医学论文中统计学表述共40页
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:3.90 MB
- 文档页数:40


医学论文中的统计学表述医学文献中统计学的应用z 医学论文中,普遍使用统计分析。
如:NEJM 杂志1990年有89%的文章使用统计分析。
z 国外的生物医学杂志通常都有专门的统计学审稿人。
z 1996年,我国申报科技成果的4586篇科研论文中,统计使用率达76%,而数据分析误用率达55.7%。
国外生物医学杂志投稿统一要求Uniform Requirements for Manuscripts Submitted to Biomedical JournalsThe International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE), 第一版:BMJ 1991; 302: 338-41.第五版:N Engl J Med 1997; 336:309-316第六版:J Epidemiol Community Health. 2004; 58(9): 731–733.论文中的统计学表述论文结构:●引言(Introduction)明确阐述研究目的(objective)●方法(Methods )阐述统计设计思路及所用统计方法●结果(Results )表述实验(观察)数据的统计分析结果●讨论(Discussion )根据统计分析结果展开论述(材料和)方法●研究对象(subjects)9来源9入选标准和排除标准9总例数9基本情况描述(如人的年龄、性别等;动物的种系、年龄、性别、体重等)●统计设计方法■调查设计•何种研究方法(前瞻性、回顾性、横断面研究等)•样本容量,抽样方法及过程•数据质量及偏倚(bias)的控制■实验设计•采用何种设计方法(如自身配对设计、成组设计、交叉设计、析因设计等)•随机化方法及各组样本容量(n)(材料和)方法■临床试验设计:•随机化方法及各组样本容量(n )•纳入和排除标准•盲法•随访(失访情况的详细阐述)•处理标准(治疗或诊断标准)●实验效应的评价指标(outcome measures)•所用评价指标及其测量方法•测量误差的控制及评价(如多中心、多测量者、多测量仪器等问题)(材料和)方法●统计方法及统计软件(方法部分的最后一段)■一般采用双侧检验,单侧检验须特别说明,并阐述理由;■采用权威的统计软件并注明版次:SPSS 19.0, SAS 6.0, STATA 10.0, BMDP, SYSTAT, SPLM 等;■统计方法具体、确切;(材料和)方法计量资料的统计分析方法一组单样本t 检验两组多组配对设计配对t 检验成组设计两独立样本t 检验配伍组设计配伍组方差分析成组设计单因素方差分析重复测量重复测量ANOVA 多重比较:SNK, LSD, Scheffe, Duncan等级资料的统计分析方法两组多组配对设计Wicoxon 符号秩和检验成组设计Mann-Whitney 检验配伍组设计Friedman 检验成组设计Kruskall Wallis 检验计数资料的统计分析方法一组单样本率的u 检验两组多个率或构成比的比较χ2检验配对设计McNemar 检验成组设计χ2检验相关与回归分析方法相关: Pearson 线性相关(正态分布资料),Spearman 相关(偏态分布或等级资料)回归分析:线性回归/非线性回归logistic 回归:—条件logistic 回归—非条件logistic 回归Cox 回归结果●统计描述■计量资料:n, ±S ( ±SE),有的还给出min 、max 、CV 。


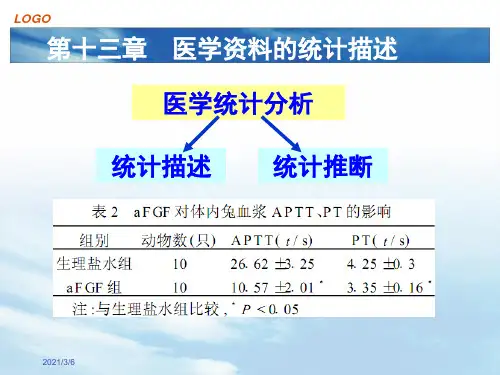




《中华消化外科杂志》对P值规范化表述的要求根据中华医学会杂志社的要求,根据人民卫生出版社的全国高等学校教材《卫生统计学》第5版,报告统计学检验的结论时,对P值小于或等于检验水准(一般为0.05)的情况,一律描述为“差异有统计学意义”,同时写明P的具体数值或相应的不等式,在用不等式表示P值的情况下,一般情况下选用P>0.05、P<0.05和P<0.01 三种表达方式即可满足需要,无须再细分为P<0.001或<0.0001。
不再采用将P<0.05描述为“差异有显著意义”(或差异有显著性)”,或将P<0.01描述为“差异有非常显著意义(或差异有非常显著性)”的表达方式。
______________________________________________论文中统计结果的表达及解释【摘要】统计学是生物医学研究所必需的重要手段, 生物医学研究的实验设计、资料收集、数据处理分析以及结论都离不开统计学应用。
生物医学研究论文主要由摘要、引言、材料与方法、结果和讨论5个部分组成, 各个部分都涉及统计结果的表达和解释, 统计学是专业结论成立与否的重要依据。
统计学应用不当不仅影响论文的科学性, 还有可能得出错误的专业结论。
【关键词】统计学科研论文统计分析统计表达近年来, 统计学在生物医学科研中的应用越来越受到重视, 统计分析结果的表达及解释已成为医学科研论文中不可缺少的重要组成部分。
除论文涉及的专业(如细胞与分子免疫学杂志为免疫学专业)和表述的文字2个方面外, 统计学是评价论文质量优劣的重要依据, 然而国内生物医学论文中统计学应用仍存在着较为严重的问题[1-4], 如2003年某大学学报拟发表论著中统计方法误用率为57%[3]。
细胞与分子免疫学杂志虽然在国内生物医学系列杂志中具有较高的学术地位[5], 但拟发表及刊出论文在科研设计、统计学分析、结果解释等方面也不同程度地存在一些问题, 作者的统计学应用水平有待进一步提高。

当前医学论文中的一些统计学问题【摘要】医学论文中的统计学问题是研究过程中不可忽视的重要环节。
本文首先介绍了医学论文中的统计学问题概述,包括样本量计算的重要性、统计学方法的选择、数据处理和分析的常见问题以及结果解读中可能存在的统计学误解。
随后提出了对医学论文中的统计学问题的建议,包括加强统计学知识培训、优化数据收集和处理流程等方面。
文章指出了未来需要关注的研究方向,呼吁学术界加强对统计学问题的重视和研究。
本文对当前医学论文中的统计学问题进行了深入的探讨和总结,旨在提高医学研究的质量和可信度。
【关键词】医学论文、统计学问题、样本量计算、统计学方法、数据处理、结果解读、建议、未来研究、总结1. 引言1.1 背景介绍在当前医学论文中,统计学问题十分普遍且重要。
由于医学研究的特殊性以及数据的复杂性,很容易出现统计学方法的选择不当、样本量计算不准确、数据处理和分析出现问题等情况。
这些问题的存在可能会导致研究结论的不准确甚至是错误,从而影响到临床实践和患者的健康。
对于医学论文中的统计学问题需要引起研究者和读者的高度重视。
只有通过正确的统计学方法和分析技术,才能够保证研究结果的科学性和可靠性。
本文旨在对当前医学论文中常见的统计学问题进行深入探讨,以期引起更多研究者对这一问题的关注,提高医学研究的质量和水平。
1.2 研究目的研究目的部分主要是为了明确本文的研究目标和意图。
在医学论文中,研究目的的明确定义了研究的发展方向和目标,能够让读者清晰地了解研究的意义和价值。
研究目的是研究者进行科学研究的根本动机,也是研究项目的核心。
在本文中,研究目的旨在探讨当前医学论文中存在的一些统计学问题,帮助读者更好地了解统计学在医学研究中的重要性和应用。
通过分析医学论文中常见的统计学问题,可以帮助研究者避免在数据处理、分析和结果解读过程中出现错误,提高研究的准确性和科学性。
研究目的还包括对当前医学研究中存在的统计学误解进行识别和探讨,以及探讨未来关于医学论文统计学问题的研究方向和发展趋势。
PreventionYANG Nan,LIN Wenhui,HU Yaoqin(Yinchuan Maternal and Child Health Hospital,Yinchuan750001,China)Abstract:Objective To explore the significance of oral health guidance to prevent oral diseases during pregnancy.Methods From February2017to February2018,979pregnant women who first came to our hospital for prenatal physical examination were selected.According to the number of the card tail,the subjects were randomly divided into experimental group(492cases)and control group(487cases).The experimental group was given oral health guidance regularly,while the control group was not given any intervention.After6months,all subjects were examined for oral health.The results were analyzed statistically to compare the effects of oral health guidance on the incidence of common oral diseases during pregnancy.Results Before the intervention,there was no significant difference in the number of oral cleaning and gingivitis between the two groups(P>0.05).After the intervention,the number of oral cleaning in the experimental group was more than that in the control group,and the number of gingivitis patients in the experimental group was less than that in the control group(P all<0.05).Compared with that before the intervention,in the experimental group the number of patients with oral cleaning increased and the number of gingivitis patients decreased(P<0.05).After6months of observation,the number of patients with oral hygiene in the experimental group was increased.The number of gingivitis patients in the control group increased(P<0.05),and there was no significant difference in the number of oral cleaning between the two groups(P>0.05).Before the intervention,there were no significant differences in the number of patients,the number of caries teeth between the two groups(P>0.05).After the intervention,the above two indicators of pregnant women in the experimental group were lower than those in the control group(P all<0.05). Conclusion Oral hygiene and health guidance have great significance in preventing oral diseases during pregnancy,might be conducive to guiding clinical practice.Key words:pregnant woman;oral hygiene;health guidance;oral diseases医学论文中统计学处理结果的解释和表达 统计结果的解释和表达:当P<0.05(或P<0.01)时,应说对比组之间的差异具有统计学意义,而不应说对比组之间具有显著性的差别;应写明所用统计分析方法的具体名称(如:成组设计资料的t检验、两因素析因设计资料的方差分析、多个均数之间两两比较的q检验等),统计量的具体值(如:t=3.45,χ2=4.68,F=6.79等),应尽可能给出具体的P值(如:P= 0.0238);当涉及总体参数(如总体均数、总体率等)时,在给出显著性检验结果的同时,再给出95%置信区间。
Ratio in Evaluating the Prognosis of Patients with SepsisZHANG Xiaobin1,LIU Dan1,YAN Jing1,LEI Mengmeng1,YANG Xiaojun2(1.School of Clinical Medicine,Ningxia Medical University,Yinchuan750004,China;2.Department of Critical Care Medicine,the General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University,Yinchuan750004,China)Abstract:Objective To investigate the value of platelet count(PC),neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio(NLR),platelet to lymphocyte ratio(PLR)in assessing prognosis of sepsis.Mothods A retrospective cohort study was conducted to select113patients of sepsis who met the Sepsis3.0diagnostic criteria admitted to the Department of Intensive Care Unit(ICU)of Ningxia Medical University from October2018to April2019.Blood routine examination(PC,NLR,PLR),hypersensitive CRP(hs-CRP),and lactic acid test results were collected during the diagnosis of sepsis.Gender,age,infection site and Acute Physiology and Chronic Health EvaluationⅡ(APACHEⅡ)scores of sepsis patients in the ICU(≤24hours)were recorded.At the same time,the survival of the patients were followed up for28days.Spearman correlation analysis was used between PC,NLR,PLR and hs-CRP,lactic acid and APACHE II scores to analyze the correlation between the three indicators and inflammatory response and prognosis.Logistic regression analysis of two categorical variables was used to select risk factors of death in patients with sepsis.The receiver operating characteristic curve(ROC)was used to assess the value of PC,NLR,and PLR for prognosis in patients of sepsis.Results Compared with the survival group,both PC and PLR were significantly reduced in the death group.Correlation analysis of PC,NLR,PLR and various indicators in sepsis patients showed that PC was significantly negative correlation with lactic acid,APACHEⅡscore(r=0.328,r=0.361,P all<0.01).There was a negative correlation between PLR and APACHE II score(r=-0.232,P<0.05).Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that only PC and APACHE II score were independent risk factors for28-day mortality in patients with sepsis(OR=0.992,95% CI:0.985-1.000;OR=1.257,95%CI:1.127-1.402).ROC curve analysis showed that both PC and PLR had predictive value for the prognosis of patients with sepsis.The area(AUC)under the ROC curve was0.737and 0.662respectively(P all<0.01).The sensitivity and specificity of predicting28-day mortality were85.30% and55.30%,respectively,when the optimal critical value of PC was79.0×109/L.When the optimal PLR threshold was159.592,the sensitivity and specificity of predicting28d death were74.70%and60.50%,respectively.Conclusion Early PC and PLR levels have good prognostic value for sepsis patients.Key words:sepsis;platelet count;neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio;platelet to lymphocyte ratio;prognosis医学论文中统计学处理结果的解释和表达 统计结果的解释和表达:当P<0.05(或P<0.01)时,应说对比组之间的差异具有统计学意义,而不应说对比组之间具有显著性的差别;应写明所用统计分析方法的具体名称(如:成组设计资料的t检验、两因素析因设计资料的方差分析、多个均数之间两两比较的q检验等),统计量的具体值(如:t=3.45,χ2=4.68,F=6.79等),应尽可能给出具体的P值(如:P= 0.0238);当涉及到总体参数(如总体均数、总体率等)时,在给出显著性检验结果的同时,再给出95%置信区间。