§33分波前干涉光场的空间相干性.
- 格式:pps
- 大小:418.50 KB
- 文档页数:20


第8卷 第6期2015年12月 中国光学 Chinese Optics Vol.8 No.6Dec.2015 收稿日期:2015⁃06⁃09;修订日期:2015⁃07⁃23 基金项目:国家高技术研究发展计划(863计划)资助项目(No.2013AAXXX1003X)Supported by National High⁃tech R&D Program of China(No.2013AAXXX1003X)文章编号 2095⁃1531(2015)06⁃1020⁃07光场空间相干性的测量方法及比较董 磊(中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所,吉林长春130033)摘要:本文归纳了基于分波前干涉原理的具有代表性的干涉测量方法———杨氏双孔干涉法、逆波前杨氏干涉法和非冗余孔径阵列干涉测量法,以及基于分振幅干涉原理的干涉测量方法———自参考干涉测量法;介绍了各种测量方法的工作原理、实验配置;比较了4种测量方法的优缺点,并给出每种方法的最佳应用领域。
本文结论可为根据对空间相干性测量的不同要求,选择合适的测量方法提供初步参考。
关 键 词:空间相干性;杨氏干涉法;逆波前杨氏干涉法;非冗余孔径干涉法;自参考干涉法中图分类号:O436.1;TH691.9 文献标识码:A doi:10.3788/CO.20150806.1020Measurement methods of optical spatialcoherence and their comparisonDONG Lei(Changchun Institute of Optics ,Fine Machines and Physics ,Chinese Academy ofScience ,Changchun 130033,China )∗Corresponding author ,E⁃mail :nodepression@Abstract :This paper concluded measurement methods based on wavefront splitted principle such as Young in⁃terference method,reversed⁃wavefront Young interference method,nonredundant array interference method and measurement methods based on amplitude splitted principle such as self⁃referencing interference method.Their basic principles and experimental setup were introduced,and then the merits and defects of these meth⁃ods were compared,and then the best applied field of each method was put forward.The conclusion of this pa⁃per could be used as elementary guidance for different demands of spatial coherence measurement to choose proper methods.Key words :spatial coherence;Young interference method;reversed⁃wavefront Young interference method;nonredundant array interference method;self⁃referencing interference method1 引 言 光场的相干性主要包含时间相干性和空间相干性。

光场空间相干性的测量方法及比较董磊【摘要】本文归纳了基于分波前干涉原理的具有代表性的干涉测量方法———杨氏双孔干涉法、逆波前杨氏干涉法和非冗余孔径阵列干涉测量法,以及基于分振幅干涉原理的干涉测量方法———自参考干涉测量法;介绍了各种测量方法的工作原理、实验配置;比较了4种测量方法的优缺点,并给出每种方法的最佳应用领域。
本文结论可为根据对空间相干性测量的不同要求,选择合适的测量方法提供初步参考。
%This paper concluded measurement methods based on wavefront splitted principle such as Young in-terference method,reversed-wavefront Young interference method,nonredundant array interference method and measurement methods based on amplitude splitted principle such as self-referencing interference method. Their basic principles and experimental setup were introduced,and then the merits and defects of these meth-ods were compared,and then the best applied field of each method was put forward.The conclusion of this pa-per could be used as elementary guidance for different demands of spatial coherence measurement to choose proper methods.【期刊名称】《中国光学》【年(卷),期】2015(000)006【总页数】7页(P1020-1026)【关键词】空间相干性;杨氏干涉法;逆波前杨氏干涉法;非冗余孔径干涉法;自参考干涉法【作者】董磊【作者单位】中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所,吉林长春 130033【正文语种】中文【中图分类】O436.1;TH691.91 引言光场的相干性主要包含时间相干性和空间相干性。

光的干涉-知识点总结干涉场强分布:亮度最大值处: 亮度最小值处:条纹间距公式空间频率:ƒ(2()()()*12121212,(,)(,)(,)(,)2cos =++=++∆I x y U x y U x y U x y U x y I I I I ϕ()()110sin 11,i k x U x y Ae θϕ+=()()220sin 22,i k x U x y A e θϕ-+=()(1220(,)sin sin x y k x ϕθθφφ∆=-++-()()122010(,)sin sin x y k x ϕθθφφ∆=-++-以参与相干叠加的两个光场参数表示:衬比度的物理意义 1.光强起伏2.相干度2.2分波前干涉2.2.1普通光源实现相干叠加的方法 (1)普通光源特性 • 发光断续性 • 相位无序性• 各点源发光的独立性根源:微观上持续发光时间τ0有限。
如果τ无限,则波列无限长,初相位单一,振幅单一,偏振方向单一。
这就是理想单色光。
(2)两种方法21212I I I I +=γ2212112⎪⎭⎫ ⎝⎛+=A A A Aγ())(cos 1)(0r I r Iϕγ∆+=1γ=0γ=01γ<< 完全相干 完全非相干 部分相干◆ 分波前干涉(将波前先分割再叠加,叠加广场来自同波源具有相同初始位相) ◆ 分振幅干涉(将光的能量分为几部分,参与叠加的光波来自同一波列,保证相位差稳定)2.2.2杨氏双孔干涉实验:两个球面波的干涉 (1) 杨氏双孔干涉实验装置及其历史意义(1) 光程差分析(要会推导)XZ(x,y)(3)干涉条纹分布xdr r r r r r r r 2))((212212122122=-+-=-, 由 x DdD xdr r xd r r =≈+=-2221212得 λπϕ2,),(==∆k x D d k y x )(2)(2),(),()(12122010r r R R t P t P P -+-=-=∆λπλπϕϕϕ2222222221)2(,)2(由 D y dx r D y dx r +++=++-=)(2)(2),(),()(12122010r r R R t P t P P -+-=-=∆λπλπϕϕϕxdr r2得 2122=-当Q 位于Z轴上时,R 1=R 2,则)),(cos 1(),(0y x I y x I ϕ∆+=(4) 非近轴近似下的干涉条纹分布亮条纹和暗条纹在空间形成一系列双叶旋转双曲面。



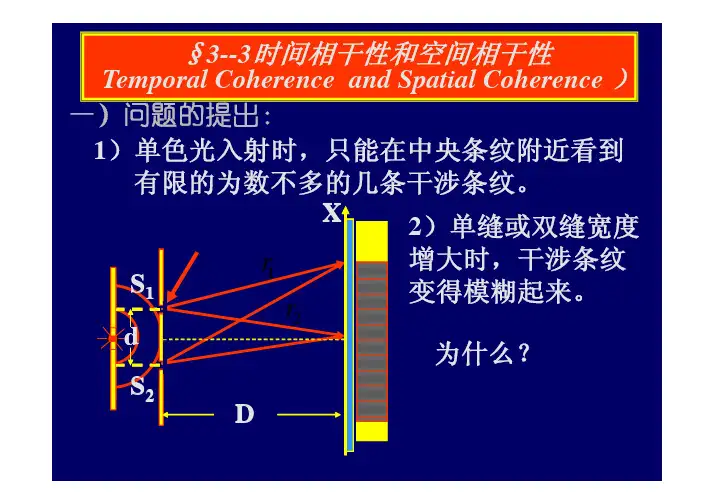
§3--3时间相干性和空间相干性Temporal Coherence and Spatial Coherence )一)问题的提出:S 2d 1r 2r 1)单色光入射时,只能在中央条纹附近看到有限的为数不多的几条干涉条纹。
2)单缝或双缝宽度增大时,干涉条纹变得模糊起来。
S 1DX O为什么?二)时间相干性XO S 1S 2d D指由原子一次发光所持续的时间来确定的光的相干性问题--原子发光时间越长,观察到清楚的干涉条纹就越多,时间相干性就越好。
1r 2r 1)两波列的光程差为零()21r r =可产生相干叠加。
X OS 1S 2d D1r 2r )(12L r r <−能参与产生相干叠加的波列长度减小干涉条纹变模糊了!P若是明纹,则明纹不亮;若是暗纹;暗纹不暗原因:XOS 1S 2dD1r 2r )(12L r r ≥−波列不能在P 点叠加产生干涉。
干涉条纹消失了!原因:P此乃高干涉级条纹看不清或消失的原因之一L<δ结论:产生光的干涉还须加一附加条件:tc L Δ=L<δ结论:产生光的干涉还须加一附加条件:tc L Δ=E 2E 1E 3tc L Δ=1)波列长度L 又称相干长度。
L 越长,光波的相干叠加长度越长,干涉条纹越清晰,相干性也越好。
注意:2)原子一次发光的时间Δt 称为相干时间。
Δt 越大,相干长度越长,相干性越好,因此用这种原子一次持续发光的时间来描述这种相干性故称为时间相干性。
三)空间相干性S 1S 2d DXOIb光源总是有一定的线度的,当光源线度不大时:从S 和S’发出的光产生的干涉条纹叠加后,仍能分辩清楚明暗条纹。
SS’S 1S 2d DXOIb当光源线度b 较大时:从S 和S’发出的光产生的干涉条纹叠加后,干涉条纹对比度降低,明暗条纹变得模糊。
SS’S 1S 2d DXOI b当光源线度b 增大到某一限度时:干涉条纹消失,S 和S’发出的光的光程差之差差λ/2SS’可见:为了产生清晰的干涉条纹,光源的线度受到一定限度。


光场空间相干性的测量方法及比较光场是一个具有幅值和相位信息的电磁波前,而光场的相干性是描述光场中波动的一致性和稳定性的性质。
光场空间相干性的测量方法包括干涉法、相位相关法、自相关法等。
下面将介绍这些方法及其比较。
1.干涉法:干涉法是通过光的干涉来测量光场的相干性。
常用的干涉仪包括两束干涉仪和腔内干涉仪。
两束干涉仪通过将待测光场与参考光场进行干涉,通过观察干涉条纹的可见度和对比度来反映光场的相干性。
腔内干涉仪则是利用光在腔内的干涉来测量光场的相干性。
干涉法可以得到较高的测量精度,但对实验环境和设备要求较高。
2.相位相关法:相位相关法是通过测量光场中不同点的相位相关性来评估光场的相干性。
常用的方法包括光学分列法、空间频谱分析法等。
光学分列法将光场分成一个小孔阵列,通过测量不同小孔接收到的光的幅度和相位,并进行相关分析来得到光场的相干性。
空间频谱分析法则是利用衍射光栅将光场分成多个光斑,通过测量不同光斑的相位差来反映光场的相干性。
3.自相关法:自相关法是通过光场的自相关函数来描述光场的相干性。
自相关函数可以通过幅度自相关和相位自相关进行测量。
幅度自相关函数描述了光场在时间轴上的相干性,可以通过光学组件如光敏电阻阵列进行测量。
相位自相关函数则描述了光场在空间上的相干性,可以通过干涉法或相位测量仪进行测量。
以上所述的方法各有优势和限制。
干涉法能够提供较高的测量精度,但对实验环境和设备要求较高;相位相关法在光学分列法中需要利用小孔阵列,对实验条件要求较高,而空间频谱分析法需要进行较复杂的数据处理;自相关法可以较为简单地测量光场的相干性,但需要利用自相关函数进行数据分析,且仅能提供光场在时间或空间上的相干性信息。
总体来说,根据实际需求选择合适的测量方法。
干涉法和相位相关法适用于对光场相干性进行详细测量和分析的科研实验;而自相关法则适用于对光场的快速评估和初步判定相干性的工程应用。
在实际应用中,也可以综合使用多种方法来获取更全面的相干性信息。
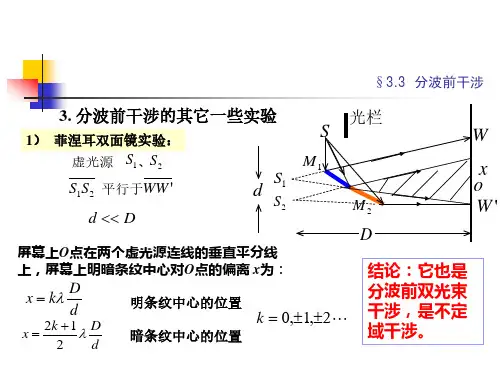
第三章干涉装置和光场的时空相干性第一课§3.1 分波前干涉装置光场的空间相干性本章将在第二章的基础上,具体讨论光的各种干涉装置和干涉仪,介绍光的干涉现象的一些实际应用。
与此同时,结合具体的干涉装置,阐明两个重要的概念—光场的空间相干性和时间相干性。
第二章中已述由于普通光源是不相干的,我们不能简单地由两个实际点光源或面光源的两个独立部分形成稳定的干涉场,为了保证相干条件,通常的办法是利用光具组将同一列波分解为二,使它们经过不同的路径后重新相遇。
由于这样得到的两个波列是由同一波列分解而来的,它们频率相同,位相差稳定,振动方向也可作到基本上平行,相干条件都得到满足,从而可以产生稳定的可观测的干涉场,分解波列的方法有:(1)分波前法:将点光源的波前分割为两部分,使之分别通过两个光具组,经衍射、反射或折射后交迭起来,在一定区域内产生干涉场。
杨氏实验是这类分波前干涉装置的典型。
(2)分振幅法:当一束光投射到两种透明媒质的分界面上时,光能一部分反射,一部分透射。
这种方法叫做分振幅法。
最简单的分振幅干涉装置是薄膜。
(3)分振动面法:利用晶体的双折射效应,使不同振动方向的光相干。
这种方法叫做分振动面法。
1. 杨氏干涉装置结构杨氏实验是分波前干涉装置的典Array型,或者说,它是下面将介绍的各种的分波前干涉装置的原型。
在杨氏实验中光具组Ⅰ,Ⅱ就是单孔屏和双孔屏(或者两条狭缝)。
光束1,2是靠衍射效应交迭起来的。
在下面的介绍中的几种装置中,光束1,2的交迭或靠反射,或靠折射形成。
2. 其他分波前干涉装置 (1)洛埃镜 如图所示,MN 是一平面反射镜,从狭缝光源S 发出的波列中的一部分掠入射到平面镜后反射到幕上,另一部分直接投射到幕上,在幕上两光束交迭区域里将出现干涉条纹。
设S' 为S 对平面镜所成的虚象,幕上干涉条纹就如同是实际光源S 和虚象光源 S'发出的光束产生的一样,因此条纹间隔的计算也可利用杨氏装置的结果。