Altera FPGA的特殊管脚的连接(中文)
- 格式:doc
- 大小:92.00 KB
- 文档页数:4

常见问题汇总1. alt2gxb模块的每个发送端都需要一个高速的pll_inclk时钟(至少100M以上),请问这个时钟一定要从FPGA外面引进来吗?通常情况下一定要从FPGA外面引进来,首选是GXB模块的专用时钟引脚,或上下BANK 的专用时钟输入脚。
时钟是至少60M以上。
2. 如果我一个FPGA里面有多个alt2gxb模块,是否能共用一个这样的输入时钟?可以。
3. gxb模块里面的Calibration clk 是干嘛用的,能不能不用它?校准内部匹配电阻用。
此时钟可以内部提供,频率在10M到125M都可以,如果外部时钟不合适的话,甚至可以用逻辑来分频(比如参考钟是156M,内部触发器作个2分频就可以用了。
4. 用到gxb模块的bank的参考电压是否必须接1.5V?因为我看到资料上有3.3V的CML和LVDS电平(附件里面的截图)gxb用1.5V 或 1.2V, 推荐客户用1.5V. 3.3v是用在别的普通bank的。
5. gxb模块的输入端如果平时不需要传数据,是否置0?还是需要我们在数据线上发送别的数据,是否gxb模块能自动发送同步码?平时可以置0,但在上电后,你必须首先发送对端接收侧的word aligner码型(通常用k28.5), 这是需要手工控制的。
6. LVDS模块没有同步码,做接收时好像没办法数据对其,比如8比特数据容易错开2、3位,我们现在是另外加逻辑把它调整过来的,请问有别的好的同步的方法吗通常需要逻辑去进行word aligner操作,如同GXB一样。
某些特定情况下可以预先知道边界。
这个问题讨论过好多次了,所谓的特定情况你可以看STRATIX II手册(不是Stratix II GX 手册),搜索“Differential I/O Bit Position”7.请问在alt2gxb模块,有两个时钟:pll_inclk和cali_clk,手册上说cali_clk要求不是很高,可以用计数器产生,那么输入的并行数据txdata_in应该用哪个时钟锁存呢?cali_clk仅用于校准内部匹配电阻用的状态机,跟业务是完全独立的。


(50条消息)Altera特殊管脚的使用(适用全系列AlteraFPGA,MSEL区别除外)1.I/O, ASDO在AS 模式下是专用输出脚,在PS 和JTAG 模式下可以当I/O 脚来用。
在AS 模式下,这个脚是CII 向串行配置芯片发送控制信号的脚。
也是用来从配置芯片中读配置数据的脚。
在AS 模式下,ASDO 有一个内部的上拉电阻,一直有效,配置完成后,该脚就变成三态输入脚。
ASDO 脚直接接到配置芯片的ASDI 脚(第5 脚)。
2.I/O,nCSO在AS 模式下是专用输出脚,在PS 和JTAG 模式下可以当I/O 脚来用.在AS 模式下,这个脚是CII 用来给外面的串行配置芯片发送的使能脚。
在AS 模式下,ASDO 有一个内部的上拉电阻,一直有效。
这个脚是低电平有效的。
直接接到配置芯片的/CS 脚(第1 脚)。
3.I/O,CRC_ERROR当错误检测CRC 电路被选用时,这个脚就被作为CRC_ERROR 脚,如果不用默认就用来做I/O。
但要注意,这个脚是不支持漏极开路和反向的。
当它作为CRC_ERROR 时,高电平输出则表示出现了CRC 校验错误(在配置SRAM 各个比特时出现了错误)。
CRC 电路的支持可以在setting 中加上。
这个脚一般与nCONFIG 脚配合起来用。
即如果配置过程出错,重新配置.4.I/O,CLKUSR当在软件中打开Enable User-supplled start-up clock(CLKUSR)选项后,这个脚就只可以作为用户提供的初始化时钟输入脚。
在所有配置数据都已经被接收后,CONF_DONE 脚会变成高电平,CII 器件还需要299 个时钟周期来初始化寄存器,I/O 等等状态,FPGA 有两种方式,一种是用内部的晶振(10MHz),另一种就是从CLKUSR 接进来的时钟(最大不能超过100MHz)。
有这个功能,可以延缓FPGA 开始工作的时间,可以在需要和其它器件进行同步的特殊应用中用到。

fpga配特殊引脚的含义(FPGA with the meaning of a special pin)FPGA with the meaning of a special pin1.I/O, ASDOIn AS mode, it is dedicated output pin, and can be used as I/O pin in PS and JTAG mode. In AS mode, this pin is the CII pin that sends the control signal to the serial configuration chip. Also used to read configuration data from the configuration chip. In AS mode, the ASDO has an internal pullup resistor, which has been in effect until the configuration is completed, and the pin becomes a three state input pin. The ASDO pin is connected directly to the ASDI pin (fifth feet) of the configuration chip.2.I/O, nCSOIn AS mode, it is a dedicated output pin that can be used as the I/O pin in PS and JTAG mode. In AS mode, this pin is used by the CII to send the enable pins to the outside serial configuration chip. In AS mode, the ASDO has an internal pullup resistor that has been in effect. This pin is active low. The /CS pin (first feet) is directly connected to the configuration chip.3.I/O, CRC_ERRORWhen the error detection CRC circuit is selected, this foot is used as the CRC_ERROR pin, and if not used by default, it is used as I/O. Note, however, that this pin does not support open drain and reverse. When it is used as CRC_ERROR, the high leveloutput indicates a CRC checksum error (when an individual bit of the SRAM is configured). CRC circuit support can be added to the setting. This foot is usually used with the nCONFIG foot. That is, if the configuration process is wrong, reconfigure it4.I/O, CLKUSRWhen the Enable User-supplled start-up clock (CLKUSR) option is opened in the software, this pin can only be used as an initialization clock input for the user. In all configuration data have been received, CONF_DONE pin will become a high level, the CII device 299 clock cycles are needed to initialize the I/O register, FPGA and so on, there are two ways, one is using the internal oscillator (10MHz), another is from CLKUSR in the clock (maximum not more than 100MHz). This feature can delay the time FPGA starts working and can be used in special applications that require synchronization with other devices.5.I/O, VREFUsed to provide a reference level for certain differential standards. If not used, you can use it as a I/O.6. DATA0Dedicated input pin. In AS mode, the configuration process is: CII sets the nCSO low, and the configured chip is enabled. CII then cooperates with DCLK and ASDO to send commands and read addresses to the configuration chip. Configure the chip and then send the data to the CII via the DATA pin. The DATA foot is attached to the CII's DATA0 foot. After all configurationdata is received by the CII, the CONF_DONE pin is released (that is, the CONF_DONE pin is not forced low) and the CONF_DONE pin is open drain (Open-Drain). At this point, the 10K will turn on a high level because the CONF_DONE will pick up a resistor on the outside. At the same time, the CII stops the DCLK signal. After the CONF_DONE becomes high (when it becomes equivalent to an input pin), the initialization process begins. So, CONF_DONE must have a 10K resistor on the outside of the foot to ensure that the initialization process starts correctly. DATA0, DCLK, NCSO, and ASDO have weak pullup resistors on their feet, and they are always valid. Upon completion of the configuration, these pins are turned into an input three state, and the level is set to a high level by an internal pullup resistor. In AS mode, the DATA0 receives the DATA (second pin) of the configuration chip.7. DCLKPS mode is input, AS mode is output. In PS mode, the DCLK is a clock input pin that is the clock that the external device sends the configuration data to the FPGA. Data is placed on the rising edge of the DCLK to data in AS mode, and the DCLK pin is a clock output pin that is configured to provide a clock. Connect directly to the DCLK pin of the configuration chip (sixth feet). No matter what configuration mode, after the configuration is completed, this foot will become three states. If an external configuration device is attached, the configuration device will set the DCLK pin to low level. If you are using the master chip, you can either set the DCLK high or you can lower the DCLK. When the configuration is complete, triggering this pin does not affect the configured FPGA. Thispin has an input Buffer that supports the hysteresis function of the Schmidt flip-flop.8. nCEDedicated input pin. This pin is an active low chip enable signal. The nCE pin is configured to enable the foot. In configuration, initialization, and user mode, the nCE pin must be set low. In the configuration of multiple devices, the nCE pin of the first device is set low, and its nCEO is connected to the nCE pin of the next device, forming a chain. The nCE pin also requires a low nCE foot in the JTAG programming mode.This pin has an input Buffer that supports the hysteresis function of the Schmidt flip-flop.9. nCONFIGDedicated input pins. This pin is a configuration control input pin. If this foot is low in user mode, the FPGA loses its configuration data and goes into a reset state and sets all the I/O feet into three states. The process of changing nCONFIG from low level to high level will initialize the reconfiguration process. If the configuration scheme uses an enhanced configuration device or EPC2, the user can connect the nCONFIG pin directly to the VCC or to the nINIT_CONF pin of the configuration chip. This pin has an input Buffer that supports the hysteresis function of the Schmidt flip-flop. In fact, in user mode, the nCONFIG signal is used to initialize the reconfiguration. When the nCONFIG foot is low, the initialization process begins. When the nCONFIG pin is low, theCII is reset and goes into the reset state. The nSTATUS and CONF_DONE pins are set low and all the I/O pins are in the three state. The nCONFIG signal must remain at least 2us. When nCONFIG returns to the high level state, the nSTATUS is released again. The reconfiguration starts. In actual application, the nCONFIG pin can be connected with a pull-up resistor of 10K to 3.3V.10. DEV_OEI/O pin or global I/O enable pin. In the Quartus II software can enable the DEV_OE option (Enable Device-wideoutput Enable), if can make this a function, this pin can be enabled when the global I/O feet, this foot function is, if it is set low, all I/O into three states.11. INIT_DONEI/O pin or drain open output pin. When this foot is enabled, the foot jumps from low to high, indicating that the FPGA has entered the user mode. If the INIT_DONE output pin is enabled, this pin cannot be used as user I/O after configuration is complete. Inside the QuartusII, this pin can be enabled by enabling the Enable INIT_DONE output option.12. nCEOI/O pin or output pin. When the configuration is complete, this pin outputs low level. In the configuration of multiple devices, this pin will connect to the next device's nCE pin. This time, it also needs a 10K pull-up resistor outside to Vccio. The configuration process of multiple devices, finally a nCEOdevice can float. If you want to use this pin as an available I/O, you need to set it up inside the software. In addition, even if the I/O, but also after the completion of the configuration.13. nSTATUSThis is a dedicated configuration status pin. Two way foot, when it is the output pin, is open drain. After power on, the FPGA immediately sets the nSTATUS foot low and releases it after power on reset (POR) and sets it high. As a status output pin, if any error occurs during configuration, the nSTATUS pin is lowered. As the status input pin, during the configuration or initialization, the external control chip can pull this pin down, and FPGA will enter the wrong state at this time. This foot can not be used as an ordinary I/O foot. The nSTATUS pin must be pulled up by a 10K ohm resistor.14. CONF_DONEThis is a dedicated configuration status pin. Two way foot, when it is the output pin, is open drain. When it is used as a status output pin, it is set low before and during configuration. Once the configuration data is received and no errors are made, the CONF_DONE will be released at the start of the initialization cycle. When used as a status input pin, after all data has been received, it should be set to a high level. After that, the device starts initialization and goes into user mode. It should not be used as a regular I/O. The outside of the foot must also be connected with a 10K ohm resistor.15. MSEL[1:0]These pins should be connected to zero or power, indicating high or low level. 00 with AS mode, 10 PS mode, AS mode is 01 FAST. If in JTAG mode, it with their 00 JTAG mode and the MSEL has nothing to do with JTAG mode, MSEL will be ignored, but because they can not float, so suggest that it be received.16 DEV_CLRnI/O or global clear input. In QuartusII, if you choose the Enable Device-Wide Reset (DEV_CLRn) this function. This pin is the global reset. When this pin is low, all registers are cleared. This pin does not affect the JTAG's boundary scan or programming operations.Application of FPGA configuration pinFor FPGA applications, you need to know the following points.The nCONFIG, nSTATUS, and CONF_DONE require the pull-up resistor of the 10K, and the nCE requires a 10K pull-down resistor;NCONFIG for configuration control, the dedicated input pin sets the low FPGA to lose data;The nSTATUS is a dedicated bidirectional pin for the FPGA. 0 indicates that the FPGA is in a busy state and is released at 1 after the pull-up, and the FPGA begins to be in configuration.CONF_DONE dedicated configuration, two-way feet, FPGA configuration is 0, after the configuration is released, the role of the external pull-up is 1. NCE configuration enables dedicated input pins. In configuration, initialization, and user mode, the nCE pin must be set low.MSEL configure pin for mode;TDI, TMS, 10K pull-up resistor, TCK, 10K pull-down resistor, for JTAG;ASDO, nCSO, DCLK and DATA0 are used for the communication between FPGA and configuration chip, and there is no pullup on the inside, and no external resistance is needed.The clock pin can only be input and cannot be output.6 、 pull / pull resistance:1) ensure that the initial values of the circuit. For example, TCK signal using a pull-down resistor. Why the pull-down resistor instead of the pull-up resistor? Because pull-down resistor makes the initial value of the TCK signal is 0, because it is a clock signal, can guarantee the clock signal in the initial value after the first rise along the edge, and the JTAG control of resistance it is on the rising edge of TCK to write configuration data within the FPGA.2) here / pull-down resistor only belongs to the recommended value, determine the value is not, the purpose is to ensure the quality of the signal. The resistance as an example, if thepull-up resistor is above 10K, the pin has an equivalent capacitance to ground, because T=RC, C by the device process, the greater the resistance, charge and discharge the longer the time, the rising edge of the slower signal, the slope is small. The rise time if more than JTAG control circuit requirements to write data within the FPGA may be wrong. So, if the pull-up resistor smaller? Will rise time smaller? Yes. Resistance decreases, rise time small, the slope becomes larger, but also brought a serious problem, if the resistance is small to a certain extent, the signal will be at the rising edge of the emergence of the red signal ringing phenomenon, will seriously. If the resistance is too small, the intrusion tolerance over current devices IO, JTAG control circuit Will burn out. So, what is the resistance to meet the general requirements of PCB using 4.7K. in general?3) to ensure the driving ability of signal. As mentioned earlier, the resistance is small, the signal slope is small, and the driving force of signals is stronger. The more resistance signal slope is bigger, and the driving force of signals is weak. This point in the JTAG daisy chain circuit and its important。

fpga与gpio连接的原理FPGA与GPIO连接的原理引言:FPGA(Field Programmable Gate Array)是一种可编程逻辑器件,它具有高度的灵活性和可重构性,可以实现各种不同的数字电路功能。
而GPIO(General Purpose Input/Output)则是一种通用输入输出接口,可以与外部设备进行数据交互。
本文将探讨FPGA与GPIO之间的连接原理。
一、FPGA的基本结构和工作原理FPGA由可编程逻辑单元(PL)和配置逻辑单元(CLB)组成。
PL负责实现特定的逻辑功能,而CLB则用于存储和配置逻辑单元的信息。
FPGA的工作原理是通过对配置逻辑单元进行重新编程,实现不同的电路功能。
FPGA芯片上有一组可编程管脚,可以与外部设备进行连接。
二、GPIO的基本概念和作用GPIO是一种通用的输入输出接口,可以用于与外部设备进行数据交互。
它可以通过编程的方式控制输入输出的电平状态,实现与外部设备的通信。
GPIO通常包含一组输入引脚和一组输出引脚,可以根据需要进行配置和使用。
三、FPGA与GPIO的连接方式FPGA与GPIO的连接方式有多种,下面将介绍两种常见的连接方式。
1. 直接连接方式最简单的方式是直接将FPGA的管脚与GPIO的引脚进行连接。
在使用之前,需要对FPGA的管脚进行配置,使其与GPIO的引脚相对应。
这种连接方式简单直接,适用于只需要少量IO口的应用场景。
2. 通过扩展芯片连接方式当需要连接大量的GPIO引脚时,可以使用扩展芯片来实现。
扩展芯片可以扩展FPGA的IO口数量,通过串行或并行的方式与FPGA进行连接。
对于大规模的应用,这种连接方式更加灵活可扩展。
四、FPGA与GPIO连接的步骤下面将介绍FPGA与GPIO连接的基本步骤。
1. 确定连接引脚需要确定FPGA上与GPIO连接的管脚和GPIO上的引脚。
这需要根据具体的FPGA和GPIO的规格书来确定。
2. 配置FPGA管脚根据连接引脚的确定,需要对FPGA上的管脚进行配置。

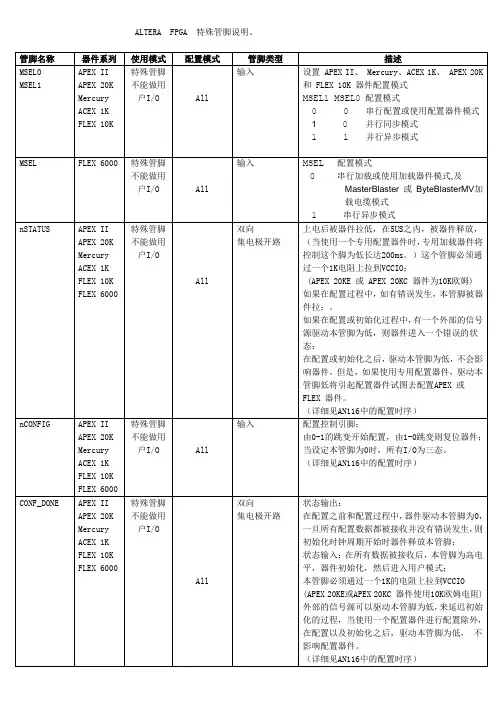
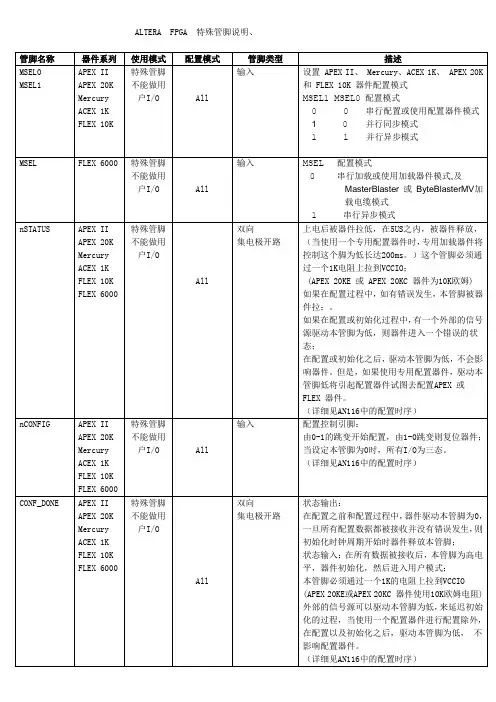
FPGA器件管脚说明用户I/O:不用解释了。
配置管脚:MSEL[1:0] 用于选择配置模式,比如AS、PS等。
DA TA0 FPGA串行数据输入,连接到配置器件的串行数据输出管脚。
DCLK FPGA串行时钟输出,为配置器件提供串行时钟。
nCSO(I/O)FPGA片选信号输出,连接到配置器件的nCS管脚。
ASDO(I/O)FPGA串行数据输出,连接到配置器件的ASDI管脚。
nCEO 下载链期间使能输出。
在一条下载链中,当第一个器件配置完成后,此信号将使能下一个器件开始进行配置。
下载链上最后一个器件的nCEO悬空。
nCE 下载链器件使能输入,连接到上一个器件的nCEO,下载链的最后一个器件nCE接地。
nCNFIG 用户模式配置起始信号。
nSTATUS 配置状态信号。
CONF_DONE 配置结束信号。
电源管脚:VCCINT 内核电压。
130nm为1.5V,90nm为1.2V。
VCCIO 端口电压。
一般为3.3V,还可以支持多种电压,5V、1.8V、1.5V。
VREF 参考电压。
GND 信号地。
时钟管脚:VCC_PLL PLL管脚电压,直接连VCCIO。
VCCA_PLL PLL模拟电压,截止通过滤波器接到VCCINT上。
GNDA_PLL PLL模拟地。
GNDD_PLL PLL数字地。
CLK[n] PLL时钟输入。
PLL[n]_OUT PLL时钟输出。
特殊管脚:VCCPD 用于寻则驱动。
VCCSEL 用于控制配置管脚和PLL相关的输入缓冲电压。
PROSEL 上电复位选项。
NIOPULLUP 用于控制配置时所使用的用户I/O的内部上拉电阻是否工作。
TEMPDIODEN 用于关联温度敏感二极管。
************************************************************************************1/1、I/O, ASDO在AS模式下是专用输出脚,在PS和JTAG模式下可以当I/O脚来用。

XilinxFPGA引脚功能详细介绍注:技术交流用,希望对大家有所帮助。
IO_LXXY_# 用户IO引脚XX代表某个Bank内唯一的一对引脚,Y=[P|N]代表对上升沿还是下降沿敏感,#代表bank号2.IO_LXXY_ZZZ_# 多功能引脚ZZZ代表在用户IO的基本上添加一个或多个以下功能。
Dn:I/O(在readback期间),在selectMAP或者BPI模式下,D[15:0]配置为数据口。
在从SelectMAP读反馈期间,如果RDWR_B=1,则这些引脚变成输出口。
配置完成后,这些引脚又作为普通用户引脚。
D0_DIN_MISO_MISO1:I,在并口模式(SelectMAP/BPI)下,D0是数据的最低位,在Bit-serial模式下,DIN是信号数据的输入;在SPI模式下,MISO是主输入或者从输出;在SPI*2或者SPI*4模式下,MISO1是SPI总线的第二位。
D1_MISO2,D2_MISO3:I,在并口模式下,D1和D2是数据总线的低位;在SPI*4模式下,MISO2和MISO3是SPI总线的MSBs。
An:O,A[25:0]为BPI模式的地址位。
配置完成后,变为用户I/O 口。
AWAKE:O,电源保存挂起模式的状态输出引脚。
SUSPEND是一个专用引脚,AWAKE是一个多功能引脚。
除非SUSPEND模式被使能,AWAKE 被用作用户I/O。
MOSI_CSI_B_MISO0:I/O,在SPI模式下,主输出或者从输入;在SelectMAP模式下,CSI_B是一个低电平有效的片选信号;在SPI*2或者SPI*4的模式下,MISO0是SPI总线的第一位数据。
FCS_B:O,BPI flash 的片选信号。
FOE_B:O,BPI flash的输出使能信号FWE_B:O,BPI flash 的写使用信号LDC:O,BPI模式配置期间为低电平HDC:O,BPI模式配置期间为高电平CSO_B:O,在并口模式下,工具链片选信号。

Altera 公司 2011年6月Subscribe© 2011 Altera Corporation. All rights reserved. ALTERA, ARRIA, CYCLONE, HARDCOPY, MAX, MEGACORE, NIOS, QUARTUS and STRATIX are Reg. U.S. Pat. & Tm. Off. and/or trademarks of Altera Corporation in the U.S. and other countries. All other trademarks and service marks are the property of their respective holders as described at /common/legal.html . Altera warrants performance of its semiconductor products to current specifications in accordance with Altera’s standard warranty, but reserves the right to make changes to any products and services at any time without notice. Altera assumes no responsibility or liability arising out of the application or use of any information, product, or service described herein except as expressly agreed to in writing by Altera. Altera customers are advised to obtain the latest version of device specifications before relying on any published information and before placing orders for products or services.101 Innovation DriveSan Jose, CA 使用Altera FPGA 中的设计安全特性本应用笔记介绍了如何使用 Altera ® 40-和28-nm FPGA 中的设计安全特性来保护您的设计免受非法复制、逆向工程以及配置文件的篡改。

1.下载口。
JTAG下载接口,对应下载的文件是SOF文件,速度快,JTAG 将程序直接下载到FPGA中,但是掉电程序丢失,平时学习推荐使用JTAG方式,最后固化程序的时候再通过AS方式将程序下载到配置芯片中即可;AS下载接口,对应下载的是POF文件,速度相对较慢,需要重新上电并且拔掉下载线,才能工作,操作相对麻烦,不推荐学习的时候使用。
2.FPGA引脚作用:(1)VCCINT:这些都是内部逻辑阵列电源电压引脚。
VCCINT还可以给输入缓冲区供电,用于LVPECL,LVDS(常规I / O和CLK引脚),差分HSTL,差分SSTL I/ O标准。
Connect all VCCINT pins to 1.2 V. Decoupling depends on the design decoupling requirementsof the specific board.所有VCCINT引脚连接至1.2 V,去耦依赖于设计脱钩的要求的具体电路板。
(2)VCCIO[1…8]: 这些I / O电源电压引脚银行1至8。
每个组可以支持不同的电压水平。
VCCIO供电到输出缓冲区,所有的I / O标准。
VCCIO供电输入缓冲区用于LVTTL,LVCMOS,1.5-V,1.8 V,2.5 V,3.3 V PCI,和3.3-V PCI-X,差分SSTL。
差分HSTL。
和LVDS lrecular我/ OL I / O标准。
验证VCCIO电压等级连接是与QuartusII软件的引脚连接一致。
去耦取决于设计去耦的具体要求的具体电路板。
(3)VREFB[1..8]N[0..3]: 为每个I / O组的输入参考电压。
这些引脚被用来作电压参考引脚。
如果没有被用,就作为普通的I/O引脚。
(4)VCCA PLL[1..4]: 模拟电源锁相环[1 ..4].将这些引脚连接到1.2 V,即使不使用PLL。
更好的,使用一个孤立的线性电源钳工性能。
一、被动串行(PS)在做PS配置时,FPGA配置数据从储存器中读出,写入到FPGA的DATA0接口上。
这些存储器是FLASH器件。
数据由DCLK时钟信号管脚的上升沿打入FPGA,每个DCLK时钟周期输入1比特数据。
·DCLK(配置时钟);·DATA0(配置数据);·nCONFIG(配置命令);·nSTATUS(状态信号);·CONF_DONE(配置完成指示)。
在PS方式下,FPGA处于完全被动地位。
FPGA接收配置时钟、配置命令和配置数据,给出配置的状态信号以及配置完成指示信号等。
在配置FPGA时,首先需要将nCONFIG拉低(至少40us),然后拉高。
当nCONFIG 被拉高后,FPGA的nSTATUS也将变高,表示这时已经开始配置,外部电路旧可以用DCLK的时钟上升沿一位一位地将配置数据写入到FPGA中。
当最后一个比特数据写入以后,CONF_DONE管脚被FPGA释放,被外部的上拉电阻拉高,FPGA随即进入初始化状态。
在完成初始化过程后,FPGA正式进入用户模式。
【注】:有的配置芯片没有nINIT_CONF管脚,只需将FPGA的nCONFIG信号弱上拉到Vcc即可。
在上电后,FPGA会在nCONFIG管脚上检测到一个从低到高的跳变沿,因此可以自动启动配置过程。
有三种配置FPGA的方法:1、使用Altera的配置芯片与FPGA相连;2、使用下载电缆通过FPGA的PS口配置;3、使用微处理器配置FPGA。
下图是使用微处理器配置FPGA的示意图:PS:用微处理器配置FPGA【注】:如果外部器件将.rbf文件配置到FPGA中,必须确保配置文件中的最低位先入。
如果比特顺序错误,将导致配置失败。
C代码实现:。
ALTERA的FPGA命名规则DIP中⽂解释:双列直插式封装。
插装型封装之⼀,引脚从封装两侧引出,封装材料有塑料和陶瓷两种。
DIP是最普及的插装型封装,应⽤范围包括标准逻辑IC,存贮器LSI,微机电路等。
PLCC中⽂解释:外形呈正⽅形,32脚封装,四周都有管脚,外形尺⼨⽐DIP封装⼩得多。
PLCC封装适合⽤SMT表⾯安装技术在PCB上安装布线,具有外形尺⼨⼩、可靠性⾼的优点。
PQFP中⽂解释:芯⽚引脚之间距离很⼩,管脚很细,⼀般⼤规模或超⼤规模集成电路采⽤这种封装形式,其引脚数⼀般都在100以上。
SOP中⽂解释:⼩外形封装(SOP)。
以后逐渐派⽣出SOJ(J型引脚⼩外形封装)、TSOP(薄⼩外形封装)、VSOP(甚⼩外形封装)、SSOP(缩⼩型SOP)、TSSOP(薄的缩⼩型SOP)及SOT(⼩外形晶体管)、SOIC(⼩外形集成电路)等。
ALTERA器件命名规则XXX XXX X X XX X1 2 3 4 5 61.前缀: EP典型器件EPC 组成的EPROM器件EPF FLEX 10K或FLFX 6000系列、FLFX 8000系列EPM MAX5000系列、MAX7000系列、MAX9000系列EPX 快闪逻辑器件2.器件型号3.封装形式:D 陶瓷双列直插 Q 塑料四⾯引线扁平封装P 塑料双列直插 R 功率四⾯引线扁平封装S 塑料微型封装 T 薄型J形引线芯⽚载体J 陶瓷J形引线芯⽚载体 W 陶瓷四⾯引线扁平封装L 塑料J形引线芯⽚载体 B 球阵列4.温度范围: C ℃⾄70℃,I -40℃⾄85℃,M -55℃⾄125℃ 5.腿数6.速度以EP2C35F672C6N为例做⼀个说明:EP2C:器件系列ALTERA35:逻辑单元数,35表⽰约有35k的逻辑单元;F:表⽰PCB封装类型,F是FBGA封装,E(EQFP)、Q(PQFP)、U(UBGA)、M(MBGA);Package Type:E: Plastic Enhanced Quad Flat Pack (EQFP)Q: Plastic Quad Flat Pack (PQFP)F: FineLine Ball-Grid Array (FBGA)U: Ultra FineLine Ball-Grid Array (UBGA)M: Micro FineLine Ball-Grid Array (MBGA)672:表⽰引脚数量,C:⼯作温度,C表⽰可以⼯作在0°C到85°C,I表⽰可以⼯作在-40°到100°C,A表⽰可以⼯作在-40°C到125°C;Operating Temperature:C: Commercial temperature (TJ = 0°C to 85°C)I: Industrial temperature (TJ = -40°C to 100°C)A: Automotive temperature (TJ = -40°C to 125°C)6:速度等级,6约最⼤是500Mhz,7约最⼤是43Mhz,8约最⼤是400Mhz;N:后缀,N表⽰⽆铅,ES⼯程样⽚。
ALTERA FPGA 配置接口标准JTAG接口:标准AS接口:标准PS接口:USB Blaster 功能概述∙支持ALTERA 公司全系列FPGA/CPLD器件∙支持ALTERA公司全系列主动串行配置器件∙支持ALTERA公司全系列增强配置器件∙支持AS﹑PS﹑JTAG三种下载模式∙高速、稳定,内部采用FT245R+CPLD设计∙支持1.2-5V编程电压∙支持SignalTap II 嵌入式逻辑分析仪∙支持Nios II嵌入式处理器的通信和调试支持的软件∙Quartus II集成开发环境∙NIOS II IDE 集成开发环境∙NIOS II EDS集成开发环境支持的器件∙CPLD:MAX3000、MAX7000A/B/S、MAX9000 和MAX II 等∙FPGA:Stratix、Stratix II、Cyclone、Cyclone II、CycloneIII、ACEX 1K、APEX 20K 和FLEX 10K 等∙主动串行配置器件:EPCS1、EPCS4、EPCS16等∙增强配置器件:EPC1、EPC4 等产品特性∙采用高速下载方案:FT245+CPLD+244,下载速度接近原厂ALTERA USB BLASTER 相比其它下载方案,如68013或C8051F等方案,速度快1-3倍与PC机的连接∙通过USB 2.0接口与计算机连接与目标板的连接∙通过JTAG、AS、PS接口与目标板连接硬件开发环境通过USB Blaster连接“FPGA/CPLD目标板”和“PC”,建立完整的硬件开发环境,对目标芯片进行编程、调试连接目标板USB Blaster可以通过三种接口连接至目标板JTAG、AS、PS接口是如何定义的?(点击查看)请注意,VCC和GND切勿接反,以免烧坏USB BlasterUSB Blaster状态灯说明∙红灯:电源灯∙绿灯:信号指示灯,进行软件下载时,绿灯亮配置清单1. USB Blaster编程器× 12. USB数据线× 13. 10-pin线× 14. 资料光盘× 1。