If引导的两种从句
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:45.94 KB
- 文档页数:11

1.if引导的条件状语从句所引导的是原因状语,可以是现实生活中已经出现的真实事件或有可能出现的事情,发生的可能性较大。
而虚拟语气所引导的往往是非真实的,对于过去,现在或将来的虚拟或推断,发生的可能性较小,或已经不可能发生了可以从2个角度去区分:1。
时态A,由if引导的条件状语从句通常都是主句为一般将来时,从句为一般现在时。
B,而在虚拟语气中,时态都是有很多,往往都是根据句子的含义判断,究竟是与现在,过去还是将来的事实相反。
2。
真实与非真实A,由if引导的条件状语从句一般都是真实的,只要所谓的条件成立,一定会成为事实B,但虚拟语气并非如此,if,既然是虚拟,就一定是非真实的,可以根据句意判断其是...条件状语从句连接词主要有 if, unless, as/so long as, on condition that 等。
if 引导的条件句有真实条件句和非真实条件句两种。
unless = if not. 例如:Let's go out for a walk unless you are too tired. 如果不太累,我们去散散步。
If you are not too tied, let's go out for a walk.You will be late ___ you leave immediately.A. unlessB. untilC. ifD. or答案A。
句意:除非你立即走,否则你就回迟到的。
可转化为 If you don't leave immediately, you will be late。
B、D句意不对,or表转折,句子如为 You leave immediately or you will be late.虚拟语气1)虚拟语气用来表示说话人的主观愿望或假想,所说的是一个条件,不一定是事实,或与事实相反。
虚拟语气在条件句中应用比较多。
2)条件句可分为两类,一类为真实条件句,一类为非真实条件句。

if引导的条件状语从句▲if 引导的条件状语从句中,if 意思为“如果”,有以下两种基本句型:▲(1) if + 从句(用一般现在时),主句(主语+ will (not) + 动词原形……)或:主句(主语+ will (not) + 动词原形……)+ if + 从句(用一般现在时)注意时态:主句用一般将来时,从句用一般现在时1如果你喜欢观光,你会爱上它的。
_________ you like _________________, you _________________ it. 2如果你沿着外滩走,你会看见很多古老的建筑。
(1)_________ you walk ____________ the Bund, you __________________ many old ________________.(2)You _________________ many old buildings ____________ you ______________________ the Bund.3如果你喜欢历史和自然美,你会爱上这个花园的。
You ______________________ this garden ____________ you _________________ history and __________________ beauty . 4如果你戴着(wear)眼镜,你会看得很清楚。
You ______________________ clearly _________ you ____________________ your glasses .5如果明天下雨,我就坐车去上学。
I _______________ to school by bus _________ it __________ tomorrow 6如果明天下雨,我们就不去野餐。
We _______________________ a picnic ________ it _________________ tomorrow.7如果他有时间,他会跟我们一起打篮球的。
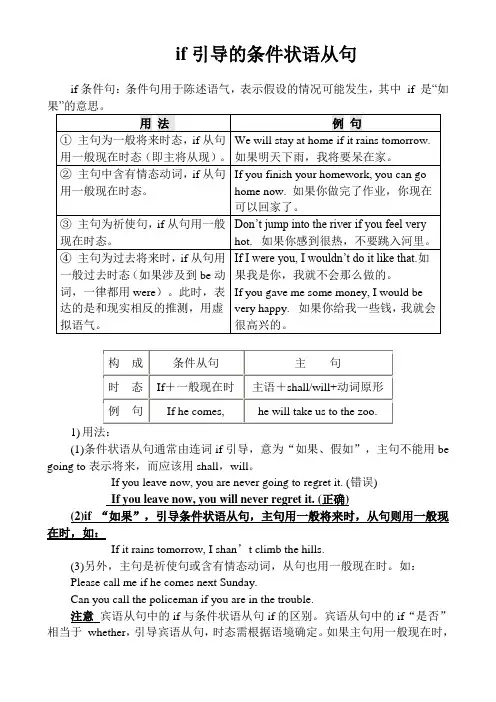
if引导的条件状语从句if条件句:条件句用于陈述语气,表示假设的情况可能发生,其中if 是“如果”的意思。
用法例句①主句为一般将来时态,if从句用一般现在时态(即主将从现)。
We will stay at home if it rains tomorrow.如果明天下雨,我将要呆在家。
②主句中含有情态动词,if从句用一般现在时态。
If you finish your homework, you can go home now. 如果你做完了作业,你现在可以回家了。
③主句为祈使句,if从句用一般现在时态。
Don’t jump into the river if you feel very hot. 如果你感到很热,不要跳入河里。
④主句为过去将来时,if从句用一般过去时态(如果涉及到be动词,一律都用were)。
此时,表达的是和现实相反的推测,用虚拟语气。
If I were you, I wouldn’t do it like that.如果我是你,我就不会那么做的。
If you gave me some money, I would be very happy. 如果你给我一些钱,我就会很高兴的。
构成条件从句主句时态If+一般现在时主语+shall/will+动词原形例句If he comes, he will take us to the zoo.1) 用法:(1)条件状语从句通常由连词if引导,意为“如果、假如”,主句不能用be going to表示将来,而应该用shall,will。
If you leave now, you are never going to regret it. (错误)If you leave now, you will never regret it. (正确)(2)if “如果”,引导条件状语从句,主句用一般将来时,从句则用一般现在时,如:If it rains tomorrow, I shan’t climb the hills.(3)另外,主句是祈使句或含有情态动词,从句也用一般现在时。
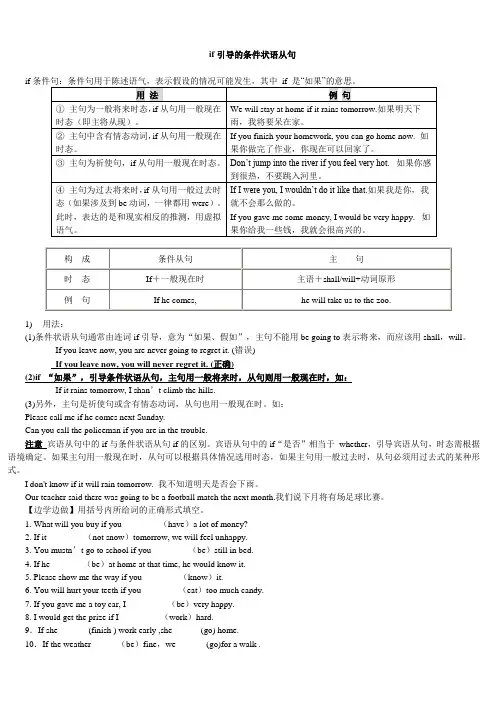
if引导的条件状语从句if1) 用法:(1)条件状语从句通常由连词if引导,意为“如果、假如”,主句不能用be going to表示将来,而应该用shall,will。
If you leave now, you are never going to regret it. (错误)If you leave now, you will never regret it. (正确)(2)if “如果”,引导条件状语从句,主句用一般将来时,从句则用一般现在时,如:If it rains tomorrow, I shan’t climb the hills.(3)另外,主句是祈使句或含有情态动词,从句也用一般现在时。
如:Please call me if he comes next Sunday.Can you call the policeman if you are in the trouble.注意宾语从句中的if与条件状语从句if的区别。
宾语从句中的if“是否”相当于whether,引导宾语从句,时态需根据语境确定。
如果主句用一般现在时,从句可以根据具体情况选用时态,如果主句用一般过去时,从句必须用过去式的某种形式。
I don't know if it will rain tomorrow. 我不知道明天是否会下雨。
Our teacher said there was going to be a football match the next month.我们说下月将有场足球比赛。
【边学边做】用括号内所给词的正确形式填空。
1. What will you buy if you ________(have)a lot of money?2. If it ________(not snow)tomorrow, we will feel unhappy.3. You mustn’t go to school if you ________(be)still in bed.4. If he _______(be)at home at that time, he would know it.5. Please show me the way if you ________(know)it.6. You will hurt your teeth if you ________(eat)too much candy.7. If you gave me a toy car, I _________(be)very happy.8. I would get the prize if I _________(work)hard.9.If she ______ (finish ) work early ,she ______(go) home.10.If the weather______(be)fine,we_______(go)for a walk .11. If I_____(have) time tonight ,I _______(finish) the book I’m reading.12. If it ______(rain) next weekend , we_______(not be able to ) plant the vegetable .13. If it_______(rain),we______(stay) at home .14.If she______(arrive) ,she _____(phone) me .15. If he_____(call),tell him I’ll ring back .二、用所给词的适当形式填空1. If you ________(feel) tired, you _________ (have) to have a rest.2. Where _____ he ____(see) the film if he _________(have) time?3. If there ____ (be) fewer trees, there _______ (be) more pollution.4. He ___ (dress) more casually if he ___ (not work) on weekends.5. If Marcia _______ (live) alone, she _______ (keep) a pet parrot.6. Lana _____ (buy) a new dress if the old one ____ (be) out of style.7. The twins _______ (fight) if they__________ (argue).8. I ______ (have) a bake sale if I ____ (need) money for education.9. Peter ____ (send) me a beautiful souvenir if he ____(tour) Spain.10. If Mr. Green _______ (say) I am hard- working, my parents ___ (feel) glad.11. I ______ (go) to the beach if it________ (not rain) this week.12. _____they ___ (have) a match if the P.E. teacher __ (be) busy?13. He ____ (write) a letter to his grandparents if he ____ (get) his report card this week.14. If she ______ (get) up late, she _____ (not catch) the early bus.15. Peter ____ (major) in English if he ____(pass) the exams in Peking University.二、完成句子1. 他如果看电视太久了,他的父母会不高兴。

if引导的条件句是什么从句if 引导的条件句有真实条件句和非真实条件句两种;1、真实条件句:叙述真实可能发生的事情;例句:If you fail in the exam,you will let him down.如果你考试不及格,你会让他失望的。
扩展资料2、非真实条件句:虚拟语气的一种,表示与实际已发生事实相反:例句:If I were you, I would invite him.如果我是你,我会邀请他。
3、另一个常用连词为unless,大多数时候意思与 if not 相近:例句:Let's go out for a walk unless you are too tired.我们出去散步吧,除非你太累了。
例句:If you are not too tired, let's go out for a walk.如果你不太累,我们出去散步吧。
条件状语从句的基本用法1、用if引导:if意为“如果”。
例句:If you cheat in the exam you’ll never get away with it.考试作弊必予追究。
2、用unless引导:unless的意思是“如果不”“除非”。
例句:Unless you go at once you will be late.如果你不马上走,就会迟到的'。
3、用as [so] long as引导:as [so] long as的意思是“如果”“只要”。
例句:I’ll remember that day as long as I live.只要我活着,我就不会忘记那个日子。
4、用in case引导:in case用连词引导条件状语从句时,其意为“如果”“万一”。
例句:In case I forget, please remind me about it.万一我忘记,请提醒我一下。
5、条件状语从句的时态:当主句为将来时态或含有将来意义时,条件状语从句习惯上要用一般现在时表示将来意义,而不能直接使用将来时态。

if引导的条件状语从句总结(精)if引导的四种条件状语从句一、零条件句/绝对真实条件句(Zero Conditional)零条件句,又叫绝对真实条件句,用于阐述事实。
用来表达在该条件下,结果一定会如此(如规则,客观规律、真理等)。
结构是:If+主语+do/does,主语+do/does。
其从句和主句的谓语动词通常为一般现在时。
二、第一条件句/相对真实条件句(First Conditional)第一条件句又叫相对真实条件句,谈论将来可能发生的事情,并考虑这件事情的结果。
强调偶然性或一次性的条件,也可以与绝对真实条件句同义。
if从句用一般现在时或其他现在时,表示将来可能发生的事情(条件);主句用一般将来时,表示这件事情的结果。
结构是:If+主语+do/does,主语+will do。
三、第二条件句/现在虚拟条件句(Second Conditional)第二条件句是虚拟条件句的一种,即现在虚拟条件句(Unreal Present),用来表达在现在或将来时间下不太可能或不可能发生的条件,这种条件句还可以用来表示试探性的、委婉的语气(可以理解为不大有自信,所以不太真实的条件)。
结构是:①与将来事实相反的非真实条件句是If+主语+should do/were to do/did,主语+would/should/could/might do;②与现在事实相反的非真实条件句是If+主语+did,主语+would/should/could/might+do。
四、第三条件句/过去虚拟条件句(Third Conditional) 第三条件句是表示与过去事实相反的虚拟语气,是用来表达如果(If)当时那样发生,另外一方面(当时)结果会如何。
通常是指过去的事情,带有一切已经太迟而不能够补救的意思。
结构是:If+主语+had done,主语+would/should/could/ might+have done。
if 条件句的时态搭配1.if从句用一般现在时,主句用一般将来时2.if从句用一般现在时,主句用may/might/canIf the fog gets thicker the plane may/might be diverted.3.if从句用一般现在时,主句用must/shouldIf you want to lose weight you must/should eat less bread.4.if从句用一般现在时,主句用一般现在时5.if从句用现在进行时,主句用一般将来时6.if从句用现在完成时,主句用一般将来时If you have finished dinner I’ll ask the waiter for the bill.。

英语语法if的用法解释英语单词if 在语法中,扮演着怎样的角色?它的用法是?下面是店铺给大家整理的英语语法if的用法解释,供大家参阅!英语语法if的用法解释1)whether和if常用来引导宾语从句,这时两者的含义区别很小,一般可通用。
例如:①I don't know whether/if they will come to help us. 我不知道他们是否来帮助我们。
②I am not sure whether/if I'll have time to go with you. 我很难说我们是否有时间跟你们一起去。
上面两句无区别。
但是,当whether与or not连成一个词组时,whether不可换用if。
例如:③I don't know whether or not they will come for our help. 我不知道他们是否要来求我们支援。
【注意】若whether和or not不连在一起,在口语中可以用if取代whether,当然也可以用whether。
例如:④I am not certain if/whether the train will arrive on time. 我没有把握火车是否准时到达。
⑤I don't careif/whether your car breaks down or not. 我不在乎您的车是否是会出故障。
此外,还有三种情况值得注意:(1)在介词后面只能用whether,不能用if。
例如:①This depends upon whether we are determined to do it. 这件事要看我们是否有决心去做。
②It depends on whether he is ready. 这件事要看他是否有准备。
③I am not interested in whether you'll come or not. 你来不来我不感兴趣。


1.if引导的条件状语从句所引导的是原因状语,可以是现实生活中已经出现的真实事件或有可能出现的事情,发生的可能性较大。
而虚拟语气所引导的往往是非真实的,对于过去,现在或将来的虚拟或推断,发生的可能性较小,或已经不可能发生了可以从2个角度去区分:1。
时态A,由if引导的条件状语从句通常都是主句为一般将来时,从句为一般现在时。
B,而在虚拟语气中,时态都是有很多,往往都是根据句子的含义判断,究竟是与现在,过去还是将来的事实相反。
2。
真实与非真实A,由if引导的条件状语从句一般都是真实的,只要所谓的条件成立,一定会成为事实B,但虚拟语气并非如此,if,既然是虚拟,就一定是非真实的,可以根据句意判断其是...条件状语从句连接词主要有 if, unless, as/so long as, on condition that 等。
if 引导的条件句有真实条件句和非真实条件句两种。
unless = if not. 例如:Let's go out for a walk unless you are too tired. 如果不太累,我们去散散步。
If you are not too tied, let's go out for a walk.You will be late ___ you leave immediately.A. unlessB. untilC. ifD. or答案A。
句意:除非你立即走,否则你就回迟到的。
可转化为 If you don't leave immediately, you will be late。
B、D句意不对,or表转折,句子如为 You leave immediately or you will be late.虚拟语气1)虚拟语气用来表示说话人的主观愿望或假想,所说的是一个条件,不一定是事实,或与事实相反。
虚拟语气在条件句中应用比较多。
2)条件句可分为两类,一类为真实条件句,一类为非真实条件句。

总结好的:if引导的条件状语从句if引导的条件状语从句if1) ⽤法:(1)条件状语从句通常由连词if引导,意为“如果、假如”,主句不能⽤be going to表⽰将来,⽽应该⽤shall,will。
If you leave now, you are never going to regret it. (错误)If you leave now, you will never regret it. (正确)(2)if “如果”,引导条件状语从句,主句⽤⼀般将来时,从句则⽤⼀般现在时,如:If it rains tomorrow, I shan’t climb the hills.(3)另外,主句是祈使句或含有情态动词,从句也⽤⼀般现在时。
如:Please call me if he comes next Sunday.Can you call the policeman if you are in the trouble.注意宾语从句中的if与条件状语从句if的区别。
宾语从句中的if“是否”相当于whether,引导宾语从句,时态需根据语境确定。
如果主句⽤⼀般现在时,从句可以根据具体情况选⽤时态,如果主句⽤⼀般过去时,从句必须⽤过去式的某种形式。
I don't know if it will rain tomorrow. 我不知道明天是否会下⾬。
Our teacher said there was going to be a football match the next month.我们说下⽉将有场⾜球⽐赛。
【边学边做】⽤括号内所给词的正确形式填空。
1. What will you buy if you ________(have)a lot of money?2. If it ________(not snow)tomorrow, we will feel unhappy.3. You mustn’t go to school if you ________(be)still in bed.4. If he _______(be)at home at that time, he would know it.5. Please show me the way if you ________(know)it.6. You will hurt your teeth if you ________(eat)too much candy.7. If you gave me a toy car, I _________(be)very happy.8. I would get the prize if I _________(work)hard.9.If she ______ (finish ) work early ,she ______(go) home.10.If the weather______(be)fine,we_______(go)for a walk .11. If I_____(have) time tonight ,I _______(finish) the book I’m reading.12. If it ______(rain) next weekend , we_______(not be able to ) plant the vegetable .13. If it_______(rain),we______(stay) at home .14.If she______(arrive) ,she _____(phone) me .15. If he_____(call),tell him I’ll ring back .⼆、⽤所给词的适当形式填空1. If you ________(feel) tired, you _________ (have) to have a rest.2. Where _____ he ____(see) the film if he _________(have) time?3. If there ____ (be) fewer trees, there _______ (be) more pollution.4. He ___ (dress) more casually if he ___ (not work) on weekends.5. If Marcia _______ (live) alone, she _______ (keep) a pet parrot.6. Lana _____ (buy) a new dress if the old one ____ (be) out of style.7. The twins _______ (fight) if they__________ (argue).8. I ______ (have) a bake sale if I ____ (need) money for education.9. Peter ____ (send) me a beautiful souvenir if he ____(tour) Spain.10. If Mr. Green _______ (say) I am hard- working, my parents ___ (feel) glad.11. I ______ (go) to the beach if it________ (not rain) this week.12. _____they ___ (have) a match if the P.E. teacher __ (be) busy?13. He ____ (write) a letter to his grandparents if he ____ (get) his report card this week.14. If she ______ (get) up late, she _____ (not catch) the early bus.15. Peter ____ (major) in English if he ____(pass) the exams in Peking University.⼆、完成句⼦1. 他如果看电视太久了,他的⽗母会不⾼兴。

if当如果讲时的用法
“if”作为英语中一个常用的连词,主要有以下两种用法:
-引导宾语从句或表语从句:当“if”用于宾语从句或表语从句时,通常翻译为“是否”。
在这种结构中,“if”引导的从句一般放在动词后,不能放在句子开头。
从句的时态根据句子的意思来确定。
例如:“She asked if he was coming to the party.”(她问他是否来参加派对。
)
-引导条件状语从句:当“if”用于条件状语从句时,通常翻译为“如果”。
这种从句可以放在句子的开头或主句之后,如果放在开头,后面通常用逗号隔开。
在条件状语从句中,通常遵循“主将从现”的原则,即主句用一般将来时,从句用一般现在时。
例如:“If it rains, we will stay at home.”(如果下雨,我们会待在家里。
)
此外,“if”从句的时态选择需要根据所表达的内容来决定。
有时候,即使从句用的是现在时态,实际上谈论的可能是未来将要发生的事情。
这是因为人们对未来的事情没有百分百的把握。
总的来说,在实际使用中,应该根据句子的结构和上下文来判断“if”的含义和从句的时态。
同时,要注意“if”引导的条件状语从句与宾语从句或表语从句在位置和功能上的区别。
1.if引导的条件状语从句和虚拟语气的区别if引导的条件状语从句所引导的是原因状语,可以是现实生活中已经出现的真实事件或有可能出现的事情,发生的可能性较大。
而虚拟语气所引导的往往是非真实的,对于过去,现在或将来的虚拟或推断,发生的可能性较小,或已经不可能发生了可以从2个角度去区分:1。
时态A,由if引导的条件状语从句通常都是主句为一般将来时,从句为一般现在时。
B,而在虚拟语气中,时态都是有很多,往往都是根据句子的含义判断,究竟是与现在,过去还是将来的事实相反。
2。
真实与非真实A,由if引导的条件状语从句一般都是真实的,只要所谓的条件成立,一定会成为事实B,但虚拟语气并非如此,if,既然是虚拟,就一定是非真实的,可以根据句意判断其是...条件状语从句连接词主要有if, unless, as/so long as, on condition that等。
if引导的条件句有真实条件句和非真实条件句两种。
unless=ifnot.例如:Let's go out for a walk unless you are too tired.如果不太累,我们去散散步。
If you are not too tied, let's go out for a walk.You will be late ___ you leave immediately.A. unlessB. untilC. ifD. or答案A。
句意:除非你立即走,否则你就回迟到的。
可转化为Ifyoudon'tleave immediately, you will be late。
B、D句意不对,or表转折,句子如为You leave immediately or you will be late.虚拟语气1)虚拟语气用来表示说话人的主观愿望或假想,所说的是一个条件,不一定是事实,或与事实相反。
虚拟语气在条件句中应用比较多。
2)条件句可分为两类,一类为真实条件句,一类为非真实条件句。
1.if引导的条件状语从句和虚拟语气的区别if引导的条件状语从句所引导的是原因状语,可以是现实生活中已经出现的真实事件或有可能出现的事情,发生的可能性较大。
而虚拟语气所引导的往往是非真实的,对于过去,现在或将来的虚拟或推断,发生的可能性较小,或已经不可能发生了可以从2个角度去区分:1。
时态A,由if引导的条件状语从句通常都是主句为一般将来时,从句为一般现在时。
B,而在虚拟语气中,时态都是有很多,往往都是根据句子的含义判断,究竟是与现在,过去还是将来的事实相反。
2。
真实与非真实A,由if引导的条件状语从句一般都是真实的,只要所谓的条件成立,一定会成为事实B,但虚拟语气并非如此,if,既然是虚拟,就一定是非真实的,可以根据句意判断其是...条件状语从句连接词主要有 if, unless, as/so long as, on condition that 等。
if 引导的条件句有真实条件句和非真实条件句两种。
unless = if not. 例如:Let's go out for a walk unless you are too tired. 如果不太累,我们去散散步。
If you are not too tied, let's go out for a walk.You will be late ___ you leave immediately.A. unlessB. untilC. ifD. or答案A。
句意:除非你立即走,否则你就回迟到的。
可转化为 If you don't leave immediately, you will be late。
B、D句意不对,or表转折,句子如为 You leave immediately or you will be late.虚拟语气1)虚拟语气用来表示说话人的主观愿望或假想,所说的是一个条件,不一定是事实,或与事实相反。
虚拟语气在条件句中应用比较多。
1.if引导的条件状语从句所引导的是原因状语,可以是现实生活中已经出现的真实事件或有可能出现的事情,发生的可能性较大。
而虚拟语气所引导的往往是非真实的,对于过去,现在或将来的虚拟或推断,发生的可能性较小,或已经不可能发生了可以从2个角度去区分:1。
时态A,由if引导的条件状语从句通常都是主句为一般将来时,从句为一般现在时。
B,而在虚拟语气中,时态都是有很多,往往都是根据句子的含义判断,究竟是与现在,过去还是将来的事实相反。
2。
真实与非真实A,由if引导的条件状语从句一般都是真实的,只要所谓的条件成立,一定会成为事实B,但虚拟语气并非如此,if,既然是虚拟,就一定是非真实的,可以根据句意判断其是...条件状语从句连接词主要有 if, unless, as/so long as, on condition that 等。
if 引导的条件句有真实条件句和非真实条件句两种。
unless = if not. 例如:Let's go out for a walk unless you are too tired. 如果不太累,我们去散散步。
If you are not too tied, let's go out for a walk.You will be late ___ you leave immediately.A. unlessB. untilC. ifD. or答案A。
句意:除非你立即走,否则你就回迟到的。
可转化为 If you don't leave immediately, you will be late。
B、D句意不对,or表转折,句子如为 You leave immediately or you will be late.虚拟语气1)虚拟语气用来表示说话人的主观愿望或假想,所说的是一个条件,不一定是事实,或与事实相反。
虚拟语气在条件句中应用比较多。
2)条件句可分为两类,一类为真实条件句,一类为非真实条件句。
“if”的两种用法|:一.意为“是否”时,引导宾语从句。
应遵循的时态是:①主现从任意。
即:当主句为一般现在时的时候,从句可根据自己的时间短语判断该用什么事态,不受主句的影响。
②主过从过。
即: 当主句为一般过去时的时候,从句使用过去的某种时态。
③[注意:①宾语从句要用陈述语序,即:主语在前,谓语动词在后]Eg: He asks if I Like English. (主现从任意)He asks if I am going to the party this evening. (主现从任意)He aske d if I liked English. (主过从过)He aske d if I was going to the party this evening.(主过从过)二.意为“如果”时,引导条件状语从句。
应遵循的事态是:①主将从现。
即:当主句为一般将来时的时候,从句使用一般现在时。
②主现从现。
即:当主句为一般现在时的时候,从句使用一般现在时。
③主过从过。
即:当主句为一般过去时的时候,从句使用过去的某种时态Eg: If you go the party, you will have a great time! (主将从现)If you ride your bike to school, you’ll be late.(主将从现)If you don’t have your ID card,you can’t go to the party.(主现从现)If you don’t listen carefully in class,you can’t do your homework. (主现从现)If you got up earlier this morning, you wouldn’t be late.(主过从过)If you didn’t finish your homework,the teacher would be angry with you.(主过从过)尤其要注意:1.当一个句子里同时出现两个“if”时,要先判断“if”是哪种意思,再判断时态。
1.if引导的条件状语从句和虚拟语气的区别if引导的条件状语从句所引导的是原因状语,可以是现实生活中已经出现的真实事件或有可能出现的事情,发生的可能性较大。
而虚拟语气所引导的往往是非真实的,对于过去,现在或将来的虚拟或推断,发生的可能性较小,或已经不可能发生了可以从2个角度去区分:1。
时态A,由if引导的条件状语从句通常都是主句为一般将来时,从句为一般现在时。
B,而在虚拟语气中,时态都是有很多,往往都是根据句子的含义判断,究竟是与现在,过去还是将来的事实相反。
2。
真实与非真实A,由if引导的条件状语从句一般都是真实的,只要所谓的条件成立,一定会成为事实B,但虚拟语气并非如此,if,既然是虚拟,就一定是非真实的,可以根据句意判断其是...条件状语从句连接词主要有 if, unless, as/so long as, on condition that 等。
if 引导的条件句有真实条件句和非真实条件句两种。
unless = if not. 例如:Let's go out for a walk unless you are too tired. 如果不太累,我们去散散步。
If you are not too tied, let's go out for a walk.You will be late ___ you leave immediately.A. unlessB. untilC. ifD. or答案A。
句意:除非你立即走,否则你就回迟到的。
可转化为 If you don't leave immediately, you will be late。
B、D句意不对,or表转折,句子如为 You leave immediately or you will be late.虚拟语气1)虚拟语气用来表示说话人的主观愿望或假想,所说的是一个条件,不一定是事实,或与事实相反。
虚拟语气在条件句中应用比较多。