定语从句与非谓语动词(
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:532.50 KB
- 文档页数:14

从句与非谓语之间的转换一、当从句的主语与主句的主语一致(定语从句的主语与先行词一致),如果从句中是:1)从句用be动词作谓语be + doing; 省略be;(例10)be + done;省略be;(例4)be + 介词短语;省略be;(例2)be + 形容词 / 副词; be变为being;(例9)be + 名词; be变为being;(例1)2)如果从句中是其他行为动词作谓语是一般现在时或一般过去时就一律用doing的进行时化简;(例3)是完成时态或after引导的一般时态,用having done化简.(例7和11)二、当状语从句的主语与主句的主语不一致时,也可按上面第一条中方法化简复合句。
化简后的短语前加上原从句中的主语即可(既是独立主格结构)。
(例5、6、8)1.When he was a young boy,he used to ask lots of questions。
= Being a young boy, he used toask lots of questions.2.When he was in the classroom, he read his book aloud。
= In the classroom, he read his bookaloud。
3.They went to the teacher for help who taught them English. = They went to the teacher teachingthem English for help。
4.When the earth is seen from space, it looks like a huge water ball。
= Seen from space, theearth looks like a huge water ball。
5.When a guest comes to your room, you can say to him "H ave a seat, please”。

非谓语动词有关从句1.非谓语动词概括:2.非谓语动词与名词性从句3.非谓语动词与定语从句4.非谓语动词与状语从句There are some people insisting that they shouldn’t learn English.一、非谓语动词概括:动名词 Ving ;此刻分词 Ving; 过去分词 ved; to do 不定式1.分词短语从实质上而言:是由动词派生而来的形容词。
如, a sleeping baby, a used car, a frightening experience, a frightened child, etc.A baby who is sleeping.A car which is used2.v ing 形式由动词的主动形式派生而来;表示主动的动作或正在进行的动作Ved 形式由动词的被动形式派生而来:表示被动的动作或已达成的动作The fallen leavesThe falling leavesThe custom fascinates me.The fascinating custom has been the subject of many books.The baby will sleep until eight.Try not to wake a sleeping baby.Some movies are rated X.Children shouldn ’ t see X-rated movies.My leg was broken in three places.My broken leg is healing slowly.The sinking ship= the ship that wassinkingThe sunken ship=the ship that has sunken.Falling leaves=Fallen leaves=3.此刻分词的达成时态:表示分词的动作发生在主句谓语动词动作以前。


非谓语动词作定语一:如何轻松精准的做此类题呢只需把握住两点:一先看非谓语动词与其逻辑主语(即定语的先行词)之间的关系,主动与被动二看非谓语动词与谓动的时间关系1与谓动同时发生2在谓动之前3在将来发生二:做题步骤:先搞清非谓语动词与先行词之间的逻辑关系1如果是主动关系,再看时间,与谓动同时发生用doing 将来发生用to do2如果是被动再看时间,与谓语动词同时发生用being done 在谓动之前用done表将来用to be done一.用不定式做定语的几种情况:(1)不定式表将来。
如:The car to be bought is for his sister.(2)用来修饰被序数词、最高级或no, all, any 等限定的中心词。
如:He is the best man to do the job.She was the first woman to win the gold medal in the Olympic Games.(3)用来修饰的词是抽象名词时用不定式,常见的有:ability, chance, idea, fact, excuse, promise, answer, reply, attempt, belief, way, reason, moment, time 等Do you have the ability to read and write in English?I have no chance to go sightseeing.二.分词作定语doing 主动进行being done 被动进行done 被动完成The houses being built are for the teachers.Things lost never come again.I have never seen a more moving movie.三、to be done , done, being done 做定语的区别三者的语态同为被动语态,区别主要集中在时态上Have you read the novel witten by Dickens?Listen! The song being sung is very popular with the students.The question to be discussed at tomorrow's meeting is a very important one.(一)、-ing形式作定语-ing 形式在句中做定语时有两种情况。
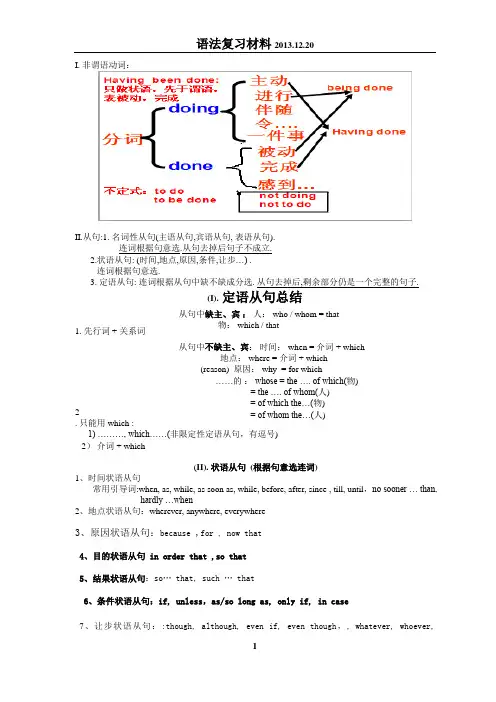
I. 非谓语动词:II.从句:1. 名词性从句(主语从句,宾语从句, 表语从句).连词根据句意选.从句去掉后句子不成立.2.状语从句: (时间,地点,原因,条件,让步…) .连词根据句意选.3. 定语从句: 连词根据从句中缺不缺成分选. 从句去掉后,剩余部分仍是一个完整的句子.(I). 定语从句总结1. 先行词 + 关系词2 . 只能用which :1) ………, which……(非限定性定语从句,有逗号)2) 介词 + which(II). 状语从句 (根据句意选连词)1、时间状语从句常用引导词:when, as, while, as soon as, while, before, after, since , till, until ,no sooner … than,hardly …when2、地点状语从句:wherever, anywhere, everywhere3、原因状语从句:because ,for , now that4、目的状语从句 in order that ,so that5、结果状语从句:so… that, such … that6、条件状语从句:if, unless ,as/so long as, only if, in case7、让步状语从句::though, although, even if, even though ,,whatever, whoever,从句中缺主、宾 : 人: who / whom = that 物: which / that 从句中不缺主、宾: 时间: when = 介词 + which 地点: where = 介词 + which (reason) 原因: why = for which ……的 : whose = the …. of which(物) = the …. of whom(人)= of which the…(物) = of whom the…(人)wherever, whenever, however, whichever ,no matter …8、方式状语从句:as if, how(III)名词性从句1.连接词 that 引导名词性从句时,只起连接作用,没有任何意思,也不充当句子成分,在宾语从句中可省略,但引导其他名词性从句时通常不省略。

定语从句和非谓语动词是高中阶段重要的两大语法项目。
定语从句的应用可以使语言表达更精确更生动,显得使用者具有较高的英语文化底蕴,但也是中学英语的难点语法项目,许多同学在学习和运用定语从句时,感到很难理解。
若将其简化,理解起来就比较简单了。
而非谓语动词的正确使用,就可以使定语从句的理解容易化,简单化,而且使语句简练、更有文采。
掌握二者的转换,有助于我们更好的理解其用法,并能够自如地运用。
下面我就着重谈谈如何将定语从句转换成非谓语动词以及转换时应注意的事项。
1定语从句转换成不定式“to do”。
定语从句的谓语动词是将来时或含有情态动词或含有序数词the next,the last等时,该定语从句转换为不定式“to do”.(1)The plane which will arrive is from Hubei.→The plane to arrive is from Hubei。
(2)The students will go to a party that will be held in our class at 7:45.→The students will go to a p arty to be held in our class at 7:45.(3)He was the first boy who came to school.→He was the first boy to come to school..2定语从句可转换成为“介词+关系代词或副词+不定式”。
“介词+关系代词”引导的定语从句和“介词+关系代词或副词+不定式”充当的定语,可以相互转换。
被这种定语修饰的名词往往在逻辑上充当不定式动作的地点、时间或工具。
例:(1)She wanted a room in which she could do her homework.→She wanted a room in which to do her homework.(2)She had only a pen with which she can write.→She had only a pen to write with.或She had only a pen with which to write.注:定语从句转换成“介词+ 关系代词+不定式”时,此时的不定式一定是及物动词,如是不及物动词,则需在动词后面加上相应的介词。

三分钟语法课:关系从句的简化今天起我们开始学习“非谓语动词”。
【回顾】通过前面的学习,我们已经知道,根据主谓结构的多少,把句子分为简单句和复杂句。
其中就包括“并列句”和“复合句”。
其中,复合句由一个主句和一个从句构成。
根据从句和主句的关系和作用,从句又分为:形容词从句——修饰和限定主句中的一个名词,作定语;The guy who was sitting next to me in the bus was from Ghana.The cupcake that was brought to the party by Sally was delicious.副词从句——修饰和限定主句、或主句中的动词,作状语;例如:He studied hard so that he could get a scholarship.When dine out together, we tell each other the most absurd stories.名词从句——代替主句中某个名词成分,作主语、宾语、表语或同位语。
例如:John remembers that he saw the lady before.It is common courtesy that one should wear black while one attendsa funeral.注意语言中有个economical原则——•能够用一句话说清的,不用两句话,这就有了复杂句;•能够用词组说清的,尽量不用复杂句,这就有了“非谓语动词”。
【概念】我们今天先从形容词从句开始。
看看从句简化的原则。
【原则1】简化从句的基本方法,是省略主语和BE动词。
例如:The cupcake that was brought to the party by Sally wasdelicious.就可以简化为:The cupcake brought to the party by Sally wasdelicious.这个brought,即“过去分词”、或“-ed分词”。

非谓语从句和定语从句非谓语从句和定语从句非谓语从句英语中的非是整个当中非常重要的部分,也是学生学习的一个难点。
其实,我们可以从从句的角度来解释非,弄清非谓语动词与从句的关系,这样会使学生对非谓语动词有更好的了解,学习起来更容易。
I. v-ing 形式与从句之间的转换1. v-ing形式作主语可换成that引导的主语从句Tom's knowing English helps him in learning French. That Tom knows English helps him in learning English.Her being out of work was unexpected. That she was out of work was unexpected.2. v-ing形式作宾语或宾补可换成that引导的宾语从句I remember having paid him for his work. I remember that I have paid him for his work.He suggests our making better use of the school library. He suggests that we (should) make better use of the school library.3. v-ing形式作表语可换成that引导的表语从句Our worry is your depending too much on him. Our worry is that you depend too much on him.The question is many people's being trapped in the fire. The question is that many people are trapped in the fire.4. v-ing形式作定语可换成that, who, which引导的定语从句We will study in the house facing south. We will study in the house that / which faces south.The man talking to my teacher is my father. The man who / that is talking to my teacher is my father.5. v-ing形式作状语可换成相应状语从句On arriving there, I will telephone you. As soon as I arrive there, I will telephone you.While waiting for the bus, I caught sight of her. While I was waiting for the bus, I caught sight of her.另外,v-ing形式在句中表伴随或作结果状语,相当于一个并列句,也可和with结构转换。

非谓语作定语和定语从句的区别
非谓语动词作定语和定语从句在语法结构和表达方式上有一些区别,具体如下:
1. 语法结构:
- 非谓语动词作定语:非谓语动词包括动词的现在分词(-ing)、过去分词(-ed)和不定式(to do),它们可以在句中作定语,修饰名词或代词。
非谓语动词作定语时,通常放在被修饰词的前面。
- 定语从句:定语从句是一个句子,由关系代词(who, whom, whose, that, which)引导,用来修饰先行词(即被修饰的名词或代词)。
2. 表达方式:
- 非谓语动词作定语:非谓语动词作定语可以提供更简洁、紧凑的表达方式。
它可以通过一个动词形式来描述被修饰词的特征、状态或行为。
- 定语从句:定语从句可以提供更详细、具体的信息,通过一个完整的句子来描述被修饰词的性质、特点或关系。
3. 语义和功能:
- 非谓语动词作定语:非谓语动词作定语主要强调动作或状态,它们可以表示正在进行的动作(-ing 形式)、已完成的动作(-ed 形式)或将要进行的动作(to do 形式)。
- 定语从句:定语从句可以提供更丰富的语义信息,包括对被修饰词的进一步解释、限定或描述。
总的来说,非谓语动词作定语和定语从句在语法结构和表达方式上有所不同。
非谓语动词作定语更简洁,强调动作或状态;而定语从句更详细,提供更多的语义信息。
在使用时,需要根据具体语境和表达需要选择合适的结构。

高考语法复习之非谓语动词做定语及与定语从句的转换编辑整理:尊敬的读者朋友们:这里是精品文档编辑中心,本文档内容是由我和我的同事精心编辑整理后发布的,发布之前我们对文中内容进行仔细校对,但是难免会有疏漏的地方,但是任然希望(高考语法复习之非谓语动词做定语及与定语从句的转换)的内容能够给您的工作和学习带来便利。
同时也真诚的希望收到您的建议和反馈,这将是我们进步的源泉,前进的动力。
本文可编辑可修改,如果觉得对您有帮助请收藏以便随时查阅,最后祝您生活愉快业绩进步,以下为高考语法复习之非谓语动词做定语及与定语从句的转换的全部内容。
非谓语动词作定语一:如何轻松精准的做此类题呢只需把握住两点:一先看非谓语动词与其逻辑主语(即定语的先行词)之间的关系,主动与被动二看非谓语动词与谓动的时间关系1与谓动同时发生2在谓动之前3在将来发生二:做题步骤:先搞清非谓语动词与先行词之间的逻辑关系1如果是主动关系,再看时间,与谓动同时发生用doing 将来发生用to do2如果是被动再看时间,与谓语动词同时发生用being done 在谓动之前用done表将来用to be done(1)不定式表将来。
如:The car to be bought is for his sister。
(2)用来修饰被序数词、最高级或 no, all, any 等限定的中心词。
如:He is the best man to do the job。
She was the first woman to win the gold medal in the Olympic Games。
(3)用来修饰的词是抽象名词时用不定式,常见的有:ability,chance, idea,fact,excuse,promise,answer, reply,attempt, belief, way, reason, moment, time 等Do you have the ability to read and write in English?I have no chance to go sightseeing.二.分词作定语doing 主动进行being done 被动进行done 被动完成The houses being built are for the teachers。

定语从句变为非谓语动词作后置定语的方法这个问题有点大,没有好好研究过,下面是临时凑的几条,不一定全面,仅供参考:▲如果定语从句的谓语是进行时态(包括用进行时态表示将来意义的用法),通常可以转化为现在分词或过去分词短语(括号内的词不省略为定语从句,省略后即为现在分词短语作定语)。
如:Do you know the woman (who is) talking to Tom? 和汤姆说话的女人你认识吗?There were some children (who were) swimming in the river. 有些小孩在河里游泳。
I didn’t talk much to the man (who was) sitting next to me. 我没和坐在我旁边的人多讲话。
Police (who are) investigating the crime are looking for three men. 调查这件罪案的警察在找寻三个人。
但是要注意的是,并非只有谓语是进行时态的定语从句才可转化为现在分词(短语),有时一般时态也可转化为现在分词(括号前的现在分词可以括号内的定语从句来改写)。
如:It is said that those eating (=who eat) the most are the least healthy. 据说吃得最多的人身体最差。
Jim has got a brother working (=who works) in a bank in London. 吉姆有一个哥哥在伦敦的一家银行里工作。
Students wanting (=who want) more information should apply in writing. 想要得到更多资料的学生应提出书面申请。
A young man writing (=who writes) novels came to speak to us yesterday. 一位写小说的青年昨天来向我们作报告。
定语从句与非谓语一、定语从句与分词1、主从句的谓语同为现在时间(一)、主从句的谓语动词的动作都是现在的一般的动作,即为一般现在时态。
例:1China is a developing country which belongs to the third world.China is a developing country belonging to the third world.China, belonging to the third world, is a developing country.China which is a developing例:2They live in a room that faces the south.They live in a room facing the south.例:3Books which are written in English are more expensive.Books written in English are more expensive.(二)、主从句的时间都表示现在,但主句的谓语表示一般状态,而从句的谓语表示现在进行的动作。
例:1Do you know the boy who is playing the violin?Do you know the boy playing the violin? Doing:主动,进行例:2The car that is being repaired is mine.The car being repaired is mine. Doing ---being done2、主从句的谓语同为过去时间。
例:1He used to live in the house which faced south.He used to live tin the house facing south.3、在某些情况下,尽管主句与从句谓语的时间不一致,但在不影响句子意思表达的情况下,可以把定语从句简化为分词短语。
定语从句与⾮谓语动词⼆.定语从句:定语从句三步:第⼀找出先⾏词(被修饰的那个名词或代词);第⼆看从句缺少什么成份(如主语、宾语或状语);第三选择合适的引导词。
注意:引导词在介词后,指⼈只能⽤whom 指物只能⽤which⾼考对定语从句的考查常涉及以下⼏个⽅⾯:【考点6】正确区别限制性定语从句与⾮限制性定语从句的结构;理解关系代词和关系副词在定语从句中的作⽤;特别注意指代整个主句内容的关系代词which引导的⾮限制性定语从句。
⾮限制性定语从句,从意义上来说,是对主语的补充说明,从结构上来看,先⾏词和定语从句之间⽤逗号隔开,He makes great progress in his English learning, which makes his mother very happy.⑧I shall never forget the day _____ Shenzhou V was launched, _____ has a great effect on my life.A. when; whichB. that; whichC. which; thatD. when; that (2004北京东城)【考点7】关系代词that,who,which以及as的⽤法区别。
指⼈时常只⽤who不⽤that的情况;指物时只⽤which不⽤that的情况;只⽤that不⽤which的情况;关系代词as与which的⽤法区别;the same … that … 与the same … as …的区别:1 其中that, who(whom),都可以指⼈,那么他们在指⼈时有什么区别呢。
[本条记忆技巧:⽤who 不⽤that 的情况“there be” “one,ones,anyone,nobody, those ” 被分割。
那⾥有(there)很多万(one)被那些⼈(those)分割。
]<1>先⾏词为those, one, anyone, nobody 等词时,⽤who不⽤that,例如:The one who knows me well is Tom.<2>在分隔型定语从句中,若先⾏词是⼈,⽤who不⽤that, 例:A new teacher will come who will teach you German.在本句中,先⾏词“teacher”和修饰限定它的从句“who will teach you German ”分离,所以我们⽤who 不⽤that。
初中英语知识点归纳定语从句中的非谓语动词定语从句是英语中常见的句子结构,它可以用来修饰前面的名词或代词,并进一步描述这个名词或代词。
在定语从句中,非谓语动词也扮演着重要的角色,起到补充说明的作用。
在本文中,我们将归纳总结初中英语中定语从句中的非谓语动词的用法。
一、带有非谓语动词的定语从句在定语从句中,非谓语动词主要有不定式、动名词和过去分词这三种形式。
它们可以替代定语从句中的谓语动词,起到修饰名词或代词的作用。
下面分别介绍三种非谓语动词的具体用法。
1. 不定式不定式作为非谓语动词在定语从句中的用法多种多样,主要包括以下几种情况:1)作定语例如:- I have a lot of books to read.(我有很多要看的书。
)- He has many friends to help him.(他有许多朋友来帮助他。
)2)作后置定语例如:- They have a lot of things to do.(他们有很多事情要做。
)- She has a lot of songs to sing.(她有很多歌要唱。
)3)作状语例如:- He studies hard to learn English well.(他努力学习英语。
)- She runs every morning to keep fit.(她每天早上跑步保持健康。
)2. 动名词在定语从句中,动名词作为非谓语动词有以下几种常见的用法: 1)作定语例如:- I have a plan of going abroad.(我有一个出国的计划。
)- He told me a story about helping others.(他给我讲了一个关于帮助他人的故事。
)2)作后置定语例如:- There is no way of solving the problem.(没有解决这个问题的办法。
)- The key to passing the exam is hard work.(通过考试的关键是努力学习。
卓越个性化教案GFJW0901学生姓名刘司惠年级高二授课时间 2012-01-01 教师姓名胡芳课时 2现在分词主动被动一般writing being written完成having written having been written过去分词主动被动一般written动名词主动被动一般writing being written完成having written having been written●动词不定式:动词不定式是由to + 动词原形构成,在句中起名词,形容词和副词的作用,可以担任除谓语以外的其它任何成分。
1. 动词不定式作主语:To mast a language is not an easy thing.To teach English is my favorite.It's my pleasure to help you.动词不定式作主语时可以放在后面,而用it 作形式主语放在原主语的位置上。
It's very kind of you to have given us much help.你给了我们那么多的帮助真是太好了。
It's necessary to find the witness. 有必要找到目击者。
2. 动词不定式作宾语:某些及物动词可以用动词不定式作宾语,这些动词有decide, begin, help, begin, want, wish, like, forget, learn, ask.What I wish is to learn English well.I like to help others if I can.3. 动词不定式作宾语补语。
We expect you to be with us. 我们希望你和我们在一起。
Please ask him to come here quickly.请叫他快过来。
4. 动词不定式作表语:What I should do is to finish the task soon. 我应该做的是赶快完成任务。
定语从句和非谓语动词定语从句和非谓语动词一直是SAT/ACT语法,甚至是理解阅读文章中长难句的重点,也是困扰很多考生的难点之一。
下面是店铺收集整理的定语从句和非谓语动词的相关内容,希望对您有所帮助!定语从句和非谓语动词解析:熟悉非谓语动词的同学们应该都知道,非谓语动词包括to do, doing和done,这三类动词的特别之处就在于它们可以在句子里面充当除谓语以外的任何成分,其中一个非常重要的用法就是位于名词后作为名词的后置定语,比如:The semiarid lands bordering the deserts exist in a delicate ecological balance and are limited in their potential to adjust to increased environmental pressures.以上例句里的非谓语动词的短语“bordering the deserts”就是用作定语来修饰前面的名词短语“the semiarid lands”。
很多同学很熟悉定语从句,而对非谓语动词的'用法总是有种望而却步的感觉。
但是细心的同学肯定会发现,其实在语法家族里,当将非谓语动词用作后置定语的时候,它与定语从句的用法是一样的,两者是名副其实地长相不同,但却有血缘关系的“远房表亲”。
比如,上面的例子我们就可以改写成定语从句:The semiarid lands which border the deserts exist in a delicate ecological balance and are limited in their potential to adjust to increased environmental pressures.再如以下带有非谓语动词短语的句子:Theorist adopting the psychodynamic approach hold that inner conflicts are crucial for understand human behavior, including aggression.我们可以改成定语从句:Theorist who adopt the psychodynamic approach hold thatinner conflicts are crucial for understand human behavior, including aggression.又如,以下的两个句子的意思是相同的:1.What audience came to see was the magic made possible by trick photography and manipulation of the cinema.2.What audience came to see was the magic that was made possible by trick photography and manipulation of the cinema.在很多情况下,学生更容易理解定语从句。