动词的时态和语态讲义
- 格式:doc
- 大小:72.50 KB
- 文档页数:9
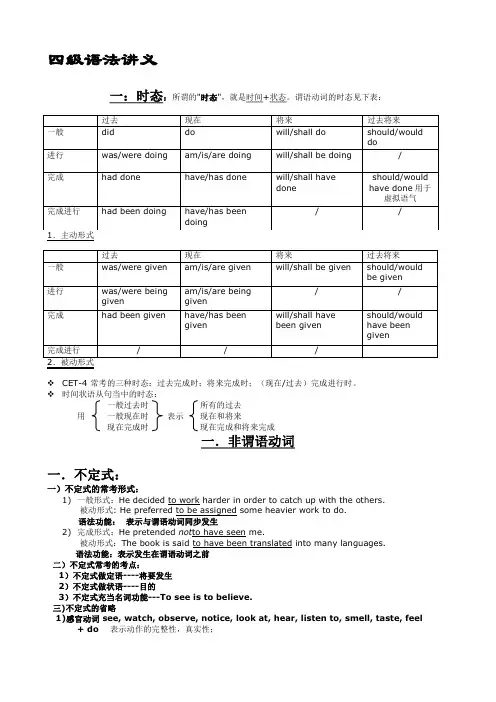
四级语法讲义一:时态:所谓的"时态",就是时间+状态。
谓语动词的时态见下表:1.主动形式2.被动形式CET-4 常考的三种时态:过去完成时;将来完成时;(现在/过去)完成进行时。
时间状语从句当中的时态:一般过去时所有的过去用一般现在时表示现在和将来现在完成时现在完成和将来完成一.非谓语动词一.不定式:一)不定式的常考形式:1)一般形式:He decided to work harder in order to catch up with the others.被动形式: He preferred to be assigned some heavier work to do.语法功能:表示与谓语动词同步发生2)完成形式:He pretended not to have seen me.被动形式:The book is said to have been translated into many languages.语法功能:表示发生在谓语动词之前二)不定式常考的考点:1)不定式做定语----将要发生2)不定式做状语----目的3)不定式充当名词功能---To see is to believe.三)不定式的省略1)感官动词 see, watch, observe, notice, look at, hear, listen to, smell, taste, feel+ do表示动作的完整性,真实性;+ doing表示动作的连续性,进行性I saw him work in the garden yesterday.昨天我看见他在花园里干活了。
(强调"我看见了"这个事实)I saw him working in the garden yesterday.昨天我见他正在花园里干活。
(强调"我见他正干活"这个动作)感官动词后面接形容词而不是副词:The cake tastes good; It feels comfortable.2) 使役动词 have bid make let 等词后不定式要省略但同1)一样被动以后要还原toI ‘d like to have John do it.I have my package weighed.Paul doesn’t have to be made to learn.3) help help sb do help sb to do help do help to do四)有些动词后只跟不定式如:want,wish,hope,manage,promise,refuse,pretend,plan, offer,decide,agree,expect allow sb to do, cause sb to do , permit sb to do, enable sb to doforce sb to do. be more likely to do love to do warn sb to do be able to dobe ambitious to do. begin to do . start to do五) 有的时候to后面要接-ing形式accustom (oneself) to; be accustomed to; face up to; in addition to; look forward to; object to; be reduced to; resign oneself to; be resigned to; resort to; sink to; be used to; be alternative to; be close/closeness to; be dedication/dedicated to; be opposition/opposed to; besimilarity/similar to.三、need/want 后的-ing形式具有被动的意思。

动词时态、语态和主谓一致高三英语一轮复习考点剖析-动词时态、语态和主谓一致考点一:考查过去进行时例1.I first met Lily five years ago. She ________ (work) as a nurse in a hospital at the time.【答案】was working【解析】考查时态。
句意:我五年前第一次见到莉莉。
她当时正在一所医院里做护士。
根据句意和时间状语at the time 可知,这里用过去进行时,强调过去某个时刻正在进行的动作,主语为she,谓语用单数。
故填was working。
考点二:考查一般过去时例2.He picked up his book and ________ reading even though it was already midnight. (continuous)【答案】continued【解析】考查时态。
句意:他拿起书继续阅读,尽管已经是午夜了。
所给单词continuous是形容词,表示“持续的”,分析句子机构,空处与picked并列作谓语,应用动词continue,表示“继续”,根据picked使用过去式形式可知,句子使用一般过去时,动词应用过去式形式continued。
故填continued。
考点三:考查现在进行时例3.—Hi, Jessy. Why are you going to work on foot today?—Well, my car ________. (repair)【答案】is being repaired【解析】考查时态和语态。
句意:——你好,杰西。
你今天为什么要步行去上班?——嗯,我的车正在修理。
根据句意提到步行上班可知,此处表示:车在修理中,时态用现在进行时,主语my car与repair(修理)之间为被动关系,所以用现在进行时的被动语态。
主语my car为单数,be动词用is。
考点四:考查现在完成时例4.The city ________ (recognize) as the musical capital of Europe since the 16th century, home to the likes of Mozart and Beethoven.【答案】has been recognized【解析】考查时态语态。

第六讲时态和语态典型例题1.高考考查的八种动词时态是:一般现在时,一般过去时,一般将来时,现在进行时,过去进行时,现在完成时,过去完成时,过去将来时。
2.考生要学会在具体语言环境下使用具体时态的能力,从NMET对动词时态的考查来看,这几年试题的灵活性正逐步加强。
题干中的有效信息由“外显的”转向“隐蔽的”,情景中可能不出现明显的时间信息。
3.预计动词时态的考核有如下趋势:经常考查时态的基本知识点,考查时注重在实际场合中的交际应用。
试题的立意由简单直接的“结构立意”(如状语从句、宾语从句等)转向了“情景立意”。
试题创设的语境明确,交际情景(对话形式占有一定比例)多是发生在学生学习或日常生活中的真实情况。
4.时态和语态是紧密相连的,高考题中经常把时态和语态一起考查。
应试高分瓶颈1.学习动词的时态和语态时,切不可脱离实际运用的语言,一味死记硬背语法规律的条条框框。
了解了时态的一些常用规则之后,要留心以英语为母语者在实际生活中是如何使用各种时态和语态的。
2.答题时,研读题干,搜索出尽可能多的“时间参照信息”,尤其是动词冗余信息中的时间信息。
发现和有效利用这些信息是解决问题的关键。
3.解决时态和语态问题,要遵循如下解题思路:①这个动作可能发生在什么时间?题千句中可参照的时间信息有哪些?U②这个动作处于什么状态,是进行中,.还是已结束(完成)?限制或修饰这个动作状态信息有哪些?③这个动作与主语的关系,是主动还是被动?只要全面细致地考虑了这些问题的答案,试题的正确答案也就水落石山?时态本类考题解答锦囊高考对时态的考查除了常用的八种时态外,还需注意以下几点:1. if,unless, even it 引导的条件状语从句中,在when, before, until(till), assoon as, the moment, once 弓I导的时间状语从句中,在no matter what / who / which / when / where, / how 或whatever, whoever, whichever, whenever, wherever, however引导的让步状语从句中,如果主句是将来时(往往出现will/ shall / can / must)或主句是祈使句,从句用一般现在时表示一般将来时。
高考英语语法复习动词的分类知识讲解cry 哭泣disappear 消失go 走,趋于live 生存,居住rise 上升,增强shiver 颤抖,哆嗦sparkle 闪耀appear 出现decay 衰退exist 存在happen 发生occur 发生,出现roar 咆哮,喧闹sigh 叹息swim 游泳arise 出现,产生deteriorate 恶化fall 落下hesitate 犹豫scream 尖叫sit 坐,位于travel 旅行collapse 倒塌die 死亡flow 流动laugh 笑quiver 颤抖smile 微笑sneeze 打喷嚏lie 躺,位于,说谎age (使)成熟,变老break 打破(记录)close 关闭,结束decrease 减少,减小end 结束,终止grow 种植,生长meet 满足,对付;相遇shake 动摇,发抖spread 散布,铺开,传播stop 断绝,停止widen 加宽,变宽begin (使)开始burn 烧毁,燃烧continue (使)继续double (使)加倍finish 完成,终结improve 改善,加强open 打开,开始show 演示,说明;显示stand 忍受,抵抗;站立tear 撕毁,流泪stretch (使)伸展;使用,消耗boil (使)蒸发,沸腾change (使)改变cook 烹饪,做菜dry 弄干,变干fly 使飘扬,飞行increase 增加run 经营,运转slow 放慢,阻碍,变慢start 启动,出发turn 使旋转,转动。

专题一动词的时态、语态和主谓一致考点1 一般时一般现在时(do/does式) ★★★典例1[2019安徽安庆二模改编,61]New year in Chinese people’s eyes means a family reunion. Every year (see) the largest annual mass migration on the planet when one sixth of the world’s population travel home to celebrate with their families.句意:在中国人眼中,新年意味着家人团聚,每年世界上六分之一的人回家与家人一起庆祝,这是地球上最大规模的年度人口迁移。
根据Every year 可知,此处应用一般现在时;再结合句意可知,主语是Every year,此处是拟人化的用法,see 在此处表示"遭受,历经",故用其第三人称单数形式。
sees典例2[2019河北邢台高三检测,61]An hour of swimming (burn) almost as many calories as an hour of running.句意:游泳一小时消耗的卡路里与跑步一小时消耗的几乎一样多。
此处叙述的是客观事实,因此用一般现在时。
burns一般过去时(did式) ★★★典例3[2020河北石家庄摸底考试,61]Translated fiction sales in the United Kingdom (rise) by 5.5 percent last year, with a growing demand for Chinese titles, said Nielsen Book on Wednesday.句意:Nielsen Book周三表示,去年英国的翻译小说销量增长了5.5%,对中文图书的需求不断增长。

一、时态、语态时态、语态需要掌握的要点:1.表达将来时的形式:(1)在时间、条件、让步从句中,一般现在时代替将来时,但要注意区别从句的类型,如:I’ll tell him when you will ring again. 我告诉他你什么时候再来电话。
(宾语从句)比较:I’ll tell him when you ring again.你再打电话时我告诉他。
(状语从句)(2)在make sure, make certain, see (to it) 后的that从句中,谓语动词用一般现在时代替将来时,如:See to it that you include in the paper whatever questions they didn’t know the answer to last time.(include 不能用will include或其他形式) 2.完成时是时态测试的重点,注意与完成时连用的句型和时间状语:(1)by/between/up to/till +过去时间、since、by the time/when +表示过去发生情况的从句,主句用过去完成时。
如:We had just had our breakfast when an old man came to the door.Between 1897 and 1919 at least 29 motion pictures in which artificial beings were portrayed had been produced.(表示1919年时已发生的情况) (2)by +将来时间、by the time/ when +谓语动词是一般现在时的从句,主句用将来完成时。
如:By the time you arrive in London, we will have stayed in Europe for two weeks.I hope her health will have improved greatly by the time we come back next year.(3)by now、since +过去时间、in/during/for/over/the past/last few(或具体数字)years/days/months,主句用现在完成时,如:The changes that had taken place in air travel during the last sixty years would have seemed completely impossible to even the most brilliant scientists at the turn of the 19th century.但在it is +具体时间since/before这一句型中,主句更多的时候不用完成时。

一、时态的数轴的思维导图have been de nghave done动词的时态和语态will do had donewill have done Past pastis doingpresentwill be doing future would have d ( ne考点一、现在时一、一般现在时1.含义1)经常性或习惯性的动作,常与表示频率的时间状语连用。
I leave home fbr school at 7 every morning.2)客观真理,客观存在,科学事实。
The earth moves around the sun.Shanghai lies in the cast of China.3)现在时刻的状态、能力、性格、个性。
Ann Wang writes good English but does not speak well.4) not....until....as...hen, before, after, not....until....等)、条件状语从句(if, unless, as long as...)中常用一般现在时表示将来Anything will become boring if you do it repetitively.As long as it doesn't rain tomorrow ,we will have a trip on schedule.2.常用的时间状语频率副词:often, usually, sometimes, always, seldom, hardly, never2)短语:every (day 等),once/twice a (week 等),on (Sunday 等),in the (morning 等),at (eight) , now and then, from time to timeHe usually goes to school by bike.3.谓语切词形式:do/does.谓语动词的被动语态:am/is/are doneIn the spoken English of some areas in the U.S, the " r" sounds at the end of the words arc dropped.练习:用所给单词的适当形式填空How close parents are to their children(have) a strong influence on the development of the children's characters.1.If your call is not answered within two minutes, you(advise) to hang up and dial again.2.We will be losing money this year unless that new economic plan of yours(work) miracle.3.It(turn) out that making a plan is easier than carrying it out.4.The growth of part-time and flexible working patterns, and of training and retraining schemes, (allow) more women to take advantage of employment opportunities.二、现在进行时.定义1)表示说话时正在进行的动作及行为;2)表示现阶段(近段时间)正在进行的动作。

动词时态和语态教案第一章:引言1.1 目的:让学生了解动词时态和语态的概念及其重要性。
1.2 内容:动词时态的概念和分类动词语态的概念和分类1.3 教学方法:讲授法:讲解动词时态和语态的概念及分类互动法:引导学生举例说明和练习第二章:动词的现在时态2.1 目的:让学生掌握现在时态的用法和构成。
2.2 内容:现在时态的定义和分类现在时态的构成和用法2.3 教学方法:讲授法:讲解现在时态的定义、分类和构成练习法:让学生通过练习题巩固现在时态的用法第三章:动词的过去时态3.1 目的:让学生掌握过去时态的用法和构成。
3.2 内容:过去时态的定义和分类过去时态的构成和用法3.3 教学方法:讲授法:讲解过去时态的定义、分类和构成练习法:让学生通过练习题巩固过去时态的用法第四章:动词的将来时态4.1 目的:让学生掌握将来时态的用法和构成。
4.2 内容:将来时态的定义和分类将来时态的构成和用法4.3 教学方法:讲授法:讲解将来时态的定义、分类和构成练习法:让学生通过练习题巩固将来时态的用法第五章:动词的被动语态5.1 目的:让学生掌握被动语态的用法和构成。
5.2 内容:被动语态的定义和分类被动语态的构成和用法5.3 教学方法:讲授法:讲解被动语态的定义、分类和构成练习法:让学生通过练习题巩固被动语态的用法第六章:动词的进行时态6.1 目的:让学生掌握进行时态的用法和构成。
6.2 内容:进行时态的定义和分类进行时态的构成和用法6.3 教学方法:讲授法:讲解进行时态的定义、分类和构成练习法:让学生通过练习题巩固进行时态的用法第七章:动词的完成时态7.1 目的:让学生掌握完成时态的用法和构成。
7.2 内容:完成时态的定义和分类完成时态的构成和用法7.3 教学方法:讲授法:讲解完成时态的定义、分类和构成练习法:让学生通过练习题巩固完成时态的用法第八章:动词的完成进行时态8.1 目的:让学生掌握完成进行时态的用法和构成。

动词的时态和语态知识总结一、动词的时态时态是指动词所表示的动作或状态发生的时间。
英语中常用的时态有以下几种:一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、现在进行时、过去进行时、将来进行时、现在完成时、过去完成时、将来完成时等。
1. 一般现在时一般现在时表示经常性、习惯性的动作或客观事实。
常与频率副词如always、often、usually等连用。
例如:- I often go to the gym.- He always arrives on time.2. 一般过去时一般过去时表示过去某个时间发生的动作或存在的状态。
常与表示过去的时间状语连用。
例如:- I visited my grandparents last weekend.- She lived in Paris for two years.3. 一般将来时一般将来时表示将来某个时间要发生的动作或存在的状态。
常与表示将来的时间状语连用。
例如:- We will have a meeting tomorrow.- He is going to travel to Japan next month.4. 现在进行时现在进行时表示现在正在进行的动作。
常由be动词的现在分词形式(-ing)构成。
例如:- They are watching a movie right now.- I am studying for my exams.5. 过去进行时过去进行时表示过去某个时间正在进行的动作。
常由be动词的过去分词形式(-ing)构成。
例如:- She was cooking dinner when I arrived.- They were playing football at that time.6. 将来进行时将来进行时表示将来某个时间正在进行的动作。
常由be动词的将来分词形式(be going to + 动词的现在分词形式)构成。
例如:- They will be having a party this time next week.- I am going to be studying abroad next year.7. 现在完成时现在完成时表示过去某个时间发生的动作对现在造成的影响或结果。

2023年高中英语语法之辨别英语时态与特殊的变化形式如何辨别英语时态一、根据时间状语与时态的对应关系动词特定的时态常常与特定的时间状语联系在一起,如由this time yesterday可知用过去进行时;由so far, in the past three years, till now可知要用完成时,等等。
1、句中含有yesterday; last year(last + 具体时间); two days ago(一段时间 + ago); just now; this morning; in 2008(in + 过去的年代); the other day; over the weekend等时间状语时,谓语动词用一般过去时;2、句中含有tomorrow; next week(next +具体时间); in two hours(in +一段时间); (how) soon; from now on; 10 years from now(一段时间+from now); in the future; in 2012(in +将来的年代); by (the end of) next month(by+将来时间); for the weekend; this afternoon; this evening; tonight; this weekend等时间状语时,谓语动词用一般将来时;3、句中既有yesterday等过去时间状语,又有一个具体时间点(at 5:00; this time; at that time)时,谓语动词用过去进行时;4、句中含有recently; in the last/past two years(in the last/past+一段时间); over the years(over the+一段时间); since 2005(since+具体时间或从句); for two years(for+一段时间,句中无其它时间状语); before(单独用于句尾)等时间状语时,谓语动词用现在完成时;5、by (the end of) last year(by+过去时间); two days before (一段时间+before); for和since说明的时间同时用于句中;by the time + 从句(过去时态)等时间状语时,谓语动词用过去完成时;6、简单句中如不含上述时间状语或有含说话时间在内的表示现在时间关系的词语时(如now; today; these days等词)解析:由时间状语at this time tomorrow可知用将来进行时,故选B。
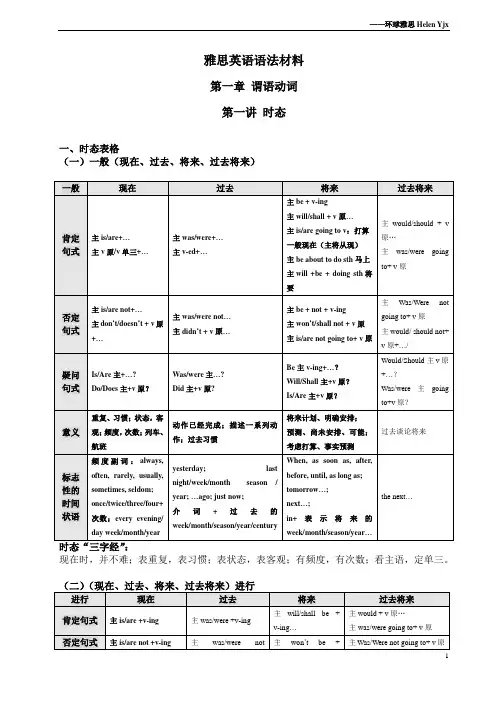
雅思英语语法材料第一章谓语动词第一讲时态一、时态表格(一)一般(现在、过去、将来、过去将来)现在时,并不难;表重复,表习惯;表状态,表客观;有频度,有次数;看主语,定单三。
(三)(现在、过去、将来、过去将来)完成(四)(现在、过去、将来、过去将来)完成进行二、基本时态演练Listening to the following conversation.(一) Task One: fill in the blanks.1. Interviewer: Your name?Peter: Peter __________. (1)2. Interviewer: ________ (2) you work or _________ (3) you a student?Peter: I’m studying really hard for my exams this month—I’m doing math’s at university—but I also________ (4) my parents out. They own a _________ (5) and I ________ (6) there as a waiter in the evenings, so I ____________ (7) a lot of free time during the week.My mom is always saying that I _____________ (8) enough in the restaurant! But I do manage to find some free time most days.3. Interviewer: Can you look at the _____ (9) and tell me whether you do any of these things and if so, how ____ (10)?Peter: I love music and I’m learning to play the piano. I ______ (11) really early and practice for an hour or so just about every day. I also play the guitar in a band with some other friends. We used to practice together at least _____________ (12) a week but these days we only manager to meet about once __________________ (13).4. Interviewer: What about the next thing on the list? -_________________ (14)?Peter: Well, I used to play them all the time but now I’m too busy studying and I _______ (15) miss them at all.5. Interviewer: Do you use a computer for other things?Peter: I use the Internet just about ________ (16) for my studies. And I also use it to _____________ (17) my friends and my family. My cousin is living in Thailand at the moment and he _______ (18) me regular emails to let me know how much fun he’s having! He’s always visiting exciting places.6. Interviewer: Now, how about _________________ (19)?Peter: Actually, I joined the local football team when I was at school and I still play _______________ (20) provided I can get to training. I much prefer playing football to watch it on TV, though I do ______________ (21) watch a match if there’s a big final or something.7. Interviewer: What about going to watch live matches?Peter: I’d love to be able to afford to go every week because I ____________ (22) my local team, but students don’t ____________ (23) have much money, you know! I can remember the ___________ (24) I went to a live match. Oh, sorry, I can see my friends—I ____________ (25)go now!(二)Task TwoRead through the conversation and find out:1. Present simple sentences:2. Present continuous:3. Past simple sentences:三、时态改错1. People should act according to what they are believing.2. In general, I think our government spent too much money on space travel.3. Nowadays, many people in my country have sent their children to single-sex schools.4. These days, more and more people traveling to very distant places for their holidays.5. I am hoping it is not too late to save the environment.6. The female hen laying on average 5 or 6 eggs per week.7. Younger drivers is more likely to be involved in a car accident.8. Most doctors are agreeing that the only way to lose weight is by doing more exercise.第二讲语态一、被动语态的形式二、被动语态使用情景(一)一般说来,当强调动作承受者,不必说出执行者或含糊不清的执行者时,多用被动式1. I agree with the statement that there should be no government restriction on creative artists who express themselves in the way they do and that they must be given freedom for the same. (IELTS 4, Band 7, p167)2. There is almost everything good in what is given to us through the media world which is made up of artists. (同上)3. In conclusion, I strongly agree with that children should be taught to cooperate rather than compete. (IELTS 5, Band 6, p167)4. It was opened in the year 1863, and it is already 140 years old. (IELTS 5, Band 7, p168)(二)在描述事件和客观事实的时候,被动语态用得更多1. The use of electricity in England is indispensed with. (IELTS 4, Band 6, p164)2. Demand for electricity in England during typical days in winter and summer is illustrated in the graph. (同上)3. The use of average English home is shown in the pie chart. (同上)(三)主语是泛指很多人或者大部分人这个方面1. A more dramatic rise is predicted between 2030 and 2040 in Japan, by which it is thought thatthe proportion of elderly people will be similar in the three countries. (IELTS 5, model answer, p162)2. It can be argued that…It is advised/believed/universally accepted/generally recognized that…It is said/reported/estimated that…(四)当上下文已经说明了动作执行者时:A law was introduced to help protect people in this situation.(五)动作的执行者并不重要时:In the factory, the shoes are cleaned and packed into boxes ready for sale.(六)需要体现动作的执行者时,加by-短语:A lot of waste materials could be recycled by large manufacturers.三、剑指考试1. To enrich vocabulary, we should read more authentic materials.可以改为:(1)(2)(3)2. It is important for nations all over the world to work hard together to control the environmental pollution.可以改为:3. I am not sure whether all the college graduates can find jobs after graduation.可以改为:4. 用适当的动词形式完成下列句子:(1)My home _____________ (locate) in the western part of the city.(2)These funds can _____________ (give) to the poorer people to help them.(3)We _____________ (not tell) that the rules had changed.(4)Children need to _____________ (teach) the correct way to behave in public.5. 句子改错:(1)The house was sell for over a million dollars.(2)The class has allowed to eat in the staff dining room during the renovations.(3)The potatoes carry along a conveyor belt to a room where they wash and peel. (4)The teacher told to take her class out of the school if the fire bell rang.(5)Smoking don’t allow in any part of the aeroplane.(6)The museum was being renovating when we were there, so we could not visit it. (7)Bus tickets can buy at any newsagents.(8)New employees have instructed not to operate the photocopier until they are trained.6. 把下面的句子改成被动语态,并决定是否需要带by-短语(1)A factory worker checks each box for quality.(2)The government does not permit children under 16 to work.(3)The washing machine is washing your clothes at the moment.(4)A mechanic will repair your car this afternoon.(5)The agent has sold our house at last.(6)Something tore the back of my coat.(7)The employer pay off the staff more for working at the weekend.(8)Burning tires give off highly toxic chemicals.第三讲虚拟语气请欣赏下列一首诗歌:If you were a teardrop in my eye,For fear of losing you, I would never cry.And if the golden sun should cease to shine its light,Just one smile from you would make my whole world bright.一、虚拟语气基本句型1. 与现在事实相反(1) If she were sick, she could stay at home and have a rest today.(2) If you watched more and talked less, we would both enjoy our film.2. 与过去事实相反(1) If they had studied earlier, they would have passed the IELTS.(2) Helen would have graduated with her class if she had been able to meet all the requirements in time.3. 与将来事实相反(1) If it snowed tomorrow, I would go skiing.(2) If it should snow tomorrow, I would go to make a snowman in front of our dormitory.(3) If you were to see your tutor, what would you tell him?4.错综的虚拟语气(1) If I were you, I wouldn’t have told that to her. (时间错综:从句现在,主句过去)(2) Had I taken my umbrella with me in the morning, I should not be wet now. (时间错综:从句过去,主句现在)5.虚拟语气的倒装可以把条件句中的if 省略掉,同时把should, were, had 等助动词提前,构成倒装句。
动词的时态一、动词基本形式(原形;第三人称单数;现在分词;过去分词;过去式)原形:位于情态动词后、助动词后、感官动词或使役动词后、跟在to后面构成动词不定式。
第三人称单数:一般现在时里,当主语是第三人称单数时,动词用第三人称单数形式。
现在分词:现在分词与be动词构成进行时态。
过去式:过去式用在一般过去时里。
过去分词:过去分词用在现在(过去)完成时和被动语态中,规则变化同过去式,不规则见不规则动词表。
二、动词的时态时间标志:1. often, usually, always, sometimes 2. every +时间类如:every day/week/month3. on Sundays;once a week;twice a day;in the morning/evening/afternoon.注意:often, usually, always在句子的位置:通常是在be动词之后,行为动词之前。
☆延续性动词与非延续性动词1.延续性动词表示能够延续的动作。
如:learn, work, stand, sleep, live, stay等。
延续性动词可以与表示时间段的状语连用。
如:You can keep the book for 5 days. 这本书你能借5天。
2.非延续性动词也称终止性动词、瞬间动词,表示不能延续的动作,这种动作发生后立即结束。
不能与时间段连用。
如: die, close, begin, come, borrow, buy等。
如果要与时间段连用,就把它转为延续性动词使用。
3.中考常见的延续性动词与非延续性动词之间的转换有:join—be in+组织机构或be a member of+组织机构;get married ——be married;catch a cold — have a cold;get to/ arrive/reach — be in;fall asleep — be asleep;die—be dead;borrow—keep;buy—have;close—be closed;fall ill—be ill;finish—be over;become — be;open—be open;come back — be back;leave — be away;come here — be here;begin/start — be on。
谓语动词的时态和语态在英语中是如何表示谓语的时态、语态和语气呢?显然,只有动词或短语动词本身是不具备这个能力的。
只有将不同的助动词和动词或短语动词构成不同的组合,才能够表示出谓语不同的时态、语态和语气,因此我们在阅读和写作的时候,都需要牢记这一点。
时态和语态的基本概念和要求时态其实包含两个概念,那就是时和体。
时:现在、过去、将来、过去将来现在:所有现在时态都是以现在时间作为参照时间的,要求谓语中的第一个词(助动词或动词和短语动词)都需要使用其现在式,及动词原形或单三形式。
过去:所有过去时态都是以过去时间作为参照时间的,要求谓语中的第一个词使用其过去式。
将来:所有将来时态都是以将来时间作为参照时间的,要求谓语中的第一个词是shall或will(后跟动词原形)。
过去将来:所有过去将来时态都是表示从过去某个时间来看将要发生的动作或存在的状态,要求谓语中的第一个词是should或would(后跟动词原形)。
体:一般、进行、完成、完成进行一般:一般体就是指谓语所表示的动作是发生在某时间或是某时间的一个习惯性动作,只需遵守时对动词组合的要求即可。
进行:进行体表示某时间点正在进行的动作或某时间段反复进行的动作(现在进行时和过去进行时偶尔可表示现在或过去打算做的或即将发生的事情),要求必须有助动词be+V-ing(现在分词)。
完成:完成体表示某时间之前就完成的动作或从某时间之前开始一直延续到该时间的动作,要求必须有助动词have+V-ed(过去分词)。
完成进行:完成进行体就是完成和进行的结合,表示某时间之前就开始,一直延续到该时间,且从该时间来看,可能刚刚停止,可能要继续下去的动作。
要求必须有助动词have +been+V-ing(现在分词)。
语态:主动语态、被动语态主动语态:表示SV结构中主语是谓语所表示动作的执行者。
谓语的动词组合只遵守时态的要求即可。
被动语态:表示SV结构中主语是谓语所表示动作的承受者。
谓语的动词组合中必须以“助动词be的某个形式+过去分词”结束。
课程主题:谓语动词学习目标掌握谓语动词的基本用法。
结合高考真题及模拟题分析谓语动词的考点。
教学内容【知识梳理】考点一动词的时态动词各种时态的形式(以do为例) ,加粗的为课标要求掌握的十大时态,其余了解即可。
一般时态进行时态完成时态完成进行时态现在do/does am/is/are doing have/has done have/has been doing 过去did was/were doing had done had been doing将来will/shall do will/shall bedoingwill/shall havedonewill/shall have beendoing过去将来would/shoulddowould/should bedoingwould/shouldhave donewould/should havebeen doing一、一般现在时 (do/does)1.表示经常或习惯性的动作,常与表频率的时间状语连用;也可表示现时的情况或状态等。
例1 New year in Chinese people’s eyes means a family reunion. Every year_sees_(see) the largest annual mass migration on the planet when one sixth of the world’s population travels home to celebrate with their families.2.表示观事实、普遍真理,不受主句的时态限制。
例2 The geography teacher told his students that the earth _moves_ (move)around the sun.3.在时间、条件状语从句中常用一般现在时代替一般将来时。
例3 My mother will be very angry with me when she _finds_ (find) out I’m lying.二、一般过去时(did)1.表示过去某个特定时间或某段时间内所发生的动作或存在的状态。
传播优秀Word 版文档 ,希望对您有帮助,可双击去除!1 / 9动词时态和语态一、动词的分类和形式:动词是表示动作和状态的词。
动词有时态、语态和语气3种形式的变化。
1、动词按其能否独立作谓语而分为:“谓语动词”和“非谓语动词”两种2、动词的4种基本形式:动词原形、过去式、过去分词和现在分词。
3、动词按其构成动词词组作用分为:实义动词、连系动词、情态动词和助动词。
1)实义动词分为及物动词和不及物动词。
还可分为持续性动词和瞬间动词;2)连系动词有两种:一种表特征或状态,另一种表状态变化过程。
4、五种不同的短语动词:1)“动词+介词”;2)“动词+副词”;3)“动词+副词+介词”;4)“动词+名词(或代词)+介词”;5)“be+形容词(包括相当于形容词的过去分词+介词”。
二、动词的时态:1、一般现在时的用法:1)表示现在的习惯,经常发生的动作或存在的状态。
2)表示主语的特征、性格和能力。
3)表示客观事实或真理。
4)表示按照计划安排好的将来行为。
(只限于是go,come, leave, start, stop, be 等开始或移动意义的词。
)2、一般过去时的用法:1)表示过去的动作或状态。
2)叙述过去连续发生的事情。
3)表示过去一段时间内经常发生的动作。
3、一般将来时的用法:1)表示将来的动作或状态。
2)表示将来的经常动作。
4、现在进行时的用法:1)表示说话时正在进行的动作。
2)表示现阶段正在进行的动作。
(说话时动作不一定进行。
)传播优秀Word版文档,希望对您有帮助,可双击去除!5、过去进行进的用法:1)过去某一时刻或某一段时间内正在进行的动作。
2)表示移动的动词:come, start, stay, leave, go等词的过去进行时可以表示过去的将来要发生的动作。
3)was going to do可以表示在过去某一时间之后发生的动作。
6、现在完成时的用法:1)表示刚刚完成的动作,常与just连用。
2)表示过去发生而持续到现在的动作或状态,甚至延续到将来。
常与since, for连用,但for, since不能与终止性的动词连用。
3)表示过去的动作对现在造成的影响或结果。
7、现在完成时与一般过去时的区别:1)现在完成时与现在有联系,它表示过去的动作对现在所产生的结果、影响。
一般过去时通常表示在过去某一具体时间发生的动作,与现在没什么联系。
2)现在完成时表示过去延续到现在的行为;一般过去时着重过去某一时刻的某一具体动作。
8、过去完成的用法:1)表示在过去某一或动作之前已经完成的动作。
常与by, before等介词短语或一个状语从句或上下文暗示。
2)表示由过去某一时间开始,一直延续到过去另一时间的动作,常和for(有时可省去)或since 构成的短语或since引导的从句连用。
9、过去将来时的用法:表示对于过去某一时刻而言将要发生的动作或存在的状态。
(一)一般现在时1.定义:表示现在的经常性、习惯性的动作或状态。
时间状语:every day; often; usually; always; seldom; sometimes2. 一般现在时可以表示客观事实或普通真理。
3. 在让步、时间和条件状语从句中以及主语是祈使句时常用一般现在时代替将来时。
1. The geography teacher told us that the earth moves (move) around the sun.2. Water boils (boil) at 100 ℃.3. The careless driver has just been fined $ 10 for stopping his car at a sign that reads (read) “NO PARKING”.4. Whatever you say (say), I will not change my mind.5. Don’t try to run before you begin (begin) to walk.6. I’ll go with you if I finish (finish) my work.(二)一般过去时定义:过去某一时间发生的动作或所处的状态。
含有“刚才,在过去”之意,暗示现在已经不这样。
传播优秀Word版文档,希望对您有帮助,可双击去除!时间状语:then; at that time; just now; three days ago; yesterday; when 或while 引导的表示过去的时间状语从句1. --- Nancy is not coming tonight. --- But she promised (promise)!2. My uncle didn’t marry (marry) until he was forty-five.3. --- You haven’t said a word about my new car, Brenda. Do you like it?--- I’m sorry I didn’t say (not say) anything about it sooner. I certainly think it’s pretty on you. 4. --- Come on in, Peter. I want to show you something.--- Oh, how nice of you! I never thought (think) you were (be) going to bring me a gift.5. --- Your phone number again! I didn’t catch (not catch) it. --- It’s 9598442.(三)一般将来时1. 定义:将来某一时刻要发生的动作或所处的状态。
时间状语:soon; next week; tomorrow 等(1) You are to do your homework before you watch TV. = have to / must “必须“(2) You are to report the police. = should / ought to “应该”(3) If we are to be there before 10, we’ll have to go now. = intend / want “打算;想”(4) What are we to do next?用于第一人称疑问句中,表示征求对方意见。
传播优秀Word版文档,希望对您有帮助,可双击去除!(5) You are not to smoke in the room. = mustn’t “禁止”,用于否定句中(6) The news is to be found in the evening newspaper. = may / can “可以;可能”【题组训练】1. If a man is to succeed (succeed), he must work as hard as he can.2. In such dry weather, the flowers will have to watered if they are to survive (survive).3. Look at these clouds. It is going to rain (rain).4. --- You’ve left the light on. --- Oh, so I have. I will go (go) and turn it off.二、进行体考点1. 定义1)现在进行时:说话时或现阶段正在发生的动作或存在的状态。
2)过去进行时:过去某个时刻或阶段正在发生的动作或存在的状态。
2. 时间状语1)现在进行时:now; right now等2)过去进行时:at this time yesterday等3. 一个长动作为背景,被一个短动作打断,长动作用进行体,短动作用一般体。
4. 进行体表示反复出现或习惯性动作,含有赞赏、厌恶、遗憾等情绪。
常与always; continually; constantly等连用。
5. 进行体表示动作的未完成性、暂时性。
1. As she was / is reading (read) the newspaper, Grammy fell / falls (fall) asleep.2. The reporter said that the UFO was travelling (travel) east to west when he saw (see) it.3. He is always thinking (think) of others first.4. He is always making (make) the same mistake.5. --- Have you moved into the new house. --- Not yet. The rooms are being painted (pain).6. Shirley was writing (write) a book about China last year but I don’t know whether she has finished it.7. Selecting a mobile phone for personal use is not easy task because technology is changing (change) so rapidly.8. I don’t really work here. I am just helping (help) out until the new secretary arrives.三、完成体考点(一)现在完成时1. 定义和时间状语:1)表示一个动作或状态开始于过去,持续到现在,(也许还将持续下去)。
时间状语:lately; recently; in the last / past few years, since then; up to now; so far 等2.) 一个发生在过去的事情对现在产生的影响。
时间状语:already; just; yet; never; before 等2. 在条件、时间或让步状语从句中,表示将来某时以前已经完成的动作3. 瞬间动词用完成时态不可以接一段时间的状语瞬间动词有:come; go; get to / reach / arrive in / arrive at; leave; buy; sell; open; close; get up; join / take part in; begin / start; return; give; borrow; lend; become; turn; bring; take; die; finish / end传播优秀Word版文档,希望对您有帮助,可双击去除!; receive / hear form; marry; break; lose; jump1. In the past few years, great changes have taken (take) place in my hometown.2. He has been (be) busy writing a book recently.3. He has written (write) 8 books so far.4. He has already turned (turn) off the light. (the light is off now)5. Has the concert started (start) yet? (Is the concert on now?)6. I have never seen (see) the film. (I don’t know the film now)7. I will not believe you unless I have seen (see) it with my own eyes.8. I will go with you as soon as I have finished (finish) my work.9. 改错1) He has come to Beijing since last year.He has been / lived in Beijing since last year.He came to Beijing last year.2) He has joined the army for 3 years.He has served in the army for 3 years.He joined the army 3 years ago.He has been a soldier for 3 years.It is / has been three years since he joined the army.(二) 过去完成时1. 定义:一件事情发生在过去,而另外一件发生在它之前的动作用过去完成时。