铝合金的机械性能
- 格式:doc
- 大小:251.00 KB
- 文档页数:7

铝合金与钢的强度对比引言:铝合金与钢是两种常见的金属材料,在工程和制造领域广泛应用。
它们在强度方面有着不同的特点和优势。
本文将就铝合金与钢的强度对比进行详细探讨。
一、铝合金的强度特点:铝合金是一种轻质金属材料,具有较高的强度与优异的机械性能。
相对于钢材来说,铝合金的密度较低,约为钢材的三分之一,因此在相同重量条件下,铝合金的强度相对较高。
铝合金的拉伸强度通常可以达到200MPa以上,属于中等强度材料。
另外,铝合金还具备良好的耐腐蚀性,能够在恶劣环境下保持稳定的性能。
二、钢的强度特点:钢是一种强度较高的金属材料,具有优异的机械性能和较高的强度。
钢的密度相对较高,约为铝合金的三倍,但钢的拉伸强度通常可以达到400MPa以上,是一种高强度材料。
钢材具有良好的可塑性和可焊性,广泛应用于建筑、汽车、航空航天等领域。
三、强度对比:从整体来看,钢的强度相对于铝合金更高。
钢的高强度使其在承受重载或高压力的工程中具有明显的优势。
例如,在建筑结构中,由于需要承受巨大的重量和力量,通常选择使用钢材作为主要结构材料。
而铝合金的强度相对较低,适用于对重量要求较轻的场合,如航空航天领域的飞机和航天器结构。
然而,在某些特定情况下,铝合金的优势也是不可忽视的。
首先,铝合金的密度较低,轻量化的特性使其成为汽车制造业中的理想材料。
汽车使用铝合金可以减轻车身重量,提高燃油效率和行驶性能。
其次,铝合金具备良好的导热性能,可以广泛应用于热交换器和散热器等领域。
此外,铝合金还具有良好的导电性和可塑性,适合制造电子产品和薄壁结构。
四、结论:铝合金和钢材在强度方面具有不同的特点和优势。
钢材具有较高的强度和可靠性,适用于承受重载和高压力的工程领域。
而铝合金由于其轻质化和特殊的物理性能,在汽车、航空航天等领域具有广泛的应用前景。
因此,在实际应用中需要根据具体情况选择合适的材料,以满足工程要求和经济效益。
参考文献:1. 钢材的强度及其分类. [引用日期:2022年12月1日]. https://www.***.com/article/12345。


adc12铝合金性能ADC12是一种常见的铝合金,被广泛应用于工业生产中。
本文将介绍ADC12铝合金的性能特点、化学成分、机械性能、热性能以及应用领域等方面的内容。
一、性能特点ADC12铝合金具有以下几个显著的性能特点:1. 优良的铸造性能:ADC12铝合金具有较低的熔点和较高的流动性,有利于铸造工艺的实施,使得其可以用于各种压铸和浇铸工艺中。
2. 良好的机械性能:ADC12铝合金具有较高的抗拉强度和维氏硬度,同时还具有良好的耐蚀性和耐磨性,使得其在多种应力条件下具有出色的机械性能。
3. 优异的热稳定性:ADC12铝合金在高温条件下能够保持其较好的机械性能,不易发生变形和破损,适合在高温工作环境中使用。
4. 良好的焊接性能:ADC12铝合金具有良好的焊接性能,可以通过多种焊接方式进行连接,广泛应用于焊接结构和焊接工艺中。
二、化学成分ADC12铝合金的化学成分如下:铝(Al):≥88.0%铜(Cu):1.5-3.5%铁(Fe):≤1.3%锰(Mn):≤0.5%镁(Mg):≤0.3%锌(Zn):≤1.0%铅(Pb):≤0.1%锡(Sn):≤0.3%其他:≤0.5%三、机械性能ADC12铝合金的机械性能如下:1. 抗拉强度:≥215 MPa2. 屈服强度:≥160 MPa3. 延伸率:≥2.0%4. 硬度(HV):≥705. 密度:2.68g/cm³四、热性能ADC12铝合金的热性能如下:1. 熔点:577-633℃2. 热膨胀系数:22.2×10-6/℃3. 热导率:93.9 W/(m•K)4. 比热容:0.897 J/(g•℃)五、应用领域基于ADC12铝合金的优良性能,它被广泛应用于各个领域,其中包括但不限于以下几个方面:1. 汽车制造:ADC12铝合金常用于汽车零部件的制造,如车轮、缸盖、曲轴和转向器件等。
其高强度和轻质特性使得车辆更加经济高效。
2. 电子产品:ADC12铝合金可用于电子产品的外壳制造,如计算机外壳、摄影器材外壳等,其高热稳定性能有助于电子产品的散热。


6061铝的机械性能6061铝是一种轻质高强、耐腐蚀、无磁性、良好的热稳定性和加工性能的材料。
6061铝有很好的综合性能,在金属中是最好的合金之一,同时具有优良的延展性、导热性和抗蠕变性能。
铝合金具有良好的机械性能。
加工性状:1.冷加工时在室温下, Al (OH)2-0.01%-0.05%,Ni0.15%-0.25%2, Ni-1.5% Pb0.04%;热处理后室温下能保持20°C以上,H2O含量在9.5%~10.0%; Zn (OH)1.2 mol/L; Al0.1%~1.0% Be0.4 mg. mol; Zr0.5 mg等含10%以上(或60%)。
使用温度:120° C~280°C;室温下,温度一般在230℃~2700℃;3 h和30 h时可继续加热至470~550℃。
氧化后保持良好的物理和化学性能。
2. Al (OH)4:6061合金具有良好的焊接性,且可以将其熔化并作为母材继续使用,以减少变形或提高其硬度。
3.Fe2O3-氧化铝基合金是一种高铝的复合材料。
由于该合金有很好的强度和优良腐蚀性能,因此可以被用来制造成各种形状和用途之各类结构件(例如建筑构件、门窗框、船体等)。
近年来应用在汽车工业上越来越多有铝挤压型材应用在车体上。
6061铝具有良好的可塑性,可以用做零部件和建筑构件。
合金特点:耐腐蚀能力强,但较脆,使用中易破碎;力学性能优异的铝合金具有优良的热稳定性,特别是焊接时热稳定性好,高温脆性和热脆性较小而保持良好状态;可制成各种形状和尺寸。
一、耐腐蚀性6061铝为含碳量较高的合金,但其化学稳定性较高,除具有一般铝的化学成分外,还具有优良的耐腐蚀性能,可加工成各种零件。
1铝合金的腐蚀主要是由阳离子溶液与氧气的作用,氧化铝的阳极在氧化过程中生成 MnO, MnO和 N,而氧化铝又是氧化的络合物,因此使阳极与阴极之间有一个钝化膜来阻止离子(或电子)直接渗透到电解质溶液中去,从而阻止阳极与电解质之间的界面腐蚀。

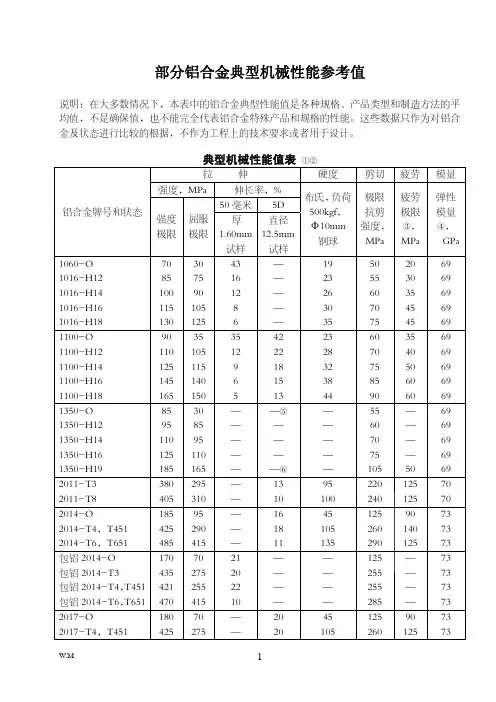
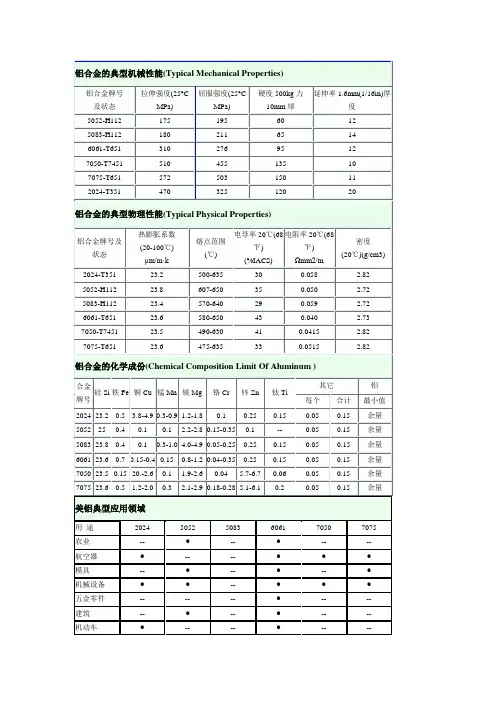
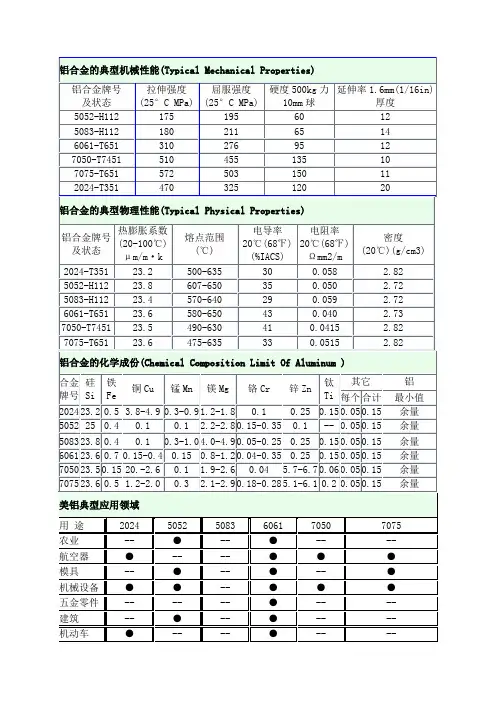
铝合金的典型机械性能(Typical Mechanical Properties)铝合金牌号及状态拉伸强度(25°C MPa) 屈服强度(25°C MPa) 硬度500kg力10mm球延伸率1.6mm(1/16in)厚度5052-H112 175 195 60 125083-H112 180 211 65 146061-T651 310 276 95 127050-T7451 510 455 135 107075-T651 572 503 150 112024-T351 470 325 120 20铝合金的典型物理性能(Typical Physical Properties)铝合金牌号及状态热膨胀系数(20-100℃)μm/m•k 熔点范围(℃) 电导率20℃(68℉)(%IACS) 电阻率20℃(68℉)Ωmm2/m 密度(20℃)(g/cm3)2024-T351 23.2 500-635 30 0.058 2.825052-H112 23.8 607-650 35 0.050 2.725083-H112 23.4 570-640 29 0.059 2.726061-T651 23.6 580-650 43 0.040 2.737050-T7451 23.5 490-630 41 0.0415 2.827075-T651 23.6 475-635 33 0.0515 2.82铝合金的化学成份(Chemical Composition Limit Of Aluminum )合金牌号硅Si 铁Fe 铜Cu 锰Mn 镁Mg 铬Cr 锌Zn 钛Ti 其它铝每个合计最小值2024 23.2 0.5 3.8-4.9 0.3-0.9 1.2-1.8 0.1 0.25 0.15 0.05 0.15 余量5052 25 0.4 0.1 0.1 2.2-2.8 0.15-0.35 0.1 -- 0.05 0.15 余量5083 23.8 0.4 0.1 0.3-1.0 4.0-4.9 0.05-0.25 0.25 0.15 0.05 0.15 余量6061 23.6 0.7 0.15-0.4 0.15 0.8-1.2 0.04-0.35 0.25 0.15 0.05 0.15 余量7050 23.5 0.15 20.-2.6 0.1 1.9-2.6 0.04 5.7-6.7 0.06 0.05 0.15 余量7075 23.6 0.5 1.2-2.0 0.3 2.1-2.9 0.18-0.28 5.1-6.1 0.2 0.05 0.15 余量美铝典型应用领域用途2024 5052 5083 6061 7050 7075农业-- ●-- ●-- --航空器●-- -- ●●●模具-- ●-- ●-- ●机械设备●●-- ●●●五金零件-- -- -- ●-- --建筑-- ●-- ●-- --机动车●-- -- ●-- --建筑产品-- ●-- ●-- --化学设备-- -- -- ●-- --集装箱-- -- -- -- -- --烹饪用具-- -- -- -- -- --圆筒或活塞●-- -- ●-- --泵体-- -- -- ●-- --电子-- -- -- ●-- --电工-- ●-- ●-- --紧固件●●-- ●●●屏蔽线-- -- -- ●-- --风叶-- -- -- ●-- --家具-- -- -- ●-- --筒状容器-- -- -- -- -- --硬件装置●-- -- ●●●医疗设备●-- -- ●-- --厨房设备-- ●-- ●-- --灯座-- -- -- -- -- --水上用途-- ●-- ●-- --机械配件●-- -- ●●●名称招牌-- -- -- -- -- --军火用品●-- -- ●●●管道-- -- -- ●-- --车体-- ●-- ●-- --娱乐设施●-- -- ●●●储存箱-- ●-- ●-- --架构-- -- -- ●-- --卡车与拖车-- ●-- ●-- --拉链-- -- -- -- -- --现货供应型号板材圆棒扁条/方条6061 T6 ●●●6061 T651 ●-- --6061 T6511 -- ●--7075 T651 ●-- --7075 T6 ●●--5052 H112 精度板●-- --5052 H32 冲压板●-- --5083 H112 ●-- --Alumould ●-- --Mic-6 ●-- --2024 ●-- --K-100 ●-- --产品参数中、美常用铝合金牌号对照表中国CHINA 美国THE UNITED STA TESL1-L6 、L5-1 1070 、1060 、1050 、1030 、1100L Y11 、L Y12 、L Y1 2017 、2024 、2117LD10 、LD5 2014 、2214LD7 2618LD9 、LD8 2018 、2218L Y16 、L Y17 2219 、2021LF21 3003LF2 、LF3 、LF4 5052 、5154 、5083LF5 、LF11 、LF6 、LF5-1 5456 、5056LD2 、LD2-1 、LD2-2 、LD30 、LD31 6165 、6061 、6055 、6063 LC6 、LC4 、LC9 7001 、7178 、7075LC5 、LC10 7076 、7175 、7079LD11 4032中国新旧合金牌号对照表(GB/T 3190-1996)新牌号旧牌号新牌号旧牌号新牌号旧牌号1A99 原LG5 2B12 原L Y9 3003 -1A97 原LG4 2A13 原L Y13 3103 -1A95 -2A14 原LD10 3004 -1A93 原LG3 2A16 原L Y16 3005 -1A90 原LG2 2B16 曾用Ly16-1 3105 -1A85 原LG1 2A17 原L Y17 4A01 原LT11080 -2A20 曾用L Y20 4A11 原LD111080A -2A21 曾用214 4A13 原LT131070 -2A25 曾用225 4A17 原LT171070A 代L1 2A49 曾用149 4004 -1370 -2A50 原LD5 4032 -1060 代L2 2B50 原LD6 4043 -1050 -2A70 原LD7 4043A -1050A 代L3 2B70 曾用LD7-1 4047 -1A50 原LB2 2A80 原LD8 4047A -1350 -2A90 原LD9 5A01 曾用2101、LF151145 -2004 -5A02 原LF21035 代L4 2011 -5A03 原LF31A30 原L4-1 2014 -5A05 原LF51100 代LF5-1 2014A -5B05 原LF101200 代L5 2214 -5A06 原LF61235 -2017 -5B06 原LF142A01 原L Y1 2017A -5A12 原LF122A02 原L Y2 2117 -5A13 原LF132A04 原L Y4 2218 -5A30 曾用2103、LF162A06 原L Y6 2618 -5A33 原LF332A10 原L Y10 2219 曾用L Y19、147 5A41 原LT412A11 原L Y11 2024 -5A43 原LF432B11 原L Y8 2124 -5A66 原LT662A12 原L Y12 3A21 原LF21 5005 -5019 -6B02 原LD2-1 7A09 原LC95050 -6A51 曾用651 7A10 原LC105251 -6101 -7A15 曾用LC15、1575052 -6101A -7A19 曾用919、LC195154 -6005 -7A31 曾用183-15154A -6005A -7A33 曾用LB7335454 -6351 -7A52 曾用LC52、52105554 -6060 -7003 原LC125754 -6061 原LD30 7005 -5056 原LF5-1 6063 原LD31 7020 -5356 -6063A -7022 -5456 -6070 原LD2-2 7050 -5082 -6181 -7075 -5182 -6082 -7475 -5083 原LF4 7A01 原LB1 8A06 原L65183 -7A03 原LC3 8011 曾用LT985086 -7A04 原LC4 8090 -6A02 原LD2 7A05 曾用705 --注意:(1)“原”是指化学成分与新牌号等同,且都符合GB3190-82规定的旧牌号。
Aluminum 7475-T651Categories: Metal; Nonferrous Metal; Aluminum Alloy; 7000 Series Aluminum AlloyMaterial Notes: Data points with the AA note have been provided by the Aluminum Association, Inc. and are NOT FOR DESIGN.Composition Notes:Composition information provided by the Aluminum Association and is not for design.Key Words: UNS A97475; ISOu(A); Aluminium 7475-T651; AA7475-T651UNS A97475; ISO AlZn5.5MgCu(A); Aluminium 7475-T7651; AA7475-T7651Vendors: Click here to view all available suppliers for this material.Please click here if you are a supplier and would like information on how to add yourlisting to this material.Printer friendly versionDownload as PDFDownload to Excel(requires Excel and Windows)PropertiesDensity 2.81 g/cc 0.102 lb/in³AA; Typical MechanicalPropertiesMetric English CommentsHardness, Brinell 150 150 500 kg load with 10 mm ball.Calculated value.Hardness, Knoop 190 190 Converted from Brinell HardnessValueHardness, Rockwell A 53.5 53.5 Converted from Brinell HardnessValueHardness, Rockwell B 87 87 Converted from Brinell HardnessValueHardness, Vickers 175 175 Converted from Brinell HardnessValueTensileStrength,Ultimate586 MPa 85000 psi AA; TypicalTensileStrength,Yield510 MPa 74000 psi AA; TypicalElongation at Break13.0 %@Diameter 12.7 mm13.0 %@Diameter 0.500 inAA; TypicalModulus of Elasticity 71.7 GPa 10400 ksi AA; Typical; Average of tension andcompression. Compression modulusis about 2% greater than tensilemodulus.PoissonsRatio0.330 0.330FractureToughness29.7 MPa-m½ 27.0 ksi-in½ plate; S-L37.4 MPa-m½ 34.0 ksi-in½ plate; T-L42.9 MPa-m½ 39.0 ksi-in½ plate; L-T Machinability 70 % 70 % 0-100 Scale of Aluminum Alloys ShearModulus27.0 GPa 3920 ksiShearStrength350 MPa 50800 psi Calculated value.Electrical Properties Metric English Comments ElectricalResistivity0.00000499 ohm-cm @Temperature 20.0 °C 0.00000499 ohm-cm@Temperature 68.0 °F AA; TypicalThermal Properties Metric English CommentsCTE, linear21.6 µm/m-°C @Temperature -50.0 - 20.0 °C 12.0 µin/in-°F@Temperature -58.0 - 68.0 °F23.2 µm/m-°C @Temperature 20.0 - 100 °C 12.9 µin/in-°F@Temperature 68.0 - 212 °FAA; Typical; average over range23.4 µm/m-°C @Temperature 20.0 - 100 °C 13.0 µin/in-°F@Temperature 68.0 - 212 °F24.3 µm/m-°C @Temperature 20.0 - 200 °C 13.5 µin/in-°F@Temperature 68.0 - 392 °F25.2 µm/m-°C @Temperature 20.0 - 300 °C 14.0 µin/in-°F@Temperature 68.0 - 572 °F25.2 µm/m-°C @Temperature 20.0 - 300 °C 14.0 µin/in-°F@Temperature 68.0 - 572 °FaverageSpecific Heat Capacity 0.880 J/g-°C 0.210 BTU/lb-°F Estimated from trends in similar Alalloys.Thermal Conductivity 138 W/m-K 960 BTU-in/hr-ft²-°F AA; Typical at 77°FMelting Point 477 - 635.0 °C 890 - 1175 °F AA; Typical range based on typicalcomposition for wrought products 1/4inch thickness or greaterSolidus 477 °C 890 °F AA; Typical Liquidus 635.0 °C 1175 °F AA; TypicalProcessing Properties Metric English CommentsAnnealing Temperature 413 °C 775 °FSolutionTemperature 516 °C 960 °F must be preceded by soak at 870 to890°FAgingTemperature 121 - 177 °C250 - 350 °FComponent Elements Properties MetricEnglish Comments Aluminum, Al88.5 - 91.5 % 88.5 - 91.5 % As remainderChromium, Cr0.18 - 0.25 % 0.18 - 0.25 % Copper, Cu 1.20 - 1.90 % 1.20 - 1.90 % Iron, Fe <= 0.12 % <= 0.12 % Magnesium, Mg1.90 -2.60 % 1.90 - 2.60 % Manganese, Mn<= 0.060 % <= 0.060 % Other, each <= 0.050 % <= 0.050 % Other, total <= 0.15 % <= 0.15 % Silicon, Si <= 0.10 % <= 0.10 % Titanium, Ti <= 0.060 % <= 0.060 % Zinc, Zn5.20 -6.20 %5.20 -6.20 %References for this datasheet.Aluminum 7075-T6; 7075-T651 Categories: M etal; Nonferrous Metal; Aluminum Alloy; 7000 Series Aluminum AlloyMaterial Notes: General 7075 characteristics and uses (from Alcoa): Very high strength material used for highly stressed structural parts. The T7351 temper offers improved stress-corrosion cracking resistance.Applications: Aircraft fittings, gears and shafts, fuse parts, meter shafts and gears, missile parts, regulating valve parts, worm gears, keys, aircraft, aerospace and defense applications; bike frames, all terrain vehicle (ATV) sprockets.Data points with the AA note have been provided by the Aluminum Association, Inc. and are NOT FOR DESIGN.Composition Notes:A Zr + Ti limit of 0.25 percent maximum may be used with this alloy designation for extruded and forged products only, but only when the supplier or producer and the purchaser have mutually so agreed. Agreement may be indicated, for example, by reference to a standard, by letter, by order note, or other means which allow the Zr + Ti limit.Composition information provided by the Aluminum Association and is not for design.Key Words: A luminium 7075-T6; Aluminium 7075-T651, UNS A97075; ISO AlZn5.5MgCu; Aluminium 7075-T6; Aluminium 7075-T651; AA7075-T6Vendors: Click here to view all available suppliers for this material.Please click here if you are a supplier and would like information on how to add yourlisting to this material.Printer friendly versionDownload as PDFDownload to Excel(requires Excel and Windows)PropertiesDensity 2.81 g/cc 0.102 lb/in³AA; TypicalMechanicalPropertiesMetric English CommentsHardness,Brinell150 150 AA; Typical; 500 g load; 10 mm ballHardness, Knoop 191 191 Converted from Brinell HardnessValueHardness, Rockwell A 53.5 53.5 Converted from Brinell HardnessValueHardness, Rockwell B 87 87 Converted from Brinell HardnessValueHardness, Vickers 175 175 Converted from Brinell HardnessValueTensileStrength,Ultimate572 MPa 83000 psi AA; Typical41.0 MPa @Temperature 371 °C5950 psi @Temperature 700 °F55.0 MPa @Temperature 316 °C7980 psi @Temperature 601 °F76.0 MPa @Temperature 260 °C11000 psi @Temperature 500 °F110 MPa @Temperature 204 °C16000 psi @Temperature 399 °F214 MPa@Temperature 149 °C31000 psi@Temperature 300 °F483 MPa@Temperature 100 °C70100 psi@Temperature 212 °F572 MPa@Temperature 24.0 °C83000 psi@Temperature 75.2 °F593 MPa@Temperature -28.0 °C86000 psi@Temperature -18.4 °F621 MPa@Temperature -80.0 °C90100 psi@Temperature -112 °F703 MPa@Temperature -196 °C102000 psi@Temperature -321 °F>= 462 MPa@Thickness 88.93 - 102 mm>= 67000 psi@Thickness 3.501 - 4.00 inPlate; T62, T651>= 490 MPa@Thickness 76.23 - 88.9 mm>= 71100 psi@Thickness 3.001 - 3.50 inPlate; T62, T651>= 496 MPa@Thickness 63.53 - 76.2 mm>= 71900 psi@Thickness 2.501 - 3.00 inPlate; T62, T651>= 510 MPa@Thickness 0.203 - 0.279 mm>= 74000 psi@Thickness 0.00800 - 0.0110 inSheet>= 524 MPa@Thickness 0.305 - 0.991 mm>= 76000 psi@Thickness 0.0120 - 0.0390 inSheet>= 524 MPa@Thickness 50.83 - 63.5 mm>= 76000 psi@Thickness 2.001 - 2.50 inPlate; T62, T651>= 531 MPa@Thickness 25.43 - 50.8 mm>= 77000 psi@Thickness 1.001 - 2.00 inPlate; T62, T651>= 538 MPa@Thickness 1.02 - 3.17 mm>= 78000 psi@Thickness 0.0400 - 0.125 inSheet>= 538 MPa@Thickness 3.20 - 6.32 mm>= 78000 psi@Thickness 0.126 - 0.249 inSheet>= 538 MPa@Thickness 6.35 - 12.7 mm>= 78000 psi@Thickness 0.250 - 0.499 inPlate; T62, T651>= 538 MPa@Thickness 12.7 - 25.4 mm>= 78000 psi@Thickness 0.500 - 1.00 inPlate; T62, T651 TensileStrength,Yield503 MPa 73000 psi AA; Typical>= 372 MPa@Thickness 88.93 - 102 mm>= 54000 psi@Thickness 3.501 - 4.00 inPlate; T62, T651>= 400 MPa@Thickness 76.23 - 88.9 mm>= 58000 psi@Thickness 3.001 - 3.50 inPlate; T62, T651>= 421 MPa@Thickness 63.53 - 76.2 mm>= 61100 psi@Thickness 2.501 - 3.00 inPlate; T62, T651>= 434 MPa@Thickness 0.203 - 0.279 mm>= 62900 psi@Thickness 0.00800 - 0.0110 inSheet>= 441 MPa@Thickness 50.83 - 63.5 mm>= 64000 psi@Thickness 2.001 - 2.50 inPlate; T62, T651>= 462 MPa@Thickness 0.305 - 0.991 mm>= 67000 psi@Thickness 0.0120 - 0.0390 inSheet>= 462 MPa@Thickness 6.35 - 12.7 mm>= 67000 psi@Thickness 0.250 - 0.499 inPlate; T62, T651>= 462 MPa@Thickness 25.43 - 50.8 mm>= 67000 psi@Thickness 1.001 - 2.00 inPlate; T62, T651>= 469 MPa@Thickness 1.02 - 3.17 mm>= 68000 psi@Thickness 0.0400 - 0.125 inSheet>= 469 MPa@Thickness 12.7 - 25.4 mm>= 68000 psi@Thickness 0.500 - 1.00 inPlate; T62, T651>= 476 MPa@Thickness 3.20 - 6.32 mm>= 69000 psi@Thickness 0.126 - 0.249 inSheet32.0 MPa@Strain 0.200 %,Temperature 271 °C4640 psi@Strain 0.200 %,Temperature 520 °F45.0 MPa@Strain 0.200 %,Temperature 316 °C6530 psi@Strain 0.200 %,Temperature 601 °F62.0 MPa@Strain 0.200 %,Temperature 260 °C8990 psi@Strain 0.200 %,Temperature 500 °F87.0 MPa12600 psi@Strain 0.200 %, Temperature 204 °C@Strain 0.200 %, Temperature 399 °F186 MPa @Strain 0.200 %, Temperature 149 °C27000 psi @Strain 0.200 %, Temperature 300 °F448 MPa @Strain 0.200 %, Temperature 100 °C65000 psi @Strain 0.200 %, Temperature 212 °F503 MPa @Strain 0.200 %, Temperature 24.0 °C73000 psi @Strain 0.200 %, Temperature 75.2 °F517 MPa @Strain 0.200 %, Temperature -28.0 °C75000 psi @Strain 0.200 %, Temperature -18.4 °F545 MPa @Strain 0.200 %, Temperature -80.0 °C79000 psi @Strain 0.200 %, Temperature -112 °F634 MPa @Strain 0.200 %, Temperature -196 °C92000 psi @Strain 0.200 %, Temperature -321 °FElongation atBreak9.00 %@Temperature -196 °C9.00 %@Temperature -321 °F11.0 %@Temperature -80.0 °C11.0 %@Temperature -112 °F11.0 %@Temperature -28.0 °C11.0 %@Temperature -18.4 °F11.0 %@Temperature 24.0 °C11.0 %@Temperature 75.2 °F14.0 %@Temperature 100 °C14.0 %@Temperature 212 °F30.0 %@Temperature 149 °C30.0 %@Temperature 300 °F55.0 %@Temperature 204 °C55.0 %@Temperature 399 °F65.0 %@Temperature 260 °C65.0 %@Temperature 500 °F70.0 %@Temperature 316 °C70.0 %@Temperature 601 °F70.0 %@Temperature 371 °C70.0 %@Temperature 700 °F>= 3.00 % @Thickness 88.93 - 102 mm>= 3.00 %@Thickness 3.501 - 4.00 inPlate; T62, T651>= 5.00 % @Thickness 0.203 - 0.279 mm>= 5.00 %@Thickness 0.00800 - 0.0110 inSheet>= 5.00 % @Thickness 50.83 - 63.5 mm>= 5.00 %@Thickness 2.001 - 2.50 inPlate; T62, T651>= 5.00 % @Thickness 63.53 - 76.2 mm>= 5.00 %@Thickness 2.501 - 3.00 inPlate; T62, T651>= 5.00 % @Thickness 76.23 - 88.9 mm>= 5.00 %@Thickness 3.001 - 3.50 inPlate; T62, T651>= 6.00 % @Thickness 25.43 - 50.8 mm>= 6.00 %@Thickness 1.001 - 2.00 inPlate; T62, T651>= 7.00 % @Thickness 0.305 - 0.991 mm>= 7.00 %@Thickness 0.0120 - 0.0390 inSheet>= 7.00 % @Thickness 12.7 - 25.4 mm>= 7.00 %@Thickness 0.500 - 1.00 inPlate; T62, T651>= 8.00 % @Thickness 1.02 - 3.17 mm>= 8.00 %@Thickness 0.0400 - 0.125 inSheet>= 8.00 % @Thickness 3.20 - 6.32 mm>= 8.00 %@Thickness 0.126 - 0.249 inSheet>= 9.00 % @Thickness 6.35 - 12.7 mm>= 9.00 %@Thickness 0.250 - 0.499 inPlate; T62, T65111.0 % @Thickness 1.59 mm11.0 %@Thickness 0.0625 inAA; Typical11.0 % @Diameter 12.7 mm11.0 %@Diameter 0.500 inAA; TypicalModulus of Elasticity 71.7 GPa 10400 ksi AA; Typical; Average of tensionand compression. Compressionmodulus is about 2% greater thantensile modulus. PoissonsRatio0.330 0.330Fatigue Strength159 MPa@# of Cycles 5.00e+823000 psi@# of Cycles 5.00e+8completely reversed stress; RRMoore machine/specimenFractureToughness17.6 MPa-m½ 16.0 ksi-in½ T651; Plate; S-L; average16.5 - 19.8 MPa-m½ 15.0 - 18.0 ksi-in½ T651; Plate; S-L18.7 MPa-m½ 17.0 ksi-in½ T651; Forgings; S-L20.0 MPa-m½ 18.2 ksi-in½ K(IC) in S-L Direction22.0 - 25.3 MPa-m½ 20.0 - 23.0 ksi-in½ T651; Plate; T-L24.2 MPa-m½ 22.0 ksi-in½ T651; Plate; T-L; average25.0 MPa-m½ 22.8 ksi-in½ K(IC) in T-L Direction28.6 MPa-m½ 26.0 ksi-in½ T651; Plate; L-T; average27.5 - 29.7 MPa-m½ 25.0 - 27.0 ksi-in½ T651; Plate; L-T29.0 MPa-m½ 26.4 ksi-in½ K(IC) in L-T Direction Machinability 70 % 70 % 0-100 Scale of Aluminum Alloys ShearModulus26.9 GPa 3900 ksiShearStrength331 MPa 48000 psi AA; TypicalElectricalPropertiesMetric English CommentsElectrical Resistivity 0.00000515 ohm-cm@Temperature 20.0 °C0.00000515 ohm-cm@Temperature 68.0 °FAA; TypicalThermalPropertiesMetric English CommentsCTE, linear21.6 µm/m-°C@Temperature -50.0 - 20.0 °C12.0 µin/in-°F@Temperature -58.0 - 68.0 °F23.4 µm/m-°C@Temperature 20.0 - 100 °C13.0 µin/in-°F@Temperature 68.0 - 212 °F23.6 µm/m-°C@Temperature 20.0 - 100 °C13.1 µin/in-°F@Temperature 68.0 - 212 °FAA; Typical; average over range24.3 µm/m-°C@Temperature 20.0 - 200 °C13.5 µin/in-°F@Temperature 68.0 - 392 °F25.2 µm/m-°C@Temperature 20.0 - 300 °C14.0 µin/in-°F@Temperature 68.0 - 572 °F25.2 µm/m-°C@Temperature 20.0 - 300 °C14.0 µin/in-°F@Temperature 68.0 - 572 °FaverageSpecific HeatCapacity0.960 J/g-°C 0.229 BTU/lb-°FThermalConductivity130 W/m-K 900 BTU-in/hr-ft²-°F AA; Typical at 77°F Melting Point 477 - 635.0 °C 890 - 1175 °F AA; Typical range based on typicalcomposition for wrought products1/4 inch thickness or greater.Homogenization may raise eutecticmelting temperature 20-40°F butusually does not eliminate eutecticmelting. Solidus 477 °C 890 °F AA; Typical Liquidus 635.0 °C 1175 °F AA; Typical ProcessingPropertiesMetric English Comments AnnealingTemperature413 °C 775 °FSolutionTemperature466 - 482 °C 870 - 900 °FAgingTemperature121 °C 250 °FComponentMetric English Comments ElementsProperties87.1 - 91.4 % 87.1 - 91.4 % As remainder Aluminum,AlChromium,0.18 - 0.280 % 0.18 - 0.280 %CrCopper, Cu 1.20 - 2.0 % 1.20 - 2.0 %Iron, Fe <= 0.50 % <= 0.50 %Magnesium,2.10 - 2.90 % 2.10 - 2.90 %Mg<= 0.30 % <= 0.30 %Manganese,MnOther, each <= 0.050 % <= 0.050 %Other, total <= 0.15 % <= 0.15 %Silicon, Si <= 0.40 % <= 0.40 %Titanium, Ti <= 0.20 % <= 0.20 %Zinc, Zn 5.10 - 6.10 % 5.10 - 6.10 %References for this datasheet.。

6061铝合金机械性能6061铝合金机械性能表现在有高抗拉强度,延伸率、弹性系数以及耐疲劳的特性。
6061铝合金的机械性能:6061的极限抗拉强度为124 MPa受拉屈服强度55.2 MPa延伸率25.0 %弹性系数68.9 GPa弯曲极限强度228 MPaBearing Yield Strength 103 MPa泊松比0.330疲劳强度62.1 MPa铝合金可以采用热处理获得良好的机械性能,物理性能和抗腐蚀性能。
可热处理强化型铝合金可以通过淬火和时效等热处理手段来提高机械性能,它可分为硬铝、锻铝、超硬铝和特殊铝合金等。
6061铝合金的热处理工艺:1)快速退火:加热温度350~410℃;随材料有效厚度的不同,保温时间在30~120min之间;空气或水冷。
2)高温退火:加热温度350~500℃;成品厚度≥6mm时,保温时间为10~30min、<6mm时,热透为止;空气冷。
3)低温退火:加热温度150~250℃;保温时间为2~3h;空气或水冷。
硅对硬质合金有腐蚀作用。
虽然一般将超过12%Si的铝合金称为高硅铝合金,推荐使用金刚石刀具,但这不是绝对的,硅含量逐渐增多对刀具的破坏力也逐渐加大。
因此有些厂商在硅含量超过8%时就推荐使用金刚石刀具。
硅含量在8%-12%之间的铝合金是一个过渡区间,既可以使用普通硬质合金,也可以使用金刚石刀具。
但使用硬质合金应使用经PVD(物理镀层)方法、不含铝元素的、膜层厚度较小的刀具。
因为PVD方法和小的膜层厚度使刀具保持较锋利的切削刃成为可能(否则为避免膜层在刃口处异常长大需要对刃口进行足够的钝化,切铝合金就会不够锋利),而膜层材料含铝可能使刀片膜层与工件材料发生亲合作用而破坏膜层与刀具基体的结合。
因为目前的超硬镀层多为铝、氮、钛三者的化合物,可能会因硬质合金基体随膜层剥落时少量剥落造成崩刃。
6061铝合金机械性能使其成为理想的结构材料,广泛用于机械制造、运输机械、动力机械及航空工业等方面,飞机的机身、蒙皮、压气机等常以铝合金制造,以减轻自重。

2a12铝合金机械参数
2A12铝合金是一种常用的铝合金材料,具有优异的机械性能。
它的机械参数包括强度、塑性和硬度等指标。
2A12铝合金具有较高的强度。
它的屈服强度为≥310MPa,抗拉强度为≥485MPa。
这意味着2A12铝合金在受力时能够承受较大的荷载,具有较好的抗拉伸性能。
2A12铝合金具有良好的塑性。
它的延伸率为≥10%,表明在受力时能够发生较大的塑性变形而不易断裂。
这使得2A12铝合金在加工过程中具有较好的可塑性,可以通过冷加工、热加工等方式进行成型。
2A12铝合金还具有一定的硬度。
它的硬度为≥110HB,表明它具有一定的抗刮擦性能和抗磨损性能。
这使得2A12铝合金在使用过程中能够更好地抵抗表面的磨损和损伤。
2A12铝合金具有较高的强度、良好的塑性和一定的硬度。
它在航空、航天、汽车、船舶等领域得到广泛应用。
随着科学技术的不断进步,人们对2A12铝合金的研究和应用也在不断深入,相信它将为各行各业带来更多的机遇和挑战。
zl105铝合金标准随着工业化的快速发展,铝合金作为一种轻质高强度的材料,被广泛应用于航空、汽车、建筑等领域。
为了保证铝合金产品的质量和安全性,国家制定了一系列的标准,其中zl105铝合金标准是其中之一。
zl105铝合金是一种铝镍合金,具有优异的耐腐蚀性和高温强度。
该合金常用于制造高速飞行器、航空发动机、高温炉具等高端产品。
为了保证产品的质量和安全性,制定了zl105铝合金标准。
zl105铝合金标准主要包括以下几个方面:1. 化学成分:zl105铝合金的化学成分应符合国家标准GB/T 3190-2008中的规定。
其中,铝的含量应不少于95%,镍的含量应在0.6%~1.2%之间。
2. 机械性能:zl105铝合金的机械性能应符合国家标准GB/T 3880.2-2012中的规定。
其中,抗拉强度应不少于360MPa,屈服强度应不少于320MPa,延伸率应不少于10%。
3. 热处理:zl105铝合金的热处理应符合国家标准GB/T 3191-2010中的规定。
其中,常规热处理工艺为固溶处理+自然时效。
固溶处理温度为530℃~550℃,保温时间为1~2小时;自然时效时间为24小时。
4. 检验方法:zl105铝合金的检验方法应符合国家标准GB/T 228-2002中的规定。
其中,化学成分检验方法采用光谱分析法;机械性能检验方法采用拉伸试验、硬度试验等方法;热处理检验方法采用金相组织观察、硬度试验等方法。
5. 其他要求:zl105铝合金还应符合国家标准GB/T 3199-2010中的规定,如表面质量、尺寸偏差、加工性能等方面的要求。
总之,zl105铝合金标准是保证产品质量和安全性的重要标准之一。
生产厂家和使用者都应该遵守相关标准,并严格执行相关检验方法,以确保产品质量和安全性。