高考二轮教师用书:第1部分 专题1 第1讲 时态和语态 含解析
- 格式:doc
- 大小:57.56 KB
- 文档页数:10

第一讲时态和语态1.(2016·高考全国乙卷语法填空)So it was a great honour to be invited backstage at the notforprofit Panda Base,where ticket money helps pay for research.I (allow) to get up close to these cute animals at the 600。
acre centre.2.(2016·高考全国丙卷语法填空)Truly elegant chopsticks might (make) of gold and silver with Chinese characters。
3.(2016·高考全国丙卷语法填空)Confucius believed knives would remind people of killings and (be)too violent for use at the table。
4.(2016·高考全国乙卷短文改错)Some people even had to waitoutside。
5.(2016·高考全国乙卷短文改错)Every day he makes sure that fresh vegetables and high quality oil are using for cooking。
6.(2016·高考全国甲卷短文改错)I thought that it is a good idea。
7.(2015·高考全国卷Ⅰ语法填空)Yangshuo (be)really beautiful。
8.(2015·高考全国卷Ⅱ语法填空)This cycle (go)day after day:The walls warm up during the day and cool off during the night and are thus always a timely offset(抵消)for the outside temperatures。
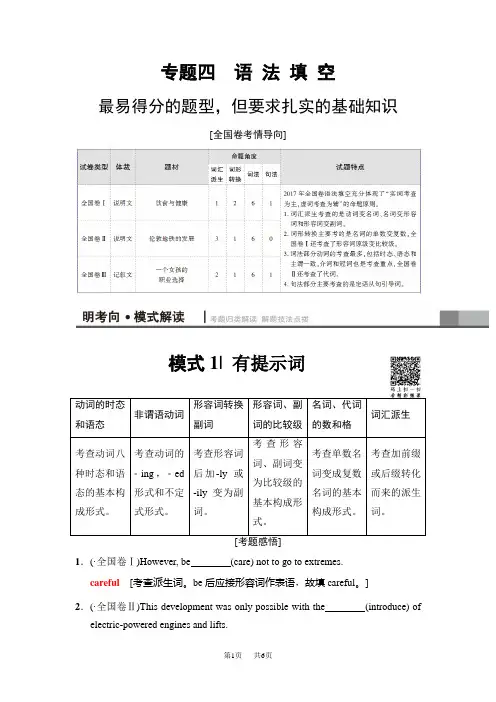
专题四 语 法 填 空最易得分的题型,但要求扎实的基础知识[全国卷考情导向]模式1| 有提示词动词的时态和语态 非谓语动词 形容词转换副词 形容词、副词的比较级 名词、代词的数和格词汇派生 考查动词八种时态和语态的基本构成形式。
考查动词的ing ,ed 形式和不定式形式。
考查形容词后加-ly 或-ily 变为副词。
考查形容词、副词变为比较级的基本构成形式。
考查单数名词变成复数名词的基本构成形式。
考查加前缀或后缀转化而来的派生词。
1.(·全国卷Ⅰ)However, be (care) not to go to extremes.careful [考查派生词。
be 后应接形容词作表语,故填careful 。
]2.(·全国卷Ⅱ)This development was only possible with the (introduce) ofelectric-powered engines and lifts.introduction[考查派生词。
冠词后表示“介绍”应用名词形式,故填introduction。
]3.(·全国卷Ⅲ)She has turned down several (invitation) to star at shows in order to concentrate on her studies.invitations[考查名词的数。
several几个,其后的名词要用复数形式,故填invitations。
]4.(·全国卷Ⅰ)When fat and salt (remove) from food, the food tastes as if it is missing something.are removed[考查时态、语态和主谓一致。
根据语境可知此处用一般现在时,由于主语fat and salt是复数概念,且与remove是被动关系,故用一般现在时的被动语态,故填are removed。

第1讲动词的时态与语态1.He hurried home,never once looking back to see if he________.(2020·江苏,27)A.was being followed B.was followingC.had been followed D.followed答案 A解析句意为:他匆忙回家了,一次也没有回头看看他是否正被跟踪。
这里if引导的宾语从句用过去进行时表示过去某一时刻(hurried home)正在进行的动作。
又因he与follow之间是被动关系,故用被动语态。
综合可知选A项。
2.He’s been informed that he ________ for the scholarship because of his academicbackground.(2020·江苏,31)A.hasn’t qualified B.hadn’t qualifiedC.doesn’t qualify D.wasn’t qualifying答案 C解析句意为:他已被告知,因为他的学术背景,他没有获得奖学金的资格。
本空的谓语动词qualify在这里用作不及物动词,表示“有资格,有权利”,此处并不表示延续性的动作,而是说明“他没有资格”这一实际情况,因此用一般现在时的否定式doesn’t qualify。
3.—________ that company to see how they think of our product yesterday?—Yes.They are happy with it.(2020·北京,24)A.Did you call B.Have you calledC.Will you call D.Were you calling答案 A解析句意为:——昨天你给那家公司打电话询问他们对我们的产品印象如何了吗?——打过了,他们对我们的产品很满意。

第一讲动词的时态和语态一时态一般时一般现在时常用来表示习惯性、经常性发生的动作或存在的状态。
1.谓语动词的构成:do/does(下面所有的谓语动词的构成皆以do为例)2.基本用法(1)表示经常性的动作常与usually, always, often, sometimes, never, every day等表示频度的时间状语连用。
◆On Monday morning it usually takes me an hour to drive to work.星期一早晨,通常花费我一小时开车去上班。
(2)表示客观真理、格言或者警句等表示客观真理时,即使主句是一般过去时,宾语从句还要用一般现在时。
◆As we all know, the earth travels around the sun.众所周知,地球围绕太阳转。
(3)表示按规定、时间表、计划或安排要发生的动作谓语动词是come, go, arrive, leave, start, begin, return, live, fly等,可以用一般现在时表示将来发生的动作。
◆My dream school starts at 8:30 a.m. and ends at 3:30 p.m.我理想的学校上午8:30上课,下午3:30放学。
(4)在时间、条件等状语从句中常用一般现在时代替一般将来时◆If you come this afternoon, we’ll have a meeting.如果你今天下午过来,我们将开个会。
(5)在某些以here,there开头的句子中,用一般现在时表示正在发生的动作或存在的状态◆Here comes the English teacher.英语老师来了。
[典例] (2017·全国卷Ⅰ语法填空)Fast food ____________(be) full of fat and salt;byeating more fast food people will get more salt and fat than they need in their diet.is解析:此处表示客观事实,应用一般现在时,故填is。

动词的时态与语态是两个非常重要的语法范畴,构成了英语语法的基本框架,几乎所有动词的考查都必须借助于时态和语态来完成。
高考试题在考查时态和语态的同时,还兼顾其他语法内容的测试,比如各种从句、强调句、倒装句等,其交叉式和复合式的特点尤为明显。
其考点主要包括:1.注重在语境中考查常见时态的区别,如一般过去时与现在完成时、一般现在时(过去时)与现在(过去)进行时的区别等。
要求准确判断动作和时间的关系,正确理解时间概念,如是现在、过去还是将来,是时间段、时间点还是时间瞬间。
2.遵循“情景立意”和“能力立意”的原则,考查在状语从句等特定语言环境中时态的代替。
要求吃透语境,摸清命题人的意图,善于捕捉句子中所隐含的时间信息,克服汉语式的惯性思维。
3.把语态与时态结合在一起,进行综合考查。
各种常用时态的被动语态的构成,仍是高考命题的热点之一,而且题干中有效信息越来越隐蔽,试题难度呈现加大的趋势。
要求明确谓语动词与主语的关系,分清是主动还是被动。
4.考查主动形式表示被动意义。
对语境理解能力的要求逐步提高,且要重视有特殊用法的动词的运用。
一、高考常考的几种易混时态的辨析1.一般现在时与现在进行时(1)一般现在时主要用于习惯性或经常性动作,常伴随使用usually,often,seldom等频度副词;现在进行时主要用于表示目前或现阶段正在进行的动作或状态,常跟now,at present等时间状语。
He usually writes a lot of letters,but he isn't writing at present.他经常写许多信,但他现在没在写。
(2)表示客观事实或普遍真理时,要用一般现在时,不能用现在进行时。
The Earth goes around the Sun.地球绕着太阳转。
2.一般过去时与过去进行时(1)一般过去时表示一个完成的动作,而过去进行时表示过去某一阶段正在进行的动作。
I was reading a novel last night.昨晚我在看小说(可能没看完)。

第一讲时态和语态(对应学生用书第3页)1.(2017·江苏高考卷)He hurried home,never once looking back to see if he ________.A.was being followed B.was followingC.had been followed D.followedA[句意:他匆匆回家,一次也没有回头看看是否正被跟踪。
这里if引导的宾语从句用过去进行时表示过去某一时刻(hurried home)正在进行的动作。
又因he 与follow之间是被动关系,故用被动语态。
]2.(2017·江苏高考卷)He's been informed that he ________ for the scholarship because of his academic background.A.hasn't qualified B.hadn't qualifiedC.doesn't qualify D.wasn't qualifyingC[句意:他被告知,因为其教育背景,他没有资格获得这笔奖学金。
根据语境可知,此处描述的是客观事实,因此使用一般现在时。
]【导学号:25874000】3.(2015·江苏高考卷)The real reason why prices ________,and still are,too high is complex,and no short discussion can satisfactorily explain this problem.A.were B.will beC.have been D.had beenA[句意:物价为什么(过去)很高,现在依然很高的真正原因很复杂,不是一个简短的讨论就可以满意地解释这个问题的。
根据后面的still are可知,此处是和“现在”对比,故用一般过去时。


专题1动词的时态与语态1.I’m calling about the apartment you________the other day.Could you tell me more about it?(2013·安徽,24) A.advertised B.had advertisedC.are advertising D.will advertise答案 A解析考查时态。
句意为:我现在打电话是咨询你前几天登广告的那所公寓的。
你能告诉我有关它的更多的信息吗?根据the other day可知,该空应用一般过去时态。
2.—Could I use your car tomorrow morning?—Sure.I________a report at home. (2013·江苏,25) A.will be writing B.will have writtenC.have written D.have been writing答案A解析考查动词时态。
句意为:——我明天上午能使用你的车吗?——当然可以。
(那时)我将在家写报告呢。
A项是将来进行时,与题意相符。
3.—What about your self-drive trip yesterday?—Tiring!The road is being widened,and we________a rough ride. (2013·江苏,34) A.had B.haveC.would have D.have had答案A解析考查时态。
句意为:——昨天的自驾游如何?——太累了。
道路正在拓宽,驾车十分难行。
由yesterday可知,应用一般过去时态。
4.Hurry up,kids!The school bus ________for us!(2013·四川,3) A.waits B.was waitingC.waited D.is waiting答案 D解析考查动词的时态。



2022年高考第二轮课时讲义专题(英语)时态语态一、考纲解读《课程标准(2017版)》要求中学生掌握常见的时态有10种,即一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、现在进行时、过去进行时、将来进行时、现在完成时、过去完成时、现在完成进行时和过去将来时,重点考查“3个一般”,即一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时;“2个进行”,即现在进行时、过去进行时和“1个完成”,即现在完成时。
而被动语态要求掌握的有7种,即一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、现在进行时、过去进行时、现在完成时、过去完成时,重点考查“3个一般”,即一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时。
时态语态除在语法填空、短文改错中直接考查外,也出现在听力、阅读、完型、写作等题型中,也就是说该语法项目贯穿于整套试卷,足见该语法项目的重要性。
二、真题探究一)真题再现语法填空中的时态语态2019课标11.In recent years some Inuit people in Nunayut ___have reported___ (report) increases in bearsightings around human settlements, leading to a belief that populations are increasing.2.Of the nineteen recognized polar bear subpopulations, three are declining, six __are__ (be)stable, one is increasing, and nine lack enough data.2018课标11.While running regularly can’t make you live forever, the review says it __is__ (be) moreeffective at lengthening life than walking, cycling or swimming.2017课标11.When fat and salt __are removed__ (remove) from food, the food tastes as if it is missingsomething.2.Fast food __is__ (be) full of fat and salt.2016课标11. So it was a great honour to be invited backstage at the not-for-profit Panda Base, where ticketmoney helps pay for research. I _was allowed__ (allow) to get up close to these cute animals at the 600-acre centre.2019课标21.Picking up her “Lifetime Achievement” award, proud Irene _declared__ (declare) she had noplans to retire from her 36-year-old business.2.Irene said, “I don't see any reason to give up work. I love coming here and seeing my familyand all the friends I ___have made__ (make) over the years.”2018课标21.Diets have changed in China -and so too has its top crop. Since 2011, the country _hasgrown___ (grow) more corn than rice.2.The Chinese Ministry of Agriculture finds that between 2005-when the government_started___ (start) a soil-testing program which gives specific fertilizer recommendations to farmers-and 2011, fertilizer use dropped by 7.7 million tons.2019课标31.Our hosts shared many of their experiences and _recommended__(recommend) wonderfulplaces to eat, shop, and visit.2.On the last day of our week-long stay, we _were invited__(invite) to attend a private concerton a beautiful farm on the North Shore under the stars, listening to musicians and meeting interesting locals.2018课标31.True to a gorilla’s unaggressive nature, the huge animal __meant___ (mean) me no real harm.He was just saying:“I’m king of this forest,and here is your reminder!”2017课标21.When all those had been done, the road surface was replaced. Steam engines _was used__(use)to pull the carriages and it must have been fairly unpleasant for the passengers, with all the smoke and noise.ter, engineers _managed___ (manage) to construct railways in a system of deep tunnels (隧道), which became known as the Tube.2017课标31.Sarah _was told__ (tell) that she could be Britain’s new supermodel earning a million dollarsin the new year.2.Sarah says, “My dad thinks I should take the offer now. But at the moment, school __comes__(come) first. I don't want to get too absorbed in modeling.”2016课标21. Leaving the less important things until tomorrow __is__ (be) often acceptable.2.It could be anything, gardening, cooking, music, sports but whatever it is, _make__ (make ) sure it's a relief from daily stress rather than another thing to worry about.2016课标31. Truly elegant chopsticks might __be made__ (make) of gold and silver with Chinese characters.2. Confucius believed knives would remind people of killings and __were_ (be) too violent for use at the table.短文改错中的时态语态2019课标2There were two reasons for the decision. One was that I was amazed at the fact that a sick person could feel much better after seeing a doctor. And the other is that I wanted to help people in need. (is---was)2019课标3I've had many dreams since I was a child. Now my dream is to open a cafe. Though it may appear simple, it required a lot of ideas and efforts. (required---requires)2018课标1During my last winter holiday, I went to the countryside with my father to visit my grandparents. I find a big change there. (find--found)2018课标2I didn’t realize how right my parents are until I entered high school.(are--were)2018课标3At that moment,I remembered that my father once said,“The classroom is a placefor learning and that include learning from textbooks,and mistakes as well.”Immediately,I raised my hand.(include--includes)2017课标1Before getting into the car, I thought I had learned the instructor’s orders, but once I started the car, my mind goes blank, I forgot what he had said to me altogether. (goes--went)2017课标2Mr. and Mrs. Zhang both work in our school. When the summer came, they will invite their students to pick the fresh vegetables. (came--comes)2017课标31. When I look at this picture of myself, I realize how fast time flies. I had grown not only physically, but also mentally in the past few years. (had--have)2. About one month after this photo was took, I entered my year of high school and become a new member of the school music club. (took—taken; become--became)2016课标11. Though not very big, the restaurant is popular in our area. It is always crowded with customers at meal times. Some people even had to wait outside. (had---have)2. Every day he makes sure that fresh vegetables and high quality oil are using for cooking. (using-used)2016课标2Some classmates suggest we go to places of interest nearby. I thought that it is a good idea. It does not cost much, yet we can still learn a lot. (thought--think)2016课标3At the first, I thought I knew everything and could make decisions by myself. However, my parents didn’t seem to think so. They always tell me what to do and how to do it. (tell--told)二)考点总结无论是语法填空还是短文改错,时态语态重点考查一般过去时和一般现在时三)解题策略说明:不带*号的项目是义务教育阶段学习过的项目(参见2011版《义务教育英语课程标准》)。
专题一单项填空注:由于个别题目涉及两个考点,故2016、2015均出现15个小题,16个考点的现象。
[题型攻略]单项填空往往只是由一、两句话构成的一个微情景,都是在真实的情景中考查对词汇、语法的掌握情况以及对语句、语境的理解。
每一个单项填空题都是一个小小的语言世界,五脏俱全,各种语法穿插其中,真可谓是“步步有陷阱”。
然而做单项填空题还是有章可循,有法可依的。
攻略1句式结构分析法分析句式结构,明确句子成分,特别是选项在句子中所充当的成分,对于选择正确答案是很有必要的。
在分析过程中,要特别留意标点符号、连词等,从而判断出这是一个简单句、并列句,还是复合句。
这类题型的选项大致分为两类:1.连词和代词的混合选项;2.纯连词。
如果是复合句,要严格按照以下两个思路答题:(1)分析何种从句;(2)分析引导词作何种成分。
[典例1](2016·浙江高考,11)Scientists have advanced many theories about whyhuman beings cry tears,none of ________ has been proved.A.whom B.whichC.what D.thatB[如果学生把先行词误认为scientists,容易错选A项。
分析句子结构可知,逗号后是“代词+of+which/whom”引导的非限制性定语从句。
先行词是many theories,指物,故关系代词只能用which。
][典例2]He wrote five novels,two of________translated into English.A.it B.themC.which D.thatB[此题很容易掉进陷阱误选C项,学生误以为后面是非限制性定语从句。
事实上translated是过去分词,而不是谓语动词,后面不是句子,不能用连词,所以正确答案是B项them。
若在translated前加上were,were translated就成了谓语动词,这时才可以选连词which。
第一讲谓语动词第一课时动词的时态和语态语法填空【典题试做】1.(2019·全国卷Ⅰ)In recent years some Inuit people in Nunavut have__reported(report) increases in bear sightings around human settlements, leading to a belief that populations are increasing.2.(2019·全国卷Ⅱ)Picking up her “Lifetime Achievement”award, proud Irene declared(declare) she had no plans to retire from her 36-year-old business.3.(2019·全国卷Ⅱ)I don’t see any reason to give up work.I love coming here and seeing my family and all the friends I have__made(make) over the years.4.(2019·全国卷Ⅲ)Our hosts shared many of their experiences and recommended(recommend) wonderful places to eat, shop, and visit.5.(2019·全国卷Ⅲ)On the last day of our week-long stay, we were__invited(invite) to attend a private concert on a beautiful farm on the North Shore under the stars, listening to musicians and meeting interesting locals.6.(2018·全国卷Ⅱ)Diets have changed in China—and so too has its top crop.Since 2011, the country has__grown(grow) more corn than rice.7.(2018·全国卷Ⅱ)The Chinese Ministry of Agriculture finds that between 2005—when the government started(start) a soil-testing program that gives specific fertilizer recommendations to farmers—and 2011,fertilizer use dropped by 7.7 million tons.8.(2018·全国卷Ⅲ)When the gorillas and I frightened each other, I was just glad to find them alive.True to a gorilla’s unaggressive nature, the huge animal meant(mean) me no real harm.9.(2017·全国卷Ⅱ)Steam engines were__used(use) to pull the carriages and it must have been fairly unpleasant for the passengers, with all the smoke and noise.However, the railway quickly proved to be a great success...10.(2017·全国卷Ⅱ)Later, engineers managed(manage) to construct railways in a system of deep tunnels(隧道), which became known as the Tube.11.(2017·全国卷Ⅲ)Sarah has__been__told/was__told(tell) that she could be Britain’s new supermodel, earning a million dollars in the next year.12.(2017·全国卷Ⅲ)Sarah says,“My dad thinks I should take the offer now.But at the moment, school comes(come) first.”1.考查的时态主要是一般现在时、一般过去时和现在完成时;2.考查被动语态的用法;3.考查主谓一致。
第一讲时态和语态1.(·江苏高考卷)He hurried home,never once looking back to see if he ________.A.was being followed B.was followingC.had been followed D.followedA[句意:他匆匆回家,一次也没有回头看看是否正被跟踪。
这里if引导的宾语从句用过去进行时表示过去某一时刻(hurried home)正在进行的动作。
又因he与follow之间是被动关系,故用被动语态。
]2.(·江苏高考卷)He's been informed that he ________ for the scholarship because of his academic background.A.hasn't qualified B.hadn't qualifiedC.doesn't qualify D.wasn't qualifyingC[句意:他被告知,因为其教育背景,他没有资格获得这笔奖学金。
根据语境可知,此处描述的是客观事实,因此使用一般现在时。
]3.(·江苏高考卷)The real reason why prices ________,and still are,too high is complex,and no short discussion can satisfactorily explain this problem.A.were B.will beC.have been D.had beenA[句意:物价为什么(过去)很高,现在依然很高的真正原因很复杂,不是一个简短的讨论就可以满意地解释这个问题的。
根据后面的still are可知,此处是和“现在”对比,故用一般过去时。
]4.(·江苏高考卷)—How much do you know about the Youth Olympic Games to be held in Nanjing?—Well,the media________ it in a variety of forms.A.cover B.will coverC.have covered D.coveredC[句意:——你对即将在南京举行的青奥会了解多少?——哦,媒体已经以各种形式进行了报道。
强调对现在造成的结果或影响,用现在完成时。
] 5.(·北京高考卷)—________ that company to see how they think of our product yesterday?—Yes.They are happy with it.A.Did you call B.Have you calledC.Will you call D.Were you callingA[句意:——昨天你给那家公司打电话询问他们对我们产品的看法了吗?——是的。
他们对产品很满意。
根据句中的时间状语yesterday可知,空格处用一般过去时。
]6.(·北京高考卷)In the 1950s in the USA,most families had just one phone at home,and wireless phones ________ yet.A.haven't inventedB.haven't been inventedC.hadn't inventedD.hadn't been inventedD[句意:在20世纪50年代的美国,大多数家庭家里只有一部电话,那时无线电话还没有被发明出来。
根据句意以及句中的关键词“In the 1950s”和yet可知,空格处用过去完成时;且“wireless phones”与动词invent之间是被动关系,所以使用过去完成时的被动语态。
]7.(·北京高考卷)People ________ better access to health care than they used to,and they're living longer as a result.A.will have B.haveC.had D.had hadB[句意:人们有了比过去更便捷的医疗保障,结果,人们的寿命更长了。
根据句意以及句中的关键信息“than they used to”可知,此处表示现在与过去的对比,所以空格处用一般现在时。
]8.(·天津高考卷)I ________ down to London when I suddenly found that I was on the wrong road.A.was driving B.have drivenC.would drive D.droveA[句意:我正开车去伦敦,这时突然发现自己走错了路。
这里使用了固定句式be doing sth.when...,表示“正在做某事时突然……”,此时主句用过去进行时,when后面的句子用一般过去时。
]一、常考的各种时态1.一般现在时(1)表示经常发生的、习惯性的动作,通常用usually,often,always,sometimes,every day,once a week等作时间状语。
I usually have my hair cut once a month.The students often do their experiments in the lab.(2)表示客观真理、格言以及不受时间限制的客观存在。
The earth moves around the sun.A bird in hand is worth two in the bush.(3)表示按时间表、计划、规定发生的动作。
The train leaves at 2:35 this afternoon.(4)主句是一般将来时的时间、条件、让步状语从句中代替将来时。
You will succeed if you try your best.Even if it rains tomorrow,the football match will take place.2.现在进行时(1)表示说话时正在进行的动作或存在的状态。
Our friends are waiting for us outside now.(2)表示现阶段正在进行的动作或发生的事情。
She is learning English at college.(3)某些短暂性动词,如come,go,start,open,close,arrive,return,begin,leave等用于进行时,表示按计划、安排即将发生的动作。
My father is coming to see me this Saturday.He is leaving for Beijing next week.(4)某些动词的进行时表示慢慢地、渐渐地发生变化。
I'm forgetting English.She is losing her eyesight.3.现在完成时(1)表示过去的动作对现在的影响或结果,常用recently,lately,ever,never,once,before,yet,just等作时间状语。
He hasn't heard any news from his son lately.Have you ever been to London?(2)表示开始于过去某一时刻,一直持续到现在而且还有可能继续下去的动作。
常用so far,up till now,since,for a long time,in the past/last few years,these days等作时间状语。
So far no life has been found outside the earth.He has learned 5,000 English words since he went to college.(3)“This/It is+the+序数词+time+that...”句式中,that后的从句用现在完成时。
This is the second time that I have visited the university.4.现在完成进行时(1)表示开始于过去某个时间、一直持续到现在而且会继续进行下去的动作。
I am very tired.I have been painting the house all the afternoon.(2)表示到目前为止的一段时间里一直反复进行的动作。
I have been calling him several times this morning,but there is no answer. 5.一般过去时(1)表示在过去某个时间发生的动作或存在的状态,常用yesterday,last year,in 1995,the other day等作时间状语。
It was a terrible piece of work you turned in yesterday.He came to work here two weeks ago.(2)在时间、条件从句中代替过去将来时。
He said he would not go if it rained.(3)有些句子,虽然没有明确的表示过去的时间状语,但实际上指的是过去发生的动作或状态,也要用一般过去时。
常见的此类动词有know,think,expect等,表示“本来认为”。
I didn't expect to meet you here.I thought he had heard the news.6.过去完成时(1)表示在过去某一时间或某一动作发生之前已经完成的动作,即“过去的过去”。
By the end of last term,we had learned 2,000 words.He had left before I got home.(2)hope,expect,think,intend,want,suppose等用于过去完成时,表示未实现的希望、打算或意图,意为“原本……”。
We had expected that you would be able to win the match.(3)“It/This/That was+the+序数词+time+that...”句式中,that后的从句用过去完成时。
It was the third time that he had made the same mistake.(4)“hardly/scarcely...when...”和“no sooner...than...”结构中,主句用过去完成时。