电子技术基础chapter1
- 格式:pptx
- 大小:483.98 KB
- 文档页数:33





Microelectronics packaging technology(R eview contents)Chapter 1:Introduction1.The development characteristics and trends of microelectronics packaging.2.The functions of microelectronics packaging.3.The levels of microelectronics packaging technology.4.The methods for chip bonding.Chapter 2:Chip interconnection technologyIt is one of the key chapters1.The Three kinds of chip interconnection, and their characteristics and applications.2.The types of wire bonding (WB) technology, their characteristics and working principles.3.The working principle and main process of the wire ball bonding.4.The major materials for wire bonding.5.Tape automated bonding (TAB) technology:1)The characteristic and application of TAB technology.2)The key materials and technologies of TAB technology.3)The internal lead and outer lead welding technology of TAB technology.6. Flip Chip Bonding (FCB) Technology1)The characteristic and application of flip chip bonding technology2)UBM and multilayer metallization under chip bump;UBM’s structure and material, and the roles ofeach layer.3)The main fabrication method of chip bumps.4)FCB technology and its reliability.5)C4 soldering technology and its advantages.6)The role of underfill in FCB.7)The interconnection principles for Isotropic and anisotropic conductive adhesive respectively. Chapter 3: Packaging technology of Through-Hole components1.The classification of Through-Hole components.2.Focused on:DIP packaging technology, including its process flow.3.The characteristics of PGA.Chapter 4:Packaging technology of surface mounted device (SMD)1.The advantages and disadvantages of SMD.2.The types of SMD.3.The main SMD packaging technologies, focused on:SOP、PLCC、LCCC、QFP.4.The packaging process flow of QFP.5.The risk of moisture absorption in plastic packages, the mechanism of the cracking caused by moistureabsorption, and solutions to prevent for such failure.Chapter 5:Packaging technology of BGA and CSP1.The characteristics of BGA and CSP.2.The packaging technology for PBGA,and its process flow.3.The characteristics of packaging technology for CSP.4.The reliability problems of BGA and CSP.Chapter 6:Multi-Chip Module(MCM)1.The classification and characteristics of MCM2. The assembly technology of MCM.Chapter 7:Electronic packaging materials and substrate technology1. The classification of the materials for electronic packaging, the main requirements for packagingmaterials.2. The types of metals in electronic packaging, and their main applications.3. The main requirements for polymer materials in electronic packaging.4.Classification of main substrate materials, and the major requirements for substrate materials.Chapter 8:Microelectronics packaging reliability1.The basic concepts of electronic packaging reliability.2.The basic concepts for failure mode and failure mechanism in electronic packaging.3.Main failure (defect) modes (types) of electronic packaging.4.The purpose and procedure of failure analysis (FA) ;Common FA techniques (such as cross section, dyeand pry, SEM, CSAM ...).5 The purpose and key factors (such as stress level, stress type …) to design accelerated reliability test. Chapter 9:Advanced packaging technologies1.The concept of wafer level packaging (WLP) technology.2.The key processes of WL-CSP.3.The concept and types of the 3D packaging technologies.Specified Subject 1:LED packaging technology1. Describe briefly the four ways to achieve LED white light, and how they are packaged?2. Describe briefly the difference and similar aspects (similarity) between LED packaging andmicroelectronics packaging.3. And also describe briefly the development trend for LED package technology and the whole LED industryrespectively.Specified Subject 2:MEMS packaging technology1.The differences between micro-electro-mechanical system (MEMS) packaging technology and theconventional microelectronics packaging technologies.2.The function requirements of MEMS packaging.Extra requirement:The common used terms (Abbreviation) for electronic packaging.。


电气工程及其自动化专业必备知识Chapter 1:电气工程基础知识⑴电流、电压和电阻⑵电路基础和欧姆定律⑶串并联电路的分析⑷电源和电能⑸电磁场基础知识Chapter 2:电路分析与设计⑴直流电路分析⑵交流电路分析⑶功率与功率因数校正⑷谐振电路设计与分析⑸数字电路设计基础Chapter 3:电机与变压器⑴三相交流电机⑵单相交流电机⑶直流电机⑷传感器与执行器⑸变压器基础知识与应用Chapter 4:电力系统与配电⑴电力系统概述⑵发电与变电⑶输电与配电系统⑷电力负荷管理⑸电能质量与调节Chapter 5:自动控制系统⑴控制系统基础⑵反馈控制系统⑶ PID 控制器⑷离散时间控制系统⑸自动化系统与工业控制Chapter 6:电气安全与规范⑴电气安全基础知识⑵国家电气安全法规与标准⑶高压电器安全操作⑷电气事故预防措施⑸地线与接地系统Chapter 7:电气测试与测量⑴仪器与测量误差⑵电气量测量⑶准确度和置信度⑷频谱分析仪与示波器⑸电气信号处理与测试工具Chapter 8:现代电气工程技术⑴电力电子技术⑵光伏与风能发电⑶电动汽车技术⑷智能电网与电力交易⑸在电气工程中的应用附件:⒈实验报告范例⒉电路设计案例⒊自动控制系统仿真软件教程⒋电气安全操作手册⒌测量仪器使用指南法律名词及注释:⒈电力法:是对电力工业进行管理和监督的法律法规。
⒉电力安全法:是为保障电力生产、供应、消费等环节的安全而制定的法律法规。
⒊电力负荷管理条例:是对电力系统负荷进行合理安排和管理的相关规定。
⒋地线:用于将设备或系统与地面接地连接的线路。
⒌接地系统:用于保护电气设备和人员免受电击的系统。
附件:⒈实验报告范例:[文件]⒉电路设计案例:[文件]⒊自动控制系统仿真软件教程:[文件]⒋电气安全操作手册:[文件]⒌测量仪器使用指南:[文件]法律名词及注释:⒈电力法:根据国家法律关于电力工业的规定。
⒉电力安全法:根据国家法律关于电力安全的规定。
⒊电力负荷管理条例:根据国家法律关于电力负荷管理的规定。
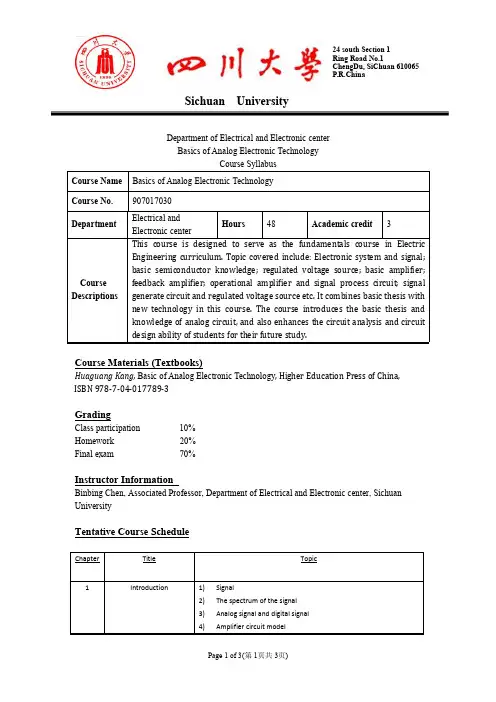
Sichuan UniversityP.R.ChinaDepartment of Electrical and Electronic centerBasics of Analog Electronic TechnologyCourse SyllabusCourse Name Basics of Analog Electronic TechnologyCourse No.907017030Department Electrical andElectronic centerHours48Academic credit3Course Descriptions This course is designed to serve as the fundamentals course in Electric Engineering curriculum.Topic covered include:Electronic system and signal; basic semiconductor knowledge;regulated voltage source;basic amplifier; feedback amplifier;operational amplifier and signal process circuit;signal generate circuit and regulated voltage source etc.It combines basic thesis with new technology in this course.The course introduces the basic thesis and knowledge of analog circuit,and also enhances the circuit analysis and circuit design ability of students for their future study.Course Materials(Textbooks)Huaguang Kang,Basic of Analog Electronic Technology,Higher Education Press of China, ISBN978-7-04-017789-3GradingClass participation10%Homework20%Final exam70%Instructor InformationBinbing Chen,Associated Professor,Department of Electrical and Electronic center,Sichuan UniversityTentative Course ScheduleChapter Title Topic1Introduction1)Signal2)The spectrum of the signal3)Analog signal and digital signal4)Amplifier circuit modelSichuan UniversityP.R.China5)The main performance indexes of Amplifier circuit2Operational amplifier1)Integrated circuit operational amplifier2)ideal operational amplifier3)Basic linear amplifier circuit4)Other applications of Noninverting input and invertinginput amplifier circuit5)The examples of SPICE simulation3Diode1)Semiconductor2)Formation and characteristics of P-N junction3)Diode4)analytical methods of diode basic circuit5)Special diode6)The examples of SPICE simulation4BJT and its amplifiercircuit 1)BJT2)common-emitter amplifier circuit3)analytical methods of amplifier circuit4)the Stability of static work point of the amplified circuits5)common-collector and common-base amplifier circuit6)combination amplify circuit7)Frequency response of amplifier circuit8)transient response of Single stage amplifier circuit9)The examples of SPICE simulation5Mosfet amplifier circuit1)MOSFET2)MOSFET amplifier circuit3)JFET4)MESFET5)Comparison of Circuit performances6)The examples of SPICE simulation6Analogue integratedcircuit 1)Biasing technique2)Differential amplifier3)transmission characteristics of Differential amplifier4)Integrated circuit operational amplifier5)major parameters of Integrated circuit operational amplifier6)Variable transconductance analog multiplier7)Noise and interference8)The examples of SPICE simulation7Feedback amplifier circuit1)The basic concept and classification of Feedback2)Four configurations of Negative feedback amplifier circuit3)Gain of Negative feedback amplifier circuit4)The influence of the negative feedback on amplifier circuitSichuan UniversityP.R.China5)Depth negative feedback6)Design of Negative feedback amplifier circuit7)Frequency response of Negative feedback amplifier circuit8)The stability of Negative feedback amplifier circuit9)The examples of SPICE simulation8Power amplifier circuit1)general issues of Power amplifier circuit2)emitter follower3)Integrated power amplifier4)The examples of SPICE simulation9signal processingand signal circuit 1)The basic concept and classification of filter circuit2)First order active filter circuit3)High order active filter circuit4)Switched Capacitor Filter5)Oscillating conditions of Sinusoidal oscillator circuit6)RC sinusoidal oscillator circuit7)LC sinusoidal oscillator circuit8)voltage comparator,Astable Multivibrator and Sawtooth wavegenerating circuit9)The examples of SPICE simulation10DC stabilized powersupply 1)Low power rectifier filter circuit2)series feed voltage regulator circuit3)switch voltage-stabilizing circuit4)The examples of SPICE simulation11computer aided analysisand design 1)SPICE program aided analysis of Electronic circuit2)SPICE program aided design of Electronic circuit。



微电子技术中的芯片设计与制造研究Chapter 1:微电子技术简介微电子技术是指将集成电路技术应用于微型电子元件制造与电路设计领域。
随着电子技术的不断发展,微电子技术已经成为了电子科技领域中备受重视的一个分支。
而芯片的设计与制造二者又是微电子技术中极为重要的一环。
芯片是微电子技术非常重要的产物,即集成电路芯片。
芯片的设计与制造涉及到很多的技术与专业知识,下面将从两个方面来进行介绍,看看其中设计与制造的具体内容。
Chapter 2:芯片设计技术2.1 功能描述与需求分析芯片的设计一开始就要涉及到芯片的功能描述与需求分析。
在此基础上,设计人员可以进一步完成芯片的结构设计、电路设计、物理设计等工作。
2.2 线路电路设计芯片的线路设计是芯片设计的重要环节,直接关系到芯片功能的实现。
线路设计是芯片设计中最基本的环节,要求设计人员具备大量的电路及其组成的对微电子元件的基础知识。
在电路设计中,设计人员要考虑到高精度、低噪声、低功率、高速度等一系列因素。
并且还需要结合分析芯片布局与每层INTO与OUT区联络的数据路径设计。
2.3 物理设计物理设计包括版图的设计、布线、填充等等。
芯片的物理设计则关系到芯片层次、面积、线宽、线距、电源布局、块间延迟等等。
对于计算机芯片来说,物理设计是非常重要的,因为计算机芯片需要大量的线路进行连接。
2.4 集成设计芯片设计中最重要的环节是对各式各样的单元电路进行集成设计。
集成设计涉及到大量的单元电路,这需要设计人员具备跨越不同专业领域的技术能力。
集成设计需要设计人员克服男女版图设计中的种种问题,在极小的空间中容纳大量电路。
Chapter 3:芯片制造技术3.1 掩模生产掩模生产是芯片制造的重要环节。
制造芯片需要许多重复的掩形生产过程,掩形相当于微电子领域中对线路板的蚀刻,以这种方法制造芯片不仅可以保证生产出来的芯片性能均一,而且对芯片制造的高效性至关重要。
3.2 光刻技术芯片制造技术中最重要的一项是光刻技术。
《电子类专业英语》课程标准一、基本信息适用对象:电子类专业制定时间:课程代码:070590 所属系部:信息工程学院学分:2 学时:36制定人:批准人:二、课程的目标1、专业能力目标培养学生掌握电子方面的专业词汇,达到一定的对应用电子英语的翻译能力,并且能够依靠自身的专业背景知识阅读电子英文技术文献的应用能力。
2、方法能力目标学会学习、学会工作,拓展信息收集和应用能力,思考和解决问题的能力,学会系统设计方法和严谨工作作风。
3、社会能力目标学会共处,学会做人,具有良好的团队精神、职业道德和社会责任感。
三、整体教学设计思路1、课程定位本课程是高职院校电子类专业的专业基础课。
本课程的功能是培养学生掌握电子方面的专业词汇,达到一定的对应用电子英语的翻译能力,并且能够依靠自身的专业背景知识阅读电子英文技术文献的应用能力。
本课程是以《大学英语》、《模拟电子技术》、《数字电子技术》、《单片机应用》等课程的基本知识、技能为基础进行学习,后续课程中的专业技能课、《毕业综合实践》都要用到本课程的知识和技能。
本课程为学生进入电子企业,从事电子产品调试与维修、电子产品开发设计助理工程师等岗位打下基础。
2、课程开发思路本课程是在电子行业专家、电子企业专家、电子专业建设指导委员会参与下,在广泛市场调查、论证、研讨基础上经过多年的试点和反复改革的基础上进行开发与建设。
本课程以“电子类专业英语”电子产品开发生产过程为教学的主线,以工作过程为导向组织课程内容和课程教学。
本课程在教学中采用以工作过程为导向的项目化教学模式,在多媒体和计算机房进行理论与实践一体化教学。
教、学、做结合,学生在解决一个个项目任务的过程中,不仅获得了专业的知识和能力,也获得了方法能力和社会能力,达到了综合的职业能力的要求。
四、教学内容1、学时分配2、教学设计五、课程考核标准说明:1、在每个学习情境完成后,有相应的教学评价与考核。
考核依据项目操作过程、完成结果以及项目报告等。