初中英语八种时态归纳总结表格版
- 格式:docx
- 大小:13.65 KB
- 文档页数:3

英语八大时态总结表英语中一共有八种时态,分别是简单现在时、现在进行时、简单过去时、过去进行时、一般将来时、将来进行时、现在完成时、过去完成时。
下面我们将对每一种时态进行详细介绍。
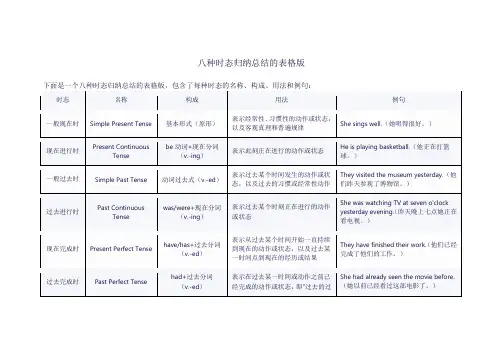
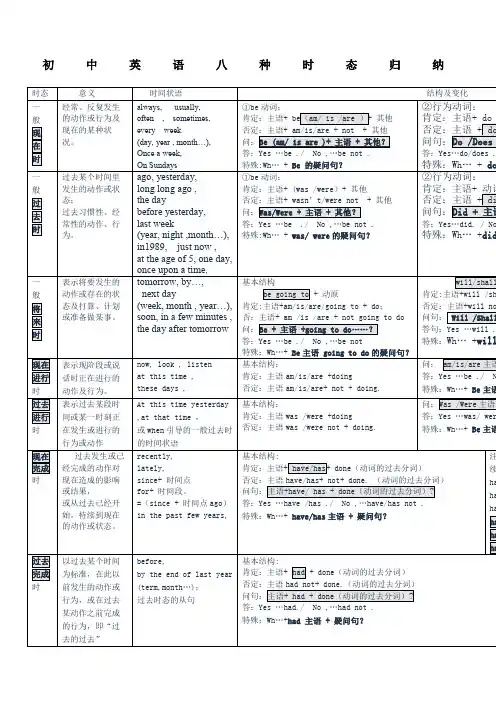
1、简单现在时简单现在时表示现在正在进行的动作或状态,也可以表示经常性、习惯性的动作或状态。
结构:主语 + 动词原形 / 动词第三人称单数形式(he, she, it)+ 其他例如:1. I eat breakfast every morning. 我每天早上吃早饭。
2. She teaches at a school. 她在一所学校教书。
2、现在进行时现在进行时表示现在正在发生的动作或状态。
结构:主语 + be动词的现在分词(am, is, are)+ 动词-ing + 其他。
例如:1. He is studying for the exam. 他正在为考试而学习。
2. We are watching a movie right now. 我们现在正在看电影。
3、简单过去时简单过去时表示在过去某个时间发生的动作或状态。
结构:主语 + 动词的过去式 / 动词的第二人称单数形式(you)+ 其他。
例如:1. They went to the beach last summer. 他们去年夏天去了海滩。
2. She talked to her friend on the phone yesterday. 她昨天给她的朋友打电话聊天了。
4、过去进行时过去进行时表示过去某个时间正在进行的动作或状态。
结构:主语 + be动词的过去分词(was, were)+ 动词的现在分词(-ing)+ 其他例如:1. They were playing soccer when it started raining. 下雨的时候他们正在踢足球。
2. She was studying when her phone rang. 她在学习的时候接到了电话。

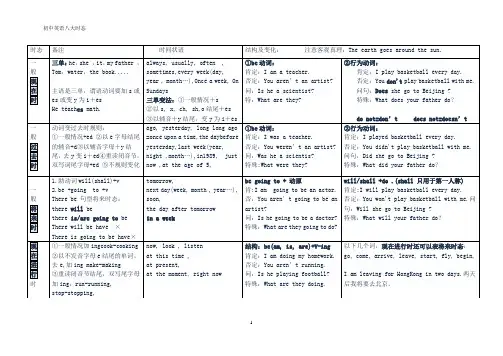
初中英语时态8种基本时态结构表在英语中,有八种基本的时态结构,它们是:1. Simple Present Tense (一般现在时)2. Present Continuous Tense (现在进行时)3. Present Perfect Tense (现在完成时)4. Present Perfect Continuous Tense (现在完成进行时)5. Simple Past Tense (一般过去时)6. Past Continuous Tense (过去进行时)7. Past Perfect Tense (过去完成时)8. Past Perfect Continuous Tense (过去完成进行时)下面是这八种时态的结构和用法:1. Simple Present Tense (一般现在时)•结构:主语 + 动词原形(不加“to”)•用法:表示现在经常、习惯性或普遍性的动作或状态。
2. Present Continuous Tense (现在进行时)•结构:主语 + 动词“to be”(am/is/are) + 动词-ing形式•用法:表示现在正在进行的动作。
3. Present Perfect Tense (现在完成时)•结构:主语 + have/has + 过去分词•用法:表示过去已经发生,对现在仍有影响的动作。
4. Present Perfect Continuous Tense (现在完成进行时)•结构:主语 + have/has been + 动词-ing形式•用法:表示从过去某时开始持续到现在的动作。
5. Simple Past Tense (一般过去时)•结构:主语 + 过去式动词•用法:表示过去某时发生的动作。
6. Past Continuous Tense (过去进行时)•结构:主语 + was/were + 动词-ing形式•用法:表示过去某时正在进行的动作。
7. Past Perfect Tense (过去完成时)•结构:主语 + had + 过去分词•用法:表示过去某时发生的动作在另一过去时间之前已经完成。

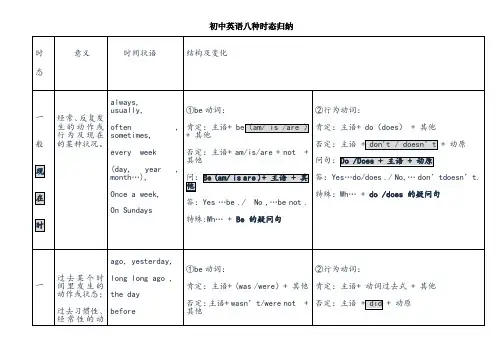

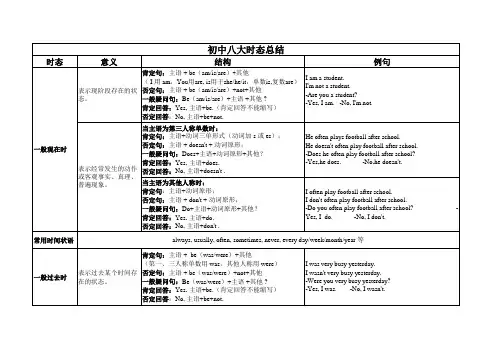
初中时态语态总结表格初中时态语态总结表格动词形式一般现在时一般过去时一般将来时完成时态进行时态被动语态一般形式 V原形+s/es V-ed will/shall+V原形have/has+V过去分词 am/is/are+V-ing am/is/are+V过去分词例句 She plays basketball. He studied English yesterday. I will go to the beach tomorrow. They have finished their homework. I am watching TV now. The book was written by Mark.时态解释表示现在发生的动作或状态。
表示过去发生的动作或状态。
表示将来发生的动作或状态。
表示过去发生并一直延续到现在的动作或状态。
表示说话时正在进行的动作或状态。
表示动作的承受者。
一般性使用主语+动词主语+动词ed 主语+will/shall+动词主语+have/has+动词ed 主语+am/is/are+动词ing 主语+am/is/are+动词过去分词一般疑问句助动词(do/does)/be动词(is/am/are)+主语+动词助动词(did)/be动词(was/were)+主语+动词助动词(will/shall)/be动词(is/am/are)+主语+动词助动词(have/has)/be动词(is/am/are)+主语+动词ed 助动词(am/is/are)/be动词(is/am/are)+主语+ 动词ing 助动词(am/is/are)/be动词(is/am/are)+主语+动词过去分词特殊疑问句疑问词+助动词(do/does)/be动词(is/am/are)+主语+动词疑问词+助动词(did)/be动词(was/were)+主语+动词疑问词+助动词(will/shall)/be 动词(is/am/are)+主语+动词疑问词+助动词(have/has)/be动词(is/am/are)+主语+动词ed 疑问词+助动词(am/is/are)/be动词(is/am/are)+主语+ 动词ing 疑问词+助动词(am/is/are)/be动词(is/am/are)+主语+动词过去分词否定句主语+助动词(do not/does not)/be动词(is/am/are not)+动词主语+助动词(did not)/be动词(was/were not)+动词主语+助动词(will/shall not)/be动词(is/am/are not)+动词主语+助动词(have/has not)/be 动词(is/am/are not)+动词ed 主语+助动词(am not/is not/are not)/be动词(is/am/are not)+动词ing 主语+助动词(am not/is not/are not)/be动词(is/am/are not)+动词过去分词情态动词主语+情态动词+动词原形主语+情态动词+动词原形主语+will/shall+情态动词+动词原形主语+have/has+情态动词+动词原形主语+am/is/are+情态动词+ 动词ing 主语+am/is/are+情态动词+动词过去分词现在进行时主语+am/is/are+V-ing 主语+was/were+V-ing 主语+will/shall+be+V-ing 主语+have/has+been+V-ing - -过去进行时主语+was/were+V-ing -- - - -将来进行时主语+will/shall+be+V-ing -- - - -完成进行时主语+have/has+been+V-ing 主语+had+been+V-ing - -- -被动语态主语+am/is/are+V过去分词主语+was/were+V过去分词主语+will/shall+be+V过去分词主语+have/has+been+V过去分词主语+am/is/are+being+V过去分词主语+am/is/are+V过去分词。

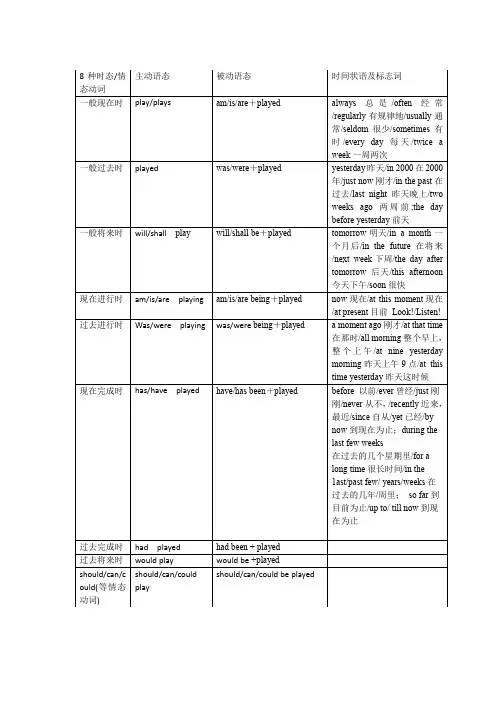
英语8大时态总结表格时态概述英语中有8大时态,它们用于表达不同时间和状态。
下面是关于这些时态的详细总结表格。
时态结构用法一般现在时主语 + 动词原形表示经常性、习惯性或普遍真理一般过去时主语 + 动词过去式表示过去发生的动作或状态一般将来时主语 + will + 动词原形表示将来发生的动作或状态现在进行时主语 + be + 动词-ing 表示现在进行的动作或状态过去进行时主语 + was/were + 动词-ing 表示过去某一时间正在进行的动作将来进行时主语 + will be + 动词-ing 表示将来某一时间正在进行的动作现在完成时主语 + have/has + 过去分词表示过去某一时间到现在的持续动作过去完成时主语 + had + 过去分词表示过去某一时间到过去的持续动作详细解释一般现在时一般现在时表示经常性、习惯性或普遍真理。
它的结构是主语 + 动词原形。
例如:•I go to school every day.•She likes to read books.•The sun rises in the east.一般过去时一般过去时表示过去发生的动作或状态。
它的结构是主语+ 动词过去式。
例如:•I went to the park yesterday.•They played soccer last week.•She bought a new car two years ago.一般将来时一般将来时表示将来发生的动作或状态。
它的结构是主语 + will + 动词原形。
例如:•I will travel to Japan next month.•They will have a party tomorrow.•She will call you later.现在进行时现在进行时表示现在正在进行的动作或状态。
它的结构是主语+ be + 动词-ing。
例如:•I am studying for the exam.•She is watching TV right now.•They are playing basketball in the park.过去进行时过去进行时表示过去某一时间正在进行的动作。
展宏学校中考英语常考八大时态与被动语态类别一般现在时现在进行时现在完成时一般将来时用途谓语结构(动词形式 ) 被动结构时态标志1.表示经常性、习惯性的动作;表示现在(说话瞬间)正2.表示客观事实或永恒真理;在进行或发生的动作。
3.表示特征、爱好、状态和能力等。
V.原或 V.三单 (he/she/it 或能够用he/she/it 代替的人或物后用三单 )am / is / are + 过分am / is / are +being+过分1. 频率副词: often;sometimes=(at 1. now = at present = righttimes); always; usually; every day now = at the moment(every + 时间 ) 2. look, listen开头的句2. 次数: twice a week子。
3. on Sundays:在每一个星期天例句 :例句 :She is watering the treesHe often cleans the room. 主(动 )now. (主动 )The roomoften by him.The trees by(被动 )her now. (被动 )1. 表示发生在过去的动表示将来某个时间要发生的作一直持续到现在; 2.动作或存在的状态。
表示发生在过去的动作对现在造成的影响或结果。
have/has + 过分 1.will + V .原2.be going to + V.原have / has been + 过分will be + 过分1. for / since+时间; 1.将来的时间: tomorrow;the day2. 副词 ever, never, yet,after tomorrow;next week ;in a fewalready 等;days;in 3 years;in the future ;this3. so far = by now=up to evening/year/weeknow; 2. at once=in a minute=right away3.soon4.in the last/past few 例句 :years;She will do it tomorrow. ( 主动 )It by her5.over the years= in tomorrow. (被动 )recent years在主从复合句中,当主句为一般将来It ’s 7 o’clock + 现在进行时、主句为祈使句、主句含有情态动时。
以下是初中英语语法八大时态总结表格:时态用法构成时间状语一般现在时表示经常发生的动作或存在的状态主语+动词原形/第三人称单数形式+其他always, usually, often,sometimes, everyday/week/month/year, etc.一般过去时表示过去发生的动作或存在的状态主语+动词过去式+其他yesterday, lastweek/month/year, etc.现在进行时表示现在正在进行的动作主语+am/is/are+现在分词+其他now, at the moment, etc.过去进行时表示过去某个时刻正在进行的动作主语+was/were+现在分词+其他at this time yesterday,etc.一般将来时表示将要发生的动作或存在的状态主语+will/shall+动词原形+其他tomorrow, nextweek/month/year, etc.过去将来时表示过去将要发生的动作或存在的状态主语+would/should+动词原形+其他the next day, etc.时态用法构成时间状语现在完成时表示过去发生的动作对现在造成的影响或结果主语+have/has+过去分词+其他already, yet, ever, never,for/since, etc.过去完成时表示过去某个时间之前已经完成的动作主语+had+过去分词+其他by the time, before, etc.需要注意的是,这些时态的构成和用法可能会有一些例外情况,具体取决于语境和句子结构。
此外,不同的教材和地区可能会有一些差异,因此在学习过程中,建议你参考多种资料,以便更好地理解和掌握这些时态。