最新化学专业英语(修订版)翻译
- 格式:doc
- 大小:182.50 KB
- 文档页数:53


化学专业英语马永祥,兰州大学出版社课文翻译14. 含氧化合物醇和酚在醇的取代物和连结体的命名中,羟基作为主要基团,是通过后缀“醇”来表示,省略母体化合物名称末尾“e”(如果有的话),例如:甲醇,2-丙醇,三苯甲醇等。
下面是一些被保留的俗名的例子:烯丙醇,叔丁醇,苄醇,乙二醇,芳香醇等。
苯和其它芳香碳环族的羟基衍生物是通过在碳氢化合物名称加后缀“醇”“二醇”等命名的,“ol”前末端的“e”要省略,例如:1,2,4-苯三醇。
以下是一些芳香族羟基化合物仍被保留的俗名。
例如:苯酚,甲酚,荼酚,邻苯二酚,间苯二酚,对苯二酚等等。
基团RO-是通过在R基名称后加后缀“氧基”而命名,例如:戊氧基,烯丙氧基,苄氧基等,仅有下列含氧基团名称的缩写是不符合这一被推荐规则的:甲氧基,乙氧基,丙氧基,丁氧基,苯氧基,异丙氧基。
除去部分成环体系,二价基团-o-x-o-通过给双二价基团-x-名称附加“二氧基”而命名,例如:乙撑二氧基,丙撑二氧基。
盐醇或酚衍生的阴离子的命名是将醇或酚名称末尾的“-ol”变成“-olate”。
这一方法适用于取代基,官能团和俗名。
例如:甲醇钾,苯酚钠。
醚化合物R1-O-R2总称为“醚”,可以通过取代基或官能团来命名。
不对称醚取代物命名法是将基团R1O-的名称作为前缀加在相应第二个基团R2前面而形成。
较高级的组分被选作母体化合物。
醚的官能团命名法则是在基团R1和R2名称后面加“醚”字即可。
例如:1-异丙氧基丙烷,甲乙醚,二乙醚,乙基乙烯基醚。
醛醛是含有连结在C原子上的(C=O)H基团的化合物,命名是通过后缀“-al”“-aldehyde”或“carbaldehyde”或者是通过加前缀“formyl-”(当作为一个碳链的末端基团存在时代表-(C=O)H),或者与俗名有关,加前缀“oxo”(代表=0),无支链的非环的单醛或二醛的名字是通过给含有相同碳原子数的烃化合物的名字加后缀“-al”(对单醛)或“dial”(对双醛)形成。

01 THE ELEMENTS AND THE PERIODIC TABLE01 元素和元素周期表The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is referred to as the atomic number, or proton number, Z. The number of electrons in an electrically neutral atom is also equal to the atomic number, Z. The total mass of an atom is determined very nearly by the total number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus. This total is called the mass number, A. The number of neutrons in an atom, the neutron number, is given by the quantity A-Z.在一个原子核中的质子数量被称为原子序数,或质子数,Z。
在一个电中性原子中的电子数量也等于原子序数,Z。
一个原子的总质量被测定是非常接近于原子核中质子和中子的总数。
这个总数被称为质量数,A。
在一个原子中的中子数量等于A – Z的数量。
The term element refers to, a pure substance with atoms all of a single kind. To the chemist the "kind" of atom is specified by its atomic number, since this is the property that determines its chemical behavior. At present all the atoms from Z = 1 to Z = 107 are known; there are 107 chemical elements. Each chemical element has been given a name and a distinctive symbol. For most elements the symbol is simply the abbreviated form of the English name consisting of one or two letters, for example:这个术语(指chemical element)也可以指由相同质子数的原子组成的纯化学物质。

化学专业英语翻译(校准版)33 化学反应速度Introduction介绍In this chapter we look into how chemical reactions occur. The principal aspect we examine is the rate of a reaction, and we shall see how it. depends on the temperature and the concentrations of the species that are present.在本章中,我们来看看化学反应是如何发生的。
我们研究的主要的方面是反应速率,我们将看到温度和存在的物质的浓度是如何影响化学反应速率的。
There are two main reasons for studying the rates of reactions. The first is the practical importance of being able to predict how quickly a reaction mixture will move its equilibrium state: the rate might depend on a number of factors under our control, such as the temperature, the pressure, and the presence of a catalyst, and, depending on our aims, we may be able to make the reaction proceed at an optimum rate. For instance, in an industrial process it might be economical for the reactions to proceed very rapidly; but not so rapidly as to produce an explosion. By contrast, in a biological process it may be appropriate for a reaction to proceed only slowly, and to be switched on and off at the demand of some activity.研究反应速率的主要原因有两个。


20THE ROLE OF PROTECTIVE GROUPS IN ORGANIC SYNTHESIS20有机合成中保护基团的使用If a satisfactory protective group has not been located,the chemist has a number of alternatives:rearrange the order of some of the steps in the synthetic scheme so that a functional group no longer requires protection or a protective group that was reactive in the original scheme is now stable;redesign the synthesis,possibly making use of latent functionality(i.e.,a functional group in a precursor form;e.g.,anisole as a precursor of cyclohexanone).Or,it may be necessary to include the synthesis of a new protective group in the overall plan.如果找不到符合要求的保护基,化学家仍然具有大量可供选择的方法:重新安排合成系统中一些步骤的顺序,保证官能团不再需要保护或者在原来的系统中的活性保护基现在变得稳定;可能利用潜在的功能重新设计合成(也就是功能性基团以前驱体形式出现;例如:茴香醚作为环己酮的前驱体)。
或者,有必要在总体计划中包括新保护基的合成.22POLYMERS22聚合物The process by which small molecules undergo multiple combinations to form macromolecules is polymerization.Small molecules from which a macromolecule or polymer can be made are called monomers.Two types of polymerization are recognized: (1)condensation polymerization and(2)addition polymerization.A polymer-forming reaction involving elimination of a small molecule such as water or alcohol between monomer units is described as condensation polymerization.In addition polymerization, unsaturated or cyclic molecules add to each other without elimination of any portion of the monomer molecule.The empirical formula of the polymer is then,of course,the same as that of the monomer.小分子进行多重结合形成大分子的过程叫做聚合反应。
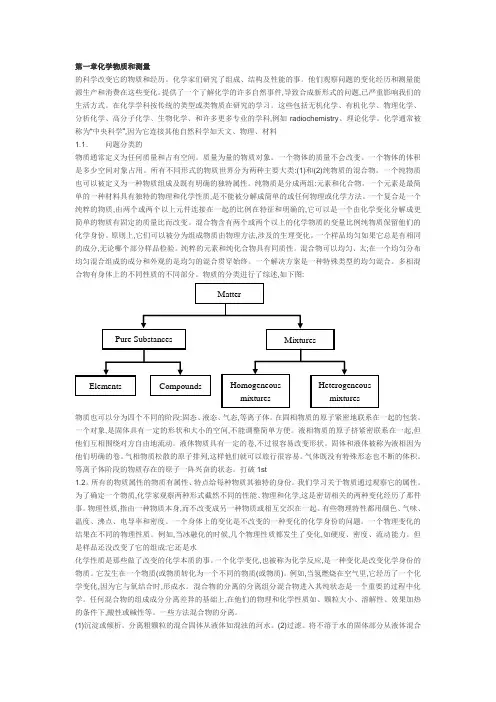
第一章化学物质和测量的科学改变它的物质和经历。
化学家们研究了组成、结构及性能的事。
他们观察问题的变化经历和测量能源生产和消费在这些变化。
提供了一个了解化学的许多自然事件,导致合成新形式的问题,已严重影响我们的生活方式。
在化学学科按传统的类型或类物质在研究的学习。
这些包括无机化学、有机化学、物理化学、分析化学、高分子化学、生物化学、和许多更多专业的学科,例如radiochemistry、理论化学。
化学通常被称为“中央科学”,因为它连接其他自然科学如天文、物理、材料1.1.问题分类的物质通常定义为任何质量和占有空间。
质量为量的物质对象。
一个物体的质量不会改变。
一个物体的体积是多少空间对象占用。
所有不同形式的物质世界分为两种主要大类:(1)和(2)纯物质的混合物。
一个纯物质也可以被定义为一种物质组成及既有明确的独特属性。
纯物质是分成两组:元素和化合物。
一个元素是最简单的一种材料具有独特的物理和化学性质,是不能被分解成简单的或任何物理或化学方法。
一个复合是一个纯粹的物质,由两个或两个以上元件连接在一起的比例在特征和明确的,它可以是一个由化学变化分解成更简单的物质有固定的质量比而改变。
混合物含有两个或两个以上的化学物质的变量比例纯物质保留他们的化学身份。
原则上,它们可以被分为组成物质由物理方法,涉及的生理变化。
一个样品均匀如果它总是有相同的成分,无论哪个部分样品检验。
纯粹的元素和纯化合物具有同质性。
混合物可以均匀、太;在一个均匀分布均匀混合组成的成分和外观的是均匀的混合贯穿始终。
一个解决方案是一种特殊类型的均匀混合。
多相混合物有身体上的不同性质的不同部分。
物质的分类进行了综述,如下图:物质也可以分为四个不同的阶段:固态、液态、气态,等离子体。
在固相物质的原子紧密地联系在一起的包装。
一个对象,是固体具有一定的形状和大小的空间,不能调整简单方便。
液相物质的原子挤紧密联系在一起,但他们互相围绕对方自由地流动。
液体物质具有一定的卷,不过很容易改变形状。

U27 The acid-base titration starts with the dissolution of the solid acid sample in deioni zed water. Add the end-pointindica tor, whichis phenol phtha lein, with two dropsto each flaskcontai ningthe acid sample and deioni zed water.Proper ly labelthe flasks. Be consis tentin all of the sample s when adding the indica tor. Swirlthe flasks untilthe solidacid is comple telydissol ved. Finall y, rinsewith deioni zed waterthreetimesaround, whichis critic al to ensure that all solidacid has been remove d from the flaskwallsand dissol ved in the soluti on. All solidpartic les must be dissol ved priorto the titrat ion.7、酸碱滴定伴随着于固体酸溶解于去离子水中发生。
在每支装有酸样品和去离子水的试管中加入两滴终点指示剂——酚酞,并在试管上贴好标签。
在加指示剂的时候保持所有样品条件一致。
震荡试管直到所有固体酸完全溶解。
最后,用去离子水冲洗试管壁周围三次,确保试管壁上的固体酸从试管上脱落并溶解于溶液中。

Elements and Compounds元素与化合物Elements are pure substances that can not be decomposed(分解) into simpler substances by ordinary chemical changes. At present there are 109 known elements. Some common elements that are familiar to you are carbon, oxygen, aluminum, iron, copper, nitrogen, and gold. The elements are the building blocks of matter just as the numerals 0 through 9 are the building blocks for numbers. To the best of1 our knowledge, the elements that have been found on the earth also comprise(包含) the entire universe.元素是单纯的物质,不能通过一般的化学变化分解成为更简单的物质。
目前已知有109个元素。
一些你熟悉的常见元素是碳、氧、铝、铁、氮和金。
元素是组成物质的基本单元,就象0到9的数字是组成数的基本单元一样。
就我们所知,已经在地球上发现的元素也是组成整个宇宙的元素。
About 85% of (85 percent of) the elements can be found in nature , usually combined with other elements in minerals and vegetable matter or in substances like water and carbon dioxide. Copper, silver, gold, and about 20 other elements can be found in highly pure forms. Sixteen elements are not found in nature; theyhave been produced in generally small amounts in nuclear explosions (爆炸)and nuclear research. They are man-made elements.大约有85%的元素可以在大自然的矿物或者植物中,以及如水和二氧化碳这样的物质中找到,通常与别的元素结合。

•Coal, petroleum and natural gas now yield their bond energies to man.煤,石油和天然气现在为人类提供各种各样的结合能。
•Salts may also be found by the replacement of hydrogen from an acid with a metal.盐也能通过用金属置换酸中的氢而获得。
•An acid was once defined as a substance that would form hydrogen ions(H+) in water solution and a base as one that would form hydroxide ions(OH-) in the same.人们曾把酸定义为在水溶液中能产生氢离子的物质,而碱则是在同样溶液中会产生氢氧根离子的物质。
•These books are packed in tens. 这些书每十本装一包。
•These products are counted by hundreds. 这些产品是成百成百计数的。
•They went out by twos and threes. 他们三三两两地出去了。
•They consulted tens of magazines. 他们查阅了几十本杂志。
•Automation helps to increase productivity hundreds of times over. 自动化使生产率提高了几百倍。
•More weight must be placed on the past history of patients. 必须更加重视患者的病史。
•The continuous process can be conducted at any prevailing pressure without release to atmospheric pressure.连续过程能在任何常用的压力下进行,而不必暴露在大气中。

Perhaps the most function definition of analytical chemistry is that it is "the qualitative and quantitative characterization of matter "也许对分析化学最实用的定义是:对物质进行定性和定量的表征。
描述这个词被广泛的使用。
它可能意味着在回答诸如“在洗发香波中是否如标签所示有维生素E”“这是一个白色阿司匹林片?”或“这块金属是铁或镍”等问题时,对样本中的化合物或元素进行鉴定。
这种类型的表征,要告诉我们什么是目前被称为的定性分析。
定性分析是鉴定一个或多个化学物质存在于一个材料中。
描述也可能意味着测定有多少种化合物或元素存在于一个样品中,回答“水杨酸在这个阿司匹林片中含量多少”或“这块钢中含有多少镍”等这些问题。
一种物质在一个样品中含量多少的这种测定被称为定量分析。
定量分析是测定某种化学物质在某个样品中的确切数量。
化学物质可能是某些元素、化合物或离子。
该药物可能有机和无机两种。
特性描述可能涉及到全分析,如构成一块钢的元素,或者表面分析,像鉴定绝大多数暴露在空气和水中的金属表面形成的氧化层的成分和厚度。
一个材料的特性描述可能超越化学分析所包括结构材料的确定,某个材料的物理性质的测量,以及物理化学参数的测量例如反应动力学。
这些测量的实例有:聚合物的结晶度(与非晶态相比)?物质失去结晶水的温度?“A牌”抗酸剂中和胃酸所需的时间?农药在阳光下的降解速度?这些不同的应用使分析化学成为广泛的学科之一在所有的科学学科中。
分析化学对于我们了解生物化学是至关重要的。
药物化学、地球化学、环境科学、大气化学,材料学中的反应像聚合物、金属合金和陶瓷技术以及许多其他科学领域。
For many years ,analytical chemistry relied on chemical reactions to identify and determine the components present in a sample.多年来,分析化学依赖化学反应,以确定出现在一个样本中的组分。
•Coal, petroleum and natural gas now yield their bond energies to man.煤,石油和天然气现在为人类提供各种各样的结合能。
•Salts may also be found by the replacement of hydrogen from an acid with a metal.盐也能通过用金属置换酸中的氢而获得。
•An acid was once defined as a substance that would form hydrogen ions(H+) in water solution and a base as one that would form hydroxide ions(OH-) in the same.人们曾把酸定义为在水溶液中能产生氢离子的物质,而碱则是在同样溶液中会产生氢氧根离子的物质。
•These books are packed in tens. 这些书每十本装一包。
•These products are counted by hundreds. 这些产品是成百成百计数的。
•They went out by twos and threes. 他们三三两两地出去了。
•They consulted tens of magazines. 他们查阅了几十本杂志。
•Automation helps to increase productivity hundreds of times over. 自动化使生产率提高了几百倍。
•More weight must be placed on the past history of patients. 必须更加重视患者的病史。
•The continuous process can be conducted at any prevailing pressure without release to atmospheric pressure.连续过程能在任何常用的压力下进行,而不必暴露在大气中。
化学专业英语修订版译文目录:1、THE ELEMENTS AND THE PERIODIC TABLE元素和周期表在原子核中质子的数目被称为原子序数,或质子数,Z;电中性原子中的电子数目也等于原子序数,Z;一个原子的总质量几乎由它的原子核中的质子和中子的总数所决定;此总量称为质量数,A;原子中中子的数目,中子数,其值由下式给出:A-Z;元素这一术语指的是,由单一种类的原子所组成的纯物质;对化学家来说“类”是由其原子序数指定的,因为这是个决定了它的化学行为的属性;目前,所有的原子从Z = 1,Z = 107都为人所知了;共有107种化学元素;每个化学元素被赋予一个名称和一个特定的符号;对于大多数的元素来说符号是简单的英文名称的缩写,由一个或两个字母组成,例如:氧==O 氮== N 氖==Ne 镁==Mg已经为人所知了很长一段时间的一些元素,其符号是基于其拉丁语中的名称,例如:铁==Feferrum铜==Cucuprum铅==Pbplumbum在表1中可以找到的元素的完整列表;早在17世纪末期,罗伯特.波义尔就开始了这项工作,他提出了现在公认的元素概念,大量的研究使我们对元素及其化合物的性质有了相当的研究;1869年,和,各自通过独立的工作,提出了周期性规律;在现代的形式中,该规律表明元素的属性和原子序数呈周期性的函数关系;换句话说,当元素依照原子序数的升序排列时,具有大致相同的特性的元素将沿着列表中的一定间隔降序排列;因此,将具有类似性质的元素排成纵列,从而将元素排成表格的形式是可能的;这种安排被称为一个周期表;每个一行中的元素构成一个周期;应当指出的是周期表的长度是变化的;有一个很短的周期只由2个元素组成,随后的两个周期各有8个元素,接下来的两个长周期各有18个元素;再接下来的一个周期包括32个元素,最后一个周期显然是不完整的;这样的安排,使得相同的垂直列中的元素具有类似的特性;这些列构成的化学族或群;那些以两个八元素周期为首的族中的元素被指定为主族元素,和其他各组的成员被称为过渡或内过渡元素;在周期表中,一条重重的阶梯线把元素们划分成金属和非金属;这条线除氢外左侧的是金属元素,而在右边是非金属元素;这种划分只是为了方便;那些与分隔线邻近的元素——准金属,既有金属的性质,又有非金属的性质;可以看出,大部分的元素,包括所有的过渡与内过渡元素,是金属元素;除氢元素——一种气体元素外,IA族的元素组成了碱金属族;它们是非常活泼的金属,它们从未在自然界中以单质状态被发现;然而,它们的化合物是广泛分布的;碱金属族的所有成员,只能形成具有1 +价的离子;与此相反,IB族的元素铜,银,和金的元素相对来说是惰性的;它们和碱金属是相似的,因为它们在化合物中以1 +的离子存在;但是,和大多数过渡元素具有的特性一样,它们形成也能形成其它价的离子;IIA族的元素就是通常所说的碱土金属;它们离子的特征价态是2 +;这些金属,尤其是组中的最后两个元素,几乎和碱金属一样活泼; IIB组元素,锌,镉,和汞比那些IIA的元素活性低,但比邻近的IB族元素活泼;它们的特征离子价态也是2 +;除硼以外,第IIIA族元素也相当活泼的金属;铝与空气反应后是惰性的,但这一表现源于这一事实:在金属表面形成了一个薄的,不可见的铝的氧化膜,该膜保护大部分金属不会进一步氧化;IIIA族的金属形成3 +价的离子;IIIB族由金属钪,钇,镧和锕组成;第IVA族由一个非金属,碳,两个准金属,硅和锗和两种金属,锡和铅组成;这些元素中的每一个都形成一些化合物,这些化合物的分子式表明四个其它的原子出现在每个IVA族原子周围;例如,四氯化碳,CCl4; IVB族金属——钛,锆和铪,也形成每个IVB族原子与四个其它原子结合的化合物,这些化合物纯的时候是非电解质;VA族的元素包括三个非金属元素——氮,磷,砷和两个金属——锑和铋;尽管它们存在分子式为N2O5,PCL5,和AsCl5的化合物,但它们都不是离子型化合物;这些元素形成的化合物——氮化物,磷化物和砷化物,其中离子的价态都是负三价; VB族的所有元素都是金属;这些元素形成这样的多种不同的化合物,它们的特点是不容易总结归纳的;除钋以外,VIA族元素是典型的非金属;他们有时也被称为硫族,来自希腊字,意思是“灰源体”;在他们与金属形成的二元化合物中它们以2-的离子价存在;ⅦA族的所有元素都是非金属元素,被称为卤素;来自希腊文,意思是“盐源体”;他们是最活泼的非金属,并能够与几乎所有的金属和大部分非金属,包括它们自己反应;ⅥB,ⅦB,VIIIB的所有元素都是金属;它们形成各种不同的化合物,在这一点上我们甚至不能举出任何能表现各族元素典型变化的例子;化学行为的周期性可以通过这样的事实阐明:不包括第一个周期,每个周期的开始,是一个非常活泼的金属;周期中的连续元素,金属性逐渐降低,最终成为非金属,最后,在ⅦA族,一个非常活泼的非金属就出现了;每个周期以惰性气体家族的一个成员结束;-------------------------------------------------------------------6、THE CLASSIFICATION OF INORGANIC COMPOUNDS无机化合物的分类化合物的分类今天成千上万的化合物已被化学家所认识;如果根据个别化合物来了解这么多化合物的性质和行为,即使其中的很小一部分也不可能;所幸的是,大多数化合物可以被归为几类;这样,如果我们能正确地对一个化合物进行分类,就可以根据已知这类化合物的性质知道这个化合物的一般性质;例如,盐酸是一种酸,因为已经熟悉酸的性质,我们就可以立即知道这一化合物的一般性质;我们学过的大多化合物可以分为酸,碱,盐,金属氧化物,非金属氧化物;在这5类化合物中,前3种—酸,碱,盐—是最重要的;如果一种酸,碱或盐溶于水中形成的溶液是电流的导体,就被称为电解质;如果没有电流产生则此化合物是非电解质;普通化合物的分类通过观察化学式我们可以将许多普通化合物分类如下:⒈⒉通常碱中存在的氢氧根写在分子式的后面;分子式的前面一般是金属;例如,OHOH3;⒊盐由金属组成,写在前面,结合非金属或基团,写在化学式的后面;如SOClO2;⒋氧化物仅包括氧和其它一种元素;如果这种元素除了氧以外是非金属,这种氧化物称为非金属或酸酐;酸酐的命名是因为在特定的条件下将水溶液加入到非金属氧化物中会生成酸;同样,如果水从含氧酸中被转移走就会生成酸酐;另一类氧化物,金属氧化物或碱酐,由氧结合金属组成;当在适当的条件下将水加入到碱酐中,有碱生成,反之亦然;酸按传统的观念,所有的酸都包含H,它可以被金属取代;在酸分子中负价的基团由非金属或基团组成负价基团;这些负价的基团被称为酸根除了氧和氢氧根;所有的酸都是共价化合物,它们的原子通过共用电子连接;当酸溶于水时,由于酸中的氢离子转移到水分子中所以形成离子——例如:H ‥‥‥‥ H﹕Cl﹕+H﹕O﹕H→H﹕O﹕H++﹕Cl﹕-这是一种配位价,水中未成对的电子结合氢离子形成水合离子;水合离子是水合物H+ 或称质子,根据这种形式酸在水溶液中电离时,我们可以利用简单的H+来写方程式;此方程式变得简单而且容易配平;酸的主要性质是提供H+的能力,因此,我们把能够提供H+的物质定义为酸; 酸的性质,一般来说,酸的水溶液的性质如下:⒈它们都有酸味;柠檬,桔子以及其它的柠檬水果由于柠檬酸的存在而具有酸味;酸奶的酸味也是因为乳酸的存在;⒉它可以使蓝石蕊变红;石蕊是一种染料,它在酸溶液中显红色,在碱溶液中显蓝色;将纸浸泡在石蕊中制成石蕊试纸;这类物质,能够确定所给的溶液是酸还是碱,我们称之为指示剂;甲基橙和酚酞是其它两种常用的指示剂;⒊它可以和某些金属反应生成氢气;这类反应经常被用来制氢气;⒋它和碱反应生成盐和水;一般的强酸有硫酸,硝酸,盐酸,氢溴酸和氢碘酸;其它的一些酸仅仅部分电离从而仅仅是中强酸或弱酸;碱所有金属的氢氧化物被分类于碱类;一般的碱如氢氧化钠,氢氧化钾,氢氧化钙和氢氧化钡可以溶于水中;如果这些化合物可以溶解于水中,所有的溶液中都会有OH- ;氨的水溶液也属于碱类,因为溶液中存在OH-;每种这类化合物都是由金属或铵根离子结合氢氧根离子形成的;正如显示酸特性的部分是H+,因此显示碱特性的部分是OH-;因此碱的概念就扩展为不能提供质子的物质; 碱的性质;一般来说金属氢氧化物的水溶液显示出以下的性质:⒈味道苦;⒉具有滑腻性;⒊可以使红色石蕊变蓝;⒋和酸生成盐和水;⒌大多数金属氢氧化物都是可溶的;一般情况下氢氧化钠,氢氧化钾,氢氧化钙,氢氧化钡和氨是可溶的;一般的强碱有氢氧化钠,氢氧化钾,氢氧化钙和氢氧化钡;盐酸和碱反应生成盐和水;酸中的氢离子结合碱中的氢氧根离子形成水分子;酸和碱的反应是中和反应;如果在反应后所有的水通过蒸发移走,碱中的正离子和酸中的负离子形成晶格的固体;证据显示化合物氯化钠,一种盐,是一种电价的化合物,可以在固体或晶体状态下电离;这种晶体由钠离子和氯离子通过定向模式组成的;一般来讲,大多数盐在晶体状态下是电价的;由定向离子通过确定的方法组成;-------------------------------------------------------------------7、The Nomenclature of Inorganic Compounds无机化合物的命名随着上千种新无机化合物的发现,我们有必要修改传统命名的规则;国际委员会已经推荐了一套化合物命名的规则,并且现在世界各地都采用了;许多旧的名字仍然在使用,但是我们将讨论新旧规则的许多例子,但以新规则为讨论重点;其中主要的变化就是被Albert Stock提出的为一些存在多种氧化态的金属的化合物氧化物、氢氧化物、盐命名的Stock方法;在这种情况下,金属氧化态是紧接着金属的英语名称之后在圆括号中用罗马数字表示,该数字与金属的氧化数一致;如果金属只有一个常见的氧化数,则不使用罗马数字;另一个重要的变化是在命名复杂的离子和配位化合物;我们推迟后者的命名直到我们讨论这些化合物;金属氧化物、酸碱、盐的命名一个学生如果掌握了给出离子电荷和较常见离子名称的价表3,他在掌握命名方面就必定有了一个好的开端;阴阳离子以恰当的比例来平衡电荷组成了化合物,并且化合物的名字来自于离子的名称,例如NaCl叫氯化钠;AlOH3叫氢氧化铝,FeBr2叫溴化铁Ⅱ或者溴化亚铁;CaC2H3O22叫乙酸钙,Cr2SO43叫硫酸铬Ⅲ或者硫酸铬,等等;表4给出一些额外金属化合物命名的例子;两种常见的系统被使用时,Stock系统是首选;注意的是,即使在这个系统中,然而阴离子的名称仍需要查化合价表4;带负电荷的离子,阴离子,可能是单原子的或者是多原子的;所有单原子的阴离子都有以 ide结尾的名字;氢氧根离子OH-和氰根离子CN-的两个多原子离子也有以ide结尾的名字;许多多原子离子除了其他元素还包含了氧元素;在这些含氧阴离子中氧原子的数量以后缀ite和ate来表示,ite和ate分别意味着较少和较多的氧原子;在某些情况下,有必要表示多于两个相同元素的氧阴离子,分别表示更少和更多氧原子的前缀hypo和per 可能被使用;一系列的氧阴离子被命名在表5中;非金属氧化物的命名仍被广泛使用的旧的命名系统使用希腊语前缀表示氧原子的数目和化合物中其他的元素;被使用的前缀有lmono-, 有时简称成 mon-, 2di-, 3tri-, 4tetra-, 5penta-, 6 hexa-, 7hepata-, 8octa-, 9nona-and 10deca-;当命名一个非金属氧化物时,渐渐地的字母a在前缀中被省略tetra并且常常mono-在所有的名称中也一起被省略;Stock系统也被用于非金属氧化物,这里的罗马数字指的是除了氧元素其他元素的氧化态;在两个系统中,除了氧元素的其他元素被首先命名,整个名称后面加上一个OXide;表6中展示了一些例子;酸的命名酸的名字可以直接从化合价表3的知识中得到,只要以下面表的形式改变酸离子阴离子的名字即可;表7展示了这种关系的例子;还有少数情况下,酸的名字可以由酸根稍稍的改变得到;例如:H2SO4是sulfuric而不是sulfic;相似的,H3PO4是phosphoric而不是phosphic;一些很少见的阴离子不包括在化合价表3中;例如:BO33-是硼酸根的离子并且H3PO3是硼酸;TeO42-是碲酸盐离子并且H2TeO4是碲酸,等等;酸式盐和碱式盐可以想象,在酸和碱的中和反应中,只有一部分氢离子被中和;因此NaOH + H2SO4-----→NaHSO4 + H2O化合物NaHSO4有酸的性质,因为它当中有氢离子,它也是一个盐,因为它既有金属阳离子有酸根;像这样的含酸性氢离子的盐叫做酸式盐;磷酸H3PO4可以逐渐的被中和成盐,NaH2PO4, Na2HPO4 和 Na3PO4;前两种是酸式盐,因为它们包含可置换的氢;一种命名这些盐的方法是把NaH2PO4叫做磷酸二氢钠,把Na2HPO4叫做磷酸氢二钠;这种算是磷酸盐在控制血液酸碱度方面起着重要作用;第三种化合物,磷酸钠Na3PO4,其中没有可置换的氢,通常被叫做正磷酸钠,或磷酸三钠用以区别前两种酸式盐;历史上,前缀bi-被用来命名一些酸式盐;在工业上,例如,NaHCO3被叫做碳酸氢钠而CaHSO32被叫做亚硫酸氢钙;因为bi-有点令人误解,故上面讨论的命名系统更可取;如果碱中的氢氧根逐渐被氢离子所中和,就很可能形成碱式盐:CaOH2 + HCl-----→CaOHCl + H2O碱式盐有碱的性质并且可以和酸反应生成正盐和水;OH基团是一个碱性基团叫做羟基集团;BiOH2NO3的名字叫做碱式硝酸铋;混盐如果酸中的氢被两种或两种以上不同的金属所替换,就形成了混盐;因此H2SO3中的两个氢原子被钠和钾取代从而生成混盐,NaKSO4硫酸氢钾;NaNH4HPO4是一个酸式混盐,它可以从尿中结晶出来;-------------------------------------------------------------------9、The coordination complex配位化合物配位化合物形成的化学基础是配位键,形成时必须有一个电子对受体和一个电子对给体;因此,配位反应是路易斯酸碱的中和过程;中心离子是路易斯酸或电子对受体,而周围的基团,叫做配体,它们是路易斯碱或电子对给体,总的来说,这个反应可以这样来表述:Mn+ + x:L -----→ M:Lxn+正向反应是配位反应而逆向反应是解离反应,不管是配位反应还是解离反应,当x大于1时,这个反应都是逐级的,所以上面的方程式是几个逐级反应的总和;配位键本质上在介于共价键包括在一些情况下双键的性质和离子键之间,例如在水溶液中的化合物NaH2Ox +,钠离子和配位水分子的相互作作用就强于在氯化钠晶体中和周围氯离子的相互作用;而在另一个极端,像FeCN64-这样的化合物就主要包含基础的共价键;这种性质上的不同由表9中的化合物说明;表中前四种化合物是类盐物质,它们的阴离子和阳离子只有一个是络合物;这显然是对于它们的水相组成来说的;然而,相同的离子在固相中依然是存在的,尽管正如表中所示,它们的分子式都被写成复盐的形式;在上面的每种情况中络合离子都在溶解过程中存在,但是在溶解过程中很少有自由配离子和水合单原子离子的踪迹;值得注意的是,配离子可以是分子,像NH3,也可以是离子的,像CN-,NO2- 或F-,在VF4H2O2-的例子中,钒就既和分子型,也和离子型的配体配位了;第五个化合物Pt2Cl44NH3,在水溶液中既包含络合阳离子也络合配位阴离子;最后一个化合物有一个表明CuCl42-络合离子存在的晶体构型,然而,当该物质溶解于水中时,混合的水合单分子离子就形成了;这清楚的说明了Cu II 和水配体形成了一种比和氯离子配体更稳定的化合物;高度的离子性使得水合Cu II 在溶液中快速的转换,在溶解过程中没有CuCl42-存在并不能证明它在固相中不存在;配位场理论已证实在配位化合物中有用的新理论是晶体场或配位场理论,该理论说明配位体被配位化合物的中心离子拉住,主要是由于中心离子的原有电荷和配位体的极性间的静电吸引力;吸引力的强弱程度决定了络合物的稳定程度;也取决于中心离子和配体的价态和尺寸; 运用这个理论,计算很多价态和尺寸等因素的能量影响,并且最终获得键能的值;后者对预测大部分化合物的性质和构型来说十分有用;配体配体必须是极性的或者是可极化的非极性配体是弱配体,并且它们通常含有能和中心离子形成配位键的未共用电子对;配体可以基于它们和金属离子形成一个键键单齿的或两个键双齿的的能力进行分类,二价的或有两个给体原子的配体,像乙二胺H2N—CH2—CH2 — NH2,是二配位的,因为它们包含两个位点,并以此和中心原子成键;配体可能还要复杂,三齿的、四齿的、甚至六齿的配体都已为人所知;多齿配体可能同时含有可与中心离子配位的中性和负电性的位点,就像甘氨酸离子:在这里含氧负离子和中性的含氮原子都有未共用的电子对并且都可以和给定的阳离子配位;其中一个例子是络合物Co H2NCH2CO2 3,在这个络合物中钴和甘氨酸离子中的一个氧都发生了配位,当多齿配体和中心离子在两个或两个以上的位点配位的时候,就形成了上述钴的乙二胺配合物那样的环状结构,这种络合物叫做螯合物,而多齿配体则叫做螯合体;配位化合物的命名和实例1、阳离子最先命名,阴离子最后命名;2、负离子的名称以o结尾,就如表10所举之例;它们是cyano-, hydroxo-,chloro-,carbonato-.按照字母顺序排列;3、中性单元历史上自有其结尾,像ammine氨, aqua-水以前是 aquo-, carbonyl 羰基, nitroso-亚硝基;4、络合物中中心离子的氧化数由元素后面括号中的罗马数字表示,当络合离子是阴离子时中5、中性络合物和阳离子的命名方法相同;6、如果该络合物是正电性的,那么要以络合物中不包含的阳离子的名称来补全化合物的名称; 这些规则将由下面的例子说明:-------------------------------------------------------------------10、Alkanes烷烃异构体的数目现在总称为烷烃的化合物也被称为饱和碳氢化合物和链烷烃;链烷烃这个词来源于拉丁文,指的是物质的化学惰性,也被用于能从石油中获得由高级烷烃组成的石蜡;已经证明戊烷三种异构体,己烷五种异构体,庚烷九种异构体等结构式的多样性随着碳含量的增加急剧增加;常见的烷烃这一系列中的所有烷烃的区别在于他们的组成上含有递增的CH2基团,并构成了一个同系列;因此,庚烷和辛烷是同一系列的烃,二十烷是甲烷的更高级同系物;饱和无支链的链状化合物及其一价基团前四个饱和的无支链的无环状的碳氢化合物被称作甲烷,乙烷,丙烷和丁烷;这一系列中更高级成员的名称是由去掉数字末尾的”a”再加上”-ane”的数字术语构成;下列表中是这些名称的例子;饱和非环碳氢化合物支链或无支链的总称为“烷烃”;饱和有支链的碳氢化合物的命名是把支链的名称加到最长链的名称前面;最长链是用阿拉伯字母从一端向另一端编号,这样选择编号方向时尽可能使支链位次具有最低的编号;当逐一比较包含着相同碳原子数目的许多位次时,根据第一个位次差异,含最低数字的是最低者;这一原则的应用与取代基的性质无关;例如:2,3,5——三甲基己烷用适当的词缀2,3,4...等作前缀表示相同的未被取代的基团;例:3,3——二甲基戊烷饱和的非环状碳氢化合物末端碳原子上去掉氢而衍生的一价基团,在命名时是将碳氢化物名称末尾的“-ane”用”yl”替换;含有自由价的碳原子被编号为“1”位,作为一类,这些基团被称作常规的或无支链的烷基;例:1—甲基戊基,2—甲基戊基,5—甲基戊基异丁基,仲丁基,叔丁基,辛戊基稳定性—化学上,烷基是相对惰性的,因为对于那些很易与烯烃和炔烃反应的试剂;它们却显出很高的惰性;例如,正己烷,不能与浓硫酸,沸腾的硝酸,熔融的氢氧化钠,高锰酸钾或铬酸反应;除了氢氧化钠外,这些试剂在常温下都易与烯烃反应;能和烷烃发生的少数几个反应几乎都需要较高的温度或特殊催化剂;卤代作用—如果把一个盛有正己烷的试管放在暗处,并用一滴溴处理,几天后原有颜色仍保留不褪色;假如将溶液暴露在太阳光下,颜色几分钟就会褪去,并且可以在试管口产生呈现出来的雾状冷凝物溴化氢;这个反应是光化学取代反应:C6H14+Br→C6H13Br+HBr烷烃的氯代比溴代更普通更有用,它不仅在光化学条件下实现,而且可以利用其它方法实现;光引发烷烃的氯代反应是将氯气分子通过均裂过程转变为氯原子,在均裂过程中,一个共价键断裂,形成这个键的每个原子仍保留一个电子;一个氯原子有奇数个或未成对的电子,它是一种自由基;由于原子具有达到最外层价电子饱和的趋势;任何自由基都是非常活泼的;光化学氯代反应是通过一系列自由基的传递进行的;它是自由基的链反应;链引发阶段1,即氯分子的均裂,产生了氯自由基;在链传递阶段,一个氯自由基和烷烃分子反应,产生氯化氢和一个烷基自由基2,这个自由基依次再和氯分子反应产生氯代烷和氯自由基3,由于第二阶段需要的氯自由基在第三阶段再生,这两个反应合起来组成链反应;在链反应中如果两个反应以极高的效率进行,将不需要进一步的光能而自动传递;然而这种效率并不是很高,因为氯自由基可能重新结合4,或与烷基自由基结合5,或与器壁碰撞消耗能量6;因此,需要持续提供光照保证引发自由基需要的充足能量;链引发阶段需要输入的光能总计为+mol;但第二阶段是放热的;因为断裂碳氢键所需的能量比氢氯键所需的能量小;第二阶段的链传递3也是放热的;事实上烷烃的氯代反应是爆性式的进行;裂解—加热到500-700℃时,更高级的烷烃经历热裂解或裂化生成小分子混合物,其中一些是饱和的,一些是不饱和的;特殊的石油馏分通过选择性的断裂产生的不饱和的碳氢化合物在化学合成上是很有用的;裂解断裂的是碳碳键而不是碳氢键;因为打开碳碳键需要的能量是247KJ/mol,而断裂碳氢键所需能量是364KJ/mol;氧化物—碳氢化合物和氧气反应放出能量,这是内燃机使用汽油作燃料的依据;一个给定的碳氢化合物释放的能量用燃烧热来表示, 用KJ/mol来表示;气态碳氢化合物的不充分燃烧在生产碳黑方面是很重要的,尤其是生产灯芯,墨汁颜料,槽法碳黑,被应用于橡胶工业的填料;天然气因为价廉,易得而被使用;炭黑的产量随。
1.有机化学Inorganic chemistry 无机化学organic chemistry物理化学physical chemistry 分析化学Analytical chemistry 生物化学biochemistry 化工原理principles of chemical engineering热力学thermodynamics2.烷烃Alkanes烯烃Alkenes 炔烃Alkynes 甲烷Methane乙烯Ethene 乙炔Ethyne环己烷Cyclohexane苯Naphthalene 醇Alcohols醚Ethers 酮Ketones醛Aldehydes酯Esters羧酸Fatty Acids胺Amines 氰Cyanides碳水化合物Carbohydrates氨基酸Amino Acides 蛋白质protein 脂质lipids3. 氨基甲酸酯carbamate沉淀precipitation测定determine 除草剂herbicide 单元操作Unit operations底物substrate 定性分析qualitative 定量分析gravimetric发色团chromophore 分离isolate 分析物analyte 反应速率Reaction rate 过滤filtration化学污染chemical pollution合成synthesize解吸附作用desorption基本原理fundamental principle科学领域scientific fields农药pesticide亲核试剂nucleophile 杀菌剂fungicide 石化产品Petrochemical 碳氢化合物Hydrocarbons 碳阳离子carbocation物性the properties of substance 新陈代谢metabolism吸附adsorption有毒化学品toxic chemical 有机氯化物Organic chloride自然变化natural changes准确度accuracy 助色团auxochrome 植物生长调节剂plant growth regulator蒸馏distillation4.烧杯beakers通风橱Furne hoods 锥形瓶Erlenmeyer圆底烧瓶Round bottom flask蒸馏烧瓶Distillation蒸发皿Evaporating dishes真空干燥器Vaccume dessicator5.Al2O3aluminium(III) oxide BaCl2 Barium(II) chloride BaI2 Barium iodide Ca(MnO4)2Calcium permanganate Cu2S copper(I) sulphide CuO Copper(II) oxide FeSO4 Iron(II) sulfate HClO4 perchloric acid H2SO4 sulphuric acid H2CO3Carbouic acide HPO4diammonium hydrogen phosphate KHSO4 potassium hydrogen sulphide KMnO4 Potassium permanganate (NH4)2CO3ammoniue carbonate (NH4)2SO4 Ammmonium sulfate N2O nitrogen(I) oxide NaH Sodium permanganate P4O6 tetraphosphorus hexaoxide PF5phosphorus pentafluoride P4O10 tetraphosphorus decaoxide Sncl4 tin(IV) chloride6.There are 20 standard amino acids , and they contain a carboxyl group ,an amino group ,and a side chain . 有20个标准氨基酸,和含有羧基、一个氨基和侧链。
化学专业英语翻译(校准版)17 OXIDA TION AND REDUCTION IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY17 有机化学氧化还原一级醇和二级醇的一个重要反应是将醇转化成tan基化合物,这也是有机化学反应中的一个典型的氧化反应的例子。
我们如何知道一个有机化合物被氧化呢?在最后一小节,我们将认识到醇转化成是一个氧化反应,因为他是通过减少铬的价态来实现的。
但也有其他的氧化剂进行的氧化反应是不明显的。
在这一章节我们的目标的能够认识到一个氧化反应或一个还原反应仅仅是通过有机化合物本身的转化检验。
这样做的程序包括了三个步骤:步骤一:针对反应物和生成物将氧化树分配到每一个碳原子上。
(它只是需要将氧化数分配到转化过程中有发生化学变化的碳原子上,其他碳原子可以被忽略)特殊碳原子的氧化数是通过考虑其在整体碳原子范围内相关电负性而被分配,如下:A.每一个电负性比碳小的元素(包括氢)跟碳结合,都会使碳原子带上一个负电荷,标记为-1B.若每一个键都是与另一个碳原子相连,则每个碳都会有一个不成对的电子,将其认为是0价。
C.若每一个键是与电负性比碳大的元素相连,则碳原子上就会带上一个正电荷,将其认为+1价。
D.综合考虑下将编号加到指定的A、B、C中去获得每个碳原子的氧化数。
让我们将这第一个步骤应用到异丙醇转化成丙酮的反应中。
因为两个甲基上的碳原子在反应中没有发生变化,所以我们不需要将氧化数分配到这两个碳原子上。
注意到对待丙酮上的碳氧双键时,是将其计为两个键的,故每个键给出+1价总的由两个键就给出了+2价。
步骤二:每个化合物的氧化数Nox是通过所有碳原子的氧化数相加而计算得来的。
在结构上,只有一个碳原子改变其氧化数,所以反应物和生成物的Nox值是等于这个碳原子分别的氧化数。
因此,反应物的氧化数为0而生成物的氧化数为+2。
在其他包含了1个碳原子以上的反应,Nox值是通过所有经历了化学变化碳原子氧化数之和而计算得到。
01 THE ELEMENTS AND THE PERIODIC TABLE01 元素和元素周期表The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is referred to as the atomic number, or proton number, Z. The number of electrons in an electrically neutral atom is also equal to the atomic number, Z. The total mass of an atom is determined very nearly by the total number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus. This total is called the mass number, A. The number of neutrons in an atom, the neutron number, is given by the quantity A-Z.质子的数量在一个原子的核被称为原子序数,或质子数、周淑金、电子的数量在一个电中性原子也等于原子序数松山机场的总质量的原子做出很近的总数的质子和中子在它的核心。
这个总数被称为大量胡逸舟、中子的数量在一个原子,中子数,给出了a - z的数量。
The term element refers to, a pure substance with atoms all of a single kind. T o the chemist the "kind" of atom is specified by its atomic number, since this is the property that determines its chemical behavior. At present all the atoms from Z = 1 to Z = 107 are known; there are 107 chemical elements. Each chemical element has been given a name and a distinctive symbol. For most elements the symbol is simply the abbreviated form of the English name consisting of one or two letters, for example:这个术语是指元素,一个纯物质与原子组成一个单一的善良。
在药房“客气”原子的原子数来确定它,因为它的性质是决定其化学行为。
目前所有原子和Z = 1 a到Z = 107是知道的;有107种化学元素。
每一种化学元素起了一个名字和独特的象征。
对于大多数元素都仅仅是一个象征的英文名称缩写形式,一个或两个字母组成,例如:oxygen==O nitrogen == N neon==Ne magnesium == Mg氮氧= = = = N霓虹灯啊= = = =不镁镁Some elements,which have been known for a long time,have symbols based on their Latin names, for example:一些元素,长久以来,根据他们的拉丁名字符号,例如:iron==Fe(ferrum) copper==Cu(cuprum) lead==Pb(plumbum)铁= =铁(铁)的铜= =铜(缓蚀剂)引线= =铅(铅)A complete listing of the elements may be found in T able 1.一个完整的上市的元素可以被发现于表1。
Beginning in the late seventeenth century with the work of Robert Boyle, who proposed the presently accepted concept of an element, numerous investigations produced a considerable knowledge of the properties of elements and their compounds1. In 1869, D.Mendeleev and L. Meyer, working independently, proposed the periodic law. In modern form, the law states that the properties of the elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers. In other words, when the elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number, elements having closely similar properties will fall at definite intervals along the list. Thus it is possible to arrange the list of elements in tabular form with elements having similar properties placed in vertical columns2. Such an arrangement is called a periodic在十七世纪后期开始的工作罗伯特·波以耳,提出当前一个元素的接受和运用的概念,产生了可观的知识大量调查的特性及其compounds1元素。
在1869年,D.Mendeleev和l .迈耶,独立工作能力,提出了周期性的律法。
在现代形式,法律规定的特性是周期函数的元素的原子编号。
换句话说,当元素的顺序列出增加原子序数、元素有相近的财产落在了明确的间隔沿名单。
由此,我们有可能安排的名单表格元素的元素有相似的性质columns2放置在垂直。
这样的安排被称为一个周期Each horizontal row of elements constitutes a period. It should be noted that the lengths of the periods vary. There is a very short period containing only 2 elements, followed by two short periods of 8 elements each, and then two long periods of 18 elements each. The next period includes 32 elements, and the last period is apparently incomplete. With this arrangement, elements in the same vertical column have similar characteristics. These columns constitute the chemical families or groups. The groups headed by the members of the two 8-element periods are designated as main group elements, and the members of the other groups are called transition or inner transition elements.每个水平排的元素构成一段时间。
但应该注意的是,不同长度的时期。
这是一个非常短只包含二元素,后面跟着两个短的每8元素,然后两个长期的18个元素组成。
下一个阶段包括32元素,最后一期明显不完整的。
这样的安排、元素在同一垂直柱有相似的特点。
这些圆柱构成化学家庭或组。
这个团体的成员为首的两8-element时期为主要集团指定的元素,其他组的成员被称为过渡或内在过渡元素。
In the periodic table, a heavy stepped line divides the elements into metals and nonmetals. Elements to the left of this line (with the exception of hydrogen) are metals, while those to the right are nonmetals. This division is for convenience only; elements bordering the line —the metalloids-have properties characteristic of - both metals and nonmetals. It may be seen that most of the elements, including all the transition and inner transition elements, are metals.在元素周期表,沉重的走线分元素到金属以及非金属矿物等。
元素的左本线(除氢)是金属,而那些右边是非金属矿物等。
这个师为方便使用,metalloids-have接壤的line-the元素的性质特点——两者都是金属以及非金属矿物等。
这可以被看见,大部分的元素,包括所有的过渡和内在过渡元素,是金属。
Except for hydrogen, a gas, the elements of group IA make up the alkali metal family. They are very reactive metals, and they are never found in the elemental state in nature. However, their compounds are widespread. All the members of the alkali metal family, form ions having a charge of 1+ only. In contrast, the elements of group IB —copper, silver, and gold—are comparatively inert. They are similar to the alkali metals in that they exist as 1+ ions in many of their compounds. However, as is characteristic of most transition elements, they form ions having other charges as well.除了氢气、气体、集团的元素是构成了碱金属的家庭。