前三章习题选讲
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:516.50 KB
- 文档页数:28


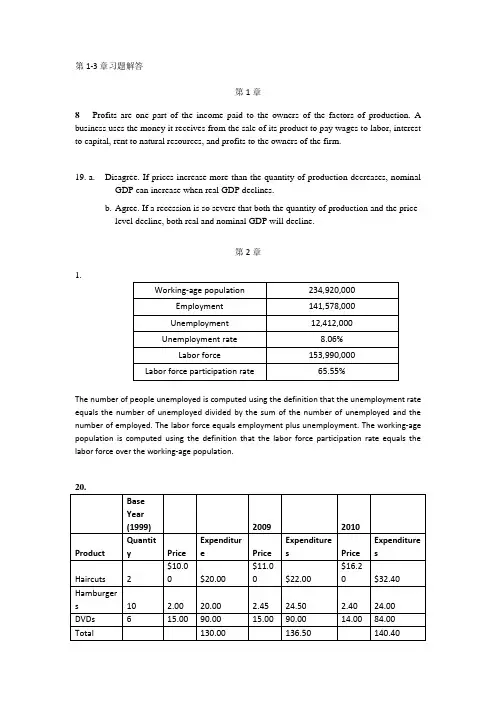
第1-3章习题解答第1章8Profits are one part of the income paid to the owners of the factors of production. A business uses the money it receives from the sale of its product to pay wages to labor, interest to capital, rent to natural resources, and profits to the owners of the firm.19.a. Disagree. If prices increase more than the quantity of production decreases, nominalGDP can increase when real GDP declines.b. Agree. If a recession is so severe that both the quantity of production and the pricelevel decline, both real and nominal GDP will decline.第2章1.The number of people unemployed is computed using the definition that the unemployment rate equals the number of unemployed divided by the sum of the number of unemployed and the number of employed.The labor force equals employment plus unemployment.The working-age population is computed using the definition that the labor force participation rate equals the labor force over the working-age population.The CPI for 2009 = [($136.50/$130)⨯100] = 105; CPI for 2010 = [($140.40/$130)⨯100] = 108.So, the inflation rate for 2010 = [((108 − 105)/105)⨯100)] = 2.9%第4章7.a. results in a movement along the per-worker production function.b. andc. result in a shift in the per-worker production function because they are likely to lead to technological change, or an increase in real GDP per hour worked, holding capital per hour worked constant.16.a.No, this data does not support the catch-up prediction.The countries with the highestinitial levels of real GDP per capita have growth rates of real GDP per capitasimilar to the countries with average initial levels of real GDP per capita.b. Yes, this data supports the catch-up prediction. The countries with the lowestinitial levels of real GDP per capita have the highest growth rates of real GDP percapita, and the countries with the highest levels of real GDP per capita have thelowest growth rates of real GDP per capita.c.No, this data does not support the catch-up prediction. The countries have roughlythe same growth rates of real GDP per capita regardless of their initial levels ofreal GDP per capita.。


第十一、十二、十三章复习主讲:王杰宗学习目标:复习前三章基础知识、总结思路与方法以及常用辅助线等。
学习内容:一、基础知识(解决看到图形想到性质的问题,要求要文字语言、图形语言、数学语言三位一体)1、全等三角形的判定与性质;2、轴对称与关于轴对称的图形的性质与判定;特别:线段的垂直平分线、角平分线、关于坐标轴对称的点的坐标的特点、做轴对称图形等3、等腰三角形的判定与性质;4、等边三角形的判定与性质;特别:直角三角形中,30º的角所对的边等于斜边的一边。
5、实数的分类;6、相反数、绝对值、非负数、数轴上的点与实数的一一对应;7、算术平方根、算术立方根;8、实数大小的比较;9、实数的相关运算。
二、思路与方法(解决被卡住的问题)1、证三角形全等找第三边(SSS)①已知两边分别相等找夹角(SAS)找是否有直角(HL)②已知两角分别相等找任一边(ASA,AAS)找另一邻角(ASA)一边及邻角分别相等找这角的另一边(SAS)找已知边的对角(AAS)③已知一边一角分别相等找另一角(AAS)一边及对角分别相等若已知角是直角,找另一边(HL)2、涉及线段(角)相等的问题①找(或构造)两线段(或两角)所在的两个三角形,证全等;②利用对称:看两线段(或两角)是不是关于某一线对称,利用对称的性质证其相等;③看两线段(或两角)是不是在一个三角形中(或能不能转换到一个三角形中),利用等角对等边(或等边对等角)的性质;④利用中垂线、角平分线的性质;⑤利用等量代换;⑥利用平行线的性质;⑦利用等(同)底等(同)高的三角形面积相等;等等。
3、涉及线段(或角)的不等关系①利用在一个三角形中,大角(边)对大边(角);②利用三角形中任意两边的和(差)大(小)于第三边;③利用外角定理;④利用整体大于部分,部分之和等于整体;4、注意;①对应角与对角、对应边与对边是不同的概念;②在涉及全等的问题中要特别注意对应关系;③注意题目中的隐含条件:如公共边、公共角、对顶角等。

泛函分析习题选讲(8)例 1 设X=C[ a,b],t 1, …,t n .,,],,[1C b a n ∈∈λλ 定义X 上的线性泛函:若.)()(,1∑==∈ni i i t x x f X x λ求证f 是X 上的有界性泛函,求f。
证明 任意x X ∈,|f(x)|=| ∑=n i i i t x 1)(λ|≤ ∑=≤n i i it x 1|)(|||λ||)(||||1∑=ni i it x λ.所以||f||≤=ni i 1.||λ存在C∈ε,1||=i ε,使||i i i λλε=。
存在,x X∈,使,,2,1,)(n i t x i i ==ε且||x||=1.这样|f(x)|=|| ∑=n i i i t x 1)(λ|=||1∑=ni i λ,所以.||f(x)||≥||1∑=ni i λ由此 ,我们证明了||f(x)||=||||1∑=ni i λ。
证毕。
例题 2 设F 是),(0+∞-∞C 上的线性泛函,(),(0+∞-∞C 的定义参见七章例题讲例5)。
若F 满足条件:若∈ϕ),(0+∞-∞C 且任意,0)(),,(≥+∞-∞∈t t ϕ则称F 是正的线性泛函,求证:),(0+∞-∞C 上的正的线性泛函的连续的。
证明 任意复值函数f ∈),(0+∞-∞C ,都可以写成+=x f iy,其中x,y是),(0+∞-∞C 中的实值函数,||x||f≤且||y||||||f ≤.而实值函数又可以x=x--x ,其中}0,max{},0,max{x x x x -==-+均是),(0+∞-∞C 中的非负函数,且.,x x x x ≤≤-+同理++-=y y y y ,和-y 是非负函数,且yy y y ≤≤-+,。
若存在M 0>,使任意非负函数ϕ,(),F M ϕϕ≤则F必有界事实上,任意0_(,),(),()()()()()()()()()4f C f x x i y y F f F x F x iF y iF y F x F x F y F y Mf+-++-+-+-+-∈-∞+∞=-+-=-+-≤+++≤若F 在0(,)C -∞+∞中的非负函数上是无界的,则存在非负函数n x 0(,)C ∈-∞+∞,nx 12n≤,()1n F x ≤1,2,,n =由于1nn n x =∑<+∞,因此第七章例题选讲例3,1nni x x==∑收敛。


第一二三章课后练习答案第一章总论复习思考题一、单项选择题1.会计所使用的主要计量尺度是( C )。
A 实物量度B 劳动量度C 货币量度D 实物量度和货币量度 2.会计的基本职能是( C )。
A 核算和管理B 控制和监督C 核算和监督 D核算和分析 3.会计的反映与监督的内容可以概括为( B )。
A 销售活动B 再生产过程中的资金运动C 生产活动D 管理活动 4.下列业务不属于会计核算范围的事项是( D )。
A 用银行存款购买材料B 生产产品领用材料C 企业自制材料入库D 与外企业签定购料合同 5.会计主体假设规定了会计核算的( B )。
A时间范围 B空间范围 C期间费用范围D成本开支范围 6.下列原则中不属于信息质量要求的原则是( C )。
A可理解性原则 B可比性原则 C 历史成本原则 D相关性原则7.200X年9月20日采用赊销方式销售产品50 000元,12月25日收到货款存入银行。
按收付实现制核算时,该项收入应属于( D )。
A 200X年9月B 200X年10月C 200X年11月D 200X年12月 8.2002年3月20日采用赊销方式销售产品60 000元,6月20日收到货款存入银行。
按权责发生制核算时,该项收入应属于( A )。
A 2002年3月B 2002年4月C 2002年5月D 2002年6月 9.建立货币计量假设的基础是( D )。
A币值变动 B人民币 C记账本位币D币值不变二、多项选择题1.企业在组织会计核算时,应作为会计核算基本前提的是( ABCE )。
A会计主体B持续经营 C货币计量 D会计原则 E会计分期2.根据权责发生制原则,下列各项中应计入本期的收入和费用的是(AD )。
A 本期销售货款收存银行 B上期销售货款本期收存银行 C本期预收下期货款存入银行 D计提本期固定资产折旧费 E以银行存款支付下期的报刊杂志费3.下列业务不属于会计核算范围的事项是( BD ) A用银行存款购买材料B编制财务计划C企业自制材料入库 D与外企业签定购料合同 E产品完工验收入库4.会计方法包括(ADE )A会计核算 B 会计决策 C 会计信息D 会计分析E 会计检查F 会计预测5.下列各种方法属于会计核算专门方法的有(ABCF )A 登记账簿B 成本计算C 复式记账D 监督检查 E预测决策 F 财产清查三、判断题1.会计分期不同,对利润总额会产生影响。

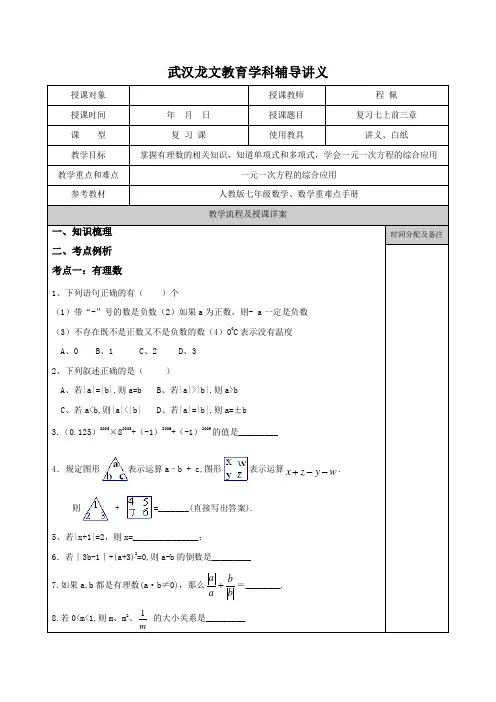
武汉龙文教育学科辅导讲义授课对象 授课教师 程 佩 授课时间 年 月 日 授课题目 复习七上前三章 课 型 复 习 课使用教具讲义、白纸教学目标 掌握有理数的相关知识,知道单项式和多项式,学会一元一次方程的综合应用教学重点和难点 一元一次方程的综合应用 参考教材人教版七年级数学、数学重难点手册 教学流程及授课详案一、知识梳理 二、考点例析 考点一:有理数1、下列语句正确的有( )个(1)带“-”号的数是负数(2)如果a 为正数,则- a 一定是负数 (3)不存在既不是正数又不是负数的数(4)00C 表示没有温度 A 、0 B 、1C 、2D 、32、下列叙述正确的是( ) A 、若|a|=|b|,则a=b B 、若|a|>|b|,则a>b C 、若a<b,则|a|<|b| D 、若|a|=|b|,则a=±b3.(0.125)2005×82005+(-1)2006+(-1)2005的值是_________4.规定图形表示运算a –b + c,图形表示运算w y z x --+.则 + =_______(直接写出答案).5、若|x+1|=2,则x=_______________;6.若∣3b-1∣+(a+3)2=0,则a-b 的倒数是_________ 7.如果a,b 都是有理数(a ·b ≠0),那么bbaa +=________. 8.若0<m<1,则m 、m 2、1m的大小关系是_________ 时间分配及备注9、(1+3+5+7+……+2005)-(2+4+6+8+……+2004)=________ 10、6999999+599999+49999+3999+299+19=_____________11、已知a 与b 互为相反数,c 与d 互为倒数,m 的绝对值为2,求 mb a ||+-cd+m 的值。
12、已知1<x<2,试确定 xx x x x x ||1|1|2|2|+----- 的值。