欧洲药典8.0-凡例双语版
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:694.71 KB
- 文档页数:24
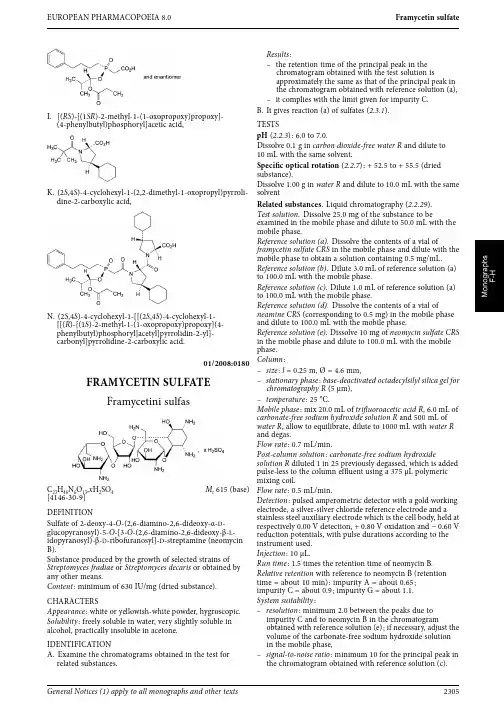
EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA 8.0FramycetinsulfateI.[(RS )-[(1SR )-2-methyl-1-(1-oxopropoxy)propoxy]-(4-phenylbutyl)phosphoryl]aceticacid,K.(2S ,4S )-4-cyclohexyl-1-(2,2-dimethyl-1-oxopropyl)pyrroli-dine-2-carboxylicacid,N.(2S ,4S )-4-cyclohexyl-1-[[(2S ,4S )-4-cyclohexyl-1-[[(R )-[(1S )-2-methyl-1-(1-oxopropoxy)propoxy](4-phenylbutyl)phosphoryl]acetyl]pyrrolidin-2-yl]-carbonyl]pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid.01/2008:0180FRAMYCETIN SULFATEFramycetinisulfasC 23H 46N 6O 13,x H 2SO 4M r 615(base)[4146-30-9]DEFINITIONSulfate of 2-deoxy-4-O -(2,6-diamino-2,6-dideoxy-α-D -glucopyranosyl)-5-O -[3-O -(2,6-diamino-2,6-dideoxy-β-L -idopyranosyl)-β-D -ribofuranosyl]-D -streptamine (neomycin B).Substance produced by the growth of selected strains of Streptomyces fradiae or Streptomyces decaris or obtained byany other means.Content :minimum of 630IU/mg (dried substance).CHARACTERSAppearance :white or yellowish-white powder,hygroscopic.Solubility :freely soluble in water,very slightly soluble inalcohol,practically insoluble in acetone.IDENTIFICATION A.Examine the chromatograms obtained in the test forrelated substances.Results :–the retention time of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution isapproximately the same as that of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a),–it complies with the limit given for impurity C.B.It gives reaction (a)of sulfates (2.3.1).TESTSpH (2.2.3):6.0to 7.0.Dissolve 0.1g in carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 10mL with the same solvent.Specific optical rotation (2.2.7):+52.5to +55.5(dried substance).Dissolve 1.00g in water R and dilute to 10.0mL with the samesolvent Related substances .Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).Test solution .Dissolve 25.0mg of the substance to beexamined in the mobile phase and dilute to 50.0mL with the mobile phase.Reference solution (a).Dissolve the contents of a vial offramycetin sulfate CRS in the mobile phase and dilute with the mobile phase to obtain a solution containing 0.5mg/mL.Reference solution (b).Dilute 3.0mL of reference solution (a)to 100.0mL with the mobile phase.Reference solution (c).Dilute 1.0mL of reference solution (a)to 100.0mL with the mobile phase.Reference solution (d).Dissolve the contents of a vial of neamine CRS (corresponding to 0.5mg)in the mobile phase and dilute to 100.0mL with the mobile phase.Reference solution (e).Dissolve 10mg of neomycin sulfate CRS in the mobile phase and dilute to 100.0mL with the mobile phase.Column :–size :l =0.25m,Ø=4.6mm,–stationary phase :base-deactivated octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5μm),–temperature :25°C.Mobile phase :mix 20.0mL of trifluoroacetic acid R ,6.0mL of carbonate-free sodium hydroxide solution R and 500mL of water R ,allow to equilibrate,dilute to 1000mL with water R and degas.Flow rate :0.7mL/min.Post-column solution :carbonate-free sodium hydroxidesolution R diluted 1in 25previously degassed,which is added pulse-less to the column effluent using a 375μL polymeric mixing coil.Flow rate :0.5mL/min.Detection :pulsed amperometric detector with a gold workingelectrode,a silver-silver chloride reference electrode and a stainless steel auxiliary electrode which is the cell body,held atrespectively 0.00V detection,+0.80V oxidation and −0.60Vreduction potentials,with pulse durations according to theinstrument used.Injection :10μL.Run time :1.5times the retention time of neomycin B.Relative retention with reference to neomycin B (retention time =about 10min):impurity A =about 0.65;impurity C =about 0.9;impurity G =about 1.1.System suitability :–resolution :minimum 2.0between the peaks due to impurity C and to neomycin B in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (e);if necessary,adjust the volume of the carbonate-free sodium hydroxide solutionin the mobile phase,–signal-to-noise ratio :minimum 10for the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c).General Notices (1)apply to all monographs and other texts2305Fructose EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA8.0Limits :–impurity A :not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (d)and taking into account the declared content of neamine CRS (1.0per cent),–impurity C :not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b)(3.0per cent),–total of other impurities :not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b)(3.0per cent),–disregard limit :area of the principal peak in thechromatogram obtained with reference solution (c)(1.0per cent).Sulfate :27.0per cent to 31.0per cent (dried substance).Dissolve 0.250g in 100mL of water R and adjust the solution to pH 11using concentrated ammonia R .Add 10.0mLof 0.1M barium chloride and about 0.5mg of phthaleinpurple R .Titrate with 0.1M sodium edetate adding 50mL ofalcohol R when the colour of the solution begins to change andcontinuing the titration until the violet-blue colour disappears.1mL of 0.1M barium chloride is equivalent to 9.606mg of SO 4.Loss on drying (2.2.32):maximum 8.0per cent,determined on 1.000g by drying at 60°C over diphosphorus pentoxide R ata pressure not exceeding 0.7kPa for 3h.Sulfated ash (2.4.14):maximum 1.0per cent,determined on 1.0g.Sterility (2.6.1).If intended for introduction into bodycavities without a further appropriate sterilisation procedure,it complies with the test for sterility.Bacterial endotoxins (2.6.14,Method D ):less than 1.3IU/mgif intended for introduction into body cavities without afurther appropriate procedure for the removal of bacterial endotoxins.ASSAYCarry out the microbiological assay of antibiotics (2.7.2).Use framycetin sulfate CRS as the reference substance.STORAGEIn an airtight container,protected from light.If the substance is intended for introduction into body cavities,store in a sterile,tamper-proof container.IMPURITIESA.R1=H,R2=NH 2:2-deoxy-4-O -(2,6-diamino-2,6-dideoxy-α-D -glucopyranosyl)-D -streptamine (neamine or neomycin A-LP),B.R1=CO-CH 3,R2=NH 2:3-N -acetyl-2-deoxy-4-O -(2,6-diamino-2,6-dideoxy-α-D -glucopyranosyl)-D -streptamine (3-acetylneamine),D.R1=H,R2=OH:4-O -(2-amino-2-deoxy-α-D -glucopyranosyl)-2-deoxy-D -streptamine (paromamine or neomycinD), C.R1=CH 2-NH 2,R2=R3=H,R4=NH 2:2-deoxy-4-O -(2,6-diamino-2,6-dideoxy-α-D -glucopyranosyl)-5-O -[3-O -(2,6-diamino-2,6-dideoxy-α-D -glucopyranosyl)-β-D -ribofuranosyl]-D -streptamine (neomycin C),E.R1=R3=H,R2=CH 2-NH 2,R4=OH:4-O -(2-amino-2-deoxy-α-D -glucopyranosyl)-2-deoxy-5-O -[3-O -(2,6-diamino-2,6-dideoxy-β-L -idopyranosyl)-β-D -ribofuranosyl]-D -streptamine (paromomycin I orneomycin E),F.R1=CH 2-NH 2,R2=R3=H,R4=OH:4-O -(2-amino-2-deoxy-α-D -glucopyranosyl)-2-deoxy-5-O -[3-O -(2,6-diamino-2,6-dideoxy-α-D -glucopyranosyl)-β-D -ribofuranosyl]-D -streptamine (paromomycin II or neomycin F),G.R1=H,R2=CH 2-NH 2,R3=CO-CH 3,R4=NH 2:3-N -acetyl-2-deoxy-4-O -(2,6-diamino-2,6-dideoxy-α-D -glucopyranosyl)-5-O -[3-O -(2,6-diamino-2,6-dideoxy-β-L -idopyranosyl)-β-D -ribofuranosyl]-D -streptamine(neomycin B-LP).01/2008:0188corrected 6.0FRUCTOSEFructosum C 6H 12O 6M r 180.2[57-48-7]DEFINITIOND -arabino -Hex-2-ulopyranose.The substance described in this monograph is not necessarily suitable for parenteral administration.CHARACTERSAppearance :white or almost white,crystalline powder.It has a very sweet taste.Solubility :very soluble in water,soluble in ethanol (96per cent).IDENTIFICATIONA.Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).Solvent mixture :water R ,methanol R (2:3V/V ).Test solution .Dissolve 10mg of the substance to beexamined in the solvent mixture and dilute to 20mL with the solvent mixture.Reference solution (a).Dissolve 10mg of fructose CRS in the solvent mixture and dilute to 20mL with the solvent mixture.Reference solution (b).Dissolve 10mg each of fructose CRS ,glucose CRS ,lactose CRS and sucrose CRS in the solvent mixture and dilute to 20mL with the solvent mixture.Plate :TLC silica gel G plate R .2306See the information section on general monographs (cover pages)。

WATER,PURIFIED纯化水H2O M r18.12 DEFINITIONWater for the preparation of medicines other than those that are required to be both sterile and apyrogenic,unless otherwise justified and authorized.定义制药用水不同于其它用水,要求它是无菌的、无热源的,除非另有调整或授权。
Purified water in bulk散装纯化水PRODUCTIONPurified water in bulk is prepared by distillation,by ion exchange,by reverse osmosis or by any other suitable method from water that complies with the regulations on water intended for human consumption laid down by the competent authority.Purified water in bulk is stored and distributed in conditions designed to prevent growth of micro-organisms and to avoid any other contamination.生产:散装纯化水是经合格的当局规定的适宜人类使用的水经蒸馏、离子交换、反渗透膜或其他任何适合的方法制备。
散装纯化水存储和分配于可防止微生物生长和可避免其他任何污染的条件下。
Microbiological monitoring During production and subsequent storage, appropriate measures are taken to ensure that the microbial count is adequately controlled and monitored.Appropriate alert and action levels are set so as to detect adverse trends.Under normal conditions,an appropriate action level is a microbial count of100CFU/mL,determined by filtration through a membrane with a nominal pore size not greater than0.45μm,using R2A agar and incubating at30-35°C for not less than5days.The size of the sample is to be chosen in relation to the expected result.微生物监测在生产和其后的存储过程中,采取适当的方式以确保水的微生物数受到足够的控制和监测。

4.1.3.Buffer solutions EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA8.0Sulfite standard solution (1.5ppm SO 2).5002900.Dissolve sodium metabisulfite R equivalent to 0.152g of Na 2S 2O 5in water R and dilute to 100.0mL with the same solvent.Dilute 5.0mL of this solution to 100.0mL with water R .To 3.0mL of the resulting solution,add 4.0mL of 0.1M sodium hydroxide and dilute to 100.0mL with water R .Thallium standard solution (10ppm Tl).5003000.Dissolve thallous sulfate R equivalent to 0.1235g of Tl 2SO 4in a 9g/L solution of sodium chloride R and dilute to 1000.0mL with the same solution.Dilute 10.0mL of the solution to 100.0mL with the 9g/L solution of sodium chloride R .Tin liposoluble standard solution (1000ppm Sn).5005000.A tin (metal)organic compound in an oil.Tin standard solution (5ppm Sn).5003100.Dissolve tin R equivalent to 0.500g of Sn in a mixture of 5mL of water R and 25mL of hydrochloric acid R and dilute to1000.0mL with water R .Dilute the solution to 100times itsvolume with a 2.5per cent V/V solution of hydrochloric acid R immediately before use.Tin standard solution (0.1ppm Sn).5003101.Immediately before use,dilute tin standard solution (5ppmSn)R to 50times its volume with water R .Titanium standard solution (100ppm Ti).5003200.Dissolve 100.0mg of titanium R in 100mL of hydrochloricacid R diluted to 150mL with water R ,heating if necessary.Allow to cool and dilute to 1000mL with water R .Vanadium standard solution (1g/L V).5003300.Dissolve in water R ammonium vanadate R equivalent to0.230g of NH 4VO 3and dilute to 100.0mL with the samesolvent.Zinc standard solution (5mg/mL Zn).5003400.Dissolve 3.15g of zinc oxide R in 15mL of hydrochloric acid Rand dilute to 500.0mL with water R .Zinc standard solution (100ppm Zn).5003401.Immediately before use,dilute with water R to 10times its volume a solution containing zinc sulfate R equivalent to0.440g of ZnSO 4,7H 2O and 1mL of acetic acid R in 100.0mL.Zinc standard solution (10ppm Zn).5003402.Immediately before use,dilute zinc standard solution (100ppm Zn)R to 10times its volume with water R .Zinc standard solution (5ppm Zn).5003403.Immediately before use,dilute zinc standard solution (100ppm Zn)R to 20times its volume with water R .Zirconium standard solution (1g/L Zr).5003500.Dissolve zirconyl nitrate R equivalent to 0.293g ofZrO(NO 3)2,2H 2O in a mixture of 2volumes of hydrochloric acid R and 8volumes of water R and dilute to 100.0mL with the same mixture of solvents.01/2014:401034.1.3.BUFFER SOLUTIONSBuffered acetone solution.4000100.Dissolve 8.15g of sodium acetate R and 42g of sodium chloride R in water R ,add 68mL of 0.1M hydrochloric acid and 150mL of acetone R and dilute to 500mL with water R .Buffer solution pH 2.0.4000200.Dissolve 6.57g of potassium chloride R in water R and add 119.0mL of 0.1M hydrochloric acid .Dilute to 1000.0mL with water R .Phosphate buffer solution pH 2.0.4007900.Dissolve 8.95g of disodium hydrogen phosphate R and 3.40g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R in water R and dilute to 1000.0mL with the same solvent.If necessary adjust the pH with phosphoric acid R .Sulfate buffer solution pH 2.0.4008900.Dissolve 132.1g of ammonium sulfate R in water R and dilute to 500.0mL with the same solvent (Solution A).Carefully and with constant cooling stir 14mL of sulfuric acid R into about 400mL of water R ;allow to cool and dilute to 500.0mL with water R (Solution B).Mix equal volumes of solutions A and B.Adjust the pH if necessary.Buffer solution pH 2.2.4010500.Mix 6.7mL of phosphoric acid R with 55.0mL of a 40g/Lsolution of sodium hydroxide R and dilute to 1000.0mL with water R .Buffer solution pH 2.5.4000300.Dissolve 100g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R in 800mL of water R ;adjust to pH 2.5with hydrochloric acid R anddilute to 1000.0mL with water R .Buffer solution pH 2.5R1.4000400.To 4.9g of dilute phosphoric acid R add 250mL of water R .Adjust the pH with dilute sodium hydroxide solution R anddilute to 500.0mL with water R .0.2M Phosphate buffer solution pH 2.5.4014100.Dissolve 27.2g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R in about900mL of water R ,adjust to pH 2.5with phosphoric acid Rand dilute to 1.0L with water R .Phosphate buffer solution pH 2.8.4010600.Dissolve 7.8g of sodium dihydrogen phosphate R in 900mL ofwater R ,adjust to pH 2.8with phosphoric acid R and dilute to1000mL with the same solvent.Buffer solution pH 3.0.4008000.Dissolve 21.0g of citric acid R in 200mL of 1M sodiumhydroxide and dilute to 1000mL with water R .Dilute 40.3mL of this solution to 100.0mL with 0.1M hydrochloric acid .0.25M Citrate buffer solution pH 3.0.4012600.Dissolve 5.3g of citric acid R in 80mL of water R .Adjust thepH with 1M sodium hydroxide and dilute to 100.0mL with water R .0.1M Phosphate buffer solution pH 3.0.4011500.Dissolve 12.0g of anhydrous sodium dihydrogen phosphate R in water R ,adjust the pH with dilute phosphoric acid R1and dilute to 1000mL with water R .Phosphate buffer solution pH 3.0.4000500.Mix 0.7mL of phosphoric acid R with 100mL of water R .Dilute to 900mL with the same solvent.Adjust to pH 3.0with strong sodium hydroxide solution R and dilute to 1000mL with water R .Phosphate buffer solution pH 3.0R1.4010000.Dissolve 3.40g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R in900mL of water R .Adjust to pH 3.0with phosphoric acid R and dilute to 1000.0mL with water R .Phosphate buffer solution pH 3.2.4008100.To 900mL of a 4g/L solution of sodium dihydrogenphosphate R ,add 100mL of a 2.5g/L solution of phosphoric acid R .Adjust the pH if necessary.Phosphate buffer solution pH 3.2R1.4008500.Adjust a 35.8g/L solution of disodium hydrogen phosphate R to pH 3.2with dilute phosphoric acid R .Dilute 100.0mL of the solution to 2000.0mL with water R .EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA 8.0 4.1.3.BuffersolutionsBuffer solution pH 3.5.4000600.Dissolve 25.0g of ammonium acetate R in 25mL of water R and add 38.0mL of hydrochloric acid R1.Adjust the pH if necessary with dilute hydrochloric acid R or dilute ammonia R1.Dilute to 100.0mL with water R .Phosphate buffer solution pH 3.5.4000700.Dissolve 68.0g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R in water R and dilute to 1000.0mL with the same solvent.Adjustthe pH with phosphoric acid R .Buffer solution pH 3.6.4000800.To 250.0mL of 0.2M potassium hydrogen phthalate R add11.94mL of 0.2M hydrochloric acid .Dilute to 1000.0mLwith water R .Buffer solution pH 3.7.4000900.To 15.0mL of acetic acid R add 60mL of ethanol (96percent)R and 20mL of water R .Adjust to pH 3.7by the addition of ammonia R .Dilute to 100.0mL with water R .Buffered copper sulfate solution pH 4.0.4001000.Dissolve 0.25g of copper sulfate R and 4.5g of ammonium acetate R in dilute acetic acid R and dilute to 100.0mL with the same solvent.0.1M Sodium acetate buffer solution pH 4.0.4013800.Dissolve 822mg of sodium acetate R in 100mL of water R (solution A).Dilute 1.44mL of glacial acetic acid R in 250mL of water R (solution B).Titrate 100mL of solution B using about 20mL of solution A.Acetate buffer solution pH 4.4.4001100.Dissolve 136g of sodium acetate R and 77g of ammonium acetate R in water R and dilute to 1000.0mL with the same solvent;add 250.0mL of glacial acetic acid R and mix.Phthalate buffer solution pH 4.4.4001200.Dissolve 2.042g of potassium hydrogen phthalate R in 50mL of water R ,add 7.5mL of 0.2M sodium hydroxide and dilute to 200.0mL with water R .Acetate buffer solution pH 4.5.4012500.Dissolve 77.1g of ammonium acetate R in water R .Add 70mL of glacial acetic acid R and dilute to 1000.0mL with water R .0.5M Ammonium acetate buffer solution pH 4.5.4014200.Mix 14.3mL of glacial acetic acid R and 470mL of water Rand adjust to pH 4.5with concentrated ammonia R .Dilute to 500.0mL with water R .0.05M Phosphate buffer solution pH 4.5.4009000.Dissolve 6.80g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R in1000.0mL of water R .The pH of the solution is 4.5.Sodium acetate buffer solution pH 4.5.4010100.Dissolve 63g of anhydrous sodium acetate R in water R ,add 90mL acetic acid R and adjust to pH 4.5,and dilute to1000mL with water R .Acetate buffer solution pH 4.6.4001400.Dissolve 5.4g of sodium acetate R in 50mL of water R ,add2.4g of glacial acetic acid R and dilute to 100.0mL withwater R .Adjust the pH if necessary.Succinate buffer solution pH 4.6.4001500.Disssolve 11.8g of succinic acid R in a mixture of 600mL ofwater R and 82mL of 1M sodium hydroxide and dilute to1000.0mL with water R .Acetate buffer solution pH 4.7.4001600.Dissolve 136.1g of sodium acetate R in 500mL of water R .Mix 250mL of this solution with 250mL of dilute acetic acid R .Shake twice with a freshly prepared,filtered,0.1g/L solution of dithizone R in chloroform R .Shake with carbon tetrachloride R until the extract is colourless.Filter the aqueous layer to remove traces of carbon tetrachloride.Acetate buffer solution pH 4.7R1.4013600.Dissolve 136.1g of sodium acetate R in 500mL of water R .Mix 250mL of this solution with 250mL of dilute acetic acid R .Acetate buffer solution pH 5.0.4009100.To 120mL of a 6g/L solution of glacial acetic acid R add 100mL of 0.1M potassium hydroxide and about 250mL ofwater R .Mix.Adjust the pH to 5.0with a 6g/L solution ofacetic acid R or with 0.1M potassium hydroxide and dilute to 1000.0mL with water R .Citrate buffer solution pH 5.0.4010700.Prepare a solution containing 20.1g/L of citric acid R and 8.0g/L of sodium hydroxide R .Adjust the pH with dilute hydrochloric acid R .0.2M Deuterated sodium phosphate buffer solution pH 5.0.4013900.Dissolve 2.76g of sodium dihydrogen phosphate monohydrate R in 90mL of deuterium oxide R ,adjust the pH with a deuterated solution of phosphoric acid R or a deuterated 1M solution of sodium hydroxide R ,dilute to 100mL with deuterium oxide R and mix.Phosphate buffer solution pH 5.0.4011300.Dissolve 2.72g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R in 800mL of water R .Adjust the pH with 1M potassium hydroxide and dilute to 1000mL with water R .Buffer solution pH 5.2.4001700.Dissolve 1.02g of potassium hydrogen phthalate R in 30.0mL of 0.1M sodium hydroxide .Dilute to 100.0mL with water R .0.067M Phosphate buffer solution pH 5.4.4012000.Mix appropriate volumes of a 23.99g/L solution of disodium hydrogen phosphate R with a 9.12g/L solution of sodium dihydrogen phosphate monohydrate R to obtain pH 5.4.Acetate-edetate buffer solution pH 5.5.4001900.Dissolve 250g of ammonium acetate R and 15g sodiumedetate R in 400mL of water R and add 125mL of glacial acetic acid R .Buffer solution pH 5.5.4001800.Dissolve 54.4g of sodium acetate R in 50mL of water R ,heating to 35°C if necessary.After cooling,slowly add 10mL of anhydrous acetic acid R .Shake and dilute to 100.0mL withwater R .Phosphate buffer solution pH 5.5.4002000.Dissolve 13.61g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R inwater R and dilute to 1000.0mL with the same solvent(solution A).Dissolve 35.81g of disodium hydrogen phosphate R in water R and dilute to 1000.0mL with the same solvent (solution B).Mix 96.4mL of solution A and 3.6mL of solution B.Phosphate-citrate buffer solution pH 5.5.4008700.Mix 56.85mL of a 28.4g/L solution of anhydrous disodium hydrogen phosphate R and 43.15mL of a 21g/L solution of citric acid R .Phosphate buffer solution pH 5.6.4011200.Dissolve 0.908g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R in water R and dilute to 100.0mL with the same solvent (solution A).Dissolve 1.161g of dipotassium hydrogenphosphate R in water R and dilute to 100.0mL with the same solvent (solution B).Mix 94.4mL of solution A and 5.6mL of solution B.If necessary,adjust to pH 5.6using solution A or solution B.4.1.3.Buffer solutions EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA8.0Phosphate buffer solution pH5.8.4002100.Dissolve1.19g of disodium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate R and8.25g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R in water R and dilute to1000.0mL with the same solvent.Acetate buffer solution pH6.0.4002200.Dissolve100g of ammonium acetate R in300mL of water R, add4.1mL of glacial acetic acid R,adjust the pH if necessary using ammonia R or acetic acid R and dilute to500.0mL with water R.Diethylammonium phosphate buffer solution pH6.0. 4002300.Dilute68mL of phosphoric acid R to500mL with water R. To25mL of this solution add450mL of water R and6mLof diethylamine R,adjust to pH6±0.05,if necessary,using diethylamine R or phosphoric acid R and dilute to500.0mL with water R.Phosphate buffer solution pH6.0.4002400.Mix63.2mL of a71.5g/L solution of disodium hydrogen phosphate R and36.8mL of a21g/L solution of citric acid R. Phosphate buffer solution pH6.0R1.4002500.Dissolve6.8g of sodium dihydrogen phosphate R in water R and dilute to1000.0mL with water R.Adjust the pH with strong sodium hydroxide solution R.Phosphate buffer solution pH6.0R2.4002600.To250.0mL of0.2M potassium dihydrogen phosphate R add 28.5mL of0.2M sodium hydroxide and dilute to1000.0mL with water R.Phosphate buffer solution pH6.4.4002800.Dissolve2.5g of disodium hydrogen phosphate R,2.5g of sodium dihydrogen phosphate R and8.2g of sodium chloride R in950mL of water R.Adjust the pH of the solution to6.4with 1M sodium hydroxide or1M hydrochloric acid,if necessary. Dilute to1000.0mL with water R.0.5M Phthalate buffer solution pH6.4.4009200. Dissolve100g of potassium hydrogen phthalate R in water R and dilute to1000.0mL with the same solvent.Adjust the pH if necessary,using strong sodium hydroxide solution R. Buffer solution pH6.5.4002900.Dissolve60.5g of disodium hydrogen phosphate R and46g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R in water R.Add100mL of 0.02M sodium edetate and20mg of mercuric chloride R and dilute to1000.0mL with water R.Imidazole buffer solution pH6.5.4003000.Dissolve6.81g of imidazole R,1.23g of magnesium sulfate R and0.73g of calcium sulfate R in752mL of0.1M hydrochloric acid.Adjust the pH if necessary and dilute to1000.0mL with water R.0.1M phosphate buffer solution pH6.5.4010800. Dissolve13.80g of sodium dihydrogen phosphate monohydrate R in900mL of distilled water R.Adjust the pH using a400g/L solution of sodium hydroxide R.Dilute to 1000mL with distilled water R.Phosphate buffer solution pH6.5.4012800.Dissolve2.75g of sodium dihydrogen phosphate R and4.5g of sodium chloride R in500mL of water R.Adjust the pH with phosphate buffer solution pH8.5R.Buffer solution pH6.6.4003100.To250.0mL of0.2M potassium dihydrogen phosphate R add 89.0mL of0.2M sodium hydroxide.Dilute to1000.0mL with water R.0.1M Phosphate buffer solution pH6.7.4014300. Dissolve15.6g of sodium dihydrogen phosphate R in water R and dilute to1.0L with the same solvent.Dissolve17.8g of disodium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate R in water R and dilute to1.0L with the same solvent.Mix the solutions,check the pH and if necessary adjust to pH6.7.Phosphate buffered saline pH6.8.4003200.Dissolve1.0g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R,2.0gof dipotassium hydrogen phosphate R and8.5g of sodium chloride R in900mL of water R,adjust the pH if necessary and dilute to1000.0mL with the same solvent. Phosphate buffer solution pH6.8.4003300.Mix77.3mL of a71.5g/L solution of disodium hydrogen phosphate R with22.7mL of a21g/L solution of citric acid R. Phosphate buffer solution pH6.8R1.4003400.To51.0mL of a27.2g/L solution of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R add49.0mL of a71.6g/L solution of disodium hydrogen phosphate R.Adjust the pH if necessary. Storage:at2°C to8°C.1M tris-hydrochloride buffer solution pH6.8.4009300. Dissolve60.6g of tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane R in 400mL of water R.Adjust the pH with hydrochloric acid R and dilute to500.0mL with water R.Buffer solution pH7.0.4003500.To1000mL of a solution containing18g/L of disodium hydrogen phosphate R and23g/L of sodium chloride R add sufficient(about280mL)of a solution containing7.8g/Lof sodium dihydrogen phosphate R and23g/L of sodium chloride R to adjust the pH.Dissolve in the solution sufficient sodium azide R to give a0.2g/L solution.Maleate buffer solution pH7.0.4003600.Dissolve10.0g of sodium chloride R,6.06g oftris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane R and4.90g of maleic anhydride R in900mL of water R.Adjust the pH using a 170g/L solution of sodium hydroxide R.Dilute to1000.0mL with water R.Storage:at2°C to8°C;use within3days.0.025M Phosphate buffer solution pH7.0.4009400.Mix1volume of0.063M phosphate buffer solution pH7.0R with1.5volumes of water R.0.03M Phosphate buffer solution pH7.0.4010300. Dissolve5.2g of dipotassium hydrogen phosphate R in900mL of water for chromatography R.Adjust the solution to pH7.0±0.1using phosphoric acid R and dilute to1000mL with water for chromatography R.0.05M Phosphate buffer solution pH7.0.4012400.Mix34mL of water R and100mL of0.067M phosphate buffer solution pH7.0R.0.063M Phosphate buffer solution pH7.0.4009500. Dissolve5.18g of anhydrous disodium hydrogen phosphate R and3.65g of sodium dihydrogen phosphate monohydrate R in 950mL of water R and adjust the pH with phosphoric acid R; dilute to1000.0mL with water R.0.067M Phosphate buffer solution pH7.0.4003800. Dissolve0.908g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate Rin water R and dilute to100.0mL with the same solvent (solution A).Dissolve2.38g of disodium hydrogen phosphate R in water R and dilute to100.0mL with the same solvent (solution B).Mix38.9mL of solution A and61.1mL of solution B.Adjust the pH if necessary.EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA 8.0 4.1.3.Buffersolutions0.1M Phosphate buffer solution pH 7.0.4008200.Dissolve 1.361g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R in water R and dilute to 100.0mL with the same solvent.Adjust the pH using a 35g/L solution of disodium hydrogen phosphate R .Phosphate buffer solution pH 7.0.4003700.Mix 82.4mL of a 71.5g/L solution of disodium hydrogen phosphate R with 17.6mL of a 21g/L solution of citric acid R .Phosphate buffer solution pH 7.0R1.4003900.Mix 250.0mL of 0.2M potassium dihydrogen phosphate R and 148.2mL of a 8g/L solution of sodium hydroxide R ,adjust the pH if necessary.Dilute to 1000.0mL with water R .Phosphate buffer solution pH 7.0R2.4004000.Mix 50.0mL of a 136g/L solution of potassium dihydrogenphosphate R with 29.5mL of 1M sodium hydroxide and dilute to 100.0mL with water R .Adjust the pH to 7.0±0.1.Phosphate buffer solution pH 7.0R3.4008600.Dissolve 5g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R and 11gof dipotassium hydrogen phosphate R in 900mL of water R .Adjust to pH 7.0with dilute phosphoric acid R or dilute sodium hydroxide solution R .Dilute to 1000mL with water R and mix.Phosphate buffer solution pH 7.0R4.4010200.Dissolve 28.4g of anhydrous disodium hydrogen phosphate R and 18.2g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R in water R and dilute to 500mL with the same solvent.Phosphate buffer solution pH 7.0R5.4011400.Dissolve 28.4g of anhydrous disodium hydrogen phosphate R in 800mL of water R .Adjust the pH using a 30per cent m/m solution of phosphoric acid R and dilute to 1000mL with water R .Tetrabutylammonium buffer solution pH 7.0.4010900.Dissolve 6.16g of ammonium acetate R in a mixture of 15mL of tetrabutylammonium hydroxide solution (400g/L)R and 185mL of water R .Adjust the pH with nitric acid R .Buffered salt solution pH 7.2.4004300.Dissolve in water R 8.0g of sodium chloride R ,0.2g of potassium chloride R ,0.1g of anhydrous calcium chloride R ,0.1g of magnesium chloride R ,3.18g of disodium hydrogen phosphate R and 0.2g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R and dilute to 1000.0mL with water R .Buffer solution pH 7.2.4004100.To 250.0mL of 0.2M potassium dihydrogen phosphate R add 175.0mL of 0.2M sodium hydroxide .Dilute to 1000.0mL with water R .Adjust the pH if necessary.Phosphate-albumin buffered saline pH 7.2.4004400.Dissolve 10.75g of disodium hydrogen phosphate R ,7.6g of sodium chloride R and 10g of bovine albumin R in water R and dilute to 1000.0mL with the same solvent.Immediately before use adjust the pH using dilute sodium hydroxide solution R or dilute phosphoric acid R .Phosphate-albumin buffered saline pH 7.2R1.4009600.Dissolve 10.75g of disodium hydrogen phosphate R ,7.6g of sodium chloride R and 1g of bovine albumin R in water R and dilute to 1000.0mL with the same solvent.Immediately before use adjust the pH using dilute sodium hydroxide solution Ror dilute phosphoric acid R .Phosphate buffer solution pH 7.2.4004200.Mix 87.0mL of a 71.5g/L solution of disodium hydrogenphosphate R with 13.0mL of a 21g/L solution of citric acid R .Imidazole buffer solution pH 7.3.4004500.Dissolve 3.4g of imidazole R and 5.8g of sodium chloride R in water R ,add 18.6mL of 1M hydrochloric acid and dilute to 1000.0mL with water R .Adjust the pH if necessary.Barbital buffer solution pH 7.4.4004700.Mix 50mL of a solution in water R containing 19.44g/L of sodium acetate R and 29.46g/L of barbital sodium R with 50.5mL of 0.1M hydrochloric acid ,add 20mL of an 85g/L of sodium chloride R and dilute to 250mL with water R .Buffer solution pH 7.4.4004600.Dissolve 0.6g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R ,6.4g of disodium hydrogen phosphate R and 5.85g of sodium chloride R in water R ,and dilute to 1000.0mL with the same solvent.Adjust the pH if necessary.Phosphate buffered saline pH 7.4.4005000.Dissolve 2.38g of disodium hydrogen phosphate R ,0.19g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R and 8.0g of sodiumchloride R in water.Dilute to 1000.0mL with the same solvent.Adjust the pH if necessary.Phosphate buffer solution pH 7.4.4004800.Add 250.0mL of 0.2M potassium dihydrogen phosphate R to 393.4mL of 0.1M sodium hydroxide .Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane buffer solution pH 7.4.4012100.Dissolve 30.3g of tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane R in approximately 200mL of water R .Add 183mL of 1M hydrochloric acid .Dilute to 500.0mL with water R .Note:the pH is 7.7-7.8at room temperature and 7.4at 37°C.This solution is stable for several months at 4°C.Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane sodium chloride buffer solution pH 7.4.4004900.Dissolve 6.08g of tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane R ,8.77g of sodium chloride R in 500mL of distilled water R .Add 10.0g of bovine albumin R .Adjust the pH using hydrochloric acid R .Dilute to 1000.0mL with distilled water R .Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane sodium chloride buffer solution pH 7.4R1.4012200.Dissolve 0.1g of bovine albumin R in a mixture containing 2mL of tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane buffer solution pH 7.4R and 50mL of a 5.84mg/mL solution of sodium chloride R .Dilute to 100.0mL with water R .Tris-sodium acetate buffer solution pH 7.4.4012900.Dissolve 6.3g of tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane R and 4.9g of anhydrous sodium acetate R in 900mL of water R .Adjust to pH 7.4with sulfuric acid R and dilute to 1000mL with water R .Tris-sodium acetate-sodium chloride buffer solution pH 7.4.4013000.Dissolve 30.0g of tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane R ,14.5gof anhydrous sodium acetate R and 14.6g of sodium chloride R in 900mL of water R .Add 0.50g of bovine albumin R .Adjust to pH 7.4with sulfuric acid R and dilute to 1000mL with water R .Borate buffer solution pH 7.5.4005200.Dissolve 2.5g of sodium chloride R ,2.85g of disodium tetraborate R and 10.5g of boric acid R in water R and dilute to 1000.0mL with the same solvent.Adjust the pH if necessary.Storage :at 2°C to 8°C.Buffer (HEPES)solution pH 7.5.4009700.Dissolve 2.38g of 2-[4-(2-hydroxyethyl)piperazin-1-yl]ethanesulfonic acid R in about 90mL of water R .Adjust thepH to 7.5with sodium hydroxide solution R .Dilute to 100mL with water R .4.1.3.Buffer solutions EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA8.00.05M Phosphate buffer solution pH7.5.4014400. Dissolve0.89g of disodium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate R in about80mL of water R.Adjust to pH7.5with an8.5per cent V/V solution of phosphoric acid R and dilute to100.0mL with water R.0.2M Phosphate buffer solution pH7.5.4005400. Dissolve27.22g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R in930mL of water R,adjust to pH7.5with a300g/L solution of potassium hydroxide R and dilute to1000.0mL with water R.0.33M Phosphate buffer solution pH7.5.4005300. Dissolve119.31g of disodium hydrogen phosphate R in water R and dilute to1000.0mL with the same solvent(solution A). Dissolve45.36g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R in water R and dilute to1000.0mL with the same solvent (solution B).Mix85mL of solution A and15mL of solution B. Adjust the pH if necessary.0.05M Tris-hydrochloride buffer solution pH7.5.4005600. Dissolve6.057g of tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane R in water R and adjust the pH with hydrochloric acid R.Dilute to 1000.0mL with water R.1M Tris-hydrochloride buffer solution pH7.5.4014500. Dissolve12.11g of tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane R in 90mL of water R,adjust to pH7.5with hydrochloric acid R and dilute to100.0mL with water R.Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane buffer solution pH7.5. 4005500.Dissolve7.27g of tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane R and 5.27g of sodium chloride R in water R,and adjust the pH if necessary.Dilute to1000.0mL with water R.Sodium citrate buffer solution pH7.8(0.034M sodium citrate,0.101M sodium chloride).4009800.Dissolve10.0g of sodium citrate R and5.90g of sodium chloride R in900mL of water R.Adjust the pH by addition of hydrochloric acid R and dilute to1000mL with water R.0.0015M Borate buffer solution pH8.0.4006000. Dissolve0.572g of disodium tetraborate R and2.94g of calcium chloride R in800mL of water R.Adjust the pH with 1M hydrochloric acid.Dilute to1000.0mL with water R. Buffer solution pH8.0.4005900.To50.0mL of0.2M potassium dihydrogen phosphate R add 46.8mL of0.2M sodium hydroxide.Dilute to200.0mL with water R.Buffer solution pH8.0R1.4010400.Dissolve20g of dipotassium hydrogen phosphate R in900mL of water R.Adjust the pH with phosphoric acid R.Dilute to 1000mL with water R.0.02M Phosphate buffer solution pH8.0.4006100.To50.0mL of0.2M potassium dihydrogen phosphate R add 46.8mL of0.2M sodium hydroxide.Dilute to500.0mL with water R.0.02M Sodium phosphate buffer solution pH8.0.4013700. Dissolve0.31g of sodium dihydrogen phosphate R in70mL of water R and adjust to pH8.0with1M sodium hydroxide,then dilute to100mL with water R.0.1M Phosphate buffer solution pH8.0.4008400. Dissolve0.523g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R and 16.73g of dipotassium hydrogen phosphate R in water R and dilute to1000.0mL with the same solvent.1M Phosphate buffer solution pH8.0.4007800.Dissolve136.1g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R in water R,adjust the pH with1M sodium hydroxide.Dilute to 1000.0mL with water R.1M Tris-hydrochloride buffer solution pH8.0.4012700. Dissolve121.1g of tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane R and 1.47g of calcium chloride R in900mL of water R.Adjust the pH with hydrochloric acid R and dilute to1000.0mL with water R.Tris-hydrochloride buffer solution pH8.0.4012300. Dissolve1.21g of tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane R and 29.4mg of calcium chloride R in water R.Adjust the pH with 1M hydrochloric acid and dilute to100.0mL with water R. Tris-sodium acetate buffer solution pH8.0.4013100. Dissolve6.3g of tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane R and 4.9g of anhydrous sodium acetate R in900mL of water R. Adjust to pH8.0with sulfuric acid R and dilute to1000mL with water R.Tris-sodium acetate-sodium chloride buffer solutionpH8.0.4013200.Dissolve30.0g of tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane R,14.5g of anhydrous sodium acetate R and14.6g of sodium chloride R in900mL of water R.Add0.50g of bovine albumin R.Adjust to pH8.0with sulfuric acid R and dilute to1000mL with water R.Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane buffer solution pH8.1. 4006200.Dissolve0.294g of calcium chloride R in40mL oftris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane solution R and adjust the pH with1M hydrochloric acid.Dilute to100.0mL with water R.Tris-glycine buffer solution pH8.3.4006300.Dissolve6.0g of tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane R and 28.8g of glycine R in water R and dilute to1000.0mL with the same solvent.Dilute1volume to10volumes with water R immediately before use.Tris-hydrochloride buffer solution pH8.3.4011800. Dissolve9.0g of tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane R in2.9L of water R.Adjust the pH with1M hydrochloric acid.Adjust the volume to3L with water R.0.05M Tris-hydrochloride buffer solution pH9.0.4013500. Dissolve0.605g of tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane R in water R.Adjust the pH with1M hydrochloric acid and dilute to100.0mL with water R.Barbital buffer solution pH8.4.4006400.Dissolve8.25g of barbital sodium R in water R and dilute to 1000.0mL with the same solvent.Tris-EDTA BSA buffer solution pH8.4.4006500. Dissolve6.1g of tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane R,2.8g of sodium edetate R,10.2g of sodium chloride R and10gof bovine albumin R in water R,adjust to pH8.4using1M hydrochloric acid and dilute to1000.0mL with water R.Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane-EDTA buffer solution pH8.4.4006600.Dissolve5.12g of sodium chloride R,3.03g oftris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane R and1.40g of sodium edetate R in250mL of distilled water R.Adjust the pH to8.4 using hydrochloric acid R.Dilute to500.0mL with distilled water R.Guanidine-tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane-EDTA buffer solution pH8.5.4014600.Dissolve1.0g of sodium edetate R,12.1g oftris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane R and57.0g of guanidine hydrochloride R in35mL of water R.Adjust topH8.5with hydrochloric acid R and dilute to100mL with water R.。

2.2.32. LOSS ON DRYING 干燥失重Loss on drying is the loss of mass expressed as per cent m/m.干燥失重指重量损失,表述为% 重量/重量Method. Place the prescribed quantity of the substance to be examined in a weighing bottle previously dried under the conditions prescribed for the substance to be examined. Dry the substance to constant mass or for the prescribed time by one of the following procedures. Where the drying temperature is indicated by a single value rather than a range, drying is carried out at the prescribed temperature +/- 2?C.方法:将要求数量的待检样品放置于预先干燥的称量瓶中,按要求条件进行干燥,直至样品干至恒重或下述程序指定的时长。
如果干燥温度给定的是一个值而不是一个范围,则在指定温度+/- 2?C进行干燥。
a) “in a desiccator”: the drying is carried out over diphosphorus pentoxide R at atmospheric atmostpheric pressure and at room temperature;“在干燥器中”:指在室温常压下,用五氧化二磷试剂,进行干燥b) “in vacuo”: the drying is carried out over diphosphorus pentoxide R, at a pressure of 1.5 kPa at room temperature;“真空”:在室温下,真空1.5kPa下,用五氧化二磷试剂进行干燥c) “in vacuo within a specified temperature range”: the drying is carried out over diphosphorus pentoxide R, at a pressure of 1.5kPa to 2.5kPa within the temperature range prescribed in the monograph;“在指定温度范围内真空下”:真空1.5kPa至2.5kPa下,各论要求的温度范围内,用五氧化二磷进行干燥d) “in an oven within a specified temperature range”: the drying is carrie d out in an oven within the temperature range prescribed in the monograph;“在烘箱里指定温度下”:在各论要求的温度范围内,用烘箱进行干燥e) “under high vacuum”: the drying is carried out over diphosphorus pentoxide R at a pressure not exceeding 0.1kPa, at the temperature prescribed in the monograph.“在高真空下”:在各论要求的温度下,不超过0.1kPa的真空下用五氧化二磷进行干燥If other conditions are prescribed, the procedure to be used is described in full in the monograph.如果需要采用其它条件,则在各论中应进行详细描述。

欧洲药典8.0版附录2.9.40是一项具有重要意义的内容,它包含了关于卫生产品和医药制剂的质量要求和标准。
在这篇文章中,我们将深入探讨这一主题,从基础概念到具体内容,帮助你更好地理解欧洲药典8.0版附录2.9.40。
1. 了解欧洲药典8.0版附录2.9.40欧洲药典是欧洲药典委员会制定的标准规范,旨在保障卫生产品和医药制剂的质量、安全和有效性。
附录2.9.40则是其中的重要内容之一,它详细规定了一系列的质量要求,涵盖了原材料的选择、生产过程的控制、成品的质量检验等方方面面。
这些要求旨在确保药品的质量稳定、安全性高、有效性强。
2. 欧洲药典8.0版附录2.9.40的具体内容欧洲药典8.0版附录2.9.40的具体内容主要包括以下几个方面:- 原材料的要求:包括对原材料的来源、制备、存储和使用的规定,确保原材料的质量稳定和可追溯性。
- 生产过程的控制:包括药品的生产工艺、设备、人员培训等方面的要求,确保生产过程稳定可控、符合GMP要求。
- 药品的质量检验:包括对成品药品的各项质量指标和检测方法的规定,确保药品符合质量标准。
3. 个人观点和理解欧洲药典8.0版附录2.9.40的具体内容凸显了对药品质量和安全的高标准要求,这种规范的制定对保障患者用药安全、促进药品质量提升有着重要的意义。
而且,这种规范也对制药企业的生产经营提出了更高的要求,能够推动行业向着更加规范、科学的方向发展。
总结回顾通过本文的阐述,相信你对欧洲药典8.0版附录2.9.40有了更深入的了解。
这一规范的制定和实施,促进了药品质量的提升、促进了医药行业的良性发展,对患者和企业来说都具有重要意义。
希望你能在日常工作和学习中,更加关注和重视这一规范,促进药品质量和安全的保障。
4. 药品质量和安全的重要性药品质量和安全对于患者的健康和生命安全具有重要的意义。
优质的药品能够有效治疗疾病,保障患者的健康。
然而,如果药品质量不达标或者存在安全隐患,可能会导致患者用药失败或者出现严重的副作用,危及患者的生命安全。

欧洲药典EP8.0-2.6.1无菌检验-sterility中英文翻译2.6.1. STERILITY2.6.1 无菌检查法The test is applied to substances, preparations or articles which, accordingto the Pharmacopoeia, are required to be sterile. However, a satisfactory result only indicates that no contaminating micro-organism has been found in the sample examined in the conditions of the test.本检查方法适用于按照药典要求应当无菌的原料、制剂或其他物质。
但是,如果按照本无菌检查法的结果符合要求,仅表明在该检查条件下未发现微生物污染。
PRECAUTIONS AGAINST MICROBIAL CONTAMINATION微生物污染防范The test for sterility is carried out under aseptic conditions. In order to achieve such conditions, the test environment has to be adapted to the way in which the sterility test is performed. The precautions taken to avoid contamination are such that they do not affect any micro-organisms which are to be revealed in the test. The working conditions in which the tests are performed are monitored regularly by appropriate sampling of the working area and by carrying out appropriate controls.无菌检测试验应在无菌的条件下进行。
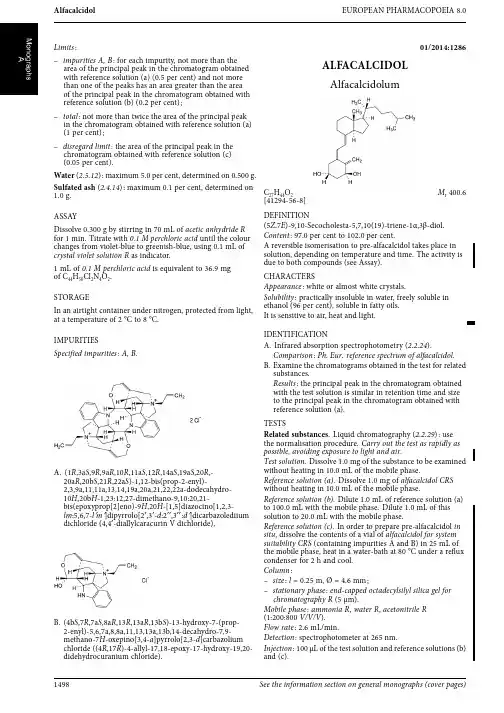
Alfacalcidol EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA8.0Limits :–impurities A,B :for each impurity,not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a)(0.5per cent)and not more than one of the peaks has an area greater than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b)(0.2per cent);–total :not more than twice the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a)(1per cent);–disregard limit :the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c)(0.05per cent).Water (2.5.12):maximum 5.0per cent,determined on 0.500g.Sulfated ash (2.4.14):maximum 0.1per cent,determined on 1.0g.ASSAYDissolve 0.300g by stirring in 70mL of acetic anhydride R for 1min.Titrate with 0.1M perchloric acid until the colour changes from violet-blue to greenish-blue,using 0.1mL of crystal violet solution R as indicator.1mL of 0.1M perchloric acid is equivalent to 36.9mg of C 44H 50Cl 2N 4O 2.STORAGEIn an airtight container under nitrogen,protected from light,at a temperature of 2°C to 8°C.IMPURITIESSpecified impurities:A,B.A.(1R ,3a S ,9R ,9a R ,10R ,11a S ,12R ,14a S ,19a S ,20R ,-20a R ,20b S ,21R ,22a S )-1,12-bis(prop-2-enyl)-2,3,9a,11,11a,13,14,19a,20a,21,22,22a-dodecahydro-10H ,20b H -1,23:12,27-dimethano-9,10:20,21-bis(epoxyprop[2]eno)-9H ,20H -[1,5]diazocino[1,2,3-lm :5,6,7-l ′m ′]dipyrrolo[2′,3′-d :2′′,3′′:d ′]dicarbazolediium dichloride (4,4′-diallylcaracurin Vdichloride),B.(4b S ,7R ,7a S ,8a R ,13R ,13a R ,13b S )-13-hydroxy-7-(prop-2-enyl)-5,6,7a,8,8a,11,13,13a,13b,14-decahydro-7,9-methano-7H -oxepino[3,4-a ]pyrrolo[2,3-d ]carbazolium chloride ((4R ,17R )-4-allyl-17,18-epoxy-17-hydroxy-19,20-didehydrocuranium chloride).01/2014:1286ALFACALCIDOLAlfacalcidolumC 27H 44O 2M r 400.6[41294-56-8]DEFINITION(5Z ,7E )-9,10-Secocholesta-5,7,10(19)-triene-1α,3β-diol.Content :97.0per cent to 102.0per cent.A reversible isomerisation to pre-alfacalcidol takes place in solution,depending on temperature and time.The activity is due to both compounds (see Assay).CHARACTERSAppearance :white or almost white crystals.Solubility :practically insoluble in water,freely soluble in ethanol (96per cent),soluble in fatty oils.It is sensitive to air,heat and light.IDENTIFICATIONA.Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).Comparison :Ph.Eur.reference spectrum of alfacalcidol .B.Examine the chromatograms obtained in the test for related substances.Results :the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in retention time and size to the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a).TESTSRelated substances .Liquid chromatography (2.2.29):use the normalisation procedure.Carry out the test as rapidly as possible,avoiding exposure to light and air.Test solution.Dissolve 1.0mg of the substance to be examined without heating in 10.0mL of the mobile phase.Reference solution (a).Dissolve 1.0mg of alfacalcidol CRS without heating in 10.0mL of the mobile phase.Reference solution (b).Dilute 1.0mL of reference solution (a)to 100.0mL with the mobile phase.Dilute 1.0mL of this solution to 20.0mL with the mobile phase.Reference solution (c).In order to prepare pre-alfacalcidol in situ ,dissolve the contents of a vial of alfacalcidol for system suitability CRS (containing impurities A and B)in 25mL of the mobile phase,heat in a water-bath at 80°C under a reflux condenser for 2h and cool.Column :–size :l =0.25m,Ø=4.6mm;–stationary phase :end-capped octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5μm).Mobile phase :ammonia R ,water R ,acetonitrile R (1:200:800V/V/V ).Flow rate :2.6mL/min.Detection :spectrophotometer at 265nm.Injection :100μL of the test solution and reference solutions (b)and (c).1498See the information section on general monographs (cover pages)EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA 8.0AlfadexRun time :twice the retention time of alfacalcidol.Identification of impurities :use the chromatogramsupplied with alfacalcidol for system suitability CRS and the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c)to identify the peaks due to impurities A and B.Relative retention with reference to alfacalcidol (retention time =about 21min):pre-alfacalcidol =about 0.88;impurity A =about 0.93;impurity B =about 1.1.System suitability :reference solution (c):–resolution :minimum 1.5between the peaks due to pre-alfacalcidol and impurity A and minimum 1.5between the peaks due to impurity A and alfacalcidol.Limits :–impurities A,B :for each impurity,maximum 0.5per cent;–unspecified impurities :for each impurity,maximum 0.10per cent;–total :maximum 1.0per cent;–disregard limit :the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b)(0.05per cent);disregard the peak due to pre-alfacalcidol.ASSAYLiquid chromatography (2.2.29)as described in the test for related substances with the following modifications.Injection :test solution and reference solutions (a)and (c).System suitability :reference solution (c):–repeatability :maximum relative standard deviation of 1per cent for the peak due to alfacalcidol after 6injections.Calculate the percentage content of C 27H 44O 2taking into account the assigned content of alfacalcidol CRS and,if necessary,the peak due to pre-alfacalcidol.STORAGEUnder nitrogen,in an airtight container,protected from light,at a temperature of 2°C to 8°C.The contents of an opened container are to be used immediately.IMPURITIESSpecified impurities:A,B .Other detectable impurities (the following substances would,if present at a sufficient level,be detected by one or other of the tests in the monograph.They are limited by the general acceptance criterion for other/unspecified impurities and/or by the general monograph Substances for pharmaceutical use (2034).It is therefore not necessary to identify these impurities for demonstration of compliance.See also 5.10.Control of impurities in substances for pharmaceutical use ):C.A.(5E ,7E )-9,10-secocholesta-5,7,10(19)-triene-1α,3β-diol (trans-alfacalcidol), B.(5Z ,7E )-9,10-secocholesta-5,7,10(19)-triene-1β,3β-diol(1β-calcidol),C.6ξ-[(3S ,5R )-3,5-dihydroxy-2-methylcyclohex-1-en-1-yl]-2-phenyl-2,5,10-triaza-4,19-dinor-9ξ-cholest-7-ene-1,3-dione.01/2012:1487ALFADEXAlfadexum[C 6H 10O 5]6M r 973[10016-20-3]DEFINITIONCyclohexakis-(1→4)-(α-D -glucopyranosyl)(cyclomaltohexaose or α-cyclodextrin).Content :97.0per cent to 102.0per cent (dried substance).CHARACTERSAppearance :white or almost white,amorphous or crystalline powder.Solubility :freely soluble in water and in propylene glycol,practically insoluble in anhydrous ethanol and in methylene chloride.IDENTIFICATIONA.Specific optical rotation (see Tests).B.Examine the chromatograms obtained in the assay.Results :the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with test solution (b)is similar in retention time and size to the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c).C.Dissolve 0.2g in 2mL of iodine solution R4by warming on a water-bath,and allow to stand at room temperature;a yellowish-brown precipitate is formed.General Notices (1)apply to all monographs and other texts1499。

1 GENERAL NOTICES凡例1.1 GENERAL STATEMENTS概述The General Notices apply to all monographs and other texts of the EuropeanPharmacopoeia.凡例的内容适用于各论和欧洲药典中的其它章节。
The official texts of the European Pharmacopoeia are published in English andFrench. Translations in other languages may be prepared by the signatoryStates of the European Pharmacopoeia Convention. In case of doubt or dispute,the English and French versions are alone authoritative.欧洲药典以英语和法语形式发行,欧洲药典委员会的签署国可将药典内容译成其它语言,但若发生争议,应以英语和法语版为权威。
In the texts of the European Pharmacopoeia, the word ‘Pharmacopoeia’ without qualification means the European Pharmacopoeia. The official abbreviation Ph.Eur. may be used to indicate the European Pharmacopoeia.在欧洲药典中,如无特殊规定,“药典”是指欧洲药典,官方缩写 Ph. Eur.也指欧洲药典。
The use of the title or the subtitle of a monograph implies that the articlecomplies with the requirements of the relevant monograph. Such references tomonographs in the texts of the Pharmacopoeia are shown using themonograph title and reference number in italics.文章中如果引用了各论中的标题和副标题意味着文章内容符合相关各论的要求。

欧洲药典-凡例1.1. GENERAL STATEMENTSThe General Notices apply to all monographs and other texts of the European Pharmacopoeia.总论的内容适用于各论和欧洲药典中的其它章节。
The official texts of the European Pharmacopoeia are published in English and French. Translations in other languages may be prepared by the signatory States of the European Pharmacopoeia Convention. In case of doubt or dispute, the English and French versions are alone authoritative.欧洲药典以英语和法语形式发行,欧洲药典委员会的签署国可将药典内容译成其它语言,但若发生争议,应以英语和法语版为权威。
In the texts of the European Pharmacopoeia, the word "Pharmacopoeia" without qualification means the European Pharmacopoeia. The official abbreviation Ph. Eur. may be used to indicate the European Pharmacopoeia.在欧洲药典中,如无特殊规定,“药典”是指欧洲药典,缩写Ph. Eur.也指欧洲药典。
The use of the title or the subtitle of a monograph implies that the article complies with the requirements of the relevant monograph. Such references to monographs in the texts of the Pharmacopoeia are shown using the monograph title and reference number in italics.文章中如果引用了各论中的标题和副标题意味着文章内容符合相关各论的要求。
![恩诺沙星欧洲药典 8[1].0 (英文版)-2](https://uimg.taocdn.com/332668390066f5335b812111.webp)
EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA 8.0Enrofloxacin for veterinaryuseApplication :5μL.Development :over 2/3of the plate.Drying :in air for 5min.Detection :spray with anisaldehyde solution R and heat at 100-105°C for 10min.Results :the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in position,colour and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution.C.Dissolve 50mg in 10mL of methylene chloride R .To 2mL of this solution,add 1mL of acetic anhydride R and 0.3mL of sulfuric acid R .A pink colour is produced.TESTSAppearance of solution .The solution is clear (2.2.1)and not more intensely coloured than reference solution Y 6(2.2.2,Method II ).Dissolve 0.1g in ethanol R and dilute to 10mL with the same solvent.Specific optical rotation (2.2.7):+145to +154(dried substance).Dissolve 0.50g in dioxan R and dilute to 50.0mL with the same solvent.Related substances .Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).Test solution.Dissolve 0.10g of the substance to be examined in the mobile phaseand dilute to 100.0mL with the mobile phase.Reference solution (a).Dilute 2.0mL of the test solution to 100.0mL with the mobile phase.Reference solution (b).Dilute 5.0mL of reference solution (a)to 100.0mL with the mobile phase.Reference solution (c).Dissolve 0.1g of 18α-glycyrrhetinic acid R in tetrahydrofuran R and dilute to 100.0mL with the same solvent.To 2.0mL of the solution,add 2.0mL of the test solution and dilute to 100.0mL with the mobile phase.Column :–size :l =0.25m,Ø=4.6mm,–stationary phase :octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5μm),–temperature :30°C.Mobile phase :mix 430volumes of tetrahydrofuran R and570volumes of a 1.36g/L solution of sodium acetate R adjusted to pH 4.8with glacial acetic acid R .Flow rate :0.8mL/min.Detection :spectrophotometer at 250nm.Injection :20μL loop injector;inject the test solution and the reference solutions.Run time :4times the retention time of enoxolone.System suitability :–resolution :minimum of 2.0between the peaks due to enoxolone and to 18α-glycyrrhetinic acid in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c).Limits :–any impurity :not more than 7times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b)(0.7per cent),–total :not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a)(2.0per cent),–disregard limit :0.5times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b)(0.05per cent).Heavy metals (2.4.8):maximum 20ppm.1.0g complies with test F.Prepare the reference solution using 2mL of lead standard solution (10ppm Pb)R .Loss on drying (2.2.32):maximum 0.5per cent,determined on 1.000g by drying in an oven at 105°C for 4h.Sulfated ash (2.4.14):maximum 0.2per cent,determined on 1.0g.ASSAYDissolve 0.330g in 40mL of dimethylformamide R .Titrate with 0.1M tetrabutylammonium hydroxide ,determining the end-point potentiometrically (2.2.20).Carry out a blank titration.1mL of 0.1M tetrabutylammonium hydroxide is equivalent to 47.07mg of C 30H 46O 4.STORAGEProtected from light.IMPURITIESA.(20β)-3β-hydroxy-11-oxo-18α-olean-12-en-29-oicacid,B.(4β,20β)-3β,23-dihydroxy-11-oxo-olean-12-en-29-oic acid.04/2010:2229corrected 7.0ENROFLOXACIN FOR VETERINARY USE Enrofloxacinum ad usumveterinariumC 19H 22FN 3O 3M r 359.4[93106-60-6]DEFINITION1-Cyclopropyl-7-(4-ethylpiperazin-1-yl)-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid.Content :98.5per cent to 101.5per cent (dried substance).CHARACTERSAppearance :pale yellowish or light yellow,crystalline powder.Solubility :practically insoluble in water,freely soluble in methylene chloride,slightly soluble in methanol.IDENTIFICATIONInfrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).Comparison :enrofloxacin CRS .General Notices (1)apply to all monographs and other texts2137Enrofloxacin for veterinary use EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA8.0TESTAppearance of solution.The solution is not more opalescent than reference suspension II(2.2.1)and not more intensely coloured than reference solution GY4(2.2.2,Method II).To1.0g of the substance to be examined add about0.25gof potassium hydroxide R and7mL of water R.Sonicate to dissolve and dilute to10.0mL with water R.Impurity A.Thin-layer chromatography(2.2.27).Prepare the solutions immediately before use.Solvent mixture:methanol R,methylene chloride R(50:50V/V). Test solution.Dissolve0.100g of the substance to be examined in the solvent mixture and dilute to5.0mL with the solvent mixture.Reference solution.Dissolve5.0mg of ciprofloxacin impurity A CRS(enrofloxacin impurity A)in the solvent mixture and dilute to50.0mL with the solvent mixture.Dilute 4.0mL of this solution to10.0mL with the solvent mixture.Plate:TLC silica gel F254plate R(2-10μm).Mobile phase:butanol R,water R,anhydrous acetic acid R, ethyl acetate R(15:15:20:50V/V/V/V).Application:10μL.Development:over3/4of the plate.Drying:in air.Detection:examine in ultraviolet light at254nm. Results:–impurity A:any spot due to impurity A is not more intense than the spot in the chromatogram obtained with thereference solution(0.2per cent).Related substances.Liquid chromatography(2.2.29).Test solution.Dissolve50mg of the substance to be examined in the mobile phase and dilute to50.0mL with the mobile phase.Reference solution(a).Dissolve10mg of enrofloxacin for system suitability CRS(containing impurities B and C)and dilute to10mL with the mobile phase.Reference solution(b).Dilute1.0mL of the test solution to 50.0mL with the mobile phase.Dilute1.0mL of this solution to10.0mL with the mobile phase.Column:–size:l=0.15m,Ø=4.6mm;–stationary phase:base-deactivated end-capped octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R(5μm);–temperature:40°C.Mobile phase:mix15volumes of methanol R and85volumes of a2.9g/L solution of phosphoric acid R,previously adjusted to pH2.3with triethylamine R.Flow rate:1.5mL/min.Detection:spectrophotometer at270nm.Injection:10μL.Run time:3times the retention time of enrofloxacin. Identification of impurities:use the chromatogram supplied with enrofloxacin for system suitability CRS and the chromatogram obtained with reference solution(a)to identify the peaks due to impurities B and C.Relative retention with reference to enrofloxacin (retention time=about16min):impurity C=about0.6; impurity B=about0.8.System suitability:reference solution(a):–resolution:minimum2.0between the peaks due to impurity B and enrofloxacin.Limits:–impurity B:not more than2.5times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained withreference solution(b)(0.5per cent);–impurity C:not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution(b)(0.2per cent);–unspecified impurities:for each impurity,not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution(b)(0.20per cent);–total:not more than5times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution(b)(1.0per cent);–disregard limit:0.5times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution(b)(0.1per cent).Heavy metals(2.4.8):maximum20ppm.Dissolve1.5g in a mixture of5mL of2M acetic acid and10mL of water R.Filter.12mL of thefiltrate after adding2mL of water R(instead of buffer solution)complies with test E.Prepare the reference solution using12mL of lead standard solution(2ppm Pb)R.Loss on drying(2.2.32):maximum1.0per cent,determined on2.000g by drying under high vacuum at120°C for6h. Sulfated ash(2.4.14):maximum0.1per cent,determined on 1.0g.ASSAYDissolve0.250g in100mL of anhydrous acetic acid R and titrate with0.1M perchloric acid determining the end-point potentiometrically(2.2.20).1mL of0.1M perchloric acid is equivalent to35.94mg ofC19H22FN3O3.STORAGEProtected from light.IMPURITIESSpecified impurities:A,B,C.Other detectable impurities(the following substances would, if present at a sufficient level,be detected by one or other of the tests in the monograph.They are limited by the general acceptance criterion for other/unspecified impurities and/or by the general monograph Substances for pharmaceutical use (2034).It is therefore not necessary to identify these impurities for demonstration of compliance.See also5.10.Control of impurities in substances for pharmaceutical use):E,F,G.A.7-chloro-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylicacid,B.ciprofloxacin,C.1-cyclopropyl-7-(4-ethylpiperazin-1-yl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid,2138See the information section on general monographs(cover pages)EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA 8.0EntacaponeE.6-chloro-1-cyclopropyl-7-(4-ethylpiperazin-1-yl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylicacid,F.1-cyclopropyl-7-(4-ethylpiperazin-1-yl)-6-fluoroquinolin-4(1H)-one,G.7-[(2-aminoethyl)amino]-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid.01/2011:2574corrected 7.3ENTACAPONEEntacaponum C 14H 15N 3O 5M r 305.3[130929-57-6]DEFINITION(2E )-2-Cyano-3-(3,4-dihydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)-N ,N -diethylprop-2-enamide.Content :98.0per cent to 102.0per cent (dried substance).CHARACTERSAppearance :greenish-yellow or yellow powder.Solubility :practically insoluble in water,soluble or sparinglysoluble in acetone,slightly soluble in anhydrous ethanol.It shows polymorphism (5.9).IDENTIFICATION Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).Comparison :entacapone CRS .If the spectra obtained in the solid state show differences,dissolve the substance to be examined and the referencesubstance separately in acetone R ,evaporate to dryness andrecord new spectra using the residues.TESTSRelated substances .Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).Usefreshly prepared solutions.Solvent mixture :tetrahydrofuran R ,methanol R (30:70V/V ).Test solution (a).Dissolve 50.0mg of the substance to beexamined in the solvent mixture and dilute to 50.0mL with the solvent mixture.Test solution (b).Dilute 5.0mL of test solution (a)to 50.0mL with the solvent mixture.Reference solution (a).Dissolve 5mg of entacaponeimpurity A CRS in the solvent mixture,add 5.0mL of test solution (a)and dilute to 25.0mL with the solvent mixture.Dilute 1.0mL of the solution to 20.0mL with the solvent mixture.Dilute 1.0mL of this solution to 10.0mL with the solvent mixture.Reference solution (b).Dilute 1.0mL of test solution (b)to 100.0mL with the solvent mixture.Reference solution (c).Dissolve 50.0mg of entacapone CRS in the solvent mixture and dilute to 50.0mL with the solvent mixture.Dilute 5.0mL of the solution to 50.0mL with the solvent mixture.Column :–size :l =0.25m,Ø=4.6mm;–stationary phase :end-capped propyl-2-phenylsilylamorphous organosilica polymer R (5μm).Mobile phase :mix 2volumes of tetrahydrofuran R ,44volumes of methanol R and 54volumes of a 2.34g/L solution of sodium dihydrogen phosphate R previously adjusted to pH 2.1with phosphoric acid R .Flow rate :1.0mL/min.Detection :spectrophotometer at 300nm.Injection :10μL of test solution (a)and reference solutions (a)and (b).Run time :2.5times the retention time of entacapone.Relative retention with reference to entacapone (retention time =about 17min):impurity A =about 0.8.System suitability :reference solution (a):–resolution :minimum 3.0between the peaks due toimpurity A and entacapone.Limits :–impurity A :not more than 1.5times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b)(0.15per cent);–unspecified impurities :for each impurity,not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b)(0.10per cent);–sum of impurities other than A :not more than twice thearea of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b)(0.2per cent);–disregard limit :0.5times the area of the principal peak inthe chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b)(0.05per cent).Heavy metals (2.4.8):maximum 10ppm.Solvent mixture :dimethylformamide R ,methanol R (25:75V/V ).1.00g complies with test H.Prepare the reference solution using 1.0mL of lead standard solution (10ppm Pb)R .After filtration,rinse the membrane filter with at least 20mL of methanol R .Loss on drying (2.2.32):maximum 0.5per cent,determined on 1.000g by drying in vacuo at 60°C.Sulfated ash (2.4.14):maximum 0.1per cent,determined on 1.0g.ASSAY Liquid chromatography (2.2.29)as described in the test forrelated substances with the following modification.Injection :test solution (b)and reference solution (c).Calculate the percentage content of C 14H 15N 3O 5from thedeclared content of entacapone CRS .STORAGE Protected from light.IMPURITIES Specified impurities:A.General Notices (1)apply to all monographs and other texts2139。

Ciprofloxacin hydrochloride EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA8.004/2011:0888corrected 7.4CIPROFLOXACIN HYDROCHLORIDE Ciprofloxacinihydrochloridum C 17H 19ClFN 3O 3,x H 2O M r 367.8(anhydrous)DEFINITION1-Cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(piperazin-1-yl)-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid hydrochloride.It containsa variable quantity of water.Content :98.0per cent to 102.0per cent (anhydrous substance).CHARACTERSAppearance :pale yellow,crystalline,slightly hygroscopicpowder.Solubility :soluble in water,slightly soluble in methanol,very slightly soluble in anhydrous ethanol,practically insoluble in acetone,in ethyl acetate and in methylene chloride.IDENTIFICATION A.Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).Comparison :ciprofloxacin hydrochloride CRS .B.0.1g gives reaction (b)of chlorides (2.3.1).TESTSSolution S .Dissolve 0.5g in carbon dioxide-free water R anddilute to 20mL with the same solvent.Appearance of solution .The solution is clear (2.2.1)and not more intensely coloured than reference solution GY 5(2.2.2,Method II ).Dilute 10mL of solution S to 20mL with carbon dioxide-freewater R .pH (2.2.3):3.5to 4.5for solution S.Impurity A .Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).Test solution .Dissolve 50mg of the substance to be examinedin water R and dilute to 5mL with the same solvent.Reference solution .Dissolve 10mg of ciprofloxacinimpurity A CRS in a mixture of 0.1mL of dilute ammonia R1and 90mL of water R and dilute to 100mL with water R .Dilute 2mL of the solution to 10mL with water R .Plate :TLC silica gel F 254plate R .Mobile phase :acetonitrile R ,concentrated ammonia R ,methanol R ,methylene chloride R (10:20:40:40V/V/V/V ).Application :5μL.Development :at the bottom of a chromatographic tank,place an evaporating dish containing 50mL of concentratedammonia R .Expose the plate to the ammonia vapour for15min in the closed tank.Withdraw the plate,transfer to a 2nd chromatographic tank and develop over 3/4of the plate.Drying :in air.Detection :examine in ultraviolet light at 254nm.Limit :–impurity A :any spot corresponding to impurity A is notmore intense than the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution (0.2per cent).Related substances .Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).Test solution .Dissolve 25.0mg of the substance to beexamined in the mobile phase and dilute to 50.0mL with themobile phase.Reference solution (a ).Dissolve 25.0mg of ciprofloxacin hydrochloride CRS in the mobile phase and dilute to 50.0mLwith the mobile phase.Reference solution (b).Dissolve 5mg of ciprofloxacin hydrochloride for peak identification CRS (containingimpurities B,C,D and E)in the mobile phase and dilute to 10.0mL with the mobile phase.Reference solution (c).Dilute 1.0mL of the test solution to 50.0mL with the mobile phase.Dilute 1.0mL of this solution to 10.0mL with the mobile phase.Column :–size :l =0.25m,Ø=4.6mm;–stationary phase :base-deactivated octadecylsilyl silica gel forchromatography R (5μm);–temperature :40°C.Mobile phase :mix 13volumes of acetonitrile R and 87volumesof a 2.45g/L solution of phosphoric acid R previously adjustedto pH 3.0with triethylamine R .Flow rate :1.5mL/min.Detection :spectrophotometer at 278nm.Injection :50μL of the test solution and reference solutions (b)and (c).Run time :2.3times the retention time of ciprofloxacin.Identification of impurities :use the chromatogram suppliedwith ciprofloxacin hydrochloride for peak identification CRSand the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b)to identify the peaks due to impurities B,C,D and E.Relative retention with reference to ciprofloxacin(retention time =about 9min):impurity E =about 0.4;impurity B =about 0.6;impurity C =about 0.7;impurity D =about 1.2.System suitability :reference solution (b):–resolution :minimum 1.3between the peaks due toimpurities B and C.Limits :–correction factors :for the calculation of content,multiplythe peak areas of the following impurities by thecorresponding correction factor:impurity B =0.7;impurity C =0.6;impurity D =1.4;impurity E =6.7;–impurity E :not more than 1.5times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c)(0.3per cent);–impurities B,C,D :for each impurity,not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c)(0.2per cent);–unspecified impurities :for each impurity,not more than 0.5times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogramobtained with reference solution (c)(0.10per cent);–total :not more than 2.5times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c)(0.5per cent);–disregard limit :0.25times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c)(0.05per cent).Heavy metals (2.4.8):maximum 20ppm.Dissolve 0.25g in water R and dilute to 30mL with the samesolvent.Carry out the prefiltration.The filtrate complieswith test E.Prepare the reference solution using 5mL of lead standard solution (1ppm Pb)R .Water (2.5.12):maximum 6.7per cent,determined on 0.200g.Sulfated ash (2.4.14):maximum 0.1per cent,determined on1.0g in a platinum crucible.1896See the information section on general monographs (cover pages)EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA 8.0CisplatinASSAYLiquid chromatography (2.2.29)as described in the test for related substances with the following modification.Injection :10μL of the test solution and reference solution (a).Calculate the percentage content of C 17H 19ClFN 3O 3.STORAGEIn an airtight container,protected from light.IMPURITIESSpecified impurities :A,B,C,D,E.Other detectable impurities (the following substances would,if present at a sufficient level,be detected by one or other of the tests in the monograph.They are limited by the general acceptance criterion for other/unspecified impurities and/or by the general monograph Substances for pharmaceutical use (2034).It is therefore not necessary to identify these impurities for demonstration of compliance.See also 5.10.Control of impurities in substances for pharmaceutical use ):F.A.7-chloro-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid (fluoroquinolonicacid),B.1-cyclopropyl-4-oxo-7-(piperazin-1-yl)-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid (desfluorocompound),C.7-[(2-aminoethyl)amino]-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid (ethylenediaminecompound),D.7-chloro-1-cyclopropyl-4-oxo-6-(piperazin-1-yl)-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylicacid,E.1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-7-(piperazin-1-yl)quinolin-4(1H )-one (decarboxylatedcompound), F.1-cyclopropyl-6-hydroxy-4-oxo-7-(piperazin-1-yl)-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid.01/2009:0599corrected 7.0CISPLATINCisplatinumPtCl 2(NH 3)2M r 300.0[15663-27-1]DEFINITIONcis -Diamminedichloroplatinum(II).Content :97.0per cent to 102.0per cent.CHARACTERSAppearance :yellow powder,or yellow or orange-yellow crystals.Solubility :slightly soluble in water,sparingly soluble in dimethylformamide,practically insoluble in ethanol (96per cent).Carry out identification test B,the tests (except that for silver)and the assay protected from light .IDENTIFICATIONFirst identification:A,B .Second identification:B,C .A.Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).Comparison :cisplatin CRS .B.Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).Test solution .Dilute 1mL of solution S2(see Tests)to 10mL with dimethylformamide R .Reference solution .Dissolve 10mg of cisplatin CRS in 5mL of dimethylformamide R .Plate :cellulose for chromatography R1as the coating substance.Pretreatment :activate the plate by heating at 150°C for 1h.Mobile phase :acetone R ,dimethylformamide R (10:90V/V ).Application :2μL.Development :over 2/3of the plate.Drying :in air.Detection :spray with a 50g/L solution of stannous chloride R in a mixture of equal volumes of dilute hydrochloric acid R and water R .Examine after 1h.Results :the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in position,colour and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution.C.Add 50mg to 2mL of dilute sodium hydroxide solution R in a glass dish.Evaporate to dryness.Dissolve the residue in a mixture of 0.5mL of nitric acid R and 1.5mL of hydrochloric acid R .Evaporate to dryness.The residue is orange.Dissolve the residue in 0.5mL of water R and add 0.5mL of ammonium chloride solution R .A yellow,crystalline precipitate is formed.General Notices (1)apply to all monographs and other texts1897。
⾊氨酸欧洲药典EP8.0Tryptophan EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA8.0Reference solution .Dissolve 25.0mg of trypsin BRP in 0.001M hydrochloric acid and dilute to 25.0mL with the same acid.Store the solutions at 0-5°C.Warm 1mL of each solution to about 25°C over 15min and use 50µL of each solution for each titration.Carry out the titration in an atmosphere of nitrogen.Transfer 10.0mL of 0.0015M borate buffer solution pH 8.0R to the reaction vessel and,while stirring,add 1.0mL of a freshly prepared 6.86g/L solution of benzoylarginine ethyl ester hydrochloride R .When the temperature is steady at 25.0±0.1°C (after about 5min)adjust to pH 8.0exactly with 0.1M sodium hydroxide .Add 50µL of the test solution and start a timer.Maintain at pH 8.0by the addition of 0.1M sodium hydroxide ,the tip of the microburette being immersed in the solution;note the volume added every 30s.Follow the reaction for 8min.Calculate the volume of 0.1M sodium hydroxide used per second.Carry out a titration in the same manner using the reference solution and calculate the volume of 0.1M sodium hydroxide used per second.Calculate the activity in microkatals per milligram using the following expression:m =mass of the substance to be examined,in milligrams;m ′=mass of trypsin BRP ,in milligrams;V =volume of 0.1M sodium hydroxide used per second by the test solution;V ′=volume of 0.1M sodium hydroxide used per second by the reference solution;A=activity of trypsin BRP ,in microkatals per milligram.STORAGEIn an airtight container,protected from light,at a temperature of 2°C to 8°C.LABELLING The label states:–the activity in microkatals per milligram;–for the amorphous substance,that it is hygroscopic.01/2009:1272corrected 7.0TRYPTOPHANTryptophanumC 11H 12N 2O 2M r 204.2[73-22-3]DEFINITION(S )-2-Amino-3-(1H -indol-3-yl)propanoic acid.Content :98.5per cent to 101.0per cent (dried substance).CHARACTERSAppearance :white or almost white,crystalline or amorphous powder.Solubility :sparingly soluble in water,slightly soluble inethanol (96per cent).It dissolves in dilute solutions of mineral acids and alkali hydroxides.IDENTIFICATIONFirst identification:A,B.Second identification:A,C,D.A.Speci?c optical rotation (see Tests).B.Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).Preparation :discs.Comparison :tryptophan CRS .C.Examine the chromatograms obtained in the test for ninhydrin-positive substances.Results :the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with test solution (b)is similar in position,colour and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a).D.Dissolve about 20mg in 10mL of water R .Add 5mL of dimethylaminobenzaldehyde solution R6and 2mL of hydrochloric acid R1.Heat on a water-bath.A purple-blue colour develops.TESTSAppearance of solution .The solution is clear (2.2.1)and not more intensely coloured than reference solution BY6(2.2.2,Method II ).Dissolve 0.1g in 1M hydrochloric acid and dilute to 10mL with the same acid.Speci?c optical rotation (2.2.7):?30.0to ?33.0(dried substance).Dissolve 0.25g in water R ,heating on a water-bath if necessary,and dilute to 25.0mL with the same solvent.Ninhydrin-positive substances .Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).Solvent mixture :glacial acetic acid R ,water R (50:50V/V ).Test solution (a).Dissolve 0.10g of the substance to be examined in the solvent mixture and dilute to 10mL with the solvent mixture.Test solution (b).Dilute 1mL of test solution (a)to 50mL with the solvent mixture.Reference solution (a).Dissolve 10mg of tryptophan CRS in the solvent mixture and dilute to 50mL with the solvent mixture. Reference solution (b).Dilute 5mL of test solution (b)to 20mL with the solvent mixture.Reference solution (c).Dissolve 10mg of tryptophan CRS and 10mg of tyrosine CRS in the solvent mixture and dilute to25mL with the solvent mixture.Plate :TLC silica gel plate R .Mobile phase :glacial acetic acid R ,water R ,butanol R (20:20:60V/V/V ).Application :5µL.Development :over a path of 15cm.Drying :in air.Detection :spray with ninhydrin solution R and heat at 100-105°C for 15min.System suitability :reference solution (c):–the chromatogram shows 2clearly separated spots.Limit :test solution (a):–any impurity :any spot,apart from the principal spot,is not more intense than the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b)(0.5per cent).Impurity A and other related substances .Liquidchromatography (2.2.29).Prepare the standard,test and reference solutions immediately before use.Buffer solution pH 2.3.Dissolve 3.90g of sodium dihydrogen phosphate R in 1000mL of water R .Add about 700mL of a2.9g/L solution of phosphoric acid R and adjust to pH 2.3with the same acid solution.Solvent mixture :acetonitrile R ,water R (10:90V/V ).3490See the information section on general monographs (cover pages)EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA 8.0TryptophanStandard solution .Dissolve 10.0mg of N-acetyltryptophan R in the solvent mixture and dilute to 100.0mL with the solvent mixture.Dilute 2.0mL of this solution to 100.0mL with the solvent mixture.Test solution (a).Dissolve 0.10g of the substance to be examined in the solvent mixture and dilute to 10.0mL with the solvent mixture.Test solution (b).Dissolve 0.10g of the substance to beexamined in the standard solution and dilute to 10.0mL with the standard solution.Reference solution (a).Dissolve the contents of a vial of 1,1′-ethylidenebistryptophan CRS (impurity A)in 1.0mL of the solvent mixture.Reference solution (b).Dissolve the contents of a vial of 1,1′-ethylidenebistryptophan CRS (impurity A)in 1.0mL of the standard solution.Reference solution (c).Dilute 0.5mL of reference solution (a)to 5.0mL with the solvent mixture.Column :–size :l =0.25m,?=4.6mm;–stationary phase :octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5µm);–temperature :40°C.Mobile phase :–mobile phase A :acetonitrile R ,buffer solution pH 2.3(115:885V/V );–mobile phase B :acetonitrile R ,buffer solution pH 2.3(350:650V/V );Time (min)Mobile phase A (per cent V/V )Mobile phase B (per cent V/V )0-1010010-45100→00→10045-65100Flow rate :0.7mL/min.Detection :spectrophotometer at 220nm.Injection :20µL of test solutions (a)and (b)and reference solutions (b)and (c).Retention time :tryptophan =about 8min;N -acetyltrypto-phan =about 29min;impurity A =about 34min.System suitability :–resolution :minimum 8.0between the peaks due toN -acetyltryptophan and impurity A in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b);if necessary,adjust the time programme for the elution gradient (an increase in the duration of elution with mobile phase A produces longer retention times and a better resolution);–signal-to-noise ratio :minimum 15for the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c);–symmetryfactor :maximum 3.5for the peak due toimpurity A in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b).–in the chromatogram obtained with test solution (a)there is no peak with the same retention time as N -acetyltryptophan (in such case correct the area of the N -acetyltryptophan peak).Limits :test solution (b):–impurity A :not more than 0.5times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) (10ppm);–sum of impurities with a retention time less than that of tryptophan :not more than 0.6times the area of the peak due to N -acetyltryptophan in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b)(100ppm);–sum of impurities with a retention time greater than that of tryptophan and up to 1.8times the retention time of N-acetyltryptophan :not more than 1.9times the area of the peak due to N -acetyltryptophan in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b)(300ppm);–disregard limit:0.02times the area of the peak due to N -acetyltryptophan in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b);disregard the peak due to N -acetyltryptophan.Chlorides (2.4.4):maximum 200ppm.Dissolve 0.25g in 3mL of dilute nitric acid R and dilute to 15mL with water R .The solution,without any further addition of nitric acid,complies with the test.Sulfates (2.4.13):maximum 300ppm.Dissolve 0.5g in a mixture of 5volumes of dilute hydrochloric acid R and 25volumes of distilled water R ,and dilute to 15mL with the same mixture of solvents.Ammonium (2.4.1,Method B ):maximum 200ppm,determined on 0.10g.Prepare the standard using 0.2mL of ammonium standard solution (100ppm NH 4)R .Iron (2.4.9):maximum 20ppm.In a separating funnel,dissolve 0.50g in 10mL of dilute hydrochloric acid R .Shake with 3quantities,each of 10mL,of methyl isobutyl ketone R1,shaking for 3min each time.To the combined organic layers add 10mL of water R and shake for3min.Examine the aqueous layer.Heavy metals (2.4.8):maximum 10ppm.2.0g complies with test D.Prepare the reference solution using 2mL of lead standard solution (10ppm Pb)R .Loss on drying (2.2.32):maximum 0.5per cent,determined on 1.000g by drying in an oven at 105°C.Sulfated ash (2.4.14):maximum 0.1per cent,determined on 1.0g.ASSAYDissolve 0.150g in 3mL of anhydrous formic acid R .Add 30mL of anhydrous acetic acid R .Titrate with 0.1M perchloric acid ,using 0.1mL of naphtholbenzein solution R as indicator.1mL of 0.1M perchloric acid is equivalent to 20.42mg of C 11H 12N 2O 2.STORAGEProtected from light.IMPURITIESA.3,3′-[ethylidenebis(1H -indole-1,3-diyl)]bis[(2S )-2-aminopropanoic]acid (1,1′-ethylidenebistryptophan),B.(S )-2-amino-3-[(3RS )-3-hydroxy-2-oxo-2,3-dihydro-1H -indol-3-yl]propanoic acid (dioxyindolylalanine), General Notices (1)apply to all monographs and other texts3491Tuberculin for human use,old EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA8.0C.R=H:(S)-2-amino-4-(2-aminophenyl)-4-oxobutanoicacid(kynurenine),E.R=CHO:(S)-2-amino-4-[2-(formylamino)phenyl]-4-oxobutanoic acid(N-formylkynurenine),D.(S)-2-amino-3-(5-hydroxy-1H-indol-3-yl)propanoic acid(5-hydroxytryptophan),F.(S)-2-amino-3-(phenylamino)propanoic acid(3-phenylaminoalanine),G.(S)-2-amino-3-(2-hydroxy-1H-indol-3-yl)propanoic acid(2-hydroxytryptophan),H.R=H:(3RS)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-9H-β-carboline-3-carboxylic acid,I.R=CH3:1-methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-9H-β-carboline-3-carboxylicacid,J.R=CHOH-CH2-OH:(S)-2-amino-3-[2-[2,3-dihydroxy-1-(1H-indol-3-yl)propyl]-1H-indol-3-yl]propanoic acid,K.R=H:(S)-2-amino-3-[2-(1H-indol-3-ylmethyl)-1H-indol-3-yl]propanoicacid,L.1-(1H-indol-3-ylmethyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-9H-β-carboline-3-carboxylic acid.01/2008:0152TUBERCULIN FOR HUMAN USE,OLD Tuberculinum pristinum ad usum humanum DEFINITIONOld tuberculin for human use consists of a?ltrate,concentrated by heating,containing the soluble products of the culture and lysis of one or more strains of Mycobacterium bovis and/or Mycobacterium tuberculosis that is capableof demonstrating a delayed hypersensitivity in an animal sensitised to micro-organisms of the same species.Old tuberculin for human use in concentrated form is a transparent,viscous,yellow or brown liquid. PRODUCTIONGENERAL PROVISIONSThe production of old tuberculin is based on a seed-lot system. The production method shall have been shown to yield consistently old tuberculin of adequate potency and safety in man.A batch of old tuberculin,calibrated in InternationalUnits by the method described under Assay and for which adequate clinical information is available as to its activity in man,is set aside to serve as a reference preparation.The International Unit is the activity of a stated quantity ofthe International Standard.The equivalence in International Units of the International Standard is stated by the World Health Organization.SEED LOTSThe strains of mycobacteria used shall be identi?ed by historical records that include information on their origin and subsequent manipulation.The working seed lots used to inoculate the media for the production of a concentrated harvest shall not have undergone more than4subcultures from the master seed lot.Only seed lots that comply with the following requirements may be used for propagation.Identi?cation.The species of mycobacterium of the master and working seed lots is identi?ed.Bacterial and fungal contamination.Carry out the test for sterility(2.6.1),using10mL for each medium.The workingseed lot complies with the test for sterility except for the presence of mycobacteria.PROPAGATION AND HARVESTThe bacteria are grown in a liquid medium which may be a glycerolated broth or a synthetic medium.Growth must betypical for the strain.The culture is inactivated by a suitable method,such as treatment in an autoclave(121°C for not lessthan30min)or in?owing steam at a temperature not lessthan100°C for at least1h.The culture liquid,from whichthe micro-organisms may or may not have been separatedby?ltration,is concentrated by evaporation,usually toone-tenth of its initial volume.The preparation is free fromlive mycobacteria.The concentrated harvest is shown tocomply with the test for mycobacteria(2.6.2)before additionof any antimicrobial preservative or other substance thatmight interfere with the test.Phenol(5g/L)or anothersuitable antimicrobial preservative that does not give rise tofalse positive reactions may be added.Only a concentrated harvest that complies with the following requirements may be used in the preparation of the?nal bulk tuberculin.pH(2.2.3).The pH of the concentrated harvest is6.5to8.Glycerol.Where applicable,determine the glycerol contentof the concentrated harvest.The amount is within the limits approved for the particular product.3492See the information section on general monographs(cover pages)。
欧洲药典8.0版3.1 用于包装容器生产的材料这一章描述的是用于药物包装容器生产的材料。
可能还用于部分或全部医疗手术器材的生产。
未包含在药典中的材料或聚合物的使用取决于主管当局的审批。
3.1.6聚丙烯用于注射液和眼用药的包装容器和包装塞定义聚丙烯是由丙烯单独聚合、或者由丙烯、乙烯(不超过25%)共同聚合而成,或者为聚丙烯、聚乙烯(不超过25%)的混合物,这些物质包含他们的同类高聚合物(C4-C10)或者羧酸或者酯类并且不超过25%。
可能含有添加剂。
成品聚合物中会添加一些特定的添加剂以使他们的化学、物理和机械性能更优,以适应预期用途。
所有这些添加剂均选自附件列表,并给出了每个产品中的最大允许含量。
产品中最多只能含有3种抗氧化剂,一种或更多润滑剂或者抗粘连剂,当材料必须提供遮光功能时,还要添加二氧化钛作为遮光剂。
—塑料添加剂07[128-37-0] 丁基羟基甲苯butylhydroxytoluene 抗氧剂BHT 限量:0.125%;—塑料添加剂09[6683-19-8] 四[β-(3,5-二叔丁基-4-羟基苯基)丙酸]季戊四醇酯[pentaerythritol tetrakys 3-(3,5-ditert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl )propionate] 抗氧剂1010限量:0.3%;—塑料添加剂13[27676-62-6] 1,3,5-三(3,5-二叔丁基-4-羟基苄基)-顺式-三嗪-2,4,6(1H,3H,5H)-三酮限量:0.3%;—塑料添加剂11[2082-79-3] 3-(3,5-二叔丁基-4-羟基苯基)丙酸正十八碳醇酯octadecyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate 抗氧剂1076 限量:0.3%;—塑料添加剂08[32509-66-3] 3-(1,1-二甲基乙基)-β-[3-(1,1-二甲基乙基)-4-羟苯基]-4-羟基-β-甲基苯甲酸-1,2-亚乙基酯Ethylene bis[3,3-bis[3-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-4-hydroxyphenyl]butanoate] 限量:0.3%;—塑料添加剂15[2500-88-1] 二(十八烷基)二硫化物dioctadecyl disulfide限量:0.3%;—塑料添加剂10[1709-70-2] 2,2′,2″,6,6′,6″-己烷-叔丁基-4,4′,4″-[(2,4,6-三甲基-1,3,5-苯基)三亚甲基]三苯酚2,2′,2″,6,6′,6″-hexa-tert-butyl-4,4′,4″-[(2,4,6-trimethyl-1,3,5-benzenetriyl)trismet hylene] triphenol 抗氧剂330 限量:0.3%;—塑料添加剂14[3806-34-6] 2,2′-二(十八烷基氧)-5,5′-螺[1,3,2-二氧亚磷酸酯]2,2′-bis(octadecyloxy)-5,5′-spirobi[1,3,2-dioxaphosphinane] 限量:0.3%;—塑料添加剂16[123-28-4] 二(十二烷基)3,3′-硫代二丙酸盐didodecyl 3,3′-sulphanediyldipropanoate限量:0.3%;—塑料添加剂17[693-36-7] 硫代二丙酸双十八酯dioctadecyl3,3′-thiodipropionate抗氧剂DSTOP 限量:0.3%;—塑料添加剂12[31570-04-4] 三(2,4-二叔丁基苯基) 亚磷酸酯tris(2,4-di-tert-butylphenyl) phosphate 抗氧剂168 限量:0.3%;以上抗氧化剂总含量不得超过0.3%。
1.1. GENERAL STATEMENTSThe General Notices apply to all monographs and other texts of the European Pharmacopoeia.总论的内容适用于各论和欧洲药典中的其它章节。
The official texts of the European Pharmacopoeia are published in English and French. Translations in other languages may be prepared by the signatory States of the European Pharmacopoeia Convention. In case of doubt or dispute, the English and French versions are alone authoritative.欧洲药典以英语和法语形式发行,欧洲药典委员会的签署国可将药典内容译成其它语言,但若发生争议,应以英语和法语版为权威。
In the texts of the European Pharmacopoeia, the word "Pharmacopoeia" without qualification means the European Pharmacopoeia. The official abbreviation Ph. Eur. may be used to indicate the European Pharmacopoeia.在欧洲药典中,如无特殊规定,“药典”是指欧洲药典,缩写Ph. Eur.也指欧洲药典。
The use of the title or the subtitle of a monograph implies that the article complies with the requirements of the relevant monograph. Such references to monographs in the texts of the Pharmacopoeia are shown using the monograph title and reference number in italics.文章中如果引用了各论中的标题和副标题意味着文章内容符合相关各论的要求。
Nizatidine EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA8.0Multiply the result obtained by the quenching correction factor in order to correct the quenching effect on the analyser response caused by the nitrous oxide matrix effect.The quenching correction factor is determined by applying a known reference mixture of nitrogen monoxide in nitrous oxide and comparing the actual content with the content indicated by the analyser which has been calibrated with an NO/N 2reference mixture.Water :maximum 67ppm V/V ,determined using an electrolytic hygrometer (2.5.28).Assay .Infrared analyser (2.5.35).Gas to be examined .The substance to be examined.It must be filtered to avoid stray light phenomena.Reference gas (a).Nitrous oxide R .Reference gas (b).A mixture containing 5.0per cent V/V of nitrogen R1and 95.0per cent V/V of nitrous oxide R .Calibrate the apparatus and set the sensitivity using reference gases (a)and (b).Measure the content of nitrous oxide in the gas to be examined.IDENTIFICATION First identification:A.Second identification:B,C.A.It complies with the limits of the assay.B.Place a glowing splinter of wood in the substance to be examined.The splinter bursts into flame.C.Introduce the substance to be examined into alkaline pyrogallol solution R .A brown colour does not develop.TESTS Examine the gaseous phase.If the test is performed on a cylinder,keep the cylinder of thesubstance to be examined at room temperature for at least 6hbefore carrying out the tests.Keep the cylinder in the vertical position with the outlet valve uppermost.Carbon dioxide :maximum 300ppm V/V ,determined using a carbon dioxide detector tube (2.1.6).Carbon monoxide :maximum 5ppm V/V ,determined usinga carbon monoxide detector tube (2.1.6).When the test iscarried out on a cylinder,use the first portion of the gas to be withdrawn.Nitrogen monoxide and nitrogen dioxide :maximum2ppm V/V ,determined using a nitrogen monoxide and nitrogen dioxide detector tube (2.1.6).Water vapour :maximum 67ppm V/V ,determined using awater vapour detector tube (2.1.6).STORAGEStore liquefied under pressure in suitable containers complying with the legal regulations.The taps and valves are not greased or oiled.IMPURITIES Specified impurities:A,B,C,D,E.A.CO 2:carbon dioxide,B.CO:carbon monoxide,C.NO:nitrogen monoxide,D.NO 2:nitrogen dioxide,E.H 2O:water.07/2012:1453NIZATIDINENizatidinumC 12H 21N 5O 2S 2M r 331.5[76963-41-2]DEFINITION(EZ )-N -[2-[[[2-[(Dimethylamino)methyl]thiazol-4-yl]methyl]sulfanyl]ethyl]-N ′-methyl-2-nitroethene-1,1-diamine.Content :97.0per cent to 102.0per cent (dried substance).CHARACTERSAppearance :almost white or slightly brownish,crystalline powder.Solubility :sparingly soluble in water,soluble in methanol.IDENTIFICATION First identification:C.Second identification:A,B,D.A.Melting point (2.2.14):131°C to 134°C.B.Ultraviolet and visible absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.25).Test solution .Dissolve 0.10g in methanol R and diluteto 100.0mL with the same solvent.Dilute 2.0mL of the solution to 100.0mL with methanol R .Spectral range :220-350nm.Absorption maxima :at 242nm and 325nm.Absorbance ratio:A 325/A 242=2.2to 2.5.C.Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).Comparison :nizatidine CRS .D.Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).Test solution .Dissolve 50mg of the substance to be examined in methanol R and dilute to 10mL with the samesolvent.Reference solution (a).Dissolve 50mg of nizatidine CRS in methanol R and dilute to 10mL with the same solvent.Reference solution (b).Dissolve 50mg of nizatidine CRS and 50mg of ranitidine hydrochloride CRS in methanol R and dilute to 10mL with the same solvent.Plate :TLC silica gel plate R .Mobile phase :water R ,concentrated ammonia R1,2-propanol R ,ethyl acetate R (4:8:30:50V/V/V/V ).Application :5μL.Development :over 2/3of the plate.Drying :in air.Detection :expose to iodine vapour until the spots are clearly visible.Examine in daylight.System suitability :reference solution (b):–the chromatogram shows 2clearly separated spots.Results :the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in position and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a).2866See the information section on general monographs (cover pages)EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA 8.0NizatidineTESTSAppearance of solution .The solution is clear (2.2.1)and not more intensely coloured than reference solution Y 5(2.2.2,Method II ).Dissolve 0.2g in a 10g/L solution of hydrochloric acid R and dilute to 20mL with the same solution.pH (2.2.3):8.5to 10.0.Dissolve 0.2g in carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 20mL with the same solvent.Related substances .Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).Solvent mixture :mobile phase B,mobile phase A (15:85V/V ).Test solution (a).Dissolve 50mg of the substance to be examined in the solvent mixture and dilute to 10.0mL with the solvent mixture.Test solution (b).Dissolve 15.0mg of the substance to be examined in the solvent mixture and dilute to 50.0mL with the solvent mixture.Reference solution (a).Dilute 1.0mL of test solution (a)to 100.0mL with the solvent mixture.Dilute 1.0mL of this solution to 10.0mL with the solvent mixture.Reference solution (b).Dissolve 15.0mg of nizatidine CRS in the solvent mixture and dilute to 50.0mL with the solvent mixture.Reference solution (c).Dissolve 5mg of the substance to be examined and 0.5mg of nizatidine impurity F CRS in the solvent mixture and dilute to 100.0mL with the solvent mixture.Reference solution (d).Dissolve 5mg of 2-(dimethylamino)thi-oacetamide hydrochloride R (impurity H hydrochloride)in the solvent mixture and dilute to 10.0mL with the solvent mixture.Dilute 1.0mL of the solution to 20.0mL with the solvent e 1.0mL of this solution to dissolve 5mg of nizatidine for system suitability CRS (containing impurities A,B,C,D,G,J and K).Column :–size :l =0.25m,Ø=4.6mm;–stationary phase :octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5μm).Mobile phase :–mobile phase A :dissolve 5.9g of ammonium acetate R in 760mL of water R ,add 1mL of diethylamine R ,and adjust to pH 7.5with acetic acid R ;–mobile phase B :methanol R ;Time (min)Mobile phase A (per cent V/V )Mobile phase B (per cent V/V )0-385153-2085→5015→5020-455050Flow rate :1.0mL/min.Detection :spectrophotometer at 254nm.Injection :20μL of test solution (a)and reference solutions (a),(c)and (d).Identification of impurities :use the chromatogramsupplied with nizatidine for system suitability CRS and the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (d)to identify the peaks due to impurities A,B,C,D,G,H,J and K;use thechromatogram obtained with reference solution (c)to identify the peak due to impurity F.Relative retention with reference to nizatidine (retention time =about 18min):impurity A =about 0.19;impurity K =about 0.21;impurity H =about 0.5;impurity B =about 0.6;impurity C =about 0.66;impurity J =about 0.7;impurity D =about 0.75;impurity F =about 1.03;impurity G =about 1.5.System suitability :–resolution :minimum 2.0between the peaks due tonizatidine and impurity F in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c);minimum 1.5between the peaks due to impurities A and K in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (d).Limits :–correction factors :for the calculation of content,multiply the peak areas of the following impurities by the corresponding correction factor:impurity B =1.7;impurity D =2.3;impurity H =0.5;–impurities A,B,C,D,F,G,H,J,K :for each impurity,not more than 3times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a)(0.3per cent);–unspecified impurities :for each impurity,not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a)(0.10per cent);–total :not more than 15times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a)(1.5per cent);–disregard limit :0.5times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a)(0.05per cent).Heavy metals (2.4.8):maximum 20ppm.Solvent :methanol R .0.5g complies with test H.Prepare the reference solution using 1mL of lead standard solution (10ppm Pb)R .Loss on drying (2.2.32):maximum 0.5per cent,determined on 1.000g by drying in an oven at 105°C.Sulfated ash (2.4.14):maximum 0.1per cent,determined on 1.0g.ASSAYLiquid chromatography (2.2.29)as described in the test for related substances with the following modifications.Mobile phase :mobile phase B,mobile phase A (35:65V/V ).Injection :test solution (b)and reference solution (b).Retention time :nizatidine =9min.Calculate the percentage content of C 12H 21N 5O 2S 2taking into account the assigned content of nizatidine CRS .IMPURITIESSpecified impurities :A,B,C,D,F,G,H,J,K.Other detectable impurities (the following substances would,if present at a sufficient level,be detected by one or other of the tests in the monograph.They are limited by the general acceptance criterion for other/unspecified impurities and/or by the general monograph Substances for pharmaceutical use (2034).It is therefore not necessary to identify these impurities for demonstration of compliance.See also 5.10.Control of impurities in substances for pharmaceutical use ):E,I.A.N ,N ′-dimethyl-2-nitroethene-1,1-diamine,B.(EZ )-N -methyl-1-(methylsulfanyl)-2-nitroethen-1-amine,General Notices (1)apply to all monographs and other texts2867Nomegestrol acetate EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA8.0C.(EZ)-N-[2-[[[2-[(dimethylamino)methyl]thiazol-4-yl]methyl]sulfinyl]ethyl]-N′-methyl-2-nitroethene-1,1-diamine,D.2-[[[2-[(dimethylamino)methyl]thiazol-4-yl]-methyl]sulfanyl]ethanamine,E.N-[2-[[[2-[(dimethylamino)methyl]thiazol-4-yl]-methyl]sulfanyl]ethyl]-2-nitroacetamide,F.(EZ)-N-methyl-N′-[2-[[[4-[[[2-[[(EZ)-1-(methylamino)-2-nitroethenyl]amino]ethyl]sulfanyl]methyl]thiazol-2-yl]methyl]sulfanyl]ethyl]-2-nitroethene-1,1-diamine,G.N,N′-bis[2-[[[2-[(dimethylamino)methyl]thiazol-4-yl]methyl]sulfanyl]ethyl]-2-nitroethene-1,1-diamine,H.2-(dimethylamino)thioacetamide,I.N-[2-[[[2-[(dimethylamino)methyl]thiazol-4-yl]methyl]sulfanyl]ethyl]-N′-methylurea,J.[2-[(dimethylamino)methyl]thiazol-4-yl]methanol,K.3-(methylamino)-5,6-dihydro-2H-1,4-thiazin-2-oneoxime.01/2008:1551corrected6.0NOMEGESTROL ACETATENomegestroliacetasC23H30O4Mr370.5[58652-20-3]DEFINITION6-Methyl-3,20-dioxo-19-norpregna-4,6-dien-17-yl acetate.Content:97.0per cent to103.0per cent(dried substance).CHARACTERSAppearance:white or almost white,crystalline powder.Solubility:practically insoluble in water,freely soluble inacetone,soluble in ethanol(96per cent).IDENTIFICATIONInfrared absorption spectrophotometry(2.2.24).Comparison:nomegestrol acetate CRS.TESTSAppearance of solution.The solution is clear(2.2.1)and notmore intensely coloured than reference solution Y5(2.2.2,Method II).Dissolve1.0g in methylene chloride R and dilute to10mLwith the same solvent.Specific optical rotation(2.2.7):−60.0to−64.0(driedsubstance).Dissolve0.500g in anhydrous ethanol R and dilute to25.0mLwith the same solvent.Related substances.Liquid chromatography(2.2.29).Test solution.Dissolve25.0mg of the substance to beexamined in methanol R and dilute to50.0mL with the samesolvent.Reference solution(a).Dilute1.0mL of the test solution to200.0mL with the mobile phase.Reference solution(b).Dissolve25.0mg of nomegestrol acetateimpurity A CRS in methanol R and dilute to50.0mL with thesame solvent.Reference solution(c).Dissolve25.0mg of nomegestrolacetate CRS in20mL of methanol R,add0.25mL of referencesolution(b)and dilute to50.0mL with the mobile phase.Column:–size:l=0.25m,Ø=4.6mm;–stationary phase:octadecylsilyl silica gel forchromatography R(5μm).Mobile phase:acetonitrile R,methanol R,water R(24:38:38V/V/V).Flow rate:1.3mL/min.Detection:spectrophotometer at245nm and at290nm.Injection:10μL.Run time:1.5times the retention time of nomegestrol acetate.Retention time at245nm:nomegestrol acetate=about17min;impurity A=about18.5min.2868See the information section on general monographs(cover pages)。
Doxylamine hydrogen succinate EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA8.0–symmetry factor :maximum 1.25for the peak due to doxycycline.Limits :–impurity A :not more than the area of the corresponding peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (e)(2.0per cent),–impurity B :not more than the area of the corresponding peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (e)(2.0per cent),–any other impurity :not more than 0.25times the area of the peak due to impurity A in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (e)(0.5per cent),–disregard limit :0.05times the area of the peak due to impurity A in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (e)(0.1per cent).Heavy metals (2.4.8):maximum 50ppm.0.5g complies with test C.Prepare the reference solution using 2.5mL of lead standard solution (10ppm Pb)R .Water (2.5.12):3.6per cent to 4.6per cent,determined on 0.200g.Sulfated ash (2.4.14):maximum 0.4per cent,determined on 1.0g.ASSAYLiquid chromatography (2.2.29)as described in the test for related substances with the following modification.Injection :test solution and reference solution (a).Calculate the percentage content of C 22H 24N 2O 8.STORAGEProtected from light.IMPURITIESA.R1=NH 2,R2=R5=H,R3=N(CH 3)2,R4=CH 3:(4S ,4a R ,5S ,5a R ,6S ,12a S )-4-(dimethylamino)-3,5,10,12,12a-pentahydroxy-6-methyl-1,11-dioxo-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydrotetracene-2-carboxamide (6-epidoxycycline),B.R1=NH 2,R2=H,R3=N(CH 3)2,R4+R5=CH 2:(4S ,4a R ,5S ,5a R ,12a S )-4-(dimethylamino)-3,5,10,12,12a-pentahydroxy-6-methylene-1,11-dioxo-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydrotetracene-2-carboxamide (metacycline),C.R1=NH 2,R2=N(CH 3)2,R3=R4=H,R5=CH 3:(4R ,4a R ,5S ,5a R ,6R ,12a S )-4-(dimethylamino)-3,5,10,12,12a-pentahydroxy-6-methyl-1,11-dioxo-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydrotetracene-2-carboxamide (4-epidoxycycline),D.R1=NH 2,R2=N(CH 3)2,R3=R5=H,R4=CH 3:(4R ,4a R ,5S ,5a R ,6S ,12a S )-4-(dimethylamino)-3,5,10,12,12a-pentahydroxy-6-methyl-1,11-dioxo-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydrotetracene-2-carboxamide (4-epi-6-epidoxycycline),E.R1=NH 2,R2=H,R3=N(CH 3)2,R4=OH,R5=CH 3:oxytetracycline,F.R1=CH 3,R2=R4=H,R3=N(CH 3)2,R5=CH 3:(4S ,4a R ,5S ,5a R ,6R ,12a S )-2-acetyl-4-(dimethylamino)-3,5,10,12,12a-pentahydroxy-6-methyl-4a,5a,6,12a-tetrahydrotetracene-1,11(4H ,5H )-dione (2-acetyl-2-decarbamoyldoxycycline).01/2013:1589DOXYLAMINE HYDROGENSUCCINATE DoxylaminihydrogenosuccinasC 21H 28N 2O 5M r 388.5[562-10-7]DEFINITIONN,N -Dimethyl-2-[(1RS )-1-phenyl-1-(pyridin-2-yl)ethoxy]ethanamine hydrogen butanedioate.Content :99.0per cent to 101.0per cent (anhydrous substance).CHARACTERSAppearance :white or almost white powder.Solubility :very soluble in water,freely soluble in ethanol (96per cent).It shows polymorphism (5.9).IDENTIFICATIONInfrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).Comparison :doxylamine hydrogen succinate CRS .If the spectra obtained show differences,dissolve the substance to be examined and the reference substance separately in methanol R ,evaporate to dryness and record new spectra using the residues.TESTSAppearance of solution .The solution is clear (2.2.1)and colourless (2.2.2,Method II ).Dissolve 0.4g in water R and dilute to 20mL with the same solvent.Related substances .Gas chromatography (2.2.28).Test solution .Dissolve 0.650g of the substance to be examined in 20mL of a 10.3g/L solution of hydrochloric acid R .Add 3mL of a 100g/L solution of sodium hydroxide R and extract with 3quantities,each of 25mL,of methylene chloride R .Combine the methylene chloride extracts and filter using hydrophobic phase-separation filter paper.Rinse the filter with 10mL of methylene chloride R and combine the rinsings with the methylene chloride extracts.Evaporate the solvent under reduced pressure at a temperature not exceeding 40°C.Dissolve the residue in 20.0mL of anhydrous ethanol R .Reference solution (a).Dilute 1.0mL of the test solution to 100.0mL with anhydrous ethanol R .Dilute 1.0mL of this solution to 10.0mL with anhydrous ethanol R .Reference solution (b).Dissolve 50mg of doxylamine for system suitability CRS (containing impurity C)in 10mL of a 10.3g/L solution of hydrochloric acid R .Add 1.5mL of a 100g/L solution of sodium hydroxide R and extract with 3quantities,each of 25mL,of methylene chloride R .Combine the methylene chloride extracts and filter using hydrophobic phase-separation filter paper.Rinse the filter with 10mL of methylene chloride R and combine the rinsings with the methylene chloride extracts.Evaporate the solvent under reduced pressure at a temperature not exceeding 40°C.Dissolve the residue in 5.0mL of anhydrous ethanol R .Column :–material :fused silica;–size :l =30m,Ø=0.53mm;2112See the information section on general monographs (cover pages)EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA 8.0Droperidol–stationary phase :poly(dimethyl)(diphenyl)siloxane R (film thickness 1.5μm).Carrier gas :helium for chromatography R .Flow rate :7mL/min.Temperature :Time (min)Temperature(°C)Column0-12160→22012-27220Injection port 250Detector250Detection :flame ionisation.Injection :1μL.Identification of impurities :use the chromatogram supplied with doxylamine for system suitability CRS and thechromatogram obtained with reference solution (b)to identify the peak due to impurity C.Relative retention with reference to doxylamine (retention time =about 12min):impurity C =about 0.96.System suitability :reference solution (b):–resolution :minimum 1.5between the peaks due to impurity C and doxylamine.Limits :–impurity C :not more than 5times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a)(0.5per cent);–unspecified impurities :for each impurity,not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a)(0.10per cent);–total :not more than 7times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a)(0.7per cent);–disregard limit :0.5times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a)(0.05per cent).Water (2.5.12):maximum 0.5per cent,determined on 2.00g.Sulfated ash (2.4.14):maximum 0.1per cent,determined on 1.0g.ASSAYDissolve 0.150g in 50mL of anhydrous acetic acid R .Titrate with 0.1M perchloric acid ,determining the end-point potentiometrically (2.2.20).1mL of 0.1M perchloric acid is equivalent to 19.43mg of C 21H 28N 2O 5.IMPURITIESSpecified impurities :C.Other detectable impurities (the following substances would,if present at a sufficient level,be detected by one or other of the tests in the monograph.They are limited by the general acceptance criterion for other/unspecified impurities and/or by the general monograph Substances for pharmaceutical use (2034).It is therefore not necessary to identify these impurities for demonstration of compliance.See also 5.10.Control of impurities in substances for pharmaceutical use ):A,B,D.A.N,N -dimethyl-2-[(1RS )-1-phenyl-1-(pyridin-4-yl)ethoxy]ethanamine, B.(1RS)-1-phenyl-1-(pyridin-2-yl)ethanol,C.N,N -dimethyl-2-[(1RS )-1-phenyl-1-(pyridin-2-yl)methoxy]ethanamine,D.phenyl(pyridin-2-yl)methanone (2-benzoylpyridine).07/2011:1010DROPERIDOLDroperidolumC 22H 22FN 3O 2M r 379.4[548-73-2]DEFINITION1-[1-[4-(4-Fluorophenyl)-4-oxobutyl]-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl]-1,3-dihydro-2H -benzimidazol-2-one.Content :99.0per cent to 101.0per cent (dried substance).CHARACTERSAppearance :white or almost white powder.Solubility :practically insoluble in water,freely soluble in dimethylformamide and in methylene chloride,sparingly soluble in ethanol (96per cent).It shows polymorphism (5.9).IDENTIFICATION First identification:A .Second identification:B,C,D .A.Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).Comparison :droperidol CRS .If the spectra obtained show differences,dissolve the substance to be examined and the reference substance separately in the minimum volume of acetone R ,evaporate to dryness on a water-bath and record new spectra using the residues.B.Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).Test solution .Dissolve 30mg of the substance to be examined in the mobile phase and dilute to 10mL with the mobile phase.Reference solution (a).Dissolve 30mg of droperidol CRS in the mobile phase and dilute to 10mL with the mobile phase.General Notices (1)apply to all monographs and other texts2113。
1 GENERAL NOTICES凡例1.1 GENERAL STATEMENTS概述The General Notices apply to all monographs and other texts of the European Pharmacopoeia.凡例的内容适用于各论和欧洲药典中的其它章节。
The official texts of the European Pharmacopoeia are published in English and French. Translations in other languages may be prepared by the signatoryStates of the European Pharmacopoeia Convention. In case of doubt or dispute, the English and French versions are alone authoritative.欧洲药典以英语和法语形式发行,欧洲药典委员会的签署国可将药典内容译成其它语言,但若发生争议,应以英语和法语版为权威。
In the texts of the European Pharmacopoeia, the word ‘Pharmacopoeia’ without qualification means the European Pharmacopoeia. The official abbreviation Ph.Eur. may be used to indicate the European Pharmacopoeia.在欧洲药典中,如无特殊规定,“药典”是指欧洲药典,官方缩写 Ph. Eur.也指欧洲药典。
The use of the title or the subtitle of a monograph implies that the articlecomplies with the requirements of the relevant monograph. Such references to monographs in the texts of the Pharmacopoeia are shown using themonograph title and reference number in italics.文章中如果引用了各论中的标题和副标题意味着文章内容符合相关各论的要求。
文章参考药典中各论内容时,以斜体的各论题目或相关数字表示。
A preparation must comply throughout its period of validity; a distinct period ofvalidity and/or specifications for opened or broached containers may bedecided by the competent authority. The subject of any other monograph must comply throughout its period of use. The period of validity that is assigned to any given article and the time from which that period is to be calculated aredecided by the competent authority in light of experimental results of stability studies.制剂在有效期内必须性质稳定,明确的有效期或说明书应由权力机构批准。
任何各论的物质也必须服从其使用期限。
任何药品的有效期和有效期的计算由权力机构经稳定性研究的试验结果决定。
Unless otherwise indicated in the General Notices or in the monographs,statements in monographs constitute mandatory requirements. Generalchapters become mandatory when referred to in a monograph, unless suchreference is made in a way that indicates that it is not the intention to make the text referred to mandatory but rather to cite it for information.除凡例和各论中另有说明,各论中的说明为强制要求;除了特定的引用信息,如果各论引用总论中内容时,该总论要求为法定要求。
The active substances, excipients, pharmaceutical preparations and other articles described in the monographs are intended for human and veterinary use (unless explicitly restricted to one of these uses). An article is not of Pharmacopoeia quality unless it complies with all the requirements stated in the monograph. This does not imply that performance of all the tests in a monograph is necessarily a prerequisite for a manufacturer in assessing compliance with the Pharmacopoeia before release of a product. The manufacturer may obtain assurance that a product is of Pharmacopoeia quality from data derived, for example, from validation studies of the manufacturing process and from in-process controls. Parametric release in circumstances deemed appropriate by the competent authority is thus not precluded by the need to comply with the Pharmacopoeia.各论中描述的活性物质,辅料,药物制剂和其它项目都是人用和兽用的(除非明确限制不可使用)。
药品项目必须符合各论的要求,否则不符合药典质量。
但并不要求产品放行前,生产商要做各论中的每项试验以满足药典要求。
生产商可通过原始数据,例如生产过程验证,和中间体控制,确保药品是否符合药典要求。
公布的环境参数,权力机构可适当采信,但不排除故意满足药典要求的可能。
The tests and assays described are the official methods upon which the standards of the Pharmacopoeia are based. With the agreement of the competent authority, alternative methods of analysis may be used for control purposes, provided that the methods used enable an unequivocal decision to be made as to whether compliance with the standards of the monographs would be achieved if the official methods were used. In the event of doubt or dispute, the methods of analysis of the Pharmacopoeia are alone authoritative. 检测和试验方法应基于药典标准的官方方法。
经权利机构允许可采用其它替代的分析方法以达到控制目的,并证明该方法是否能达到各论各标准。
若出现争论或异议,应以药典方法为准。
Certain materials that are the subject of a pharmacopoeial monograph may exist in different grades suitable for different purposes. Unless otherwise indicated in the monograph, the requirements apply to all grades of the material. In some monographs, particularly those on excipients, a list offunctionality-related characteristics that are relevant to the use of the substance may be appended to the monograph for information. Test methods for determination of one or more of these characteristics may be given, also for information.药典各论中的某些物质有多个等级可满足各种需要,除各论中另有说明,要求适用于各等级。
在一些各论中,特别是辅料,一系列相关的功能特性都有介绍,其中给出了一些特性的检测方法。
Quality systems. The quality standards represented by monographs are valid only where the articles in question are produced within the framework of a suitable quality system.质量体系:在适宜的质量体系架构下,产生有疑问的项目时,应以各论中的质量标准为法定标准。