完整版瞬间性动词与延续性动词新
- 格式:docx
- 大小:11.38 KB
- 文档页数:6


英语动词分类记忆I.主要常用不及物的动词。
不及物动词后面不能跟宾语。
只能用以:"主+谓"结构。
agree disagree quarrel shout cry laughwait remain sleep rest head exist live danceII. 延续动词与瞬间动词表示的动作在瞬间就可以完成, 瞬间动词的完成时态不能跟表示一段时间的时间状语连用。
1) 用于完成时的区别延续动词表示经验、经历;瞬间动词表示行为的结果,不能与表示段的时间状语连用。
He has completed the work.他已完成了那项工作。
(表结果)I've known him since then.我从那时起就认识他了。
(表经历)2)用于till / until从句的差异延续动词用于肯定句,表示"做……直到…" 瞬间动词用于否定句,表示"到…,才……"He didn't come back until ten o'clock.他到10 点才回来。
He slept until ten o'clock.他一直睡到10点。
典型例题1. You don't need to describe her. I ___ her several times.A. had metB. have metC. metD. meet答案B. 首先本题后句强调对现在的影响,我知道她的模样,你不用描述。
再次,several times 告知为反复发生的动作,因此用现在完成时。
2.---I'm sorry to keep you waiting.---Oh, not at all. I ___ here only a few minutes.A. have beenB. had beenC. wasD. will be答案A. 等待的动作由过去开始,持续到现在,应用现在完成时。
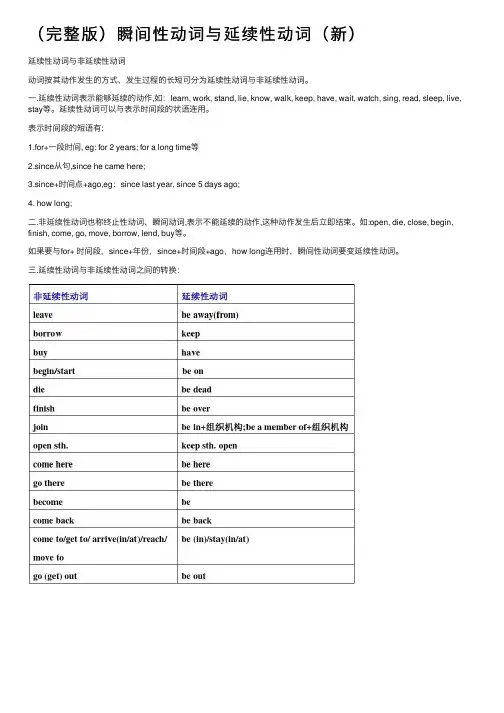
(完整版)瞬间性动词与延续性动词(新)延续性动词与⾮延续性动词动词按其动作发⽣的⽅式、发⽣过程的长短可分为延续性动词与⾮延续性动词。
⼀.延续性动词表⽰能够延续的动作,如:learn, work, stand, lie, know, walk, keep, have, wait, watch, sing, read, sleep, live, stay等。
延续性动词可以与表⽰时间段的状语连⽤。
表⽰时间段的短语有:1.for+⼀段时间, eg: for 2 years; for a long time等2.since从句,since he came here;3.since+时间点+ago,eg:since last year, since 5 days ago;4. how long;⼆.⾮延续性动词也称终⽌性动词、瞬间动词,表⽰不能延续的动作,这种动作发⽣后⽴即结束。
如:open, die, close, begin, finish, come, go, move, borrow, lend, buy等。
如果要与for+ 时间段,since+年份,since+时间段+ago,how long连⽤时,瞬间性动词要变延续性动词。
三.延续性动词与⾮延续性动词之间的转换:例:(1)他死了三年了。
误:He has died for three years.正:He has been dead for three years.正:He died three years ago.正:It is three years since he died.正:Three years has passed since he died.(2) 他来这⼉五天了。
误:He has come here for five days.正:He has been here for five days.正:He came here five days ago.正:It is five days since he came here.正:Five days has passed since he came here. (1)、(2)句中的die、come为终⽌性动词,不能与表⽰"段时间"的状语连⽤。

完成时态瞬间动词变延续性动词规则表延续性动词与终止性动词:动词按其动作发生的方式,动作发生过程的长短,分为延续性动词和终止性动词。
延续性动词表示的动词是一种延续的动作,这种动词可以延续下去或产生持久的影响。
如:learn,work,stand,lie,know,walk,keep,have,wait,watch,sing,read,sleep,live终止性动词也称非延续性动词、瞬间动词,表示的动作不能延续,即动作发生立即结束,产生某种结果。
在有了某种结果之后,就不能再继续下去。
如:leave,start,set out,arrive,reach,get to,begin,stop,shut,turn off,marry,put,put on,get up,wake,fall,join,receive,finish,end,complete,become,come,go,die,close,open,break,give,jump,buy,borrow等。
1.终止性动词的用法1)终止性动词可用来表示某一动作的完成,因此可用于现在完成时。
如:The plane has arrived飞机到了。
I have finished my homework.我已完成了作业。
2)终止性动词表示的动作极其短暂,不能持续,所以其现在完成时(只限于肯定式)不能和表示一段时间的状语连用。
如:①他死了三年了。
误:He has died for three years.②他来这儿三个月了。
误:he has come here for three months.①②两句中的动词die和come都为终止性动词,它们可用于完成时,但不能同表示一段时间的状语for three years /months连用。
那这两句如何译成英语呢?我们可采用下列方法:A.用能够表示持续状态的相应的延续性动词替换句中的终止性动词。
如:①He has been dead for three years.②He has been here for three months.将短暂性动词改为相应的延续性动词或短语和一段时间连用,其常用的方法有如下几种:a.用相应的延续性动词替换的主要有:buy→have,borrow→keep,come /go /become→be,catch /get a cold→have a cold,get to know→know等。

完成时态瞬间动词变延续性动词规则表延续性动词与终止性动词:动词按其动作发生的方式,动作发生过程的长短,分为延续性动词和终止性动词。
延续性动词表示的动词是一种延续的动作,这种动词可以延续下去或产生持久的影响。
如:learn,work,stand,lie,know,walk,keep,have,wait,watch,sing,read,sleep,live终止性动词也称非延续性动词、瞬间动词,表示的动作不能延续,即动作发生立即结束,产生某种结果。
在有了某种结果之后,就不能再继续下去。
如:leave,start,set out,arrive,reach,get to,begin,stop,shut,turn off,marry,put,put on,get up,wake,fall,join,receive,finish,end,complete,become,come,go,die,close,open,break,give,jump,buy,borrow等。
1.终止性动词的用法1)终止性动词可用来表示某一动作的完成,因此可用于现在完成时。
如:The plane has arrived飞机到了。
I have finished my homework.我已完成了作业。
2)终止性动词表示的动作极其短暂,不能持续,所以其现在完成时(只限于肯定式)不能和表示一段时间的状语连用。
如:①他死了三年了。
误:He has died for three years.②他来这儿三个月了。
误:he has come here for three months.①②两句中的动词die和come都为终止性动词,它们可用于完成时,但不能同表示一段时间的状语for three years /months连用。
那这两句如何译成英语呢?我们可采用下列方法:A.用能够表示持续状态的相应的延续性动词替换句中的终止性动词。
如:①He has been dead for three years.②He has been here for three months.将短暂性动词改为相应的延续性动词或短语和一段时间连用,其常用的方法有如下几种:a.用相应的延续性动词替换的主要有:buy→have,borrow→keep,come /go /become→be,catch /get a cold→have a cold,get to know→know等。


一.瞬间动词和延续性动词的含义及用法瞬间动词(非延续性动词或短暂性动词):是指动作在很短时间内完成, 无延续性。
如come go 等终止性动词和延续性动词:延续性动词: live ,run, stay, clean ,play ,hold ,watch ,teach, read ,study, teach ,eat ,drink ,write ,dance , sing ,smoke瞬间性动词:open, stop ,like ,love ,die ,win ,close ,shot ,begin ,start enter ,finish1.终止性动词:表示不能延续的动作,即动作发生后立即结束。
如:begin,arrive,borrow,buy,break,close,come,fall,dic,finish,go,leave,lend,mary,reach,receive,open,sell ,start,stop等。
终止性动词的肯定式是不能持续的,所以不能和表示一段时间的状语连用,终止性的否定式就可以和表一段时间的状语连用,因为否定本身就是可以延续的。
如:have a cold是持续性动词,表示“状态”,可与表延续性的时间状语连用,不定冠词不能省略。
I′ve had a cold since my arrival.I didn′t go to school because I had had a bad cold for days.catch / take ,get a cold是短暂性动作,表“动态”:它不能和延续性时间状语连用,不定冠词“a”可有可无,catch可用代替。
Put on your coat ,or you′ll catch / take / get a cold.Take care not to get cold.但是,若cold前有形容词修饰时,则不定冠词不能省。
如:Brown has taken a slight cold.注意下列句子:I have caught a cold for over a week.(×)I have had a cold for over a week.( )2. 延续性动词:表示可以延续一段时间的动作或状态。

短暂性动词和延续性动词可以从字面上理解,持续的动作就是延续动词,反之就是瞬间动词(短暂动词),这个有这种感觉还是很好理解的,你看看下面的浅谈吧延续性动词:live,run,stay,clean,play,hold,watch,teach,read,study,teach ,eat,drink,write,dance, sing,smoke瞬间性动词:open,stop,like,love,die,win,close,shot,begin,startenter,finish1、终止性动词:表示不能延续的动作,即动作发生后立即结束。
如:begin,arrive,borrow,buy,break,close,come,fall,dic,finish,go ,leave,lend,mary,reach,receive,open,sell,start,stop等。
终止性动词的肯定式是不能持续的,所以不能和表示一段时间的状语连用,而终止性的否定式就可以和表一段时间的状语连用,因为否定本身就是可以延续的。
如:have a cold是持续性动词,表示“状态”,可与表延续性的时间状语连用,不定冠词不能省略。
I′ve had a cold since my arrival(到达n.).I didn′t go to school because I had had a bad cold for days. catch a cold是短暂性动作,表“动态”:它不能和延续性时间状语连用,不定冠词“a”可有可无,catch可用take,get代替。
Put on your coat,or you′ll catch/take/get a cold.Take care not to get cold.但是,若cold前有形容词修饰时,则不定冠词不能省。
如:Brown has taken a slight cold.注意下列句子:I have caught a cold for over a week.(×)I have had a cold for over a week.( )2、延续性动词:表示可以延续一段时间的动作或状态。

常用瞬间动词变延续性动词表①have arrived at/in sp, got to/reached sp, come/gone/ moved to sp→have been in sp②have come/gone back, returned→have been back③have come/gone out→have been out④have become→have been⑤have closed/opened→have been closed/open⑥have got up→have been up⑦have died→_have been dead⑧have left sp→__have been away from sp⑨have fallen asleep/gone to sleep→have been asleep⑩have finished/ended/completed→_have been over⑪have married→have been married⑫have started/begun to do sth→have done sth⑬have begun→_have been on⑭have borrowed→_have kept⑮have bought→have had⑯have lost→haven’t had⑰have put on→have worn⑱have caught/got a cold→have had a cold⑲have got to know→have known⑳have gone to→have been inhave joined/taken part in the league/the Party/the army→have been a member of the league/the Party/the army, have been in the league/the Party/the army,have been the Party's member/the league member/the soldier。

现在完成时中瞬间动词变延续性动词总结现在完成时是英语语法中常见的一种时态,它表示动作或者状态在过去某个时间开始,持续到现在,或者已经完成的时间段内发生。
在现在完成时中,瞬间动词有时会变成延续性动词,这在英语语法中是一个比较有趣的现象。
下面来分析一下为什么会这样。
1. 什么是瞬间动词和延续性动词瞬间动词通常指的是那些比较短暂的、没有持续时间的动作,通常在句子中使用简单过去时态。
比如,"I saw a movie",这个动作只发生了一次,没有继续的过程。
而延续性动词常常表达的是可以持续一段时间的动作或状态,比如"teach",“run”,“live”等。
在句子中通常使用进行时态。
2. 瞬间动词变成延续性动词的情况在现在完成时中,瞬间动词有时会变成延续性动词。
这种情况通常出现在以下几种情况中:第一种情况,瞬间动词变成了有一个延续的结果的动词,比如"break","finish"和"lose"。
这些动词的结果可以一直持续到现在,因此它们在现在完成时中会变成延续性动词。
比如,"I have broken my arm",意思是我的手臂已经断了,这个状态可以持续到现在。
第二种情况,瞬间动词描述的动作发生了多次,这时候它会被视为是一个持续性的动作。
比如,"I have seen that movie three times",意思是我已经看过那部电影三次了,这个动作发生了多次,因此会被视为是延续性的动作。
第三种情况,瞬间动词变成了一个过程中的动作,这个动作可以持续一段时间。
比如,"I have been to Paris",这个动作是一个瞬间的动作,但是在这个语境中,它变成了一个动作过程中的一部分,这个过程可以持续一段时间。
3. 瞬间动词变成延续性动词的影响在英语语法中,瞬间动词变成延续性动词有时候会导致一些语法错误和表达上的混淆。

完成时态瞬间动词变延续性动词规则表延续性动词与终止性动词:动词按其动作发生的方式,动作发生过程的长短,分为延续性动词和终止性动词。
延续性动词表示的动词是一种延续的动作,这种动词可以延续下去或产生持久的影响。
如:learn,work,stand,lie,know,walk,keep,have,wait,watch,sing,read,sleep,live终止性动词也称非延续性动词、瞬间动词,表示的动作不能延续,即动作发生立即结束,产生某种结果。
在有了某种结果之后,就不能再继续下去。
如:leave,start,set out,arrive,reach,get to,begin, stop,shut,turn off,marry,put,put on,get up,wake,fall,join,receive,finish,end,complete,become,come,go,die,close,open,break,give, jump,buy,borrow等。
1.终止性动词的用法1)终止性动词可用来表示某一动作的完成,因此可用于现在完成时。
如: The plane has arrived飞机到了。
I have finished my homework.我已完成了作业。
2)终止性动词表示的动作极其短暂,不能持续,所以其现在完成时(只限于肯定式)不能和表示一段时间的状语连用。
如:①他死了三年了。
误:He has died for three years.②他来这儿三个月了。
误:he has come here for three months.①②两句中的动词die和come都为终止性动词,它们可用于完成时,但不能同表示一段时间的状语for three years /months连用。
那这两句如何译成英语呢?我们可采用下列方法:A.用能够表示持续状态的相应的延续性动词替换句中的终止性动词。
如:①He has been dead for three years.②He has been here for three months.将短暂性动词改为相应的延续性动词或短语和一段时间连用,其常用的方法有如下几种:a.用相应的延续性动词替换的主要有:buy→have,borrow→ keep,come /go /become→be,catch /get a cold→have a cold,get to know→know等。
一.瞬间动词和延续性动词的含义及用法瞬间动词(非延续性动词或短暂性动词):是指动作在很短时间内完成, 无延续性。
如come go 等终止性动词和延续性动词:延续性动词: live ,run, stay, clean ,play ,hold ,watch ,teach, read ,study,teach ,eat ,drink ,write ,dance , sing ,smoke瞬间性动词:open, stop ,like ,love ,die ,win ,close ,shot ,begin ,start enter ,finish1. 终止性动词:表示不能延续的动作,即动作发生后立即结束。
如:begin,arrive,borrow,buy ,break,close,come,fall,dic,finish,go,leave,lend,mary,reach,receiv e,open,sell ,start,stop 等。
终止性动词的肯定式是不能持续的,所以不能和表示一段时间的状语连用,终止性的否定式就可以和表一段时间的状语连用,因为否定本身就是可以延续的。
如:have a cold是持续性动词,表示“状态”,可与表延续性的时间状语连用,不定冠词不能省略。
I ′ve had a cold since my arrival.I didn′t go to school because I had had a bad cold for days.catch / take ,get a cold是短暂性动作,表“动态”:它不能和延续性时间状语连用,不定冠词“a ”可有可无,catch 可用代替。
Put on your coat ,or you′ll catch / take / get a cold.Take care not to get cold.但是,若cold 前有形容词修饰时,则不定冠词不能省。
最佳答案since+时间点for+时间段eg:He has kept the book for two weeks.He borrowed the book since two weeks ago.注意动词的时态,for后面是一段时间,动词用完成式,而since后面是一个时间点,动词用过去式。
两周前的一天,与for two weeks 的两个星期这样14天相比是一个点。
一、延续性动词延续性动词表示的动作不但可以延续,而且可以产生持久的影响。
常见的这类动词有:be,have,keep,know,learn,lie,live,read,sing,sleep,stand,stay,wait,walk,watch等。
延续性动词的用法很广,但常见于现在完成时中的句子中,且常与for,how,long,since等引导的表示一段时间的状语或状语从句连用。
例如:1.I have learned more than 1,000 Chinese words since I came to China.自从来到中国,我已经学会了l,000多个汉字。
2.We have lived in Linqing since we came here.自从来到这儿,我们就一直住在临清。
3.I have kept the picture for about three years.这张画我保存了大约三年。
二、终止性动词终止性动词又称为瞬间动词或非延续性动词,它表示的动作不能延续,也就是说动作一旦发生就立即结束,并产生某种结果。
常见的这类动词有:accept,arrive,become,begin,borrow,break,buy,catch,close,come,die,end,fall,finish,get,give,go,join,leave,put,reach,receive,shut,start,stop等。
终止性动词用在现在完成时要注意下面三点:(一)终止性动词可直接用来表示某一动作的完成。
延续性动词与瞬间动词的转换一、瞬间动词也叫短暂性动词或终止性动词。
这种动词是指它们动作的开始也就意味着动作的结束,所以不能直接跟表示一段的时间状语(比如for或since引导的表示一段时间的状语或用how long 来提问)连用。
那么,如何使瞬间动词与表示一段时间的状语连用呢?此时,我们可以将当短暂性动词与一段时间连用时,就要转化为延续性动词。
二、瞬间动词与延续性动词的区别:1、用于完成时的区别1)延续动词表示经验、经历;2)瞬间动词表示行为的结果,不能与表示一段的时间状语连用。
eg. 1.He has completed the work.他已完成了那项工作。
(表结果)2.I've known him since then.我从那时起就认识他了。
(表经历)2、用于till和until从句的差异1)延续动词用于肯定句,表示“做……,直到……”2)瞬间动词用于否定句,表示“到……,才……”eg. 1.He didn't come back until ten o'clock. 他到10点才回来。
2.He slept until ten o'clock.他一直睡到10点。
三、瞬间动词到延续性动词的转换:这里对一些词做一些总结:瞬间动词可转换的延续性动词(组)arrive be herebegin/start be ondie be deadfall ill/sick/asleep be ill/sick/asleepget up be upgo out be outfinish be overput on wear或be onopen be open(adj.)join be in或bea member of…close be closedgo to school be a studentborrow keepbuy havecatch(a cold) have(a cold)get to know knowbegin to study studycome to work workget up be upleave be away from如:1.He has been a soldier for three years. 他参军三年了。
延续性动词与非延续性动词
动词按其动作发生的方式、发生过程的长短可分为延续性动词与非延续性动词。
一.延续性动词表示能够延续的动作,如:learn, work, stand, lie, know, walk, keep, have, wait, watch, sin g, read, sleep, live, stay等。
延续性动词可以与表示时间段的状语连用。
表示时间段的短语有:
1. fo叶一段时间, eg: for 2 years; for a long time 等
2. since 从句,since he came here;
3. since+时间点+ago,eg: since last year, since 5 days ago;
4. how long;
二.非延续性动词也称终止性动词、瞬间动词,表示不能延续的动作,这种动作发生后立即结束。
如:open, die, close, begin, finish, come, go, move, borrow, lend, buy 等。
如果要与fo叶时间段,since+年份,since+时间段+ago,how long连用时,瞬间性动词要变延续性
动词。
三.延续性动词与非延续性动词之间的转换:
例:(1)他死了三年了。
误:He has died for three years.
正: He has been dead for three years.
正:He died three years ago.
正: It is three years since he died.
正:Three years has passed since he died.
(2)他来这儿五天了。
误:He has come here for five days.
正: He has been here for five days.
正: He came here five days ago.
正: It is five days since he came here.
正: Five days has passed since he came here. (1)、(2)句中的die、come为终止性动词,不能与表示" 段时间"的状语连用。
那么,应如何正确表达呢?可以采用下面的四种方法:
(1) 将句中终止性动词转换为相应的延续性动词,如上面两例中的第一种正确表达方式.
(2) 将句中表示"段时间"的状语改为表示过去确定时间的状语,如下面两例中的第二种正确表达方
式。
⑶用句型"It is+段时间+si nee..."表达原意,如上面两例中的第三种正确表达方式。
⑷用句型"时间+has passed+since.."表达原意,如上面两例中的第四种正确表达方式。
四、终止性动词可用于现在完成时否定式中,成为可以延续的状态,因而可与表示一段时间的状语
连用。
如:1.He has n't left here si nce 1986.
2」have n't heard from my father for two weeks.
五、终止性动词的否定式与until/till连用,构成"not+终止性动词+until/till ..."的句型,意为" 直
到……才……"。
如: 1. You can't leave here until I arrive. 直到我到了,你才能离开这里。
2. I will not go to bed until I finish drawing the picture tonight. 今天晚上直到我画完画,我才上床
睡觉。
六、终止性动词可以用于when 引导的时间状语从句中,但不可以用于while 引导的时间状语
从句中。
when 表示的时间是"点时间"(从句谓语动词用终止性动词),也可以是"段时间"(从句谓语动词用延续性动词)。
而while 表示的是一个较长的时间或过程,从句谓语动词用延续性动词。
如: 1. When we reached London, it was twelve o'clock. (reach 为终止性动词)
2. Please look after my daughter while/when we are away. (be away 为延续性动词短语)
七、终止性动词完成时不可与how long 连用(只限于肯定式)。
如: 误:How long have you come here?
正:How long have you been here? 正:When did you come here?
补充练习:
1. When he arrived at the bus stop, the bus ___ for 20 minutes.
A. has left
B. had left
C. has been away
D. had been away
2. I ___ the League for 5 years so far.
A. joined
B. have joined
C. have been in
3. The factory ___ s ince the February of 1988.
A . has been open B. has opened C. was open D. opened
4. Mary and Rose _____ friends since they met in 2000.
A. have made
B. have been
C. made
D. have become
5. You mustn't __ u ntil he comes back.
A. be away
B. leave
C. be left
6. The meeting _____ for a week now.
A. has finished
B. has ended
C. has been over
7. Miss Gao ____ this school for nearly 5 years.
A. has been in
B. has come to
C. has taught
8. Ben _____ a teacher for 4 years .
A. has been
B. has become
C. was
D. became
9. I ____ home for a week.
A. have returned
B. have been back
C. returned
10. How long _____ he _______ ?
A. died
B. has, died . has, been dead
11. ______ He at eight yesterday afternoon.
A. slept
B. was sleeping
C. has sleep
D. had slept
12. __________ He the car for a week.
A. bought
B. has bought
C. has had
13. How long ___ you _____ ill ? Two weeks.
A. did fall
B. have, fell
C. have, been
14.Since 2000, he ____ his hometown.
A. has left
B. has moved away
C. has been away from
15.I'll lend you the book , but you can only ___ it for 2 days.
A. borrow
B. keep
C. take
16. ____________ The bus on the road for 2 hours so far.
A. has stopped
B. stopped
C. has been
17. __________ Are you the jacket these days?
A. wearing
B. putting on
C. dressing
D. on
18. He ______ foe 2 hours.
A. got up
B. has got up
C. has been up
19. Tom is ill in hospital. He _____ a cold for several days.
A. is
B. catches
C. has caught
D. has had
20. How long can I _______ the book? ------------ Two weeks.
A. borrow
B. lend
C. get
D. keep
1---5 D C A B B; 6---10 C A A B C; 11---15 B C C C B; 16---20 C A C D D。