管理经济学 第4讲 竞争与市场势力
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:218.00 KB
- 文档页数:42

管理经济学的主要内容
管理经济学是一门研究企业与经济活动的科学,其主要内容包括以下方面:
1.市场需求与供给分析:通过研究市场需求和供给的变化,企业可以确定市场的价格和数量,以提高企业经营效益。
2.成本与生产分析:通过研究企业的生产成本及其对生产的影响,以确定最优生产量和最低成本,从而增加企业利润。
3.企业战略分析:研究企业在市场中的竞争状况和竞争策略,以制定最优的发展战略和市场定位策略。
4.决策分析:研究企业决策的目标、过程和方法,以提高决策效率和准确性。
5.风险与不确定性分析:研究企业面临的风险和不确定因素,以制定合适的风险管理策略。
6.组织设计与管理:研究企业组织结构和管理方式,以提高组织效率和员工绩效。
7.战略合作与联盟:研究企业间的合作和联盟关系,以增强企业的竞争力和市场地位。
总之,管理经济学涉及到企业经济活动的方方面面,是企业管理和经营的重要理论基础和实践指导。
- 1 -。
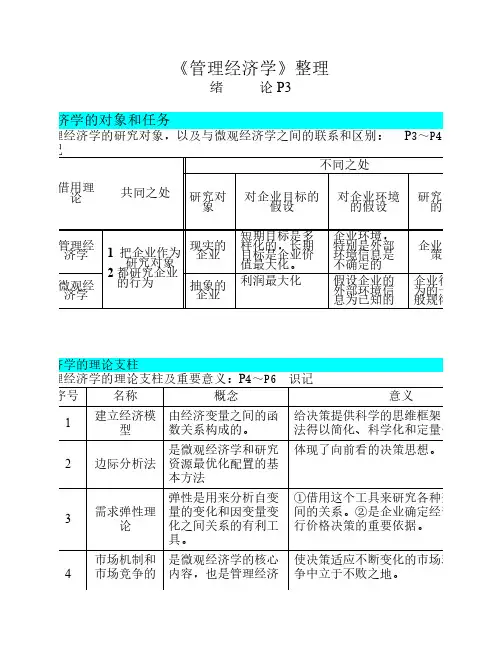
《管理经济学》整理绪论 P3管理经济学的对象和任务一、管理经济学的研究对象,以及与微观经济学之间的联系和区别:P3~P4识记借用理论共同之处不同之处研究对象对企业目标的假设对企业环境的假设研究目的管理经济学 1 把企业作为研究对象2 都研究企业的行为现实的企业短期目标是多样化的,长期目标是企业价值最大化。
企业环境,特别是外部环境信息是不确定的企业决策微观经济学抽象的企业利润最大化假设企业的外部环境信息为已知的企业行为的一般规律管理经济学的理论支柱二、管理经济学的理论支柱及重要意义:P4~P6 识记序号名称概念意义1建立经济模型由经济变量之间的函数关系构成的。
给决策提供科学的思维框架,使决策方法得以简化、科学化和定量化。
2边际分析法是微观经济学和研究资源最优化配置的基本方法体现了向前看的决策思想。
3需求弹性理论弹性是用来分析自变量的变化和因变量变化之间关系的有利工具。
①借用这个工具来研究各种变量变化之间的关系。
②是企业确定经营方针和进行价格决策的重要依据。
4市场机制和市场竞争的是微观经济学的核心内容,也是管理经济使决策适应不断变化的市场环境,在竞争中立于不败之地。
基本原理学的重要组成部分。
5边际收益递减规律要求在生产过程中,在各种投入要素之间保持最适度的比例关系。
决定了企业成本的习性和变化规律。
6机会成本原理是指资源用于次好用途时所能获得的价值。
用机会成本做决策,能判断资源是否真正得到了最优使用。
是提高我国管理决策水平的一项重要任务。
7货币的时间价值是指因放弃现在使用资金的机会,可以换取的按放弃时间的长短计算的回报,最常见的是利息。
只有计算资金的货币价值,才能正确评价投资的经济效益。
企业的目标三、管理经济学的决策准则对短期目标的设计和安排要服从于长期目标,在短期内,企业可以暂时放弃或减少对利润的追求。
1、企业目标短期目标—是多样化的,它包括投资者、顾客、债权人、职工、政府、社会公众,以及技术改造。



管理经济学中英文术语及其解释Ability-to-Pay principle (税收的)能力支付原则the idea that taxes should be levied on a person according to how well that person can shoulder the burdenAbsolute advantage绝对优势the comparison among producers of a good according to their productivityAccounting profit会计利润total revenue minus total explicit costAdverse selection逆向选择the tendency for the mix of unobserved attributes to become undesirable from the standpoint of an uninformed partyAgent代理人 a person who is performing an act for another person, called the principalArrow ‟s impossibility theorem阿罗不可能定理a mathematical result showing that, under certain assumed conditions, there is no scheme for aggregating individual preferences into a valid set of social preferencesAverage fixed cost平均固定成本fixed costs divided by the quantity of outputAverage revenue平均收益total revenue divided by the quantity soldAverage tax rate平均税率total taxes paid divided by total incomeAverage total cost平均总成本total cost divided by the quantity of outputAverage variable cost平均可变成本variable costs divided by the quantity of outputBenefits principle受益原则the idea that people should pay taxes based on the benefits they receive from government servicesBudget constraint预算约束the limit on the consumption bundles that a consumer can afford Budget deficit预算赤字an excess of government spending over government receiptsBudget surplus预算盈余an excess of government receipts over government spending Business cycle经济周期fluctuations in economic activity, such as employment and production Capital资产the equipment and structures used to produce goods and servicesCartel卡特尔a group of firms acting in unisonCircular-flow diagram循环流向图 a visual model of the economy that shows how dollars flow through markets among households and firmsCoase theorem科斯定理the proposition that if private parties can bargain without cost over the allocation of resources, they can solve the problem of externalities on their ownCollusion共谋an agreement among firms in a market about quantities to produce or prices to chargeCommon resources共源goods that are rival but not excludableComparative advantage比较优势the comparison among producers of a good according to their opportunity costCompensating differential补偿性工资差别 a difference in wages that arises to offset the nonmonetary characteristics of different jobsCompetitive market竞争性市场 a market with many buyers and sellers trading identical products so that each buyer and seller is a price takerComplements互补性商品two goods for which an increase in the price of one leads to a decrease in the demand for the otherCondorcet paradox孔多塞悖论(投票悖论)the failure of majority rule to produce transitive preferences for societyConstant returns to scale规模报酬不变the property whereby long-run average total cost staysthe same as the quantity of output changesConsumer surplus消费者剩余 a buyer‟s willingness to pay minus the amount the buyer actually paysCost成本the value of everything a seller must give up to produce a goodCost-benefit analysis成本收益分析 a study that compares the costs and benefits to society of providing a public goodCross-price elasticity of demand需求的交叉价格弹性 a measure of how much the quantity demanded of one good responds to a change in the price of another good, computed as the percentage change in quantity demanded of the first good divided by the percentage change in the price of the second goodDeadweight loss无谓损失the fall in total surplus that results from a market distortion, such as a taxDemand curve需求曲线 a graph of the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity demandedDemand schedule需求表 a table that shows the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity demandedDiminishing marginal product边际产品递减the property whereby the marginal product of an input declines.As the quantity of the input increasesDiscrimination歧视the offering of different opportunities to similar individuals who differ only by race, ethnic group, sex, age, or other personal characteristicsDiseconomies of scale规模不经济the property whereby long-run average total cost rises as the quantity of output increasesDominant strategy占优策略 a strategy that is best for a player in a game regardless of the strategies chosen by the other playersEconomic profit经济利润total revenue minus total cost, including both explicit and implicit costsEconomics经济学the study of how society manages its scarce resourcesEconomies of scale规模经济the property whereby long-run average total cost falls as the quantity of output increasesEfficiency效率the property of society getting the most it can from its scarce resources Efficiency wages效率工资above-equilibrium wages paid by firms in order to increase worker productivityEfficient scale有效规模the quantity of output that minimizes average total costElasticity弹性 a measure of the responsiveness of quantity demanded or quantity supplied to one of its determinantsEquilibrium均衡 a situation in which the price has reached the level where quantity supplied equals quantity demandedEquilibrium price均衡价格the price that balances quantity supplied and quantity demanded Equilibrium quantity均衡数量the quantity supplied and the quantity demanded at the equilibrium priceEquity平等the property of distributing economic prosperity fairly among the members of societyExcludability排他性the property of a good whereby a person can be prevented from using it Explicit costs显性成本input costs that require an outlay of money by the firmExports出口goods produced domestically and sold abroadExternality外部性the uncompensated impact of one person‟s actions on the wellbeing of a bystanderFactors of production生产要素the inputs used to produce goods and servicesFixed casts固定成本costs that do not vary with the quantity of output producedFree rider免费搭车者 a person who receives the benefit of a good but avoids paying for it Game theory博弈论the study of how people behave in strategic situationsGiffen good吉芬商品 a good for which an increase in the price raises the quantity demanded Horizontal equity横向公平the idea that taxpayers with similar abilities to pay taxes should pay the same amountHuman capital人力资本the accumulation of investments in people, such as education andon-the-job trainingImplicit costs隐性成本input costs that do not require an outlay of money by the firmImport quota进口配额 a limit on the quantity of a good that can be produced abroad and sold domesticallyImports进口goods produced abroad and sold domesticallyIncome effect收入效应the change in consumption that results when a price change moves the consumer to a higher or lower indifference curveIncome elasticity of demand需求的收入弹性 a measure of how much the quantity demanded of a good responds to a change in consumers‟ income, computed as the percentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in incomeIndifference curve无差异曲线 a curve that shows consumption bundles that give the consumer the same level of satisfactionInferior good低档物品 a good for which, other things equal, an increase in income leads to a decrease in demandInflation通货膨胀an increase in the overall level of prices in the economyIn-kind transfers实物转移支付transfers to the poor given in the form of goods and services rather than cashInternalizing an externality外部性的内在化altering incentives so that people take account of the external effects of their actionsLaw of demand需求定理the claim that, other things equal, the quantity demanded of a good falls when the price of the good risesLaw of supply and demand需求与供给定理the claim that the price of any good adjusts to bring the quantity supplied and the quantity demanded for that good into balanceLiberalism自由主义the political philosophy according to which the government should choose policies deemed to be just, as evaluated by an impartial observer behind a “veil of ignorance”Libertarianism自由至上主义the political philosophy according to which the government should punish crimes and enforce voluntary agreements but not redistribute incomeLife cycle生命周期the regular pattern of income variation over a person‟s lifeLump-sum tax定额税 a tax that is the same amount for every personMacroeconomics宏观经济学the study of economy-wide phenomena, including inflation, unemployment, and economic growthMarginal changes边际变动small incremental adjustments to a plan of actionMarginal cost边际成本the increase in total cost that arises from an extra unit of production Marginal product边际产品the increase in output that arises from an additional unit of input Marginal product of labor劳动的边际产品the increase in the amount of output from an additional unit of laborMarginal rate of substitution边际替代率the rate at which a consumer is willing to trade one good for anotherMarginal revenue边际收益the change in total revenue from an additional unit soldMarginal tax rate边际税率the extra taxes paid on an additional dollar of incomeMarket市场 a group of buyers and sellers of a particular good or serviceMarket economy市场经济an economy that allocates resources through the decentralized decisions of many firms and households as they interact in markets for goods and services Market failure市场失灵 a situation in which a market left on its own fails to allocate resources efficientlyMarket power市场势力the ability of a single economic actor (or small group of actors) to have a substantial influence on market pricesMaximin criterion极大极小准则the claim that the government should aim to maximize the well-being of the worst-off person in societyMedian voter theorem中位选举人定理 a mathematical result showing that if voters are choosing a point along a line and each voter wants the point closest to his most preferred point, then majority rule will pick the most preferred point of the median voterMicroeconomics微观经济学the study of how households and firms make decisions and how they interact in marketsMonopolistic competition垄断竞争 a market structure in which many firms sell products that are similar but not identicalMonopoly垄断 a firm that is the sole seller of a product without close substitutesMoral hazard道德风险the tendency of a person who is imperfectly monitored to engage in dishonest or otherwise undesirable behaviorNash equilibrium纳什均衡 a situation in which economic actors interacting with one another each choose their best strategy given the strategies that all the other actors have chosenNatural monopoly自然垄断 a monopoly that arises because a single firm can supply a good or service to an entire market at a smaller cost than could two or more firmsNegative income tax负所得税 a tax system that collects revenue from high-income households and gives transfers to low-income householdsNormal good正常商品 a good for which, other things equal, an increase in income leads to an increase in demandNormative statements规范性表述claims that attempt to prescribe how the world should be Oligopoly寡头 a market structure in which only a few sellers offer similar or identical productsOpportunity cost机会成本whatever must be given up to obtain some itemPerfect complements完全互补品two goods with right-angle indifference curvesPerfect substitutes完全替代品two goods with straight-line indifference curvesPermanent income持久性收入 a person‟s normal incomePhillips curve菲利普斯曲线 a curve that shows the short-run tradeoff between inflation and unemploymentPigovian tax庇古税 a tax enacted to correct the effects of a negative externalityPositive statements实证表述claims that attempt to describe the world as it isPoverty line贫困线an absolute level of income set by the federal government for each family size below which a family is deemed to be in povertyPoverty rate贫困率the percentage of the population whose family income falls below an absolute level called the …poverty linePrice ceiling价格天花板(上限) a legal maximum on the price at which a good can be sold Price discrimination价格歧视the business practice of selling the same good at different prices to different customersPrice elasticity of demand需求的价格弹性 a measure of how much the quantity demanded of a good responds to a change in the price of that good, computed as the percentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in pricePrice elasticity supply供给的价格弹性 a measure of how much the quantity supplied of a good responds to a change in the price of that good, computed as the percentage change in quantity supplied divided by the percentage change in pricePrice floor价格地板I下限) a legal minimum on the price at which a good can be sold Principal委托人 a person for whom another person, called the agent, is performing some act Prisoners‟ dilemma囚徒困境 a particular “game” between two captured prisoners that illustrates why cooperation is difficult to maintain even when it is mutually beneficialPrivate goods私人物品goods that are both excludable and rivalProducer surplus生产者剩余the amount a seller is paid for a good minus the seller‟s cost Production function生产函数the relationship between quantity of inputs used to make a good and the quantity of output of that goodProduction possibilities frontier生产可能性曲线 a graph that shows the combinations of output that the economy can possibly produce given the available factors of production and the available production technologyProductivity生产率the quantity of goods and services produced from each hour of a worker‟s timeProfit利润total revenue minus total costProgressive tax累进税 a tax for which high-income taxpayers pay a larger fraction of their income than do low-income taxpayersProportional tax比例税 a tax for which high-income and low-income taxpayers pay the same fraction of incomePublic goods公共产品goods that are neither excludable nor rivalQuantity demanded需求数量the amount of a good that buyers are willing and able to purchase Quantity supplied供给数量the amount of a good that sellers are willing and able to sell Regressive tax累退税 a tax for which high-income taxpayers pay a smaller fraction of their income than do low-income taxpayersRivalry竞争the property of a good whereby one person‟s use diminishes other people‟s use Scarcity稀缺性the limited nature of society‟s resourcesScreening筛选an action taken by an uninformed party to induce an informed party to reveal informationShortage短缺 a situation in which quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied Signaling信号显示an action taken by an informed party to reveal private information to anuninformed partyStrike罢工the organized withdrawal of labor from a firm by a unionSubstitutes替代品two goods for which an increase in the price of one leads to an increase in the demand for the otherSubstitution effect替代效应the change in consumption that results when a price change moves the consumer along a given indifference curve to a point with a new marginal rate of substitution Sunk cost沉淀成本 a cost that has already been committed and cannot be recoveredSupply curve供给曲线 a graph of the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity suppliedSupply schedule供给表 a table that shows the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity suppliedSurplus过剩 a situation in which quantity supplied is greater than quantity demandedTariff关税 a tax on goods produced abroad and sold domesticallyTax incidence税收归宿the manner in which the burden of a tax is shared among participants in a marketTotal cost总成本the market value of the inputs a firm uses in productionTotal revenue (for a firm)总收益the amount a firm receives for the sale of its outputTotal revenue (in a market)总收益the amount paid by buyers and received by sellers of a good, computed as the price of the good times the quantity soldTragedy of the Commons公共地的悲剧a parable that illustrates why common resources get used more than is desirable from the standpoint of society as a wholeTransaction costs交易成本the costs that parties incur in the process of agreeing and following through on a bargainUnion工会 a worker association that bargains with employers over wages and working conditionsUtilitarianism功利主义the political philosophy according to which the government should choose policies to maximize the total utility of everyone in societyUtility效用 a measure of happiness or satisfactionValue of the marginal product边际产品价值the marginal product of an input times the price of the outputVariable costs可变成本costs that vary with the quantity of output producedVertical equity纵向公平the idea that taxpayers with a greater ability to pay taxes should pay larger amountsWelfare福利government programs that supplement the incomes of the needyWelfare economics福利经济学the study of how the allocation of resources affects economic well-beingWillingness to pay支付意愿the maximum amount that a buyer will pay for a goodWorld price世界价格the price of a good that prevails in the world market for that good。



管理经济学第一讲均衡价格理论与价格机制一、管理经济学的研究对象与方法1.微观经济学以单个经济单位的经济行为为对象,研究资源配置。
2.管理经济学微观经济学原理与方法在企业管理决策中的运用。
1952年美国乔尔·丁出版了第一本《管理经济学》,宣告了这门学科的诞生。
3.管理经济学的研究方法·实证分析VS规范分析·局部均衡分析VS一般均衡分析·静态分析、比较静态分析VS动态分析·边际分析VS经济模型分析·供求分析·长短期分析二、需求理论1.需求与需求量(Qd)需求=欲望+购买力2.影响需求量的因素①商品自身价格 Qd与P负相关)②相关商品价格(P·替代品正相关·互补品负相关③收入水平(Y)正相关④偏好(T)⑤预期(E)↑价格看涨→当前Qd↓价格看跌→当前Qd3.需求定律、需求曲线、需求表与需求函数①需求定律 Qd与P反向变化的规律②需求曲线③需求函数 Qd =f(P、PO、Y、T、E)Qd=f(P)=a-bp(a、b>0)④需求表4.需求定律的例外(Qd与P正相关)①吉芬商品(1845年爱尔兰饥荒)②炫耀性商品5.需求量的变化与需求的变化Qd=f(价格,其他因素)①需求量的变化:价格变化对Qd的影响,用沿着需求线的运动表示②需求的变化:其他因素变化对Qd的影响,用整个需求线的平移表示③例证:控制香烟Qd·税率↑→P↑→Qd↓·警告、禁做广告→Qd↓三、供给理论1.供给与供给量(QS)2.影响因素①自身价格 QS与P正相关②相关商品价格③成本、技术④预期价格看涨→当前QS↓价格看跌→当前QS↑3.供给定律、供给曲线、供给函数与供给表①供给定律:QS与P同向变化的规律②供给曲线③供给函数QS=c+dp(c、d>0)④供给表4.供给量的变化与供给的变化QS=f(价格,其他因素)①供给量的变化:价格变化对QS影响,用沿着供给线的运动表示。

第四章生产分析生产理论涉及企业用资源(投入)生产产品(产出)的全过程。
在这个过程中,企业面临着两个基本的生产决策;1.如何组织劳动、资本等生产要素的投入,最有效地把既定的产量生产出来?2.如果企业需要扩大生产能力,应该怎样进行规划?通过本章的理论研究,我们可以对这两个问题作出解答,加深对企业生产决策的理解,并为更深入的分析打下基础。
第一节生产与生产函数一、生产与生产要素生产,指企业把其可以支配的资源转变为物质产品或服务的过程。
这一过程不单纯指生产资源物质形态的改变,它包含了与提供物质产品和服务有关的一切活动。
企业的产出,可以是服装、面包等最终产品;也可以是再用于生产的中间产品,如布料、面粉等。
企业的产品还可以是各种无形的服务。
生产要素:企业进行生产,需要有一定数量可供支配的资源作为投入,如土地、厂房、设备和原材料、管理者和技术工人等。
这些企业投入生产过程用以生产物质产品或劳务的资源称为生产要素或投入要素。
经济学中为方便起见,一般把生产要素分为三类:①劳动,包括企业家才能;②土地、矿藏、森林、水等自然资源;(3) 资本,已经生产出来再用于生产过程的资本品。
二、生产函数所谓生产函数(production function),就是指在特定的技术条件下,各种生产要素一定投入量的组合与所生产的最大产量之间的函数关系式,其一般形式为:Q = f(L,K,…T)简化形式:假定企业只生产一种产品,仅使用劳动与资本两种生产要素,分别用L和K表示,则方程可以简化为Q = f(L,K)三、短期生产和长期生产短期生产(shor trun),指的是期间至少有一种生产要素的投入量固定不变的时期,这种固定不可变动的生产要素称为固定要素或固定投入(fixedinputs);长期生产(Long run),则指生产期间所有生产要素的投入量都可以变动的时期,这些可以变动的生产要素称为可变要素或可变投入(variable inputs)。


管理经济学知识点总结管理经济学是一门将经济学原理应用于企业管理决策的学科,它帮助管理者理解市场力量、成本结构、资源配置以及企业战略等方面的问题。
以下是管理经济学的一些核心知识点总结:1. 需求与供给分析- 需求法则:价格下降,需求量上升;价格上升,需求量下降。
- 供给法则:价格上升,供给量上升;价格下降,供给量下降。
- 市场均衡:需求与供给相等时的价格和数量。
2. 边际分析- 边际成本(MC):增加一单位产出所增加的总成本。
- 边际收益(MR):增加一单位产出所增加的总收入。
- 边际利润:MR - MC,当边际利润为正时,增加产出是有利的。
3. 成本结构- 固定成本:不随产量变化的成本。
- 变动成本:随产量变化的成本。
- 总成本:固定成本加变动成本。
- 平均成本:总成本除以产量。
4. 规模经济与规模不经济- 规模经济:随着产量增加,单位成本下降。
- 规模不经济:随着产量增加,单位成本上升。
5. 市场结构- 完全竞争市场:许多买家和卖家,产品同质,无市场力量。
- 垄断竞争:许多卖家,产品有差异,存在市场力量。
- 寡头市场:少数卖家,产品可能同质或有差异,存在市场力量。
- 垄断:单一卖家,产品无替代品,有极大市场力量。
6. 价格歧视- 价格歧视:对不同消费者或不同时间、地点的相同产品收取不同价格。
7. 投资决策- 净现值(NPV):投资项目现金流的现值减去初始投资。
- 内部收益率(IRR):使NPV等于零的折现率。
8. 风险与不确定性- 风险:可量化的不确定性。
- 不确定性:不可量化的未知因素。
9. 企业战略- 成本领先战略:通过规模经济和效率降低成本,成为市场低成本生产者。
- 差异化战略:提供独特的产品或服务,满足特定消费者需求。
10. 政府干预与市场失灵- 政府干预:通过税收、补贴、价格控制等手段影响市场。
- 市场失灵:市场不能有效分配资源的情况,如公共品、外部性等。
11. 信息不对称- 信息不对称:市场中的一方比另一方拥有更多相关信息。
可编辑修改精选全文完整版管理经济学第1章导论1.1 管理经济学——运用经济理论和决策方法;解决企业管理决策问题;寻求最优化解决方案1.2 决策模型(见右图)1.3 经济利润及其来源1.3.1 会计利润和经济利润会计利润=销售收入-会计成本经济利润=销售收入-机会成本决策的基础是经济利润1.3.2 机会成本1.业主以自有资金办企业——利息2.业主自兼经理——从事其它工作的收入3.闲置设备再用来生产产品——零4.设备由生产A改为生产B ——生产A的利润收入5.存货市价改变——市价6.以市价进物料、劳动力、贷款——同会计成本7.设备折旧——设备期初价值与期末价值之差1.3.3 经济利润引导资源优化配置1.3.4 经济利润和正常利润正常利润是资金的机会成本;是吸引业主投资的最低报酬1.3.5 外显成本与内含成本内含成本由机会成本的存在引起,但不等于机会成本。
机会成本=外显成本+内含成本例1:某人甲以自有资金100万元投资办企业,乙借入100万元投资办企业,市场利率为10%。
甲、乙办企业的会计成本和机会成本各是多少?例2:甲、乙企业年使用钢材均为10万吨。
甲企业使用的是存货,当时购买价格为4 000元/吨,乙企业按现在市价买进,价格为5 000元/吨。
甲、乙企业年使用钢材的会计成本和机会成本各是多少?例3:某业主甲自己管理企业,他若到别处工作,年收入50 000元。
业主乙聘用经理管理企业,年支付工资50 000元。
业主甲、乙管理企业的会计成本和机会成本各是多少?例4:方案1:机器甲原来闲置,现用来生产产品B,所需人工、材料费按现行市价计算为1000元,折旧费为200元(假定折旧费与机器甲期初、期末的价值差额相等)方案2:机器乙原来生产产品A,利润收入为200元,现改为生产产品B,所需人工、材料费按现行市价计算为1000元,折旧费为200元(假定折旧费与机器甲期初、期末的价值差额为400元)试求两个方案的会计成本和机会成本。
管理经济学复习资料整理版第一章市场供求理论1、什么是需求/供给,影响需求/供给的因素有哪些?需求 demand:消费者在一定时期内,在各种可能的价格水平上愿意而且能够购买的商品数量需求的影响因素:(4条即可满分)①该商品的价格(price, P)②消费者的收入(income,I)③相关商品的价格(Pr)④消费者的偏好(preference,Pf)⑤消费者对价格的预期(Pe)⑥消费者数量(N)⑦广告费用(A)供给supply:生产者在一定时期内,在各种可能的价格下,愿意而且能够出售的该种商品的数量影响厂商供给量的因素:(4条即可满分)①商品自身的价格(price, P)②厂商的生产成本(C, cost)③相关商品的价格(Pr)④生产的技术水平(T,生产函数)⑤生产者对未来价格走势的预期(Pe)⑥行业内厂商的数量(N)2、市场均衡是如何形成的?当市场达到均衡时,在当前价格水平上,消费者愿意而且能够购买厂商愿意而且能够提供的所有商品,即此时,市场上此类商品的价格为“均衡价格",销售量(产量)为“均衡产量”,Qd=Qs。
第二章需求理论1、三种弹性的定义、计算公式需求的价格弹性表示在一定时期内,一种商品的需求量对于该商品价格变化的反应程度Ep=(dQ/dP)。
(P/Q)需求的收入弹性在一定时期内,消费者收入变化引起的对某种商品需求量的变化程度,即需求量变化对收入变化的反应程度Ei= =(dQ/dM)。
(M/Q)需求的交叉弹性一定时期内一种商品需求量的变动对其他相关商品价格变动的反应程度E xy=(dQ x/dP y)(P y/Q x)※2、需求价格弹性的因素有哪些?①商品对消费者的必要程度②替代品的可获得性:食盐与食糖③消费预算在总收入中的份额:火柴与汽车④所考察的消费者调整需求量的时间※3、需求价格弹性对销售收入的影响总收益与其主导作用(占优)的变量(价格或产量)有着相同的变化方向.需求的价格弹性决定了价格变化对总收益的影响。