ß-内酰胺核中的5环结构内有一个碳原子取代了硫,并在C2、C3有一个不饱和键。
美罗培南与亚安培南的主要区别在于导入了1ß-甲基,因此美罗培南对肾脱氢肽酶具有稳定性,另外在 C2位侧链处有取代,从而增强了美罗培南抗绿脓杆菌的效力。
碳青霉烯通过结合青霉素结合蛋白(PBP)显示其抑制细胞壁合成的能力,致使细胞的胞浆渗透压改变和细胞溶解。
2.体外抗菌活性亚胺培南、美洛培南对大多数革兰阳性、阴性需氧菌、厌氧菌及多重耐药菌均有较强的抗菌活性,但耐甲氧西林葡萄球菌、屎肠球菌、嗜麦芽寡养单胞菌等对本品耐药。
亚胺培南在浓度8mg•L-1时,可抑制90%以上的主要致病菌。
而抗革兰阴性需氧菌及厌氧菌的效力美罗培南是与亚安培南的2~16倍,对铜绿假单胞菌的抗菌活性是亚胺培南的2-4倍。
亚安培南抗革兰阳性菌,特别是金葡菌和肠球菌的效力是美罗培南的2~4倍。
与青霉素敏感的肺炎链球菌比较,两种药物对耐青霉素的肺炎链球菌的最小抑菌浓度有所升高,但该菌仍对碳青霉烯敏感。
3.抗菌耐药性虽然临床使用亚胺培南/西司他丁已数年,但对碳青霉烯耐药的菌株很少,仅有黄单胞菌、粪肠球菌和耐苯甲氧青霉素的葡萄球菌。
绿脓杆菌等一般对亚胺培南耐药,但对美罗培南仍可能敏感。
两种碳青霉烯均不被质粒携带的TEM酶(通常是肠杆菌科产生),如广谱ß-内酰胺酶水解,也不受肠道菌属、粘质沙雷菌和假单胞所产生的染色体类ß-内酰胺酶的影响。

比较美罗培南和亚胺培南-西司他丁治疗重症肺部感染的临床效果摘要】目的探讨分析对重症肺部感染患者采用美罗培南与亚胺培南-西司他丁治疗的疗效。
方法此次研究对象选自我院2021年4月到2022年4月期间收治的重症肺部感染患者,共计56例,按照数字表法对其分组:分别是研究组28例和参照组28例。
其中接受亚胺培南-西司他丁的为参照组,给予美罗培南治疗的为研究组,观察对两组的治疗效果。
结果两组的治疗有效率对比,研究组高于参照组(P<0.05);两组的治疗恢复情况对比,研究组优于参照组(P<0.05)。
结论根据本次研究的结果可以确认,对重症肺部感染患者采用美罗培南治疗的效果更为确切,还可以有效缩短对其治疗时间,加快其病情恢复。
【关键词】重症肺部感染;美罗培南;亚胺培南-西司他丁;治疗效果;对比分析Abstract] Objective To investigate and analyze the efficacy of meropenem and imipenem cilastatin in the treatment of patients with severe pulmonary infection. The total number of patients in the study group was 28 cases of severe lung infection from 2024 to 2021. Methods: according to the number of patients in the study group, 28 cases were selected from 2024 months. Among them, those who received imipenem cilastatin were the reference group and those who were treated with meropenem were the study group. The therapeutic effects of the two groups were observed. Results the effective rate of the study groupwas higher than that of the reference group (P < 0.05); Compared with the treatment recovery of the two groups, the study group was better than the reference group (P < 0.05). Conclusion according to theresults of this study, it can be confirmed that meropenem is moreeffective in the treatment of patients with severe pulmonary infection. It can also effectively shorten the treatment time and accelerate the recovery of their condition.【 key words 】 severe pulmonary infection; Meropenem; Imipenem cilastatin; Therapeutic effect; comparative analysis随着现在自然环境的恶化,致使呼吸系统疾病在临床上越发常见。



肺部感染属于常见的一种在肺泡腔等肺部实质发生炎症的呼吸道感染疾病,患者大多发病急,病因在于致病菌感染,临床症状表现为咳嗽、咳痰、胸痛、咳血、发烧、乏力等。
患者若不及时治疗,很容易进一步发展为重症肺部感染(如老年人、有合并多种基础疾病史),从而在短时间内出现意识障碍、休克、肝肾功能不全,甚至出现死亡,极大地威胁了患者的生命健康。
目前研究发现,造成重症肺部亚胺培南西司他丁钠和美罗培南对重症肺部感染患者的疗效及对细菌清除率、炎症因子水平的影响翁朝航厦门巿海沧医院,福建厦门 361026[摘要]目的:研究亚胺培南西司他丁钠和美罗培南对重症肺部感染患者的疗效及对细菌清除率、炎症因子水平的影响。
方法:选取2017年12月—2019年12月期间我院收治的120例重症肺部感染患者为观察对象,随机分为对照组和观察组,其中对照组60例患者在常规治疗基础上静脉滴注亚胺培南西司他丁钠;观察组60例患者在常规治疗基础上静脉滴注美罗培南,两组患者均治疗2周。
记录并对比两组患者治疗后的临床疗效、细菌清除率以及炎症因子水平的差异。
结果:经治疗后,观察组的总有效率(95.00%)显著高于对照组(81.67%),差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);观察组患者革兰阳性菌清除率及总体细菌清除率高于对照组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05);两组革兰阴性菌及真菌清除率比较,差异不具有统计学意义(P>0.05);两组患者经过治疗后的血清肿瘤坏死因子α、白介素-6、C反应蛋白以及降钙素原水平均明显低于治疗前,且观察组的各项炎症因子指标降低幅度较对照组更显著,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);两组患者治疗期间不良反应发生率比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。
结论:美罗培南在治疗重症肺部感染患者中具有较好的临床疗效,可显著改善患者的临床症状,提高细菌清除率,降低炎症因子水平,建议临床推广。
[关键词]亚胺培南西司他丁钠;美罗培南;重症肺部感染;疗效;细菌清除率;炎症因子[中图分类号]R969.4;R563.1 [文献标识码]A [文章编号]1672-2809(2020)19-0034-04Effects of Imipenem Cilastatin Sodium and Meropenem on Bacterial Clearance Rate and Inflammatory Factors in Patients with Severe Pulmonary InfectionWENG ChaohangXiamen Haicang Hospital, Xiamen Fujian 361026, China.[Abstract] Objective: To study the efficacy of imipenem cilastatin sodium and meropenem in the treatment of severe pulmonary infection and the influence on bacterial clearance rate and inflammatory factors. Methods: 120 patients with severe pulmonary infection in our hospital from December 2017 to December 2019 were selected as the observation objects and randomly divided into the control group and the observation group. 60 patients in the control group were given imipenem cilastatin sodium intravenous drip on the basis of conventional treatment; 60 patients in the observation group were treated with meropenem on the basis of conventional treatment, both groups were treated for 2 weeks. The clinical efficacy, bacterial clearance rate and inflammatory factor levels of the two groups were recorded and compared. Results: After treatment, the total effective rate of the observation group (95.00%) was significantly higher than that of the control group (81.67%), the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05); the Gram-positive bacteria clearance rate and the overall bacterial clearance rate of the observation group were higher than those of the control group, the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05); there was no significant difference in the clearance rate of Gram-negative bacteria and fungi between the two groups (P>0.05); After treatment, the serum tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin-6, C-reactive protein and calcitonin in the two groups were significantly lower than before treatment, and the inflammatory factors in the observation group decreased more significantly than those in the control group (P<0.05); there was no significant difference in the incidence of adverse reactions between the two groups during the treatment (P>0.05). Conclusion: Meropenem in the treatment of patients with severe pulmonary infection has good clinical efficacy, can significantly improve the clinical symptoms of patients, improve the bacterial clearance rate, reduce the level of inflammatory factors, it is recommended that clinical promotion.[Key Words] Imipenem Cilastatin Sodium; Meropenem; Severe Pulmonary Infection; Efficacy; Bacterial Clearance Rate; Inflammatory Factors作者简介:翁朝航,本科,副主任医师。

34·罕少疾病杂志 2022年02月 第29卷 第 2 期 总第151期【第一作者】翟磊磊,女,主治医师,主要研究方向:难治性肾病。
E-mail:********************【通讯作者】翟磊磊·论著· 肺部感染是严重感染疾病之一,是一种严重的呼吸道肺炎疾病,致死率在全球排名第三[1]。
发病率较高且有较多的致病因素,以病毒、细菌和非典型病原体感染为常见病因。
因感染病灶所引起的炎症反应,导致抗炎和促炎介质的表达异常,临床症状大多为发热、咳嗽,严重者甚至出现休克、呼吸衰竭和多器官功能衰退。
由青霉素结构改造而成的新型β-内酰胺抗菌药物称为碳青霉烯类抗菌药[2]。
美罗培南和亚胺培南-西司他丁均属于碳青霉烯类广谱抗菌药,均有高度稳定性和广谱性,适用于多种病原体所致的肺部感染[3-4]。
如何有效的治疗控制住肺部感染关键是正确使用适合的抗菌药物,本研究通过对60例重症肺部感染患者分别给予美罗培南和亚胺培南-西司他丁治疗,对比两者的治疗作用。
1 资料与方法1.1 一般资料 本研究已通过本院伦理委员会的审查,并获得患者知情同意书。
选择60例在本院接受肺部感染的患者(2018年12月至2019年12月),依据随机数字表法分成:观察组(美罗培南)30例,对照组(亚胺培南-西司他丁)30例。
纳入标准:通过病原菌检查并确诊为肺部感染者。
排除标准:对碳青霉烯类药物过敏患者;有其他重要器官功能异常的患者;有肺结核或肿瘤的患者;妊娠或哺乳期的患者;接受治疗前2两天有抗菌药物治疗史的患者。
2组患者的一般情况具有可比性(P >0.05),见表1。
美罗培南与亚胺培南-西司他丁治疗重症肺部感染的效果比较翟磊磊*濮阳市中医医院临床医药科 (河南 濮阳 457000)【摘要】目的 比较美罗培南和亚胺培南-西司他丁治疗重症肺部感染的临床疗效。
方法 将60例在我院进行诊治的重症肺部感染患者按随机数字表法分为对照组(n=30)与观察组(n=30)。
亚胺培南/西司他丁与美罗培南对下呼吸道感染患者的临床用药研究作者:崔华来源:《中外医疗》 2013年第34期崔华吉林市解放西路西医内科门诊部,吉林吉林 132000[摘要] 目的比较与分析亚胺培南西司他丁与美罗培南对下呼吸道感染患者的临床治疗效果。
方法将64例下呼吸道感染门诊资料随机分为两组:选择美罗培南药物进行治疗的32例为对照组,选择亚胺培南/西司他丁药物进行治疗的32例为观察组,所有患者在不同药物治疗后按照文中疗效标准进行电话随访调查和指标统计并比较差异性。
结果观察组患者治疗后痊愈19例,显效11例,总有效率93.8%,与对照组疗效结果具有一致性,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),观察组在用药期间出现恶心呕吐者1例,出现精神症状者1例,不良反应发生率为6.3%,与对照组相比具有一致性,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。
结论下呼吸道感染患者使用亚胺培南/西司他丁与美罗培南均具有满意的临床效果。
[关键词] 亚胺培南;西司他丁;美罗培南;下呼吸道感染患者[中图分类号] R563.1[文献标识码] A[文章编号] 1674-0742(2013)12(a)-0113-02下呼吸道感染在临床上属于常见的微生物感染疾病之一,对该类患者的治疗应该首先明确致病的病原体种类,才能选择高效的、有针对性的治疗药物(防止抗生素滥用)。
随着医药工业事业的快速发展,对由细菌引起的感染临床上可以选择进行治疗的抗生素种类也日益增多,而细菌的耐药菌株也明显增多,而分子生物学和血清学研究快速发展,又使人们对支原体或军团菌感染的认识有很大提高[1-2],为比较与分析亚胺培南西司他丁与美罗培南对下呼吸道感染患者的临床作用效果,该研究回顾性总结2011年3月—2013年4月期间64例下呼吸道感染患者,现报道如下。
1 资料与方法1.1 一般资料该研究资料为下呼吸道感染患者64例门诊资料,其中包括男33例,女31例,年龄范围为28~57岁,平均年龄为(39.2±14.5)岁,统计资料入选标准:所有下呼吸道感染患者均知情且同意配合该研究进行的电话随访调研。
亚胺培南西司他丁钠与美罗培南比较
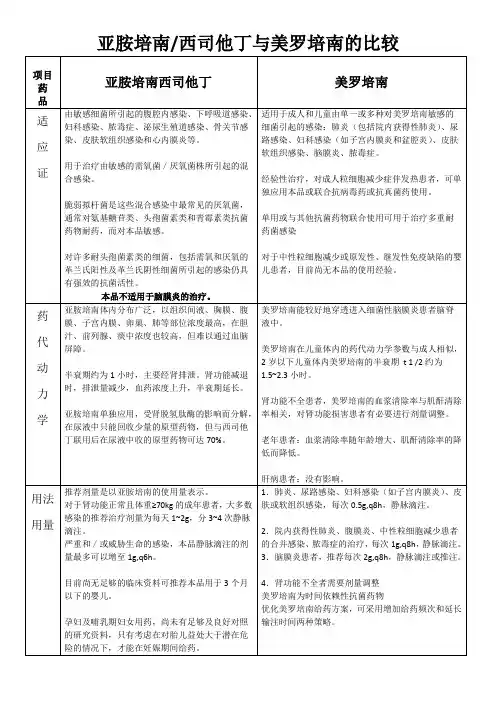
1,适应症比较:美罗培南适应症与亚胺培南西司他丁基本相同,但亚胺培南西司他丁说明书明确指出本品不适于脑膜炎的治疗,因其对血脑屏障的透过能力差,而美罗培南可用于脑膜炎的治疗,其在脑膜炎症时可透过血脑屏障,达到有效抑菌浓度。
(摘自药品说明书)
2,抗菌谱比较:两者抗菌谱都极为广泛,对大多数革兰氏阳性、阴性需氧菌及厌氧菌均有抗菌作用,但是耐甲氧西林金葡菌及凝固酶阴性葡萄球菌对亚胺培南耐药,而美罗培南对凝固酶阴性葡萄球菌有抗菌活性,对耐甲氧西林金葡菌无抗菌活性(对万古霉素敏感)。
神经外科感染常见细菌为金葡菌及凝固酶阴性葡萄球菌,因此选用美罗培南较好。
(摘自《中华人民共和国药典临床用药须知》2005版)。
3,产生耐药机制比较:美罗培南与亚胺培南相比,进入细菌除通过膜孔蛋白-D通道外,还可通过其他膜孔蛋白通道进入细菌,因此,细菌对美罗培南产生耐药几率远远低于亚胺培南(摘自《美罗培南体外抗菌监测》北京协和医院)。
4,不良反应比较:亚胺培南可致抽搐等严重中枢神经系统不良反应,不用于中枢神经系统感染的治疗,而美罗培南与中枢神经系统γ-氨基丁酸受体亲和力远低于亚胺培南,故抽搐、癫痫等中枢神经系统不良反应发生率更低,同时所致肾功能损害和恶心、呕吐等胃肠道反应亦少。
(摘自《中华人民共和国药典临床用药须知》2005版)。
综上所述,对于神经系统感染选用美罗培南较为合理。