斯伦贝谢petrel教程3
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:3.18 MB
- 文档页数:41
斯伦贝谢公司Petrel & Eclipse授权教程
1.连接校园网络;
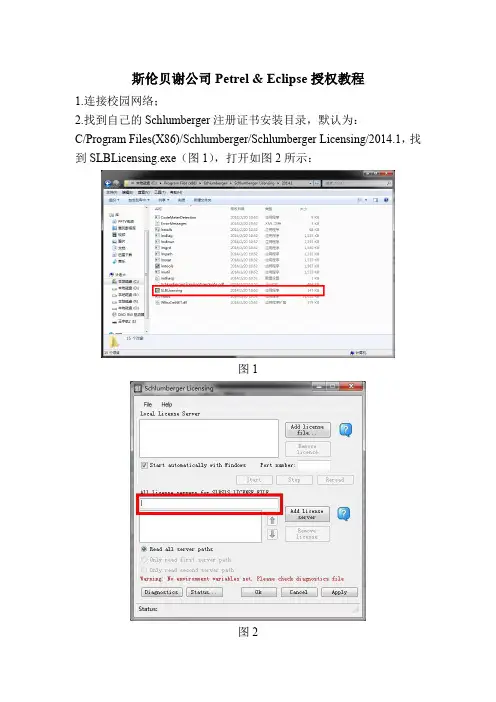
2.找到自己的Schlumberger注册证书安装目录,默认为:
C/Program Files(X86)/Schlumberger/Schlumberger Licensing/2014.1,找到SLBLicensing.exe(图1),打开如图2所示:
图1
图2
3.在图2红色框区域输入:*************.222.72,然后点击Add License server,结果如图3所示
图3
然后依次点击Apply、Ok,证书服务加载完毕。
4.打开电脑中Petrel安装目录,默认为:
C/Program Files/Schlumberger/Petrel 2014,找到Petrel.exe,如图4所示。
图4 5.打开软件,出现如图5界面。
图5
6.选中如图红色区域,点击ok,即可打开软件,如下图所示。
图6
7.大部分用户在这一步即可完成软件的授权过程,如按照上述步骤无法完成,可尝试以下操作:
(1)关闭电脑防火墙;
(2)设置hosts文件,具体操作为:
修改电脑里C/windows/system32/drivers/etc 目录下的hosts文件,里面加一条:
118.228.222.72 DELL-PC。




Petrel操作技巧Petrel 地震地质解释和建模使⽤技巧2015斯伦贝谢科技服务(北京)有限公司Copyright Notice2015 Schlumberger. All rights reserved.No part of this manual may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or translated in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying and recording, without the prior written permission of Schlumberger Information Solutions, 5599 San Felipe, Suite 1700, Houston, TX 77056-2722.DisclaimerThe License Agreement governs use of this product. Schlumberger makes no warranties, express, implied, or statutory, with respect to the product described herein and disclaims without limitation any warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose. Schlumberger reserves the right to revise the information in this manual at any time without notice.Trademark InformationSoftware application names used in this publication are trademarks of Schlumberger. Certain other products and product names are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective companies or organizations.⽬录1.1 斜井井轨迹在Well Section窗⼝中的4种投影⽅式原理 (4)1.2 Well section下打印连井剖⾯图 (8)1.3 well section下设置隐含的边界显⽰单曲线道局部充填 (11)1.4 well section下井上解释断层断距显⽰ (15)1.5 在指定深度范围内修改测井曲线 (18)1.6 Petrel和Excel⼀体化快速⽣成测井解释成果表 (19)1.7 Petrel2014如何加载TVD/TVDSS索引的测井曲线 (23)1.8 对不同井的测井曲线使⽤不同的算法进⾏粗化 (25)1.9 拼接不同深度段的测井曲线 (27)1.10 每种沉积相的测井曲线范围统计 (29)1.11 3Dwindow中如何连接well top (32)1.12 Petrel中如何快速⽣成断层Polygon (33)1.13 surface上对特定polygon范围进⾏单独赋值 (34)1.14 如何实现多边形的合并Merge Polygons (37)1.15 Petrel如何在Surface上显⽰图⽚ (40)1.16 如何将多个surface对应的的平均值同时输出到excel表格中 (42) 1.17 根据两个Surface⽣成TST和TVT Map (43)1.18 如何将Well heads在Surface附近显⽰ (45)1.19 在Make surface的时候如何将结果往边界多边形外扩⼀些 (47) 1.20 如何计算某个zone内饱和度曲线的加权平均值 (50)1.21 如何由离散相曲线计算砂体或薄互层的厚度 (51)1.22 如何批量⽣成zone的厚度图 (53)1.23 计算特定井和特定Zone的砂层厚度 (54)1.24 批量计算单井上每个zone中砂岩段的数量 (56)1.25 ⽤曲线截断创建离散的净厚度图 (60)1.26 地震体三维渲染显⽰不清晰时的解决⽅法 (64)1.27 如何使⽤⽤户⾃定义边界切割地震体 (65)1.28 三维显⽰沿层切割地震体 (67)1.29 如何在Petrel中如何往已有的Survey中加载相邻位置的地震体 (68) 1.30 如何计算多⼝井周层⾯属性统计值 (71)1.31 Petrel中地震Vintage的管理 (76)1.32 Petrel中如何按地震⼯区加载⼆维地震数据 (80)1.33 Petrel 2014中合成地震记录显⽰设定 (84)1.34 Petrel 2014中对于切地震剖⾯的快速设置 (87)1.35 Petrel中如何对地震数据进⾏抽稀 (88)1.36 Petrel中如何沿井轨迹提取地震数据的振幅 (89)1.37 Petrel中如何实现地震解释层位的合并 (90)1.38 如何加载2D数据 (92)1.39 依据Horizon和Fault剪切地震数据体 (93)1.40 如何在Petrel移动地震数据体 (94)1.41 按⽤户⾃定义范围到处2D地震测线 (96)1.42 Petrel如何加载信息缺失的⼆维地震数据 (101)1.43 将Jason 的⼦波加载到Petrel中 (105)1.44 如何在Petrel中提取可靠的⼦波 (107)1.45 如何在Function window按照某⼀曲线的属性显⽰交会图 (109) 1.46 如何在Function window按照深度筛选交会图 (110)1.47 如何⽤Zone log过滤直⽅图 (113)1.48 如何合并多井的Checkshot数据到⼀个⽂件夹 (114)1.49 Petrel中如何做好井震对⽐ (116)1.50 如何将井分层与矫正后的Vo⾯均显⽰在X,Y,V域 (123)1.51 如何批量输出井斜 (125)1.52 使⽤部分井进⾏Data Analysis (126)1.53 Petrel 中如何批量修改井类型 (130)1.54 如何加载多⼝井轨迹在⼀个⽂件 (131)1.55 Petrel⼯区井的X坐标没区带号 (134)1.56 井坐标为经纬度如何加载 (135)1.57 ⼀种简单安全的⽅式添加⾃定义井符号 (136)1.58 Petrel中蚂蚁体的运算技巧 (140)1.59 Petrel蚂蚁体介绍及参数设置 (144)1.60 如何利⽤蚂蚁体提取⼩断裂 (151)1.61 如何⽣成Azimuthal Map (155)1.62 如何在Petrel中加载经纬度的点数据 (157)1.63 使⽤⾃定义速度函数进⾏时深转换 (159)1.64 在Function Window中如何如⽤第三变量调整数据点的颜⾊ (161) 1.65 Petrel中如何创建客户化岩性符号 (162)1.66 Petrel如何按宽度显⽰岩性 (164)1.67 如何批量移动断层 (168)1.68 如何⽣成⽤户⾃定义的离散属性⾯ (170)1.69 如何在Petrel中有效地组织数据 (173)1.70 如何在Petrel中⾃动形成断层多边形 (175)1.71 如何使⽤Clean Project History选项清理⼯区历史 (177)1.72 神经⽹络分类中的主成分分析 (178)1.73 如何对井⼀定范围外的⽹格粗化的同时保留井附近的原始⽹格 (182) 1.74 以⼀种⾃定义的⽅式进⾏⽹格粗化 (186)1.75 如何在现有速度模型中加⼊其他速度异常体 (188)1.76 Petrel2014 Structural Framework⼯区保存错误解决⽅案 (189)1.77 剥蚀带的建模技术 (191)1.78 在属性建模中使⽤Local varying azimuth (192)1.79 多条⼆维测线速度数据建⽴速度模型 (195)1.80 如何对属性模型进⾏切割或者局部更新 (203)1.81 ⼀个简单的⼯作流计算⼏个层⾯的均值并输出 (205)1.82 如何⽤Petrel Workflow快速整理层位数据 (207)1.83 如何⽤Petrel Workflow快速整理断层多边形数据 (210)1.84 运⽤workflow批量⽣成变化变程的属性模型 (211)1.85 运⽤Workflow统计地震测线长 (214)1.86 运⽤Workflow统计井间距离 (215)1.87 运⽤Workflow批量⽣成断层与上下盘层位交线 (218)1.88 Petrel全新的断层解释-建模⼀体化⼯作流 (220)1.89 使⽤Inspector⼯具修改模型中单个⽹络的属性 (221)2.1 PetroMod中如何优化断层在剖⾯上的形态 (223)2.2 PetroMod 中如何进⾏油源对⽐ (225)2.3 PetroMod模型在Petrel中显⽰ (228)3.1 GeoX中如何客户化输出GeoX Report到Excel中 (230)3.2 GeoX新许可设置流程 (237)1.1 斜井井轨迹在Well Section窗⼝中的4种投影⽅式原理在Petrel的连井剖⾯窗⼝(Well Section Window)中显⽰斜井轨迹是⼀个⼗分实⽤的功能。

BTEC INTERNATIONAL LEVEL2QUALIFICATIONS IN ENGINEERINGUNIT3:INVESTIGATING AN ENGINEERING PRODUCTUnit 3: Investigating an Engineering ProductDelivery guidanceApproaching the unitThis unit is mandatory for all sizes and pathways other than the Award size (where it is an optional unit) and should be delivered early in a programme, as a good knowledge and understanding of engineering materials and processes will support learning in many other units.The focus of this unit is for learners to investigate and analyse the materials and processes used in the component parts of engineering products. Learners should be given full access to a range ofengineering products that are made from at least two component parts and from different materials.For example, for an adjustable wrench you may ask learners to focus on the main body and the handle cover, for a low voltage circuit tester you may ask learners to focus on the spike and the end cap and for an emergency stop unit you may ask learners to focus on the push button and the surfacemounting case. All of these engineering products have at least two component parts that aremanufactured using different processes and made using different materials. It would be ideal iflearners were able to disassemble the engineering products so they can see all of the details and how they are assembled, although it is recognised that this may be difficult. Learners must be provided with support to understand the purpose and function of each chosen engineering product as well as the chosen component parts of each engineering product. This understanding is essential and a really important factor that enables learners to carry out a contextual investigation and analysis of thereasons why the specific materials and specific processes have been used to make them.Nonetheless, the delivery approach should be mainly practical and should encourage learners to develop their knowledge of how to use various engineering processes (plus the related practical skills) and how to work with various materials when making a range of component parts. This background understanding will support learners to recognise why certain materials and processes are the most suitable for making a range of component parts. Again, it would be ideal if learners could actually make some of the component parts from the chosen engineering products, although it is again recognised that this may be difficult.The key to learner success in this unit is to bring together the practical knowledge of materials and processes with a contextual understanding of why the materials have been used in the component parts of engineering products and why the processes have been used to make the component parts.You could use a range of delivery methods in this unit, such as:•discussions - class and small group•individual or group presentations - covering engineering materials/properties,engineering processes/features and scales of production•demonstrations - covering the safe preparation, set-up and use of differentengineering processes to machine, shape, manipulate, cast, mould and joindifferent engineering materials•engineering product/component part analyses - illustrating contextual information about why the specific materials and specific processes have been used to makethem•worksheets and example assessments - to confirm knowledge and understanding.You can involve local employers in the delivery of this unit if there are localDelivering the Learning aimsLearning aims A and BThe most appropriate approach when delivering the Learning aims for this unit is to consider how the Topics (A1, A2 etc) from the Content section in the unit specification link together.An integrated rather than a sequential approach to delivery would be most appropriate.You could start most of the lessons by introducing some materials and their properties and some processes and their key features, as well as the different scales of production (at appropriate points). It will be important to ensure full coverage of Topics A1 to A4 and Topics B1 to B5 in the Content section of the Unit 3 specification during these presentations. Use some easily accessible engineering products (from those available in the centre, for example the Sample Pearson Set Assignment Brief for Unit 3 includes an engineers’ vice) to explain the reasons for the selection and application of the materials in the component parts of the engineering products and the reasons for the selection and application of the processes used when making the component parts of the engineering products.The bulk of the delivery for this unit should focus on the learners actually using various engineering processes (plus the related practical skills) and various materials to make a range of component parts.Demonstrate to learners how to safely use different engineering processes to, for example (not an exhaustive list):•drill, turn and mill a carbon steel cap (Topics B1, A1, A4 and B5)•shear, bend and fold an aluminium container lid (Topics B2, A1, A4 and B5)•vacuum form the cover for a LDPE key pad (Topics B3, A2, A4 and B5)Learners should be given time to safely use the different engineering materials and processes to make the component parts of engineering products. Learners will gain most of their knowledge and understanding for this unit from this practical experience of using materials and processes and the Tutor should try to ensure the fullest coverage of Topics A1 to A4 and Topics B1 to B4 in the Content section of the Unit 3 specification during these activities. The Tutor should also emphasise to learners that safety is vital but that they are not looking for accuracy or efficiency when making the component parts; the really important aspect of this practical learning is to recognise the characteristics of different materials and what different processes can do.Central to the required learning is the review activities to contextualise the understanding. Learners should already know the function and purpose of the component parts they have made and they should then assess why the materials used were suitable and why the processes used were suitable.After this it would be appropriate to move into specific investigative activities related to the component parts of engineering products. Tutors should provide a range of physical examples of engineering products that are made from at least two component parts and from different materials (the engineering products should be different from those shown to learners before but should be of a similar level of complexity). Learners could move around on a carousel and complete a template worksheet that requires them to carry out an analysis activity for the two specified component parts of each engineering product. The analysis activity could be based on the Sample Pearson Set Assignment Brief but for different engineering products. Before this the Tutor needs to emphasise to learners that they must, during the analysis activities: a) link the purpose and function of each component part to the favourable properties of the specificmaterial/s used; and b) consider details such as the materials, features, purpose and function of each component part and the scales of production required when reviewing the specific processes used. The outcomes of these activities could be discussed in class and small group sessions to confirm knowledge and understanding and any gaps in learning.This type of delivery approach will provide an enjoyable and practical ‘hands-on’ knowledge and understanding of engineering materials and processes and why they are used for certain engineering products. A mainly theoretical and classroom-based approach to delivery is unlikely to motivate learners and may not lead to learning that can be applied during other units.Assessment modelAssessment guidanceThe unit is assessed by a Pearson Set Assignment (PSA). The assessment is set by Pearson and must be taken under controlled conditions before it is marked by Tutors.There are 30 guided learning hours (GLH) assigned to the unit, of which 4 hours will be required for assessment.Pearson Set Assignments are available from September each year and are valid for one year only. Delivery must cover all of the Content in the unit specification and prepare learners to takethe PSA and produce evidence that meets the requirements laid out in the Assessmentcriteria and Essential information for assessment decisions sections of the unitspecification. Sample Assessment Materials are available on the Pearson website. Thesecan be used or adapted to help learners prepare for assessment.Getting startedThis gives you a starting place for one way of delivering the unit, based around the recommended assessment approach in the specification.Details of links to other BTEC units and qualifications, and to other relevant units/qualificationsThis unit links to:•Unit 6: Engineering Materials•Unit 8: Machining Techniques•Unit 9: Engineering Design•Unit 10: Engineering Fitting and Assembly•Unit 13: Operations and Maintenance of Mechanical Systems and Components.ResourcesIn addition to the resources listed below, publishers are likely to produce Pearson-endorsed textbooks that support this unit of the BTEC International L2 qualifications in Engineering. Check the Pearson website at: (/endorsed-resources) for more information as titles achieve endorsement.For this unit, learners must have access to:• a workshop environment and tools, equipment and resources as required so that learners can safely use different engineering processes to machine, shape, manipulate, cast, mould and join different engineering materials to make the component parts of engineeringproducts•physical examples of a range of engineering products with at least two component parts - the component parts for each engineering product should be made from different materials and manufactured using different processes.TextbooksClarke, S. et al. (2012) BTEC First in Engineering Student Book, Harlow: Pearson Education, ISBN 9781446902431Godfrey, N. and Wallis, S. (2004) GCSE Engineering, Cheltenham: Nelson Thornes, ISBN 9780748785513Tooley, M. (2010) BTEC First Engineering, 2nd Edition, Oxford: Newnes, ISBN 9781856176859 Tooley, M. et al. (2008) Edexcel Diploma:Engineering Level 2 Higher Diploma Student Book, Oxford: Heinemann, ISBN 9780435756208Tooley, M. (2002) Engineering GCSE, Oxford: Newnes, ISBN 9780750665766Wallis, S. et al. (2010) BTEC First Engineering, London: Hodder Education, ISBN 9781444110524 Websites/bitesize/guides/z8kmcj6/revision/3 - metals and alloys/plastic4 - polymers/composite-materials/ - composites/equip1/equipex1.htm - materials and processes/processes/processes_home/process.cfm - processesPearson is not responsible for the content of any external internet sites. It is essential for tutors to preview each website before using it in class so as to ensure that the URL is still accurate, relevant and appropriate. We suggest that tutors bookmark useful websites and consider enabling students to access them through the school/college intranet.。
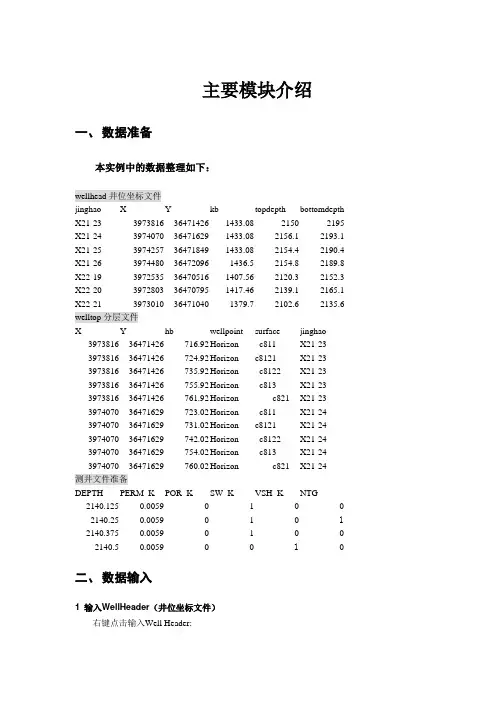
主要模块介绍一、数据准备本实例中的数据整理如下:wellhead井位坐标文件jinghao X Y kb topdepth bottomdepth X21-233973816364714261433.0821502195 X21-243974070364716291433.082156.12193.1 X21-253974257364718491433.082154.42190.4 X21-263974480364720961436.52154.82189.8 X22-193972535364705161407.562120.32152.3 X22-203972803364707951417.462139.12165.1 X22-213973010364710401379.72102.62135.6 welltop分层文件X Y hb wellpoint surface jinghao 397381636471426-716.92Horizon c811X21-23397381636471426-724.92Horizon c8121X21-23397381636471426-735.92Horizon c8122X21-23397381636471426-755.92Horizon c813X21-23397381636471426-761.92Horizon c821X21-23397407036471629-723.02Horizon c811X21-24397407036471629-731.02Horizon c8121X21-24397407036471629-742.02Horizon c8122X21-24397407036471629-754.02Horizon c813X21-24397407036471629-760.02Horizon c821X21-24测井文件准备DEPTH PERM_K POR_K SW_K VSH_K NTG 2140.1250.00590100 2140.250.0059010 1 2140.3750.00590100 2140.50.005900 1 0二、数据输入1 输入WellHeader(井位坐标文件)右键点击输入Well Header:文件类型里选:well heads(*.*)2 输入Well Tops(分层文件):右键点击Well Tops文件夹并选择Import (on Selection);文件类型里选:Petrel Well Tops (ASCII)3 输入输入Well Logs右键点击Wells 文件夹,选择Import (on Selection); 文件类型:well logs(ASCII)input Data logs specify logs to be load 加载per,perm,sw vash,ntg 等数据。

Petrel软件实例操作流程目录第一章Petrel简介一、安装并启动Petrel (01)二、界面介绍 (02)第二章Petrel处理流程介绍一、数据准备 (07)二、断层建模 (14)三、Pillar Gridding (22)四、Make H orizon (27)五、深度转换(可选步骤) (32)六、Layer ing (34)七、建立几何建模 (35)八、数据分析 (36)九、相建模 (42)十、属性建模 (51)十一、体积计算 (60)十二、绘图 (64)十三、井轨迹设计 (66)十四、油藏数值模拟的数据输入和输出 (69)第一章Petrel简介一、安装并启动Petrel把安装盘放入光驱,运行Setup.exe程序,根据提示就可以顺利完成安装,在安装的过程中同时安装DONGLE的驱动程序,安装的过程中不要把DONGLE插入USB插槽,安装完毕,再插入DONGLE,如果LICENSE过期,请和我们技术支持联系。
然后按下面的顺序打开软件。
1. 双击桌面上的Petrel图标启动Petrel。
2. 如果是第一次运行Petrel,在执行Petrel运行前会出现一个Petrel的介绍窗口。
3. 打开Gullfaks_Demo项目。
点击文件>打开项目,从项目目录中选择Gullfaks_2002SE.pet。
二、界面介绍(一)、菜单条/ 工具条与大多数PC软件一样,Petrel软件菜单条有标准的“文件”、“编辑”、“视图”、View等下拉菜单,以及一些用于打开、保存project的标准工具,在菜单条下面的工具条里还有更多工具。
在Petrel里,工具条还包含显示工具。
此外在第二个工具条里还有位于Petrel 项目窗口的右端的按钮,它具有附加的Petrel相关的功能。
后面的工具条称为功能条,这些工具是否有效取决于选择进程表中的哪个进程。
操作步骤1.点击上面工具条中的每一项看会出现什么。
你可以实践一些更感兴趣的选项。
Learn log地质建模工作流程:地震解释地质对比测井曲线加载断层模型测井曲线处理、解释油组构造模型岩石物性曲线岩性模型岩石物理模型成果输出及地质分析功能键:1、ctrl+Shift+鼠标左键放大缩小图形。
鼠标左键+上滚轮(鼠标中键),放大缩小图形。
2、ctrl+鼠标左键图形平移上滚轮(鼠标中键),图形平移3、鼠标左键图形旋转建新工区lxj1 .pet一、建井文件夹new well folder在Insert的new folders→点New Well Floders1、加头文件在lxj1.pet Input窗下,右健点Wells→选Import (on select)…出现Import File输入窗中,点Petrel projects –-> cha19 → Well-data目录, 选文件名:文件类型:well heads(*.*)文件格式例子:WellName X-Coord Y-Coord KB TopDepth BottomDepth Symbol0 2534 Oil34/10-A-15 61757.5 30147.1 23.6 0 3133 Gas34/10-A-21 62165.3 32653.8 12.6 0 2431 Dry34/10-A-27 66552.1 31629.3 23.6 0 2986 MinorOil ......按打开,出现Import Well Heads窗,图如下:在窗口中参考Header info提供的列位置,填好列号,例如井名Name 1列X-坐标X-coordina 2列Y-坐标Y-coordina 3列补心Kelly bushing 4列井符号Well symbol 7列顶界深Top depth 5列底界深Bottom depth 6列在Extend well处选顶扩展或底扩展多少米,例如20米。
按OK,确定。
如果有不合适的井数据,会有提示指出,表示那些井不被加入。