孤岛运行方式下微电网有功功率优化策略研究
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:255.92 KB
- 文档页数:5

微电网孤岛运行模式下的协调控制策略一、概述随着分布式发电技术的不断发展,微电网作为一种新型电力系统结构,以其灵活的运行方式和较高的能源利用效率,逐渐成为解决能源问题的有效途径。
微电网孤岛运行模式是指在主电网故障或需要独立运行时,微电网能够脱离主电网并维持自身稳定运行的状态。
孤岛运行模式下的微电网面临着电源输出功率波动、负荷需求变化以及多源协调控制等诸多挑战。
研究微电网孤岛运行模式下的协调控制策略具有重要的理论价值和实践意义。
在孤岛运行模式下,微电网需要依靠内部的分布式电源和储能系统来满足负荷需求,并实现功率平衡。
分布式电源如风力发电、光伏发电等具有间歇性和随机性,导致输出功率不稳定;负荷需求也会随着时间和场景的变化而波动。
这些不确定性因素给微电网的稳定运行带来了极大的挑战。
为了应对这些挑战,需要设计一种有效的协调控制策略,以实现微电网孤岛运行模式下的稳定运行和优化管理。
该策略需要综合考虑分布式电源的出力特性、储能系统的充放电策略以及负荷需求的变化规律,通过合理的控制算法和优化方法,实现微电网内部的功率平衡、电压稳定和频率稳定,同时提高能源利用效率和经济性。
本文将围绕微电网孤岛运行模式下的协调控制策略展开研究,首先分析微电网的基本结构和孤岛运行的特点,然后探讨协调控制策略的设计原则和关键技术,最后通过仿真实验验证策略的有效性和优越性。
1. 微电网的基本概念与特点作为现代电力系统的一个重要组成部分,是指由分布式电源、储能装置、能量转换装置、负荷、监控和保护装置等构成的小型发配电系统。
它既可以与外部电网并网运行,也可以在孤岛模式下独立运行,实现自我控制、自我保护和能量管理,形成一个高度自治的电力网络。
微电网具备几个显著的特点。
它具备微型化的特征,电压等级低,系统规模小,通常服务于特定区域或用户群体。
这种小规模的发配电系统使得微电网更加灵活和易于部署。
微电网的电源多样,以可再生能源为主,如太阳能、风能等分布式电源,同时也可包括传统的小型发电机组和储能装置。
并网运行模式下,微电网系统对微源的可靠性要求不高;孤岛运行模式下,则需要依靠可靠的DG和储能系统来保证微电网平稳运行。
为此,本文以风光储多种微源低压微电网作为研究对象,采用基于主从控制的源荷平衡控制策略,确保在孤岛运行模式下微电网功率保持平衡、电压和频率保持稳定。
通过MATLAB建立微电网模型,仿真结果验证了低压微电网在孤岛运行模式下,采用该控制策略的可行性和有效性。
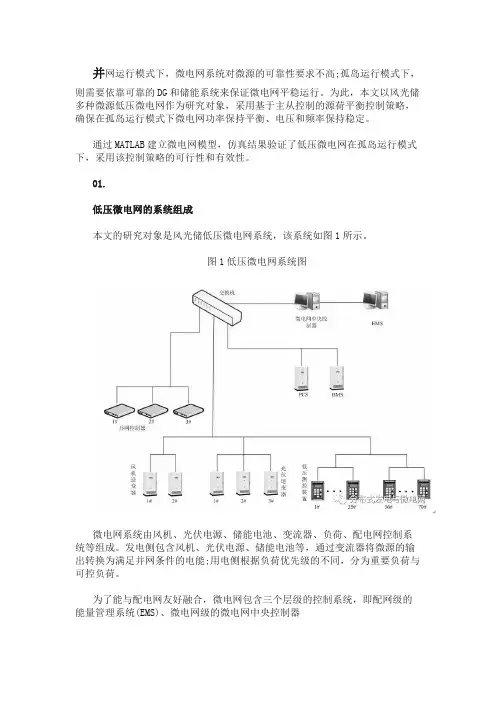
01.低压微电网的系统组成本文的研究对象是风光储低压微电网系统,该系统如图1所示。
图1低压微电网系统图微电网系统由风机、光伏电源、储能电池、变流器、负荷、配电网控制系统等组成。
发电侧包含风机、光伏电源、储能电池等,通过变流器将微源的输出转换为满足并网条件的电能;用电侧根据负荷优先级的不同,分为重要负荷与可控负荷。
为了能与配电网友好融合,微电网包含三个层级的控制系统,即配网级的能量管理系统(EMS)、微电网级的微电网中央控制器(MicroGridCentralController,MGCC)单元级的微源和负荷的就地控制器,三者互为联系协调配合,保障微电网稳定运行。
微源控制器包含在逆变器中,将微源的运行状况实时地送往MGCC;负荷控制器为低压测控装置,一方面可将负荷用电情况送往MGCC,另一方面可根据MGCC的指令投切负荷;MGCC根据单元级控制系统上送的电气信息对微电网进行统一协调控制,同时接收EMS下发的调控指令。
另一方面,微电网的运行与各微源特性、负荷特性密切相关,为了平抑DG的出力波动以及负荷的需求波动,对储能系统进行有效的能量管理至关重要。
同时,微电网的孤岛运行亟需解决电压和频率的管理、微源和负荷的平衡等问题,因此,需要可靠的储能系统充放电策略和源荷协调控制策略保证微电网的平稳运行。
02.孤岛模式下低压微电网的控制策略2.1微源控制策略光伏、风机、储能电池等DG经过电能变换装置接入微电网,其基本控制方法包括V/f(恒压/恒频)控制、PQ(恒功率)控制和Droop(下垂)控制等[9]。

摘要摘要微网系统是由各种微源、负荷、储能系统和控制装置等组成的小型电网,是一组能够实现自我管理、保护和控制的自治系统。
微网既可以独立运行,也可以并网运行,一定程度促进了分布式电源与可再生能源的大规模投入,是实现主动式配电网的一种有效方式。
微网具有供电灵活、供电质量高和安全可靠等诸多优点,但微网在运行过程中,如果控制策略采取不当,将会引起系统损耗增加、系统稳定性变差等问题。
本文在对比分析现有最大功率点追踪、孤岛运行、并网运行等控制策略的基础上,提出了微网孤岛/并网运行优化方案,具体研究内容包括以下几个方面:首先,构建了风机、蓄电池和光伏电池等微源的数学模型,并进行了模型搭建和仿真,结合逆变器拓扑结构,分析了分布式电源的传统控制方法;其次,在常用MPPT 算法的基础上,针对光伏输出最大功率在多峰值情况下会陷入局部最优的问题,采用了灰狼算法进行最大功率点跟踪的策略,并结合系统特点对算法进行了优化,进一步提高了最大功率点的搜索精度和收敛速度;接下来,针对下垂控制策略不适用低压微网孤岛运行的缺点,提出了基于虚拟阻抗的改进下垂控制策略,有效地实现了有功功率和无功功率的耦合,改善了系统的稳定性,仿真结果验证了所提方法的有效性;最后,针对采用传统PI进行并网控制时存在的坐标变换复杂、抗干扰能力弱的弊端,提出了改进PR的控制策略,优化了计算过程。
仿真结果表明,优化后的控制策略有效减少了并网谐波电流的产生,提高了系统的稳定性。
关键词:微网优化下垂控制灰狼算法改进PR控制AbstractMicrogrid system is a small power grid composed of various micro-sources,loads, energy storage systems and control devices.It is an autonomous system capable of self-management,protection and control.The micro grid can be operated independently or connected to the grid,which promotes the large-scale investment of distributed power supply and renewable energy to a certain extent,and is an effective way to realize the active distribution network.Microgrid has many advantages such as flexible power supply, high power supply quality,safety and reliability,etc.However,if the control strategy is not adopted properly during the operation of microgrid,the system loss will increase and the system stability will vary.Based on the comparative analysis of the existing control strategies such as maximum power point tracking,island operation and grid-connected operation,this paper proposes the optimization scheme of microgrid island/grid-connected operation.The specific research contents include the following aspects:Firstly,the mathematical models of microsources such as fans,accumulators and photovoltaic cells are constructed,and the model construction and simulation are carried out.The traditional control methods of distributed power supply are analyzed based on the inverter topology.Secondly,on the basis of the common MPPT algorithm,aiming at the problem that the maximum power of photovoltaic output will fall into the local optimization under the condition of multiple peaks,the gray Wolf algorithm is adopted for the maximum power point tracking strategy,and the algorithm is optimized according to the characteristics of the system,which further improves the search accuracy and convergence speed of the maximum power point.Next,aiming at the disadvantage that the droop control strategy is not suitable for low-voltage microgrid island operation,an improved droop control strategy based on virtual impedance is proposed,which effectively realizes the coupling of active power and reactive power and improves the stability of the system.Simulation results verify the effectiveness of the proposed method.Finally,aiming at the disadvantages of complex coordinate transformation and weak anti-interference ability in grid-connected control with traditional PI,an improved control strategy for PR is proposed and the calculation process is optimized.Simulation results show that the optimized control strategy can effectively reduce the generation of grid-connected harmonic current and improve the stability of the system.Key words:Microgrid Optimization Droop control Grey wolf algorithm Improved PR control目录摘要 (I)Abstract (II)第1章绪论 (1)1.1课题研究背景及意义 (1)1.2国内外研究现状 (2)1.2.1国外研究现状 (2)1.2.2国内研究现状 (3)1.3微网的分类 (4)1.3.1交流微网 (4)1.3.2直流微网 (5)1.3.3交直流微网 (6)1.4论文研究的主要内容 (7)第2章风光储微源模型的建立及仿真 (9)2.1风机模型的建立及仿真 (9)2.1.1风机模型的建立 (9)2.1.2风机模型的仿真 (12)2.2蓄电池模型的建立及仿真 (13)2.2.1蓄电池模型的建立 (13)2.2.2蓄电池模型的仿真 (15)2.3光伏电池模型的建立及仿真 (16)2.3.1光伏电池模型的建立 (16)2.3.2光伏电池模型的仿真 (18)2.4本章小结 (19)第3章微网逆变器的数学模型及控制方法 (20)3.1微网逆变器的数学建模及其拓扑结构 (20)3.1.1微网逆变器的数学建模 (20)3.1.2微网逆变器的拓扑结构 (20)3.2微网分布式电源传统控制方法 (21)3.2.1恒功率控制策略 (22)3.2.2恒压恒频控制策略 (23)3.2.3传统下垂控制策略 (24)3.3本章小结 (26)第4章基于改进灰狼算法的光伏系统最大功率点跟踪 (27)4.1常用最大功率点跟踪算法 (27)4.1.1恒定电压法 (27)4.1.2扰动观测法 (28)4.1.3电导增量法 (29)4.1.4常用MPPT算法的局限性 (30)4.2最大功率点跟踪算法的优化 (31)4.2.1灰狼算法 (31)4.2.2改进灰狼算法 (33)4.3改进灰狼算法仿真结果分析 (35)4.3.1模型的搭建 (35)4.3.2仿真结果分析 (35)4.4本章小结 (37)第5章基于改进下垂控制的微网孤岛运行控制策略研究 (38)5.1微网逆变器输出功率特性 (38)5.2基于虚拟阻抗改进下垂控制策略的研究 (39)5.2.1下垂控制策略原理 (39)5.2.2改进下垂控制策略的研究 (40)5.3.3基于虚拟阻抗的改进下垂控制策略 (42)5.3逆变器电压电流双闭环设计 (42)5.4微网离网仿真结果分析 (44)5.4.1模型的搭建 (44)5.4.2仿真结果分析 (47)5.5本章小结 (50)第6章基于改进PR控制的微网并网运行控制策略研究 (51)6.1PI控制策略 (51)6.2PR控制策略研究 (53)6.3改进PR控制策略 (54)6.4微网并网仿真结果分析 (56)6.4.1模型的搭建 (56)6.4.2仿真结果分析 (57)6.5本章小结 (59)第7章结论与展望 (60)7.1结论 (60)7.2展望 (60)致谢 (61)参考文献 (62)作者简介 (66)攻读硕士学位期间研究成果 (67)第1章绪论1.1课题研究背景及意义随着人们生活水平的提高,经济飞速的发展,全世界共同面对两大问题是能源和环境问题。

第1章前言第1章前言1.1选题的背景及研究的目的和意义由于煤、石油和天然气等一次能源的日益枯竭,以及人们对能源的依赖程度日益增大,能源问题越来越制约着我国电力系统的发展。
而燃煤为主的火力发电造成大气环境污染、化石燃料大量排放造成的温室效应导致气候变暖等问题已经成为了全球性的难题。
因此如何保证电力能够安全与稳定的供应成为了亟待解决的问题。
电力生产在最初阶段的方式是集中发电、远距离输电、大电网之间相互联系,其过程存在三个特点:即电力生产的整体性、同时性与随机性。
整体性与同时性即发电、输电和供配电的过程是不可分割的并且同时进行的,其中任何一个环节出现问题,电力生产都将难以完成。
而电力生产的随机性则指负荷、设备异常情况以及电能质量等都在随时变化着,因此在电力生产中需要做到实时调度与安全监控,能够跟踪随机事件的动态情况,以确保电网的安全运行。
但是电力建设成本高,运行难度比较大,已经越来越难以满足当今社会对电力的可靠性和安全性的需求。
近几年来,我国多个地区出现罕见的用电高峰,期间的多次事故给国家和人民造成了重大的经济损失。
美欧地区也有很多国家发生过多次大面积停电事故,致使大电网的脆弱性日益暴漏出来。
现如今,一次能源日益枯竭,环境污染问题也日益严重,传统大电网的脆弱性日益暴漏,致使全球化电力市场改革进程加快,在此背景下有学者提出了分布式发电系统这个概念。
分布式发电被认为是减少环境污染、提高能源的利用效率、增强电能供应的可靠性以及可以满足社会发展对电力日益增长的需求等的一种有效的解决途径。
分布式电源经常分散布置在用户的周围,其发出功率为数千瓦到百兆瓦不等。
相比于传统的集中式供电,分布式电源的安装位置比较灵活,并且比较分散,能更好的利用当地的资源分布,更能适应电力的需求;并且分布式电网与大电网之间又可以相互备用,有效地提高了电能的利用率,供电可靠性明显增强;输电和变电的过程中又可以减轻故障对其造成的影响,可以有效的提高电能质量;能够避免各地区电网之间由于电压和频率波动而相互造成的影响,从而可以防止由于局部电力故障而造成电网大面积的停-1 -电事故,等等。




微电网的孤岛检测与孤岛划分1. 本文概述随着全球能源需求的不断增长和电网结构的日益复杂,微电网作为一种新型的分布式能源系统,其发展受到了广泛关注。
微电网能够整合多种分布式能源资源,如太阳能、风能、储能设备等,以实现高效、可靠的能源供应。
微电网在运行过程中可能会遇到“孤岛”现象,即部分微电网在主电网故障或计划中断时,未能及时从主电网中脱离,形成独立运行的孤岛。
本文旨在深入探讨微电网的孤岛检测与孤岛划分问题。
本文将介绍微电网的基本概念、运行原理以及孤岛现象的定义和分类。
随后,我们将重点分析现有的孤岛检测方法,包括被动检测和主动检测两大类,并评估这些方法在实际应用中的优缺点。
进一步地,本文将探讨孤岛划分的策略和方法。
孤岛划分是指将微电网划分为若干个子系统,以优化能源管理、提高系统稳定性和效率。
我们将分析不同的孤岛划分算法,包括基于遗传算法、粒子群优化算法和人工智能方法的划分策略,并讨论这些方法在实际操作中的适用性和效果。
本文将结合案例分析,探讨孤岛检测与划分在实际微电网中的应用,以及这些技术对提高微电网运行效率和可靠性的贡献。
通过本文的研究,我们期望为微电网的孤岛检测与划分提供理论支持和实践指导,促进微电网技术的进一步发展和应用。
2. 微电网的基本原理微电网(Microgrid)是一种小型电网,它能够集成多种分布式能源资源,包括可再生能源如太阳能、风能,以及传统能源如小型燃气轮机等。
微电网的主要特点是能够在与主电网连接或孤立状态下运行,为局部区域提供稳定和高效的电力供应。
本节将详细探讨微电网的基本原理,包括其结构、运行模式及关键技术。
微电网的结构通常包括四个主要部分:分布式能源(DERs)、能量存储系统、负荷和控制系统。
分布式能源是微电网的核心,负责发电能量存储系统如电池用于平衡供需波动负荷则指微电网服务的用户和设备控制系统则负责监控和优化微电网的运行。
微电网主要有三种运行模式:并网模式、孤岛模式和混合模式。

孤岛式交流微电网储能系统的控制策略摘要:随着新能源技术的快速发展,微电网作为一种灵活的供电模式获得广泛关注。
其中,储能系统是微电网的重要组成部分,对于提高微电网的可靠性、供能质量、经济性和环保性等方面具有重要意义。
本文研究了孤岛式交流微电网储能系统的控制策略,主要包括控制目标、控制策略和控制方法等方面,针对储能系统中常见的电池组进行深入分析,提出了基于状态反馈的PID控制算法,设计了仿真实验和实验验证,分析了不同场景下的控制效果和应用前景。
研究结果表明,基于状态反馈的PID控制算法可以有效提高储能系统的动态响应和控制精度,降低系统能量损耗和电池寿命消耗,提高系统性能稳定性和可靠性,具有良好的实际应用价值。
关键词:微电网;储能系统;控制策略;电池组;PID控制算法Abstract: With the rapid development of new energy technologies, microgrids have gained widespread attention as a flexible power supply mode. Among them, energy storage system is an important part of microgrid, which plays an important role in improving the reliability, power quality, economy and environmental protection of microgrid. This paper studies the control strategy of energy storage systemin isolated AC microgrid, including control objectives, control strategies and control methods. Aiming at the common battery group in energy storage system, a state feedback PID control algorithm is proposed, and simulation experiments and experimental verification are designed to analyze the control effect and application prospect in different scenarios. Theresults show that the state feedback PID control algorithm can effectively improve the dynamic response and control accuracy of the energy storage system, reduce the system energy loss and battery life consumption, improve the performance stability and reliability of the system, and has good practical application value.Keywords: microgrid; energy storage system; control strategy; battery group; PID control algorithmWith the increasing development of renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power, microgrids have become an important research and application field in recent years. However, the fluctuation andintermittent nature of renewable energies pose great challenges to the stability and reliability of microgrids. Energy storage systems, as an important component of microgrids, can effectively compensatefor the intermittent characteristics of renewableenergy sources, improve the power supply stability and quality, and reduce the energy loss in the system.To ensure the effective operation of energy storage systems in microgrids, it is essential to develop appropriate control strategies. Among various control algorithms, the PID control algorithm is widely used due to its simple structure, easy implementation, and good control effect. In recent years, researchers have conducted a lot of research on the PID control algorithm for energy storage systems in microgrids and achieved promising results.One of the advantages of the state feedback PIDcontrol algorithm is that it can effectively improve the dynamic response and control accuracy of the energy storage system. By accurately detecting the state of the system, the PID controller adjusts the corresponding control parameters in real-time, which can effectively reduce the response time and overshoot of the system, and improve the control accuracy. Moreover, the PID control algorithm can suppress the system's steady-state error and ensure the stability of the system's output.Another advantage of the state feedback PID control algorithm is that it can reduce the energy loss andbattery life consumption of the energy storage system. By adjusting the charge and discharge status of the battery group based on the system state information, the PID controller can effectively prevent overcharging and over-discharging of the battery, prolong the battery life, and reduce the energy loss caused by unnecessary charging and discharging.In addition, the state feedback PID control algorithm can improve the performance stability and reliability of the energy storage system. The PID controller can adjust the control parameters in real-time based on the system state information, which can ensure the stability of the system's output and reduce the impact of external disturbances on the system. Moreover, the PID control algorithm can also improve the system's fault tolerance and reduce the probability of system failures.Overall, the state feedback PID control algorithm has good practical application value in the control of energy storage systems in microgrids. It caneffectively improve the dynamic response and control accuracy of the system, reduce the energy loss and battery life consumption, improve the performance stability and reliability of the system, and has broad application prospects in different scenariosContinuing on the topic of energy storage systems in microgrids, one of the main challenges that such systems face pertains to the integration of renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power. These sources are intermittent in nature and subject to fluctuations, making it difficult for the energy storage system to effectively balance supply and demand.One potential solution to this challenge is to implement predictive control algorithms in the energy storage system. These algorithms are designed to anticipate changes in renewable energy output and adjust the energy storage system accordingly, allowing it to more effectively manage energy flow and balance supply and demand.In addition to improving the operational efficiency of the energy storage system, predictive control algorithms can also help to extend the lifespan of batteries used in the system. By better managing the charge and discharge cycles of the batteries, predictive control algorithms can reduce the strain on the batteries and help to prevent premature failure.Another area of research in energy storage systems for microgrids is the use of advanced monitoring andcontrol technologies. These technologies can help to improve the accuracy and reliability of system performance, while also providing greater insight into energy flow and usage patterns.For example, the use of real-time monitoring and control systems can provide instant feedback on system performance, allowing operators to quickly identify and address any issues that may arise. This can help to reduce downtime and minimize the risk of system failures in the event of unexpected events such as equipment malfunctions or extreme weather conditions.Overall, the field of energy storage systems for microgrids is rapidly evolving, with new technologies and approaches being developed and implemented on a regular basis. As renewable energy sources continue to play an increasingly important role in the global energy landscape, it is likely that energy storage systems will become ever more important in providing stable and reliable energy supply to communities and businesses around the worldIn addition to technological advancements, there are also policy and regulatory challenges that affect the deployment of energy storage systems in microgrids. One of the main barriers is the lack of clear andconsistent regulations that govern the use of energy storage systems in local energy systems. This is particularly challenging in developing countries where regulatory frameworks are often weak or nonexistent.Another issue is the lack of financial incentives for energy storage systems, especially in regions where electricity prices are low or subsidies are providedto fossil fuel-based generation sources. As a result, the economic benefits of energy storage systems arenot always clear, making it difficult for investors to justify the upfront costs of these systems.Despite these challenges, there are some successstories of microgrids with energy storage systems that have provided reliable and affordable energy to communities, businesses, and institutions. For example, in India, a remote village in the state of Bihar was electrified using a solar-powered microgrid with battery storage, providing reliable electricity to the community for the first time. Similarly, the Rockefeller Foundation has launched a program thataims to promote the adoption of renewable energy and energy storage systems in rural villages in Africa and Asia, with a goal of providing reliable electricity to over 1 billion people by 2030.In conclusion, energy storage systems are vital forthe development of sustainable and reliable microgrids. Advances in technology, such as improved battery chemistries and control systems, are making energy storage systems more efficient, affordable, and scalable. However, policy and regulatory challenges remain, and more work is needed to create an enabling environment for the deployment of energy storage systems in microgrids. With the continued growth of renewable energy sources and the increasing demand for reliable electricity, energy storage systems are setto play an increasingly important role in powering the world's communities and businessesIn conclusion, energy storage systems have a critical role in the transition towards a more sustainable energy future. The advancements in technology,including battery storage and control systems, have made energy storage systems more practical and cost-effective. Despite these improvements, there are still policy and regulatory hurdles that need to be addressed to ensure widespread deployment of energy storage systems in microgrids. As renewable energy sources continue to grow, energy storage systems will become increasingly important in meeting the demandfor reliable electricity in communities and businesses。


微电网孤岛运行时的频率控制策略一、概述随着分布式可再生能源,如太阳能和风能的大规模并网,微电网作为一种能够整合这些分散能源的有效方式,正日益受到关注。
微电网不仅可以提高能源利用效率,降低传输损耗,而且能够在主电网发生故障时,以孤岛模式独立运行,保证关键负荷的连续供电。
微电网孤岛运行时的频率稳定性是一个亟待解决的问题。
由于分布式电源的随机性和不可预测性,微电网中的有功功率和无功功率的平衡容易受到影响,从而导致频率波动。
研究微电网孤岛运行时的频率控制策略,对于提高微电网的稳定性和可靠性具有重要意义。
本文旨在探讨微电网孤岛运行时的频率控制策略。
将简要介绍微电网的基本结构和运行特性,以及孤岛运行时面临的挑战。
将重点分析几种常见的频率控制策略,包括基于下垂控制的策略、基于有功功率和无功功率控制的策略以及基于储能系统的策略。
将讨论这些策略的优势和局限性,以及未来可能的研究方向。
通过本文的研究,期望能为微电网的频率控制提供有益的参考和启示。
1. 微电网的定义与特点微电网(MicroGrid),也称作微网,是一种由分布式电源、储能装置、能量转换装置、负荷、监控和保护装置等组件构成的小型发配电系统。
这种系统是一个可以实现自我控制、保护和管理的自治系统,通过其内部的控制和管理机制,实现功率平衡控制、系统运行优化、故障检测与保护、电能质量治理等功能。
分散化:微电网的能源和负载分布在不同的地点,减少了对传统大电网的依赖,提高了系统的可靠性和灵活性。
可靠性高:微电网中的设备可以互相备份,当某一设备出现故障时,其他设备可以迅速补充能量,保证微电网的正常运行。
节能环保:微电网中的能源来源多种多样,如太阳能、风能、水能等可再生能源,符合节能环保的理念。
灵活性强:微电网既可以独立运行,也可以与主电网相连,实现能量互补和互联互通,具有较强的适应性和灵活性。
经济性优:微电网的建设成本相对较低,能源使用效率高,可以在一定程度上降低用户的能源成本。
风光柴储孤立微电网系统协调运行控制策略设计一、本文概述随着全球能源结构的转型和可持续发展目标的提出,微电网作为一种集成多种分布式电源和负荷的电力系统,受到了广泛关注。
其中,风光柴储孤立微电网系统,凭借其独立运行、自给自足的特性,在偏远地区、海岛等无常规电网覆盖的地方具有广泛的应用前景。
然而,风光柴储微电网中由于各类分布式电源的间歇性和不确定性,使得系统的稳定运行面临诸多挑战。
因此,研究风光柴储孤立微电网系统的协调运行控制策略,对于提高系统的供电可靠性、优化能源利用效率和促进可再生能源的发展具有重要意义。
本文旨在探讨风光柴储孤立微电网系统的协调运行控制策略设计。
文章将介绍风光柴储微电网的基本结构和特点,分析系统面临的主要问题和挑战。
接着,将深入研究适用于该系统的协调运行控制策略,包括功率平衡控制、能量管理优化、故障检测和恢复等方面的内容。
在此基础上,文章将提出一种基于多代理系统的协调运行控制策略,通过仿真实验验证其有效性和优越性。
文章将总结研究成果,并展望风光柴储孤立微电网系统未来的发展方向和应用前景。
通过本文的研究,旨在为风光柴储孤立微电网系统的稳定运行提供理论支持和实践指导,推动可再生能源在微电网领域的应用和发展。
二、风光柴储孤立微电网系统分析孤立微电网系统,作为一种集成了风力发电、光伏发电、柴油发电以及储能设备等多种能源形式的电力系统,具有自主供电、独立运行和高度可控等特点。
这种系统能够在主电网无法覆盖或供电不稳定的地区提供稳定、可靠的电力供应,对提升能源利用效率、优化能源结构、保护生态环境具有重要意义。
风光柴储孤立微电网系统中的风力发电和光伏发电部分,依赖自然环境条件,具有间歇性和随机性。
风力发电受风速变化影响,光伏发电则受光照强度和时间影响。
因此,这两部分电源的输出功率具有较大的波动性和不确定性。
为了平抑这种波动性,需要引入储能设备,如蓄电池、超级电容等,来存储多余电能,并在风力或光照不足时释放电能,以维持电网的稳定运行。
基于Multi-agent的微电网运行与控制的研究刘增环;李洁【摘要】为了提高微电网并网和孤岛两种模式切换的平滑性,增加其运行的可靠性,对基于Multi-agent系统理论的微电网控制模型进行了深入的研究,提出了新的控制模型。
该模型增加了孤岛检测agent,根据电压和频率的变化及时判断孤岛的出现,使各微源可以迅速选择各自的控制方式,在实现微电网局部自治和保证微电网运行的安全性和可靠性的基础上,提高了微电网控制系统的快速反应能力。
试验仿真结果证明了新模型的可行性和有效性。
%In order to improve the smoothness of the micro-grid during switching between grid-connected mode and island mode, and enhance the reliability of the operation, the micro-grid control model based on theory of multi-agent system is researched in-depth, and the new model is proposed. The island detection agent is added in new model, the appearance of the island can be judged timely in accordance with the variation of voltage and frequency and each micro source can quickly select their control mode. On the basis of implementing micro-grid local autonomy, and ensuring security and reliability of micro-grid operation, the high speed response capability of the micro-grid control system is increased. The results of experiment and simulation verify the feasibility and effectiveness of the new model.【期刊名称】《自动化仪表》【年(卷),期】2015(000)004【总页数】5页(P13-17)【关键词】微电网控制模型;多智能体系统;孤岛检测;恒功率控制;恒频恒压控制;超级电容【作者】刘增环;李洁【作者单位】河北工程大学信息与电气工程学院,河北邯郸 056038;河北工程大学信息与电气工程学院,河北邯郸 056038【正文语种】中文【中图分类】TM743为了解决全球面临的能源短缺危机和缓解环保压力等问题,微电网作为一种新的供电模式应运而生。
第48卷第17期电力系统保护与控制Vol.48 No.17 2020年9月1日Power System Protection and Control Sep. 1, 2020 DOI: 10.19783/ki.pspc.191177直流微电网孤岛运行控制策略研究董继军1,陈 浩1,周雪松2,刘 敏3,王应华1,王海蓉1(1.国网湖北省电力有限公司黄石供电公司,湖北 黄石 435000;2.天津理工大学,天津 300384;3.天津守中电力科技有限公司,天津 300384)摘要:针对湖北黄石地区楼宇建筑直流微电网孤岛运行场景,提出一种光伏和储能电池的协调控制策略。
基于直流微电网系统的实时状态,根据直流母线电压数值对微电网的运行模式进行划分,并设置变流器动作阈值,微电网内的各变流器根据母线电压所处的区间范围,执行相应的控制策略,满足微电网的能量平衡及电压稳定性需求。
考虑微电网内部储能电池状态的一致性要求,针对电池变流器提出一种基于电池荷电状态(State of Charge, SOC)的协调控制策略,在电池的充放电过程中,根据不同电池组之间的容量差异进行功率分配,避免相同的充放电效率导致过充或过放现象。
最后通过Matlab/Simulink对所提控制策略进行仿真验证分析。
关键词:直流微电网;孤岛运行;直流母线电压;控制策略;荷电状态;功率分配Research on control strategy of a DC microgrid in isolated operationDONG Jijun1, CHEN Hao1, ZHOU Xuesong2, LIU Min3, WANG Yinghua1, WANG Hairong1(1. State Grid Huangshi Electric Power Supply Company, Huangshi 435000, China; 2. Tianjin University of Technology,Tianjin 300384, China; 3. Tianjin Shouzhong Electric Power Technology Co., Ltd., Tianjin 300384, China)Abstract: A coordinated control strategy of a photovoltaic and energy storage battery is proposed for the isolated island operation scenario of building a DC microgrid in Huangshi, Hubei Province. Based on the real-time state of the DC micro grid system, the operation mode of the micro grid is divided according to the DC bus voltage value, and the action threshold of the converter is set. Each converter in the micro grid executes the corresponding control strategy according to the range of the bus voltage to meet the energy balance and voltage stability requirements of the micro grid. Considering the consistency of the battery state in the microgrid, a coordinated control strategy based on State Of Charge (SOC) is proposed for the battery converter. In the process of battery charging and discharging, the power rate is distributed according to the capacity difference between different battery groups to avoid overcharge or overdischarge caused by the same charging and discharging efficiency. Finally, Matlab/Simulink is used to verify the control strategy proposed in this paper.This work is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51877152).Key words: DC micro-grid; isolated operation; DC bus voltage; control strategy; state of charge; power allocation0 引言能源紧缺和环境保护等问题推动着分布式可再生能源微电网技术的不断进步。
多微网配电系统的分层孤岛运行及保护控制一、本文概述随着可再生能源的大规模接入和电力电子技术的快速发展,多微网配电系统已成为现代电力系统的重要组成部分。
多微网配电系统由多个微网组成,每个微网可以独立运行,也可以在必要时与其他微网或主网进行互联。
这种系统的灵活性使得它能够在不同运行条件下实现优化运行,提高电力系统的可靠性和经济性。
然而,多微网配电系统的复杂性也带来了新的挑战,特别是在孤岛运行模式下,如何确保系统的稳定运行和保护控制成为亟待解决的问题。
本文旨在研究多微网配电系统的分层孤岛运行及保护控制策略。
介绍了多微网配电系统的基本结构和运行特点,包括微网之间的互联方式、能量管理策略等。
然后,重点分析了分层孤岛运行模式下的系统稳定性问题,包括电压波动、频率偏移等,并提出了相应的优化措施。
在此基础上,研究了保护控制策略,包括故障检测、隔离和恢复等,以确保系统在发生故障时能够快速、准确地响应。
本文的研究内容对于提高多微网配电系统的稳定性和可靠性具有重要意义。
通过深入分析和优化分层孤岛运行模式下的系统性能,可以为实际工程应用提供有力支持。
本文提出的保护控制策略可以为电力系统的安全稳定运行提供有力保障。
本文的研究方法和结论对于推动多微网配电系统的发展和应用具有重要价值。
未来,随着可再生能源的进一步普及和电力电子技术的不断进步,多微网配电系统将在电力系统中发挥更加重要的作用。
因此,深入研究多微网配电系统的运行特性和保护控制策略,对于实现电力系统的可持续发展具有重要意义。
二、多微网配电系统概述随着可再生能源的快速发展和分布式发电技术的日益成熟,多微网配电系统逐渐成为了现代电力系统的重要组成部分。
多微网配电系统由多个微电网组成,每个微电网都可以独立运行,也可以与主网或其他微电网进行互联。
这种系统结构不仅提高了电力系统的灵活性和可靠性,还有助于实现可再生能源的大规模接入和高效利用。
多微网配电系统的主要特点包括:一是灵活性高,每个微电网可以根据实际需求独立运行或并网运行;二是可靠性强,当一个微电网发生故障时,其他微电网可以迅速接管负荷,保证电力系统的稳定运行;三是可再生能源接入方便,微电网可以接入风能、太阳能等多种可再生能源,提高电力系统的清洁度和可持续性。
光储微网系统并网孤岛运行控制策略一、本文概述随着全球能源结构的转型和可再生能源的大力发展,光储微网系统作为一种集光伏发电、储能技术和微电网技术于一体的新型电力系统,正逐渐受到广泛关注。
光储微网系统不仅能够有效整合分布式能源,提高能源利用效率,还能在并网和孤岛两种模式下稳定运行,为现代电力系统的灵活性和可靠性提供了有力支撑。
然而,如何制定和优化光储微网系统在并网与孤岛模式下的运行控制策略,仍是一个亟待解决的问题。
本文旨在深入研究光储微网系统在并网和孤岛模式下的运行控制策略。
通过对光储微网系统的基本组成、工作原理及运行特性进行分析,结合国内外相关研究成果和工程实践经验,探讨适合我国电力系统实际情况的控制策略。
文章将重点分析并网模式下光储微网系统的功率控制、电压和频率调节等问题,以及孤岛模式下系统的能量管理、负荷分配和稳定性保障等关键技术。
还将探讨如何根据不同场景和需求,对控制策略进行优化,以实现光储微网系统的高效、安全、稳定运行。
通过本文的研究,期望能为光储微网系统的设计、建设和运营提供有益的参考和指导,推动我国可再生能源和智能电网技术的发展,为实现碳达峰、碳中和目标贡献力量。
二、光储微网系统结构及特点光储微网系统是一种集成光伏发电、储能系统和微电网技术的分布式能源系统。
其系统结构主要包括光伏发电单元、储能单元、能量管理单元和微电网控制单元。
光伏发电单元:光伏发电单元是光储微网系统的核心部分,通过光伏效应将太阳能转化为直流电能。
光伏阵列通常由多个光伏组件串联和并联组成,以满足不同光照条件下的电能输出需求。
储能单元:储能单元是光储微网系统的重要组成部分,用于存储光伏发电单元产生的多余电能。
储能单元通常采用锂离子电池、铅酸电池或超级电容器等储能设备,以实现电能的高效存储和快速释放。
能量管理单元:能量管理单元是光储微网系统的“大脑”,负责实时监测和预测系统的运行状态,根据电能需求和供给情况,制定合理的能量管理策略。