-中医学英文词汇
- 格式:doc
- 大小:199.50 KB
- 文档页数:10

中医英语词汇中医学是中国传统医学的一部分,拥有丰富的词汇和术语。
在全球范围内,中医学已经成为一门备受关注的学科。
为了更好地促进中医学的国际交流,以下是一些中医英语词汇的介绍。
1. 中医学 (Traditional Chinese Medicine, TCM): 中医学是通过整体观念和系统化的理论体系,对人体生理与病理进行分析和治疗的医学体系。
2. 阴阳 (Yin and Yang): 阴阳是中医学中的基本概念之一,代表了宇宙和万物中相互依存、相互对立、相互转化的两个相对方面。
在人体中,阴阳平衡是保持健康的基础。
3. 气 (Qi): 气是中医学中的重要概念,指的是生命活动中的能量。
气的流动和平衡对于身体健康至关重要。
4. 经络(Meridians): 经络是中医学中描述人体气血运行通路的概念。
通过调理经络可以调整身体的功能和气血流动。
5. 穴位 (Acupoints): 穴位是经络上的特定点位,通过刺激这些穴位可以改善身体的健康状况。
6. 中药 (Traditional Chinese Medicine, TCM): 中药是中医学中使用的草药、矿物和动物制品的总称。
中药通过调整身体的阴阳平衡和气血流动来治疗疾病。
7. 针灸 (Acupuncture): 针灸是中医学中常用的治疗方法,通过插入细针刺激穴位来调整身体的功能和气血流动。
8. 推拿 (Tuina): 推拿是一种中医学的按摩疗法,通过按摩经络和穴位来调节身体的气血流动,舒缓疼痛和改善健康。
9. 拔罐 (Cupping): 拔罐是中医学中常用的一种疗法,通过在皮肤上制造负压来促进血液循环和淋巴流动,增强身体的免疫力和代谢功能。
10. 艾灸 (Moxibustion): 艾灸是一种中医学的疗法,通过点燃艾草或艾条对穴位进行刺激,促进气血流动和身体的自愈能力。
以上只是中医学中部分重要词汇的介绍,中医学是一个复杂而庞大的学科,拥有非常丰富的文化内涵。

中医词语对应的英文翻译以下是一些中医常用词语及其对应的英文翻译,供参考。
1. 中药:Chinese medicine2. 针灸:Acupuncture3. 脉象:Pulse condition4. 望、闻、问、切:Observation, listening, inquiry, palpation5. 辨证论治:Syndrome differentiation and treatment6. 气滞血瘀:Qi stagnation and blood stasis7. 气血两虚:Qi and blood deficiency8. 风寒感冒:Wind-cold感冒9. 湿热证:Damp-heat syndrome10. 脾胃虚弱:Spleen-stomach weakness11. 肝火旺盛:Liver fire flaming12. 心火旺盛:Heart fire flaming13. 肺热咳嗽:Lung heat cough14. 脾虚泄泻:Spleen deficiency diarrhea15. 肾虚腰痛:Kidney deficiency waist pain16. 湿温病:Damp-heat disease17. 风湿病:Rheumatism18. 痛经:Menstrual pain19. 月经不调:Menstrual irregularity20. 更年期综合症:Menopause syndrome21. 肥胖症:Obesity22. 高血压病:Hypertension23. 糖尿病:Diabetes24. 失眠:Insomnia25. 抑郁症:Depression26. 焦虑症:Anxiety disorder27. 自闭症:Autism28. 强迫症:OCD (Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder)29. 多动症:ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder)30. 老年痴呆症:Alzheimer's disease31. 帕金森病:Parkinson's disease32. 癌症:Cancer33. 白血病:Leukemia34. 心脏病:Heart disease35. 肝病:Liver disease36. 肾病:Kidney disease37. 肺病:Lung disease38. 高脂血症:Hyperlipidemia39. 甲亢:Hyperthyroidism40. 甲减:Hypothyroidism41. 黄褐斑:Chloasma42. 白癜风:Vitiligo43. 牛皮癣:Psoriasis44. 带状疱疹:Shingles45. 水痘:Chickenpox46. 麻疹:Measles47. 风疹:Rubella (German measles)48. 痄腮:Mumps (耳下腺炎)49. 红眼病(急性结膜炎):Red eye (acute conjunctivitis)50. 中耳炎:Otitis media (middle ear infection)请注意,这些翻译可能并不完全准确或具体,因为中医是一个非常复杂和深奥的医学系统,其概念和术语往往难以用简单的英文词汇来表达,仅供参考。
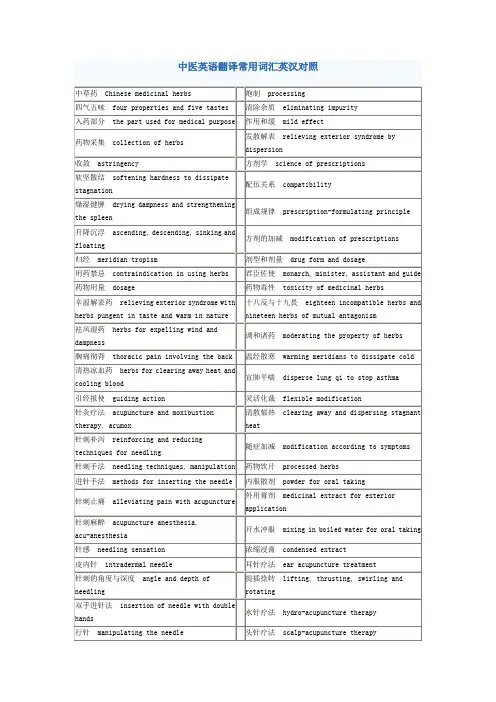

中医的专业术语英文翻译大家在写中医论文时候常常遇到一些不容易翻译的词汇,yjbys 网整理了中医的专业术语英文翻译,方便大家写作。
快来点赞吧。
中国医药学:traditional Chinese medicine中医基础理论:basic theory of traditional Chinese medicine临床经验:clinical experience辨证论治:treatment based on syndrome differentiation本草:materia medica //medicinal herbs中药Chinese herbs四气五味:four properties and five tastes针灸acupuncture and moxibustion各家学说theories of different schools汗法: diaphoresis /diaphoretic therapy下法:purgative therapy吐法:emetic therapy补土派:school of invigorating the earth病因学说:theory of etiology养生:health-cultivation医疗实践medical practice治疗原则:therapeutic principles寒凉药物:herbs of cold and cool nature滋阴降火:nourishing yin to lower fire瘀血致病:disease caused by blood stasis先天之精:congenital essence气的运动变化:movement and changes of qi。

中医英语词汇汇总(总13页)--本页仅作为文档封面,使用时请直接删除即可----内页可以根据需求调整合适字体及大小--Lesson One History of Traditional Chinese Medicine中医术语acupunture and moxibusion 针灸health maintenance 养生drugs cold and cool 寒凉药the school of cold and cool 寒凉派diaphoesis emesis purgation 汗吐下the school of purgation 攻下派exagenous pathogenic factors 外邪reinforcing the earth 补土internal impairment of spleen and stomach would bring about vorious diseases 内伤脾胃百病由生yang is usually redundant ,while yin is frequently deficient.阳常有余阴常不足nourishing yin 滋阴medicinal herbs 草药blood stagnation 淤血warm and inorgorate the spleen and stomach 温养脾胃中国医药学: traditional Chinese medicine中医基础理论: basic theory of traditional Chinese medicine临床经验: clinical experience辨证论治: treatment based on syndrome differentiation; pattern identification and treatment本草: materia medica中药: Chinese materia medica; Chinese medicinals中草药: Chinese medicinal herbs四气五味: four properties and five tastes针灸: acupuncture and moxibustion各家学说: theories of different schools汗法: diaphoresis; sweating therapy下法: purgative therapy; precipitation吐法: emetic therapy; vomiting therapy补土派: school of invigorating the earth病因学说: etiology养生: health cultivation; health improvement; health preservation医疗实践: medical practice治疗原则: therapeutic principles寒凉药物: cold and cool medicinals滋阴降火: nourishing yin to reduce fire瘀血: blood stasis正气: healthy qi病邪: pathogenic factor整体观念: holism; holistic concept气血运行: circulation of qi and blood自然现象: natural phenomenaLesson Two Materialism and Dialectics in Traditional Chinese Medicine中医术语Materialism 唯物主义dialectics 辩证法celestial qi 天气terrestrial qi 地气the interaction between yin and yang 阴阳相互作用the lucid yang ascends to constitute the earth 清阳为天qi transformation 气化essence 精prenatal essence 先天之精shen(spirit) 神pathological factor 邪气the opposition and unity of yin and yang 阴阳对立统一the motion and changes of yin and yang 阴阳运动变化organic whole 有机整体Five kinds of visceral qi 五脏之气five emotional changes 五志excessive rage impairs the liver 怒伤肝excessive joy impairs the heart 喜伤心excessive meditation impairs the spleen 思伤脾excessive melancholy impairs the lung 悲伤肺excessive fright impairs the kidney 恐伤肾routine treatment and contray treatment 正治反治tit-for-tat(or blow-for-blow) 正治reinforcing therapy 补法purging therapy 泄法differential application and therapeutic methods 异法方宜mental activity 神志活动the heart is the king organ responsible for the activity of thinking consciousness 心为君主之官主神志意识will 意termed 志thinking 思wisdom 智summer-heat 暑热zheng qi ( healthy qi ) 正气Lesson Three The Basic Characteristics of TCMmaterilism and dialectics 唯物论和辨证法the concept of organic whole 整体观念treatment based on syndrone differentian 辨证论治drawing yin from yang 从阴引阳treating the nights for curing disease on the left 从右治左treating the same disease with different therapies 同病异治treating differnt disease with the same therapy 异病同治clear away fire in the heart 清心火sprouting occurs in spring ,growth in summer,transformationg in latesummer ,reaping in autumn andstoring in winter 春生夏长秋收冬藏the relation between pachogenic factors and healthy qi 正邪关系the four diagnosic methods 四诊purging the small intestine 泻小肠spring is usually marked by warrachs , summer by heat ,late summer by dampness ,autumn by dryness and winter by cold 春暖夏暑长夏秋燥冬寒the interstitial space are open when one swears clothes in summer天暑衣厚则奏理开哲学概念: philosophical concept对立统一: opposition and unity相互消长: mutual waning and waxing阴阳属性: nature of yin and yang相互转化: mutual transformation相互联系: interrelation相互制约: mutual restraint动态平衡: dynamic equilibrium阴平阳秘: yin and yang in equilibrium相互依存: interdependence阴阳的互根互用: interdependence between yin and yang阴阳离绝: dissociation of yin and yang阴阳转化: transformation between yin and yang阳消阴长: yang waning while yin waxing阴胜则阳病: predominance of yin leading to disorder of yang阳胜则热: predominance of yang generating heat寒极生热: extreme cold generating heat热极生寒: extreme heat generating cold相反相成: opposite and supplementary to each other生理功能: physiological functions病理变化: pathological changes临床诊断: clinical diagnosis阳胜生外热: exuberance of yang leading to exterior heat阳中求阴: obtaining yin from yang阳虚则寒: yang deficiency leading to heat阳损及阴: impairment of yang involving yin阴中之阳: yang within yin阴阳两虚: simultaneous deficiency of yin and yang阳虚发热: fever due to yang deficiency阴阳学说: theory of yin and yang症状与病名stomatitis 口腔炎 proctoptosis脱肛dysentery 痢疾hysteroptosis子宫脱垂measles 麻疹 ulcer溃疡the collapse of zhongqi 中气下陷Lesson Four The Theory of Yin and Yang中医术语相互消长:growth and decline between yin and yang阴阳属性:yin and yang properties相互转化:inter-transformation相互依存:interdependence between yin and yang阴阳的无限可分性:the infinite divisibility of yin and yang阴平阳秘:yang steadies while yin calms阳消阴长:waning of yang will lead to waxing of yin阳胜则热:predominance of yang gives rise to heat syndrome寒极生热:extreme cold brings on heat热极生寒:extreme heat brings to cold阴中之阴:yin within yin阳中之阳:yang within yang阴中之阳:yin within yang阳中之阴:yang within yin阴阳互根:interdependence between yin and yang阴阳自和:natural harmony of yin and yang春生sprouting in spring夏长growing in summer秋收reaping in autumn冬藏 storing in winter相互制约:mutual opposition and restriction between yin and yang动静升降出入motion and quiescence ,ascending and descending exiting and entering孤阳不升,孤阴不长if only yang exists ,there will be no birth,if only yin exists,there will be no growth .动态平衡 dynamic equilibrium阴胜则热excess of yang causing heat阴阳失调:imbalance between yin and yangyin-yang disharmony wiseman 02/ 谢竹藩04阴阳两虚 deficiency of both yin and yangdual vacuity of yin and yang wiseman 02阴阳乖戾 dysequilibrium between yin and yangying-yang imbalance 谢竹藩04阴阳离决 separation of yin and yangwhile yin is (exuberant)prevails, there is cold wiseman 02阳胜则热 when yang prevails, there is heat wiseman 02阳胜则阴病when yang prevails, yin ails wiseman 02阴胜则阳病when yin prevails, yang ails wiseman 02阳虚则外寒when yang is vacuous, there is external cold wiseman 02阴虚则内热 when yin is is vacuous, there is internal heat wiseman 02阴损及阳 detriment to yang affects yin wiseman 02阳损及阴exuberant yin repelling yang wiseman 02阴虚火盛exuberant yin vacuity fire wiseman 02 exuberance of fire/due to yin-deficiency 简明汉英中医词典2002李照国阴虚火旺 effulgent yin vacuity fire wiseman 02 yin vacuity fire effulgent wiseman 02yin deficiency with effulgent fire 中医药常用名词术语英译 2004。

中医的专业术语英文翻译中医的专业术语英文翻译大家在写中医论文时候常常遇到一些不容易翻译的词汇,yjbys网整理了中医的专业术语英文翻译,方便大家写作。
快来点赞吧。
中国医药学:traditional Chinese medicine中医基础理论:basic theory of traditional Chinese medicine临床经验:clinical experience辨证论治:treatment based on syndrome differentiation本草:materia medica //medicinal herbs中药Chinese herbs四气五味:four properties and five tastes针灸acupuncture and moxibustion各家学说theories of different schools汗法: diaphoresis /diaphoretic therapy下法:purgative therapy吐法:emetic therapy补土派:school of invigorating the earth病因学说:theory of etiology养生:health-cultivation医疗实践medical practice治疗原则:therapeutic principles寒凉药物:herbs of cold and cool nature滋阴降火:nourishing yin to lower fire瘀血致病:disease caused by blood stasis先天之精:congenital essence气的运动变化:movement and changes of qi形与神俱:inseparability of the body and spirit神明: spirit/mental activity脏腑:zang-organs and fu-organs/viscera功能活动:functional activities形神统一:unity of the body and spirit阴阳失调:imbalance of yin and yang正邪相争:struggle between healthy qi and pathogenic factors 治未病prevention of disease调养 to cultivate health正气 healthy qi病邪 pathogenic factor疾病的防治 prevention and treatment of disease整体观念 concept of holism五脏five zang-organs六腑six fu-organs经络系统system of meridians and collaterals形神统一unity of the body and spirit有机整体organic wholeness表里关系exterior and interior relation开窍opening into生长化收藏five element function脉象pulse conditions正邪关系the states of pathogenic factors and healthy qi自然现象natural phenomena哲学概念philosophical concept对立统一unity and opposites相互消长mutual waning and waxing阴阳属性nature of yin and yang相互转化mutual transformation相互联系interrelation相互制约mutual restraint动态平衡dynamic balance阴平阳秘yin and yang in equilibrium阳消阴长 yang waning and yin waxing阴胜则阳病predominance of yin leading to disorder of yang 阳胜则热 predominance of yang generating heat寒极生热 extreme cold generating heat热极生寒extreme heat generating cold相反相成 opposite and supplementary to each other生理功能physiological functions病理变化pathological changes临床诊断clinical diagnosis有机整体organic wholeness/entirety正邪斗争struggle between healthy qi and pathogenic factors 绝对偏盛absolute predominance阳虚则寒yang deficiency leading to cold阳损及阴consumption of yang involving yin阴液不足insufficiency of yin-fluid病机pathogenesis五行学说theory of five elements运动变化motion and variation条达舒畅free development相生相克mutual generation and restriction生我我生to be generated and to generate克我我克to be restricted and to restrict生中有制restriction within generation克中有生generation within restriction木曰曲直Wood is characterized by growing freely and peripherally火曰炎上Fire is characterized by flaming up土曰稼穑Earth is characterized by cultivation and reaping金曰从革Metal is characterized by change水曰润下Water is characterized by moistening anddownward flowing方位配五行correspondence of the directions to the five elements相乘相侮over-restriction and reverse restriction土乘木The wood over-restrains the earth土虚木乘 Earth deficiency leading to over-restriction by wood 金虚木侮metal deficiency leading to counter-restriction by wood生克制化interrelationship between generation and restriction制则生化restriction ensuring generation传变transmission of disease母病及子disease of the mother-organ affecting the child-organ子病犯母disease of the child-organ affecting the mother-organ肝肾精血不足insufficiency of kidney and liver essence and blood肝阳上亢hyperactivity of liver yang藏象学说 theory of visceral manifestations五脏六腑 five zang-organs and six fu-organs奇恒之府 extraordinary fu-organs水谷精微 cereal nutrients传化水谷 transmissions and transformation of food贮藏精气 storage of essence表里关系 interior and exterior relationship治疗效应 curative effect临床实践 clinical practice藏而不泻 storage without excretion心肝血虚deficiency of heart and liver blood心肝火旺exuberance of heart and liver fire心火亢盛exuberance of heart fire滋肾养肝nourishing the kidney and liver肝阴不足insufficiency of the liver yin温肾健脾warming the kidney and strengthening the spleen 肾阳式微declination of kidney yang脾阳不振inactivation of spleen yang肝旺脾虚hyperactivity of the liver and weakness of the spleen 脾胃虚弱weakness of the spleen and stomach平肝和胃soothing the liver and harmonizing the stomach水湿停聚retention of water-dampness肾阴不足insufficiency of kidney yin心肾不交disharmony between the heart and kidney水火不济discordance between water and fire阴阳俱损simultaneous consumption of yin and yang阴阳两虚simultaneous deficiency of both yin and yang损其有余reducing excess补其不足supplementing insufficiency阴中求阳obtaining yang from yin虚寒证deficiency-cold syndrome扶阳益火strengthening yang to increasing fire祛风散寒eliminating wind to dispersing cold消导积滞promoting digestion and removing food retention 潜阳息风suppressing yang to quench wind阴阳的互根互用interdependence of yin and yang相互依存interdependence。

中医英文词汇1. 中医学(Traditional Chinese Medicine, TCM)2. 经络学(Meridianology)3. 气(Qi)4. 血(Xue)5. 阴阳(Yin-Yang)6. 五行(Five Elements)7. 经络(Meridian)8. 穴位(Acupoint)9. 针灸(Acupuncture)10. 拔罐疗法(Cupping Therapy)11. 刮痧疗法(Gua Sha Therapy)12. 中草药(Chinese Herbal Medicine)13. 草药学(Herbology)14. 方剂(Prescription)15. 药膳(Medicated Diet)16. 气功(Qigong)17. 太极拳(Tai Chi)18. 推拿按摩(Tui Na Massage)19. 中医诊断(TCM Diagnosis)20. 脉诊(Pulse Diagnosis)21. 舌诊(Tongue Diagnosis)22. 中医治疗(TCM Treatment)23. 经络按摩(Meridian Massage)24. 中医保健(TCM Wellness)25. 中医病因学(TCM Pathology)26. 中风(Stroke)27. 心血管疾病(Cardiovascular Disease)28. 消化系统疾病(Digestive System Disorders)29. 呼吸系统疾病(Respiratory System Disorders)30. 神经系统疾病(Neurological Disorders)31. 内分泌系统疾病(Endocrine Disorders)32. 妇科疾病(Gynecological Disorders)33. 男科疾病(Andrology)34. 儿科疾病(Pediatrics)35. 皮肤病(Dermatological Disorders)36. 风湿病(Rheumatological Disorders)37. 肿瘤学(Oncology)38. 精神疾病(Psychiatric Disorders)39. 疼痛管理(Pain Management)40. 康复医学(Rehabilitation Medicine)41. 中医养生(TCM Health Preservation)42. 养生学(Health Cultivation)43. 中医美容(TCM Beauty Therapy)44. 中医理疗(TCM Physical Therapy)45. 中医药化学(TCM Medicinal Chemistry)46. 中医药制剂学(TCM Pharmaceutical Preparations)47. 中医药法学(TCM Jurisprudence)48. 中医药教育(TCM Education)49. 中医药研究(TCM Research)50. 中医药文化(TCM Culture)。

中国传统文化有关的英语词汇以下是更多与中国传统文化有关的英语词汇及翻译:1. 四大发明:The Four Great Inventions- 造纸术:Paper-making- 印刷术:Printing- 火药:Gunpowder- 指南针:Compass2. 中医:Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)- 中药:Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) herbs- 针灸:Acupuncture- 推拿:Tuina3. 传统文学:Traditional Literature- 诗经:The Book of Songs- 唐诗:Tang Poetry- 宋词:Song Ci- 明清小说:Ming and Qing Novels4. 工艺美术:Arts and Crafts- 景泰蓝:Cloisonné- 刺绣:Embroidery- 陶瓷:Ceramics- 木雕:Wood Carving5. 饮食文化:Food Culture- 筷子:Chopsticks- 茶道:Tea Ceremony- 八大菜系:Eight Major Cuisines6. 传统历法:Traditional Calendar- 农历:Lunar Calendar- 二十四节气:The 24 Solar Terms7. 传统礼仪:Traditional Etiquette- 鞠躬:Bow- 抱拳礼:Fist-andPalm Salutation- 敬茶:Offering Tea8. 哲学概念:Philosophy Concepts- 和谐:Harmony- 中庸:The Doctrine of the Mean- 礼:Ritual这些词汇可以帮助你更好地理解和描述中国传统文化。
如果你对某一特定领域的传统文化词汇有具体需求,请告诉我,我将尽力提供相关词汇和翻译。

中医英语重要词汇针灸:acupuncture and moxibustion。
经络:meridian/channel and collateral。
表:exterior,里:interior。
归经:meridians tropism舌象:淡红舌:light red tongue,淡白舌:pale tongue。
薄苔:thin coating。
厚苔:thick coating,润:moist,燥dry,腻:greasy。
绛:crimson。
枯荣老嫩:flourishing,withered,tough ,tender.方剂:formula,prescription 配伍关系:compatibility/combination relationship。
方剂的加减:modification of prescription .药~medicinal 君臣佐使:sovereign,minister,assistant,guide。
症状:手足厥冷:reversal cold of hand and feet,哮:wheezing 哮喘:asthma。
恶心:nausea,痢疾:dysentery。
自汗:spontaneous sweating,尿频:frequent urination,带下:leukorrhea。
便溏:loose stool。
便秘:constipation,面色:complexion。
里急后重:tenesmus。
呕吐:vomiting,嗳气:belching.得神:presence of vitality,呃逆:hiccup,太息:sighing.小便:urine,大便:stool。
口渴:thirst。
胁痛:hypochondriac pain,咯血:hemoptysis,胸痛:chest pain,眩晕:vertigo/dizziness,心悸:palpitation,腹痛:abdominalpain。

中医英语重要词汇针灸:acupuncture and moxibustion。
经络:meridian/channel and collateral。
表:exterior,里:interior。
归经:meridians tropism淡红舌:light red tongue,淡白舌:pale tongue。
薄苔:thin coating。
厚苔:thick coating,润:moist,燥dry,腻:greasy。
绛:crimson。
枯荣老嫩:flourishing,withered,tough,tender.,prescription配伍关系:compatibility/combination relationship。
方剂的加减:modification of prescription .药~medicinal君臣佐使:sovereign,minister,assistant,guide。
手足厥冷:reversal cold of hand and feet,哮:wheezing 哮喘:asthma。
恶心:nausea,痢疾:dysentery。
自汗:spontaneous sweating,尿频:frequent urination,带下:leukorrhea。
便溏:loose stool。
便秘:constipation,面色:complexion。
里急后重:tenesmus。
呕吐:vomiting,嗳气:belching. 得神:presence of vitality,呃逆:hiccup,太息:sighing.小便:urine,大便:stool。
口渴:thirst。
胁痛:hypochondriac pain,咯血:hemoptysis,胸痛:chest pain,眩晕:vertigo/dizziness,心悸:palpitation,腹痛:abdominal pain。
游走性关节疼痛:migratory arthralgia pain。

•The six exogenousɛkˈsɑdʒənəs] factors 外感六淫•The seven emotions 七情•Improper [ɪmˈprɔpə] diet 饮食失调(不适当)•Over strain 过度疲劳•Lack of physical exercise 缺乏锻炼·Traumatic injuries;external[eksˈtə:nl] injury 创伤、外伤Traumatic [trɔ:ˈmætɪk]外伤用的•Bitten by animal and insect 蛇虫鼠咬·Stagnated blood and phlegm[flem] fluid[ˈflu:ɪd]瘀血痰湿[ˈstæɡneit]vi.停滞, 不流动, 不发展phlegm [flem] 1.痰2.冷静,镇定fluid [ˈflu:ɪd]液体流体·外感: diseases caused by exogenous evils[ekˈsɔdʒinəs]外因的·六淫: six evils[ˈi:vəl]坏的•风邪: wind - evil•寒邪: cold - evil•暑邪: summer heat-evil•湿邪: wetness - evil•燥邪: dryness - evil•火邪: fire - evil•热邪: heat - evil·惊恐伤肾: fear impairing kidney[imˈpɛə] vt.损害, 削弱•悲忧伤肺: sadness impairing lung•思虑伤脾: worry impairing spleen·暴喜伤心: overwhelming joy impairing heart [ˌəuvəˈhwelm] vt难以禁受•大怒伤肝: rage impairing liver vi.n•deficiency[diˈfiʃənsi] 虚•excess 实超过, 过多之量•exterior 表 interior 里•Yin 阴 Yang 阳 Cold 寒 Heat 热· rising and falling of vital energy and evils 邪正盛衰[ˈvaitəl] 必不可少的·阴阳失调 disharmony of Yin and Yang [ˈdisˈhɑ:məni]不调和·气血失调 disorder of Qi and Blood·虚中夹实, deficiency complicated with excess·上盛下虚, excess in upper and deficiency in lower·真实假虚, true excess disease with false deficient manifestation·表虚/实, exterior deficiency/excess·里虚/实, interior deficiency/excess·阳盛/虚, yang excessiveness / deficiency·阴阳偏衰, deficiency of either yin or yang·虚阳上浮, deficient yang with upper manifestation显示·阴虚发热, fever due to yin deficiency•阴虚火旺, hyperactivity of fire due to yin deficiency活动过度•虚火上炎, deficient fire flaring up 加剧、突发vi•阳损及阴, yang deficiency involving yin•亡阴/阳, yin/yang depletion [dɪˈpli:ʃən]用尽•阴阳离决, divorce of yin-yang 分离•真寒假热, true cold disease with false heat manifestation 表现•寒热错杂, intermingled cold and heat [ˌɪntəˈmɪŋgəl] vt、vi(使)混合•表热里寒, exterior heat with interior cold•Four diagnostic 四诊•Inspection Observation 望诊检查,视察•Listening and smelling闻诊•Inquiry Auscultation and Olfaction 问诊•Palpation and pulse taking切诊 [pʌls]•Body palpation按诊•Abdominal examination 腹诊 [æbˈdɔmənəl] 腹部•Symptoms 症状[ˈsimptəm]•Syndrome 综合症[ˈsindrəum]•Physiotherapy 物理疗法[ˌfiziəuˈθerəpi]•Sign 体征•心悸 Palpitation [pælpiˈteiʃn]•怔忡 Fearful throbbing[θrɔb]vi搏动•乏力 Lack of strength•目眩 dizzy vision[ˈdizi] 眩晕 [ˈviʒən] 视力, 视觉•眩晕 dizziness•头重 heavy-headedness•神疲 lassitude of spirit [ˈlæsɪˌtju:d] 无精打采•昏厥 fainting[feint]•多梦 profuse dream [prəˈfju:s] 浪费的•健忘 forgetfulness•胸闷 oppression in the chest [əˈpreʃən]压抑•短气 shortness of breath•烦躁 agitation[ˌædʒɪˈteɪʃən]•反胃 stomach reflux [ˈri:flʌks]逆流,退潮•恶心 nausea [ˈnɔ:zi:ə,•干呕 dry retching[retʃ]vi 干呕•呕吐 vomiting[ˈvɔmit] vt.vi .n•呃逆 hiccup[ˈhɪkəp]•吐酸 acid regurgitation [ˈæsid] ,酸的[riˌɡə:dʒiˈteiʃən]回流•痞满 stuffiness and fullness,闷•胃脘痛 stomach duct pain [dʌkt] 导管•口苦 bitter taste in the mouth•口臭 fetid mouth odor [ˈfetɪd] 恶臭的 [ˈəudə]气味,名声•口淡 bland taste in the mouth[blænd] 清淡的•厌食 anorexia[ˌænəˈreksi:ə]•fear of cold 畏寒•aversion to cold 恶寒. [əˈvə:ʃən] 厌恶•shivering 寒战的 [ˈʃivəriŋ]•High fever 壮热•tidal fever 潮热[ˈtaɪdl]•alternating chills and fever 寒热往来 [ˈɔ:ltɜ:ˌnɪtɪŋ]交替的[tʃil]寒冷· Vexing heat in the chest, palms and soles 五心烦热[ˈveksɪŋ] 使人烦恼的[pɑ:m] 手掌[səul]脚心· nasal congestion 鼻塞 [ˈneɪzəl]鼻的 [kənˈdʒestʃən] 阻塞•dyspnea 喘[disˈpni:ə]•frequent urination 小便频数 [ˈjuəriˈneiʃən]撒尿•reddish red urine 小便黄赤 [ˈredɪʃ]淡红色的[ˈjuərin•inhibited urination 小便不利 [ɪnˈhɪbɪtɪd] 压抑的,拘谨的•hematuria 尿血•Stone strangury 石淋[ˈstræŋɡjuri]•sloppy stool 便溏 [ˈslɔpi:] 太稀的 [stu:l] 大便•Hard bound stool 大便硬结 [baund]被捆绑的•diarrhea 泄泻 [ˌdaɪəˈri:ə]•tenesmus 里急后重 [təˈnezməs]•Qi collapse 气脱 [kəˈlæps] 倒塌, 崩溃•Qi stagnation 气滞stægˈneɪʃən]•Blood stasis 血瘀 [ˈsteisis]•Flooding 血崩•sunken middle qi 中气下陷 [ˈsʌŋkən] 下陷的•insufficiency of middle qi 中气不足 [ˌɪnsəˈfɪʃənsi:] 不足•disharmony of qi and blood 气血失调 [ˈdisˈhɑ:məni] 不调和•dual deficiency of qi and blood 气血两虚 ['duəl]两部分的, •blazing of qi and blood 气血两燔 [ˈbleiziŋ]炽热的•Heat entering pericardium 热入心包 [ˌperiˈkɑ:djəm]心包膜· impairment of fluid 伤津 [imˈpɛəmənt]损伤•器质性精神障碍 Organic psychoses [psai'kəusi:z]•精神分裂症 Schizophrenia [,skidzəu'freniə]•情感性精神障碍 Affective psychoses [psai'kəusi:z]•神经症 Neuroses [njuə'rəusi:z]情感 affection情绪 emotion心境 mood自知力 insight定向力 orientation精神障碍 Mental illness精神紊乱 Mental disorder•器质性精神病 organic psychosis [ɔ:'ɡænik] [psai'kəusis]•遗忘综合症amnestic [æm'nistic] syndrome•谵妄 delirium [di'liriəm]•痴呆 dementia [di'menʃiə]•精神分裂症 schizophrenia [,skidzəu'freniə]•偏执型paranoid ['pærənɔid] type•紧张型catatonic [,kætə'tɔnik] type•青春型 hebephrenic type•单纯型 simple type•未分化型 Undifferentiated [,ʌndifə'renʃieitid] type•残留型 Residual type•精神分裂症后抑郁 Post-schizophrenia depression [,skidzəu'freniə]神经症 neurosis [njuə'rəusis]恐惧症 phobia ['fəubiə]焦虑症 Anxiety广泛性焦虑症 generalized anxiety disorder[dɪsˈɔrdɚ] 不适;疾病强迫症 obsessive-compulsive disorder obsessive[əbˈsɛsɪv, ɑb-]固执偏执的compulsive[kəmˈpʌlsɪv] 极有趣的,令人着迷的2. 因着迷而引起的,上瘾的3. 强迫性的•心境障碍 mood disorder•狂躁 mania•抑郁 depression•易激惹 irritability [,iritə'biləti]•双相障碍 biplor disorder•意志增强 hyperbulia [haipə'bjuliə]•意志减弱 hypobulia [haipɔ'bjuliə]•恶劣心境 dysthymic [dis'θimik] disorder•环性心境障碍 cyclothymia [,saikləu'θaimiə]•抗抑郁药antidepressant drugs [,æntidi'presənt]Inspection of Vitality [vaɪˈtælɪti:] 生活力/complexion 面色[kəmˈplekʃən] aggravated(加剧)alcohol酒精•coldness of limbs•The patient has been drinking alcohol for more than 20 years.·patient has repeated attacks of stomachache for 20 years with marked deterioration(恶化) when he is hungry, relief after food intake.For the recent half year, the symptoms above became more serious which were manifested as consistent pain in the stomach, belching[beltʃ]嗳气and regurgitation[riˌɡə:dʒiˈteiʃən回流, moving and distending[dɪˈstend] 肿胀 pain due to fullness in chest and abdomen æbˈdəʊmən] 腹部 and anorexia[ˌænəˈreksi:ə] (厌食)。
一、绪论中医学TCM(Traditional Chinese Medicine),中医学理论体系的形成Origination of TCM, 形成formation, 发展development 中医学理论体系的基本特点The basic characteristic of Traditional Chinese Medicine theory整体观the whole concept, 辨证论治syndrome differentiation and treatment第一章阴阳五行学说阴阳Yin-yang , 阴阳的特性the property of yin-yang阴阳之间的相互关系Interaction between yin and yang阴阳对立制约Opposition of yin and yang阴阳互根互用Interdependence between yin and yang阴阳消长平衡Wane and Wax between yin and yang阴阳相互转化Mutual transformation between yin and yang阴阳学说在中医学中的应用The applications of the theory of yin-yang in TCM说明人体的组织结构Explanation of the histological structure of the human body 解释人体的生理功能Explanation of the physiology function activity of the human body阐释病理变化Explanation of pathogenesis阴阳偏盛Relative predominance of yin or yang阳偏盛Relative predominance of yang阴偏盛Relative predominance of yin阴阳偏衰Relative decline of yin or yang阳偏衰Relative decline of yang阴偏衰Relative decline of yinthe five elements, 五行五行特性the five elements property第二章中医学的生理观藏象“Zangxiang”,五脏five Zang-organs, 六腑six fu-organs,生理功能the physiological functions , 气qi, 血blood , 津液body fluid,气的生成、运动和分类the production ,moving and classification of qi,血的生成和运行the production and circulation of blood津液的生成、输布和排泄the production and transportation and metabolism of body fluid.气、血、津液的功能The physiological functions of qi, blood and body fluid心The heart,主血脉Governing blood主神志controlling the mind在体合脉governs the vessels开窍于舌opens into the tongue其华在面External manifestation on the face肝The liver,主疏泄To dredge and regulate, 主藏血Storing blood在体合筋The liver governing the tendons其华在爪The external manifestation of the liver on the nails开窍于目The liver opening into the eyes脾the spleen,主运化To govern the transportation and transformation主统血To command blood, 主升elevating在体合肌肉,主四肢the spleen governing the muscles and the four limbsThe spleen opening into the mouth开窍于口.其华在唇The external manifestation on the lip肺The lung,主气,司呼吸Dominating qi,controlling the respiratory movement主宣发、肃降dispersing and descending通调水道The regulation of water passage朝百脉、主治节?the lung is connected with all the vessels, regulation the qi activity in the whole body在体合皮the lung governing the skin其华在毛Eexternal manifestation on the body hair开窍于鼻The lung opening into the nose肾The kidney,藏精store essence, 主水To govern water, 主纳气To govern reception of qi在体合骨The kidney governing the bones开窍于耳及二阴The kidney opening into the ears, the external genitals and the anus 其华在发External manifestation on the hair胆The gallbladder, 贮藏和排泄胆汁store and excrete the bile胃The stomach, 受纳、腐熟水谷receive and digest food主通降?the stomach functions to descend?,?unobstructed condition小肠The small intestine, 受盛化物To receive the chime and transform泌别清浊To separate the lucid from the turbid大肠The large intestine, 主传化糟粕transmitting and excreting the waste of food storing and discharging urine The bladder ,膀胱气的生成The production of qi气的运动The moving of qiThe physiological functions of qi气的功能推动作用Propelling function温煦作用Warming function防御作用Protecting and defencive function固摄作用Fixating function气化作用Qi-transforming function元气primordial qi, 宗气pectoral qi, 营气nutrient-qi, 卫气defensive qi第三章中医学的病理观病因 Causes of disease病因的概念及分类concept, classification of causes of disease.六淫的概念concept of six pathogenic factors;,,六淫致病的共同特点the general pathogenic characters of six pathogenic factors;六淫(风、寒、暑、湿、燥、火)的性质与致病特点nature, pathogenic characters of every six pathogenic factors(including wind,cold,Summer-heat,Dampness,Dryness,Heat (fire))主要的临床表现main clinic manifestations风Wind其性开泄,易袭阳位Wind tend to float, disperse, go upward attack the upper and outside parts风性善行而数变wind tends to move and change风为百病之长,易夹杂其他外感之邪Wind tends to be complicated by other pathogenic factors寒Cold易伤阳气Cold tends to impair yang寒性凝滞Cold tends to coagulate寒性收引Cold tends to contract暑Summer-heatSummer-heat is hot其性炎热暑性升散,耗气伤津Summer-heat tends to disperse and elevate,consume the qi and body fluid暑多夹湿Summer-heat often complicated by dampness湿Dampness湿性重浊dampness is heavy and turbid湿易阻遏气机dampness tends to block qi湿性黏滞dampness is sticky and stagnant湿性趋下, 易袭阴位dampness tends to move downward,attack the lower and inside parts燥Dryness燥易伤津Dryness consume the body fluid燥性干涩Dryness is xerotic and unsmooth燥易伤肺Dryness tends to impair the lung火Heat (fire)其性炎上Heat(fire) tends to flame up易伤津耗气Heat(fire) tends to consume qi and impair body fluid易生风动血Heat(fire) tends to produce wind and disturb blood易致肿疡Heat(fire) tends to cause swelling and ulceration七情内伤的概念、The concept of internal impairment due to the seven emotions,七情致病的特点the pathogenic characters of the seven emotions痰饮、瘀血的概念、形成及致病特点The basic concept, the formation and the pathogenic characteristics of phlegm ,rheum and blood stasis痰饮phlegm ,rheum 瘀血blood stasis发病的基本原理The pathogenesis of occurrence of disease in TCM病机的概念,The concept of mechanism of pathological changes;病机the mechanism of pathological changes;邪正盛衰predomination and decline of pathogenic factors and healthy qi;阴阳失调imbalance between yin and yang;气血津液失常disorder of qi, blood and body fluid.第四章中医诊断疾病的方法中医诊法The concept of the TCM diagnostic methods中医诊断的理论依据the theory foundation of the TCM diagnostic methods.望神Inspection of spirit, 望色Inspection of complexion, 望排出物Inspection of excreta ,望舌Inspection of tongue,Existence of spirit (得神),Lack of spirit(少神),Loss of spirit (失神)False spirit(假神)Normal complexion 常色Morbid complexion 病色Red colour ,White colour ,Yellow colour, Bluish colour,Blackish colour临床意义clinical significance ;望舌的方法Methods for inspection of tongue舌苔tongue coat舌红red tongue淡白舌/舌淡Light-whitish tongue青紫舌Cyanotic and purplish tongue问诊inquiry, 主诉chief complaint, 病史history of present illness问现在症inquiry of the present symptomsAversion to cold and fever(恶寒发热)Cold sensation without fever(但寒不热)Fever without cold sensation(但热不寒)Alternate cold and fever(寒热往来)诊脉的部位与方法The Regions and methods for taking pulse脉诊taking pulse, 正常脉象normal pulseCunkou(寸口)cun(寸), guan(关),chi(尺).辨证的概念The concept of differentiation of syndrome表里辨证External and internal differentiation of syndromes,External syndromes, 表证.里证internal syndromes,寒热辨证cold and heat differentiation of syndromes,寒证cold f syndromes,热证heat syndromes,虚实辨证asthenia and sthenia differentiation of Syndromes,虚证asthenia Syndromes,实证sthenia Syndromes,临床特点clinical character and difference.八纲辨证Syndromes differentiation with eight principles气血津液辨证syndrome differentiation with qi, blood and body fluid,第五章中医学的防治原则治则治法therapeutic methodstherapeutic principles ,正治反治Contrary treatment, Routine treatment ,治本treat “ben”(deal with the root cause)治标Treating biao(acute symptoms bring on great suffering to the patients, or threaten life or tend to transmit and change) in emergency ,扶正与祛邪Strengthening healthy qi and eliminating pathogenic factors,调整阴阳Regulation of yin and yang,三因制宜Abidance by individuality, locality and seasons.第六章中药基本知识中药Chinese Medicinal Herbs四气four properties、寒热温凉cold, hot, warm, cool五味five flavors、辛、甘、酸、苦、咸pungent, sweet, sour, bitter and salty.、the action of lifting, lowering, floating and sinking,升降浮沉.归经channel tropism、毒性toxicity中药的配伍、用药禁忌Contraindication and Compatibility of Chinese Medicinal Herbs中药的剂量Dosage of Chinese Medicinal Herbs第七章方剂基本知识方剂的组成原则The principle of the composition of prescriptions,Monarch drug (jun) 君Minister drug (chen) 臣Adjuvant drug (zuo) 佐Guide drug (shi) 使组成变化the modification of the composition of a prescription.方剂的组成、用法、功效、临床应用、方解:Ingredients, administration, function,clinical application and elucidation of the prescriptions第二章中医学的生理观第三节经络经络the meridians;十二经脉twelve regular meridians十二经脉走向与交接规律direction, joint law of the twelve channels、十二经脉循行分布规律distributing law of the twelve channels ,十二经脉表里络属关系exterior-interior relationship of the twelve channels ,十二经脉流注方向和次序等flowing direction and order of the twelve channels;第八章针灸学基本知识第二节刺灸方法刺法(针法)Acupuncture techniques; 进针Needling methods (insertion methods, Needling manipulation methods)得气arrival of Qi针刺意外和防治处理Management of possible accidents (emphasize 晕针fainting) 灸法moxibustion,第八章针灸学基本知识第一节腧穴腧穴概念;腧穴分类;腧穴定位方法;腧穴的作用the point/acupoint (definition/concept, classification, location method, function)腧穴的定位、归经、基本主治功能:location, channel tropism and the basic special treatment function of the point/acupoint下列腧穴的定位、基本主治功能:手太阴肺经:列缺;The lung channel of Hand-Taiyin: LieQue (Lu7)手阳明大肠经:合谷;The large intestine channel of Hand-Yangming: Hegu (LI4) 足阳明胃经:足三里;The stomach channel of Foot-Yangming: Zusanli (ST36)足太阴脾经:三阴交;The spleen channel of Foot-Taiyin: Sanyinjiao (SP6)手少阴心经:神门;The heart channel of Hand-shaoyin: Shenmen (HT7)手太阳小肠经:听宫;The small intestine channel of Hand-taiyang: Tinggong (SI19) 足太阳膀胱经:委中;The urinary Bladder channel of Foot-Taiyang:Weizhong(BL40),足少阴肾经:涌泉;The Kidney channel of Foot-shaoyin: Yongquan(KI 1)手厥阴心包经:内关;The Pericardium channel of hand-Jueyin: Neiguan (PC6) Hand-Shaoyang:of channel ) (Sanjiao warmer triple The 手少阳三焦经:外关;Waiguan (SJ5 ),足少阳胆经:风池;The Gall Bladder channel of Foot-shaoyang: Fengchi (GB20) 足厥阴肝经:太冲;The Liver channel of Foot-Jueyin: Taichong (LR3)任脉:关元、膻中;The Ren channel :Guanyuan (RN4), Tanzhong (RN17)督脉:大椎、人中;The Du channel : Mingmen(GV 4), Dazhui (DU14), Shuigou (DU26),经外奇穴:印堂、太阳;Extraordinary acupoints: Yintang(EX-HN 3), Taiyang(EX-HN 5)。
传统中医学英语词汇传统中医学词汇是由诺贝笔翻译公司整理一阳 quotfrist yang Shaoyang Channelquot 一阴 quotfrist yin Jreyin Channelquot 一逆 one mista ade in treatment 一息 respiration 一侧的 unilateral 一日量 daily dose 一服药 a dose of medicine 一夫法 finger breadth measurement 一身痛重 general pain and heaviness 乙癸同源Yithe live and Guithe Kidney bejing the same source 二阴 quottwo lower orifices ie the external urethral orifice and the anusquot 二浊reddish and whitish turbid urine 二十八脉 twenty-eight kinds of pulse condition 二阳并病 Shaoyang syndrome complicated by Taiyang syndrome 二便不利 difficulty in urination and defecation 二便失禁 urinaryand fecal incontinence 十问 inquire about ten aspects of the patient 十剂 ten kinds ofprescription 十八反 eighteen incompatible medicaments 十二剂 twelve kinds ofprescription 十二节 twelve joints 十二禁 twelve contraindications 十二经 twelveregular channels 十二时 traditional twelve two-hour periods 十二脏twelve internal organs 十二怪脉 quotten moribund pulses ten kinds of paradoxical pulse conditionquotthe thirteen medical 十九畏 nineteen nedicaments of nutual antagonism 十三科specialties 十四经 the fourteen channels 十五络脉 fifteen main collaterals 十二节刺twelve methods of needling 十二经别 branches of the twelve regular channels 十二经筋 muscle along the twelve regular channels 十二皮部 twelve skin areas 十六郄穴sixteen cleft points 十四经穴 quotaccupuncture points on the fourteen regular channelsfifteen main collaterals points 十二经动acupoints on regular channelsquot 十五络穴脉 arteries of the twelve channels 十二井穴 twelve well-points 十二经之海 sea of thetwelve channels 丁痂 scar 丁奚疳 infantile malnutrition due to excessive feeding 丁躬势 bowing 丁字形骨折 T-shaped fracturre 七方 quotseven prescriptions Seven formulaequot 七恶 the symtoms and signs indicating poor prognosis of suppurativeinfections of the exterior part of the body 七窍 seven orifices 七情seven emotions 七疝 seven kinds of hernia 七伤 1.seven kinds of impairments 2.seven symptoms suggesting consumption of the kidney-qi 七冲门 seven important portals 七怪脉quotseven moribund pulses seven paradoxical pulse conditions seven fatal pulseconditionsquot 七日风脐风 neonatal tetanus 七星针梅芬针 seven star needle 八纲the eight principal syndromes serving as guidelines in diagnosis 八法 eight therapeutic methods 八廓 the eight regions of the white of the eye 八溪 eight joints 八会穴quoteight hui-points eight influential pointsquot 八片锦 different pictures of superficial venules of index finger in children as a reference for diagnosis 八纲辨证 analyzing anddifferentiating pathological conditions in accordance with the eight principal syndromes八脉交会穴 eight confluence points 人中疔 boi on philtrum 人咬伤human bite bite by man 人迎脉 Renying pulse 人背复位 back-carrying reduction 人痘接种 humanvariolation 人工牛黄 quotartificial ox gallstone Calculus Bovis Factitiusquot 人事不省神昏 unconsciousness 入臼 joint reduction 儿风 eclampsia 儿病恶阻儿茶quotcatechu blzck catechu Catechuquot 儿枕痛 after-pains 儿捧母心breechpresentation 儿科四大要证 four chief diseases in pediatrics 九刺nine types ofneedling 九气 nine kinds of illness due to disturbance of qi 九窍nine orifices 九脏nine internal organs 九虫病 parasitic diseases 九窍出血 bleedingfrom the nineorifices 九六补泻法 nini-six reinforcing-reducing method 刀伤incised wound 刀晕traumatic syncope 刀创伤 drug for incised wound 刀斧伤 wound byknife or ax 三宝quotthree exxentialsessence qi and configurative forcequot 三痹three types of arthralgiz 三刺齐刺 three-stratum puncture 三法 quotthree therapeutic methods-diaphoresis emesis and purgationquot 三伏quot1.three periods of dog days 2.the third period of dog daysquot 三关the three passes 三焦 quottri-jiao sanjiao triple warmer triple heaterquot 三毛丛聚 clump hair 三品 three grades of medicines 三消three types of diabetes 三因 three categories etiologic factors 三虫病 three intestinal parasitoses 三春柳柽柳三焦病 disease of tri-jiao 三焦经 Tri-jiao Channel 三焦咳tri-jiao cough 三棱针 quotthree-deged needle tri-ensiform needlequot 三陷证 threetypesof inward penetration of pyogenic agent 三阳病 disease of the three yang channels 三阳经 three yang channels 三阳络 Sanyanglo 三阴病diseases of the three yin channels 三阴经 three yin channels 三阴痉convulsion with symptoms of three yinthree-yin malaria 三板疗法 quottri-tabular massage massage with channels 三阴疟three Kinds of boardsquot 三部九候 three portions and nine pulse-takings 7 三焦辨证differentiation of syndrome according to the pathological changes of trijiao 三焦实热heat in tri-jiao of excess type 三焦虚寒 cold syndromes ofdeficiency type 三阳合病disease involving all three yang channels 三点挤压法 three-point pressure method 三焦主决渎 the triple warmer manages the dredging of water pathway 干便 dry stool 干疽 cellulitis at the anterolateral aspect of the shoulder 干咳quotdry cough unproductive coughquot 干呕 retching 干陷 dry type of inward penetation of pyogenic agent 干癣1.chronic eczema2.neurodermatitis 干皮 dried bark 干血劳 emaciation due to blood disorders 干胁痛 dry hypochondriac pain 干脚气 dry beriberi 干霍乱 dr cholera 干眼症 xerophthalmia 干拔罐 1.dry cupping 2.ordinary cupping 土earthin fiveelements 土方 quotfolk recipe local recipequot 土疳针眼 hordeolum 土栗 infection of the heel 土风疮 popular urticaria 土生甘 sweet flavour is attributed to earth 土生金 earth generates metal 土克水 earth restricts water 土脯子 mantis cheeks 土乘水earth subjugates water 土不制水 earth fails to control water 土生万物 earth produces myriads of things 土喜温燥 earth prefers warmth and dryness 土郁夺之 Dampnessaccumulated in the spleenearth should be removed 8 下胞 Lower eyelid 下膊 forearm下法 quotpurgation purgative therapyquot 下疳 chancre 下膈 intake of food in the morning and vomiting in the evening 下工 quotan inferior medical worker an inexperienced healerquot 下骨 sending down the fishbone 下极 1.anus 2.perineum 3.area between inner canthi 4.another name for Hengku 下焦 quotlower-jiao lower warmer lower heater lower burnerquot 下利 diarrgea 下迫 tenesmus 下气 quot1.atherapeutic mithod to keep the adverse qi flowing downward2.aerofluxus breaking wind3.qu of the lower part of the bodyquot 下窍 lower orifices 下泉urine 下乳催乳lactogenesis 下脘 1.phlorus 2.Hsiawan 下陷中气下陷 descending disorders 下消quotdiabetes of the kindney type diabetes incolving the lower-jiaoquot 下搭手 lowerback cellulitis 下丹田 lower elixir field 下发背 quotlumbar carbuncle deep-rooted ulcer in the lumbar regionquot 下焦病 lower-jiao syndrome 下马痈 acute pyogenicinfection of right 下石疽 indurated mass of knee 下牙床 mandible 下注疮 eczema ofshank 下病上取 treating diseases of the lower part of the body by needling points on theupper part of the body 下腹胀气 flatulence in the lower abdomen 下汲肾阴consumption of the kidney-yin by the excessive heart fire 下焦如渎lower-jiaoresembling water passages 下焦主出 The Lower-jiao is in charge of excretory system 下厥上竭 exharstion of blood with cold limbs 下厥上冒dizzeness caused by adverse flow of qi 下利清谷 diarrhea with undigested food in the stool 下损及上 dusease inthe lower part affecting the upper 下胎毒法 dispelling toxic heat and meconium gathered at the fetus for the new born 下者举之 Sinking disorders should be treated with drugs of raising property prolapse and ptosis must be treated with the lifting methodto reinforce the vital function of the spleen 下焦湿热 downward flow of damp and heat 下利赤白 dysenteric diarrhea 下横骨伤 fracture ofpublic bone 下行通路 descendingpathway 大夫 quotan officials title in the feudal age now used for a doctor in northernChinaquot 大肠 large intestine 大毒 extremely poisonous drugs 大方heavyprescription 大分 distinct line between large muscles 大风麻风大腹upper abdomen大谷 large space between muscles 大汗 quotprofuse sweating byperhidrosis excessive perspirationquot 大经 rge channels 2.the needling of points on a large channel exhibiting symptoms 大厥 coma 大络large collatereals 大脉 quotlarge pluse gigantic pulsequot 10 大衄profuse bleeding from the mouth and nose 大气 quotatmosphere airquot 大溲解 quotdefecation bowel movementsquot 大泻 vigorous reduction 大医respected doctor 大针 large needle 大眦内眦 great canthus 大节 large joints 大产feces stooldefecation 大耳 mycrotia 大肉 large muscles 大嘴 eutocia 大便macrostomia 大肠病 disease of large intestine 大肠经 quotLarge Intestine Channel LIquot 大肠虚 asthenia of large intestine 大肠痈 acute appendictis 大肠胀 flatulenceof large intestine 大方科 speciality of internal medicine 大瘕泄dysentery 大结胸large accumulation of phlegm-heat in the chest 大头垫 megacaput pad 大头风大头瘟infection with swollen head 大腿疽股疽大腿痈 carbuncle of thigh 大泻刺 drainageneedling 大指间 web of great toe 大周天 large cirde of vital energy 大眦漏漏睛dacryocystitis 大方脉 adults pulse 大出血 quotmassive hemorrhagehematorrheaquot 大肠气 inguinal hernia 大麻风 quotlepra leprosyquot 大便溏 loose stool 大补元气invigorating primodial qi 大肠寒结 constipation due to retention of cold-pathogen in large intestine 大肠滑脱 prolapse of rectum 大肠气滞 qi stagnation of large intestine 大肠热结 large intestinal 11 大肠湿热large intestinal damp-heat 大肠虚寒asthenia-cold of large intestine 大肠液亏 deficiency of fluid in large intestine 大方脉科 internal medicine 大风恶疫麻风大肉陷下 obvious emaciation and muscular atrophy 大头伤寒大头瘟大眦脓漏 dacryocystitis with pyorrhea 大气疗法aerotherapy 大风荷毒 most dangerous pathogenic factors 大肠津亏fluid deficiency in the large intestine 大便干结 dry stool 大便不通constipation 大便色黑 quotblackstool melenaquot 大便如漆 tarry stools 大便失禁 incontinence offeces 大便困难dyschesia 大便频数 frequency of bowel movement 大汗淋漓 profuse perspiration 大骨枯槁 bones become dry and brittle 大渴引饮 extreme thirst 大肠主传导 largeintestine takes charge of transportation 大实有羸状 appearance of deficiency in extreme excess 兀兀欲吐 intense nausea 万灵药 panacea 寸 alength measurement corresponding to the middle segment of ones middle finger 寸脉 cun pulse 寸口脉cunkou pulse 寸白虫 proglottid of tapeworm 寸白虫病 taeniasis 寸、关、尺quotcunguanand chiinchbarand cubitquot 上胞 upper eye lid 上膊 upper arm 上膈quotpostcibal vomitingvomiting immediately after in gestionquot 12上工quotShang-gongsuperior medical workerquot 上火 sufering from excessive internal heat 上焦 quotupper-jiaoupper warmerupper heaterquot 上气 1.abnormal rising of qi 2.the upper qi 上窍 upper orifices 上脘1.shangwan2.episgastrium 上消 diabetesinvolving the upper-jiao 上搭手 cellulitis near the scapular region 上丹田 upper elixir field 上腭痈 abscess on palate 上耳背 Shangerpei 上发背 suppurative inflammation of the uppermost part of the back 上横骨sternal notch 上马痈 left buttock carbuncle 上石疽 upper stony mass behind the ear 上水鱼 abscess of the popliteal region 上牙床upper warmer upper dental bed 上肢瘫 paralysis of upper extremities 上焦证syndrome 上胞下垂 quotptosisblepharoptosisquot 上病下取 treating diseases in the upper part by managing the lower 上膈下膈 upper stenosis and lower stenosis 上寒下热 cold in the upper and heat in the lower 上焦病症 syndrome of the upper-jiao 上焦如雾 the upper-jiao resembling a sprayer 上焦主纳 The upper-jiao is in charge ofsyncope due to exhaustion receiving 上骱手法 reduction ofdislocation 上厥下竭below 上气喘促 shortness of breath 上热下寒 heat in the upper and cold in the lower 上实下虚 excess in the upper and deficiency in the lower 上损及下 the upper effecting the lower 上吐下泻 vomiting and diarrhea 上下配穴 quotcoordination of the acupionts of the upper with those of the lower superior-inferior point associationquot 上虚下实 deficiency in the upper and excess in the lower 上肢不遂moter impairment of the upper extremities 上翘下钩势 dorso-extension and ventro-flexion exercise 口quotmouthoral cavityquot 口臭 quotfoul breath halitosisquot 口疮quotaphthaecanker sorequot 口淡 tastelessness 口服 quotper oralper osquot 口疳 aphthae in children 口紧唇紧口噤 quotlockjaw trismusquot 口苦 bitter taste 口软flaccidity of mouth in infants 口水 quotsalivaspittlequot 口酸 sour taste 口口呙 wry mouth 口咸 saltytaste 口吃 quotstutterstammerquot 口糜 erosion of mucous membranceof the oral carity 口渴 thirst 口不仁 numbness of mouth 口齿科 specialty of stomatology and dentistry 口甘甜 sweet taste 口疳风舌头泡 blisters of the tongue 口丫疮 quotulceron the angle of lipsperlechequot 口中和 normal sense of mouth 口臭口烂 halitosis and aphthosis 口唇发紫 cyanotic lips 口唇紧缩唇紧口干唇裂dry mouth with cracked lips 口噤唇青 trismus with cyanotic lips 口舌糜烂aphthous stomatitis 14 口涎外溢quot1.involuntary drooling 2.sialorrheaptyalismsialismexcessive flow of salivaquot 口眼口呙斜 quot1.facia hemiparalysis deviation of the eye and mouth wry mouth withdistorted eyesquot 口中无味口淡 flat feeling in mouth 口干唇燥 dry mouth and lips 口不知谷味 loss of appetite 口齿咽喉科 quot1.Department of the Mouth Teath and Throat 2.specialty of mouth tooth-throatquot 口沃沫多唾 excessive salivation with froth 千日疮 verruca vulgaris 千岁疮流注疮 widespread scrofula 久咳 chroniccough 久痢 protracted drsentery 久疟 chronic malaria 久痔肛漏 recto-analfistula 久泻 chronic diarrhea 久热伤阴 persistent fever injuring yin essence 久不受孕 fail to be impregnated for a long time 久泻不止 chromic diarrhea 丸剂 quotpillbolusquot 广肠sigmoidorectum 广疮杨梅疮 syphilis 广明 anterosuperior part of the human body 丫叉毒丫刺毒 pustule in the web between the fiest and second metacarpals 亡血quothemorrhage bleadingquot 亡阳 quotyang depletionyang exhaustionquot 亡阴quotyin depletionyin exhaustionquot 亡血家 patient with hemorrhagic diathesis 尸厥corpse-like syncope 尸体 quotcorpsecadaverquot 尸咽 quotophthalmo-oro-genital syndromeBehcets syndromequot 卫 defensive function 卫气defensive energy 卫分证quot weifen syndromefebrile disease at wei phasesyndrom of wei systemquot 卫生局quothealth bureau sanitary bureauquot 卫生学 sanitary science 卫气不固表气不固wei-energy fail to protect the body 卫气同病 quotsyndrome of both weifen and qufensyndrome of both qi and wei systemsquot 卫气管血辨证analysing anddifferentiating the development of an epidemic febrile disease by studying condition ofthe four systems 女科 quot1.womens diseasesgynecology andobstertrics 2.medicaldepartment for womendepartment of gyhecology and obstetricsquot 女医1.womanjaundice due to sexual physician 2.physician who attends to womens diseases 女劳疸intemperance 女劳复 relapse of disease due to intemperance in sexual life 女子胞uterus 女阴溃疡 ulcerative vulvitis 小产 quotabortion miscarriagequot 小肠 thesmall intestine 小毒 d toxicity 2.drugs with a little toxicityslightly poisonousdrugsquot 小方 quotminor prescriptionminor or mild prescriptionquot 小分 smalllower abdomen 小逆 minor mistake in treatment 小space between muscles 小腹少腹溲 urine 小溪溪谷小心心包络命门小眦 quotlateral canthus external canthusquot 小耳 microtia 小眼 microphthalmus 小嘴 microstomia 小便quoturine urination micturitionquot 小肠病 disorder of the small intestine 16 小肠经手太阳小肠经 smallintestine channel 小肠咳 quotsmall intestine cough cough accompanied by flatulencequot 小肠疝气 hernia 小肠痈 small intestinal abscess 小肠胀flatulence of the small intestine 小方科 specialty of pediatrics 小腹满distension of lower addomen 小夹板 splintlet 小结胸 accumulation of phligm-heat in the chest 小伤寒quotcommon cold common cold of wink-cold typequot 小舌头 uvula 小腿疽胫疽 legcellulitis 小中风 faint 小周天 a small circle of the evolutive 小眦漏 fistula in the lateral canthus 小方脉 infantile pulse 小腹疽痈carbuncle of lower abdomen 小便短赤 scanty dark urine 小便短小 oliguria 小便黄赤 dark urine 小便辣痛ardor urine 小便淋沥 dribbling urination 小便涩痛 difficulty and pain in micturition 小便灼热burning sensation during urination 小肠实热 excessive heat in the small intestine 小肠虚寒 hypofunction of the small intestine with cold manifestations 小儿暴惊 suddenfright in children 小儿表热 exterior-heat syndrome in children 小儿虫吐 parasitevomiting in children 小儿喘急 dyspnea in children 小儿卒利 acute infantile diarrhea in children 17 小儿扎目 incessant winking of eyes in children 小儿发热 fever inchildren 小儿发痧 eruptive disease in children 小儿疳眼 eye disorder due to malnutrition in children 小儿寒吐 vomiting in children due to cold 小.。
05.001治则principle of treatment对临床的具体立法、处方、用药等具有普遍的指导意义,在治疗疾病时必须遵循的基本原则。
05.002治病求本treatment aiming at itsroot causes针对产生疾病的根本原因进行治疗的原则。
05.003急则治标symptomatic treatment inacute condition 与缓则治本相对而言,在大出血、暴泻、剧痛等标症甚急的情况下,及时救治标病,如止血、止泻、止痛等,然后治其本病的治疗原则。
05.004缓则治本radical treatment inchronic case 与急则治标相对而言,在病势缓和、病情缓慢的情况下,针对本病的病机治疗或采取调理、补益为主的治疗原则。
05.005标本兼治treating bothmanifestation and rootcause of disease 针对病证出现的标本并重的情况,采用治标与治本相结合的治疗原则。
05.006治未病preventive treatment ofdisease 采取一定的措施防止疾病产生和发展的治疗原则,包括未病先防和既病防变两个方面。
05.007同病异治treating same diseasewith different methods 表现相同的疾病,可因人、因时、因地的不同,或由于病情的发展、病机的变化、正邪的消长等差异,采取不同治法的治疗原则。
05.008异病同治treating differentdiseases with samemethod 表现不同的疾病,由于发病机理相同,采取相同治法的治疗原则。
05.009因时制宜treatment in accordancewith seasonal conditions 考虑到时令气候寒热燥湿的不同而选择适宜的治法、方药的治疗原则。
05.010因地制宜treatment in accordancewith local conditions 考虑到地域环境的不同而选择适宜的治法、方药的治疗原则。
中医①traditional Chinese medicine②traditional Chinese physician ①中医学的简称。
②本学科专业职业队伍。
中药 Chinese materia medica 在中医理论指导下应用的药物。
包括中药材、中药饮片和中成药等。
中医学 traditional Chinese medicine 以中医药理论与实践经验为主体,研究人类生命活动中健康与疾病转化规律及其预防、诊断、治疗、康复和保健的综合性科学。
中药学 Chinese materia medica 中药学科的统称。
研究中药基本理论和各种药材饮片、中成药的来源、采制、性能、功效、临床应用等知识的学科。
中医药 traditional Chinese medicine and pharmacology 中医与中药的合称。
中医药学 traditional Chinese medicine and pharmacology 中医学与中药学的合称,侧重反映中医与中药两者共同发展,密不可分。
中西医结合 integration of traditional and western medicine 现代医学等现代科学知识及手段来继承和发展中医药,中西医学相互补充,取长补短,诊治疾病的医学形式。
中医基础理论 basic theory of traditional Chinese medicine 研究和阐明中医学的基本概念、基本理论、基本规律、基本原则的学科。
中医诊断学 diagnostics of traditional Chinese medicine 根据中医学的理论体系,研究诊察病情、判断病种、辨别证候的基础理论、基本知识和基本技能的学科。
方剂学 prescriptions of Chinese materia medica 研究治法与方剂配伍规律及其临床运用的学科。
中医内科学 internal medicine of traditional Chinese medicine 研究外感温病、内伤杂病等内科疾病诊治与预防的临床中医学。
一、绪论中医学TCM(Traditional Chinese Medicine),中医学理论体系的形成Origination of TCM, 形成formation, 发展development中医学理论体系的基本特点The basic characteristic of Traditional Chinese Medicine theory整体观the whole concept, 辨证论治syndrome differentiation and treatment第一章阴阳五行学说阴阳Yin-yang , 阴阳的特性the property of yin-yang阴阳之间的相互关系Interaction between yin and yang阴阳对立制约Opposition of yin and yang阴阳互根互用Interdependence between yin and yang阴阳消长平衡Wane and Wax between yin and yang阴阳相互转化Mutual transformation between yin and yang阴阳学说在中医学中的应用The applications of the theory of yin-yang in TCM说明人体的组织结构Explanation of the histological structure of the human body解释人体的生理功能Explanation of the physiology function activity of the human body阐释病理变化Explanation of pathogenesis阴阳偏盛Relative predominance of yin or yang阳偏盛Relative predominance of yang阴偏盛Relative predominance of yin阴阳偏衰Relative decline of yin or yang阳偏衰Relative decline of yang阴偏衰Relative decline of yin五行the five elements,五行特性the five elements property第二章中医学的生理观藏象“Zangxiang” ,五脏five Zang-organs, 六腑six fu-organs,生理功能the physiological functions ,气qi, 血blood , 津液body fluid,气的生成、运动和分类the production ,moving and classification of qi,血的生成和运行the production and circulation of blood津液的生成、输布和排泄the production and transportation and metabolism of body fluid.气、血、津液的功能The physiological functions of qi, blood and body fluid心The heart,主血脉Governing blood主神志controlling the mind在体合脉governs the vessels开窍于舌opens into the tongue其华在面External manifestation on the face肝The liver,主疏泄To dredge and regulate, 主藏血Storing blood在体合筋The liver governing the tendons其华在爪The external manifestation of the liver on the nails开窍于目The liver opening into the eyes脾the spleen,主运化To govern the transportation and transformation主统血To command blood, 主升elevating在体合肌肉,主四肢the spleen governing the muscles and the four limbs开窍于口The spleen opening into the mouth其华在唇The external manifestation on the lip肺The lung,主气,司呼吸Dominating qi,controlling the respiratory movement主宣发、肃降dispersing and descending通调水道The regulation of water passage朝百脉、主治节‘the lung is connected with all the vessels, regulation the qi activity in the whole body在体合皮the lung governing the skin其华在毛Eexternal manifestation on the body hair开窍于鼻The lung opening into the nose肾The kidney,藏精store essence, 主水To govern water, 主纳气To govern reception of qi在体合骨The kidney governing the bones开窍于耳及二阴The kidney opening into the ears, the external genitals and the anus 其华在发External manifestation on the hair胆The gallbladder, 贮藏和排泄胆汁store and excrete the bile胃The stomach, 受纳、腐熟水谷receive and digest food主通降‘the stomach functions to descend’,‘unobstructed condition小肠The small intestine, 受盛化物To receive the chime and transform泌别清浊To separate the lucid from the turbid大肠The large intestine, 主传化糟粕transmitting and excreting the waste of food膀胱The bladder ,storing and discharging urine气的生成The production of qi气的运动The moving of qi气的功能The physiological functions of qi推动作用Propelling function温煦作用Warming function防御作用Protecting and defencive function固摄作用Fixating function气化作用Qi-transforming function元气primordial qi, 宗气pectoral qi, 营气nutrient-qi, 卫气defensive qi第三章中医学的病理观病因 Causes of disease病因的概念及分类concept, classification of causes of disease.六淫的概念concept of six pathogenic factors;,,六淫致病的共同特点the general pathogenic characters of six pathogenic factors;六淫(风、寒、暑、湿、燥、火)的性质与致病特点nature, pathogenic characters of every six pathogenic factors(including wind, cold,Summer-heat,Dampness,Dryness,Heat (fire))主要的临床表现main clinic manifestations风Wind其性开泄,易袭阳位Wind tend to float, disperse, go upward attack the upper and outside parts风性善行而数变wind tends to move and change风为百病之长,易夹杂其他外感之邪Wind tends to be complicated by other pathogenic factors寒Cold易伤阳气Cold tends to impair yang寒性凝滞Cold tends to coagulate寒性收引Cold tends to contract暑Summer-heat其性炎热Summer-heat is hot暑性升散,耗气伤津Summer-heat tends to disperse and elevate,consume the qi and body fluid暑多夹湿Summer-heat often complicated by dampness湿Dampness湿性重浊dampness is heavy and turbid湿易阻遏气机dampness tends to block qi湿性黏滞dampness is sticky and stagnant湿性趋下, 易袭阴位dampness tends to move downward,attack the lower and inside parts燥Dryness燥易伤津Dryness consume the body fluid燥性干涩Dryness is xerotic and unsmooth燥易伤肺Dryness tends to impair the lung火Heat (fire)其性炎上Heat(fire) tends to flame up易伤津耗气Heat(fire) tends to consume qi and impair body fluid易生风动血Heat(fire) tends to produce wind and disturb blood易致肿疡Heat(fire) tends to cause swelling and ulceration七情内伤的概念、The concept of internal impairment due to the seven emotions,七情致病的特点the pathogenic characters of the seven emotions痰饮、瘀血的概念、形成及致病特点The basic concept, the formation and the pathogenic characteristics of phlegm ,rheum and blood stasis痰饮phlegm ,rheum 瘀血blood stasis发病的基本原理The pathogenesis of occurrence of disease in TCM病机的概念,The concept of mechanism of pathological changes;病机the mechanism of pathological changes;邪正盛衰predomination and decline of pathogenic factors and healthy qi;阴阳失调imbalance between yin and yang;气血津液失常disorder of qi, blood and body fluid.第四章中医诊断疾病的方法中医诊法The concept of the TCM diagnostic methods中医诊断的理论依据the theory foundation of the TCM diagnostic methods.望神Inspection of spirit, 望色Inspection of complexion, 望排出物Inspection of excreta ,望舌Inspection of tongue,Existence of spirit (得神),Lack of spirit(少神),Loss of spirit (失神)False spirit(假神)Normal complexion 常色Morbid complexion 病色Red colour ,White colour ,Yellow colour, Bluish colour,Blackish colour临床意义clinical significance ;望舌的方法Methods for inspection of tongue舌苔tongue coat舌红red tongue淡白舌/舌淡Light-whitish tongue青紫舌Cyanotic and purplish tongue问诊inquiry, 主诉chief complaint, 病史history of present illness问现在症inquiry of the present symptomsAversion to cold and fever(恶寒发热)Cold sensation without fever(但寒不热)Fever without cold sensation(但热不寒)Alternate cold and fever(寒热往来)诊脉的部位与方法The Regions and methods for taking pulse脉诊taking pulse, 正常脉象normal pulseCunkou(寸口)cun(寸), guan(关),chi(尺).辨证的概念The concept of differentiation of syndrome表里辨证External and internal differentiation of syndromes,表证External syndromes,里证internal syndromes,寒热辨证cold and heat differentiation of syndromes,寒证cold f syndromes,热证heat syndromes,虚实辨证asthenia and sthenia differentiation of Syndromes,虚证asthenia Syndromes,实证sthenia Syndromes,临床特点clinical character and difference.八纲辨证Syndromes differentiation with eight principles气血津液辨证syndrome differentiation with qi, blood and body fluid,第五章中医学的防治原则治则therapeutic principles , 治法therapeutic methods正治Routine treatment , 反治Contrary treatment,治本treat “ben”(deal with the root cause)治标Treating biao(acute symptoms bring on great suffering to the patients, or threaten life or tend to transmit and change) in emergency ,扶正与祛邪Strengthening healthy qi and eliminating pathogenic factors,调整阴阳Regulation of yin and yang,三因制宜Abidance by individuality, locality and seasons.第六章中药基本知识中药Chinese Medicinal Herbs四气four properties、寒热温凉cold, hot, warm, cool五味five flavors、辛、甘、酸、苦、咸pungent, sweet, sour, bitter and salty.升降浮沉the action of lifting, lowering, floating and sinking,、归经channel tropism、毒性toxicity中药的配伍、用药禁忌Contraindication and Compatibility of Chinese Medicinal Herbs中药的剂量Dosage of Chinese Medicinal Herbs第七章方剂基本知识方剂的组成原则The principle of the composition of prescriptions,Monarch drug (jun) 君Minister drug (chen) 臣Adjuvant drug (zuo) 佐Guide drug (shi) 使组成变化the modification of the composition of a prescription.方剂的组成、用法、功效、临床应用、方解:Ingredients, administration, function,clinical application and elucidation of the prescriptions第二章中医学的生理观第三节经络经络the meridians;十二经脉twelve regular meridians十二经脉走向与交接规律direction, joint law of the twelve channels、十二经脉循行分布规律distributing law of the twelve channels ,十二经脉表里络属关系exterior-interior relationship of the twelve channels ,十二经脉流注方向和次序等flowing direction and order of the twelve channels;第八章针灸学基本知识第二节刺灸方法刺法(针法)Acupuncture techniques; 进针Needling methods (insertion methods, Needling manipulation methods)得气arrival of Qi针刺意外和防治处理Management of possible accidents (emphasize 晕针fainting) 灸法moxibustion,第八章针灸学基本知识第一节腧穴腧穴概念;腧穴分类;腧穴定位方法;腧穴的作用the point/acupoint (definition/concept, classification, location method, function)腧穴的定位、归经、基本主治功能:location, channel tropism and the basic special treatment function of the point/acupoint下列腧穴的定位、基本主治功能:手太阴肺经:列缺;The lung channel of Hand-Taiyin: LieQue (Lu7)手阳明大肠经:合谷;The large intestine channel of Hand-Yangming: Hegu (LI4) 足阳明胃经:足三里;The stomach channel of Foot-Yangming: Zusanli (ST36) 足太阴脾经:三阴交;The spleen channel of Foot-Taiyin: Sanyinjiao (SP6)手少阴心经:神门;The heart channel of Hand-shaoyin: Shenmen (HT7)手太阳小肠经:听宫;The small intestine channel of Hand-taiyang: Tinggong (SI19) 足太阳膀胱经:委中;The urinary Bladder channel of Foot-Taiyang: Weizhong(BL40),足少阴肾经:涌泉;The Kidney channel of Foot-shaoyin: Yongquan(KI 1)手厥阴心包经:内关;The Pericardium channel of hand-Jueyin: Neiguan (PC6)手少阳三焦经:外关;The triple warmer (Sanjiao ) channel of Hand-Shaoyang:Waiguan (SJ5 ),足少阳胆经:风池;The Gall Bladder channel of Foot-shaoyang: Fengchi (GB20) 足厥阴肝经:太冲;The Liver channel of Foot-Jueyin: Taichong (LR3)任脉:关元、膻中;The Ren channel :Guanyuan (RN4), Tanzhong (RN17)督脉:大椎、人中;The Du channel : Mingmen(GV 4), Dazhui (DU14), Shuigou (DU26),经外奇穴:印堂、太阳;Extraordinary acupoints: Yintang(EX-HN 3), Taiyang(EX-HN 5)。