船舶漆的介绍
- 格式:docx
- 大小:61.04 KB
- 文档页数:2




Marine Paint GuideUpdated: 16/12/141. Definitions and abbreviationsTOLERANCESThe numerical information quoted on marine product datasheets has been derived from laboratory test data obtained under controlled conditions for the products described. Whilst every effort has been made to ensure accuracy, this information will be subject to minor variations obtained in normal manufacturing tolerances, and any fluctuations in ambient conditions during the application and curing periods.GLOSS LEVELTypical gloss values have been determined in accordance with ISO2813:1994/ Corr 1:1997 using a 60° gloss head or, for North America,ASTM-D-523. The categories used in the data sheet are:Finish (sheen)Gloss (60°) headMatt0-15Eggshell16-30Semi-gloss31-60Gloss61-85High gloss>85In practice, the level of sheen and surface finish will be dependent upon a number of factors, including application and the condition of the surface to be overcoated.DRY FILM THICKNESS(DFT)The measured thickness of the final dried film applied to the substrate.WET FILM THICKNESS (WFT)The initial thickness of the wet coating applied to the substrate.VOLUME SOLIDSThe volume solids figure given on the product data sheet is the percentage of the wet film, which remains as the dry film, and is obtained from a given wet film thickness under specified application method and conditions. These figures have been determined under laboratory conditions using a modification of the test method described in ISO 3233:1998/Corr 1:1999 –Determination of Volume Solids by Measurement of Dry Film Density. The modification is technically equivalent involving the use of slightly smaller glass slides. For North America, volume solids are measured by ASTM-D-2697 (1986) which determines the volume solids of a coating using the recommended dry film thickness of the coating quoted on the product data sheet, and a specified drying schedule at ambient temperature, i.e. 7 days at 25°C + 1°C.DRYING TIMEThe drying times quoted in the product data sheet have beendetermined in the laboratory using a typical dry film thickness, the ambient temperature quoted in the relevant product data sheet, and the appropriate testmethod, i.e.Touch Dry (ISO 1517 - 1973) - The surface drying state of a coating when Ballotini (small glass spheres) can be lightly brushed away without damaging the surface of the coating.Hard Dry (ISO 9117-1990) - The condition of the film in which it is dry throughout its thickness, as opposed to that condition in which the surface of the film is dry but the bulk of the coating is still mobile.This through drying state is determined by the use of a “mechanical thumb” device “in situ”at the temperature quoted.In North America the Touch Dry, Hard Dry and Re-coat times are determined in accordance with ASTM-D-1680 (1995) using sections7.5, 7.7 and 7.8 respectively.The drying times achieved in practice may show some slight fluctuation,particularly in climatic conditions where the substrate temperature differs significantly from the ambient air temperature and because of variations in practical dry film thickness.OVERCOATING INTERVALThe product data sheet gives both a “minimum” and a “maximum”overcoating interval and the figures quoted at the various temperatures are intended as guidelines, consistent with good painting practices.Certain terms require elaboration as follows:MinimumThe “minimum overcoating time” quoted is an indication of the time required for the coating to attain the necessary state of dryness and hardness to allow the application of a further coat of paint without the development of any film irregularities such as lifting or loss of adhesion of the first coat (ASTM-D-1640). It assumes:(i)the coating has been applied at the normal recommended thickness.(ii)environmental conditions both during and after application were as recommended forthat particular coating, especially in respect of temperature, relative humidity andventilation.(iii)the paint used for overcoating is suitable for that purpose.(iv)an understanding of the “method of application”. For example, if a coating can be applied by both brush and spray it is expected that overcoating may be carried outmore rapidly if sprayed and it is the “lowest” figure that is quoted.If the above conditions are not met, the quoted minimum overcoating times are liable to variation and will invariably have to be extended.MaximumThe “maximum overcoating time” indicates the allowable time period within which overcoating should take place in order to ensure acceptable intercoat adhesion is achieved.ExtendedWhere an “extended” overcoating time is stated, the anticipated level of intercoat adhesion can only be achieved if:(i) the coating has been applied in accordance with good painting practices and at the specified film thickness.(ii) the aged coating has the “intended” surface characteristics required for long term overcoatability. For example, an over- applied epoxy MIO may not have its usual “textured”surface and will no longer be overcoatable after ageing unless it is abraded.(iii) the coating to be overcoated must be intact, tightly adherent, clean, dry and free from all contaminants. For example, the leached layer on an antifouling coating is usually porous and friable and must be removed to provide the necessary surface for overcoating.(iv) coatings having a glossy surface which could have a detrimental effect on the adhesion of subsequent coats should be treated by light surface abrasion, sweep blasting, or other suitable processes which will not cut through or detract from the performance of the underlying coating.(v) in some situations, and with specific products, it may be necessary to high pressure fresh water wash prior to overcoating.It should be recognised that the level of intercoat adhesion obtained is also dependent upon the chemistry of the “topcoat”. By their nature,primers or undercoats will have inherently better adhesion than finish coats.The measurement of ultimate “adhesion strength” can often be a difficult process, and interpretation of results can be subjective. Excellent adhesion does not necessarily mean good performance, nor does relatively poor adhesion necessarily mean poor performance.Although the adhesion of coatings applied to aged / cured coatings may be deemed satisfactory for the specified end use, actual numerical values obtained for adhesion may be less than with coatings applied within“minimum / short” overcoating intervals.FLASH POINTThe minimum temperature at which a product, when confined in a Setaflash closed cup, must be heated for the vapours emitted to ignite momentarily in the presence of aflame (ISO 3679:1983). In North America Flash Point is determined in accordance with ASTM-D-3278(1996).VOLATILE ORGANIC COMPOUND (VOC)VOC content is the weight of volatile organic compounds which participate in atmospheric photochemical reactions for litre of paint.Legislative requirements differ from country to country, and from region to region, and are constantly being reviewed. Values quoted for VOC on the product data sheet are calculated from the product formulation or have been determined practically in the laboratory using one of the following published test methods:-UK-PG6/23(92), Appendix 3This test method was published in February 1992, by the UK Department of the Environment as part of the Secretary of State’s Guidance Note(PG6/23(92)), issued as a guide to local authorities on the appropriate techniques to control air pollution, in order to achieve the objectives laid down in the Environmental Protection Act 1990. The method described in Appendix 3 includes guidance on the method of meeting VOC of coatings, as applied to demonstrate compliance with Clause 19 of the Guidance Note.USA - EPA Federal Reference Method 24The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), published procedures for demonstration of compliance with VOC limits under Federal Reference Method 24 “The Determination of Volatile Matter Content, Density,Volume Solids and Weight Solids of Surface Coatings”. This method was originally published in the Federal Register in October 1980, and coded40 CFR, Part 60, Appendix A, and amended in 1992 to incorporate instructions for dealing with multi-component systems, and a procedure for the quantitative determination of VOC exempt solvent.It is recommended that users check with local agencies for details of current VOC regulations, to ensure compliance with any local legislative requirements when proposing the use of any coating.EU Council Directive 1999/13/ECThe purpose of this directive is to prevent or reduce the direct and indirect effects of the emission of volatile organic compounds into the environment, mainly into air, and the potential risks to human health. In essence the directive sets emission limits for coatings users(installations), these differ by application and for old/new installations. For the purpose of the Directive a Volatile Organic Compound (VOC) is defined as:“Any organic compound having at 293.15 K a vapour pressure of 0.01kPa or more, or having a corresponding volatility under the particular conditions of use.”WORKING POT LIFEThe maximum time during which the product supplied as separate components should be used after they have been mixed together at the specified temperature.The values quoted have been obtained from a combination of laboratory tests, and application trials, and refer to the time periods under which satisfactory coating performance will be achieved.Application of any product after the working pot life has been exceeded will lead to inferior product performance, and must NOT be attempted,even if the material in question appears liquid in the can.SHIPPING WEIGHTThe shipping weights quoted are typical values and refer to the total weight of the product supplied plus the weight of the can and are for guidance only. They will vary according to the specific colour. These weights are quoted for individual components and do not take into account any additional packaging weight attributable to cartons, etc. Factory supplied material will show differences to the figures quoted on the product Technical Data Sheet.SHELF LIFEThe shelf life quoted on the product datasheets is generally a conservative value, and it is probable that the coating can be applied without any deterioration in performance after this period has elapsed.Exceeding the shelf life of a product does not necessarily render it unusable. However, if the specified shelf life has been exceeded, it is recommended that the condition of the material is checked before any large scale application is undertaken using materials beyond the quoted shelf life. If this occurs, contact International for advice on how to progress.。

船舶涂料配套手册一、引言船舶涂料是用于船舶表面保护和装饰的涂料,其性能直接影响到船舶的耐久性和外观效果。
本手册主要介绍船舶涂料的选择、施工和维护,以便船舶使用者能够正确选择和使用船舶涂料,保障船舶的使用寿命和外观。
二、船舶涂料的分类1.底漆:底漆是船舶涂装中的第一道涂层,用于表面预处理,增强涂层附着力和防腐性能。
2.面漆:面漆是船舶涂装的最后涂层,用于增强船舶的美观性和保护作用。
3.防腐涂料:防腐涂料用于保护船舶金属材料免受腐蚀。
4.防污涂料:防污涂料用于减少船舶船底的附着物,减少摩擦阻力,提高船舶的航行性能。
三、船舶涂料的选择原则1.适应环境:根据船舶使用环境选择涂料,如沿海航行、淡水航行、高温环境、低温环境等。
2.适应材料:涂料的基材应适应船舶的材料,如钢铁船、铝合金船、玻璃钢船等。
3.满足性能要求:根据船舶的使用要求选择涂料,如耐水性、耐酸碱性、耐热性、耐候性等。
4.节能低碳环保:选择符合环保要求的涂料,减少对环境的污染。
四、船舶涂料的施工原则1.基材处理:船舶涂装前必须对基材进行适当处理,包括除锈、抛光、清洗等,以保证涂料的附着力。
2.涂装系统:按照涂料供应商提供的建议,选择符合要求的涂装系统,包括底漆和面漆。
3.合理施工:根据涂料的施工要求,控制涂刷厚度、干燥时间等参数,确保涂料施工的质量。
五、船舶涂料的维护保养1.定期检查:定期对船舶涂层进行检查,发现问题及时修补,防止涂层老化和脱落。
2.防潮防晒:船舶在非使用期间应确保船舶涂层免受露天曝晒和潮湿环境的侵蚀。
3.规范操作:船舶使用人员应规范操作,避免对涂层造成机械损伤。
六、船舶涂料的常见问题及解决方法1.泛白:涂料表面出现白色斑点,可能是涂料中含有过多的湿气。
解决方法是检查涂料配方,减少湿气含量。
2.脱落:涂层脱落,可能是涂装前基材处理不当,或是涂料与基材不相容。
解决方法是加强基材处理工作,选择相容性良好的涂料。
3.龟裂:涂料出现细小龟裂,可能是施工压力不均匀导致的。

船是海洋的出航专用工具,要想一艘船可用的长期,就务必要在船的不一样部位涂上不一样的漆料,才能够让船的使用寿命更为长期,可是并不是所有的地区都应用同样的漆料,要不然会出现反实际效果,当期我来教你船舶油漆种类和主要用途,期待对您有协助!1.最先是船壳位置和人的全面发展,要刷油漆的情况下,一般应用船舶红丹防锈漆.各色各样的醇酸船壳漆和船舶亚克力聚氨酯漆,抗腐蚀并且不容易非常容易划花。
2.船舶氯化橡胶漆也常常能够工程施工用在船只流槽.船壳.人的全面发展等位置的防腐蚀。
3.配套设施的正中间漆一般是应用船舶环氧树脂云铁正中间漆。
面漆一部分能够应用船只环氧树脂环氧底漆.船只环氧树脂磷酸锌面漆及无机物氯化镁锌面漆等。
4.船壳.主甲板及人的全面发展:广泛采取的环氧树脂油漆和聚氨酯漆或是是醇酸船壳油漆,正中间漆一般应用环氧树脂云铁正中间漆,面漆能够应用环船舶氧环氧底漆.环氧树脂磷酸锌面漆还是醇酸面漆。
5.外船的流槽一部分:钛酸异丙酯塑胶油漆.环氧树脂云铁正中间漆和船舶环氧树脂环氧底漆等。
6.船下一部分:船下一部分一般要考虑到防腐蚀和耐污因此广泛应用船舶环氧树脂沥清防污漆。
7.运输船的客舱用平常的两次环氧树脂漆料就充足了.如果是成品油批发轮,货油仓就需要用对应的特涂漆料了.8.发动机舱及人的全面发展內部就用平常的醇酸漆料充足了.人的全面发展及其舱口,面漆用一般环氧树脂漆料,油漆可挑选聚氨酯材料或是环氧树脂油漆。
对于船的防护空舱,则必须应用环氧树脂类漆料,那样才能够才算得上恰当的刷油漆分派!总而言之给船刷油漆是一件不易的事儿,不一样的位置要考虑到不一样的受浸蚀水平这些,全是你采用不一样漆料的参照,最终,想要知道大量的有关漆料专题讲座的文章内容会在人们的官在网上开展查看,这也是当期的船舶油漆种类和主要用途的所有内容,感谢您的观看!(船舶油漆种类和主要用途)如果还想了解更多瓷砖知识可以关注欧神诺。
欧神诺瓷砖,高端瓷砖定制家,23年品质坚守,2000万高端家庭的选择,装修用好砖,就选欧神诺瓷砖.。

船舶管系油漆标识颜色说明Paint colours for marine pipes and their identification symbols一、管路的油漆颜色与所在舱室的颜色相同,识别符号用不同颜色的油漆涂剧,以表示管内流体的性质,识别符号表示液体的用途或压力,蒸汽类管路和识别符号油漆的涂刷。
识别符号的颜色不应与管路颜色相问,如遇相同或相近时,应将识别符号涂在白色辅助圈上,辅助圈的宽度应比识别符号每边加宽50mm。
二、管路和识别符号的油漆颜色:卫生水管路与舱室颜色相同,舷外水冷印管路与舱室颜色相同,压载舱管路与舱室颜色相同,液体燃料运行管路与舱室颜色相同,领体燃料回油或油管路与舱室颜色相同,滑油运行管路与舱室颜色相同,污油管路与验室颜色相同,传动管路应与舱室颜色相同,中、低压空气管路应与舱室颜色相同,高压空气管路应与舱室颜色相同。
说明如下:①船舶卫生水管路-白色②船舷外水冷却管路-白色③锅护吹灰或各型管路-红色④排气或废气管路-红色⑤液压传法管路-黄色⑥压空气管路-蓝色⑦高压空气管路-蓝色三、船舶管系基本识别颜色及含义:绿色——海水(舷外水)银色——蒸汽棕色——液体燃料黄色——润滑油浅蓝色——空气和氧类气体红色——消防灰色——淡水黑色——废污液体蓝色——制冷剂四、管路的油漆颜色是表示管内流体的性质,并涂在管子的全长上,识别符号表示流体的用途或压力,识别符号的颜色,蒸汽类管路为红色,其他为白色,举例如下:结语:船舶管系管径小于和等于15mm的管路的识别符号,其箭头尺寸可按实际情况适当缩小。
在某些由于本身的定型而有明显区别的管路(如主机排汽或废气,循环冷却,锅炉烟肉等);以机器设备或减压装置等附近的仪表接管,可不涂识别符号;小型船船的管路简单,很易识别。
可以不涂识别符号,但用船部门认为需要时,亦可涂刷。

姓名:叶晓凤学号: 090601146 系别:化学与环境科学系专业: 化学教育本科(1)班年级: _ 09级 - 指导老师: _ 林德娟(教授)船舶涂料叶晓凤(漳州师范学院化学与环境科学系09化本1班)摘要:这里在对船舶涂料(船底防腐和防污漆、船壳漆、甲板漆、内舱漆以及阻尼降噪等特种涂料)的防腐蚀性、水性化和高固体分化关注的同时,对船舱涂料的安全性、防腐长效性等方面进行了较为全面的综述。
还介绍了新型船舶防污涂料即低表面能防污涂料,无锡自抛光类防污涂料,仿生涂料,导电涂料,硅酸盐防污涂料及相关防污剂的研究进展,对新型防污涂料的发展作出展望。
同时船舶防火涂料也不容忽视。
关键词:船舶涂料、船舱涂料、防腐、防污、防火、1 前言:海洋环境是十分严酷的腐蚀环境,船舶长期处于这样的海洋环境中,腐蚀极其严重,而涂料一直是其最主要的防腐手段。
海洋防腐和防污涂料是构成海洋涂料的基础。
根据各种设施的使用环境和要求不同,又衍生出各种系列产品,例如,船舶涂料、海洋工程设施用重防腐涂料等。
其中,船舶涂料叉分为船底防腐和防污漆、船壳漆、甲板漆、内舱漆以及阻尼降噪等特种涂料。
由于船舱的特殊性,人们除了关注船舱涂料的耐蚀性外,还特别关注其毒性问题。
因为涂层的耐蚀性影响到船舶的服役时间和服役性能,而涂层的毒性问题则关系到船员的人身健康与安全。
为此这里在对船舶涂料的防腐蚀性、水性化和高固体分化关注的同时,对船舱涂料的安全性、防腐长效性等方面进行了较为全面的综述。
船舶在航行过程中,会受到污损生物的附着。
传统的船舶防污涂料大多使用有毒的防污剂(锡、铜等)杀死附着生物,以达到防止生物污损的目的。
这种有毒防污剂进入海洋环境后,性质稳定不易分解,最终会随着食物链进入人的体内,并破坏生态平衡。
在过去的几十年中被广泛使用的有机锡防污涂料,已被国际海事组织禁止使用。
人们还认识到氧化亚铜和其它类似杀菌剂带来的负面影响,最终也会放弃使用这类防污剂。
鉴于此,对于船舶用新型无毒长效防污涂装材料的研发已迫在眉睫。


船舶油漆知识1.船舶用油漆进行维修保养的目的是什么?营运中的船舶用油漆进行维修保养是为了最大限度地延长船舶内部、外部和各种设备的使用寿命,并尽可能减少船底海生物,以减少船舶阻力。
因此营运中的船舶应制定并全面实施一套长期的、预防性的维修保养计划,这包括定时冲洗、补涂和一段时间后的通油。
2.船舶油漆的优点有哪些?油漆,也称涂料,它美观耐用,具有光泽,特别是船舶油漆,它具有防晒、防锈、防油、防蚀、防污、耐磨、耐寒、抗高温等多项优良性能,因而是船舶建造、坞修及日常维修保养中所不可缺少的重要生产物料。
3.油漆施工时对天气有何要求?油漆施工,工厂称为涂装,船上也俗称油漆。
油漆施工的基本要求是:天气晴朗、无风、无污、空气中湿度在90%以内。
4.船舶进坞修理时,油漆施工前对构件表面应如何处理?(1)在船厂进坞修理时,首先用高压淡水冲洗掉船体上因海水而沾上的盐分,然后再用喷砂法(或称抛丸法,俗你"打砂"),将锈皮和已剥离的漆皮打掉,经油漆代表、船舶机务代表或船方验收,认为符合要求后才能对船体表面进行油漆;(2)在无法喷砂或不值得喷砂(小面积)的地方,可采用打磨和敲铲方法除锈,敲铲采用除锈锤、铲刀刷钢丝刷用人工方法进,而机械打磨则通常用风动工具,如风动榔头、砂轮和旋转金属件等进行构件表面除锈,除锈完毕后要用压缩空气吹净表面粉尘,用淡水冲洗一遍则更好。
(3)对于双组份的油漆,在涂漆前也要求将表面打磨粗糙,以增加油漆表面的附着力。
5. 喷砂除锈分为几个等级?各个等级的标准如何?分为四个等级: Sa一1:Sa一2; Sa一2.5; Sa一3:各个级别的标准是:Sa一1:仅清除浮锈及杂物;Sa一2-2/3表面见不到污锈,构件表面的锈包及锈皮彻底除掉;Sa一2.5:表面处理到近出白的程度,往往在仅用新钢板时才用此等级;Sa一3:除去一切锈迹、漆皮及杂物,使金属表面完全出白,呈现出金属白色光泽。
此等级平常很少使用。
环氧磷酸锌底漆标准
环氧磷酸锌底漆是一种常用的防腐底漆,具有优异的防腐性能和附着力,被广
泛应用于钢结构、船舶、桥梁等领域。
本文将详细介绍环氧磷酸锌底漆的标准,包括其技术要求、应用范围、施工要求等方面的内容。
首先,环氧磷酸锌底漆的技术要求包括外观、干膜厚度、附着力、硬度、耐蚀
性等指标。
在外观方面,底漆应无明显的气泡、麻点、流挂等缺陷,颜色应均匀一致。
干膜厚度应符合设计要求,且应具有良好的附着力和硬度,以保证涂层的耐久性。
同时,底漆的耐蚀性也是一个重要指标,应能在恶劣环境下长期保持良好的防腐性能。
其次,环氧磷酸锌底漆的应用范围涵盖了各种钢结构表面的防腐涂装,包括钢
结构建筑、桥梁、管道、储罐、船舶等。
在这些领域,底漆不仅要求具有良好的防腐性能,还要求具有良好的施工性能和适应性,能够适应不同的工况和环境要求。
另外,环氧磷酸锌底漆的施工要求也是至关重要的。
在施工过程中,需要严格
按照产品说明书和相关标准进行操作,包括表面处理、底漆稀释、涂装方法、涂层干燥等方面的要求。
只有严格按照要求进行施工,才能确保涂层的质量和性能。
总的来说,环氧磷酸锌底漆是一种性能优良的防腐底漆,具有广泛的应用前景。
通过严格遵守相关标准和技术要求,可以确保底漆具有良好的性能和稳定的质量,为各种钢结构的防腐涂装提供可靠保障。
以上就是对环氧磷酸锌底漆标准的详细介绍,希望能对相关行业人士有所帮助,谢谢阅读。
目前船上使用的保养漆主要有四类,分别为醇酸漆、氯化橡胶漆、环氧漆及聚安酯漆。
四种油漆各有其独特的性质、优缺点、应用范围、相应的使用技术要求。
由于船员对油漆的性质及用处了解不多、认识不够,造成了船舶上油漆使用的混乱,甚至使用不当造成经济损失,下面就油漆的性质、船舶保养中遇到的问题及使用方法介绍如下。
一、醇酸漆、氯化橡胶漆、环氧漆、聚安酯漆的特点、应用范围1.醇酸油漆以醇酸树脂为主,按各种品种的要求加入所需的颜料及助剂等,研磨而成。
是目前国内生产量最大的一类涂料。
优点是价格便宜、施工简单、对施工环境要求不高、漆膜光亮丰满,平整柔韧,对金属有很好的附着力,耐久性和耐候性较好,装饰性和保护性都比较好。
缺点是干燥较慢、涂膜不易达到较高的要求,漆膜脆,温差变化大时漆膜会开裂。
该种油漆漆膜薄,一般漆膜厚度在40~50μm,固体含量低、涂布率小、一般干燥时间为8~15h,5℃以下油漆不干。
醇酸漆一般用于货舱、甲板、舱盖及生活区建筑等。
但该漆不能用于压载水舱及淡水舱。
2.氯化橡胶漆氯化橡胶是由天然或合成橡胶经氯化改性后得到的白色或微黄色粉末,无味、无毒,对人体皮肤无刺激性,具有良好的粘附性、耐化学腐蚀性、快干性、防透水性和难燃性。
氯化橡胶防腐涂料广泛用作建筑涂料、化工防腐涂料、阻燃涂料、船舶及海洋钢结构防腐涂料,与常温固化环氧树脂涂料并列为当今世界防腐涂料的两大体系。
优点为漆膜的水蒸气和氧气透过率极低,仅为醇酸树脂的1/10,因此具有良好的耐水性和防锈性能。
耐日光老化,保护中层和底层涂层。
使用方便。
单组份,开桶后搅匀即可使用。
可采用高压无气喷涂、刷涂、辊涂等多种方法施工。
干燥快,施工不受季节限制。
从-20~40℃均可正常施工,间隔4~6h 即可重涂。
对钢铁、混凝土、木材均有良好的粘结力,防腐蚀性能好。
氯化橡胶漆有着很好的附着力,它可以被自身的溶剂所溶解,所以涂层与涂层之间的附着力很好,涂层即使过了1~2年,其重涂性仍然很好。
官网:
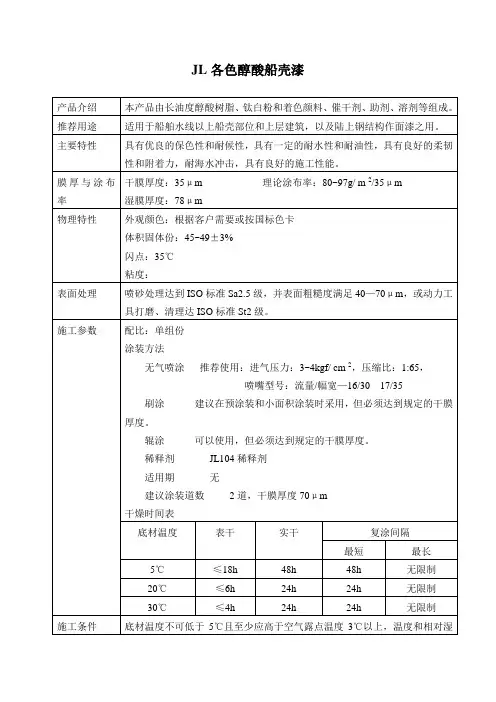
船舶漆的介绍
船舶漆就是涂装于船舶内外各部位、以延长船舶使用寿命和满足船舶的特种要求的各种油漆。
船舶漆是船舶底漆、船底防锈漆、船底防污漆、船舶水线漆系列、船壳及上层建筑用漆、各类船舶舱室用漆— 压载水舱漆、油舱漆、饮水舱漆、干货舱漆等一系列油漆组成的。
车间底漆包括:酚醛改性磷化底漆、环氧富锌底漆、正硅酸酯锌
粉底漆、不含金属锌粉底漆。
防锈底漆包括:磷酸锌防锈漆、锌黄防锈漆、红丹防锈漆、其他防锈漆。
船底漆,也是船水下部位的用漆包括:船漆防锈漆和船底防污漆。
其中船底防锈漆又包括:沥青船底防锈漆、氯化橡胶船底防锈漆、环氧沥青船底防锈漆;船底防污漆包括:溶解型--沥青系氧化亚铜防污漆;接触型--氯化橡胶、乙烯类 氧化亚 铜防污漆;扩散型:有机锡防污漆;自抛光防污漆--有机锡高聚物防污漆。
船舶漆的涂装:船体原材料表面处理要求:
1. 船体外板、甲板板、舱壁板、舷墙板、上层建筑外板,内地板和组合型材等内部用板材,在下料前采用抛丸处理,达到瑞典除锈标准Sa
2.5,并立即喷涂富锌车间底漆一度。
2. 船体内部用型材等采用喷砂处理,达到瑞典除锈标准Sa2.5
,并立即喷涂富锌车间底漆一度。
官网:
3. 表面处理后,应尽快喷涂车间底漆,不允许在钢材表面出现返锈后再涂装。
郑州强邦涂料有限公司主要定位生产各种工业重防腐漆、特种漆、有机硅耐高温漆、磁漆、调和漆、氟碳漆、环氧漆、丙烯酸聚氨酯类漆,船舶漆、高氯化橡胶类漆、航标漆管道防腐漆、烟囱漆、汽车防腐漆、抗电弧漆、工程机械防腐漆、过氯乙烯漆、防火漆、高分子防腐漆、冷镀锌漆、PVC漆、塑料漆、玻璃钢漆、马路划线漆、反光路线漆、OM烟道防腐涂料、高模数硅酸锂防腐涂料、水性带锈防锈防腐涂料、漆酚螯合高聚合防腐涂料、地坪漆、氨基漆、硝基漆、环保水性漆等优质产品。
涵盖航天、海洋船舶、石油管道、机械制造、汽车工业等领域。
有意向可点击咨询。