重邮软件工程专业综合英语作业
- 格式:docx
- 大小:17.06 KB
- 文档页数:2

2022年重庆邮电大学软件工程专业《操作系统》科目期末试卷A(有答案)一、选择题1、一个多道批处理系统中仅有P1,和P2两个作业,P2比P1晚5ms到达。
它们的计算和I/O操作顺序如下:P1:计算60ms,I/O 80ms,计算20msP2:计算120ms,I/O 40ms,计算40ms。
若不考虑调度和切换时间,则完成两个作业需要的时间最少是()。
A.240msB.260msC.340msD.360ms2、下列关于批处理系统的叙述中,正确的是()I.批处理系统允许多个用户与计算机直接交互II.批处理系统分为单道批处理系统和多道批处理系统III.中断技术使得多道批处理系统的1/O设备可与CPU并行工作A.仅II、IIIB.仅IIC.仅I、IID. 仅I、III3、为多道程序提供的共享资源不足时,可能会产生死锁。
但是,不当的()也可能产生死锁。
A.进程调度顺序B.进程的优先级C.时间片大小D.进程推进顺序4、下面哪个不会引起进程创建()A.用户登录B.作业调度C.设备分配D.应用请求5、进程和程序的本质区别是()A.前者分时使用CPU,后者独占CPUB.前者存储在内存,后者存储在外存C.前者在一个文件中,后者在多个文件中D.前者为动态的,后者为静态的6、为了使多个进程能有效地同时处理输入和输出,最好使用()结构的缓冲技术。
A.缓冲池B.循环缓冲C.单缓冲D.双缓冲7、 CPU输出数据的速度远远高于打印机的速度,为解决这一矛盾,可采用()。
A.并行技术B.通道技术C.缓冲技术D.虚存技术8、若文件f1的硬链接为f2,两个进程分别打开fl和f2,获得对应的文件描述符为fd1和fd2,则下列叙述中,止确的是()I.fl和f2的读写指针位置保持相同II.fl和f2共享同个内存索引节点III.fdl 和fd2分别指向各自的用户打开文件表中的一项,A.仅IIB. 仅II、IIIC.仪I、IID. I、II和II9、一个磁盘的转速为7200r/min,每个磁道有160个扇区,每个扇区为512B.那么理想情况下,其数据传输率为()。

计算机专业英语作业答案(供参考)计算机专业英语作业1第1-3章作业一.Vocabulary( 词汇)(一).Translate the following words and expressions into Chinese(写出下列词组的汉语。
) 1.central processing unit(CPU)中央处理器 2.title bar 标题栏3.operating system 操作系统4.personal computer 个人计算机5.menu bar 菜单栏6.desk publishing 桌面排版7.electronic spreadsheet 电子表格8.hard disk 硬盘9.database 数据库10.Cursor 光标(二).Fill in the blanks with the corresponding English abbreviations.(根据汉语写出相应的英语缩写。
)1.随机存储器RAM 2.只读存储器ROM3.传输控制协议TC P 4.数字视频光盘DVD5.通用串行总线USB 6.计算机辅助设计CAD7.计算机辅助制造CAM 8.中央处理器CPU(三).Translate the following Chinese into English.(根据汉语写出相应的英语。
)1.键盘keybord 2.鼠标mouse 3.扫描仪scanner4.打印机printer 5.输入input 6.输出output7.显示器monitor 8.存储器storage 9.数据库database 10.操作系统operating system 11.应用软件application software 12.字处理器word processor 13.网络浏览器web browser二.Tell whether the following statements are true(T) or false(F).(判断正误。


计算机专业英语大作业Patterns Instruction in Software EngineeringAbstract:The paper deals with a training system with a client-server architecture created for students who are learning to design and implement object-oriented software systems with reusable components, and also targeting those users who wish become accustomed with (or improve their skills related to) software design.The paper briefly presents the design patterns which are to be found in the software library, as well as the manner of applying them.The user of such a system has five types of patterns at his/her disposal (Factory Method, Builder, Command, Mediator, Observer), out of which will be able to chose one/more than one, depending on the requirements of the system proposed for design.1.IntroductionMotto: “The software design patterns help you learn more from other people’s successes than from your own failures”[Mark Johnson] .A software system is a dynamic entity that undergoes multiple changes during its life-cycle, under the influence of factors such as: new user requirements, adding new functionalities, environment adjustment, etc.Therefore, apart from fulfilling those functions which it was designed to fulfill, a software application must be easily changeable, with some of its modules eventually re-used.Having this goal, the application must fulfill certain requirements regarding robustness, mobility, flexibility, scalability, etc.The software design principles are regarded as ways of obtaining the right and re-usable design.By applying abstractization and OOP languages polymorphic techniques, the open-shut principle and the substitution principle (Liskov) upon classes of problems, common solutions were reached –solutions which make up the so-called design patterns.The software patterns facilitate re-using design and architecture.If the design and/orarchitecture of a system were built with design patterns (techniques which have proven efficient), then they will be more accessible and easier to understand by those software developers who build new systems based on old design.The patterns help the software specialist chose that design that makes the system re-usable.In software engineering, “design pattern”(DP) means a solution applicable to a certain type of problems.A design pattern is a description model of how a problem should be solved.A pattern cannot be directly transformed in source code.The purpose of design patterns is to enable a “good”object-oriented design, and more than that –to make it reusable (which is more important than reusing the code, regardless of the fact that reusing the design often implies reusing the code).The quality of software design is proportional to the experience and previous knowledge of the one performing it.An expert applies solutions previously used and proven efficient for similar problems.When the expert finds a solution considered acceptable, he/she uses it again.Design patterns solve specific design problems, making the OO more flexible, elegant and reusable.DP help beginners with software design, proposing patterns based on previous experience.A user who is familiar with the DP-s can apply them instantly in order to solve specific problems, without having to rediscover them.By using the software design patterns while designing an object-oriented architecture, one is guaranteed to obtain system compliance to software engineering principles, while also preserving the qualities of “good design”: reusable, flexible, robust .2.Design PatternsDepending on the DP purpose, the authors of GoF [4] proposed three main categories of patterns: creational patterns, structural patterns and behavioral patterns.These are the most well-known DP, but not the only ones.Other types of patterns emerged –more or less popular –as well as variations of the GoF patterns.A pattern has four essential components:: the name of the DP must describe in a few words a design pattern problem, its solutions and the solution’s effects.2.Problem: describes the situations when the pattern is applicable, explaining the problem as well as its context.3.Solution: describes the components of the design, the relationships between them, the responsibilities of each component and the way they interact.The solution does not describe a specific design for a certain situation or a correct implementation, because a pattern has a general character, referring to a plethora of contexts.The DP presents an abstract description of a problem and a general arrangement of the components (classes and objects) that solve the described problem.4.Effects: refer to the results of applying the pattern, which are very important when we evaluate the alternatives and we estimate the costs and benefits of applying the pattern.The effects of a pattern are also to be perceived in the flexibility, extensibility and portability of a system.DP identifies the classes and instances which participate, their role, collaboration and responsibility sharing between them.The design patterns that the user of the proposed system has at hand are: Factory Method and Builder (from the Creational Patterns category), Command, Mediator and Observer, (from the Behavioral Patterns category).3.The Architecture of the SystemThe platform is designed as a distributed application, providing the option of distance learning/tutoring by means of a computer network or the Internet.The application can be classified as having “three - tier" architecture, the Client part being represented by the configuration module and the tutoring material presentation module.The user connects to the system by means of a Login module, monitored by an Administrator agent (CerberusAgent).After authentication the user may have access to a configuring instrument (if the user connected to the system is the tutor) or to the user interface by means of which the learning material will be presented (if the user is a student).This part of the application will be monitored by an interface agent (InterfaceAgent).The application server contains the agent platform that monitors the student activity, and a web server responsible for delivering the learning material to the user interface (Apache Tomcat).The third level consists of a xml database (Apache Xindice), which stores information about the structure of the course, student models, etc.The MTS training system is designed for students which learn to design and implement object-oriented software systems, with re-usable components, but also for those users who wish to become familiar with (or improve) software design.We present the approach of a multi-agent intelligent platform for tutoring student which provides a Student Model.The “modeling student process”used the overlay architecture (common for many tutoring systems) combined with the Bayesian Theory of Probability .The system’s tasks are distributed among the intelligent agents (software agents), each having clearly specified individual roles as following: administrator (Cerberus Agent); interface (InterfaceAgent); tutor (Tutor Agent); student (Student Agent).Moreover, the system has “three-tier”architecture and was implemented in Java language.We may well imagine software agents attached to every application or tutoring environment, each having an explicit representation of the users’objectives, of their plans and resources.These agents communicate and negotiate with each other in order to fulfill their individual or group objectives.The multi-agent tutoring system (MTS) was designed and implemented within the Computer Science Department, in which research focused upon “modeling”the student with a view to identifying the most suitable methods and tutoring strategies by taking into account individual knowledge and abilities.The user of this kind of system has all five types of previously described patterns at his/her disposal (Factory Method, Builder, Command, Mediator, Observer), out ofwhich will be able to use one or more, depending on the requirements of the system that needs to be designed.Depending on the needs of the user that must fulfill the requirements of the system, one selects from Tutor Agent the design patterns best suited for those functions.The patterns help build the menus of the application and the user interface.Then the database is built, as the user has permanent access to an example of application as similar as possible to the one which needs to be carried out.In order to develop an application, the student must know the Java programming language, must be familiar with MySql data servers and must be able to use the Eclipse platform.The Eclipse platform is an open source framework from IBM which aims to provide a variety of basic services for software developers [6].4.ConclusionsThe system wishes to be a useful working instrument for software application development training, for both students and other types of users.A design pattern together with an example of using that pattern may become a way of working in software design.Moreover, in this case applying design patterns –therefore design principles - in carrying out an object-oriented application results into a reusable design and reusable modules / components.Also, the resulting code enjoys more robustness and flexibility, these two characteristics being essential for developing new modules that would add new functionalities and operations to the application; the design/code of the application is open to extension and closed for changes, according to OCP.Another important aspect relates to the maintenance activities which the designed application will undergo along its life-cycle: they will more cost effective, as no change will disseminate through the entire system, the application code being built so that it isolates the volatile classes (according to the principle of reversing dependencies), the dependencies being in the way”details depend upon abstractization”and not the other way around.The software patterns ensurecompliance to design principles, as they contribute to obtaining a steady and efficient system, and they provide design discipline for st but not least, using such a system in software engineering learning makes the process much more attractive and efficient.The design patterns approach in software engineering training fits the pedagogical Schemas Theory (created by Bartlett at the beginning of the 20th century) .A brief representation of the particular knowledge of the training domain can help the trainee to easier absorb the new information, while the organization and structuring of the knowledge as patterns will guide him/her in finding (remembering) the necessary information in a certain context.We believe that within such an approach one can create a training ontology from Software Engineering.软件工程模式教学摘要:本页处理一种C/S架构旳训练系统, 为学习设计和实行一种面向对象旳用可重用组件旳软件系统旳学生而设计, 也将目旳瞄准那些顾客谁但愿成为(或提高他们旳有关技能)软件设计习惯。
2022年重庆邮电大学软件工程专业《计算机网络》科目期末试卷A(有答案)一、选择题1、()不是对网络模型进行分层的目标。
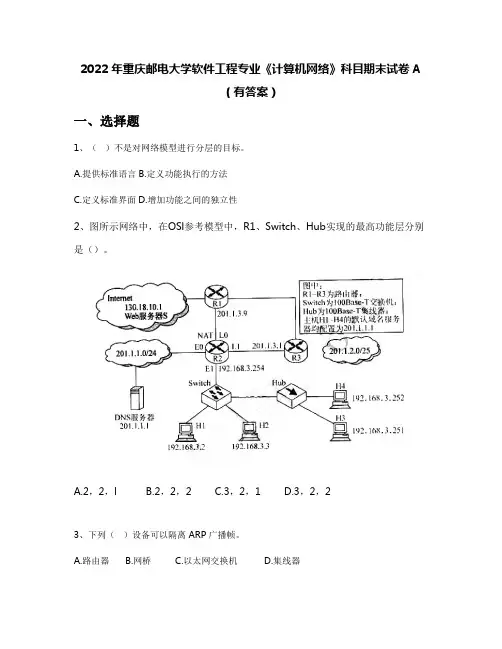
A.提供标准语言B.定义功能执行的方法C.定义标准界面D.增加功能之间的独立性2、图所示网络中,在OSl参考模型中,R1、Switch、Hub实现的最高功能层分别是()。
A.2,2,lB.2,2,2C.3,2,1D.3,2,23、下列()设备可以隔离ARP广播帧。
A.路由器B.网桥C.以太网交换机D.集线器4、路由器的分组转发部分由()部分组成。
A.交换结构B.输入端口C.输出端口D.以上都是5、下列关于循环冗余校验的说法中,()是错误的。
A.带r个校验位的多项式编码可以检测到所有长度小于或等于r的突发性错误B.通信双方可以无需商定就直接使用多项式编码C.CRC可以使用硬件来完成D.在数据链路层使用CRC,能够实现无比特差错的传输,但这不是可靠的传输6、为了检测5比特的错误,编码的海明距应该为()。
A.4B.6C.3D.57、主机甲与主机乙之间已建立一个TCP连接,双方持续有数据传输,且数据无差错与丢失。
若甲收到1个来自乙的TCP段,该段的序号为1913,确认序号为2046,有效载荷为100B,则甲立即发送给乙的TCP段的序号和确认序号分别是()。
A.2046,2012B.2046,2013C.2047,2012D.2047,20138、假设某应用程序每秒产生一个60B的数据块,每个数据块被封装在一个TCP报文中,然后再封装到一个IP数据报中,那么最后每个数据报所含有的应用数据所占的百分比是()(注意:TCP报文和IP数据报的首部没有附加字段)。
A.20%B.40%C.60%D.80%9、若甲向乙发起一个TCP连接,最大段长MSS-1KB,RTT-5ms,乙开辟的接收缓存为64KB,则甲从连接建立成功至发送窗口达到32KB,需经过的时间至少是()。
A.25msB.30msC.160msD.165ms10、不使用面向连接传输服务的应用层协议是()。

2022年重庆大学软件工程专业《计算机网络》科目期末试卷A(有答案)一、选择题1、在OSl参考模型中,自下而上第一个提供端到端服务的是()。
A.数据链路层B.传输层C.会话层D.应用层2、因特网采用的核心技术是()。
A.TCP/IPB.局域网技术C.远程通信技术D.光纤技术3、BGP报文封装在()中传送。
A.以太帧B.IP数据报C.UDP报文D.TCP报文4、路由器的分组转发部分由()部分组成。
A.交换结构B.输入端口C.输出端口D.以上都是5、以下哪种滑动窗口协议收到的分组一定是按序接收的()。
I.停止-等待协议 II.后退N帧协议 III.选择重传协议A. I,IIB. I,IIIC.II,IIID.都有可能6、PPP提供的功能有()A.一种成方法B.链路控制协议(LCP)C.网络控制协议(NCP)D.A.B和C都是7、若甲向乙发起一个TCP连接,最大段长MSS-1KB,RTT-5ms,乙开辟的接收缓存为64KB,则甲从连接建立成功至发送窗口达到32KB,需经过的时间至少是()。
A.25msB.30msC.160msD.165ms8、UDP数据报比IP数据报多提供了()服务。
A.流量控制B.拥塞控制C.端口功能D.路由转发9、UDP报文头部不包括()。
A.目的地址B.源UDP端口C.目的UDP端口D.报文长度10、下列关于SMTP的叙述中,正确的是()。
I.只支持传输7比特ASCII码内容II支持在邮件服务器之间发送邮件III支持从用户代理向邮件服务器发送邮件IV支持从邮件服务器向用户代理发送邮件A.仅I、II和IIIB.仅I、II和IVC.仅I、III和IVD.仅II、III和IV11、电子邮件经过MIME扩展后,可以将非ASCII码内容表示成ASCII码内容,其中base64的编码方式是()。
A.ASCII 码字符保持不变,非ASCII 码字符用=XX表示,其中XX是该字符的十六进制值B.不管是否是ASCII 码字符,每3个字符用另4个ASCII字符表示C.以64为基数,将所有非ASCII 码字符用该字符的十六进制值加64后的字符表示D.将每4个非ASCII码字符用6个ASCHI码字符表示12、()被用于计算机内部的数据传输。

软件工程英语作文Software engineering is a field that constantly evolves and adapts to new technologies and methodologies. It requires a combination of technical skills, problem-solving abilities, and creativity. The process of developing software involves various stages, including planning, designing, coding, testing, and maintenance.In software engineering, collaboration and communication are crucial. Team members need to work together effectively, share ideas, and provide feedback to ensure the success of a project. It's important to have good interpersonal skills and the ability to work well in a team environment.One of the key principles of software engineering is to write clean and maintainable code. This involves following coding standards, using consistent naming conventions, and writing comments to explain the purpose of the code. By writing clean code, it becomes easier for other developersto understand and modify the software in the future.Software engineering also involves the use of various tools and technologies to aid in the development process. These can include integrated development environments (IDEs), version control systems, and automated testing frameworks. Keeping up to date with the latest tools and technologies is essential for software engineers to stay competitive in the industry.Quality assurance is an important aspect of software engineering. Testing software for bugs and errors iscrucial to ensure that it meets the requirements and functions as intended. This can involve various types of testing, such as unit testing, integration testing, and user acceptance testing.Continuous learning is a fundamental part of being a software engineer. With new technologies emerging all the time, it's important to stay updated and expand one's skill set. This can involve taking courses, attending workshops, or simply experimenting with new technologies in personalprojects.In conclusion, software engineering is a dynamic and challenging field that requires a combination of technical skills, teamwork, and continuous learning. It's a field that offers plenty of opportunities for growth and innovation, making it an exciting career choice for those passionate about technology.。

软件工程英文作文英文:Software engineering is a field that involves the development and maintenance of software systems. It is a complex process that requires a combination of technical skills, creativity, and project management expertise. As a software engineer, I have to be proficient in programming languages, software design patterns, and testing methodologies. I also need to be able to communicate effectively with other team members, stakeholders, and clients.One of the most important aspects of software engineering is the software development life cycle (SDLC). This is a process that involves planning, designing, coding, testing, and maintaining software systems. Each stage ofthe SDLC is crucial to the success of the project, and any errors or issues that arise during one stage can have a significant impact on the entire project.In addition to technical skills, software engineers also need to have strong project management skills. This involves being able to manage timelines, budgets, and resources effectively. It also involves being able to communicate with stakeholders and clients to ensure that their needs are being met.Overall, software engineering is a challenging but rewarding field. It requires a combination of technical and soft skills, as well as a willingness to learn and adapt to new technologies and methodologies.中文:软件工程是一个涉及软件系统开发和维护的领域。

软件工程复习题PART-A Multiple-c hoice Questions1.When should the system testing phase begin? ( C )A. After beta testingB. Before unit testingC. After white box testingD. Before functional testing2.Which is included in the software requirements specification? ( C )A. error handlingB. data descriptionC. functional descriptionD. performance description3.Which factors must be most considered when developing acceptance criteria?( B )A. user availabilityB. match with requirementsC. ability to benchmark systemD. schedule of system delivery4.Software _____ is work done to enhance software functionality, correct errors and improvethe performance of software. ( B )A. re-designsB. MaintenanceC. CorrectionsD. Re-engineering5.Which type of testing is not a part of system testing? ( D )A. Stress testingB. Function testingC. White box testingD. Incremental testing6.Which are included in the software requirements specification? ( B, D )A. error handlingB. functional descriptionC. data descriptionD. maintainability description7. A data dictionary was created during the requirements analysis phase of a softwareengineering project. What information does it contain? ( A,B,D )A. interfaceB. data typeC. restrictionsD. content description8.What is configuration management in software engineering?( C )A. overall management of the design of the systemB. management of the configurable components in a systemC. the identification of the configuration of a system at discreet points in time to controlchanges to the configurationD. in object-oriented programming, the management of objects that control theconfiguration of some other function(s) in the systemPART-B Fill up the blanks1.Most product need ___maintenance_______ because of wear and tear caused by theusage2.__Evolutionary___________ Model is known as the successive versions model3.ISO is abbreviated as____International Standard Organization _________4.__Verification _________ is the process of determining whether one phase of a softwareproduct confirms to its previous phase5.Black-box testing is also known as____ Functional testing or Closed Box ______6.White-box testing is also called the __Structural testing. or Open Box ____7.__ Software reverse engineering ___ is the process of recovering the design and therequirement specification of product from an analysis of its code8.__ Software Life Cycle____ is the series of identifiable stage that a software productundergoes during its life timePART–C Answer the following in one or two sentences each question1.Define software EngineeringAns:It is an approach to develop software using engineering approachEngineering approach meansHEAVY USE OF PAST EXPERIENCEOPTIMIZATIONCOST EFFECTIVENESS2.What is meant by software configuration management?Ans:Software configuration management is the art of identifying, organizing and controlling modifications to the software being built by a programming team 3.Explain Characteristics of a Good SRS Document.Ans:a.It should be concise and at the same time unambiguous.b.It should be consistent.c.It should be complete.d.It should be well-structured and easily modifiable.4.Generate test cases to compute the square root of integer values in the rangebetween 0 and 2000 using Boundary Value Analysis.Ans:{0, 1, 2000, 2001}Boundary Value Analysis5.What is a Formal Technique?Ans:A formal technique is a mathematical method to specify a hardware and/orsoftware system, to verify whether a specification is realizable, to validate whether an implementation satisfies its specification and to prove properties ofa system without necessarily running the system, etc.6.Define Software Life Cycle Model.Ans:Software life cycle is the series of identifiable stage that a software product undergoes during its life time7.Define Fan-OutAns: It is a measure of the number of modules that are directly controlled by a given module. A design having modules with high fan-out is not a good design as such modules would lack cohesion.8.Explain the need of an SRS Document.Ans:a.An SRS establishes the basis for agreement between the client and thesupplier on what the software product will do.b.An SRS provides a reference for validation of the final product.c. A high quality SRS is a prerequisite to high-quality software.d. A high-quality SRS reduces the development cost.9.Generate test cases to compute the square root of integer values in the rangebetween 0 and 5000 using Boundary Value Analysis.Ans:{0, 1, 5000, 5001}Boundary Value Analysis10.Define Decision tableAns:Decision table specify which variables are to be tested, what actions are to betaken and the order in which decision making is to be performed.PART–D Write Short notes1.Empirical Estimation TechniquesAns:Empirical estimation techniques are based on making an educated guess of the project parameters. Although empirical estimation techniques are based on common sense, and experience over the years. The two most widely used empirical estimation techniques are•Expert JudgmentIt is one of the most widely used estimation techniques. In this approach an expert makes an educated guess of the problem size after analyzing the problem thoroughly•Delphi TechniqueIt tries to overcome some of the short coming of the previous method. It is carried out by a team composed of a group of experts and a coordinatoranization and Team StructuresAns:Every software organization handles several projects. Software organizations assign a team of engineers to handle a software project. There are a few standard ways in which software organizations and teams are structured.There are essentially two broad ways in which a software development organization is structured:•Functional format•Project formatTeam StructureProblems of different complexities and sizes require different team structures. For effective solution, usually every organization has a standard formal team structure. The three common formal team structures followed by most organizations are•Democratic Team Structure•Chief Programmer Team Structure•Mixed Team Structure3.Code InspectionsAns:Code inspections aim explicitly at the discovery of commonly made mistakes. Most software development companies collect statistics to identify the type of errors most frequently committed. Such a list of commonly committed(提交)errors can be used during code inspections to keep a look-out for possible errors.The following is a list of some classical programming errors which can be looked for during code inspections:►Use of uninitialized variables.►Jumps into loops.►Non terminating loops.►Incompatible assignment.►Array indices out of bounds.►Improper storage allocation and deallocation.4.Black-Box TestingAns:This testing methodology looks at what are the available inputs for an application and what the expected outputs are that should result from each input. It is not concerned with the inner workings of the application, the process that the application undertakes to achieve a particular output or any other internal aspect of the application that may be involved in the transformation of an input into an output.Most black-box testing tools employ either coordinate based interaction with the applications graphical user interface (GUI) or image recognition.An example of a black-box system would be a search engine.You en ter text that you want to search for in the search bar, press “Search” and results are returned to you.In such a case, you do not know or see the specific process that is being employed to obtain your search results, you simply see that you provide an input – a search term – and you receive an output – your search results5.Data Flow Diagrams (DFDs)Ans:The DFD (also known as the bubble chart) is a simple graphical notation that can be used to represent a system in terms of the input data to the system, various processing carried out on these data and the output data generated by the systemPrimitive Symbols Used for Constructing DFDsThere essentially five different symbols used to construct DFDs. These primitive symbols are depicted in BELOWFIGURE6.Risk (danger or loss) ManagementAns:A risk is any unfavorable (not encouraging or pleasing) event orcircumstances that can occur while a project is underway.Risk management aims at dealing with all kinds of risks that might affect aproject. Risk management consists of three essential activities:Risk Identification,Risk assessment,Risk containmentPART–E Solve the Problems1.Given Control flow graph G of a program for GCD .Calculate the cyclomaticcomplexity.Ans:Given a control flow graph G of a programThe cyclomatic complexity V(G) can be computed asV(G) = E-N+2Where,N is the number of nodes of the control graphE is the number of edges in the control flow graphEdge =8 and Node =6By substituting the values in Cyclomatic complexity formula we get, V(G)= 8 – 6 + 2The cyclomatic complexity = 4pare different software life cycle modelsAns:3.Mention Guidelines for Constructing DFDsAns:Some simple guidelines for constructing the DFD representation of a system, which have been developed after studying the different mistakes that beginners usually make while constructing the DFD model of systems are as follows:►The context diagram should depict the system as a single bubble. Many beginners commit the mistake of drawing more than one bubble in the contextdiagram.►All external entities interacting with the system should be represented only in the context diagram and these should not appear at other levels of the DFD.►Only 3 to 7 bubbles per diagram should be allowed, i.e. each bubble should be decomposed to between 3 and 7 bubbles.►A DFD does not represent control information such as when or in what order different functions (processes) are invoked and nor does it represent theconditions under which different functions are invoked.►All the functionalities of the system must be captured by the DFD model, i.e. no function of the system specified in the SRS document should be overlookedSRS.4.Calculate the length and volume of the f ollowing source code using Hallstead’sTechniquemain ( ){int a, b, c, avg;scanf (“%d %d %d”, &a, &b, &c);avg = (a + b + c) / 3;printf (“Average = %d”, avg);}Ans:The total number of unique operators ( n1 ) are : 12The total number of unique operands ( n2 ) are : 11Estimated Length = (12 * log 12 + 11 * log 11)= (12 * 3.58 + 11 * 3.45)= (43 + 38)= 81Volume = Length * log (23)= 81 * 4.52= 3665.Explain Classical Waterfall ModelAns:Feasibility studyThe aim of the feasibility study is to determine whether developing the product is financially and technically feasibleRequirement analysis and specification phasThe aim of the requirement analysis and specification phase is to understand the exact requirements of the customer and to document them properly. This phase consists of two distinct activities:Design phaseThe goal of the design phase is to transform the requirements specification into a structure that is suitable for implementation in some programming language. Two distinct design approaches followed in different industries are:Coding and Unit TestingThe purpose of this phase (also called the implementation phase) of software development is to translate the software design into source code. The end product ofthe implementation phase is a set of program modules that have been individually tested.Implementation phaseDuring this phase the different modules are integrated in a planned manner. The different modules making up a system are almost never integrated in a single shot. The goal of system testing is to ensure that the developed system functions according to its requirements as specified in the SRS document. The system testing usually consisting of three different kinds of testing activities6.List three major types of risks in a software projectAns:A project can be affected by a variety of risks. The three main categories of risks which can affect a software project are:•Project risksBudgetary, schedule, personnel, resource, customer-related problems etc.•Technical risksPotential design, implementation, interfacing, testing and maintenance problems. In addition, ambiguous specification, incomplete specification, changing specification, technical uncertainty and technical obsolescence.•Business risksThese risks include building an excellent product that no one wants, not fulfilling budgetary or personnel commitments etc.。

Chapter 1 An Introduction to Software Engineering1. Why software engineering is important?软件工程由应对软件危机也产生,软件工程的发展极大地完善了我们的软件。
软件工程的研究使得我们对软件开发活动有个更深入的了解,并且已经找到了进行软件描述、设计和实现的有效方法。
软件工程中新的标记发和工具大大降低了制作大型、复杂系统的工作量2. What is software? What is software engineering?软件工程是一门工程学科,包括了软件开发的各个方面,从最初的系统描述一直到使用后的系统维护,都属于其学科范畴。
3. What is the difference between software engineering and computer science?计算机科学研究的是构成计算机和软件系统基础的有关理论和方法,耳软件工程则研究软件制作中的实际问题。
计算机科学侧重理论和基础; 软件工程侧重软件开发和交付的实际活动。
4. What are the attributes of good software?软件除了提供基本的功能,对用户来说是还应该是可维护的、可依赖的和可接受的。
可维护性,软件必须能够不断变化以满足变化;可依赖性,软件必须可以被信赖;有效性,软件不能浪费系统资源;可用性,使用起来比较容易5. What is CASE?CASE 工具是一些软件系统,被设计成支持软件过程中的常规活动,如编辑设计图表、检查图表的连贯性、跟踪已经运行的程序测试等。
6. What is the difference between software engineering and system engineering?系统工程侧重于计算机系统开发的所有方面,包括硬件、软件和处理工程。
软件工程是整个系统的一部分,它关心系统中基础软件、控制软件、应用软件和数据库的开发。

软件工程专业英文作文英文,As a software engineering professional, I findthe field to be both challenging and rewarding. Throughout my career, I've encountered various aspects of software engineering that have broadened my understanding and skill set.One fundamental aspect of software engineering is the development process. It involves stages like requirements gathering, design, implementation, testing, and maintenance. Each stage presents its own set of challenges and requires specific expertise. For example, during the requirements gathering phase, communication skills are crucial to understanding the needs of the stakeholders and translating them into technical requirements. This often involves conducting interviews, surveys, and workshops to gather comprehensive information.Once the requirements are gathered, the design phase comes into play. This is where creativity meets technicalproficiency. Designing software architecture that is scalable, maintainable, and efficient requires careful consideration of various factors such as performance, security, and usability. In my experience, using design patterns and architectural principles has been instrumental in creating robust software solutions.Implementation is where the code comes to life. Writing clean, readable, and maintainable code is essential for long-term success. This phase often involves collaboration with other team members through techniques like pair programming or code reviews to ensure code quality and adherence to coding standards.Testing is another critical aspect of software engineering. It's not just about finding bugs; it's about ensuring that the software meets the specified requirements and behaves as expected under different conditions. Automated testing frameworks and techniques like unit testing, integration testing, and end-to-end testing helpin achieving comprehensive test coverage and identifying issues early in the development cycle.Finally, maintenance is an ongoing process in software engineering. As technology evolves and user needs change, software must be updated and maintained to stay relevantand effective. This involves fixing bugs, adding new features, optimizing performance, and addressing security vulnerabilities.中文,作为一名软件工程专业人士,我发现这个领域既具有挑战性又有回报。
软件工程英语文档:Documents软件工具:Software Tools工具箱:Tool Box集成工具:Integrated Tool软件工程环境:Software Engineering Environment传统:Conventional经典:Classical解空间:Solution Domain问题空间:Problem Domain清晰第一,效率第二Clarity the first, Efficiency the next.设计先于编码Design before coding使程序的结构适合于问题的结构Make the program fit the problem 开发伴随复用,开发为了复用Development with reuse, Development for reuse.靠度量来管理:Management by Measurement 软件度量学:Software Metrics 软件经济学:Software Economics 软件计划WHY软件分析WHAT 软件实现HOW软件生存周期过程的开发标准Standard for Developing Software Life Cycle Process软件开发模型:Software Development Model编码员:Coder瀑布模型:Waterfall Model快速原型模型:Rapid Prototype Model增量模型:Incremental Model线性思维:Linear Thinking演化模型:Evolutionary Model 螺旋模型:Spiral Model对象:Object类:Class继承:Inheritance聚集:Aggregation消息:Message面向对象=对象Object+分类Classification+继承Inheritance+消息通信Communication with Messages构件集成模型:Component Integration Model转换模型:Transformational Model净室软件工程:Cleanroom Software Engineering净室模型:Cleanroom Model软件需求规格说明书:Software Requirement Specification ,SRS 分析模型:Analysis Model便利的应用规约技术:Facilitated Application Specification Techniques ,FAST结构化语言:Structured Language 判定树:Decision Tree基数:Cardinality事件轨迹:Event Trace对象-关系Object-Relationsship 结构化分析:SA(Structured Analysis)由顶向下,逐步细化Top-Down Stepwise Refinement面向对象分析:Object-Oriented Analysis包含:Contains临近:Is Next To传到:Transmits to来自:Acquires from管理:Manages控制:Controls组成:Is Composed of细化:Refinement抽象:Abstraction模块:Module策略:Strategy信息隐藏:Information Hiding数据封装:Data Encapsulation抽象数据类型:Abstract Data type 模块化设计:Modular Design分解:Decomposition模块性:Modularity单模块软件:Monolithic Software模块独立性:Module Independence内聚:Cohesion偶然性内聚:Coincidental Cohesion逻辑性内聚:Logical Cohesion 时间性内聚:Temporal Cohesion 过程性内聚: Procedural Cohesion通信性内聚: Communicational Cohesion顺序性内聚:Sequential Cohesion 功能性内聚:Functional Cohesion 非直接偶合:No Direct Coupling 数据偶合:Data Coupling特征偶合:Stamp Coupling控制偶合:Control Coupling外部偶合:External Coupling公共偶合:Common Coupling 内容偶合: Content Coupling由底向上设计:Bottom-Up Design自顶向下设计:Top-Down Design 正式复审:Formal Review非正式复审:Informal Review走查,排练:Walk-Through会审:Inspection映射:Mapping传入路径:Afferent path传出路径:Efferent path变换中心:Transform Center接受路径:Reception path动作路径:Action path事务中心:Transaction Center分支分解:Factoring of Brandches瓮形:oval-shaped一个模块的控制域:Scope of Control一个模块的作用域:Scope of Effect结构化程序设计:Structured Programming通心面程序:Bowl of Spaghetti 流程图:Flow Diagram编码:Coding方框图:Block DiagramPDL (Pidgin):Program Design Language伪代码:Pseudo CodeJSD:Jackson System Development 对象建模技术:Object Modeling Technique基础设施:Infrastructure控制线程:Thread of Control保护者对象:Guardian Object协议:protocolUML:Unified Modeling Language OMG:Object Management Group 统一方法:Unified Method关联:Association泛化:Generalization依赖:Dependency 结点:Node接口:Interface包:Package注释:Note特化:Specialization元元模型:Meta-Meta Model用户模型:User Model静态图:Static Diagram动态图:Dynamic Diagram用例视图:Use Case View逻辑视图:Logical View并发视图:Concurrent View构件视图:Component View实现模型视图:Implementation Model View部署视图:Deployment View航向:Navigability重数:Multiplicity共享聚集:Shared Aggregation 组合:Composition泛化:Generalization简单消息:Simple Message同步消息:Synchronous Message 异步消息:Asynchronous Message事件说明:Event_Signature守卫条件:Guard_Condition动作表达式:Action_Expression发送子句:Send_Clause时序图:Sequence Diagram协作图:Collaboration Diagram 前缀:Predecessor循环子句:Iteration-Clause活动图:Activity Diagram构件图:Component Diagram配置图:Deployment Diagram建模过程指导(RUP):Rational Unified Process可执行代码:Executalbe Codes 实现:Implementation编码风格:Coding Style标准:Classical控制流的直线性:Linearity of Control Flow 程序风格设计要素:先求正确后求快Make it right before you make it faster.先求清楚后求快Make it clear before you make it faster.求快不忘保持程序正确Keep it right when you make it faster.保持程序简单以求快Keep it simple to make it faster.书写清楚,不要为“效率”牺牲清楚Write clearly-don't sacrifice clarity for "efficiency"文档化:Code Documentation内部文档编制:Internal Documentation序言:Prologue用户友善:User Friendly纠错:Debugging测试用例:Test Case穷举测试:Exhaustive Testing选择测试:Selective Testing静态分析:Static Analysis黑盒测试:Black Box Testing白盒测试:White Box Testing等价分类:Equivalence Partioning边界值分析法:Boundary Value Analysis所谓猜错:Error Guessing因果图:Cause-Effect Graph逻辑覆盖测试法:Logic Coverage Testing试凑:Trial and Error回溯:Back Tracking病因排除法:Cause Elimination 测试纠错:Debugging by Testing 蛮力纠错技术:Debugging by Brute Force回归测试:Regression Testing单元测试:Unit Testing综合测试:Integration Testing确认测试: Validation Testing系统测试:System Testing模块测试:Module Testing 高级测试:Higher order Testing 不可达的:Unreachable办公桌检查:Desk Check走查:Walk-Through代码会审:Code Inspection测试驱动模块:Test Driver测试桩模块:Test Stub群:Cluster混合方式测试:Sandwich Testing 渐增式测试:Incremental Testing 非渐增式:Non-Incremental配置复审:Configuration Review 测试终止标准:Test Completion Criteria基于线程的测试:Thread-Based Testing基于使用:Use-Based基于构件的软件开发:Component Based Software Development ,CBSD领域工程:Domain Engineering 需求规约:RequirementsSpecification变体:Variant组件对象模型,COM:Componet Object Model对象链接与嵌入:Object Linking and Embedding公共对象请求代理体系结构,CORBA:Common Object Request Broker Architecture枚举分类:Enumerater Classification呈面分类:Faceted Classification 属性-值分类:Attribute-Value Classification应用系统工程,ASE:Application System Engineering完善性维护:Perfective Maintenance适应性维护:Adaptive Maintenance纠错性维护:Corrective Maintenance 预防性维护:Preventive Maintenance结构化的翻新:Structured Retrofit可维护性:Maintainability可理解性:Understandability可修改性:Modifiability可测试性:Testability调用图:Call Graph交差引用表:Cross-Reference Directory数据封装技术:Data Encapsulation维护申请单MRF:Maintenance Request Form软件问题报告单SPR:Software Problem Report软件修改报告单SCR: Software Change Report修改控制组CCB:Change Control Board软件配置:Software Configuration版本控制库:Version Control Library活动比:Activity Ratio工作量调节因子EAF:Effort Adjustment Factor软件再工程:Software Reengineering逆向工程:Reverse Engineering 重构:Restructure演化性:Evolvability问题定义:Problem Definition系统目标与范围的说明:Statement of Scope and Objectives 可行性研究:Feasibility Study系统流程图:System Flowchart 成本-效益分析:Cost-Benifit Analysis风险识别:Risk Identification风险预测:Risk Projection风险估计:Risk Estimation风险评价:Risk Assessment估算模型:Estimation Model 资源模型:Resource Model构造性成本模型:Constructive cost Model组织:Organic半独立:Semidetached嵌入:Embeded算法模型:Algorithmic Model分类活动结构图WBS:Work Breakdown Structure人员-时间权衡定律People-Time Trade-Off Law无我小组:Egoless Team主程序员小组:Chief-Programmer Team PERT:Program Evaluation and Review Technique关键路径:Critical Path知识产权:Intellectual Property 靠质量来管理:Management by Measurement质量保证:Quality Assurance质量认证: Quality Certification质量检验:Quality Inspection全面质量管理TQC:Total Quality Control质量体系:Quality System计划-实施-检查-措施 Plan-Do-Check-Action合格论证:Conformity Certification可靠性:Reliability效率:Efficiency运行工程:Human Engineering正确性:Correctness使用性:Usability完整性:Integrity可理解性:Understandability可测试性:Testability可修改性:Modifiability可移植性:Portability可维护性:Maintainability可适应性:Flexibility可重用性:Reusability交互操作性:Interoperability 验证与确认:Verification and Validation ,V&V基线:Baselines平均故障时间:Mean Time To Failure ,MTTF错误传入:Error Seeding冗余:Redundancy容错:Fault Tolerance公理化归纳断言法:Axio-Matic Inductive Assertion循环不变式:Loop Invariant能力成熟度模型:Capability Maturity Model关键过程域:Key Process Area ,KPA关键实践:Key Practice初始级:Initial可重复级:Repeatable已定义级:Defined已管理级:Managed优化级:Optimizing主任评估师:Lead Assessor极值程序设计:Extreme Programming自适应软件开发:Adaptive Software Development轻载:Light weight重载:Heavy Weight返工:Rework进度:Schedule时间:Duration成本:Cost代码行LOC:Lines of Code面向功能:Function-Oriented面向规模: Size-Oriented功能点:Function Points权系数:Weighting Coefficient用户输入:User Input用户输出: User Output用户查询: User Inquirty主文件处理:Master File外部界面:External Interface TCF:Technical Complexity Factor 技术复杂性因子测度:Measurement最终用户:End-User;计算机辅助软件工程CASE:Computer Aided Software Engineering拉出:pull-out下拉: pull-down一致性:Unification自动化:Automation过程模型:Process Model软件开发环境SDE:Software Development Environment软件设计支持环境PSE:Programming Support Environment集成化项目支持IPSE:Integrated Project Support Environment集成化框架:Integration Framework质量从头抓起:Quality from Beginning 缺陷:Defect变更请求:Change Request功能扩充:Enhancement Request。
第⼀次软件⼯程作业(Onewhowantstowearthecrown,Bearsthec。
回顾你过去将近3年的学习经历1.当初报考的时候,是真正的喜欢计算机这个专业吗?报考时对于计算机专业只能说不讨厌,也可以认为对其没有任何的感觉。
有⼀个⽐我⾃⼰还注意我未来的⽼妈,我的报考只能通过⼀个词来形容:理智在没有考试前,我的⽼妈就直接把我带到⼀个⼼理学的机构,开始做各种潜⼒测试、职业测试,从测试出的性格特点,兴趣特点,思维特点等等测试出我⽐较适合什么职业、什么⼯作,测试结果排名第⼀的是数学与数学应⽤专业,然后是管理学、法学,之后才是计算机专业,我⽼妈果断从各种因素去掉了法学和管理学,根据我⾼考前的模拟测试成绩只留下两个选项:⼀个东财国际贸易学院的2+2数学与数学应⽤,另⼀个就是沈航计算机学院的计算机科学与技术。
⾼考分下来感觉东财的有点困难,果断的选择沈航的计算机专业。
选专业的时候⾃⼰也⾮常的迷茫,⼜觉得⽼妈的选择很有道理,报考也就听从指挥了。
2.你现在后悔选择了这个专业吗?从各种就业形势,⼯资收⼊等⽅⾯并不觉得后悔。
很期待从事计算机专业我的未来会是什么样的!因为理智的专业选择在上⼤学之后还是觉得专业选的很不错,没什么后悔可⾔。
虽然个⼈对法学有着崇⾼的向往,并且很憧憬检察官这个职位。
但⽣活还是要现实⼀点,如果现在让我再选⼀遍⾃⼰的专业我还是会选择计算机专业。
3.你认为你现在最喜欢的领域是什么?对于游戏开发等⽅⾯有兴趣。
⼤学三年除了基础的课程的学习之外,在⼤⼆的时候选择了计算机博弈这门选修课,课上⽼师要求把⼀个VB版的井字棋改成VC版的井字棋,这是我第⼀次接触简单的⼩游戏编程,当时编程时虽然相当的艰难,但结果很是令⼈开⼼。
对于⾃⼰喜欢的游戏开发还是有⼀点幻想吧,觉得如果能参与到⼀个⾮常厉害的游戏软件开发中真的是⾮常令⼈兴奋的⼀件事。
Knowing yourself is the beginning of all wisdom.总结你现在已经掌握的知识1.你都具备哪些专业知识和能⼒?现在在学校对计算机专业的学习⼀些专业课例如:C语⾔程序设计、⾼级程序设计、数据结构、⽹络原理、组成原理、编译原理、单⽚机、软件⼯程等。
重邮摸底试题及答案一、选择题(每题2分,共20分)1. 计算机网络中,用于实现数据传输的协议是()。
A. HTTPB. FTPC. TCP/IPD. SMTP答案:C2. 在计算机操作系统中,进程和线程的区别在于()。
A. 进程是程序的执行,线程是程序的调度B. 进程是程序的调度,线程是程序的执行C. 进程和线程都是程序的执行D. 进程和线程都是程序的调度答案:A3. 下列选项中,不属于数据库管理系统的是()。
A. MySQLB. OracleC. SQL ServerD. Photoshop答案:D4. 在编程语言中,用于定义类的关键字是()。
A. classB. structC. functionD. interface答案:A5. 以下哪个选项是面向对象编程中的概念?()A. 函数B. 过程C. 模块D. 对象答案:D6. 在HTML中,用于定义文档标题的标签是()。
A. <h1>B. <title>C. <p>D. <head>答案:B7. 在JavaScript中,用于创建数组的关键字是()。
A. arrayB. listC. setD. var答案:A8. 在C语言中,用于声明一个整型变量的关键字是()。
A. intB. floatC. charD. double答案:A9. 在Python中,用于实现循环的关键字是()。
A. forB. whileC. repeatD. loop答案:A10. 在Java中,用于实现异常处理的关键字是()。
A. tryB. catchC. throwD. all of the above答案:D二、填空题(每题2分,共20分)1. 在HTML中,用于定义超链接的标签是____。
答案:<a>2. 在CSS中,用于设置字体颜色的属性是____。
答案:color3. 在JavaScript中,用于定义函数的关键字是____。
重邮软件工程专业综合英语作业
(最新版)
目录
1.软件工程专业综合英语作业的背景和目的
2.重邮软件工程专业的特点和优势
3.综合英语作业的内容和要求
4.如何完成综合英语作业
5.对综合英语作业的期望和意义
正文
一、软件工程专业综合英语作业的背景和目的
随着全球化的不断深入,英语作为国际通用语言,已经成为学术交流、商务沟通、技术研发等领域的必备技能。
在我国,软件工程专业作为一门实践性很强的学科,对英语能力的要求也越来越高。
为了提高重邮软件工程专业学生的英语应用能力,培养具有国际竞争力的软件人才,学校设置了综合英语作业这一课程,旨在通过实践性的英语作业,让学生在真实的语境中提高英语水平。
二、重邮软件工程专业的特点和优势
重庆邮电大学软件工程专业作为国家级特色专业,具有雄厚的师资力量、丰富的教学资源和良好的实验环境。
该专业注重培养学生的创新能力和实践能力,紧密结合产业发展需求,设置了一系列实践性强、富有挑战性的课程。
此外,重邮软件工程专业还与国际知名企业和高校开展了广泛的合作,为学生提供了实习、实训、留学等机会,使学生在校期间就能接触到国际前沿的技术和理念。
三、综合英语作业的内容和要求
综合英语作业的内容主要包括阅读理解、翻译、写作等,要求学生能
够熟练地运用英语语法和词汇,准确地表达思想和观点。
此外,作业还要求学生具备一定的逻辑思维和分析能力,能够从多角度思考问题,提出有价值的见解。
为了保证作业的质量,学校还设置了严格的评分标准和考核制度,鼓励学生认真对待每一次作业。
四、如何完成综合英语作业
要完成综合英语作业,首先要做好时间规划,保证每个任务都有充足的时间完成。
其次,要注重阅读理解,多阅读英文文献和资料,提高自己的英语阅读速度和理解能力。
同时,要加强写作训练,多进行英文写作练习,提高自己的写作水平。
最后,要善于利用课外资源,如参加英语角、与外教交流等,提高自己的英语实际应用能力。
五、对综合英语作业的期望和意义
通过综合英语作业的学习,我们期望重邮软件工程专业的学生能够具备扎实的英语基础和较强的英语应用能力,能够在学术交流、技术研发等领域游刃有余地运用英语。