国际结算——托收业务操作参考资料
- 格式:doc
- 大小:155.50 KB
- 文档页数:4



国际结算——托收业务操作参考资料1、托收的概念:是指由债权人(一般为出口商)开出汇票,委托当地银行通过其在国外的分行或代理行向债务人(一般为进口商)收取款项的结算方式。
2、托收的分类:托收方式的种类有光票托收与跟单托收两类。
光票托收:是指不附商业单据的金融单据托收。
跟单托收:是指对下列单据的托收a. 附有商业单据的金融单据b. 不附有金融单据的商业单据3、托收的当事人及其责任(1)出票人(principal):又称“本人”是委托银行取得国外付款人的付款或承兑后向其交单的人,通常就是出口方,出票人及托运人。
(2)托收行(remitting bank)它是委托人的代理人,为委托人转托国外分行或代理行办理托收的银行,通常为出口地银行。
(3)代收行(collecting bank)它是托收行的代理人,接受代收行的指示,在取得国外付款人的付款或承兑后向其交单,并最终得到付款的银行,通常为进口地银行。
(4)付款人(drawee)它是按照托收指示作成提示的被提示人,通常为进口商。
(5)提示行(presenting bank)它是向汇票付款人做成提示的代收行。
如果托收行不指定一家特定提示行,多数情况下提示行就是代收行,但也有时提示行与代收行是分离的两家银行。
(6)需要是的代理人(representative in case of need)这是委托人指定的付款地的代理人,其作用是在付款人拒绝付款、拒收货物时,代表委托人接受单据并处理货物。
托收当事人之间的关系如下,点击观看托收结算方式一般流程:4、托收特点:(1)属于逆汇范畴(2)代表商业信用(3)主要用于国际贸易结算业务5、跟单托收的交单条件跟单托收依据交单条件分为承兑交单、即期交单和远期付款交单3种。
(点击黑体弹出)(1)跟单即期付款交单(DOCUMENT AGAINST PAYMENT AT SIGHT):俗称D/P AT SIGHT,指开出的汇票是即期汇票,进口商见票,只有付完货款,才能拿到商业单据。



一、实验目的通过本次国际结算托收实验,使学生了解国际结算托收的基本概念、流程和操作方法,掌握托收业务的操作技能,提高学生在国际贸易中的风险防范意识。
二、实验内容1. 托收的概念与种类2. 托收业务的流程3. 托收当事人及其责任4. 托收业务的风险与防范5. 实际操作演练三、实验过程1. 托收的概念与种类托收是指债权人为向境外债务人收取销售货款或劳务价款,开具汇票委托债权人所在地的银行向债务人收款的结算方式。
托收可分为光票托收和跟单托收两大类。
2. 托收业务的流程(1)委托人(出票人)向托收行提交托收申请书,并附上相关单据。
(2)托收行审核委托人提交的申请书和单据,无误后向代收行发出托收委托书。
(3)代收行收到托收委托书后,通知债务人支付款项。
(4)债务人支付款项后,代收行将款项划拨给托收行。
(5)托收行将款项划拨给委托人。
3. 托收当事人及其责任(1)委托人:委托人即为出票人,负责向托收行提交托收申请书和单据,并承担托收过程中可能产生的风险。
(2)托收行:托收行负责审核委托人提交的申请书和单据,向代收行发出托收委托书,并在收到代收行划拨的款项后,将款项划拨给委托人。
(3)代收行:代收行负责接收托收委托书,通知债务人支付款项,并将款项划拨给托收行。
(4)债务人:债务人即为付款人,负责按照托收委托书的要求支付款项。
4. 托收业务的风险与防范(1)买方风险:债务人可能因各种原因拒绝付款,导致委托人无法收回货款。
防范措施:选择信誉良好的债务人,签订合同约定付款期限,并采取必要的法律手段追讨欠款。
(2)卖方风险:委托人可能因单据不符、手续不齐全等原因导致无法收回货款。
防范措施:确保单据齐全、手续完备,并加强对委托人的信用评估。
(3)国家风险:债务人所在国家可能因政策、经济等原因导致无法支付款项。
防范措施:关注债务人所在国家的政治、经济状况,选择信誉良好的债务人。
5. 实际操作演练(1)选择一个托收业务案例,分析案例中的托收流程、当事人及其责任。

国际结算托收业务流程一、托收的概念。
托收啊,就像是一个中间人帮忙收款的感觉。
比如说,你在国外有个客户,你给人家发了货,但是你又不好意思直接去要钱,这时候就可以找银行来帮忙。
银行呢,就按照你的指示,去跟那个外国客户要钱。
这就是托收的一个大概的样子啦。
二、托收的当事人。
1. 委托人。
委托人就是那个想要收钱的人,就像前面说的,你给国外发货的这个人就是委托人啦。
委托人得把相关的票据啊、单据啥的都交给银行,让银行知道是怎么回事儿,收多少钱,有啥特殊要求之类的。
委托人可重要了,要是没有委托人的这些指示,银行都不知道该咋干活呢。
2. 托收行。
托收行就是委托人这边的银行,就像是委托人的小助手。
委托人把事情交给托收行,托收行就得负责把这个事儿办好。
它要按照委托人的要求,把那些票据啊、单据啥的寄给国外的代收行。
而且托收行还得时不时地盯着这事儿,看看钱收得咋样了。
3. 代收行。
代收行在国外呢,它是托收行的小伙伴。
托收行把东西寄给代收行,代收行就负责去跟那个外国客户要钱。
代收行得按照托收行的指示来办事,要是有啥问题,还得跟托收行沟通呢。
4. 付款人。
付款人就是那个应该付钱的人啦,就是国外收到货的那个客户。
他看到代收行来要钱,要是没啥问题,就得乖乖付钱。
三、托收的业务流程。
1. 委托人准备单据。
委托人要先把那些跟货物有关的单据准备好,像提单啊、发票啊之类的。
这些单据可重要了,就像是货物的身份证一样。
没有这些单据,付款人可能都不认账呢。
委托人把这些单据整理好之后,就得填写托收申请书,告诉托收行自己的要求,比如说啥时候收钱啊,要是收不到钱怎么办之类的。
2. 托收行受理业务。
托收行收到委托人的单据和申请书之后,就得检查一下。
看看单据齐不齐,申请书上的要求清不清楚。
要是有问题,就得让委托人修改。
要是没问题呢,托收行就根据委托人的要求,制作托收委托书,然后把单据和托收委托书一起寄给代收行。
3. 代收行向付款人提示单据。
4. 付款人付款或拒付。

案例1 托收单据丢失责任划分案案情:山东A公司于X年4月11日出口欧盟B国果仁36吨,金额32100美元,付款方式为D/P AT SIGHT。
A公司于4月17日填写了托收委托书并交单至我国Z银行, Z银行于4月19日通过DHL邮寄到B国W银行托收。
5月18日,A公司业务员小李突然收到外商邮件,说货物已经到达了港口,询问单据是否邮寄,代收行用的哪一家。
小李急忙联系托收行,托收行提供了DHL号码,并传真了邮寄单留底联。
小李立即发送传真给外商,并要求外商立即联系W银行。
第二天客户回复说银行里没有此套单据。
A公司领导十分着急,小李质疑托收行没有尽到责任,托收行业务主管不同意A公司的观点,双方言辞激烈。
压力之下,托收行于5月20日和5月25日两次发送加急电报。
W银行于5月29日回电报声称“我行查无此单”。
但W银行所在地的DHL提供了已经签收的底联,其上可以清楚看到签收日期和W银行印章。
A公司传真给了客户并请转交代收行。
然而,W 银行不再回复。
外商却于6月2日告诉小李,B国市场行情下跌,必须立即补办提单等单据,尽快提货,否则还会增加各种占港费等,后果将很严重。
重压之下,A公司于6月4日电汇400元相关机构挂失FORMA证书,同时派人到商检局开始补办植物检疫证等多种证书。
困难的是补提单,船公司要求A公司存大额保证金到指定帐户(大约是出口发票额的2倍),存期12个月,然后才能签发新的提单。
6月9日代收行突然发送电报称“丢失单据已经找到,将正常托收”。
此刻,无论A公司还是托收行都长出了一口气,这的确是皆大欢喜的结果,不幸中的万幸。
然而这个事件让A公司乱成一团,花费和损失已经超过本次出口预期利润。
分析:根据《托收统一规则》第4条明确规定,“与托收有关的银行,对由于任何通知、信件或单据在寄送途中发生延误和(或)失落所造成的一切后果,或对电报、电传、电子传送系统在传送中发生延误、残缺和其他错误,或对专门性术语在翻译上和解释上的错误,概不承担义务或责任。

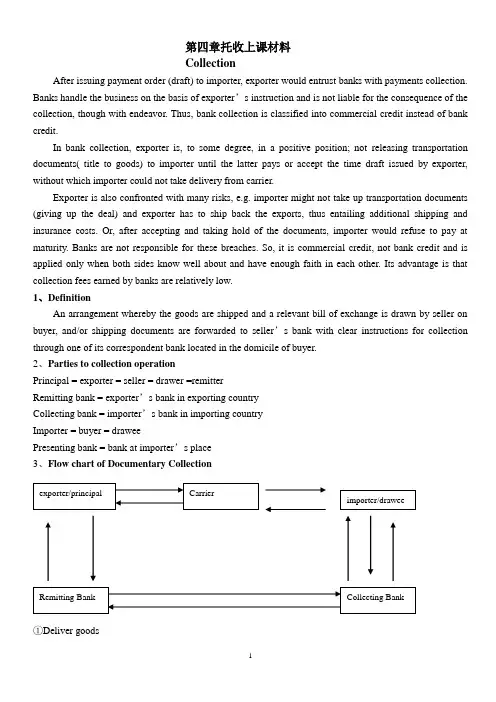
第四章托收上课材料CollectionAfter issuing payment order (draft) to importer, exporter would entrust banks with payments collection. Banks handle the business on the basis of exporter’s instruction and is not liable for the consequence of the collection, though with endeavor. Thus, bank collection is classified into commercial credit instead of bank credit.In bank collection, exporter is, to some degree, in a positive position; not releasing transportation documents( title to goods) to importer until the latter pays or accept the time draft issued by exporter, without which importer could not take delivery from carrier.Exporter is also confronted with many risks, e.g. importer might not take up transportation documents (giving up the deal) and exporter has to ship back the exports, thus entailing additional shipping and insurance costs. Or, after accepting and taking hold of the documents, importer would refuse to pay at maturity. Banks are not responsible for these breaches. So, it is commercial credit, not bank credit and is applied only when both sides know well about and have enough faith in each other. Its advantage is that collection fees earned by banks are relatively low.1、DefinitionAn arrangement whereby the goods are shipped and a relevant bill of exchange is drawn by seller on buyer, and/or shipping documents are forwarded to seller’s bank with clear instructions for collection through one of its correspondent bank located in the domicile of buyer.2、Parties to collection operationPrincipal = exporter = seller = drawer =remitterRemitting bank = exporter’s bank in exporting countryCollecting bank = importer’s bank in importing countryImporter = buyer = draweePresenting bank = bank at importer’s place3、Flow chart of Documentary Collection①Deliver goods②B/L③Documents and Instructions (Application)④Rept.⑤Collection Order or Instruction & docs.⑥Present⑦Pay⑧Release Documents D/A or D/P⑨Credit Advice or Debit Authorization⑩Hand in B/L((11))Deliver goods4、Delivering documents = Delivering goodsBuyer must take delivery of goods with bill of Lading (B/L), which is receipt issued by carrier when receiving goods delivered by seller for transportation. Importer must take delivery of goods against it. Without B/L, buyer could not get the goods at the carrier. For sight payment, only when buyer pay the sight draft drawn by seller would collecting bank release documents(B/L) to buyer. For time bill, only when buyer accepts time draft drawn by seller would collecting bank release documents to importer.(1)Documents against documents D/A①Time draft &other docs+application②Collection order& time draft & docs③Present time draft for acceptance④Accepted draft⑤docs= goods(The risk is that buyer would not pay after taking the goods,thoughgoods have been taken away.)⑥Present accepted draft for payment(Collecting bank keeps accepteddraft for exporter and at maturity, presents it for payment.)⑦pay(2)Document against payment D/P at sight①Sight draft& other docs,etc②Collection Order & sight Draft and docs③Presents for payment (Only one presentment for payment )(So, it is demanded that payment must be made on first presentation.)④Pay after checking (Importer would try to delay payment to wait the arrival of goods ) ⑤docs(3)Documents against payment at tenor D/P at tenor①Time draft & other docs ,application ②Collection order& time draft and other docs ③Present time draft for acceptance ④No docs after acceptance⑤pay (After payment at maturity, buyer gets documents.) ⑥docs(4)Documents against time promissory note made by buyer①Apply Docs.②Collection order & docs demanding time promissory note made by buyer(The risk is that buyer would not pay after taking the goods.)③Advise and demanding documents against time promissory note made by importer.④Time promissory note⑤docs⑥(Collecting bank keeps promissory note for seller and at maturity, presents it for payment.)Present timePromissory Note for payment⑦pay5、Presenting bank①ion&documents②Collection order&documents③Forwarddocuments④present6、In case of needCase of need might be seller’s close friend or agency in importing country, who would arrangeshipping back the goods or selling the goods to other buyer in importing country.①Documents (Application)②Collection Order and documents(In case of need, look for XXX)③present④refuse⑤present⑥Pay & take over docs.Exporter might have mentioned “case of need”on the draft when issuing it if exporter expects the possibility of importer’s dishonor.7、Types of collection(1): Documentary Collection①Deliver goods②B/L③Commercial docs+ financial Instrument OR not+ Application④Collection Order & docs,esp. transporting documents + bill of exchange or not⑤D/A or D/P ⑤present⑥Pay⑦Hand in B/L⑧Deliver goodsDocuments are released to importer against his payment or acceptance/Sometimes, importer pays against commercial documents, e.g. commercial invoice without financial draft to avoid stamp duty. (2): Clean Collection①Send sample ②Rept.③Delivery advice(①,②, ③,Post receipt is sent to buyer’s country together with sample by post office.) ④Hand in Delivery adv.⑤sample (④,⑤, Importer takes the advice to post office and get sample against it.) ⑥Only draft+Application⑦Collection Order& draft (Payment must be made through bank ) ⑧Present draft ⑨PayDividend warrant and time promissory note can also be used in clean collection (3): Direct Collection①Sign long terms contract with bank (Omit a tache, save much time )②Prenumbered presigned collection order③Deliver goods④B/L⑤Fill in collection order and forward documents and collection order directly to(As if it is sent by remitting bank whose responsibility is the same as under documentary collection.)⑥D/A or D/P (⑥present)⑦Pay⑧Hand in B/L⑨Deliver goods8、Collection order = Collection Instruction①Application filled in by exporter②Collection Order filled in by remitting bank[①, ②They are the same in contents, for remitting bank carry out order given by exporter (principal).]Specimen of collection orderPlease Collect the Under-mentioned Foreign Bill and /or Documents①Draft &other docs②Collection order& time draft & docs (Banks endeavor to collect for principals, but not responsible for unfavorable results.)③pay④docs(2)Bank’s responsibility①Banks must act upon the instructions given by principals②Banks check the documents received against order to see if there is any missingThe principal must be informed of any documents missing.③Banks are not responsible for examining the contents of documents, e.g. any discrepancies between docs.Sight bill: presentation for paymentTime bill: presentation for acceptance, then, presentation for payment10、Risks for exporter(1)Risks for exporter under documentary collection①Refuse to pay or accept time draft on some small inadvertent infraction of the sales contract.②Demand deep cut down of price, or refuse to accept the goods.③A heavy storage charge, fire insurance, demurrage and great expenses and time delay if court action is taken.(2)Risks for exporter under term payment①At the maturity of draft, importer refuses to pay②The excuse might be defective quality and ask for cut down of price or not having foreign exchange approved by authority.(3)Summary of possible reasons for dishonor①Economic reasons:e.g. defective quality of goods, short of flowing capital, downturn ofmarket, bankruptcy of importer,etc.②Political reasons: war, turbulence, foreign exchange control, having not got import license,etc.③The credit risk of importer (fraud) etc.(4)Protection for exporter ——Credit investigationFinancial credit and operational style of importerMarket trend of importing countryWhether import license or foreign exchange has been approved by relative authority.Whether political situation in importing country is steadyWhether a case of need could be found once dishonor happens, who could help handle returned goods, e.gwarehousing and insuring the goods, arranging shipmentof returned goods, finding another buyer for exporter, etc.Exporter could find an agency (usu.banks) to aid the investigation.To buy export credit insurance at government agency(e.g. import/export bank).Have direct control over documents, esp. the transporting documents,e.g. the consignee should be “to t he order of shipper, or collecting bank (with consent of collecting bank)”, which could be endorsed to importer only when payment is made.If it is non-negotiable transport document (e.g. airway bill), collecting bank should be the consignee who could issue delivery order to importer after the payment.(5)Example, Hedging OperationOn July 20,2000 an I/E corporation of China expected to receive €200 millions in 3 months and the spot rate of €is RMB7.6450, and 3-month forward rate is 7.6250 ~ 7.6630. As €has been weak against USD, to protect against the risk of €’s devaluation, the corporation signed a 3-month forward contract with Bank of China. After July 20, €devalued from USD0.91 all the way to USD 0.83. On Oct. 23, when the settlement was made € depreciated to RMB6.9570.Question: If the corporation was not engaged inhedging operation, how much loss would it suffer? And what is the percentage of the loss to the total amount of the contract?Answer :11、(1)Risks for importer under collection①Might be fraudulent documents.②Might be defective or dummy or not the model ordered by importer③Late shipment,and miss the optimal selling seasons.④In advance payment , can not inspect goods beforehand.⑤Dishonor would ruin importer’s reputation.(2)Protection for importerInvestigate exporter’s reputation and deal only with Credit worthy exporters.If it is time payment, payment time can be XX days/months after Bill of Lading date, which means that earlier delivery,earlier payment.Choose the most the favorable procedure of documents delivery basing on the credit standing, financial capability, market trend.e.g. if price is going high, use D/P. If price is going down,use D/A.Use D/P at tenor as possible as you can to confirm if goodsarrive at the harbor of your country.12、(1)Bill purchased under Documentary CollectionBank’s financing to exporterThere is no payment guarantee from collecting bank. So, remitting bank provide the service only for credit worthy client s.①Sight or time bill & full set of original Bill of Lading and apply for discounting the bill. ②Discounted amount③Collection Order & docs④Credit Advice or Debit Authorization ⑤Docs ⑥Pay ⑦Present(2)Discounting bill under documentary collectionThe payee on the draft is normally the discounting bank,e.g.13、Trust Receipt under D/P at tenor (1)This is Bank’s financingto importer①Time draft& other docs②Collection order & time draft and other docs ③Present time draft for acceptance ④Acceptance& IOU=T/R ⑤docs(④, ⑤ Importer borrows B/L and other documents by writing a Trust Receipt (T/R),usu. with permission of exporter.)⑥Accepted Bill &T/R ⑦pay(⑥, ⑦After selling the goods importer retires the bill with the money.) (2)The obligation of trustee, explanation of some points ①Not to put the goods in pledge to other personsthat is; trustee cannot pledge the goods to other banks for credit.②To settle claims of the collecting bank before liquidation in case of the trustee ’s bankruptcy.If trustee goes bankrupt, the entrusted goods would not joint the liquidation or entruster has first lien over the entrusted goods.③Entrusted goods should be stored and booked separately from other goods and can be examined by entruster any time.④Money from sale of entrusted goods should go directly to entruster ’s account. (3)Risks for collecting bank in T/R financingTrust Receipt does not prevent trustee from selling goods to (a third party) someone who buys the goods for value and without notice of trust (the goods does not belong to trustee). If trustee runs away with the money, the entruster could not sue the third party. Laws protects the purchaser in good faith.So, entruster usu. demands that a guarantor (usu. a bank) should sign the T/R in addition to trustee ’s signature.The principal presents an application for collection accompanied by draft and documents to the remitting bank for collection.An application for collection shows as follows:Commercial documents surrendered are below:B/L in triplicate, two originals and one copyInvoice in triplicate, two originals and one copyInsurance policy in duplicate, one original and one copyCertificate of origin in duplicate, One original and one copyPacking list in duplicate, One original and one copyCollection instructions are given below:Deliver documents against paymentRemit the proceeds by airmailAirmail advice of paymentCollection charges outside China from drawee, waive if refused by him.Airmail advice of non-payment with reasonsProtest waivedWhen collected, please credit proceeds to principal’s account with remitting bank. Remitting bank complete a collection instruction in accordance with principal’s application to add other requirements as follows:Ref No. OC2576459Date: 15 July,2000Please collect and remit proceeds to Bank of China, New York for credit of our account with them under their advice to usPlease produce a collection instruction attaching draft and documents to be forwarded to the collecting bank, Banque du Paris, Paris.Collection InstructionORIGINALTO:_________________ Date:_______Our Ref. No_______Dear Sirs,Please follow instruction marked”x”□Deliver documents against payments/acceptance.□Remit the proceeds by airmail/cable.□Airmail/cable advice of payment/acceptance.□Collect charges outside_____ from drawee,waive if refuse by him.□Collect interest for delay in payment____days after sight at____% per annum.□Airmail/cable advice of non-payment/non-acceptance with reasons.□Protest for non-payment/non-acceptance.□Protest waived.□When accepted, please advise us giving due date.□When collected, please credit our account with___.□Please collect and remit proceeds to ____for credit of our account with them under their advice to us. □Please collect proceeds and authorize us by airmail/cable to debit your account with us.Special InstructionsThis collection is subject to Uniform Rules for collection(1995 Revision) ICC Publication No.522Authorized signature(s)TRUST RECEIPTTO:__________ ________,________Received from the said bank a full set of shipping document evidencing the merchandise having an invoice value of______say______ as follows:And in consideration of such delivery in trust ,the undersigned hereby undertakes to land, pay customs duty and/or other charges or expenses ,store, hold and sell and deliver to purchasers the merchandise specified herein ,and to receive the proceeds as trustee for the said bank , and the undersigned promises and agrees not to sell the said merchandise or any part thereof on credit , but only for cash for a total amount not less than the invoice value specified above unless otherwise authorized by the said bank in writing.The undersigned further acknowledges assents and agrees that in the event the whole or any part of the merchandise specified herein is sold or delivered to a purchaser or purchaser any proceeds derived or to be derived from such sale or delivery shall be considered the property or the said bank and the undersigned hereby grants to be said bank full authority to collect such proceeds directly from the purchaser or purchaser without reference to the undersigned.The guarantor, as another undersigned, guarantees to the said bank the faith and proper fulfillment of the terms and conditions of the trust receipt.Guaranteed by: signed by:_____________ _______________________ ___________。

一、实验目的本次实验旨在通过模拟国际结算中的托收业务,使学生掌握托收的基本流程、操作方法和相关风险控制,提高学生对国际结算实践操作能力的认识。
二、实验背景在国际贸易中,托收作为一种常见的结算方式,其优势在于简化了结算流程,降低了交易成本,同时具有较好的安全性和灵活性。
本实验以我国某进出口公司与美国某公司之间的贸易合同为背景,模拟托收业务操作。
三、实验内容1. 托收业务流程(1)买卖双方签订贸易合同,约定采用托收方式结算。
(2)出口商(卖方)按照合同规定,将货物装运完毕,向银行提交托收申请书,并附上全套商业单据。
(3)托收行审核单据无误后,将单据寄送给进口商所在地的代收行。
(4)代收行收到单据后,通知进口商付款。
(5)进口商在规定期限内付款后,代收行将款项划拨给托收行。
(6)托收行收到款项后,将款项划拨给出口商。
2. 托收业务操作(1)出口商填写托收申请书,注明托收金额、付款期限、付款条件、付款人信息等。
(2)出口商向银行提交全套商业单据,包括发票、装箱单、提单、保险单等。
(3)银行审核单据无误后,将单据寄送给代收行。
(4)代收行通知进口商付款。
(5)进口商在规定期限内付款后,代收行将款项划拨给托收行。
(6)托收行收到款项后,将款项划拨给出口商。
四、实验分析1. 托收业务的优势(1)简化结算流程,降低交易成本。
(2)具有较高的安全性和灵活性。
(3)适用于各种贸易合同,适用于不同国家和地区。
2. 托收业务的风险(1)进口商可能因各种原因拒绝付款,导致出口商货款无法收回。
(2)托收过程中可能发生单据丢失、延误等问题。
(3)托收行可能因操作失误导致款项错划。
五、实验结论通过本次实验,我们掌握了托收业务的基本流程和操作方法,认识到托收业务的优势和风险。
在实际操作中,应注意以下几点:1. 确保单据齐全、准确,避免因单据问题导致托收失败。
2. 严格审查进口商的信用状况,降低风险。
3. 与托收行保持良好沟通,确保托收业务顺利进行。
第1篇一、实验目的本次实验旨在让学生了解托收业务的操作流程、适用范围以及在实际业务中的应用,掌握托收业务的风险与防范措施,提高学生对国际结算业务的认知和实际操作能力。
二、实验内容1. 托收业务的定义托收业务是指委托人(收款人)委托银行向付款人(债务人)收取款项的一种结算方式。
在托收业务中,银行作为中介机构,负责传递单据和通知付款,但不承担付款责任。
2. 托收业务的类型(1)光票托收:仅凭债权债务凭证(如汇票、本票、支票等)进行托收。
(2)跟单托收:凭跟单汇票或单据进行托收。
3. 托收业务的操作流程(1)委托人向托收行提交托收申请书和单据。
(2)托收行审核托收申请书和单据,确认无误后,向付款人发出托收通知。
(3)付款人收到托收通知后,按照托收指示进行付款或拒绝付款。
(4)托收行将款项划拨给委托人。
4. 托收业务的适用范围托收业务适用于以下情况:(1)商品交易中的货款结算。
(2)非商品交易中的款项结算,如租金、佣金、运保费等。
(3)国际贸易中的支付结算。
5. 托收业务的风险与防范措施(1)信用风险:付款人可能拒绝付款或无力付款。
防范措施:严格审查付款人的资信状况,选择信誉良好的付款人;在托收指示中明确付款条件,如逾期付款的罚金等。
(2)操作风险:银行在办理托收业务过程中可能出现的错误。
防范措施:加强内部管理,严格执行操作规程;加强员工培训,提高业务水平。
(3)汇率风险:汇率变动可能给委托人带来损失。
防范措施:采用远期汇率进行结算,锁定汇率风险。
三、实验步骤1. 模拟托收业务场景假设我方公司(委托人)向国外客户(付款人)出口一批货物,货款总额为10万美元。
根据合同约定,采用跟单托收方式进行结算。
2. 填写托收申请书委托人填写托收申请书,注明付款人信息、托收金额、单据种类、付款条件等。
3. 提交单据委托人将商业发票、装箱单、运输单据等单据提交给托收行。
4. 托收行审核托收行审核托收申请书和单据,确认无误后,向付款人发出托收通知。
国际结算——托收业务操作参考资料
1、托收的概念:是指由债权人(一般为出口商)开出汇票,委托当地银行通过其在国外的分行或代理行向债务人(一般为进口商)收取款项的结算方式。
2、托收的分类:托收方式的种类有光票托收与跟单托收两类。
光票托收:是指不附商业单据的金融单据托收。
跟单托收:是指对下列单据的托收
a. 附有商业单据的金融单据
b. 不附有金融单据的商业单据
3、托收的当事人及其责任
(1)出票人(principal):又称“本人”是委托银行取得国外付款人的付款或承兑后向其交单的人,通常就是出口方,出票人及托运人。
(2)托收行(remitting bank)
它是委托人的代理人,为委托人转托国外分行或代理行办理托收的银行,通常为出口地银行。
(3)代收行(collecting bank)
它是托收行的代理人,接受代收行的指示,在取得国外付款人的付款或承兑后向其交单,并最终得到付款的银行,通常为进口地银行。
(4)付款人(drawee)
它是按照托收指示作成提示的被提示人,通常为进口商。
(5)提示行(presenting bank)
它是向汇票付款人做成提示的代收行。
如果托收行不指定一家特定提示行,多数情况下提示行就是代收行,但也有时提示行与代收行是分离的两家银行。
(6)需要是的代理人(representative in case of need)
这是委托人指定的付款地的代理人,其作用是在付款人拒绝付款、拒收货物时,代表委托人接受单据并处理货物。
托收当事人之间的关系如下,点击观看托收结算方式一般流程:
4、托收特点:
(1)属于逆汇范畴
(2)代表商业信用
(3)主要用于国际贸易结算业务
5、跟单托收的交单条件
跟单托收依据交单条件分为承兑交单、即期交单和远期付款交单3种。
(点击黑体弹出)
(1)跟单即期付款交单(DOCUMENT AGAINST PAYMENT AT SIGHT):俗称D/P AT SIGHT,指开出的汇票是即期汇票,进口商见票,只有付完货款,才能拿到商业单据。
(2)远期付款交单(DOCUMENTS AGAINST PAYMENT OF USANCE BILL):出口商开出远期汇票,进口商向银行承兑于汇票到期日付款交单的付款交单方式。
(3)承兑交单方式(DOCUMENT AGAINST ACCEPTANCE):俗称D/A,代收银行在进口商承兑远期汇票后向其交付单据的一种方式。
点击观看承兑付款交单流程
6、跟单托收中的汇票与单据
(1)托收汇票的出票人是出口商或卖方,付款人是进口商或买方。
收款有三种情况:
a. 受益人是收款人。
当它把跟单托收汇票提交托收行时,受益人应做成托收背书交托收行。
b. 托收行是收款人。
汇票注明托收出票条款,用以表明为了托收目的而做成汇票收款人,当它把跟单托收汇票寄给代收行之前,均应做成托收背书给代收行。
c. 代收行是收款人。
代收行受到跟单汇票以前,该汇票不需要背书,汇票应注明托收出票条款。
(2)托收中的运输单据。
因运输方式不同,运输单据可以分为海运提单、,航空运单、铁路运单、多式联运单据等。
海运提单具有货物所有权凭证的性质。
(3)其他托收单据。
除了汇票和运输单据之外,跟单托收委托人还必须提交其他商业单据,其种类取决与合同条款,所提交的单据应能在表面上证明卖方已履行了所承担的合同义务。
7、银行在托收业务中的资金融通
在托收业务中,银行只作为代理人行事,不提供信用保障,但是在适当的条件下,银行也可以为进出口商提供融资便利,具体方法有以下几种:
(1)托收押汇(collection bill purchased,简称B/P)。
托收行承做托收押汇,在出口商委托时买入全套商业单据,提前支付绝大部分贷款给出口商,从而缓解其资金周转的困难。
(2)托收预付款(advance against collection)。
实际上是部分押汇与部分托收的结合做法。
托收行只对托收总金额的一定比例提供押汇融资,在扣除相应的利息及费用后,将净额预付给出口商,其余部分作托收处理。
(3)承兑信用。
是指进口商或出口商签发以融资银行为付款人的融通汇票,由融资银行提供承兑信用,然后通过贴现以取得资金的融资方式。
(4)信托收据(trust receipt)。
所谓信托收据,是指进口商承认以信托的方式向代收行借出全套商业单据时出具的证明。
进口商借得单据后,处理货物,回笼资金,在承兑汇票到期时支付足额货款,赎回信托收据,该项融资业务即告结束。
这种做法是D/P托收的变通,又称为见票后若干天付款开交单,以开出信托收据换取单据。
(D/P at □□days after sight to issue trust receipt in exchange for documents,简称D/P,T/R。
程序如下:
值得注意的是:凭信托收据提取的货物其产权仍属银行,进口商处于代为保管货物的地位,称为被信托人或代保管人。
如果该项融资得到过委托人的同意或授权,则风险由委托人自负;如果未经委托人同意,而是由代收行主动提供这项融资,则风险由代收行承担,届时代收行必须对托收行支付票款,就好像是进口商已经支付一样。
(5)担保提货(shipping guarantee)。
在有些特殊情况下,托收项下的货物可能早于商业单据抵达进口地港口。
由于没有正本提单,进口商无法提货,而延期提货会使进口商增加额外开支,或者承受进口商品行情下跌,市价回落的风险。
因此进口商回向代收行申请银行担保,凭担保在没有正本提单的情况下提货,银行保证向承运人赔偿因为不凭正本提单交货而遭受的损失。
8、托收支付方式的利弊分析
在托收业务中,出口方面临的风险远远大于进口方所面临的风险。
最低限度来说,出口商在获得进口商支
付的款项之前,要以自有资金或者银行贷款从事商品的生产或购买、包装、装运、保险等一系列活动。
这无疑占用企业的流动资金或是增加企业财务负担,加大成本开支。
从信用风险的角度看,从订立贸易合同到代收行提示进口方付款或承兑期间,由于国际商品市场的变化、进口商国内经济的变化、进口商经营状况的变化等各种原因,都有可能导致进口商不愿意或不能够履行付款的义务,或者迫使出口商降低商品的价格,这对出口商无疑是一个严重的打击。
装运后、付款前出人意料的政治风险和不可抗力,对进口商来说几乎毫无损失,对出口商而言损失将是不可补偿的。
因此,如果不是跨国公司内部之间的国际交易,如果不是长期战略伙伴关系之间的国际交易,出口商在决定对进口商实行托收结算时,必须注意:
1、通过金融机构或商务机构对进口商的资信状况,财务状况和经营状况进行尽可能详尽可靠的调查,避免与不存在的公司,资信差的公司以托收方式结算。
2、对进口国所在国家的政治经济,法制情况有一个大致的了解,尽量避免与政治动荡,经济状况恶化的国家的公司以托收方式结算。
3、尽量采取付款交单的方式,在取得付款之前牢牢掌握物权,避免财货两空的情况发生。
在付款交单国际结算方式中,进口商有可能在单到货为到的情况下,或是即便是在货物到达而无法检验商品的情况下付款。
也就是说,进口商有可能面临付款后发现货物不符的风险。
为避免此种情况的发生,进口商应尽量选择信誉好的出口商。
另外可以通过第三方尤其是官方出具商品检验证书等措施,监督出口商装运符合售货合同的商品。