不定式的时态和语态
- 格式:doc
- 大小:64.00 KB
- 文档页数:9

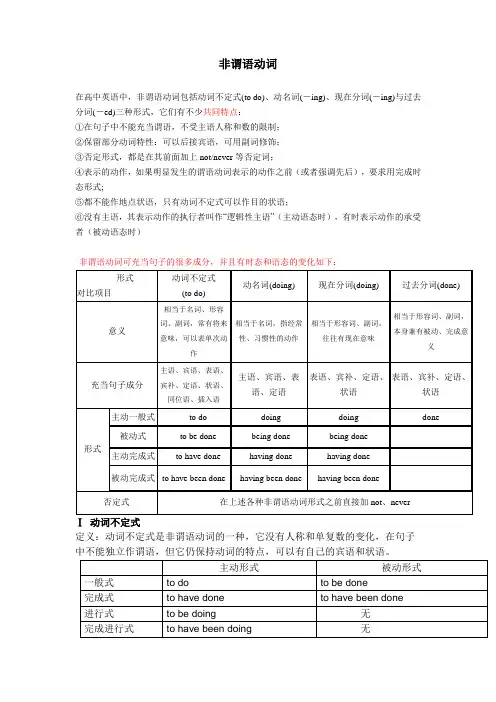
非谓语动词在高中英语中,非谓语动词包括动词不定式(to do)、动名词(-ing)、现在分词(-ing)与过去分词(-ed)三种形式,它们有不少共同特点:①在句子中不能充当谓语,不受主语人称和数的限制;②保留部分动词特性:可以后接宾语,可用副词修饰;③否定形式,都是在其前面加上not/never等否定词;④表示的动作,如果明显发生的谓语动词表示的动作之前(或者强调先后),要求用完成时态形式;⑤都不能作地点状语,只有动词不定式可以作目的状语;⑥没有主语,其表示动作的执行者叫作“逻辑性主语”(主动语态时),有时表示动作的承受者(被动语态时)非谓语动词可充当句子的很多成分,并且有时态和语态的变化如下:Ⅰ动词不定式定义:动词不定式是非谓语动词的一种,它没有人称和单复数的变化,在句子中不能独立作谓语,但它仍保持动词的特点,可以有自己的宾语和状语。
一、不定式的时态和语态:1. 动词不定式的时态1). 一般式:当不定式表示的动作或状态发生几乎同时或晚于谓语动词表示的动作或状态时用一般式;eg. ①He seemed to be tired.②The building to be finished next month is for our teachers.2). 进行式:当不定式表示的动作或状态与谓语正好同时发生时,用进行式。
eg. ①When I went to his home, he happened to be traveling around the world.②I didn`t expect you to be working in such bad conditions.3). 完成式:当不定式所表示的动作或状态明显发生在谓语动词之前,用完成式;eg. ①He is said to have written a novel about the Long March.②He is said to have been taught French when he was a child.4). 完成进行式:如果不定式表示的动作发生在谓语动词之前,强调一直在进行或有可能继续进行,用完成进行式.eg. ①We are happy to have been working with the experts all the month.②I suspected him to have been playing instead of studying.5. 不定式的语态:1)当不定式的逻辑主语是其表示的动作的执行者时,一般要用主动式;eg. ①The workers are to build the great bridge.当不定式的逻辑主语正好是其表示的动作的承受者时,一般要用被动式(to be done).eg. ①The great bridge is to be built by the workers.2) 若是明显发生在谓语动作之前,而且含有被动含义,就用完成被动式( to have been done).eg. ①He is said to have written a novel about the Long March.②He is said to have been taught French when he was a child.二、不定式的功能:1. 不定式做主语:不定式做主语一般表示具体的某一次动作,而动名词doing 表示习惯的,经常的动作。

不定式的时态+不定式的语态不定式的时态1. 一般时(to do);I begin to understand the truth.Would you like to come to my birthday party?Did you go to visit the Great Wall last year ?2. 现在时(to be doing);He seems to be following us.I happened to be standing next to him when he fell to the ground.The teacher happened to be correcting our papers when I came in.3. 完成时(to have done);He seems to have caught a cold.Im sorry to have given you so much trouble.I hope to have finished the work by now.4. 完成进行时(to have been doing);He seems to have been waiting a long time.He pretended to have been studying.He was said to have been teaching in high school for 2 years.不定式的被动语态1.不定式一般时的被动语态(to be done);Did it need to be done so soon?She cant bear to be laughed at.There was a lot of rubbish to be got rid of.2.不定式完成时的被动语态(to have been done);Im pleased to have been given this opportunity.The work seemed to have been finished before the deadline. Its said to have been built in the Ming dynasty.。

动词不定式1、不定式的时态和语态:一般式:完成式:进行式:不定式的一般式表示的动作与谓语动词表示的动作一般没有时间先后顺序。
不定式的完成式表示额动作一般发生在谓语动词之前,强调动作的先后顺序。
不定式的进行式表示的动作一般与谓语动词同时进行。
翻译下列句子:1)I hope to finish reading the book again.2) You appear to have travelled quite a lot.3) It’s nice to be sitting here with you.4) I am v ery happy to be praised.5) It is impossible for him to be appointed.2、不定式的句法功能1)作主语To succeed calls for hard work.(不定式在句中作主语相当于名词或代词。
)It seemed selfish of him not to give them anything. (不定式作主语往往用形式主语it 代替)It’s difficult for us to finish the work in a week.2)作宾语不定式一般作动词的宾语,不直接作介词的宾语,但“疑问词+不定式”结构可以作介词的宾语。
如:Y our father has at last decided to quit smoking.Talk with friends about where to shop.只接to do 作宾语的常见动词有:afford, agree, arrange, ask, care, choose, decide, demand, determine, expect, help, hope, plan, hesitate, long, manage, offer, prepare, refuse, pretend, promise, want, intend ,prefer3)作表语,可以表示主语的具体内容,目的。


动词不定式的时态与语态动词不定式是动词的一种非谓语形式,在句中不能单独作谓语。
但动词不定式仍具有动词的性质,它不但可以有自己的宾语和状语,从而构成动词不定式短语,它还可以有时态和语态的变化,即一般式、进行式、完成式和被动式。
1.动词不定式的一般式动词不定式的一般式表示的动作通常与主要谓语的动作同时或几乎同时发生,或是在它之后发生。
I happened to be there. 我当时刚好在那里。
(同时发生)To catch the plane, you'd better hurry to the air port by taxi. 为了赶飞机,你最好赶紧乘出租车去机场。
(to catch the train发生在hurry to the station之后)2.不定式的进行式动词不定式的进行式表示的动作与谓语动词所表示的动作同时发生。
Tom pretended to be reading the newspaper when his father came into the room. 他父亲走进房间时,汤姆装着在读报纸。
My brain doesn’t seem to be working well today.我的脑子今天似乎不大好使。
3.不定式的完成式动词不定式的完成式表示的动作在谓语表示的动作之前发生。
I'm sorry to have kept you waiting. 我很抱歉让你久等了。
I meant t o have finished my work last night, but I didn't feel very well. 我本来想昨晚完成工作的,但是我感觉身体不舒服。
It has been an honor for me to have been invited to your country. 对我来说,被邀请来你们国家是一件很荣幸的事情。
4.动词不定式的完成进行式动词不定式的完成进行式表示的动作在谓语动词所表示的动作之前一直在进行。


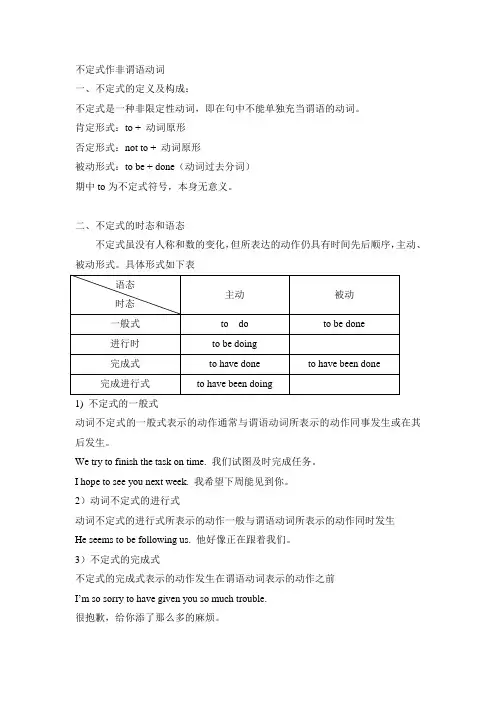
不定式作非谓语动词一、不定式的定义及构成:不定式是一种非限定性动词,即在句中不能单独充当谓语的动词。
肯定形式:to + 动词原形否定形式:not to + 动词原形被动形式:to be + done(动词过去分词)期中to为不定式符号,本身无意义。
二、不定式的时态和语态不定式虽没有人称和数的变化,但所表达的动作仍具有时间先后顺序,主动、被动形式。
具体形式如下表1) 不定式的一般式动词不定式的一般式表示的动作通常与谓语动词所表示的动作同事发生或在其后发生。
We try to finish the task on time. 我们试图及时完成任务。
I hope to see you next week. 我希望下周能见到你。
2)动词不定式的进行式动词不定式的进行式所表示的动作一般与谓语动词所表示的动作同时发生He seems to be following us. 他好像正在跟着我们。
3)不定式的完成式不定式的完成式表示的动作发生在谓语动词表示的动作之前I’m so sorry to have given you so much trouble.很抱歉,给你添了那么多的麻烦。
4)动词不定式的被动形式○1动词不定式的一般式被动语态通常表示将来的动作。
The flowers need to be watered. 这些花需要浇水了。
○2不定式的完成式被动语态表示的动作发生在谓语动作之前。
The room seems to have been tidied up already. 这个房子似乎已经整理过了。
三、不定式的用法1)作主语动词不定式作主语,相当于名词或代词的作用To learn an art well is very hard. 学好一门艺术很难。
★动词不定式作主语往往用形式主语it代替,然后不定式置于句尾。
上面的句子可改写为It is very hard to learn an art well.2) 作宾语动词不定式一般作动词或介词的宾语I really want to watch the football match.He has no idea of how to answer this question.3) 作宾语补足语○1后接带to的不定式作宾语补足语的动词有:ask, tell, beg, like, love, would like, order, teach, want, allow, encourage, wish等。


英语中不定式的时态、语态和用法讲解在谓语以外的句子成分中使用的动词一定要变词形(不能用动词原形),把动词原形变成不定式、-ing式或者过去分词,所以我们把这三种动词形式称为非谓语动词。
不定式的时态和语态:不定式共有4种时态形式(均是主动语态),另有2种被动语态形式:不定式的用法:不定式可以充当主语、表语、宾语、定语、状语。
1)作主语To work hard doesn’t necessarily mean getting high grades.下苦功不一定就能获得高分。
For one to do a good deed is very easy.一个人做一件好事很容易。
2)作表语My job is to take care of children.我的工作是照看小孩。
Her plan is to build a highway for the villagers.她的计划是为村民们建一条公路。
3)作宾语不定式作宾语的场合很多,以下是能够带不定式作宾语的动词:ask, want, agreeexpect, like, hatehope, wish, trystart, begin, offerprefer, continue, manageforget, promise, meanintend, attempt, decidedetermine, pretend, learndesire, choose, telladvise, show, discussI asked to be the first volunteer.我要求当第一名志愿者。
Do you want to leave here?你想要离开这里?We all agreed to do the spring cleaning.我们都同意过进行春季大扫除的。
He hopes to be chosen.他希望被选中。
有几十个动词后面不能接不定式作宾语,只能接-ing式,查阅公众号宾语部分。
不定式的用法和动词不定式的时态动词不定式是英语语法中的一种形式,它由不定式标志to加上动词的原形构成。
不定式在句子中可以充当名词、形容词或副词,具有一定的时态和语态。
一、不定式的基本用法1. 作主语:动词不定式可以在句子中作主语,表示某种动作、状态或观点。
- To learn a foreign language is important.- To be honest is always appreciated.2. 作宾语:动词不定式可以作及物动词的宾语,表示及物动词的动作或含义。
- I want to travel around the world.- She decided to quit her job.3. 作表语:动词不定式可以作系动词的表语,表示主语的身份、职业、特点等。
- Her dream is to become a doctor.- The important thing is to keep calm in any situation.4. 作定语:动词不定式可以修饰名词或代词,表示名词或代词的用途、目的等。
- I have a book to read.- We have a meeting to attend tomorrow.5. 作状语:动词不定式可以在句中作状语,表示目的、原因、结果、时间等。
- He exercises every day to stay healthy. (目的)- She cried so hard as to lose her voice. (结果)二、动词不定式的时态动词不定式有两种时态:一般时和完成时。
1. 一般时不定式:使用动词的原形表示不定式的一般时态。
- I hope to visit my grandparents next week.- She likes to read books in her free time.2. 完成时不定式:使用动词的完成时形式,由“to have + 动词的过去分词”构成。
不定式的用法教师版一、不定式的时态和语态很抱歉让你等了那么长时间。
I'm sorry to have kept you waiting so long.很高兴和你一起共事。
I am very glad to be working with you.被给予机会在会上发言我感到荣幸。
I think it's an honor to have been given a chance to speak at the meeting.二、不定式的句法功能1.不定式作主语(1)不定式作主语可以用于句首像那样做是愚蠢的。
To act like that is foolish.(2) 不定式作主语也可以用it 作形式主语,把真正的主语不定式短语置于句末。
并常用于以下句式中:①It+be+名词+to do照顾老人是我们的职责。
It's our duty to take good care of the old.②It takes sb+some time+to do你花了多久完成这个工作?How long did it take you to finish the work?③It+be+形容词+for sb+to do你抽这么多烟对身体很不好。
It is not good for you to smoke so much.注:在句型③中,常用表示客观情况的形容词,如:easy, difficult, hard, important, possible, impossible, comfortable, necessary, better;the first, the next, the last, the best, too much, too little, not enough④It+be+形容词+of sb+to do把老师说的一切都记下来是不明智的。
It is stupid of you to write down everything the teacher says.注:在句型④中,常用careless,clever,good,foolish,honest,kind,lazy,nice,right,silly,stupid,wise rude, clever, foolish, thoughtful, thoughtless , brave, considerate, selfish等表示赞扬或批评的词。
一、非谓语动词的定义:
非限定动词,在句中不能单独作谓语,因此也叫非谓语动词,包括动词不定式(the infinitive)、动名词(the gerund)、现在分词(the Present participle)、过去分词(the Past Participle)四种形式。
现把其用法辨析如下
非谓语动词的句法作用
(表一)
二.非谓语动词的时态和语态:
1.不定式的时态和语态
(表二)
(表三)
(表四)
通过上述几个表格的比较,我们可以知道四种非谓语动词的时态和语态形式,下面我们再总结一下:1.非谓语动词的否定式:一律直接在非谓语动词之前加not 即可。
例如:(1)The doctor advised me not to smoke.
(2)I regret not having gone together with her.
(3)Not having been there before, I don’t know the shortest way to the railway station.
(4)Not educated well, he found it difficult to solve such a complicate problem.
2.非谓语动词的完成式:
不定式的否定式我们只要在原来不定式中的动词之前加have即可,然后把原来的动词变为它的过去分词即可,如to do→not have done. 而过去分词只有一种形式,即done.
下面我们重点来看现在分词和动名词的完成形式。
现在分词和动名词完成形式是完全一样的,其变化规律是:一律在现在分词或动名词的一般式之前加having→having done,再把原来的现在分词或动名词变为它的过去分词。
如stud y →having studied
3.非谓语动词的被动式:
不定式的被动:看表二
现在分词和过去分词的被动:看表三
动名词的被动:看表四
从第二点我们可以知道现在分词和过去分词都可以表被动,那么他们有什么区别?
区别:现在分词的被动形式除了可以表示被动之外,还可以表示进行
过去分词除了表示被动之外还可以表示完成
例如:(1)The house being built now will be a hospital.
(2) The house built last year is a hospital.
下面我们重点讨论一下现在分词和过去分词在句子中的用法。
通过表一,我们知道现在分词和过去分词在句子中可以作表语、定语、状语、补足语,但下面我们仅从后三种情况来讨论现在分词和过去分词,要讨论这三种情况,我们关键要记住两句话:
现在分词表主动、进行
过去分词表被动、完成
记住这两句话之后,我们要搞清楚到底现在分词与谁的关系是主动关系,过去分词与谁的关系是被动关系,这我们就得结合分词在句子中的作用来考虑。
作定语: 现在分词——与被修饰词是主动关系
过去分词——与被修饰词是被动关系
作状语:现在分词——与句子主语是主动关系
过去分词——与句子主语是被动关系
作宾补:现在分词——与动词的宾语是主动关系
过去分词——与动词的宾语是被动关系
例如:Tell the children playing there to stop to have a rest.
He is a great leader loved and admired by all.
Hearing the news, he couldn’t help crying.
Built in 490,the temple is over 1500 years old
I saw the bike being repaired
Helen had to shout to make herself heard
下面我们重点讨论一下现在分词和过去分词作状语的用法:
我们都知道分词作状语时,分词的逻辑主语要与句子的主语一致,但是什么是分词的逻辑主语呢?分词的逻辑主语又如何与主句的主语一致呢?
何谓分词的逻辑主语。
分词属于非谓语动词,即不可作谓语,而我们知道,在句子单中,只有谓语才会有主语(主语--- 动作的发出者),所以分词没有自己真正的主语。
但是我们也知道,分词属于非谓语动词的一种形式,分词也表示动作,而动作必然会有动作的发出者,所以我们把理论上和逻辑上的分词动作的发出者叫做分词的“逻辑主语”。
下面我们来看一道题,通过这道题来理解分词的逻辑主语如何与主句的主语一致。
Finding her car stolen, ___________________________.
A. a policeman was asked to help
B. the area was searched thoroughly
C. it was looked for everywhere
D. she hurried to a policeman for help
通过上一道题我们理解了分词作状语,分词的逻辑主语如何与句子的主语一致(也可以说分词
的逻辑主语就是句子主语)。
我们做选择题时一定要注意这一点。
但是我们也发现在有的时候,分词的逻辑主语与句子的主语不一致。
例如:
Spring coming, the field are full of life.
Weather permitting, we’ll have an outing tomorrow.
在这两个句子中,分词的逻辑主语与句子的主语不一致,分词有了自己独立的逻辑上的主语,我们把这种结构叫做分词的“独立主格”。