南方科技大学生物小鼠解剖英文实验报告
- 格式:doc
- 大小:486.00 KB
- 文档页数:7

实验动物的解剖实验报告实验动物的解剖实验报告引言实验动物在科学研究中扮演着重要的角色。
解剖实验是一种常见的科学手段,通过对实验动物进行解剖,可以深入了解其内部结构和器官功能,为科学研究提供有力的支持。
本文将对实验动物的解剖实验进行报告,以展示其中的重要性和科学价值。
实验动物的选择在解剖实验中,选择适合的实验动物非常重要。
常见的实验动物包括小鼠、大鼠、兔子、猪等。
根据实验目的和研究领域的不同,选择相应的实验动物进行解剖实验。
例如,小鼠和大鼠常用于基因研究和药物试验,而兔子则常用于心血管系统和生殖系统的研究。
在本次实验中,我们选择了小鼠作为实验动物。
实验动物的准备工作在进行解剖实验之前,需要对实验动物进行一系列的准备工作。
首先,需要确保实验动物的健康状况良好,没有患有任何疾病。
其次,需要对实验动物进行麻醉,以确保其在实验过程中不会感受到疼痛。
麻醉后,实验动物会进入无意识状态,方便进行后续的操作。
解剖实验的步骤解剖实验的步骤主要包括开腹、取出内脏、观察和记录。
首先,我们用手术刀在实验动物的腹部进行切口,小心地切开皮肤和腹膜,直至暴露内腔。
接着,我们将内脏逐一取出,包括肝脏、心脏、肺、胃等。
在取出内脏的过程中,需要小心操作,以免损伤重要的器官。
观察和记录在取出内脏后,我们需要对其进行观察和记录。
通过观察内脏的颜色、形状、大小等特征,可以初步了解实验动物的器官状态。
同时,我们还可以进一步观察内脏的组织结构和细胞形态,通过显微镜等工具进行细致的观察。
在观察的同时,我们需要将所得到的数据进行记录,以备后续分析和研究之用。
实验动物的解剖实验的意义实验动物的解剖实验具有重要的科学意义。
首先,通过解剖实验可以深入了解实验动物的内部结构和器官功能,为研究其生理、病理过程提供重要的参考。
其次,解剖实验可以帮助我们研究人类疾病的发生机制,为寻找治疗方法提供线索。
例如,通过解剖实验,我们可以观察和分析实验动物的病变情况,从而更好地理解和治疗人类疾病。

姓名班级学号实验日期2014.5.21科目实验名称Mouse Dissection合作者指导教师成绩LAB 10: Mouse DissectionIntroduction:In biomedical research, animal models are always regarded as indispensable tools. They contribute to the scientific discovery in biology and our understanding of the functions of individual genes, even the mechanism of different diseases. Typically, although mice are different from humankind in size and appearance, they have a distinct genetic similarity. At the same time, mice have an efficient ability to reproduce, so they are important research tools for experiments in the lab.In this experiment, we will exercise to dissect a mouse, so that we can observe the inside of a mammalian body to identify the female and male mice. Learning and recognizing the anatomical structure of mice, including.Materials and Methods:Materials:Operation plate, Scissor, Forceps, Alcohol cotton, Mouse.Methods: [we get a male mouse]Part 1: Observations of external features. Make a table T-1.1.Having an overhead view, identify the mouse’s head, neck, truck, and tail; observe the dorsal and ventral surfaces. Roughly record what is seen.2.Observe the thorax which is supported by the rib cage, and the abdomen, and the details of appendages attached to the abdomen.3.Find the mouth, two external nostrils, two external auditory canals, and anus, which are on the body surface.4.Have a simply look at the surface of reproductive organ, prepuce, urethral and penis including.And locate the saclike scrotum; feel for the paired testes in the scrotum. Note the roughfeatures.Part 2: Observation of organs and structures inside the mouse. [Open the Ventral Body Cavities, Thoracic Cavity, and Abdominopelvic Cavity in order. We must break the ribs near the attachment to the vertebral column to fold back the upper flaps.] Make a table T-2.1.Ventral Body Cavities.a. Make a longitudinal incision through the skin with a dissecting scissor, from the neck to thepreputial opening. Pierce the body wall below the ribs, with the blades angled upward, sothat it won’t damage the internal organs.b. Pull the sides of the longitudinal incision, and look for the diaphragm. Then make two2. Thoracic Cavity.a. After opening, observe the heart and cut the thymus away so that we can observe the heartclearly.b. Make sure the location of lung, find the trachea and bronchus. Note the features in table T-2.3.Abdominopelvic Cavity.a.Observe the liver which is posterior to the diaphragm, look for the gallbladder.b.Locate the stomach, and then examine the spleen. Note where the small intestine is, and lookfor the pancreas (can secrete insulin). Take photos and record the features.c.Find the place where small intestine empties into large intestine. Observe the short rectumwhich is near to anus, and cecum.d.Separate the esophagus, dorsal mesentery, and the descending portion of the large intestine.Give the urinary bladder.e.Find two kidneys, and the urethra connected to them, the ureter start from the central ofkidney.f.Examine the organs of the reproductive system. Use scissors to open the scrotum to exposethe testis, and then find the coiled epididymis and vas deferens.g.Roughly observe a mouse of the opposite sex.Results:Part 1: table T-1As we can see, the blood vessels on the ear are apparent, and the penis is wrapped in prepuce. The saclikePart 2: table T-2The bronchi can carry air from the trachea toward the lungs, during the process of inspiration.The small intestine is longest organ in the body, filling most of the Abdominopelvic cavity.Pancreas produces enzymes for the digestion of food and, as a part of the endocrine system, it secretes insulin into the blood.The system of female mouse is similar to male we observe, except the reproductive organs. Discussions:Question 1: How to distinguish female and male mouse?From the appearance of external genital organs, we can recognize them, the difference of penisand vagina mouth is apparent. Besides, the female mouse has many visible nipples and theRespiratory system: lungs, trachea, bronchus.Digestive system: stomach, spleen, pancreas, liver, gallbladder. Urinary system: kidney, ureter, urinary bladder.Reproductive system: penis, prepuce, saclike scrotum.References:/article/495ba8413be36138b30ede13.html/link?url=0rmCCGLBKZt3--XtPeTfAzxlE3TKwCkGpt9pNOCfExKwE_xen4UsnC PSEESJL YLa-uCgEjRaB17EuNGatXZr3q/link?url=ijiTYru5lEYl1NIVmt_oa8ahhUc5NMksycmM_FukfG80Fn7N6yt1GlD00RXaz4aBJIUH8YSM0sbyr_NWszwF3a/link?url=6e5jeclQ_pBDBEadBRpQrOXzQOTKXPP_fVYZ1UaYWVSVGsUtQg0BoDWUQ3hg_kHXnWmkmBYq0xf7M10V9Mnx5aContribution statements:%%% is responsible for recording the phenomena, when %%% operates the mouse, and %%% prepares the materials needed.Figures:TailFigure 1-1 Figure 1-2The view of the ventral surface the view of the dorsal surface (belly) (back) MouthNeck Saclike scrotumThorax HeadEarFootAnusFigure 2-1 Figure 2-2 Figure 2-3 The view of mouse after being The mouse after being open Some organs cut through the skin. the ventral body cavity.Heart Stomach Trachea.Figure 2-4 Figure 2-4 Figure 2-5The view of Thoracic Cavity. The inside view of abdomen. The inside view of thorax.Figure 2-6. Figure 2-7Intestines. Some organs of digestive system. DiaphragmLung,4 pieces.ThymusLarge Intestine CecumSmallintestine Pancreas.Spleen.Penis. KidneyUrinary bladderFigure 2-8 Figure 2-9 The view of inside reproductive organ.Figure 2-10 Figure 2-11 Figure 2-12 The gallbladder The adrenal gland. The ureter. Vas deferens.Epididymis第页。

第1篇一、实验目的本次实验旨在通过对小鼠进行解剖,了解小鼠的主要器官位置和结构,掌握解剖技巧,提高实验操作能力,为后续的生物学和医学研究打下基础。
二、实验材料与工具1. 实验动物:成年小鼠(体重约20-30g)2. 实验器材:解剖台、剪刀、镊子、解剖刀、解剖针、解剖剪、解剖显微镜、生理盐水、酒精、碘酒、棉球等三、实验步骤1. 实验动物准备:将小鼠置于解剖台上,用棉球蘸取适量的生理盐水湿润小鼠的皮肤,以便于解剖操作。
2. 解剖过程:(1)切开皮肤:用剪刀沿小鼠腹部正中线剪开皮肤,注意避免损伤内脏器官。
(2)暴露内脏:用镊子提起皮肤,显露内脏器官,包括心脏、肺、肝脏、胃、小肠、大肠、肾脏、膀胱、生殖器官等。
(3)解剖器官:用解剖刀和剪子依次解剖各个器官,观察其位置、形态和结构特点。
(4)记录数据:详细记录每个器官的位置、形态、大小等数据。
3. 实验结果分析:(1)心脏:心脏位于胸腔中央,呈红褐色,分为左右两个心房和两个心室,心脏壁由心肌组成。
(2)肺:肺位于胸腔两侧,呈粉红色,肺泡是肺的基本结构单位,肺泡壁与毛细血管壁紧密相连,有利于气体交换。
(3)肝脏:肝脏位于腹腔右上侧,呈红褐色,具有解毒、代谢和储存营养物质等功能。
(4)胃:胃位于腹腔左侧,呈粉红色,分为贲门、胃底、胃体和幽门,胃壁具有分泌胃酸和消化酶的功能。
(5)小肠:小肠位于腹腔中部,分为十二指肠、空肠和回肠,是消化吸收的主要场所。
(6)大肠:大肠位于腹腔右下方,分为盲肠、阑尾、结肠和直肠,主要吸收水分和电解质。
(7)肾脏:肾脏位于腹腔腰部,呈红褐色,具有过滤血液、生成尿液和调节体内水分和电解质平衡等功能。
(8)膀胱:膀胱位于腹腔底部,呈粉红色,是储存尿液的器官。
(9)生殖器官:雄性小鼠的生殖器官包括睾丸、附睾、阴茎等;雌性小鼠的生殖器官包括卵巢、输卵管、子宫和阴道等。
四、实验心得体会1. 解剖操作过程中,要熟练掌握解剖刀、剪子等工具的使用方法,注意操作规范,避免损伤内脏器官。

医学生解剖豚鼠实验报告摘要本实验旨在通过解剖豚鼠,研究其解剖结构与生理功能,并进一步了解豚鼠在医学研究中的应用价值。
实验中,我们通过外部解剖和内脏解剖两部分,对豚鼠的解剖结构进行了全面的观察和记录。
通过实验结果,我们可以了解到豚鼠作为实验动物在医学研究中的重要性,以及对疾病模型的建立与药物研发方面的应用前景。
引言豚鼠(Cavia porcellus)作为实验室动物中的常见实验对象,在医学研究中起到了重要的作用。
豚鼠具有生理结构与人类相似,且容易饲养和繁殖的特点,因而广泛应用于疾病模型的建立与药物研发等领域。
通过对豚鼠解剖结构的研究,可以更全面地了解其生理功能及其在医学研究中的应用价值。
材料与方法实验材料- 豚鼠(Cavia porcellus): 5只;实验仪器- 外科手术刀;- 外科手术剪;- 解剖镊子;- 显微镜;- 显微刀;- 标本玻片。
实验步骤1. 通过外部解剖观察,并进行记录。
包括体长、体重、四肢、躯干、头部器官以及皮肤状态的描述;2. 进行内脏解剖。
首先,使用外科手术刀剪开腹部,注意避开内脏器官。
然后,使用解剖镊子和手术剪剪断连接组织,将内脏器官完整地取出,并进行记录;3. 将重要的组织器官进行显微切片。
首先,将取出的组织器官放置在标本玻片上。
然后,使用显微刀将组织切片,并进行染色和固定。
最后,放置在显微镜下,观察并记录组织结构。
结果外部解剖观察豚鼠体长约15cm,体重约300g。
四肢短小,有指(趾)趾有4个。
躯干背部略呈弧形,腹部凹陷。
头部器官包括鼻子、眼睛及耳朵。
皮肤光滑,毛细而密集。
内脏解剖- 豚鼠的呼吸系统由气管、支气管和肺组成。
肺形状扁平,红色且富有弹性。
呼吸系统的主要功能是将空气引入体内,并经过气体交换满足氧气需求;- 循环系统由心脏、血管和血液组成。
豚鼠的心脏位于胸腔中,由四个腔室组成:左右心房和左右心室。
心脏的收缩和舒张使得血液流动,在全身输送氧气和养分;- 消化系统包括口腔、食道、胃、小肠和大肠。


小鼠的解剖实验预习报告
小鼠的解剖实验预习报告
一、实验目的
1、通过观察小鼠了解其外形特征
2、通过对小鼠内脏结构的观察了解哺乳动物内脏结构特点
二、实验内容
1、小鼠的外形观察
2、小鼠的内脏器官观察
三、实验材料和用品
活的小鼠、解剖器、解剖盘、骨剪、棉花等
四、实验操作及观察
1、外形
全身被毛,身体分为头、颈、躯干、尾和四肢。
一对眼,有上下眼睑。
一对大而薄的外耳壳。
鼻孔一对,其下方具有肉质唇的口。
五趾型四肢,指端具爪。
雄性身体后端有2个孔与外界相通,雌性阴部有3个孔与外界相通;雄性后腹部有一个突出的阴茎,距离尾基部较远,雌性后腹部有一个稍微突出的尿乳头,距离尾基部较近,成熟个体可见雌性腹部的乳头。
2、处死方法
药物法、断颈法
3、解剖
剪开腹部皮肤并将其与下方肌肉分离,然后剪开腹部肌肉,沿腹中线剪开腹壁至胸骨后方,并沿胸骨两侧剪断肋骨,将胸骨剪去,露出胸腔和腹腔器官。
(1)消化系统
口腔,唾液腺,食管,胃,肝,小肠,大肠
(2)排泄系统
一对肾,左肾比右肾稍低。
肾上腺。
输尿管。
膀胱。
尿道
(3)生殖系统
雄性:睾丸、附睾、输精管、尿道、附性腺
雌性:卵巢、输卵管、子宫、阴道
(4)胸腔脏器观察
在横隔前方有2个胸腔和一个围心腔。
胸腔内有肺。
围心腔内有心脏以及腹面淡粉色的胸腺,幼鼠胸腺较发达。
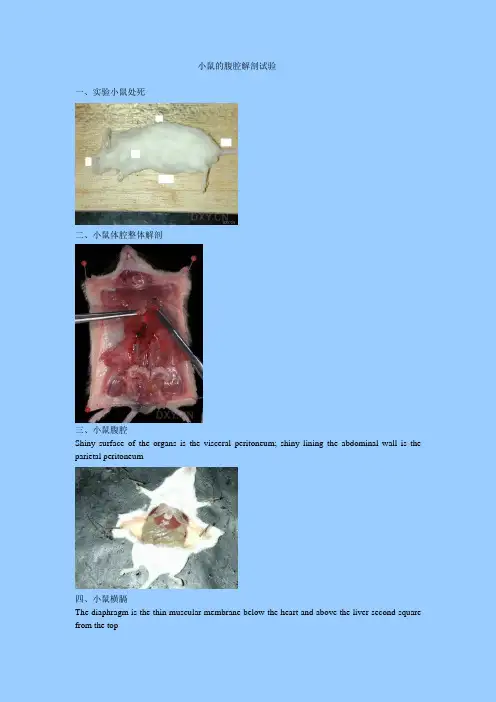
小鼠的腹腔解剖试验一、实验小鼠处死二、小鼠体腔整体解剖三、小鼠腹腔Shiny surface of the organs is the visceral peritoneum; shiny lining the abdominal wall is the parietal peritoneum四、小鼠横膈The diaphragm is the thin muscular membrane below the heart and above the liver second square from the top五、小鼠腹腔重要脏器一览Ignore the top square lung in thorax. From there down are the liver; stomach; spleen; left kidney; left seminal vesicle and the urinary bladderFrom the left: liver; small intestine; large intestine; spleen; urinary bladder; left testisFrom the top: heart; diaphragm; gall bladder between the right lateral and medial lobes of the liver; left medial lobe of liver; spleen; large intestineFrom the left: coiled oviduct; left uterine horn; left ovary above the left oviduct; note that the uterus is bicornuateFemale reproductive organs六、小鼠心脏和肺Heart ventricles and left lungLungs inflated by blowing into nostrils七、小鼠腹腔脏器相互关系简图图一图二。

小鼠解剖实验报告°实验五:小鼠解剖实验吴雪薇 121140059一、实验目的1、通过实验学习给小鼠注射、灌胃等技术操作2、了解戊巴比妥对哺乳动物的影响3、复习解剖的基本操作4、通过实验了解小鼠唾液腺的结构5、通过实验了解小鼠体内器官、系统构造二、实验原理1、小鼠唾液腺唾液腺由颌下腺、腮腺、舌下腺组成,颌下腺最明显,颌下腺两边弥散的是腮腺,舌下腺连于颌下腺上,容易与颌下腺上连的淋巴结搞混。
2、会厌软骨会厌软骨即构成会厌的软骨,形状扁平,像树叶,下部附着在喉结的内壁上。
会厌是喉头上前部的树叶状结构,由会厌软骨和黏膜构成。
呼吸或说话时,会厌向上,使喉腔开放;咽东西时,会厌向下,盖住气管,使东西不至进入气管内。
3、小鼠体内结构(1)胸腔:胸腔内的结构主要有食道、心、肺。
(2)腹腔:主要有胃、肝、胆、胰、脾、肠、肾(包括肾上腺)、输尿管、膀胱和生殖器官:卵巢、输卵管、子宫(雌),睾丸、附睾、精囊腺、输精管(雄)。
(3)胸腔与腹腔由膈膜隔开。
三、实验器材注射器、烧杯、灌胃针、解剖盘、解剖剪刀、镊子、解剖针、钉子四、实验材料小鼠1只、戊巴比妥溶液五、实验操作1、抓取一只小鼠,拎住尾巴根部,使其前肢抓在抹布上,后肢提起,用注射器向其腹腔注射0。
5ml戊巴比妥溶液。
2、将小鼠放在烧杯中,观察它的反应.3、待小鼠不再动时,用注射器向其腹腔再注射0.5ml戊巴比妥溶液,使其死亡.4、将小鼠放在解剖盘上,用大头针将四肢固定在解剖盘上。
5、用解剖剪刀,从靠近肛门处剪开表皮直至口腔,观察唾液腺。
6、剪开口腔,观察会厌软骨。
7、剪开腹腔和胸腔,观察小鼠体内结构.8、处理小鼠,清洗、整理实验器材。
六、实验结果1、观察注射戊巴比妥溶液后的小鼠本次实验第一次注射,注射了0.4ml的戊巴比妥溶液,第二次注射了0.6ml。
小鼠先是身体颤抖,趴在烧杯底不怎么动,后开始出现用爪子挠脸的行为,然后开始乱动甚至依靠烧杯壁直立起来,最后倒下,身体仍在颤抖且较剧烈,在大约两分半后不怎么动了,但身体还在颤抖。

局部解剖实验报告本次实验旨在对动物体内的局部结构进行解剖,以便更深入地了解其组织构成和功能。
通过实验,我们希望能够对解剖学知识有更全面的认识,并为相关医学研究提供参考。
首先,我们选择了小鼠作为实验对象。
小鼠是常见的实验动物,其体型较小,易于操作,且具有代表性。
在实验开始前,我们对实验器材进行了消毒处理,以确保实验过程的卫生和安全。
在实验过程中,我们首先对小鼠的头部进行解剖。
通过仔细剥离皮肤和软组织,我们观察到了头部骨骼的结构。
颅骨的骨缝清晰可见,颞骨、颞肌和颞神经等局部结构也得到了充分展示。
这些结构的解剖对于理解小鼠头部的功能和病理变化具有重要意义。
接着,我们对小鼠的胸腔进行了解剖。
通过剖开胸腔,我们观察到了心脏、肺部和气管等重要器官。
心脏的组织结构清晰可见,心脏壁的厚度、心脏瓣膜的开合情况等细节也得到了详细观察。
肺部的解剖让我们更加了解了呼吸系统的构造和功能。
最后,我们对小鼠的腹部进行了解剖。
消化系统的器官,如胃、肝脏、胰腺和肠道等,都得到了充分展示。
我们观察到了这些器官的组织结构和血管分布情况,这对于研究小鼠的消化生理和病理变化具有重要意义。
通过本次实验,我们对小鼠的局部结构有了更深入的了解,也为相关研究提供了重要的解剖学资料。
在未来的医学研究中,我们将继续深入探索动物体内的结构和功能,为人类健康事业做出更多的贡献。
总结,本次实验对小鼠的头部、胸腔和腹部进行了详细的解剖,为解剖学知识的学习和医学研究提供了重要的资料。
我们将继续深入研究动物体内的结构和功能,为医学科研事业贡献力量。

小鼠解剖实验报告实验目的:探究小鼠的结构组成和解剖特点,加深对小鼠解剖学知识的理解。
实验材料:1. 已处死的小鼠2. 解剖刀、鑷子、剪刀等解剖工具3. 解剖台4. 放大镜5. 电子秤6. 啤酒中心7. 小夹子和贴标签的笔实验步骤:1. 实验前准备:a. 准备解剖工具,确保其清洁和锋利。
b. 将小鼠放置在解剖台上,注意小鼠放置时身体的方向。
2. 外部观察:a. 观察小鼠的体型和身体颜色。
b. 使用放大镜仔细观察小鼠的头部、四肢和尾巴等部分。
3. 体重测定:a. 将已处死的小鼠放在电子秤上,记录体重。
4. 解剖:a. 使用解剖刀从腹部切开小鼠的皮肤,剪除腹部肌肉。
b. 注意不要切破腹膜和其他内脏器官。
c. 观察和记录小鼠的腹部脏器,如胃、肝,以及消化系统、呼吸系统和泌尿系统等。
5. 骨骼观察:a. 将小鼠的四肢和头部通过小夹子固定在解剖台上。
b. 用解剖刀小心地切除肌肉和软组织,暴露骨骼结构。
c. 仔细观察小鼠的骨骼组成,包括脊柱、肋骨和四肢骨骼等,记录和标记。
6. 结论:通过上述步骤,我们得出了关于小鼠的结构组成和解剖特点的观察结果和记录。
根据这些观察结果,我们得出了一些结论和发现。
实验注意事项:1. 在进行解剖实验前,确保小鼠已经处死。
2. 解剖工具需保持清洁和锋利,以免对解剖过程造成干扰。
3. 在切割小鼠的皮肤和组织时,要小心操作,避免切破内脏器官。
4. 在观察和记录解剖过程中,要仔细观察和描述相关结构,并使用贴标签的笔进行标记。

一、实验目的1. 通过对动物内脏的解剖,了解动物内脏器官的结构和功能。
2. 培养观察和识别动物内脏器官的能力。
3. 学习和掌握动物解剖的基本方法和技巧。
二、实验材料与仪器1. 实验动物:小白鼠(雄性)2. 实验器材:解剖盘、手术刀、解剖剪、镊子、解剖针、解剖针头、解剖放大镜、解剖图谱、生理盐水、75%酒精、碘酒、消毒棉签等。
三、实验步骤1. 解剖准备:将小白鼠处死,然后用生理盐水洗净其体表,置于解剖盘上。
2. 观察外形:仔细观察小白鼠的外形,了解其头、颈、躯干、四肢、尾等部位的结构。
3. 解剖皮肤:用手术刀在小白鼠的腹部做一横切口,用解剖剪剪开皮肤,暴露出腹部肌肉。
4. 解剖肌肉:沿腹中线切开肌肉,用镊子将肌肉向两侧轻轻拉开,暴露出内脏器官。
5. 观察内脏器官:- 消化系统:观察胃、小肠、大肠、肝脏、胆囊、胰腺等器官的位置、形态和结构。
- 呼吸系统:观察气管、支气管、肺等器官的位置、形态和结构。
- 循环系统:观察心脏、血管等器官的位置、形态和结构。
- 泌尿系统:观察肾脏、输尿管、膀胱等器官的位置、形态和结构。
- 生殖系统:观察睾丸、卵巢、输卵管、子宫等器官的位置、形态和结构。
6. 观察血管和神经:用解剖放大镜观察血管和神经的分布情况,了解其与器官的连接关系。
7. 解剖完毕:将内脏器官按顺序摆放好,用碘酒和酒精消毒,然后进行清洗和干燥处理。
四、实验结果1. 消化系统:小白鼠的消化系统由胃、小肠、大肠、肝脏、胆囊、胰腺等器官组成。
胃呈囊状,小肠分十二指肠、空肠和回肠,大肠分盲肠、结肠和直肠,肝脏呈红褐色,胆囊呈囊状,胰腺呈粉红色。
2. 呼吸系统:小白鼠的呼吸系统由气管、支气管和肺组成。
气管呈管道状,支气管呈树枝状,肺呈海绵状。
3. 循环系统:小白鼠的循环系统由心脏、血管组成。
心脏呈红色,分为四个腔室,血管呈管状,分布全身。
4. 泌尿系统:小白鼠的泌尿系统由肾脏、输尿管、膀胱组成。
肾脏呈红褐色,输尿管呈管状,膀胱呈囊状。
第1篇一、实验目的1. 学习和掌握小鼠的解剖学结构,了解其内部器官的分布和功能。
2. 培养实验操作技能,包括动物抓取、麻醉、解剖等。
3. 增强对生物学基本知识的理解和应用能力。
二、实验材料与仪器1. 实验动物:健康昆明小鼠2只2. 实验仪器:解剖台、手术刀、剪刀、镊子、解剖剪、解剖针、生理盐水、纱布、注射器、酒精、棉球、解剖显微镜等。
三、实验步骤1. 动物准备- 将小鼠置于解剖台上,用纱布包裹四肢,使其固定。
- 用酒精棉球对小鼠进行消毒。
- 在小鼠的头部进行标记,以便后续操作。
2. 麻醉- 称量小鼠体重,根据体重计算所需戊巴比妥钠的剂量。
- 将戊巴比妥钠溶液注射至小鼠腹腔,剂量为0.5ml/100g体重。
- 观察小鼠的反应,待其进入麻醉状态。
3. 解剖- 在小鼠腹部正中线处切开皮肤,暴露腹壁肌肉。
- 用解剖剪沿腹壁肌肉剪开,暴露腹腔。
- 观察腹腔内的器官,包括肝脏、胃、肠、脾、肾脏、卵巢/睾丸等。
4. 器官分离- 用解剖剪将肝脏、胃、肠、脾、肾脏、卵巢/睾丸等器官与腹腔相连的组织分离。
- 将器官放在解剖显微镜下观察,记录其形态和结构。
5. 系统观察- 观察心脏,记录其形态、大小和结构。
- 观察肺脏,记录其形态、大小和结构。
- 观察大脑,记录其形态、大小和结构。
- 观察眼睛,记录其形态、大小和结构。
- 观察骨骼系统,记录其形态、大小和结构。
6. 器官保存- 将器官用生理盐水清洗,并用纱布包裹。
- 将器官放入福尔马林溶液中保存。
四、实验结果1. 腹腔器官- 肝脏:呈暗红色,质软,表面光滑。
- 胃:呈暗红色,质软,分为胃底、胃体和胃窦。
- 肠:呈暗红色,质软,分为小肠和大肠。
- 脾:呈暗红色,质软,呈椭圆形。
- 肾脏:呈红褐色,质软,呈豆形。
- 卵巢/睾丸:呈淡红色,质软,呈椭圆形。
2. 系统器官- 心脏:呈粉红色,质软,分为心房和心室。
- 肺脏:呈粉红色,质软,呈海绵状。
- 大脑:呈粉红色,质软,分为大脑半球、小脑和脑干。
解剖小白鼠实验报告
实验目的:了解小白鼠内部器官的结构和功能。
实验材料:小白鼠、解剖工具(手术剪刀、手术剪、解剖刀、显微镜等)。
实验步骤:
1. 利用手术剪刀和手术剪将小白鼠的皮毛剪去,清洗干净。
2. 将小白鼠放在解剖板上,用手将前腿向后拉伸来暴露胸腔。
3. 用手术剪切开小白鼠的腹部,小心不要伤到内脏器官。
4. 将腹部切开后,用显微镜观察和描述小白鼠的内脏器官,如心脏、肺、肝脏、胃等。
5. 用解剖刀将每个器官逐一剖开,观察器官的内部结构和颜色。
6. 观察和记录器官的形状、大小和位置等信息。
7. 对观察到的有意义的发现,如异常结构或病变等进行描述和记录。
实验结果:
在解剖过程中观察到小白鼠的心脏位于胸腔中央,左侧为主。
肺部位于心脏的两侧,颜色粉红,肺组织细密。
肝脏位于腹腔上方,呈棕红色,质地较硬。
胃位于肝脏下方,呈C型弯曲状。
实验结论:
经过解剖观察,我们了解到小白鼠的内脏器官结构和位置,心脏、肺、肝脏和胃分别负责不同的功能,如循环系统、呼吸系
统、消化系统等。
通过这次实验,加深了我们对小白鼠内部器官的认识,为进一步研究生理和病理提供了基础。
小鼠解剖实验报告反思总结1.引言1.1 概述概述部分的内容:小鼠解剖实验是一种常见的实验方法,通过对小鼠进行解剖观察,可以了解小鼠的解剖结构和器官功能,以及对药物的影响等。
本实验旨在通过解剖实验,深入了解小鼠的生理和解剖结构,为医学研究提供重要的数据和信息。
然而,在进行小鼠解剖实验的过程中,我们也需要充分考虑动物权益和道德原则,尽量减少对小鼠的伤害,遵循科学伦理和道德规范。
因此,本报告将对小鼠解剖实验进行全面的分析和反思,旨在提出改进建议,为未来的实验提供借鉴。
1.2 文章结构文章结构部分内容:本文主要分为引言、正文和结论三个部分。
引言部分包括对小鼠解剖实验的概述,文章结构的介绍以及实验的目的。
正文部分包括实验过程、倫理問題和实验效果评估三个小节。
其中实验过程介绍了实验的设计和步骤,仪器和材料的使用以及实验结果的分析。
倫理問題部分涉及实验中的倫理標準,动物权益和道德考量的讨论。
实验效果评估部分包括实验效果的分析,实验局限性的总结以及改进建议的提出。
结论部分对实验进行总结回顾,分享实验经验,并展望未来的研究方向。
1.3 目的:本实验旨在通过实际操作,加深学生对小鼠解剖结构的理解,掌握解剖技巧和方法,培养学生的动手能力和科学素养。
同时,通过实验过程中的倫理問題和实验效果评估,引导学生思考动物权益和实验道德,促进学生的全面发展和人文关怀意识。
希望通过本实验,学生能够以更加负责任和关爱的心态对待动物,并且能够对实验结果进行客观评价和整理,为未来的科学研究提供参考和借鉴。
分的内容2.正文2.1 实验过程:2.1.1 实验设计和步骤:本次实验的设计主要是通过解剖小鼠来观察其内部器官结构和功能,以便更深入地了解小鼠生理和病理状态。
在实验过程中,我们首先对小鼠进行标本准备,包括给予麻醉和取得实验所需的小鼠标本。
随后,我们进行了解剖操作,根据实验要求依次打开小鼠的腹腔和胸腔,以便观察其肝脏、肺部、心脏等重要器官的结构和功能。
解剖小鼠实验报告
《解剖小鼠实验报告》
实验目的:通过解剖小鼠,观察其器官结构和功能,为进一步研究小鼠生理学提供基础数据。
实验方法:选择健康的小鼠作为实验对象,先行麻醉后进行解剖。
首先将小鼠固定在解剖台上,然后进行剖腹操作,依次取出心脏、肝脏、肺部、肾脏等器官,进行观察和记录。
实验结果:经过解剖观察,发现小鼠心脏为四腔结构,肝脏呈红褐色,肺部呈粉红色,肾脏呈肾形,均符合正常小鼠的器官结构。
在进一步观察中,发现小鼠心脏搏动规律,肝脏有明显的血管分布,肺部有明显的气囊结构,肾脏有清晰的肾小球和肾管结构。
实验结论:通过解剖小鼠实验,我们成功观察到了小鼠的器官结构和功能,为进一步研究小鼠的生理学提供了重要的基础数据。
同时,对小鼠的解剖观察也有助于我们更深入地了解小鼠的生理特点和生命活动规律,为医学研究和药物研发提供了重要参考。
实验展望:在今后的研究中,我们将继续深入探讨小鼠的生理特点和生命活动规律,加强对小鼠器官结构和功能的研究,为医学和生物学领域的发展做出更大的贡献。
同时,我们也将继续改进实验方法,提高实验效率和数据准确性,为小鼠解剖实验的进一步研究打下坚实的基础。
一、实验目的1. 熟悉动物器官病理实验的基本操作步骤。
2. 学习观察和分析动物器官病理变化,了解常见病理现象。
3. 提高实验技能和理论联系实际的能力。
二、实验材料与器材1. 实验动物:小鼠2. 器材:解剖台、解剖剪、镊子、解剖针、手术刀、剪刀、组织剪、解剖盘、生理盐水、固定液、染色液、显微镜等。
三、实验方法1. 实验动物处死:采用颈椎脱臼法处死小鼠,确保动物死亡。
2. 器官采集:迅速打开小鼠腹腔,取出心、肝、脾、肺、肾等器官,置于生理盐水中清洗。
3. 器官固定:将清洗干净的器官放入固定液中固定24小时。
4. 器官切片:将固定好的器官进行切片,切片厚度约为5μm。
5. 染色:将切片放入染色液中染色,如苏木精-伊红染色。
6. 显微镜观察:将染色后的切片置于显微镜下观察,记录病理变化。
四、实验结果与分析1. 心脏(1)心肌纤维排列紊乱,出现纤维化。
(2)心肌细胞肿胀,核增大,核仁明显。
(3)部分心肌细胞坏死,出现空泡变。
2. 肝脏(1)肝细胞肿胀,胞质疏松,出现水样变性。
(2)肝细胞坏死,出现嗜酸性小体。
(3)肝细胞再生,出现肝细胞分裂相。
3. 脾脏(1)脾窦扩张,充满红细胞。
(2)脾索增宽,出现纤维化。
(3)脾小体增大,出现淋巴细胞浸润。
4. 肺脏(1)肺泡间隔增宽,出现纤维化。
(2)肺泡腔内充满红细胞和渗出物。
(3)肺泡上皮细胞肿胀,出现水样变性。
5. 肾脏(1)肾小球肿胀,毛细血管扩张。
(2)肾小管上皮细胞肿胀,出现水样变性。
(3)肾小管腔内充满蛋白管型。
五、实验结论本次实验通过观察小鼠心脏、肝脏、脾脏、肺脏和肾脏的病理变化,了解了动物器官在病理状态下的形态学特征。
实验结果表明,器官病理变化主要包括细胞肿胀、坏死、纤维化、炎症等。
这些病理变化是疾病发生、发展过程中的重要环节,对于疾病的诊断、治疗和预防具有重要意义。
六、实验讨论1. 实验过程中,器官采集和固定是关键步骤,需迅速、准确地进行。
2. 切片厚度和染色方法对实验结果有一定影响,需严格控制。
实验动物英文作文下载温馨提示:该文档是我店铺精心编制而成,希望大家下载以后,能够帮助大家解决实际的问题。
文档下载后可定制随意修改,请根据实际需要进行相应的调整和使用,谢谢!并且,本店铺为大家提供各种各样类型的实用资料,如教育随笔、日记赏析、句子摘抄、古诗大全、经典美文、话题作文、工作总结、词语解析、文案摘录、其他资料等等,如想了解不同资料格式和写法,敬请关注!Download tips: This document is carefully compiled by theeditor. I hope that after you download them,they can help yousolve practical problems. The document can be customized andmodified after downloading,please adjust and use it according toactual needs, thank you!In addition, our shop provides you with various types ofpractical materials,such as educational essays, diaryappreciation,sentence excerpts,ancient poems,classic articles,topic composition,work summary,word parsing,copyexcerpts,other materials and so on,want to know different data formats andwriting methods,please pay attention!I once had a guinea pig as a pet. It was so cute and furry. I loved to play with it.Another time, I saw some mice in the lab. They were scurrying around.There was also a rabbit in the experiment. It looked a bit scared.I remember going to a place where they had a lot of monkeys. They were very active.。
姓名班级学号实验日期2014.5.21科目实验名称Mouse Dissection合作者指导教师成绩LAB 10: Mouse DissectionIntroduction:In biomedical research, animal models are always regarded as indispensable tools. They contribute to the scientific discovery in biology and our understanding of the functions of individual genes, even the mechanism of different diseases. Typically, although mice are different from humankind in size and appearance, they have a distinct genetic similarity. At the same time, mice have an efficient ability to reproduce, so they are important research tools for experiments in the lab.In this experiment, we will exercise to dissect a mouse, so that we can observe the inside of a mammalian body to identify the female and male mice. Learning and recognizing the anatomical structure of mice, including.Materials and Methods:Materials:Operation plate, Scissor, Forceps, Alcohol cotton, Mouse.Methods: [we get a male mouse]Part 1: Observations of external features. Make a table T-1.1.Having an overhead view, identify the mouse’s head, neck, truck, and tail; observe the dorsal and ventral surfaces. Roughly record what is seen.2.Observe the thorax which is supported by the rib cage, and the abdomen, and the details of appendages attached to the abdomen.3.Find the mouth, two external nostrils, two external auditory canals, and anus, which are on the body surface.4.Have a simply look at the surface of reproductive organ, prepuce, urethral and penis including.And locate the saclike scrotum; feel for the paired testes in the scrotum. Note the roughfeatures.Part 2: Observation of organs and structures inside the mouse. [Open the Ventral Body Cavities, Thoracic Cavity, and Abdominopelvic Cavity in order. We must break the ribs near the attachment to the vertebral column to fold back the upper flaps.] Make a table T-2.1.Ventral Body Cavities.a. Make a longitudinal incision through the skin with a dissecting scissor, from the neck to thepreputial opening. Pierce the body wall below the ribs, with the blades angled upward, sothat it won’t damage the internal organs.b. Pull the sides of the longitudinal incision, and look for the diaphragm. Then make two2. Thoracic Cavity.a. After opening, observe the heart and cut the thymus away so that we can observe the heartclearly.b. Make sure the location of lung, find the trachea and bronchus. Note the features in table T-2.3.Abdominopelvic Cavity.a.Observe the liver which is posterior to the diaphragm, look for the gallbladder.b.Locate the stomach, and then examine the spleen. Note where the small intestine is, and lookfor the pancreas (can secrete insulin). Take photos and record the features.c.Find the place where small intestine empties into large intestine. Observe the short rectumwhich is near to anus, and cecum.d.Separate the esophagus, dorsal mesentery, and the descending portion of the large intestine.Give the urinary bladder.e.Find two kidneys, and the urethra connected to them, the ureter start from the central ofkidney.f.Examine the organs of the reproductive system. Use scissors to open the scrotum to exposethe testis, and then find the coiled epididymis and vas deferens.g.Roughly observe a mouse of the opposite sex.Results:Part 1: table T-1As we can see, the blood vessels on the ear are apparent, and the penis is wrapped in prepuce. The saclikePart 2: table T-2The bronchi can carry air from the trachea toward the lungs, during the process of inspiration.The small intestine is longest organ in the body, filling most of the Abdominopelvic cavity.Pancreas produces enzymes for the digestion of food and, as a part of the endocrine system, it secretes insulin into the blood.The system of female mouse is similar to male we observe, except the reproductive organs. Discussions:Question 1: How to distinguish female and male mouse?From the appearance of external genital organs, we can recognize them, the difference of penisand vagina mouth is apparent. Besides, the female mouse has many visible nipples and theRespiratory system: lungs, trachea, bronchus.Digestive system: stomach, spleen, pancreas, liver, gallbladder. Urinary system: kidney, ureter, urinary bladder.Reproductive system: penis, prepuce, saclike scrotum.References:/article/495ba8413be36138b30ede13.html/link?url=0rmCCGLBKZt3--XtPeTfAzxlE3TKwCkGpt9pNOCfExKwE_xen4UsnC PSEESJL YLa-uCgEjRaB17EuNGatXZr3q/link?url=ijiTYru5lEYl1NIVmt_oa8ahhUc5NMksycmM_FukfG80Fn7N6yt1GlD00RXaz4aBJIUH8YSM0sbyr_NWszwF3a/link?url=6e5jeclQ_pBDBEadBRpQrOXzQOTKXPP_fVYZ1UaYWVSVGsUtQg0BoDWUQ3hg_kHXnWmkmBYq0xf7M10V9Mnx5aContribution statements:%%% is responsible for recording the phenomena, when %%% operates the mouse, and %%% prepares the materials needed.Figures:TailFigure 1-1 Figure 1-2The view of the ventral surface the view of the dorsal surface (belly) (back) MouthNeck Saclike scrotumThorax HeadEarFootAnusFigure 2-1 Figure 2-2 Figure 2-3 The view of mouse after being The mouse after being open Some organs cut through the skin. the ventral body cavity.Heart Stomach Trachea.Figure 2-4 Figure 2-4 Figure 2-5The view of Thoracic Cavity. The inside view of abdomen. The inside view of thorax.Figure 2-6. Figure 2-7Intestines. Some organs of digestive system. DiaphragmLung,4 pieces.ThymusLarge Intestine CecumSmallintestine Pancreas.Spleen.Penis. KidneyUrinary bladderFigure 2-8 Figure 2-9 The view of inside reproductive organ.Figure 2-10 Figure 2-11 Figure 2-12 The gallbladder The adrenal gland. The ureter. Vas deferens.Epididymis第页。