Server 2008 R2 事件查看器实现日志分析
- 格式:docx
- 大小:2.64 MB
- 文档页数:9

建立安全日志记录为了让大家了解如何追踪计算机安全日志功能的具体方面,首先需要了解如何启动安全日志。
大多数Windows计算机(除了某些域控制器版本系统)默认情况下不会向安全日志(Security Log)启动日志记录信息。
这样的设置有利也有弊,弊的方面在于,除非用户强迫计算机开始日志记录安全事件,否则根本无法进行任何追踪。
好的方面在于,不会发生日志信息爆满的问题以及提示日志已满的错误信息,这也是Windows Server 2003域控制器在没有任何预警下的行为。
安全日志事件跟踪可以使用组策略来建立和配置,当然你可以配置本地组策略对象,但是这样的话,你将需要对每台计算机进行单独配置。
另外,你可以使用Active Directory内的组策略为多台计算机设置日志记录配置。
要建立安全日志追踪,首先打开连接到域的计算机上的Group Policy Management Console (GPMC,组策略管理控制台),并以管理员权限登录。
在GPMC中,你可以看到所有的组织单位(OU)(如果你事先创建了的话)以及GPO(如果你创建了两个以上),在本文中,我们将假设你有一个OU,这个OU中包含所有需要追踪相同安全日志信息的计算机,我们将使用台式计算机OU和AuditLog GPO。
编辑AuditLog GPO然后展开至以下节点:Computer Configuration\Policies\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Local Policies\Audit Policy类别控制范围的简要介绍以下是关于每种类别控制范围的简要介绍:审计帐户登录事件–每次用户登录或者从另一台计算机注销的时候都会对该事件进行审计,计算机执行该审计是为了验证帐户,关于这一点的最好例子就是,当用户登录到他们的Windows XP Professional计算机上,总是由域控制器来进行身份验证。

sql server 2008数据库操作日志SQL Server 2008数据库操作日志详解SQL Server 2008是微软推出的一款关系型数据库管理系统。
在数据库操作中,无论是进行插入、更新、删除等操作,都会在操作时生成一条日志记录,即数据库操作日志。
本文将深入解析SQL Server 2008数据库操作日志,从日志类型、作用、管理与分析等多个角度进行探讨,希望能为读者提供一个全面的了解。
一、数据库操作日志的类型SQL Server 2008数据库操作日志主要分为两种类型:事务日志和错误日志。
1. 事务日志事务日志是数据库操作中最重要的一部分,用于记录每个事务的操作信息。
事务被视为一组相互关联的操作,在其执行过程中要么全部成功提交,要么全部失败回滚。
事务日志记录了这些操作的顺序和内容,可以在事务提交或回滚时进行恢复和重做。
2. 错误日志错误日志主要用于记录数据库操作中的错误信息。
当数据库处于故障状态或者操作产生与预期结果不符的异常情况时,错误日志记录了相关的错误信息。
这些错误信息对于排查和解决问题非常重要。
二、数据库操作日志的作用数据库操作日志在数据库管理中起到了至关重要的作用,具体体现在以下几个方面。
1. 恢复和重做事务日志记录了数据库操作的完整历史,可以用于数据库故障后的恢复和重做。
当数据库遭受意外损坏或崩溃时,可以通过日志文件对数据库进行恢复,确保数据的丢失量最小。
2. 保证数据一致性数据库操作往往涉及多个数据表之间的关系,事务日志的存在可以保证多表操作的一致性。
如果某个操作在执行过程中发生了意外中断,数据库可以利用事务日志回滚到操作前的状态,确保数据库的一致性。
3. 监控和分析数据库操作日志可以用于监控和分析数据库的性能、资源使用情况和操作规律。
通过对日志的分析,可以发现系统瓶颈和异常情况,及时调整和优化数据库配置,提高数据库的性能和稳定性。
三、数据库操作日志的管理与分析对于SQL Server 2008数据库操作日志的管理和分析,有一些常用的操作方法和工具。


S ly.li2011/6/17 MSN sly.li@1. Event ID :8003 Source: MRxSmbDespritionThe master browser has received a server announcement from the computer SZE200408055 that believes that it is the master browser for the domain on transport NetBT_T cpip_{E020FE1D-2341-4. The master browser is stopping or an election is being forced.8003DCA. .TCP/IP NetBTUDPUDP 8003B.C. computer browser\services.msc computer browser,\\2. Event ID :5722 Source:NETLOGONDespritionThe session setup from the computer M EPTSERVER failed to authenticate. The name(s) of the account(s) referenced in the security database is MEPTSERVER$. The following error occurred:DCPDC BDCPDC NT47XP2000200330CISCO spanning tree spanning tree3. Event ID29DespritionThe time provider NtpClient is configured to acquire time from one or more time sources, however none of the sources are currently accessible. Noattempt to contact a source will be made for 960 minutes. NtpClient has no source of accurate timetime server:;, DC PING,;,Windows Server 2003Windows NTPWindowsA. cmd EnterB. Enterw32tm /config /manualpeerlist:NTP_server_IP_Address,0x8/ syncfromflags:MANULnet stop w32timenet start w32timeWindows Server 2003 Windows NTPWindows (W32Time) W32Timehotfix 830092hotfix 8300928008203800WindowsServer 2003 Windows XP W32Time ID 504. Event ID :7031 Source:Service Control M anagerDesprition:The Distributed T ransaction Coordinator service terminated unexpectedly. It has done this 1 time(s). The following corrective action will be taken in 1000 milliseconds: Restart the servicemsdtc:HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CIDHKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\MSDTCHKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\MSDTCmsdtcMSDTC5. DNS,ADDNS DNS---DNS AD°A c ti ve D i r ec t o rActive DirectoryDNSDNSDNS AD6. Event ID :1202 Source:SceCli Type:waringDespritionSecurity policies were propagated with warning. 0x534 : No mapping between account names and security IDs was doneWin32 SCECLI 1202 SCECLI 1202°D escri p ti o0x534Event Type:WarningEvent Source:SceCliEvent Category:NoneEvent ID:1202Date:MM/DD/YYYYTime:HH:MM:SS AM|PMUser:N/AComputer:%ComputerName%Description:Security policies are propagated with warning.0x534:No mappingbetween account names and security IDs was done.Please look for more details in TroubleShooting section in Security Help0x534:N o mapping between account names and security IDs was done. 0x5340x6fc:The trust relationship between the primary domain and the trusted domain failed.0x6fc(SID)1)a)b)HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\WindowsNT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon\GPExtensions\{827D319E-6EAC-11D2-A4EA-00C04F7 9F83A}c)ExtensionDebugLevelDWORD2d)2)Entersecedit /refreshpolicy machine_policy /enforce%SYSTEMROOT%\Security\LogsWinlogon.log3) Enterfind /i "cannot find" %SYSTEM ROOT%\security\logs\winlogon.log (find /i "" %SYSTEMROOT%\security\logs\winlogon.log)°C anno t fi nd M i chae l A l exande MichaelAlexander MichaelAlexanderMichelleAlexander4)SCECLI 1202Enterc:\>find /i ± %SYSTE M ROO T\security\templates\policies\gpt*.* c:\>find /i"M ichaelAlexander" %SYSTEM ROOT%\security\templates\policies\gpt*.* ---------- D:\WINNT\SECURITY\TEMPLATES\POLICIES\GPT00000.DOM---------- D:\WINNT\SECURITY\TEMPLATES\POLICIES\GPT00001.INF---------- D:\WINNT\SECURITY\TEMPLATES\POLICIES\GPT00002.INFSeInteractiveLogonRight = TsInternetUser,*S-1-5-32-549,*S-1-5-32-550,MichaelAlexander,*S-1-5-32-551,*S-1-5-32-544,*S-1-5-32-548---------- D:\WINNT\SECURITY\TEMPLATES\POLICIES\GPT00003.DOM GPT00002.inf (GPO)SeInteractiveLogonRight SeInteractiveLogonRight °Logon l oca llSeInteractiveLogonRight Logon locallyM icrosoft Windows 2000 Server Resource Kit °D i s tri bu t ed Systems Guide5) GPO 4°G P O Pa t hGPOPath={6AC1786C-016F-11D2-945F-00C04FB984F9}\M ACHINE°G P O ath=\M ACHINE GPO GUID6) GPO Resource Kit Gpotool.exeEntergpotool /verboswe5 GUID GUIDPolicy {6AC1786C-016F-11D2-945F-00C04FB984F9} Policy OK Details:------------------------------------------------------------DC: Friendly name:Default Domain Controllers PolicyGPO0x2:The system cannot find the file specified.0x20x534 0x6fc 0x21)a)b)HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\WindowsNT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon\GPExtensions\{827D319E-6EAC-11D2-A4EA-00C04F7 9F83A}c)ExtensionDebugLevelDWORD2d)2)Entersecedit /refreshpolicy machine_policy /enforce%SYSTEMROOT%\Security\LogsWinlogon.log3) Enterfind /i "cannot find" %SYSTEMROOT%\security\logs\winlogon.log°C anno t fi nd M i chae l A l exande MichaelAlexander MichaelAlexanderMichelleAlexander4)SCECLI 1202Enterc:\>find /i ± %SYSTE M ROO T\security\templates\policies\gpt*.*c:\>find /i"MichaelAlexander" %SYSTEMROOT%\security\templates\policies\gpt*.* ---------- D:\WINNT\SECURITY\TEMPLATES\POLICIES\GPT00000.DOM---------- D:\WINNT\SECURITY\TEMPLATES\POLICIES\GPT00001.INF---------- D:\WINNT\SECURITY\TEMPLATES\POLICIES\GPT00002.INFSeInteractiveLogonRight =TsInternetUser,*S-1-5-32-549,*S-1-5-32-550,JohnDough,*S-1-5-32-551,*S-1-5-32-544,*S-1-5-32-548---------- D:\WINNT\SECURITY\TEMPLATES\POLICIES\GPT00003.DOM GPT00002.inf GPOSeInteractiveLogonRight SeInteractiveLogonRight°Logon l oca llSeInteractiveLogonRight Logon locallyM icrosoft Windows 2000 Server Resource Kit °D i s tri bu t ed S ys t e m s G u i d5) GPO 4°G P O Pa t hGPOPath={6AC1786C-016F-11D2-945F-00C04FB984F9}\M ACHINE°G P O ath=\M ACHINE GPO GUID6) GPO Resource Kit Gpotool.exeEntergpotool /verbose5 GUID GUIDPolicy {6AC1786C-016F-11D2-945F-00C04FB984F9} Policy OKDetails:------------------------------------------------------------DC: Friendly name:Default Domain Controllers PolicyGPO°M i chae l A l exande0x5:Access denied.0x51)HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\WindowsNT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon\GPExtensions\{827D319E-6EAC-11D2-A4EA -00C04F7 9F83A}ExtensionDebugLevelDWORD22)Entersecedit /refreshpolicy machine_policy /enforce%SYSTEMROOT%\Security\LogsWinlogon.log3) Enterfind /i "error opening" %SYSTEMROOT%\security\logs\winlogon.log°E rr o r open i ng Dnscache Dnscache Dnscache DNS4)Enterfind /i "security\templates\policies\gpt*.*"d:\>find /i "dnscache" %windir%\security\templates\policies\gpt*.*---------- D:\WINNT\SECURITY\TEMPLATES\POLICIES\GPT00000.DOM---------- D:\WINNT\SECURITY\TEMPLATES\POLICIES\GPT00001.INF---------- D:\WINNT\SECURITY\TEMPLATES\POLICIES\GPT00002.INFDnscache,3,"D:AR(A;;CCDCLCSWRPWPDTLOCRSDRCWDWO;;;LA)"---------- D:\WINNT\SECURITY\TEMPLATES\POLICIES\GPT00003.DOM5) GPO Resource Kit Gpotool.exeEntergpotool /verbose5 GUID GUIDPolicy {6AC1786C-016F-11D2-945F-00C04FB984F9} Policy OK Details:------------------------------------------------------------DC: Friendly name:Default Domain Controllers Policy6) GPO0x4b8:An extended error has occurred.0x4b80x4b81)HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\WindowsNT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon\GPExtensions\{827D319E-6EAC-11D2-A4EA -00C04F7 9F83A}ExtensionDebugLevelDWORD22)Entersecedit /refreshpolicy machine_policy /enforce%SYSTEMROOT%\Security\LogsWinlogon.log3) Microsoft 0x4b8Microsoft260715Event ID 1000 1202278316ESENT ID 100012024124547. win2003DC dcdiag,net share,net viewdcdiagS tarting test: NetLogons[DC02] An net use or LsaPolicy operation failed with error 64,S tarting test: M achineAccount Could not open pipe with [DC02]:failed with 64:S tarting test: ServicesCould not open Remote ipc to [DC02]:failed with 64:S tarting test: kcceventFailed to enumerate event log records, error......................... DC02 failed test kcceventS tarting test: systemlogFailed to enumerate event log records, error......................... DC02 failed test systemlognet shareC:\>net shareShare name Resource Remark--------------------------------------------------------------------IPC$ IPCC$ C:\D$ D:\ADMIN$ C:\WINDOWSMNS_FSW_acl-mailclusterC:\MNS_FSW_DIR_acl-mailclusterNETLOGON C:\WINDOWS\SYSVOL\sysvol\acl.corp\SCRIPTSLogon server shareshare D:\sharesoftware D:\softwareSYSVOL C:\WINDOWS\SYSVOL\sysvol Logon server shareThe command completed successfully.net viewC:\>net view \\DCSystem error 64 has occurred.The specified network name is no longer available.server server5WIN2003SP2IBMRSS TCP1) regedit2)HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Tcpip\Param eters3) EnableTCPChimney4) 05) EnableRSS6) 07) EnableTCPA8) 09)8. ,1 ADMTADMT ADMTC$ ADMIN$ ADMT MicrosoftActive Directory 2 Windows 2000 Windows Server 2003/kb/326480/zh-cn9. event id:675672644671Event id:675 .Event id:672Event id:644Event id:67110. PDC DNS DHCP WINS pingIP DHCP WINS DNS IP DHCP DNS WINSA PTR PDC BDCPTR DNSadministrator DHCP DNS11. Event id :1988:: NTDS Replication:ID: 1988: 2010-5-21: 17:47:56: NT AUTHORITY\ANONYMOUS LOGON: GZPDCSVR1:Active Directory (DC) Active DirectoryActive DirectoryDCDC1DC2repadmin /removelingeringobjectsRepadminrepadmin /removelingeringobjects1)2) Active Directory3)/advisory_moderepadmin /removelingeringobjectsrepadmin /removelingeringobjectsWindows Server 20031) Repadmin Repadmin Windows Server 2003 CD-ROMWindows Server 2003CD_Drive:\Support\Tools °Sup t oo l s.m s2) repadmin /removelingeringobjectsDestination_domain_controller Source_domain_controller_GUID Directory_partition /advisory_mode Enter3) /advisory_mode ID 1988Active Directory/advisory_ modeRepadmin /advisory_ mode Destination_domain_controller (DNS) IP ID 1988dc_listrepadmin /removelingeringobjects dc_listrepadmin /listhelp EnterSource_domain_controller_GUIDGUID GUIDrepadmin /showrepl /v <> Enter GUID °DC ob j ec t GU IActive Directory GUID°A c ti ve D i r ec t o r ya)b) °N T D S°DN S°_m s dcs forest_root_ GUIDGUID Repadmin GUID Repadmin°_m s dcs forest_root_domain_Directory_partition (DN)object_distinguished_name(dc=domain_DN)(cn=Configuration,dc=forest_root_DN)(cn=Application_directory_partition_name,dc=domain_DN)(cn=Application_directory_partition_name,dc=forest_root_DN)(cn=Schema, cn=Configuration,dc=,dc=forest_root_DN)4)5)ID:1937::(DC) DC DCDC DC DC:Source_domain_controller_GUID._msdcs.forest_rootID:1945::(DC)DC:DC= DN_of_lingering_objectGUID:object_GUIDDC:Source_domain_controller_GUID._msdcs.forest_rootID:1939::(DC)DCDCDCDCDC:Source_domain_controller_GUID._msdcs.forest_root236)Windows Server 2003 Microsoft°L i nge ri ng O b j ec tRemoval/windowsserver/en/library/1465D773-B763-45EC-B971-C23CDC27400E1033.mspx12. Event ID 8crypt32ID 8:</msdownload/update/v3/static/tr ustedr/en/authrootseq.txt>Internet WindowsUpdateUpdateRootCertificatesMicrosoftUpdate, Internet ,1. , /2. /Windows3. UpdateRootCertificates , WindowsUpdateRootCertificates WinHTTP API WindowsUpdate, Proxycfg.exeProxycfg.exe, WinHTTP 1. " <Systemroot> \ System 32 " Proxycfg.exeProxycfg.exe Systemroot> " \ System 32 "Microsoft830605 (/kb/830605/) Proxycfg.exe WinHTTP 5.1, Proxycfg.exeWinHTTP, proxycfg , RETURN, " Direct "Microsoft XML Parser (MSXML) 3.0 SP 1 , " ", proxycfg-d ,RETURN WinHTTP, - proxycfg-d , RETURNproxycfg - p , ,RETURN,Proxycfg.exe ReadMe.txtInternetExplorer Internet, WinInet , WinHTTP , proxycfg - u ,RETURNMicrosoftInternet (IIS)13. Event ID: 4007:: DNS:ID: 4007: 2010-7-7: 17:28:40: N/A: AD-SERVER:DNS ForestDnsZones.might ActiveDirectory _msdcs.might DNSActive Directory:0000: 0d 00 00 00 ....1)2)HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\WindowsNT\CurrentVersion\DNS Server\Zones3)4)Microsoft14. Event ID:1010 Event id :1016Event ID1014Event ID1010DHCPDHCPDHCPEvent ID1016DHCP :DHCPDHCPEvent ID1014jet -1032 JetDHCP: JetBackup1) C:\WINDOWS\system32\dhcp2) DHCP indexing3) DHCP C:\WINDOWS\System324) DHCP5) For fast searching indexing service6) chkdsk c: /f15. Event ID 4Source KerberosType: ErrorDescription:The kerberos client received a KRB_AP_ERR_M ODIFIED error from the server SZ201006A04$. The target name used was cifs/. This indicates that the password used to encrypt the kerberos service ticket is different than that on the target server. Commonly, this is due to identically named machine accounts in the target realm (), and the client realm. Please contact your system administratorDC PDC Kerberos (KDC)1)2) KDCNetdom PDCPDCnetdom resetpwd /server:/userd:\administrator /passwordd:3) secure channel DC4) DC5) KDCTarget Principal Name is Incorrect16. Evenit ID:13 Event ID:16Event ID:13Source: :AutoEnrollmentType: ERRORDescrptions:Automatic certificate enrollment for local system failed to enroll for one Domain Controller certificate (0x800706ba). The RPC server is unavailable.Event ID:16Type: ERRORDescrptions:Automatic certificate enrollment for local system failed to enroll for one Domain Controller certificate (0x800706ba). The RPC server is unavailable.DC4OS2003R2 SP22003 SP2GC DC81) 0x800706BADNS DNS2) 0x80070005windows 2003 sp1Domain Users"Domain Computers", "Domain Controllers"CERTSVC_DCOM_ACCESS.DCOM securitycertutil -setreg SetupStatus -SETUP_DCOM_SECURITY_UPDATED_FLAGnet stop certsvcnet start certsvc17. Event ID:4Event ID:4Source KerberosType:ErrorDescription:The kerberos client received a KRB_AP_ERR_M ODIFIED error from the server SZ201006A04$. The target name used was cifs/.This indicates that the password used to encrypt the kerberos service ticket is different than that on the target server. Commonly, this is due to identically named machine accounts in the target realm (), and the client realm. Please contact your system administrator.secure channel DC PDC Kerberos (KDC)1)2) KDCNetdom PDCPDCnetdom resetpwd /server:/userd:administrator /passwordd:PDC3) secure channel DC4) DC5) KDC18. Event ID:13555 Event ID:13552Event ID:13508Event ID:13555Description:[1] FRS:net stop ntfrsnet start ntfrs[2] DFS Active Directory:(ntbackup -)DCntbackup ) DC ±sysvols)[3] DFS Active Directory(3-a) DC Dfs Dfs(3-b) Active Directory (3-c)(->->->NTDS ->(3-c) (ntbackup -)DC(3-d) sysvol (3-a)[4] Windows(4-a) DFS(4-b) net stop ntfrs(4-c) rd /s /q c:\windows\ntfrs\jet(4-d) net start ntfrs(4-e) ( 5 )(4-a):(4-a) (4-e)Event ID:13552Description:"DOMAIN SYSTEM VOLUME (SYSVOL SHARE)":-------- NTFS 5.0DNS """NCAD1""c:\windows\sysvol\domain""c:\windows\sysvol\staging\domain""c:\windows\ntfrs\jet"WindowsFRS FrsErrorMismatchedJournalIdEvent ID:13508Description: NCAD1 NCAD2 c:\windows\sysvol\domain DNS FRS[1] FRS DNS [2] FRS [3] Active Directory1) NetLogon FRSNet Stop NetlogonNet Stop NTFRS2) C:\Windows\Ntfrs\Jet Ntfrs.jdb3) C:\Windows\Ntfrs\Jet\Sys Edb.chk4) C:\Windows\Ntfrs\Jet\Log Edb.log Res1.log Res2.log5)HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\NtFrs\Parameters\Backup/Restore/Process at S tartup6)Value name: BurFlagsData type: REG_DWORDRadix: HexadecimalValue data: D47) NetLogon FRSNet start NetlogonNet start NTFRS19. netbios:computer1netbioscomputer2,Windows Server 2003 Support\Tools Windows Server 2003 NetdomNetdom RenameComputer:Netdom renamecomputer /newname:/userD: /passwordD:/userO:/passowrdO::netdom renamecomputer computer1 /newname:computer2 /userD:administrator /pasordD:pwd /userO:administrator /passwordO:pwd /force /reboot:60computer1computer2,/force ,/reboot:606020. 2008R2 AD AD RM SRMS AD SCPRMS ToolkitRMS ToolkitCMD RMS ToolKit ADScpRegister:C:\Program Files\RMS SP2 Administration Toolkit\ADScpRegister ADScpRegister.exe unregisterscpRMS Toolkit:/downloads/en/details.aspx?FamilyID=bae62cfc-d5a 7-46d2-9063-0f6885c26b98&DisplayLang=enadsiedit.mscadsiedit.mscConfiguration [*.*.COM]->CN=Configuration,DC=*,DC=*->CN=Services->CN=RightsManag ementServicesCN=RightsM anagementServices21.1RSAT Windows Server 2008 Windows Vista SP1 Windows Server 2003 /2008[\\]Regional Options Extension/en-us/library/cc754496.aspxOverview of Preferences/en-us/library/cc732027.aspxWindows Server 2008Windows Server 2003 RSAT Windows Server 2008 Windows Vista SP1Windows Server 2008Windows Vista SP1VistaCSEs Windows XP Service Pack 2 (SP2)Windows Server 2003 Service Pack 1 (SP1) Windows VistaCSEsWindows Server 2008/kb/2HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Control Panel\InternationalWindows Server 2008 RSAT Windows Vista SP1custom.adm1.2. [HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Control Panel\International]3. Windowsregedit /s <\\server\share\RegionalSetting.regregedit /s \\server\share\RegionalSetting.reg4. GPOMicrosoftWindows 2000/kb/22. Windows Server 2008 Internet Explorerinetesc.adm Windows Server 2008 Internet Exploreradm GPO /downloads/details.aspx?FamilyID=d41b036c-e2e1-4960-99bb-9757f7e9e31b&DisplayLang=en1. GPO GPO Internet Explorer2. GPO3. /4. adm5. (ADM)6. Internet ExplorerWindows 200323."ShowStatus 0""ShowStatus "3""Docked"ShowStatus "4ShowStatusDim WshShellSet WshShell = WScript.CreateObject("WScript.Shell")WshShell. RegWrite" HKCU\Software\Microsoft\CTF\LangBar\ShowS tatus", 4, "REG_DWORD24. ADAMdsdbutil.exe ADAM:TechNet AD LDSAD LDS/zh-cn/library/1. ADAM ADAMActive Directory2. dsdbutil.exeAD LDS/zh-cn/library/25.Active Directory , UserAccountControlProperty flag Value in hexadecimal Value in decimalACCOUNTDISABLE0x0002 2:(&(objectCategory=person)(objectClass=user)(!userAccountControl:1.2.840.11 3556.1.4.803:=2))csvde -d "dc=<Domain>,dc=<com>" -r "(&(objectCategory=person)(objectClass=user)(!userAccountControl:1.2.840.1 13556.1.4.803:=2))" -f enabled.csvcsvde -d " dc=<Domain>,dc=<com>" -r "(&(objectCategory=person)(objectClass=user)(userAccountControl:1.2.840.11 3556.1.4.803:=2))" -f disabled.csvUserAccountControl :UserAccountControl/?id=Microsoft(R) Windows(R) 2000 Windows Server(R) 2003 Active Directory Windows Server 2008Microsoft TechNet AD DS/zh-cn/library/cc770394.a26.1.2.GPO/?id=Windows 2000/?id=278295Locking Down Windows Server 2003 T erminal Server Sessions/downloads/details.aspx?FamilyID=7f272fff-9a6e-40 c7-b64e-7920e6ae6a0d&DisplayLang=en27. W indows Server 2008Windows Server 2008Active DirectoryActive Directory 3.1(ADMT v3.1)28. W indows Server 2008Win Server 2008Vista SP1domain downleveldownlevel Kerberos0xc000018b - STATUS_NO_TRUST_SAM_ACCOUNT Windows Server2008VistaSP1 NTLMNLTEST.exeNltest /domain_trusts0: <Domain 1> (NT 4) (Direct Inbound)1: <Domain 2> (NT 5) (Direct Inbound)2: <Domain 3> (NT 5) (Direct Inbound)"NT 4"downlevelActive Directory downlevel"nltest /domain_trusts""NT 5"downlevel Kerberos"STATUS_NO_TRUST_SAM_ACCOUNT"Windows Server 2008 Vista SP1 Windows Server 2003 Vista RTM Windows Server 2008 Vista SP1 NTLM29. Internet Explorer?Active Directory Internet Explorer Windows IE IE(GPO),GPOInternet Explorer1. Gpt.iniGPO IEAK\Install.ins Install.insGPO2. Internet Explorer Internet ExplorerPreference M ode Preference M odeIntranetInternet Explorer Preference M odePreferences\\Internet Explorera)b) \\Internet Explorerc)d)e)a) IEb) \Windows\Internet Explorerc) Internet Explorerd)e) --Internet Explorer-Internet Explorer--30. Event ID1035Event ID:1036 DHCP Server W indows Server 2008Windows Server 2008 (RODC)DHCPDHCP <>。

sql server 2008数据库操作日志-回复SQL Server 2008数据库操作日志是数据库管理系统中的一个重要功能,用于记录和追踪数据库操作的详细信息。
SQL Server 2008数据库操作日志可以帮助管理员了解数据库的使用情况,还可以用于故障排除和恢复。
在本文中,我们将一步一步回答以下问题:SQL Server 2008数据库操作日志是什么?为什么数据库操作日志如此重要?如何配置和管理SQL Server 2008数据库操作日志?如何使用数据库操作日志进行故障排除和恢复?一、SQL Server 2008数据库操作日志是什么?SQL Server 2008数据库操作日志是SQL Server 2008数据库管理系统中的一个特殊文件,用于记录数据库中发生的每个操作的详细信息。
这些操作包括插入、更新和删除数据,以及创建、修改和删除数据库对象等。
数据库操作日志包含了数据库的完整操作历史,包括事务的开始和结束,以及每个操作的执行结果。
日志文件记录了每个操作的详细信息,包括操作的时间戳、操作类型、操作的对象和操作者等。
二、为什么数据库操作日志如此重要?数据库操作日志在数据库管理中起着重要的作用。
以下是数据库操作日志的重要性所在:1.数据恢复:数据库操作日志可以用于数据库的故障恢复。
通过分析日志文件,可以重建数据库,并将损坏或丢失的数据恢复到一个一致的状态。
2.故障排除:数据库操作日志可以用于识别和解决数据库操作中的问题。
通过分析日志文件,管理员可以找到引起错误和异常的原因,并采取适当的措施来修复这些问题。
3.性能优化:数据库操作日志还可以用于分析数据库的性能问题。
通过查看日志文件中的操作,管理员可以了解数据库的实际使用情况,找出潜在的瓶颈和优化机会,并采取相应的措施来提高数据库的性能。
三、如何配置和管理SQL Server 2008数据库操作日志?SQL Server 2008数据库操作日志的配置和管理包括以下步骤:1.启用日志记录:在SQL Server 2008中,默认情况下,数据库操作日志是启用的。

维护服务器安全维护技巧之日志分析事件查看器相当于操作系统的保健医生,一些“顽疾”的蛛丝马迹都会在事件查看器中呈现,一个合格的系统管理员和安全维护人员会定期查看应用程序、安全性和系统日志,查看是否存在非法登录、系统是否非正常关机、程序执行错误等信息,通过查看事件属性来判定错误产生的来源和解决方法,使操作系统和应用程序正常工作。
本文介绍了事件查看器的一些相关知识,最后给出了一个安全维护实例,对安全维护人员维护系统有一定的借鉴和参考。
(一)事件查看器相关知识1.事件查看器事件查看器是Microsoft Windows 操作系统工具,事件查看器相当于一本厚厚的系统日志,可以查看关于硬件、软件和系统问题的信息,也可以监视Windows 操作系统中的安全事件。
有三种方式来打开事件查看器:(1)单击“开始”-“设置”-“控制面板”-“管理工具”-“事件查看器”,开事件查看器窗口(2)在“运行”对话框中手工键入“%SystemRoot%\system32\eventvwr.msc /s”打开事件查看器窗口。
(3)在运行中直接输入“eventvwr”或者“eventvwr.msc”直接打开事件查看器。
2.事件查看器中记录的日志类型在事件查看器中一共记录三种类型的日志,即:(1)应用程序日志包含由应用程序或系统程序记录的事件,主要记录程序运行方面的事件,例如数据库程序可以在应用程序日志中记录文件错误,程序开发人员可以自行决定监视哪些事件。
如果某个应用程序出现崩溃情况,那么我们可以从程序事件日志中找到相应的记录,也许会有助于你解决问题。
(2)安全性日志记录了诸如有效和无效的登录尝试等事件,以及与资源使用相关的事件,例如创建、打开或删除文件或其他对象,系统管理员可以指定在安全性日志中记录什么事件。
默认设置下,安全性日志是关闭的,管理员可以使用组策略来启动安全性日志,或者在注册表中设置审核策略,以便当安全性日志满后使系统停止响应。
MS SQL Server 2008 R2(简体中文版)
日志收缩详解
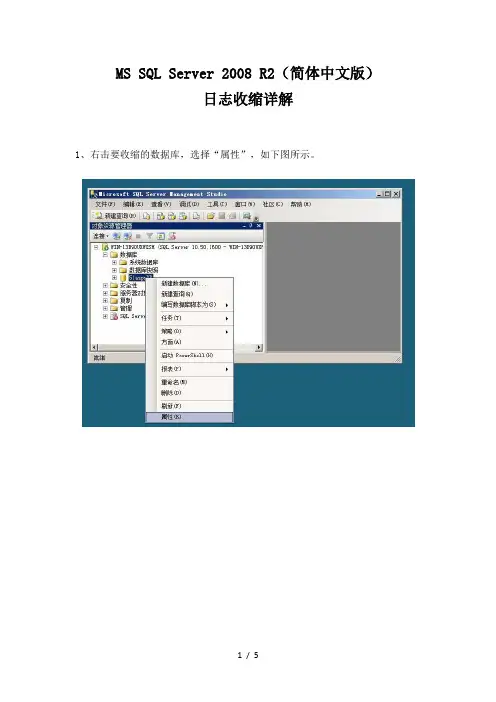
1、右击要收缩的数据库,选择“属性”,如下图所示。
2、在弹出的窗口左侧“选择页”中点击“选项”,在右侧选择“恢复模式”值为“简单”,点击“确定”按钮,如下图所示。
3、右击数据库,选择“任务”-“收缩”-“文件”,如下图所示:
4、在“收缩文件”对话框中,选择“文件类型”值为“日志”,在收缩操作中选择“在释放未使用的空间前重新组织页”,将文件收缩到指定大小,单击“确定”按钮,完成日志收缩。
5、右击数据库,选择“属性”,在弹出的窗口左侧“选择页”中点击“选项”,在右侧选择“恢复模式”值为“完整”,点击“确定”按钮即可。
[文档可能无法思考全面,请浏览后下载,另外祝您生活愉快,工作顺利,万事如意!]。

安全日志分析服务器事件日志和数据流量分析随着互联网技术和网络安全威胁的不断发展,越来越多的企业与组织开始关注网络安全问题,其中安全日志分析是网络安全保护的关键环节之一。
本文将讨论安全日志分析的两个方面:服务器事件日志分析和数据流量分析。
一、服务器事件日志分析服务器事件日志是对一个系统内发生的事件进行记录的文件,这些事件包括警告、错误、信息等。
服务器事件日志分析是通过对这些事件进行收集和分析,来检测和诊断系统的问题或异常情况。
服务器事件日志分析的主要目的是监视和管理整个系统内的事件,以及对问题进行定位和处理。
通过对服务器事件日志的分析,我们可以做到以下几点:1. 识别与排除系统故障。
2. 检测安全漏洞,并迅速采取措施。
3. 及时发现系统内的错误、故障、崩溃等问题,并解决它们。
4. 了解和掌握整个系统的运行情况,为后续的管理和优化提供支持。
二、数据流量分析数据流量分析是通过对网络上的数据流进行监测和分析,以发现网络攻击、垃圾邮件等恶意行为,并及时采取应对措施。
数据流量分析是以网络流量为基础,通过对数据流量的内容、流量大小等进行分析,来发现可能存在的恶意攻击行为。
数据流量分析主要包括以下几个方面:1. 数据流量监控:对网络上所有数据流量进行监控,并采用多种技术手段进行分析和处理。
2. 异常检测:对网络上的异常数据流量进行检测,以及异常数据的去除。
3. 可视化展示:将分析结果通过图形化界面展现出来,方便管理员进行查看和管理。
通过数据流量分析,我们可以有效地防范网络攻击、提高整个网络的安全性。
数据流量分析可以帮助我们找出网络上可能存在的安全问题,并采取有效的预防和处置措施。
总结:对于网络安全而言,安全日志分析是一项至关重要的任务,它为网络安全保护提供了重要的技术支持。
通过对日志事件和数据流量进行分析,我们可以有效地防范安全威胁、提高网络安全性。
希望本文能够让大家更好地了解和掌握安全日志分析的相关技术和应用。

解析win7WinServer2008⽤户登录⽇志Logon Type 2 – InteractiveThis is what occurs to you first when you think of logons, that is, a logon at the console of a computer. You’ll see type 2 logons when a user attempts to log on at the local keyboard and screen whether with a domain account or a local account from the computer’s local SAM. To tell the difference between an attempt to logon with a local or domain account look for the domain or computer name preceding the user name in the event’s description. Don’t forget that logon’s through an KVM over IP component or a server’s proprietary “lights-out” remote KVM feature are still interactive logons from the standpoint of Windows and will be logged as such.Logon Type 3 – NetworkWindows logs logon type 3 in most cases when you access a computer from elsewhere on the network. One of the most common sources of logon events with logon type 3 is connections to shared folders or printers. But other over-the-network logons are classed as logon type 3 as well such as most logons to IIS. (The exception is basic authentication which is explained in Logon Type 8 below.)Logon Type 4 – BatchWhen Windows executes a scheduled task, the Scheduled Task service first creates a new logon session for the task so that it can run under the authority of the user account specified when the task was created. When this logon attempt occurs, Windows logs it as logon type 4. Other job scheduling systems, depending on their design, may also generate logon events with logon type 4 when starting jobs. Logon type 4 events are usually just innocent scheduled tasks startups but a malicious user could try to subvert security by trying to guess the password of an account through scheduled tasks. Such attempts would generate a logon failure event where logon type is 4. But logon failures associated with scheduled tasks can also result from an administrator entering the wrong password for the account at the time of task creation or from the password of an account being changed without modifying the scheduled task to use the new password.Logon Type 5 – ServiceSimilar to Scheduled Tasks, each service is configured to run as a specified user account. When a service starts, Windows first creates a logon session for the specified user account which results in a Logon/Logoff event with logon type 5. Failed logon events with logon type 5 usually indicate the password of an account has been changed without updating the service but there’s always the possibility of malicious users at work too. However this is less likely because creating a new service or editing an existing service by default requires membership in Administrators or Server Operators and such a user, if malicious, will likely already have enough authority to perpetrate his desired goal.Logon Type 7 – UnlockHopefully the workstations on your network automatically start a password protected screen saver when a user leaves their computer so that unattended workstations are protected from malicious use. When a user returns to their workstation and unlocks the console, Windows treats this as a logon and logs the appropriate Logon/Logoff event but in this case the logon type will be 7 – identifying the event as a workstation unlock attempt. Failed logons with logon type 7 indicate either a user entering the wrong password or a malicious user trying to unlock the computer by guessing the password.Logon Type 8 – NetworkCleartextThis logon type indicates a network logon like logon type 3 but where the password was sent over the network in the clear text. Windows server doesn’t allow connection to shared file or printers with clear text authentication. The only situation I’m aware of are logons from within an ASP script using the ADVAPI or when a user logs on to IIS using IIS’s basic authentication mode. In both cases the logon process in the event’s description will list advapi. Basic authentication is only dangerous if it isn’t wrapped inside an SSL session (i.e. https). As far as logons generated by an ASP, script remember that embedding passwords in source code is a bad practice for maintenance purposes as well as the risk that someone malicious will view the source code and thereby gain the password.Logon Type 9 – NewCredentialsIf you use the RunAs command to start a program under a different user account and specify the /netonly switch, Windows records a logon/logoff event with logon type 9. When you start a program with RunAs using /netonly, the program executes on your local computer as the user you are currently logged on as but for any connections to other computers on the network, Windows connects you to those computers using the account specified on the RunAs command. Without /netonly Windows runs the program on the local computer and on the network as the specified user and records the logon event with logon type 2.Logon Type 10 – RemoteInteractiveWhen you access a computer through Terminal Services, Remote Desktop or Remote Assistance windows logs the logon attempt with logon type 10 which makes it easy to distinguish true console logons from a remote desktop session. Note however that prior to XP, Windows 2000 doesn’t use logon type 10 and terminal services logons are reported as logon type 2.Logon Type 11 – CachedInteractiveWindows supports a feature called Cached Logons which facilitate mobile users. When you are not connected to the your organization’s network and attempt to logon to your laptop with a domain account there’s no domain controller available to the laptop with which to verify your identity. To solve this problem, Windows caches a hash of the credentials of the last 10 interactive domain logons. Later when no domain controller is available, Windows uses these hashes to verify your identity when you attempt to logon with a domain account.<?xml version="1.0"encoding="utf-8"standalone="yes"?><Events><Event><System><Provider Name="Microsoft-Windows-Security-Auditing"Guid="{54849625-5478-4994-A5BA-3E3B0328C30D}" /><EventID>4624</EventID><Version>0</Version><Level>0</Level><Task>12544</Task><Opcode>0</Opcode><Keywords>0x8020000000000000</Keywords><TimeCreated SystemTime="2010-09-23T02:09:22.030125300Z" /><EventRecordID>14583</EventRecordID><Correlation /><Execution ProcessID="616"ThreadID="708" /><Channel>Security</Channel><Computer>dc10101-PC</Computer><Security /></System><EventData><Data Name="SubjectUserSid">S-1-5-18</Data><Data Name="SubjectUserName">DC10101-PC$</Data><Data Name="SubjectDomainName">WORKGROUP</Data><Data Name="SubjectLogonId">0x3e7</Data><Data Name="TargetUserSid">S-1-5-18</Data><Data Name="TargetUserName">SYSTEM</Data><Data Name="TargetDomainName">NT AUTHORITY</Data><Data Name="TargetLogonId">0x3e7</Data><Data Name="LogonType">5</Data><Data Name="LogonProcessName">Advapi</Data><Data Name="AuthenticationPackageName">Negotiate</Data><Data Name="WorkstationName" /><Data Name="LogonGuid">{00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000}</Data><Data Name="TransmittedServices">-</Data><Data Name="LmPackageName">-</Data><Data Name="KeyLength">0</Data><Data Name="ProcessId">0x240</Data><Data Name="ProcessName">C:\Windows\System32\services.exe</Data><Data Name="IpAddress">-</Data><Data Name="IpPort">-</Data></EventData><RenderingInfo Culture="zh-CN"><Level>Information</Level><Task>Logon</Task><Opcode>Info</Opcode><Channel>Security</Channel><Provider>Microsoft Windows security auditing.</Provider><Keywords><Keyword>Audit Success</Keyword></Keywords></RenderingInfo></Event><Event><System><Provider Name="Microsoft-Windows-Security-Auditing"Guid="{54849625-5478-4994-A5BA-3E3B0328C30D}" /><EventID>4624</EventID><Version>0</Version><Level>0</Level><Task>12544</Task><Opcode>0</Opcode><Keywords>0x8020000000000000</Keywords><TimeCreated SystemTime="2010-09-23T13:09:22.802965700Z" /><EventRecordID>14589</EventRecordID><Correlation /><Execution ProcessID="616"ThreadID="8644" /><Channel>Security</Channel><Computer>dc10101-PC</Computer><Security /></System><EventData><Data Name="SubjectUserSid">S-1-5-18</Data><Data Name="SubjectUserName">DC10101-PC$</Data><Data Name="SubjectDomainName">WORKGROUP</Data><Data Name="SubjectDomainName">WORKGROUP</Data><Data Name="SubjectLogonId">0x3e7</Data><Data Name="TargetUserSid">S-1-5-21-1970735100-597249049-2926331685-1000</Data><Data Name="TargetUserName">dc10101</Data><Data Name="TargetDomainName">dc10101-PC</Data><Data Name="TargetLogonId">0x26358257</Data><Data Name="LogonType">7</Data><Data Name="LogonProcessName">User32</Data><Data Name="AuthenticationPackageName">Negotiate</Data><Data Name="WorkstationName">DC10101-PC</Data><Data Name="LogonGuid">{00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000}</Data><Data Name="TransmittedServices">-</Data><Data Name="LmPackageName">-</Data><Data Name="KeyLength">0</Data><Data Name="ProcessId">0x280</Data><Data Name="ProcessName">C:\Windows\System32\winlogon.exe</Data><Data Name="IpAddress">127.0.0.1</Data><Data Name="IpPort">0</Data></EventData><RenderingInfo Culture="zh-CN"><Level>Information</Level><Task>Logon</Task><Opcode>Info</Opcode><Channel>Security</Channel><Provider>Microsoft Windows security auditing.</Provider><Keywords><Keyword>Audit Success</Keyword></Keywords></RenderingInfo></Event></Events>using System;using System.Collections.Generic;using System.Windows.Forms;using System.Text.RegularExpressions;using System.Xml;namespace WindowsServerLogonAnalyse{public class LogonEventRecord{public int EventRecordID { get; set; }public DateTime TimeStamp { get; set; }public int LogonType { get; set; }public string UserName { get; set; }public string ComputerName { get; set; }}public partial class Form1 : Form{List<LogonEventRecord> logList = new List<LogonEventRecord>();int[] logonTypeArray = new int[] {2,3,4,5,7,8,9,10,11};string xmlLogFilePath = string.Empty;public Form1(string xmlLogFilePath){InitializeComponent();this.xmlLogFilePath = xmlLogFilePath;}private string ConvertToValidXml(string rawXml){string ret = rawXml;// ⽤IE打开,最前⾯有空格,违反xml格式约定须去掉ret = ret.TrimStart(' ');// ⽤IE打开,有折叠横线,须去掉ret = Regex.Replace(ret, Environment.NewLine + "- <", Environment.NewLine + "<");// Message⾥包含破坏xml的⾮法字符ret = Regex.Replace(ret, @"<Message>.*?</Message>", string.Empty);// 若不去掉命名空间,⽤XPath时会遇到⿇烦ret = ret.Replace(@"xmlns=""/win/2004/08/events/event""", string.Empty);return ret;}private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e){{webBrowser1.Navigate(this.xmlLogFilePath);}private void webBrowser1_DocumentCompleted(object sender, WebBrowserDocumentCompletedEventArgs e){WebBrowser browser = (WebBrowser)sender;if (browser.ReadyState == plete){try{string xmlContent = browser.Document.Body.OuterText;xmlContent = ConvertToValidXml(xmlContent);XmlDocument doc = new XmlDocument();doc.LoadXml(xmlContent);//foreachforeach (int LogonType in this.logonTypeArray){logList.AddRange(GetRecordsByLogonType(doc, LogonType));}}catch (Exception ex){// 在WebBrowser的事件处理函数中发⽣异常,程序会继续执⾏,所以要在这⾥加个断点以便查看错误MessageBox.Show(ex.Message);throw;}}}private List<LogonEventRecord> GetRecordsByLogonType(XmlDocument doc, int LogonType){List<LogonEventRecord> ret = new List<LogonEventRecord>();// 找出所有满⾜条件的Event,条件是其⼦元素满⾜EventData/Data/@Name='LogonType'并且EventData/Data=要找的LogonTypeXmlNodeList logonEventList = doc.SelectNodes(string.Format("/Events/Event[EventData/Data/@Name='LogonType'][EventData/Data={0}]",LogonType));foreach (XmlNode node in logonEventList){LogonEventRecord record = new LogonEventRecord();record.LogonType = LogonType;erName = node.SelectSingleNode("EventData/Data[@Name='TargetUserName']").InnerText;record.TimeStamp = DateTime.Parse(node.SelectSingleNode("System/TimeCreated").Attributes["SystemTime"].Value);puterName = node.SelectSingleNode("System/Computer").InnerText;record.EventRecordID = int.Parse(node.SelectSingleNode(@"System/EventRecordID").InnerText);ret.Add(record);}return ret;}}}。

服务器日志监控与分析技巧随着互联网的快速发展,服务器扮演着越来越重要的角色,而服务器日志监控与分析则成为保障服务器正常运行和性能优化的关键。
通过对服务器日志进行监控和分析,可以及时发现问题、优化性能、提升安全性。
本文将介绍一些服务器日志监控与分析的技巧,帮助管理员更好地管理服务器。
一、选择合适的日志监控工具在进行服务器日志监控与分析之前,首先需要选择一款合适的日志监控工具。
常见的日志监控工具包括ELK Stack(Elasticsearch、Logstash、Kibana)、Splunk、Graylog等。
这些工具都具有强大的日志采集、存储、搜索和可视化功能,可以帮助管理员更好地监控和分析服务器日志。
二、设置合理的日志级别在服务器日志监控中,设置合理的日志级别是非常重要的。
日志级别分为DEBUG、INFO、WARN、ERROR、FATAL等不同级别,管理员可以根据需要设置不同的日志级别。
一般来说,生产环境下建议将日志级别设置为WARN或以上,避免过多无关的日志信息影响监控效果。
三、定时清理日志文件服务器产生的日志文件会占用大量的磁盘空间,如果不及时清理,会导致磁盘空间不足的问题。
因此,定时清理日志文件是服务器日志监控与分析的重要环节。
管理员可以编写脚本定时清理过期的日志文件,释放磁盘空间,确保服务器正常运行。
四、监控关键指标在进行服务器日志监控与分析时,需要监控一些关键指标,如CPU 利用率、内存利用率、磁盘空间利用率、网络流量等。
通过监控这些关键指标,管理员可以及时发现服务器的异常情况,采取相应的措施进行处理,确保服务器的稳定运行。
五、建立告警机制建立告警机制是服务器日志监控与分析的重要一环。
管理员可以根据监控指标设置相应的告警规则,当服务器出现异常情况时,及时发送告警通知,以便管理员能够及时处理问题,避免影响业务运行。
六、日志分析与优化除了监控服务器日志外,日志分析也是非常重要的一环。
通过对服务器日志进行分析,可以发现潜在的问题和优化空间,提升服务器性能和安全性。

电脑系统日志的查看与分析在我们日常使用电脑的过程中,电脑系统会默默地记录下各种操作和事件,这些记录被称为系统日志。
系统日志就像是电脑的“日记”,它详细地记载了电脑运行的点点滴滴。
通过查看和分析系统日志,我们可以了解电脑的运行状况、发现潜在的问题,并采取相应的措施来解决它们。
接下来,让我们一起深入了解电脑系统日志的查看与分析。
一、什么是电脑系统日志电脑系统日志是一个记录系统活动和事件的文件或数据库。
它包含了关于操作系统、应用程序、硬件设备以及用户操作等方面的信息。
系统日志的类型多种多样,常见的有系统日志、应用程序日志、安全日志等。
系统日志通常记录了系统的启动和关闭时间、系统错误和警告信息、硬件设备的连接和断开情况等。
应用程序日志则记录了特定应用程序的运行情况,如软件的安装、更新、错误和异常等。
安全日志主要关注与系统安全相关的事件,如用户登录和注销、权限更改、文件访问等。
二、为什么要查看和分析系统日志1、故障排查当电脑出现故障或异常时,系统日志可以提供重要的线索。
例如,如果电脑频繁死机或蓝屏,通过查看系统日志中的错误代码和相关信息,我们可以初步判断问题的所在,是硬件故障、驱动程序问题还是系统文件损坏等。
2、安全监控系统日志可以帮助我们监测是否有未经授权的访问、恶意软件的活动或其他安全威胁。
通过分析安全日志中的登录记录和权限更改信息,我们可以及时发现异常情况并采取措施加以防范。
3、性能优化了解系统的资源使用情况和性能瓶颈对于优化电脑性能至关重要。
系统日志可以提供有关 CPU 使用率、内存占用、磁盘 I/O 等方面的信息,帮助我们找出性能不佳的原因,并进行相应的调整和优化。
4、合规性要求在一些企业和组织中,出于合规性的要求,需要对电脑系统的活动进行记录和审计。
系统日志可以作为证据,证明系统的操作符合相关的法规和政策。
三、如何查看电脑系统日志不同的操作系统查看系统日志的方法略有不同。
以下是常见操作系统的查看方法:1、 Windows 系统在 Windows 系统中,我们可以通过以下步骤查看系统日志:(1)按下“Win +R”组合键,打开“运行”对话框,输入“eventvwrmsc”并回车。
获取服务器日志的方法有很多种,以下是一些常见的方法:
1. 通过事件查看器查看日志:大多数服务器都自带事件查看器,可以通过它来查看服务器的运行日志。
打开事件查看器后,可以看到系统日志、应用程序日志、安全日志等多个分类,根据需要选择相应的日志进行查看。
2. 使用命令行工具查看日志:可以使用一些命令行工具来查看服务器的日志。
例如,在Linux系统中,可以使用tail、grep等命令来查看日志文件。
在Windows系统中,可以使用PowerShell等命令来查看日志文件。
3. 使用第三方工具查看日志:还有一些第三方工具可以帮助我们查看服务器的日志。
例如,Logstash可以帮助我们将日志集中管理,并提供搜索、分析和可视化等功能。
Graylog也是一个开源的日志管理平台,可以帮助我们管理和分析大量的日志数据。
4. 远程访问服务器查看日志:如果无法直接连接到服务器,可以通过远程访问的方式查看服务器的日志。
例如,使用SSH协议可以远程连接到Linux服务器,并使用命令行工具查看日志文件。
使用远程桌面协议可以远程连接到Windows服务器,并使用事件查看器查看日志文件。
需要注意的是,在获取服务器日志时,需要遵守相关的法律法规和隐私保护规定,确保不会侵犯他人的合法权益。
同时,为了确保日志的安全性和完整性,建议定期备份和加密传输服务器日志。
服务器日志分析技巧随着互联网的快速发展,服务器日志分析变得越来越重要。
通过分析服务器日志,我们可以了解网站的访问情况、用户行为、系统性能等信息,为网站优化和安全防护提供重要参考。
本文将介绍一些服务器日志分析的技巧,帮助您更好地利用日志数据。
一、选择合适的日志格式在进行服务器日志分析之前,首先需要选择合适的日志格式。
常见的日志格式包括Apache的Common Log Format(CLF)、Combined Log Format等。
不同的日志格式记录的信息不同,需要根据实际需求选择合适的格式。
同时,可以通过配置服务器,调整日志格式,记录更详细的信息,以便更好地进行分析。
二、使用日志分析工具为了更高效地分析服务器日志,可以借助各种日志分析工具。
常用的日志分析工具包括ELK Stack(Elasticsearch、Logstash、Kibana)、Splunk、AWStats等。
这些工具可以帮助用户实时监控日志、进行数据可视化、生成报表等,提高日志分析的效率和准确性。
三、关注关键指标在进行服务器日志分析时,需要关注一些关键指标,包括:1. 访问量和访问来源:了解网站的访问量、访问来源,可以帮助我们了解网站的受欢迎程度,优化推广策略。
2. 用户行为:分析用户在网站上的行为路径、停留时间等信息,可以帮助我们了解用户需求,优化网站内容和布局。
3. 错误日志:及时发现并解决网站的错误和异常,保障网站的稳定性和安全性。
4. 系统性能:监控服务器的性能指标,如CPU、内存、网络等,及时发现并解决性能瓶颈,提高网站的访问速度和稳定性。
四、结合其他数据源除了服务器日志,还可以结合其他数据源进行分析,如数据库、用户行为数据等。
通过综合分析不同数据源的信息,可以更全面地了解网站的运行情况,为网站优化和改进提供更多的参考依据。
五、定期备份和清理日志为了节省存储空间和提高分析效率,建议定期备份和清理服务器日志。
可以根据实际情况设置日志的保存时间和存储位置,确保日志数据的安全和可用性。
windows server 2008日志审计策略摘要:1.Windows Server 2008 日志审计策略简介2.日志审计策略的配置方法3.日志审计策略的应用场景4.优化日志审计策略的技巧5.总结正文:Windows Server 2008 日志审计策略简介Windows Server 2008 是微软推出的一款服务器操作系统,为了提高系统的安全性,日志审计策略被广泛应用于该系统中。
日志审计策略是一种记录系统事件和用户活动的策略,通过对这些事件和活动的审计,管理员可以更好地了解系统的运行状况,及时发现并处理潜在的安全隐患。
日志审计策略的配置方法在Windows Server 2008 中,配置日志审计策略主要包括以下几个步骤:1.打开“服务器管理器”,点击“配置”选项卡,然后点击“日志和警报”按钮。
2.在“日志和警报”界面中,点击“审计策略”按钮。
3.在“审计策略”界面中,可以选择不同的审计类别,如系统、应用、安全等,并为每个类别配置审计事件。
4.配置完审计事件后,点击“应用”按钮,将配置的审计策略应用到相应的目标上。
5.最后,点击“确定”按钮,完成日志审计策略的配置。
日志审计策略的应用场景Windows Server 2008 日志审计策略广泛应用于以下场景:1.安全事件审计:通过审计系统日志,管理员可以及时发现并处理安全事件,如未经授权的访问、恶意软件攻击等。
2.系统性能审计:通过审计应用日志,管理员可以了解系统的性能状况,如CPU、内存、磁盘等资源的使用情况,从而优化系统性能。
3.合规性审计:通过审计用户活动日志,管理员可以确保用户的行为符合公司的合规要求,如访问权限控制、数据保护等。
优化日志审计策略的技巧1.合理配置审计事件:根据实际需求,选择需要审计的事件,避免审计过多的无用事件,以减轻系统负担。
2.定期审查审计策略:随着时间的推移,审计策略可能不再适应实际需求,因此需要定期审查并调整审计策略。
Server--R-事件查看器实现日志分析————————————————————————————————作者:————————————————————————————————日期:Server 2008 R2 事件查看器实现日志分析在 windows server 2008 R2 中,可以通过点击 "开始" -> "管理工具" -> "事件查看器" ,来打开并查看各种类型的系统内置日志记录;让我们来做一个实际练习:使用事件查看器检查各种帐户的登录事件,包括系统内置的特殊帐户,以及大家熟悉的administrator 管理员帐户。
一般而言,在启动服务器后,一个叫做 winlogon.exe 的进程会先以NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM (帐户域\帐户权限)登录,然后进入要求用户键入ctrl + alt + del 并输入帐密的登录界面,此时,winlogon.exe 检查并验证用户的输入,通常的做法是将用户键入的密码以某种哈希算法生成密文,将其与SAM 数据库文件中的密文进行比对,如果一致则该账户通过验证并登录,然后赋予相应的权限。
所有这些过程都会被记录进系统内置的"安全"类型日志,可以通过事件查看器浏览;除了 winlogon.exe 进程外,其它一些系统进程也会在用户登录前,使用特殊帐户先行登录。
这些登录事件同样可以在事件查看器中一览无遗,(例如,一个叫做 services.exe 的系统服务进程,使用 NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM (帐户域\帐户权限)登录,然后它会创建数个 svchost.exe子进程,而每个 svchost.exe 进程都会启动并纳宿一些基本的windows 服务,而许多用户空间的应用程序将使用这些服务,实现它们的功能)下面结合图片讲解事件查看器在这两个场景中的应用:一,首先按照上述步骤打开事件查看器,在左侧窗口中展开 "Windows 日志"节点,选取"安全"项目,此时在中间的窗口会列出自系统安装以来,记录的所有安全事件,假设我们要查看最近24 小时以内的帐户登录与验证,审核,权力指派等事件,可以在"安全"项目上右击鼠标,在弹出的上下文菜单中选择"筛选当前日志(L)"二,在打开的对话框中,切换到"筛选器"标签,在"记录时间(G)"右侧的下拉列表中,选择"近24 小时",然后点击下方的确定按钮三,显示出筛选的结果,下面这张图显示了在24 小时内纪录的73 项安全事件(Microsoft Windows 安全审核是准确的称呼),你可以按照日期与时间列排序事件,或者按照事件ID,任务类别(我觉得翻译成事件类别会比较好理解)来排序时间,我们关注的是"登录"与"特殊登录"事件,因此需要选择以任务类别排序.下图中没有按照任务类别排序,而是默认按照日期与时间排序,其优点是,可以追踪在系统启动过程中,哪个系统进程使用哪个系统内置帐户登录,并且可以直观地看出它们之间的先后次序.通过上面的分析,你是否已经直观地感受到事件查看器的强大功能?下面让我们再看另一个例子:使用事件查看器浏览,因远程过程调用(RPC)服务启动失败,导致我们无法以管理员登录windows server 2008 R2 的事件记录.先纠正一个普遍存在的错误理解;RPC 监听在本地环回(127.0.0.1)地址的135 端口,出于安全考虑,很多人会将这个端口关闭,以阻止蠕虫病毒与攻击者入侵,但是我们会发现这个地址上的135 端口始终关不掉而因此忧心忡忡;其实,127.0.0.1:135 是必须的,如果该端口不打开,则说明RPC 服务没有启动,从而导致很多依赖RPC 的其它系统服务无法启动,再说,除非你手动通过 services.msc 服务管理器来禁用它,否则通过其它手段是很难关闭的(包括修改注册表键值),我们真正应该关闭并警惕的,是那些监听在非本地环回的135 端口,例如192.168.0.1:135 ,因为这个地址是可以与远程主机的地址通信的,攻击者可以扫描监听在这个地址端口上的程序漏洞,并远程执行恶意代码(通过Metasploit 即可办到),从而入侵我们的服务器.如果关不掉,也可以使用windows 高级防火墙来禁止该地址端口上的出入站流量.总之,本地环回的135 端口是必须打开的,这并非是恶意软件,木马程序开放的端口,否则你连windows 桌面都无法登录.如果无法登录windows server 2008 R2 服务器的桌面,并且系统提示RPC 服务启动失败,无法读取用户profile ,那么可以进入安全模式,运行 services.msc ,找到其中的 Remote Procedure Call (RPC) 以及 RPC Endpoint Mapper(RpcEptMapper) ,将这两个服务设置为自动启动,然后运行msconfig ,在"服务"标签中,确保勾选了 RPC Endpoint Mapper ,点确定后重启系统,以正常模式进入,应该就能用管理员账户登录了.下图给出了一个事件查看器中的一项RPC 服务启动失败信息:11。
winserver2008r2开机显示group policy client的解决方法【原创实用版3篇】目录(篇1)1.引言2.group policy client 的作用3.winserver2008r2 开机显示 group policy client 的原因4.解决方法5.总结正文(篇1)一、引言在企业级操作系统中,Windows Server 2008 R2 是一款非常受欢迎的服务器操作系统。
然而,在使用过程中,可能会遇到开机显示 group policy client 的问题。
本文将为您介绍如何解决这一问题。
二、group policy client 的作用Group Policy Client(组策略客户端)是 Windows 系统中的一个重要组件,负责从域控制器获取并应用组策略设置。
组策略可以对计算机进行各种配置,如安装软件、设置用户权限等。
当 group policy client 出现问题时,可能会影响到计算机的正常运行。
三、winserver2008r2 开机显示 group policy client 的原因Windows Server 2008 R2 开机显示 group policy client 的原因可能有以下几点:1.组策略设置错误:如果域控制器上的组策略设置有误,可能会导致客户端开机时出现问题。
2.客户端与域控制器通信故障:如果客户端与域控制器之间的网络连接有问题,可能会导致 group policy client 无法正常工作。
3.客户端系统文件损坏:如果客户端系统的组策略相关文件损坏,可能会导致开机时出现异常。
四、解决方法针对上述原因,我们可以尝试以下解决方法:1.检查并修复组策略设置:登录到域控制器,检查组策略设置,确保没有错误的设置。
如果有问题,及时进行修复。
2.检查网络连接:确保客户端与域控制器之间的网络连接正常。
可以尝试重启网络设备或者检查网络线路。
Server 2008 R2 事件查看器实现日志分析
在 windows server 2008 R2 中,可以通过点击 "开始" -> "管理工具" -> "事件查看器" ,来打开并查看各种类型的系统内置日志记录;让我们来做一个实际练习:使用事件查看器检查各种帐户的登录事件,包括系统内置的特殊帐户,以及大家熟悉的administrator 管理员帐户。
一般而言,在启动服务器后,一个叫做 winlogon.exe 的进程会先以
NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM (帐户域\帐户权限)登录,然后
进入要求用户键入ctrl + alt + del 并输入帐密的登录界面,此时,winlogon.exe 检查并验证用户的输入,通常的做法是将用户键入的密码以某种哈希算法生成密文,将其与SAM 数据库文件中的密文进行比对,如果一致则该账户通过验证并登录,然后赋予相应的权限。
所有这些过程都会被记录进系统内置的"安全"类型日志,可以通过事件查看器浏览;
除了 winlogon.exe 进程外,其它一些系统进程也会在用户登录前,使用特殊帐户先行登录。
这些登录事件同样可以在事件查看器中一览无遗,
(例如,一个叫做 services.exe 的系统服务进程,使用 NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM (帐户域\帐户权限)登录,然后它会创建数个 svchost.exe子进程,而每个 svchost.exe 进程都会启动并纳宿一些基本的windows 服务,而许多用户空间的应用程序将使用这些服务,实现它们的功能)
下面结合图片讲解事件查看器在这两个场景中的应用:
一,首先按照上述步骤打开事件查看器,在左侧窗口中展开 "Windows 日志"节点,选取"安全"项目,此时在中间的窗口会列出自系统安装以来,记录的所有安全事件,假设我们要查看最近24 小时以内的帐户登录与验证,审核,权力指派等事件,可以在"安全"项目上右击鼠标,在弹出的上下文菜单中选择"筛选当前日志(L)"
二,在打开的对话框中,切换到"筛选器"标签,在"记录时间(G)"右侧的下拉列表中,选择"近24 小时",然后点击下方的确定按钮
三,显示出筛选的结果,下面这张图显示了在24 小时内纪录的73 项安全事件(Microsoft Windows 安全审核是准确的称呼),你可以按照日期与时间列排序事件,或者按照事件ID,任务类别(我觉得翻译成事件类别会比较好理解)来排序时间,
我们关注的是"登录"与"特殊登录"事件,因此需要选择以任务类别排序.
下图中没有按照任务类别排序,而是默认按照日期与时间排序,其优点是,可以追踪在系统启
动过程中,哪个系统进程使用哪个系统内置帐户登录,并且可以直观地看出它们之间的先后次序.
通过上面的分析,你是否已经直观地感受到事件查看器的强大功能?
下面让我们再看另一个例子:使用事件查看器浏览,因远程过程调用(RPC)服务启动失败,导致我们无法以管理员登录windows server 2008 R2 的事件记录.
先纠正一个普遍存在的错误理解;
RPC 监听在本地环回(127.0.0.1)地址的135 端口,出于安全考虑,很多人会将这个端口关闭,以阻止蠕虫病毒与攻击者入侵,但是我们会发现这个地址上的135 端口始终关不掉而因此忧心忡忡;
其实,127.0.0.1:135 是必须的,如果该端口不打开,则说明RPC 服务没有启动,从而导致很多依赖RPC 的其它系统服务无法启动,
再说,除非你手动通过 services.msc 服务管理器来禁用它,否则通过其它手段是很难关闭的(包括修改注册表键值),
我们真正应该关闭并警惕的,是那些监听在非本地环回的135 端口,例如192.168.0.1:135 ,因为这个地址是可以与远程主机的地址通信的,攻击者可以扫描监听在这个地址端口上的程序漏洞,并远程执行恶意代码(通过Metasploit即可办到),从而入侵我们的服务器.
如果关不掉,也可以使用windows 高级防火墙来禁止该地址端口上的出入站流量.
总之,本地环回的135 端口是必须打开的,这并非是恶意软件,木马程序开放的端口,否则你连windows 桌面都无法登录.
如果无法登录windows server 2008 R2 服务器的桌面,并且系统提示RPC 服务启动失败,无法读取用户profile ,那么可以进入安全模式,运行 services.msc ,找到其中的 Remote Procedure Call (RPC) 以及 RPC Endpoint Mapper(RpcEptMapper) ,将这两个服务设置为自动启动,然后运行msconfig ,
在"服务"标签中,确保勾选了 RPC Endpoint Mapper ,点确定后重启系统,以正常模式进入,应该就能用管理员账户登录了.
下图给出了一个事件查看器中的一项RPC 服务启动失败信息:。