美国大学英语写作Chapter对比和比较PPT课件
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:127.50 KB
- 文档页数:14

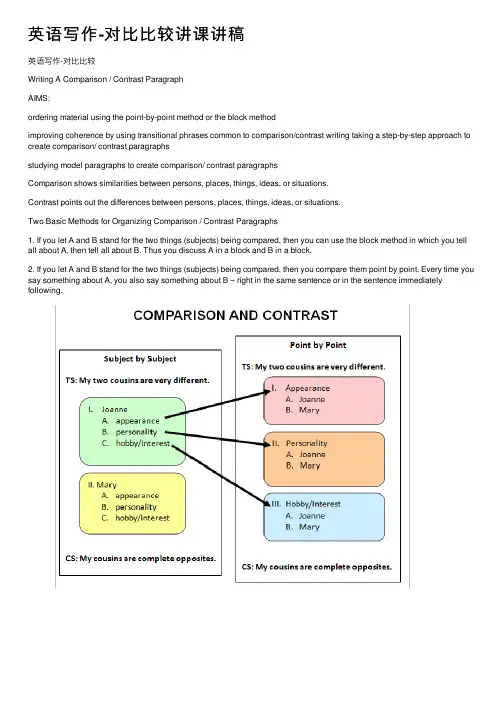
英语写作-对⽐⽐较讲课讲稿英语写作-对⽐⽐较Writing A Comparison / Contrast ParagraphAIMS:ordering material using the point-by-point method or the block methodimproving coherence by using transitional phrases common to comparison/contrast writing taking a step-by-step approach to create comparison/ contrast paragraphsstudying model paragraphs to create comparison/ contrast paragraphsComparison shows similarities between persons, places, things, ideas, or situations.Contrast points out the differences between persons, places, things, ideas, or situations.Two Basic Methods for Organizing Comparison / Contrast Paragraphs1. If you let A and B stand for the two things (subjects) being compared, then you can use the block method in which you tell all about A, then tell all about B. Thus you discuss A in a block and B in a block.2. If you let A and B stand for the two things (subjects) being compared, then you compare them point by point. Every time you say something about A, you also say something about B – right in the same sentence or in the sentence immediately following.The Topic SentenceYour topic sentence should identify both items (subjects) to be compared or contrasted and tell the reader exactly what you are going to say about these items (attitude).e.g., (poor) Our pup, Tuffy is different from our cat, Hector.(good) The difference in temperament between our pup, Tuffy, and our cat, Hector, is a constant source of amusement.The BodyOnce you have decided on a good topic sentence, list all the points of comparison/ contrast that you can think of. Next, reviewthe list and eliminate any points, which are irrelevant or unimportant. Now, organize your details in a logical sequence, and begin your rough draft.The ConclusionThe most effective conclusion for a comparison/contrast paragraph is usually a final sentence, which reinforces the controlling idea.e.g., If you could see Tuffy and Hector together, you could scarcely help laughing at the contrast between these two household playmates.A Good Example of the Block Method:Students who have Mr. Jones and Mr. Smith are immediately aware of the difference in the lecturing manner of each teacher. Mr. Jones has a pleasant voice, which helps hold the interest of the students. He pronounces clearly in a rhythmic pattern emphasizing key words. His moderate tone and inflected words make his lectures interesting. Mr. Jones also adds humour to his subject, and hewel comes questions from students who don’t understand the material. He takes his time and explains slowly. He tries to make sure that his students understand a concept before he moves on to something new, and he is very enthusiastic about his subject. Mr. Smith, on the other hand, has a different tone, pronunciation, expression and attitude from Mr. Jones. He has a booming voice, which commands rather than teaches, and sometimes it is hard to understand because he runs his words together. His lectures are not as interesting as those of Mr. Jones, either, because Mr. Smith speaks in a boring monotone. He also hates to be interrupted; feeling that he must cover everything. Mr. Smith teaches every class in a serious, determined mood. Thus, as the above points illustrate, the lectures of Mr. Jones and Mr. Smith are quite different.A Good Example of the Point-by-Point Method:Students who have Mr. Smith and Mr. Jones are immediately aware of the difference in the lecturing manner of each teacher. Mr. Jones has a pleasant voice, which helps hold the interest of the students. Mr. Smith, however, has a booming voice, which commands rather than teaches. Mr. Jones pronounces clearly in a rhythmic pattern emphasizing key words. On the other hand, Mr. Smith mumbles, running his words together. The moderate tone and inflected words of Mr. Jones make his lectures more interesting than those of Mr. Smith, who speaks in a boring monotone. Mr. Jones also adds humour to the subject, whereas Mr. Smith is always serious about each lesson. Mr. Jones welcomes questions from students who don’t understand the material, as compared to Mr. Smith who hates to be interrupted. Mr. Jones takes his time and explains slowly, whereas Mr. Smith rushes through each lesson. Mr. Jones is very enthusiastic about his subject: he tries to make sure everyone understands a concept before he moves on to something new. Mr. Smith, however, is always in a determined mood; he feels that he must cover everything. Each teacher has a different voice, tone, pronunciation, expression, and attitude: and as a result, their lectures are quite different. COMPARE AND CONTRAST Key Wordscomparison:like similar as same in the same way too bothmost important have in common the same as similarly as well as。



大学英文作文对比下载温馨提示:该文档是我店铺精心编制而成,希望大家下载以后,能够帮助大家解决实际的问题。
文档下载后可定制随意修改,请根据实际需要进行相应的调整和使用,谢谢!并且,本店铺为大家提供各种各样类型的实用资料,如教育随笔、日记赏析、句子摘抄、古诗大全、经典美文、话题作文、工作总结、词语解析、文案摘录、其他资料等等,如想了解不同资料格式和写法,敬请关注!Download tips: This document is carefully compiled by theeditor. I hope that after you download them,they can help yousolve practical problems. The document can be customized andmodified after downloading,please adjust and use it according toactual needs, thank you!In addition, our shop provides you with various types ofpractical materials,such as educational essays, diaryappreciation,sentence excerpts,ancient poems,classic articles,topic composition,work summary,word parsing,copyexcerpts,other materials and so on,want to know different data formats andwriting methods,please pay attention!Studying in high school and studying in college are two completely different experiences. In high school, you have a set schedule and are told what classes to take. In college, you have the freedom to choose your own schedule and classes.High school teachers often remind students about homework and upcoming tests, while college professors expect students to be responsible for keeping track of assignments and deadlines on their own.In high school, students are usually required to attend class every day, while in college, attendance policies vary by professor and class. Some professors may not take attendance at all, while others may have strict attendance policies.High school classes typically have around 20-30 students, while college lectures can have anywhere from 50to 300 students. This means that college students may have less interaction with their professors compared to high school students.In high school, students are often involved in extracurricular activities and sports teams, while in college, there are even more opportunities to get involved in clubs, organizations, and intramural sports.In high school, students may have a part-time job or participate in internships, but in college, students are often encouraged to seek out internships and co-op opportunities to gain real-world experience in their field of study.Overall, the transition from high school to college can be a big adjustment, but it also offers a lot more freedom and opportunities for personal and academic growth.。





英语写作-对比比较Writing A Comparison / Contrast ParagraphAIMS:ordering material using the point-by-point method or the block methodimproving coherence by using transitional phrases common to comparison/contrast writing taking a step-by-step approach to create comparison/ contrast paragraphsstudying model paragraphs to create comparison/ contrast paragraphsComparison shows similarities between persons, places, things, ideas, or situations.Contrast points out the differences between persons, places, things, ideas, or situations.Two Basic Methods for Organizing Comparison / Contrast Paragraphs1. If you let A and B stand for the two things (subjects) being compared, then you can use the block method in which you tell all about A, then tell all about B. Thus you discuss A in a block and B in a block.2. If you let A and B stand for the two things (subjects) being compared, then you compare them point by point. Every time you say something about A, you also say something about B – right in the same sentence or in the sentence immediately following.The Topic SentenceYour topic sentence should identify both items (subjects) to be compared or contrasted and tell the reader exactly what you are going to say about these items (attitude).e.g., (poor) Our pup, Tuffy is different from our cat, Hector.(good) The difference in temperament between our pup, Tuffy, and our cat, Hector, is a constant source of amusement.The BodyOnce you have decided on a good topic sentence, list all the points of comparison/ contrast that you can think of. Next, review the list and eliminate any points, which are irrelevant or unimportant. Now, organize your details in a logical sequence, and begin your rough draft.The ConclusionThe most effective conclusion for a comparison/contrast paragraph is usually a final sentence, which reinforces the controlling idea.e.g., If you could see Tuffy and Hector together, you could scarcely help laughing at the contrast between these two household playmates.A Good Example of the Block Method:Students who have Mr. Jones and Mr. Smith are immediately aware of the difference in the lecturing manner of each teacher. Mr. Jones has a pleasant voice, which helps hold the interest of the students. He pronounces clearly in a rhythmic pattern emphasizing key words. His moderate tone and inflected words make his lectures interesting. Mr. Jones also adds humour to his subject, and hewel comes questions from students who don’t understand the material. He takes his time and explains slowly. He tries to make sure that his students understand a concept before he moves on to something new, and he is very enthusiastic about his subject. Mr. Smith, on the other hand, has a different tone, pronunciation, expression and attitude from Mr. Jones. He has a booming voice, which commands rather than teaches, and sometimes it is hard to understand because he runs his words together. His lectures are not as interesting as those of Mr. Jones, either, because Mr. Smith speaks in a boring monotone. He also hates to be interrupted; feeling that he must cover everything. Mr. Smith teaches every class in a serious, determined mood. Thus, as the above points illustrate, the lectures of Mr. Jones and Mr. Smith are quite different.A Good Example of the Point-by-Point Method:Students who have Mr. Smith and Mr. Jones are immediately aware of the difference in the lecturing manner of each teacher. Mr. Jones has a pleasant voice, which helps hold the interest of the students. Mr. Smith, however, has a booming voice, which commands rather than teaches. Mr. Jones pronounces clearly in a rhythmic pattern emphasizing key words. On the other hand, Mr. Smith mumbles, running his words together. The moderate tone and inflected words of Mr. Jones make his lectures more interesting than those of Mr. Smith, who speaks in a boring monotone. Mr. Jones also adds humour to the subject, whereas Mr. Smith is always serious about each lesson. Mr. Jones welcomes questions from students who don’t understand the material, as compared to Mr. Smith who hates to be interrupted. Mr. Jones takes his time and explains slowly, whereas Mr. Smith rushes through each lesson. Mr. Jones is very enthusiastic about his subject: he tries to make sure everyone understands a concept before he moves on to something new. Mr. Smith, however, is always in a determined mood; he feels that he must cover everything. Each teacher has a different voice, tone, pronunciation, expression, and attitude: and as a result, their lectures are quite different. COMPARE AND CONTRAST Key Wordscomparison:like similar as same in the same way too bothmost important have in common the same as similarly as well ascontrast:although yet whereas however but while differ instead unlessunlike on the contrary contrary to even though on the other handthe reverseWhen you compare one subject to another, you show how the two are alike, or similar. Example: The dog, like the cat, is a household pet.When you contrast two subjects, you show how they are different.Example: The dog, unlike the cat, is dependent on its master.Sometimes, both comparison and contrast are used in the same sentence.Example: Both the dog and the cat make good household pets, but adog requires more attention than a cat.ExerciseRead the paragraphs and answer the questions below. Thousands of years ago the Native people of North America had to build houses that fit their life. One kind of house was a tipi. The Plains people lived in tipis. Tipis were easy to put up and take down. In fact, it only took about half an hour to set them up. This was perfect for the Plains people who spent their time hunting and following herds of animals.The Inuit, who lived in the cold Arctic region, spent part of the year living in igloos. Igloos were temporary homes like tipis. However, they were built for the cold winter months, whereas a tipi could be used year round. Both tipis and igloos had one main room that the family lived in and were usually made for a single family. Tipis and igloos were made of very different materials. Igloos were made from blocks of snow stacked on top of each other, while tipis were made from buffalo hide, tree bark, or grass. The shape of tipis and igloos was also different. Tipis were cone-shaped, using three or four poles for support. In contrast, igloos were dome-shaped.1. Is this paragraph comparing and contrasting two things?Yes No2. If no, how do you know it is not a compare and contrast paragraph?3. If yes, what two things are being compared?4. Circle the key words in the paragraph that show that the author was comparing and contrasting information.~~ In-class exercise: Using Comparison/Contrast ~~To get some practice using comparison/contrast as a rhetorical technique, prepare to write acomparison/contrast paragraph(s) based on one of the following topics (or come up with one you like better):•High school and College•Raising a pet and raising a child•Two career choices or majors you're contemplating•Two colleges you've considered attending•Two jobs you've had•Two books you've read, or two movies you've seen•Two close friends•Two teachersOnce you decide on your subject, follow the three steps below to help you practice using this technique. STEP 1: Establish categories to focus your analysis.For example, if you're comparing colleges, your categories might be curriculum, price, location, and social life.Brainstorm and then decide upon several appropriate categories for your topic which will focus how you look at each subject. List them below:STEP 2: Brainstorm raw material by applying these categories to questions about your subject.Based on the categories you arrived at above, ask what is similar and what is different about the two subjects. Write down everything you can think of—you can rearrange it later.Comparisons (similarities) between___________________and _______________________.1.2.3.4.5.Contrasts (differences) between _____________________and _______________________.1.2.3.4.5.Step 3: Assemble your analysis.Now examine the points you made and compile your raw material into paragraphs by using one or both of the methods described in Chapter Six (pp. 339-341). Write a topic sentence to focus yourcomparison/contrast; it should state your subjects and the assertion you want to make about them as a result of your analysis. After you write your topic sentence, write the paragraph(s) below. Attach extra paper if you run out of room. If you think it will help you get a clearer idea how to assemble your work, view a completed sample.。