伊顿离合器基础知识(中英版)-伊顿
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:7.26 MB
- 文档页数:66





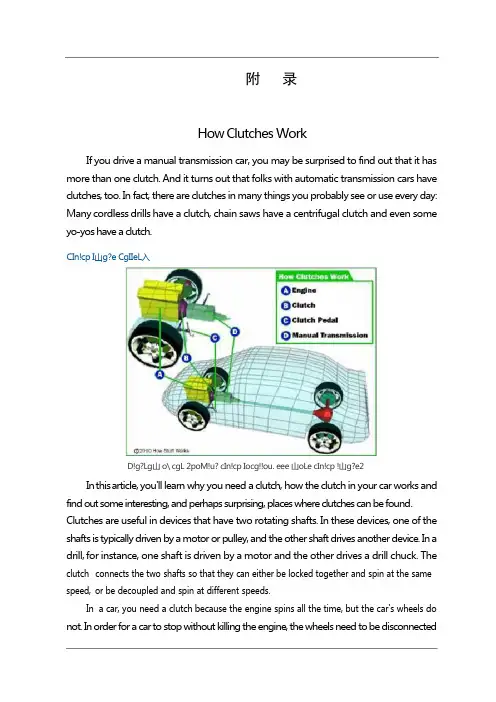
附录How Clutches WorkIf you drive a manual transmission car, you may be surprised to find out that it has more than one clutch. And it turns out that folks with automatic transmission cars have clutches, too. In fact, there are clutches in many things you probably see or use every day: Many cordless drills have a clutch, chain saws have a centrifugal clutch and even some yo-yos have a clutch.CIn!cp I山g?e CgIIeL入D!g?Lg山 o\ cgL 2poM!u? cIn!cp Iocg!!ou. eee 山oLe cIn!cp !山g?e2In this article, you'll learn why you need a clutch, how the clutch in your car works and find out some interesting, and perhaps surprising, places where clutches can be found. Clutches are useful in devices that have two rotating shafts. In these devices, one of the shafts is typically driven by a motor or pulley, and the other shaft drives another device. In a drill, for instance, one shaft is driven by a motor and the other drives a drill chuck. The clutch connects the two shafts so that they can either be locked together and spin at the same speed,or be decoupled and spin at different speeds.In a car,you need a clutch because the engine spins all the time,but the car's wheels do not. In order for a car to stop without killing the engine, the wheels need to be disconnectedf rom the engine somehow. The clutch allows us to smoothly engage a spinning engine to a non-spinning transmission by controlling the slippage between them.To understand how a clutch works, it helps to know a little bit about friction, which is a measure of how hard it is to slide one object over another. Friction is caused by the peaks and valleys that are part of every surface -- even very smooth surfaces still have microscopic peaks and valleys. The larger these peaks and valleys are, the harder it is to slide the object. You can learn more about friction in How Brakes Work.A clutch works because of friction between a clutch plate and a flywheel. We'll look at how these parts work together in the next section.Fly Wheels,Clutch Plates and FrictionIn a car’s clutch, a flywheel connects to the engine, and a clutch plate connects to the transmission. You can see what this looks like in the figure below.When your foot is off the pedal, the springs push the pressure plate against the clutch disc, which in turn presses against the flywheel. This locks the engine to the transmission input shaft, causing them to spin at the same speed.Pressure plateThe amount of force the clutch can hold depends on the friction between the clutch plate and the flywheel, and how much force the spring puts on the pressure plate. The friction force in the clutch works just like the blocks described in the friction section of How Brakes Work, except that the spring presses on the clutch plate instead of weight pressing the block into the ground.W h en the clutch pedal is pressed, a cable or hydraulic piston pushes on the release fork, which presses the throw-out bearing against the middle of the diaphragm spring. As the middle of the diaphragm spring is pushed in, a series of pins near the outside of the spring causes the spring to pull the pressure plate away from the clutch disc (see below). This r eleases the clutch from the spinning engine.Common ProblemsFrom the 1950s to the 1970s, you could count on getting between 50,000 and 70,000 miles from your car's clutch. Clutches can now last for more than 80,000 miles if you use them gently and maintain them well. If not cared for, clutches can start to break down at 35,000 miles. Trucks that are consistently overloaded or that frequently tow heavy loads can also have problems with relatively new clutches.Photo courtesy Carolina MustangClutch plateThe clutch only wears while the clutch disc and the flywheel are spinning at different speeds. When they are locked together, the friction material is held tightly against the flywheel, and they spin in sync. It's only when the clutch disc is slipping against the flywheel that wearing occurs. So, if you are the type of driver who slips the clutch a lot, you'll wear out your clutch a lot faster.Sometimes the problem is not with slipping, but with sticking. If your clutch won't release properly, it will continue to turn the input shaft. This can cause grinding, or completely p revent your car from going into gear. Some common reasons a clutch may stick are: Broken or stretched clutch cable - The cable needs the right amount of tension to push and pull effectively.Leaky or defective slave and/or master clutch cylinders - Leaks keep the cylinders from building the necessary amount of pressure.Air in the hydraulic line - Air affects the hydraulics by taking up space the fluid needs to build pressure.Misadjusted linkage - When your foot hits the pedal, the linkage transmits the wrong amount of force.Mismatched clutch components - Not all aftermarket parts work with your clutch.depress fully. If you have to press hard on the pedal, there may be something wrong. Sticking or binding in the pedal linkage, cable, cross shaft, or pivot ball are common causes. S o metimes a blockage or worn seals in the hydraulic system can also cause a hard clutch. Another problem associated with clutches is a worn throw-out bearing, sometimes called a clutch release bearing. This bearing applies force to the fingers of the spinning pressure plate to release the clutch.If you hear a rumbling sound when the clutch engages,you might have a problem with the throw-out.Types of ClutchesThere are many other types of clutches in your car and in your garage.An automatic transmission contains several clutches. These clutches engage and disengage various sets of planetary gears. Each clutch is put into motion using pressurized hydraulic fluid. When the pressure drops, springs cause the clutch to release. Evenly spacedridges, called splines, line the inside and outside of the clutch to lock into the gears and the clutch housing. You can read more about these clutches in How Automatic Transmissions Work.An air conditioning, compressor in a car has an electromagnetic clutch. This allows the compressor to shut off even while the engine is running. When current flows through a magnetic coil in the clutch, the clutch engages. As soon as the current stops, such as when you turn off your air conditioning, the clutch disengages.Most cars that have an engine-driven cooling fan have a thermostatically controlled viscous clutch -- the temperature of the fluid actually drives the clutch. This clutch is positioned at the hub of the fan, in the airflow coming through the radiator. This type of clutch is a lot like the viscous coupling sometimes found in all-wheel drive cars. The fluid in the clutch gets thicker as it heats up, causing the fan to spin faster to catch up with the engine rotation. When the car is cold, the fluid in the clutch remains cold and the fan spins s lowly, allowing the engine to quickly warm up to its proper operating temperature.Many cars have limited slip differentials or viscous couplings, both of which use clutches to help increase traction. When your car turns, one wheel spins faster than the other, which makes the car hard to handle. The slip differential makes up for that with the help of its clutch. When one wheel spins faster than the others, the clutch engages to slow it down and match the other three. Driving over puddles of water or patches of ice can also spin your wheels. You can learn more about differentials and viscous couplings in How Differentials Work.Gas-powered chain saws and weed eaters have centrifugal clutches, so that the chains or strings can stop spinning without you having to turn off the engine. These clutches work automatically through the use of centrifugal force. The input is connected to the engine crankshaft. The output can drive a chain, belt or shaft. As the rotations per minute increase, w eighted arms swing out and force the clutch to engage. Centrifugal clutches are also often found in lawn mowers, go-karts, mopeds and mini-bikes. Even some yo-yos are m anufactured with centrifugal clutches.C lu tches are valuable and necessary to a number of applications. For more information on clutches and related topics, check out the links on the following page.离合器工作原理如果您驾驶手动变速箱的汽车,您可能会惊讶地发现,它有一个以上的离合器。


t f i h S a r t l U n a l l a t s n I ™” M D “Medium Duty Clutch in 4 Steps! :l a i r e t a M e c n e r e f e R LMT-1314C e clutch. h t k c o l n u l l i w s i h T . 0 0 5 1 e v o b a M P R e n i g n e e s a e r c nt code and n e m e g a g n e s i d h c t u l c a t e s l l i w s i h t od o te r u l i a . r a e go t n i o g t o n l l i w n o i s s i m s n a rt e h t d n a e d o c : e t o N other r o s n o i t po e c n a ts i se R r e p m a T S S V e l b a m m a r g o r P g the required n i hc a e r t n e ve r p h c i h w s t i m i l d e ep s e n i g n e l a i c i f i t r a t of the clutchn e m e g a g n e s idr ep o r p t n e v e r p y a m M P R 0 0 5 1e options may need to s e h T .n o it a l l a t s n i l a i t i n i r e t f a e c i v e d g n i k c o l locking device is disengaged. h- c t u l c e h t r e t f a l i t n u d e l b a s i d e b with Service Rangerh c t u l c e t a r b i l a c e R / a t a d h c t u l c e v a . n o y e k n r u n the gear display. o s i ” N “ d i l o s a y f i r e . e n i g n e t r a t SNote: If Ser v iceRanger is available, proceed to Step 12.“Special Functions” mode is activated.arrows indicating UltraShift Touch Point Resent is selected).After the “1” is displayed, depress the throttle pedal to the floor and hold for 3-5 seconds (the gear display will change back to a “0” with down arrows indicating the routine has been successfully completed.Key off or select any mode and the UltraShift systemreturns to normal operation. Gen 3• Using se rvice ranger, select “Advanced Product Function” • Select UltraShift transmission model (Gen 3) from menu tree in the upper left.• Select the V PA/SnapShot Utility and launch the function. • Read the APF description and select “Next” • Enter the vehicle info and select “Next.”• Select “V PA” from the dropdown “Data Source” field.• Enter an output file name and location using Browse Button or use default filename and location shown.Note: If the default filename and location is used, the VPA data file will be saved to the ServiceRangerData folder in the VPA subfolder on the C:\drive.• Select the “start transfer” button to download data from transmission controller and then select “Next.” • The output file can now be viewed, select “Finish” • Select “Clutch Se rvice Utility” to launch function. • Read the APF description then select “Next.”• Select the “Clear Clutch Data” button to clear data from transmission controller.• If successful proceed to next step, if unsuccessful exit function and re-enter. Contact Roadranger Call Center 1-800-826-4357 for help.• Select the “Calibrate Clutch” button to calibrate new cultch and then Select “Finish” when complete.le e h w y l F d n a g n i s u o H l e e h w y l F e n i g n E e r u s a e M e v o m e R . r a e w h c t u l c e r u t a m e r p e b l l i w e r e h t r o s n o i t a c if i c e p s e s e h t t e e m t s u m l e e h w y l f d n ag n i s u oh l e e h w y l f e ni g n E : g n i w o l l o f e h t k c e h c d n a r o t a c i d n i l a i d a e s U . y r d d n a n a e l c e b t s u m s e c a f r u s t c a t n o c e g u a g l l A . g n i r a e B t o l i P d l o t u o n u R e c a F l e e h w y l F o t e s a b r o t a c i d n i l a i d e r u c e S t u P . e c a f g n i s u o h l e e h w y l f h t i w t c a t n o c n i r e g n i f e g u a g r e t u o e h t r a e n e c a f l e e h w y l f e n o l e e h w y l f e t a t o R . e g d e s i t u o n u r m u m i x a M . n o i t u l o v e r .) m m 0 2 . ( " 8 0 0 . Runout e r o B g n i r a e B t o l i P o t e s a b r o t a c i d n i l a i d e r u c e S n o i t i s o P . e c a f g n i s u o h l e e h w y l f s t c a t n o c t i t a h t o s r e g n i f e g u a g e t a t o R . e r o b g n i r a e b t o l i p . n o i t u l o v e r e n o l e e h w y l f " 5 0 0 . s i t u o n u r m u m i x a M . ) m m 3 1 . (. D . I g n i s u o H l e e h w y l F o t e s a b ro t a c i d n i l a i d e r u c e S r e g n i f e g u a g t u P . t f a h s k n a r c g n i s u o h l e e h w y l f t s n i a g a e n o l e e h w y l f e t a t o R . D . I t o l i p t u o n u r m u m i x a M . n o i t u l o v e r .) m m 0 2 . ( " 8 0 0 . s i e c a F g n i s u o H l e e h w y l F o t e s a b r o t a c i d n i l a i d e r u c e S . e g d e r e t u o e h t r a e n l e e h w y l f t c a t n o c n i r e g n i f e g u a g t u P l e e h w y l f f o e c a f h t i w e n o l e e h w y l f e t a t o R . g n i s u o h t u o n u r m u m i x a M . n o i t u l o v e r .) m m 0 2 . ( " 8 0 0 . s i Eaton Corporation • Truck Components OperationsP .O. Box 4013 • Kalamazoo, MI 49003 USA ww ©2011 Eaton Corporation • All rights rese rved.Printed in USA. CLMT1320 0911 WPEaton DM ClutchesMore time on the roadCheck T ransmission For W ear Replace any worn components.the disc.Remove the guide studs and install the two remaining mounting bolts. Tighten the clutch mounting bolts in a crossing pattern as on any other clutch and torque to3/8"-16 UNC X 2.25" with lockwashers, minimum grade 5 covered by the Hex Cap Screw specification under ASME B18.2.1 1996. Torque to 30 - 35 lbs. ft.。

附录A对于手动挡的车型而言,离合器是汽车动力系统的重要部件,它担负着将动力与发动机之间进行切断与连接的工作。
在城市道路或者复杂路段驾驶时,离合器成了我们最频繁使用的部件之一,而离合器运用的好坏,直接体现了驾驶水平的高低,也体现了对于车辆保护的好坏。
正确使用离合器,掌握离合器的原理以在特殊情况下利用离合器来解决问题,是每个驾驶手动挡车型的车友应该掌握的。
所谓离合器,顾名思义就是说利用“离”与“合”来传递适量的动力。
离合器由摩擦片,弹簧片,压盘以及动力输出轴组成,布置在发动机与变速箱之间,用来将发动机飞轮上储存的力矩传递给变速箱,保证车辆在不同的行驶状况下传递给驱动轮适量的驱动力和扭矩,属于动力总成的范畴。
在半联动的时候,离合器的动力输入端与动力输出端允许有转速差,也就是通过其转速差来实现传递适量的动力。
离合器分为三个工作状态,即不踩下离合器的全连动,部分踩下离合器的半连动,以及踩下离合器的不连动。
当车辆在正常行驶时,压盘是紧紧挤靠在飞轮的摩擦片上的,此时压盘与摩擦片之间的摩擦力最大,输入轴和输出轴之间保持相对静摩擦,二者转速相同。
当车辆起步时,司机踩下离合器,离合器踏板的运动拉动压盘向后靠,也就是压盘与摩擦片分离,此时压盘与飞轮完全不接触,也就不存在相对摩擦。
最后一种,也就是离合器的半连动状态。
此时,压盘与摩擦片的摩擦力小于全连动状态。
离合器压盘与飞轮上的摩擦片之间是滑动摩擦状态。
飞轮的转速大于输出轴的转速,从飞轮传输出来的动力部分传递给变速箱。
此时发动机与驱动轮之间相当于一种软连接状态。
一般来说,离合器是在车辆起步和换挡的时候发挥作用,此时变速箱的一轴和二轴之间存在转速差,必须将发动机的动力与一轴切开以后,同步器才能很好的将一轴的转速保持与二轴同步,挡位挂进以后,再通过离合器将一轴与发动机动力结合,使动力继续得以传输。
在离合器中,还有一个不可或缺的缓冲装置,它由两个类似于飞轮的圆盘对在一起,在圆盘上打有矩形凹槽,在凹槽内布置弹簧,在遇到激烈的冲击时,两个圆盘之间的弹簧相互发生弹性作用,缓冲外界刺激。

更多信息请到RoadRanger网站查询:警告标识本手册中的有些段落会有DANGER,WARNING,或者CAUTION的标识。
这些段落包含特殊的安全信息,进行操作之前必须通读理解这些信息,并在操作过程中留意。
DANGER:该标识表明如果不遵守规定的操作程序,会有人员严重受伤或死亡的可能。
WARNING:该标识表明有直接的危险存在,如果不遵守规定的操作程序,会有人员严重受伤的可能。
CAUTION:该标识表明如果不遵守规定的操作程序,会导致车辆损坏或财产损失。
注意:在操作过程中注意细节有助于故障诊断或系统维修。
操作变速器前通读本手册车辆启动前驾驶员要坐在驾驶员座椅上,按空档(N),拉起手刹如果启动发动机时变速器没有在空档位(N),立刻检查车辆你在操作车辆过程中如果要停车或暂时下车,一定要按空档(N),拉起手刹,并在车轮处加塞块出于安全的原因,变速器挂档前请踩住刹车踏板进行任何焊接操作前,24V电池的正极和负极必须完全断开高压警告标识使用二氧化碳或者干粉灭火器,电池盒中的电池为锂离子电池高压线束为橙红色,并在接头位置有警告标签所有Eaton的柴油混合动力车辆在车内都有高压元件位置图不要切断或移动橙红色高压线束,参见高压元件位置图不要切割或打开电池盒,参见高压元件位置图不要切割或打开逆变器,参见高压元件位置图本手册中的紧急关机程序会说明如何在紧急情况时关闭电源警告标识 (i)紧急关机程序 (1)发生火灾时的紧急程序 (2)发生交通事故时的紧急程序 (2)高压元件特征 (3)换档按钮说明 (4)启动和停车 (5)倒档 (6)前进档-自动换档模式 (6)前进档-手动换档模式 (6)低速档 (7)再生制动模式 (7)一般型号信息 (8)故障排除 (9)档位卡死 (9)正确润滑 (10)正确的油面高度: (11)混合动力冷却系统 (11)紧急关机程序方法1:关钥匙(推荐)发动机会关闭仪表盘会关闭混合动力系统会关闭混合动力电池只在电池盒中有电方法2:断开24V电池发动机会关闭仪表盘会关闭方法3:拔掉混合动力控制器的保险丝(30A)混合动力系统会关闭混合动力电池只在电池盒中有电这些程序只适用于紧急情况,车辆维修时请参见《维修手册》中的相关内容发生火灾时的紧急程序如果车辆发生火灾:1.使用二氧化碳或者干粉灭火器,电池盒中的电池为锂离子电池高压线束为橙红色,并在接头位置有警告标签所有Eaton的柴油混合动力车辆在车内都有高压元件位置图不要切断或移动橙红色高压线束,参见高压元件位置图不要切割或打开电池盒,参见高压元件位置图不要切割或打开逆变器,参见高压元件位置图发生交通事故时的紧急程序如果条件允许,请把车推到路肩上并停车1.拉手刹2.按空档(N)3.关钥匙4.如果安全的话,下车高压线束为橙红色,并在接头位置有警告标签所有Eaton的柴油混合动力车辆在车内都有高压元件位置图不要切断或移动橙红色高压线束,参见高压元件位置图不要切割或打开电池盒,参见高压元件位置图不要切割或打开逆变器,参见高压元件位置图高压元件特征所有的高压线束为橙红色,并在接头位置有警告标签;每一个高压元件都有明显的警告或危险标识。