小学英语四种时态详解
- 格式:doc
- 大小:38.50 KB
- 文档页数:2

小学英语四种时态总结英语语法中的时态是非常重要的一部分,正确使用时态可以使语言表达更加准确和清晰。
在小学英语学习阶段,学生们需要掌握四种基本的时态,它们分别是一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时和现在进行时。
下面将对这四种时态进行总结和归纳,希望能够帮助学生们更好地理解和掌握这些时态的用法。
一、一般现在时。
一般现在时表示的是经常性或习惯性的动作,或者是客观事实。
在句子中,一般现在时的动词形式不随主语的变化而变化,即动词用原形。
例如:1. I play football every Sunday.(我每个星期天都踢足球。
)。
2. She likes singing.(她喜欢唱歌。
)。
3. The sun rises in the east.(太阳从东方升起。
)。
二、一般过去时。
一般过去时表示的是发生在过去的动作或状态。
在句子中,一般过去时的动词形式通常是动词的过去式。
例如:1. I watched a movie last night.(昨晚我看了一部电影。
)。
2. They played basketball yesterday.(他们昨天打篮球。
)。
3. She lived in London for ten years.(她在伦敦住了十年。
)。
三、一般将来时。
一般将来时表示将来某个时间要发生的动作或状态。
在句子中,一般将来时通常使用助动词“will”或“shall”加上动词的原形。
例如:1. I will go to the park tomorrow.(我明天要去公园。
)。
2. She shall visit her grandparents next week.(她下周要去看望她的祖父母。
)。
3. We will have a party on Friday.(我们星期五要举办派对。
)。
四、现在进行时。
现在进行时表示现在正在进行的动作,或者是现阶段正在发生的动作。
在句子中,现在进行时的动词形式是“be”动词的现在分词形式。

(完整版)小学英语语法_四大时态(可编辑修改word版)四大时态复习1. 一般现在时(1)一般现在时的构成(肯定句)☆be 动词:主语+be(am,is,are)+其它。
如:I am a boy.我是一个男孩。
☆行为动词:主语+行为动词(+其它)。
如:We study English.我们学习英语。
☆当主语为第三人称单数(he, she,it)时,要在动词后加"-s"或"-es"。
如:Mary likes Chinese. 玛丽喜欢汉语。
(2)一般现在时的变化☆. be 动词的变化。
[否定句]:主语+ be + not +其它。
如:He is not a worker.他不是工人。
[一般疑问句]:Be +主语+其它。
如:-Are you a student? -Yes.I am. / No, I'm not.[特殊疑问句]:疑问词+一般疑问句。
如:Where is my bike?☆.行为动词的变化。
[否定句]:主语+ don't( doesn't ) +动词原形(+其它)。
如:I don't like bread.当主语为第三人称单数时,要用doesn't 构成否定句。
如:He doesn't often play.[一般疑问句]:Do( Does ) +主语+动词原形+其它。
如:- Do you often play football?- Yes, I do. / No, I don't.当主语为第三人称单数时,要用does 构成一般疑问句。
如:- Does she go to work by bike? - Yes, she does. / No, she doesn't.[特殊疑问句]:疑问词+一般疑问句。
如:How does your fathergo to work?*动词+s 的变化规则1.一般情况下,直接加-s,如:cook-cooks, milk-milks2.以s. x. sh. ch. o 结尾,加-es,如:guess-guesses, wash-washes, watch-watches, go-goes3.以“辅音字母+y”结尾,变y 为i, 再加-es,如:study-studies2. 现在进行时(1)一般现在时的构成:be(am,is, are)+ 动词的ing 形式。

小学英语四种时态详解一、一般现在时1、主要描述经常会发生的动作、状态或不变的真理。
2、句末常出现every day/week/year/Monday , in the morning;句中常有always, usually, often, sometimes3、①组成1.主语+be+名词(形容词)I am a student.He is tall.②否定句:在be 后加notI am not a student.He is not tall.③疑问句:be 动词提前到第一位。
Are you a student?Yes,I am./No,I am not.Is he tall?Yes,he is./No,he isn’t.4、①组成2.主语+动词+地点+时间We go to school on Monday.He goes to the park on Sunday.②否定句:主语+don’t/doesn’t+动词原形+地点+时间We don’t go to school on Saturday.He doesn’t go to the park on Sunday.③疑问句:在句首加do或does,动词恢复原形。
Do you go to school on Monday?Yes, we do./ No, we don’t.Does he go to the park on Sunday?Yes, he does./ No, he doesn’t.5、动词第三人称单数变化①在原单词末尾加s , 如:like –likes②单词以o, sh, ch, s, x 结尾加es, 如:go –goes③单词末尾为辅音+y,去y加ies 如:study- studies二、现在进行时1、主要叙述正在发生的事情。
2、句末常出现now;句首常出现look, listen。
3、①组成:主语+be +动词ing形式I am reading English.They are swimming.He is playing football.②否定句:在be后加notI am not reading English.They are not swimming.He is not playing football.③疑问句:将be 放到句首。

一般过去时的陈述句:主语+动词过去式+宾语一般过去时的否定句:主语+didn't +动词原形+宾语主语+ was/were not +宾语一般过去时的一般疑问句:Did + 主语+ 动词原形+宾语was/were +主语+宾语示过去某个时间发生的动作或存在的状态,常和表示过去的时间状语连用,如:yesterday, last night, in 1999, two weeks ago等;②表示过去经常或反复发生的动作,常和often, always等表示频度的副词连用;③规则动词过去式的构成如下:1在动词原形末尾+ed: look—looked, play—played2结尾是e的动词+d: live—lived, hope—hoped3结尾是“元音字母+辅音字母”的重读音节词,先双写这个辅音字母,再+ed: stop—stopped, trip—tripped4结尾是“辅音字母+y”的动词,先变y为i,再+ed: study—studied, carry—carried④不规则动词要逐一记忆,可参考不规则动词表;一般过去时的特殊疑问句::特殊疑问词+一般过去时的一般疑问句一般过去时态: 1 表示过去已经发生的事情,通常用“last week, ju st now, yesterday”等词; 2 be 动词的过去式: am/is—was are—were I/He/she/it wasnot…. You/we/they were…. 一般疑问句was, we re 放在句首; 3过去式基本结构肯定句Positive 动词过去式 I we nt shopping last night. 否定句Negative Didn’t + 动词原形 I d idn’t go shopping las t night. 一般疑问句Yes/No Did …+ 动词原形… Did you go shopping last night 特殊疑问句wh- What did…+ 动词原形… What did you do last night 4动词过去式的变化:规则动词的变化:一般动词 +ed planted,watered,climbed 以不发音的e 结尾 +d liked 辅音字母加y结尾 -y+ ied study—studied, cry- cr ied 重读闭音节单词,末尾只有一个辅音字母双写最后一个字母+ed st op –stopped plan - planned 不规则动词的变化:原形过去式原形过去式原形过去式原形过去式 sweep swept teach taught have had go went keep kept think thought do did find found sleep sl ept buy bought eat ate say said feel felt drink drank is/am wa s take took read read give gave are were mean meant put put si ng sang drive drove meet met cut cut begin began speak spoke m ake made let let ring rang write wrote see saw fly flew run ra n ride rode come came draw drew sit sat hear heard tell told g row grew learn learned/ learnt get got know knew一般现在时的陈述句:主语+动词原形或单三形式动词根据主语的变化而变化+宾语一般现在时的否定句:主语+don't/doesn't +动词原形+宾语主语+ am/is/are +not +宾语一般现在时的一般疑问句:Do/Does +主语+动词原形+宾语 Is / Are +主语+ 宾语特殊疑问句:特殊疑问词+一般现在时的一般疑问句1表示经常发生的动作或事情,通常用“usually, often, every day, sometimes,always,never”等词; 2基本结构: I / You / We / They He / She / It 肯定句Positive 动词原形V 动词第三人称单数形式V+S 否定句Negative don’t + 动词doesn’t + 动词原形一般疑问句Yes/No Do… Yes, I do. Does…动词原形…No,she doesn’t. wh- What do … How does she…动词原形… 3 动词第三人称单数形式 a. Most verbs +s walk-walks b. Verbs ending in a consonant +y -y +ies fly-flies c. Verbs ending in s, sh, ch or x +es watch-watches d. Others do-does ,have-has, go-goes现在进行时的陈述句:主语+ Be + 现在分词+ 宾语现在进行时的否定句:主语+ be+ not+ 现在分词+宾语现在进行时的一般疑问句:Be+主语+现在分词+宾语现在进行时的特殊疑问句:特殊疑问词+一般疑问句现在进行时,:1表示正在发生的动作,通常用“now,look”. 2基本形式:be + 动词+ing eg: I amnot doing my homework. You/We/They arenot reading. He/She/It isnot eating. What are you doing Is he reading 3动词的现在分词形式do+ing Most verbs +ing walk—walking Verbs ending in e -e + ing come—coming Short verbs ending in a vowel + a consonant Double consonant run-running swim-swimming一般将来时的陈述句:主语+will/be going to + 动词原形+宾语一般将来时的否定句:主语+won't/be+not going to +动词原形+宾语一般将来时的一般疑问句:Will + 主语+动词原形+宾语 Be + 主语+ going to +动词原形+宾语一般将来时的特殊疑问句:特殊疑问词+一般将来时的一般疑问句一般将来时: 一般将来时表示将来打算做的事或将要发生的事情; 结构:be going to +动词原形例如:I’m going to visit my grandpa next week. 与这个时态连用的时间状语常用: tonight, tomorrow, the day after tomorrow, next week, in three hours, two days later 等; 一般将来时态与其它结构表将来情况的区别:一般将来时态:主要从时间的角度表将要发生的动作或情况;一般将来时除了使用“shall/will + V…”以外,也可以使用下列的句式来表达; 1.be going to + V … 即将会……;打算将…… be going to 结构:①表主观上打算或准备做某事时; ②表有发生某事的预兆时; . They are going to have a competition with us in studies. It is going to rain. 据以上区别,故下面一句是错的: I am going to be eighteen years old next year. 应改为: I shall be eighteen years old next year. be about to do sth 结构:意为“刚要做某事”、“马上要做某事”强调时间之紧迫性; . We are about to discuss this problem. 我们将马上讨论这个问题; be to do sth 结构:表示按计划、安排、规定将实施某事或表示注定会发生某事; . When is the train to leave. shall与will用法的区别详见shall与will用法的区别及它两过去式用法的区别4. 一般将来时①一般将来时表示将来某一时间的动作或状态;常与tomorrow, next week, from now on, in the future等连用;②由助动词shall第一人称/will第二、三人称+动词原形构成;③美国英语则不管什么人称,一律用will;④“be going to+动词原形”表示即将发生的或最近打算进行的事:We are going to have a meeting today. 今天我们要开会;⑤一些动词go,come,start,move,sail,leave,arrive,stay等的进行时态可表示近期的计划和打算:I'm leaving for Beijing.我要去北京;⑥“be to+动词原形”。

小学英语的四种时态知识点1.一般现在时(1)句中be动词和动词一般情况下只能有一种而且也必须有一种。
如:The children are very happy on Christmas Day .She often does some housework at the weekend .(2)一般现在时中的be动词:一般用原形:am is aream用于第一人称单数(I);is用于第三人称单数(he she it和其他人名或称谓,如:Ben his sister等);are用于第二人称单数(you)和所有复数(包括第一人称复数we、第二人称复数you;第三人称复数they和其他复数,如the children 、his parents等)。
(3)一般过去时中的动词:有两种情况:第一种情况:主语是第三人称单数(he she it 和其他,如Helen 、her cousin 等),动词后一般加s或es。
第二种情况:主语不是第三人称单数,动词都用原形。
(4)一般现在时判断依据(如何判断一个句子是一般现在时):△be动词是am、is、are△动词用原形或加s、es△没有时间状语或有usually、often、everyday、sometimes等不是具体的时间(5)有用的的依据:Be动词是is、am ←→名词用原形(这里包括可数名词的单数和不可数名词)Be动词是are ←→名词加s或es动词加s或es ←→主语是第三人称单数动词用原形←→主语不是第三人称单数(6)情态动词:我们现在学过的情态动词有:can、must、should、would。
情态动词后动词总是用原形。
(不受其他任何条件影响)2.一般过去时(1)句中be动词和动词一般情况下只能有一种而且也必须有一种。
如:The girls were on the grass just now .They visited my parents last weekend .(2)一般过去时中的be动词:一般用过去式:was werewas用于第一人称单数(I)和第三人称单数(he she it和其他人名或称谓,如:Ben 、his sister等);were用于第二人称单数(you)和所有复数(包括第一人称复数we、第二人称复数you;第三人称复数they 和其他复数,如the children 、his parents等)。

千里之行,始于足下。
小学四种英语时态的归纳总结小学英语时态的归纳总结在小学阶段学习英语,掌握四种基本的时态是非常重要的。
这四种时态分别是一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时和现在进行时。
以下是对这四种时态的归纳总结。
一、一般现在时(Simple Present Tense)1. 表示经常性的动作或状态。
例如:I play basketball every Saturday.2. 在陈述句中,主语和动词要一致。
例如:He likes to watch movies.3. 在否定句中,用do / does + not + 动词原形。
例如:She does not like vegetables.4. 在疑问句中,用do / does + 主语 + 动词原形?例如:Do you have any pets?5. 用于表示客观事实、经验等。
二、一般过去时(Simple Past Tense)1. 表示过去发生的动作或状态。
例如:I watched a movie yesterday.2. 在陈述句中,动词过去式的变化规则是直接加-ed。
例如:We played soccer last week.3. 在否定句中,用did + not + 动词原形。
例如:She did not go to school yesterday.4. 在疑问句中,用did + 主语 + 动词原形?例如:Did you finishyour homework?第1页/共3页锲而不舍,金石可镂。
三、一般将来时(Simple Future Tense)1. 表示将来发生的动作或状态。
例如:I will go to the park tomorrow.2. 在陈述句中,用will / shall + 动词原形。
例如:She will visither grandparents next week.3. 在否定句中,用will not / won't + 动词原形。
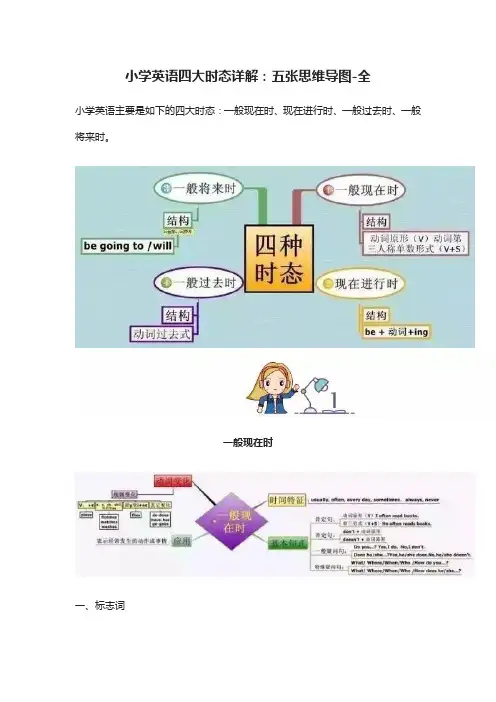
小学英语四大时态详解:五张思维导图-全小学英语主要是如下的四大时态:一般现在时、现在进行时、一般过去时、一般将来时。
一般现在时一、标志词always(总是)usually(通常)often(经常)sometimes(有时)never(从不)every(每一)二、基本用法1.表示事物或人物的特征、状态。
2.表示经常性、习惯性的动作。
3.表示客观现实。
三、构成1.be动词:主语+be动词(am isare)+其它.2.行为动词:主语+行为动词+其它。
四、句型肯定句:A. be 动词:be+主语+其它。
B. 行为动词:主语+动词(注意人称变化)+其它。
否定句:A.be动词:主语+be+not+其它。
B.行为动词:主语+助动词(do/does)+not+d动词原形+其它一般疑问句:A.be动词:be+主语+其它。
B.行为动词:助动词(Do/Does)+主语+动词原形+其他.特殊疑问词:疑问词+一般疑问句现在进行时一、标志词now(现在), look(看),listen(听)二、基本用法表示现阶段正在进行的动作三、基本结构1.肯定句:主语+be动词+动词现在分词(ing)+其它。
2.否定句:主语+be动词+not+动词现在分词(ing)+其它。
3.一般疑问句:be动词+主语+现在分词(ing)+其它。
4.特殊疑问句:疑问词+一般疑问句。
一般将来时一、标志词tomorrow(明天),soon(不久),will(将要=be going to)二、基本用法表示在在将来某个时间要发生的动作或存在的状态。
三、基本结构1.肯定句:主语+ be going to + 动词原形。
主语+will+动词原形。
2.否定句:主语+ be going to +动词原形。
主语+won’t + 动词原形3.一般疑问句:Be + 主语+ going to+动词原形Will + 主语+ 动词原形4.特殊疑问句:疑问词+一般疑问句一般过去时一、标志词yesterday(昨天),ago(以前),before(在...之前)二、用法1.表示过去某个时间发生的动作或存在的状态,常和表示过去的时间状语连用。

六年级四大时态知识点归纳总结英语六年级四大时态知识点归纳总结简介:英语六年级时态是学习英语语法中的重要部分,掌握好时态的用法对于学习英语有着至关重要的作用。
本文将对六年级学生需要掌握的四大时态进行总结和归纳,旨在帮助同学们更好地理解和运用这些知识点。
一、一般现在时1. 表示经常性、习惯性或普遍真理的动作或状态。
例句:I play soccer every Sunday.(我每个星期天踢足球。
)2. 用于第三人称单数,动词需加s。
例句:He goes to school by bus.(他乘公交车去学校。
)3. 特殊疑问句中动词放在句首,而一般疑问句中用助动词do或does。
例句:Where do you live?(你住在哪里?)Does she like ice cream?(她喜欢冰淇淋吗?)4. 否定形式在动词前加don't或doesn't。
例句:I don't like broccoli.(我不喜欢花椰菜。
)He doesn't play the guitar.(他不弹吉他。
)二、一般过去时1. 表示过去某个时间发生的动作或状态。
例句:I watched a movie yesterday.(我昨天看了一部电影。
)2. 动词过去式一般在动词后加-ed,但也有一些不规则动词。
例句:She ate an apple for breakfast.(她吃了一个苹果作早餐。
)3. 特殊疑问句和一般疑问句中用助动词did。
例句:What did you do yesterday?(昨天你做了什么?)Did they go to the park?(他们去公园了吗?)4. 否定形式在动词前加didn't。
例句:I didn't swim in the lake.(我没有在湖中游泳。
)They didn't finish their homework.(他们没有完成作业。


小学英语时态总结及用法一、一般现在时用法:1.表示经常性、习惯性的动作或存在的状态。
2.表示客观事实或普遍真理。
例句:I often go to school by bus.(我经常乘公交车去上学。
)The sun rises in the east.(太阳从东方升起。
)二、现在进行时表示正在进行的动作或情况。
常与now, at this moment, these days等时间状语连用。
例句:They are playing football now.(他们现在正在踢足球。
)I am studying English these days.(这些天我正在学习英语。
)三、一般过去时用法:表示过去某个时间发生的动作或存在的状态。
常与yesterday, last week, ago等时间状语连用。
例句:I went to the park yesterday.(我昨天去了公园。
)She had a cold last week.(她上周感冒了。
)四、一般将来时用法:表示将来某个时间要发生的动作或存在的状态。
常与tomorrow, next week, in the future等时间状语连用。
例句:I will go to the zoo tomorrow.(我明天要去动物园。
)They are going to have a party next week.(他们下周要举行一个聚会。
)五、现在完成时用法:表示过去发生的动作对现在造成的影响或结果。
常与already, yet, just, ever, never等副词连用。
例句:I have already finished my homework.(我已经完成了我的家庭作业。
)She has never been to Beijing.(她从未去过北京。
)通过以上总结,希望同学们能够更好地掌握小学英语中的基本时态及其用法,为日后的英语学习打下坚实的基础。

小学英语四种时态1.一般现在时态概念:表示经常发生的或习惯性的动作或目前的状态。
规律:一般用动词原形,当主语为第三人称单数的一般现在时,动词要加s ,es ,标志性的单词:always ,usually ,often ,sometimes 如:She usually goes to school on foot2.现在进行时态概念:表示说话时正在发生或进行着的动作。
规律:be 动词ing 形式。
标志性的单词:look ,now ,listen 如:Look ,the boy is playing football 。
3.一般将来时态概念:表示将来发生的动作或情况。
规律:be going to do ,will do 。
标志性的单词:tomorrow ,the day after tomorrow ,next Sunday … 如:Mr Brown is going to visit Hong Kong tomorrow 。
4.一般过去时态概念:表示过去某一时刻或某一时间内发生的动作或情况。
标志性的单词:yesterday ,last Monday ,before ,ago,the day before yesterday 规律:(1)一般情况动词后面加ed ; 如:worked ,cleaned ,washed ,(2)以不发音e结尾的动词加d就要以了; 如:lived ,moved ,loved(3)以辅音加y结尾的动词把y改成i再加ed ; 如:study– studied ,carry—carried(4)重读闭音节的动词要双写末尾的辅音字母再加ed; 如:stop—stopped shop—shopped skip--- skipped(5)特殊变化:见不规则动词表。
小学英语固定搭配Good night 晚安.in the morning 在早上at noon 在中午in the afternoon 在下午in the evening 在傍晚at night 在夜间have/eat breakfast 吃早饭have/eat lunch 吃午饭have/eat supper(dinner) 吃晚饭read a book 读书sing a song 唱歌have a meeting 开会have class 上课have a party 聚会have a competition 竞赛have a sleep 睡觉have a snack 吃零食have a picnic 野餐have a buffet dinner 吃自助餐draw pictures 画画listen to music 听音乐listen to the radio 听收音机learn English 学习英语learn Chinese 学习语文Learn math 学习数学tell stories 讲故事take a walk 散步ask and answer questions 问答问题fly a kite 放风筝ride a bike 骑自行车ride a horse 骑马play computer games 玩电脑游戏play games 做游戏play hide and seek 玩捉迷藏do homework 做作业watch TV 看电视take a shower 洗淋浴take a bath 洗澡open the door 开门open the window 开窗户close the door 关门close the window 关窗户paly football 踢足球/打橄榄球play basketball 打篮球play volleyball 打排球play badminton 打羽毛球play golf 打高尔夫球play bowling 打保龄球play table tennis 打乒乓球play baseball 打棒球play tennis 打网球play soccer 踢足球play hockey 打曲棍球play chess 下棋go fishing 去钓鱼go swimming 去游泳go shopping 去购物go skating 去滑冰go bike-riding/ go cycling 去骑自行车go sking 去滑雪go camping 去野营listen to the news 听新闻read the newspaper 看报read the magazine 看杂志go to school 去上学go home 回家go to the park 去公园go to the zoo 去动物园go to the library 去图书馆go to the hospital 去医院go to the cinema 去电影院go to see a film /movie去看电影get up 起床go to bed 上床go to sleep 去睡觉brush the teeth 刷牙wash the hands 洗手wash the face 洗脸wash clothes 洗衣服air the room 给房间通风make the bed 铺床sweep the floor 扫地mop the floor 拖地clean the room 打扫房间climb the trees 爬树climb the mountains 爬山cook the meals 做饭drink milk/juice/coca cola 喝牛奶/果汁/可乐play the piano 弹钢琴play the violin 拉小提琴play the drum 打鼓play the guitar 弹吉他play the xylophone 弹木琴play the flute 吹笛子play the harp 弹竖琴play the erhu 拉二胡play the zither 弹古筝play the banjo 弹班卓play the trumpet 吹小号stay at home 呆在家里at home 在家at school 在学校at church 在教堂make a cake 做蛋糕take pictures/photos 照相comb hair 梳头发have a haircut 理发go away 走开at the weekend 在周末stand up 起立sit down 坐下New year 元旦Spring Festival 春节Lantern Festival 元宵节Spring Cleaning Day 清明节Dragon Boat Festival 龙舟节International labour day 国际劳动节Trees planting day 植树节Children's day 儿童节Party's day 党的生日Army's day 建军节Teacher's day 教师节National day 国庆节Thanksgiving day 感恩节Chrismas day 圣诞节in the morning 在早上at noon 在中午in the afternoon 在下午in the evening 在傍晚at night 在夜间have/eat breakfast 吃早饭have/eat lunch 吃午饭have/eat supper(dinner) 吃晚饭read a book 读书sing a song 唱歌have a meeting 开会have class 上课have a party 聚会have a competition 竞赛have a sleep 睡觉have a snack 吃零食have a picnic 野餐have a buffet dinner 吃自助餐draw pictures 画画listen to music 听音乐listen to the radio 听收音机learn English 学习英语learn Chinese 学习语文Learn math 学习数学tell stories 讲故事take a walk 散步ask and answer questions 问答问题fly a kite 放风筝ride a bike 骑自行车ride a horse 骑马play computer games 玩电脑游戏play games 做游戏play hide and seek 玩捉迷藏do homework 做作业watch TV 看电视take a shower 洗淋浴take a bath 洗澡open the door 开门open the window 开窗户close the door 关门close the window 关窗户paly football 踢足球/打橄榄球play basketball 打篮球play volleyball 打排球play badminton 打羽毛球play golf 打高尔夫球play bowling 打保龄球play table tennis 打乒乓球play baseball 打棒球play tennis 打网球play soccer 踢足球play hockey 打曲棍球play chess 下棋go fishing 去钓鱼go swimming 去游泳go shopping 去购物go skating 去滑冰go bike-riding/ go cycling 去骑自行车go sking 去滑雪go camping 去野营listen to the news 听新闻read the newspaper 看报read the magazine 看杂志go to school 去上学go home 回家go to the park 去公园go to the zoo 去动物园go to the library 去图书馆go to the hospital 去医院go to the cinema 去电影院go to see a film /movie去看电影get up 起床go to bed 上床go to sleep 去睡觉brush the teeth 刷牙wash the hands 洗手wash the face 洗脸wash clothes 洗衣服air the room 给房间通风make the bed 铺床sweep the floor 扫地mop the floor 拖地clean the room 打扫房间climb the trees 爬树climb the mountains 爬山cook the meals 做饭drink milk/juice/coca cola 喝牛奶/果汁/可乐play the piano 弹钢琴play the violin 拉小提琴play the drum 打鼓play the guitar 弹吉他play the xylophone 弹木琴play the flute 吹笛子play the harp 弹竖琴play the erhu 拉二胡play the zither 弹古筝play the banjo 弹班卓play the trumpet 吹小号stay at home 呆在家里at home 在家at school 在学校at church 在教堂make a cake 做蛋糕take pictures/photos 照相comb hair 梳头发have a haircut 理发go away 走开at the weekend 在周末stand up 起立sit down 坐下New year 元旦Spring Festival 春节Lantern Festival 元宵节Spring Cleaning Day 清明节Dragon Boat Festival 龙舟节International labour day 国际劳动节Trees planting day 植树节Children's day 儿童节Party's day 党的生日Army's day 建军节Teacher's day 教师节National day 国庆节小学英语动词过去式agree 同意agreedask 问askedanswer 回答answeredbecome 成为becamebegin 开始beganbring 带来broughtbuy 买boughtcall 呼叫calledcarry 搬运carriedcatch 抓住caughtcheck 检查checkedclean 清洁cleanedclimb 爬climbedcome 来camecook 煮cookedcut 切cutdance 跳舞danceddo 做diddraw 画drewdrink 喝drankdrive 驾驶droveeat 吃ateenjoy 欣赏enjoyedfeel 感觉feltfly 飞fliedforget 忘记forgotfish 钓鱼fishedget 得到gotgive 给gavego 去wentgrow 成长grewhave 有hadhear 听到heardhelp 帮助helpedjump 跳jumpedkeep 保存keptknow 知道knewlearn 学习learned listen 听listenedlike 喜欢likedlook 看lookedlive 生活livedlove 喜爱lovedmake 做mademeet 遇见metmove 移动moved need 需要needed open 打开opened paint 画paintedpick 摘pickedplay 玩playedplan 计划planned practise 练习practised prefer 更喜欢preferred put 放putread 读readride 骑roderun 跑ransay 说saidsee 看sawsit 坐satskip 跳skippedspeak 说spokestart 开始startedstay 停留stayed sweep 扫sweptstudy 学习studied swim 游泳swamtalk 谈话talkedtake 带去tookteach 教taughtthank 谢谢thanked tell 告诉toldthink 想thought travel 旅游traveledtry 试trieduse 使用used wake 醒来woke walk 走路walked want 想wanted wash 洗washed watch 看watched water 浇水watered wave 挥动waved work 工作worked worry 担心worried write 写wrote小学英语可数名词复数形式1)以y结尾的专有名词,或元音字母+y 结尾的名词变复数时,直接加s变复数。
小学4种时态知识点总结一、什么是时态?在语法中,时态是指动词的形式和使用方式,用来表示动作或状态发生的时间。
时态可以分为过去、现在和将来三个主要时态。
二、过去时态过去时态表示动作或状态发生在过去的时间。
常见的过去时态有以下几种:1.一般过去时一般过去时用于表示过去某个时间发生的动作或状态,通常与时间状语词(如yesterday,last week等)一起使用。
例如:•I played basketball yesterday.(我昨天打篮球。
)•She visited her grandparents last week.(她上周去拜访了她的祖父母。
)2.过去进行时过去进行时表示过去某个时间正在进行的动作。
它由“was/were + 动词的ing形式”构成。
例如:•He was studying when I called him.(我给他打电话时,他正在学习。
)•They were playing in the park yesterday afternoon.(他们昨天下午在公园里玩。
)3.过去完成时过去完成时表示在过去某个时间之前已经完成的动作。
它由“had + 过去分词”构成。
例如:•She had already finished her homework when her friend came.(她朋友来的时候,她已经完成了作业。
)•They had gone home before it started raining.(下雨之前,他们已经回家了。
)4.过去完成进行时过去完成进行时表示过去某个时间开始并持续到另一个过去时间的动作。
它由“had been + 动词的ing形式”构成。
例如:•He had been studying English for two hours when his friend called him.(他朋友给他打电话时,他已经学习了两个小时的英语了。
)•They had been waiting for the bus for half an hour before it finally arrived.(公共汽车终于来了之前,他们已经等了半个小时了。
小学的四大时态知识点总结时态是英语中非常重要的一部分,它指明动作或状态发生的时间。
在英语中,有四个基本的时态:一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时和现在进行时。
这篇文章将对这四大时态知识点进行总结,帮助小学生更好地理解和掌握它们。
一、一般现在时1.1 表示习惯性或经常性的动作或状态一般现在时用来表示经常性或习惯性的动作或状态。
例如:I go to school every day.(我每天去学校。
)1.2 表示客观真理或普遍事实一般现在时也用来表示客观真理或普遍事实。
例如:Water boils at 100 degrees Celsius.(水在100摄氏度时煮沸。
)1.3 表示现在的情况或状态一般现在时还可以用来表示当前的情况或状态。
例如:She looks very happy today.(她今天看上去很开心。
)二、一般过去时2.1 表示过去发生的动作或状态一般过去时用来表示过去发生的动作或状态。
例如:They played basketball yesterday.(他们昨天打篮球。
)2.2 表示过去的习惯或经常性动作一般过去时还可以表示过去的习惯或经常性动作。
例如:I always watched TV after school when I was young.(我小的时候放学后经常看电视。
)2.3 表示过去的客观真理或普遍事实一般过去时也可以用来表示过去的客观真理或普遍事实。
例如:People believed the earth was flat in ancient times.(古代人相信地球是扁的。
)三、一般将来时3.1 表示将来要发生的动作或状态一般将来时用来表示将来要发生的动作或状态。
例如:I will go to the park tomorrow.(我明天会去公园。
)3.2 表示对将来的预测或打算一般将来时还可以表示对将来的预测或打算。
例如:I think it will rain this afternoon.(我觉得今天下午会下雨。
小学的四大时态知识点总结小学英语教学中,时态是学生必须掌握的基本语法点之一。
以下是小学阶段学生需要掌握的四大时态知识点的总结:1. 一般现在时(Simple Present Tense)- 用法:表示经常发生的动作或状态,或者表示客观事实。
- 结构:主语 + 动词原形/动词的第三人称单数形式(如:He/She/It + 动词-s/-es)。
- 例句:She goes to school every day.(她每天去上学。
)2. 现在进行时(Present Continuous Tense)- 用法:表示正在进行或发生的动作。
- 结构:主语 + be动词(am/is/are)+ 动词的现在分词形式(-ing)。
- 例句:They are playing football now.(他们现在正在踢足球。
)3. 一般过去时(Simple Past Tense)- 用法:表示过去发生的动作或状态。
- 结构:主语 + 动词的过去式。
- 例句:He visited his grandparents last week.(他上周拜访了他的祖父母。
)4. 一般将来时(Simple Future Tense)- 用法:表示将来发生的动作或状态。
- 结构:主语 + will + 动词原形;或主语 + be going to + 动词原形。
- 例句:She will go to the library tomorrow.(她明天将去图书馆。
)掌握这些基本时态对于小学生来说至关重要,它们是构建句子和表达思想的基础。
在学习过程中,学生应该通过大量的练习和实际应用来加深对这些时态的理解和运用。
同时,老师和家长也应该鼓励学生在日常生活中使用英语,以提高他们的语言能力。
通过不断的练习和应用,学生将能够更加熟练地掌握这些时态,并在英语交流中更加自信。
小学英语四种时态精讲一般现在时1.概念:一般现在时表示经常的、习惯性的动作或存在的状态,表示客观存在的事件2.构成:一般现在时的构成主要有两种形式,一般现在时用行为动词的原形,但第三人称单数作主语时,动词的词尾要加-S。
:(1)be型:句子的谓语动词是(am,is或are):a.肯定句中,只出现be,如:I am a student.我是一名学生。
b.否定句中,要在be后面加not,如:She isn't a teacher.她不是教师。
c.一般疑问句,要将be放在句子开头(注意句首字母大写),句尾用问号,答语用Yes,主语+be.或No,主语+be+not.如:—Are you ready?—你准备好了吗?—Yes,I am.—是的,我准备好了。
(—No,I'm not.—不,我没准备好。
)(2)DO型:句中的谓语动词为实义动词(也叫行为动词):a.肯定句中,只出现实义动词,如:I get up in the morning.我早晨起床。
b.否定句中,要在实义动词前面加do(does)+not,do(does)作助动词,本身无意义,常与not缩写成don't(doesn't),如:I don't like vegetables.我不喜欢蔬菜。
c.一般疑问句,要在句子开头加助动词Do(does),句尾用问号,简略答语用Yes,主语+do(does).或No,主语+do(does)+not.如:—Do you like oranges?—你喜欢桔子吗?—Yes,I do.—是的,我喜欢。
(—No,I don't.—不,我不喜欢。
)3.标志词:every…, sometimes, on Sunday,usually,often,always 现在一般时动词变化的规则是:1.如果主语是名词复数和第一人称I、 we ,谓语动词不用做任何变化,即仍然用动词原型表示:We usually go to school at 7:30. 我们通常7:30上学去。
1.现在进行时①标志词---- now, listen, look,表示正在发生的事情或进行的动作。
②结构:1.人/物+ 2. be动词(am, is, are) + 3.动词ing. eg:He is running now.Look! It is snowing. Sam is swimming. Tom is playing table tennis.Listen! Amy and lingling are singing and dancing in the park.③一般疑问句将be动词提前,否定句在be动词后+not. eg: Is he running now? / He is not(He isn’t) running now.Are they playing football now? / They are not (They aren’t )playing football now.2.一般现在时①表示经常出现,或者反复发生的事情或动作,②标志词----often, usually, sometimes, always, every③结构:1.人/物+ 2.动词原形/动词三单形式+ 3.其他;④当主语为第三人称单数(单个人/物/地点):he,she, it, Jenny, my sister,Beijing, Shouguang等,动词后加s或es.eg:He runs every day. Tom has got a new bag. Xiaoming studiesvery hard every day. Mr Smart speaks Chinese very well. They often read books .问句借助于do, does。
否定句借助于don’t, doesn’t,后面动词一定要还原。
Does he run every day? / He doesn’t run every day.Do they often read books? / They don’t often read books.3.一般过去时①表示发生在过去的事情或者事件,标志词----in the past,then, two hours (ago), yesterday, last week,last month; last year。
小学阶段四种时态复习
通常在句子中有以下的词:now, look, listen.
句子的结构如下:肯定句:主语+be动词+ V.ing…
否定句:主语+be动词+not + V.ing…
一般疑问句:be动词+主语+ V.ing…?
am,is,are的用法口决:我用am,你用are,is 跟着她,他,它,单数is,复数are其中,动词的ing形式有如下方法:
A. 在动词后直接加ing: go- going , wash-washing, fly—flying
B. 以单个元音+单个辅音+e结尾,去掉e加ing, 如:drive—driving;ride—riding;make—making
C. 某些单词要双写词尾的字母:swim- swimming;run—running;get—getting;
eg:1. I am listening to the music now.
否定:__________________________ 一般疑问句:________________________
2. Listen! She is singing .
否定:__________________________ 一般疑问句:________________________
常与every…, always, usually, often, sometimes等表经常的时间状语连用。
注:当主语是第三人称单数时,谓语动词也要用第三人称单数。
动词第三人称单数:A:直接加s (如,plays)
B:以ch,sh,s,x结尾的单词加es(如,washes, watches)
C:以辅音字母加y结尾的单词,变y为i加es。
(studies)
句子结构:肯定句:主语+ V.(主语为三单时加s)…
否定句:主语+助动词do/does+ not + V.(原型)…
一般疑问句:助动词Do/Does +主语+ V.(原型)…?
eg:1. We often play in the playground after school.
否定:__________________________ 一般疑问句:________________________
2. He usually gets up at six o’clock.
否定:__________________________ 一般疑问句:________________________
3. Mike sometimes goes to the park with his sister.
否定:__________________________ 一般疑问句:________________________
4 The sun rises in the east. (太阳从东边升起)
否定:__________________________ 一般疑问句:________________________
:表示事情已经发生。
常见时间状语:last, yesterday, just now, … ago,
句子结构:肯定句:主语+ V.ed…
否定句:主语+助动词did+ not + V.(原型)…
一般疑问句:助动词Did +主语+ V.(原型)…?
eg:1. I had an exciting party last weekend.
否定:__________________________ 一般疑问句:________________________
2. They all went to the mountains yesterday morning.
否定:__________________________ 一般疑问句:________________________
3. The pen was on the desk just now.
否定:__________________________ 一般疑问句:________________________ be动词用过去式:am,is—was; are—were
句子结构:肯定句:主语+ was/were…
否定句:主语+ + was/were +not +…
一般疑问句:was/were+主语+…?
Eg 1. I was a student some years ago.
否定:__________________________ 一般疑问句:________________________
常见时间状语:next,tomorrow, soon等表示将来的时间。
句子结构:be going to+动词原形;
肯定句:主语+be动词+going to + V原形…
否定句:主语+be动词+not + going to + V原形…
一般疑问句:be动词+主语+ going to + V原形…?eg:1. I am going to play football this afternoon.
否定:__________________________ 一般疑问句:______________________ 2. We are going to New York next week.
否定:__________________________ 一般疑问句:______________________ 3. Nancy is going to play the piano tomorrow.
否定:__________________________ 一般疑问句:______________________。