语言学教程morphology
- 格式:doc
- 大小:21.00 KB
- 文档页数:2

Chapter 3 LexiconTime periods: two classesTeaching contents:definition of a wordThe formation of wordsTeaching aims and requirementsLearn by heart:1. The classifications of morphemes, such as free morpheme and bound morpheme, stem, root, inflectional affix and derivational affix.2. Two ways of word-formation such as inflections and derivations.Know:1. The definition of morphemes, free morphemes, bound morphemes, stem, root, affix, inflection and derivation and so on.2. Two different fields of morphology, including inflectional morphology and derivational morphology.Understand:1. Definition of a word2. The classifications of word according to different aspects3. The formation of wordsTeaching focus and difficulties:Focus:1. The definition of morphemes, free morphemes, bound morphemes, stem, root, affix, inflection and derivation and so on.2. The classifications of morphemes, such as free morpheme and bound morpheme, stem, root, inflectional affix and derivational affix.3. Two ways of word-formation such as inflections and derivations.Difficulty:1. Classification of morphemes2. Inflection and derivations.1. Review what we have learned in last chapter, and ask some students to answer the following questions: (5m)1) How are English consonants classified2) How are English Vowels classified3) What are phonemes and allophones2. Study Definition of a wordA word is a minimal free form of a language that has a given sound and meaning and syntactic function.Zhang Weiyou (1999)a minimum free formStability --internal structure (can’t rearrange)relative uninterruptibility --internal structure (can’t insert) Classification of words(1)Basic word stock & non-basic vocabularyContent words & functional wordsNative words & borrowed wordsVariable words & invariable wordsOpen-class words & closed-class wordsTraditional parts of speech & additional four categoriesClassification of words (2)Variable words & invariable words (variability)—variable words: the words whose form is changeable, words which might appear in different inflective and derivative forms, v. n.—invariable words: the words whose form is unchangeable, words which usually occur in the same form such as: since, in, for, of, at, on Classification of words (3)Open-class words & closed-class words (membership)--open-class words: membership is unlimited, n. v. (economic words, scientific words.)--closed-class words: membership is comparatively limited. Pronouns, conj, prep. Articles.Classification of words (4)Traditional parts of speech & additional four categoriesTraditional parts of speech:N. v. adj. Adv. Prep. Conj.Additional four categoriesParticles : 小品词infinite maker ‘to’, negative maker ‘not’, subor dinate units in verbal phrases.Auxiliaries: 助词(助动词、情态动词)Pro-form 代词形式 pro-v. pro-adj.. He likes the animal, so do i.. The desk is white, so is the chair.Determiners 限定词‘the’, ‘a’, ‘some’, ‘all’. ‘all the beautiful Chinese girls’,3. Study The formation of word1) Ask the students to skip over this section and find out the answers to the following questions:a. What is morphologyb. What is morpheme What is the biggest difference between morpheme and phonemec. How can we classify morphemes2) 3.2.1 MorphologyDefinition: the study of word-formation, or the internal structure of words, or the rules by which words are formed from smaller components: morphemes.For example:Verbs are formed by adding –ify to either an adjective (adj.) or a noun (n.)在形容詞或名詞加-ify變成動詞*simple (adj.) simplify (v) 簡化*quality (n) qualify (v)使具有資格*identity (n) identify (v) 認出MorphemesThe most basic element of meaning is traditionally called morpheme.The smallest meaningful components of words..: boyish孩子氣的;男孩似的boy, -ish (two morphemes)3) 3.2.2 Types of morphemes (1)Those that may constitute words by themselves,自由形式的詞素本身就是一個詞,可以單獨使用.: boy, girl, table, nation.Free morphemes PK Bound morphemesThose that cannot occur alone,Bound morpheme includes two types: roots and affixes..: -s in dogs, -ed in worked, dis- in dislike, un- in unable.A certain affix here refers to an inflectional affix: grammatical endingsTypes of morphemes (2)Root: the part left when all the affixes are removed 词根Stem: the part left when a certain affix is removed 词干Affix: the part which is attached to other words; usually bound morphemes 词缀.: friend as in unfriendliness.Roots may be:Free: those that can stand by themselves,.: black+board; nation+-al; orbound: those that cannot stand by themselves,.: -ceive in receive, perceive, conceive.Affix: normally divided into:Prefix (dis-, un-) prefixes occur at the beginning of a word.suffix (-en, -ify) at the endinfix (foot-feet) in the middlePrefix 前綴mis- 誤 mistake 誤解over- 過分 overdo 做得過分Prefixed modify the meaning of the stem, but usually do not change the part of speech of the original word.Exceptions are the prefixes be-, and en(m)-.Added to adjectives or nouns they turn the words into verbs.Suffixes modify the meaning of the original word and in many cases change its part of speech.Accordingly, there are noun-forming suffixes, adjective-forming suffixes, adverb-forming suffixes, and verb-forming suffixes.-er teacher, writer-ician “...(專)家,...工作者” electrician電工-bility “能力” possibility可能性-hood “時期” childhood幼年時期,童年時期-age “(人生的)某一時期” orphanage孤兒-ary (adj) elementary基本的, secondary第二位的-ful (adj) beautiful美麗的, delightful愉悅的, sorrowful悲傷的-en (V 使..) weaken使變弱 , darken, deepen-ize (v …化) modernize使現代化-ly (adj+ -ly=adv n + -ly= adj) slowly慢慢地, friendly友善的-ward (往…方向) forward(adv)往前, eastward往東Stem: a morpheme or combination of morphemes to which an inflectional affix may be added,.: friend+-s; write+-ing, possibility+-es.A stem can be a bound root, a free morpheme, or a derived form itself..:*toler- (root) + affix –ate: tolerate忍受*quick (free morpheme) + affix –ly: quickly *careless (a derived form) + affix lessInflectional affix: Bound morphemes which are for the most part purely grammatical markers, signifying such concepts as tense, number, case etc..: -ed, -s, -erHe had regular features. 他五官端正。




Chapter 3 Morphology 形态学1.Definition 定义Morphology is a branch of grammar which studies the internal structure of words and the rules by which words are formed.形态学是语法学的一个分支,它研究的是单词的内在结构及单词的构成规则。
The aim of morphology is to find out these rules.形态学的任务就是要找出这些规则(单词构成的规则)。
Morphology is divided into two sub-branches: inflectional morphology and lexical or derivational morphology. The former studies the inflections and the latter the study of word-formation.形态学可以划分两个分支:屈折形态学和词汇形态学(也叫派生形态学)。
前者研究的是单词的屈折变化,后者研究的是构词法。
2.Morpheme 词素Morpheme: the smallest meaningful unit of language 词素:语言中最小的意义单位Just as a phoneme is the basic unit in the study of phonology, so is a morpheme the basic unit in the study of morphology.正如音位是音系学研究中的基本单位一样,词素是形态学研究中的基本单位。
Monomorphemic words 单词素单词Types of morphemes 词素的类型Free morphemes 自由词素The morphemes that are independent units of meaning and can be used freely all by themselves are called free morphemes. Such as help, table,room, mate, quick, able.这些词素是独立的、可以自由使用的意义单位,所以它们就被称作自由词素。
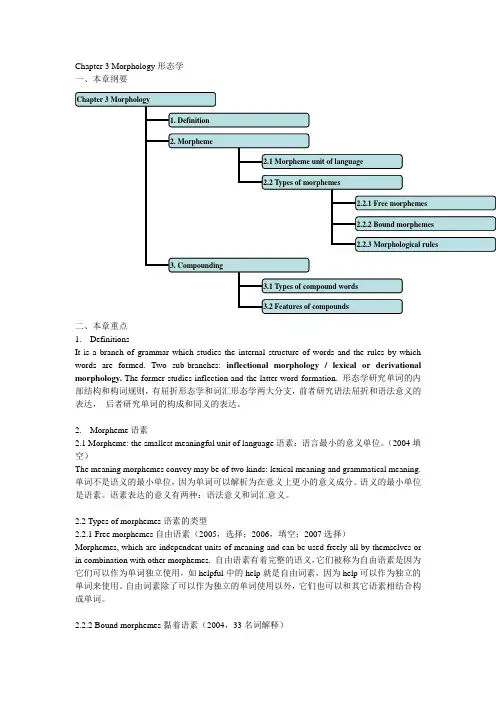
Chapter 3 Morphology形态学一、本章纲要二、本章重点1.DefinitionsIt is a branch of grammar which studies the internal structure of words and the rules by which words are formed. Two sub-branches: inflectional morphology / lexical or derivational morphology. The former studies inflection and the latter word-formation. 形态学研究单词的内部结构和构词规则,有屈折形态学和词汇形态学两大分支,前者研究语法屈折和语法意义的表达,后者研究单词的构成和同义的表达。
2.Morpheme语素2.1 Morpheme: the smallest meaningful unit of language语素:语言最小的意义单位。
(2004填空)The meaning morphemes convey may be of two kinds: lexical meaning and grammatical meaning. 单词不是语义的最小单位,因为单词可以解析为在意义上更小的意义成分。
语义的最小单位是语素。
语素表达的意义有两种:语法意义和词汇意义。
2.2 Types of morphemes语素的类型2.2.1 Free morphemes自由语素(2005,选择;2006,填空;2007选择)Morphemes, which are independent units of meaning and can be used freely all by themselves or in combination with other morphemes. 自由语素有着完整的语义,它们被称为自由语素是因为它们可以作为单词独立使用,如helpful中的help就是自由词素,因为help可以作为独立的单词来使用。





Morphology 词法studies the internal structures of words and word formation rules. It divided into two fields:inflectional morphology(屈折词法) and derivational/lexical morphology(派生词法). It studies the different categories of morphemes( bound, free, derivational and inflectional) morphological rulesMorpheme is a minimal meaningful grammatical unit in a language. 词素Free morpheme s: those that can exist as individual words 自由语素Lexical morphemes实词Functional morphemes 虚词Bound morphemes(粘着词素): those that can not occur alone as separate words.Roots(词根),the most important part of a word that carries the principal meaningAffixes(词缀): those that lexically depend on roots and do not convey the fundamental meaning of words.Position: prefixes, suffixes and inffixes(中缀)Function: inflectional affixes and derivational affixes 屈折词法派生词法Inflectional affixes: indicate grammatical function, do not produce new words or cause a change in grammatical class. Number, gender, tense, aspect, case and degree (8个:-s,-s,’s, -ing, -ed,-en,-er,est )Derivational affixes: produce new words, some change grammatical classes of words.root词根the basic part of a word that can’t be further analyzed without total loss of its identity Base 词基: the form that a derivational affix is attachedStem 词干: the form that an inflectional affix is attachedMorphs语子are related to morphemes in general and allomorphs are related to a specific morpheme.empty morph 空语子: a morph which has form but no meaning. children=child+r+enzero morph 零语子: a morph which has meaning but no form. They work in Nanjing. Allomorphs 词素变体: the realizations of a particular morpheme. /in/,/il/ /ir/,/im/Morphemic analysis: to analyse the number of morphemes and the relationships between the morphemes.linear order of morphemes: the horizontal order or the sequential characteristics of morphemes in a wordhierarchical order: the internal structure or relationships of the morphemes.Immediate constituent analysis(IC analysis)to divide the morphemes of a word into two groups and then divide them into sub-groups and so on, until the irreducible constituents or the morphemes are obtained.morphological rule s: the rules that determine how morphemes are combined into new words.word-formation processes: the rule-governed processes of forming new words on the basis of already existing linguistic resources.productive ones: derivation(派生), conversion(转换) and compounding(复合);less productive ones:blending(拼缀法), clipping(截短法), backformation(逆成法),acronymy(首字母法)Derivation: a process in which one or more affixes are attached to a root or a base to produce a new word known as derived words.compounding:a process in which two or more free morphemes are combined to form a new word called compound word or compound.A solid compound: two words are written together: fingerprint, sunburn doorknob.Open compound: the words are written separately: April Fool’s day, Boston terrier. Conversion: a process to turn a owrd into a new word class without the addition of affix blending: to delete parts of two words and combine the remaining parts to form a new word. clipping: to form a new word by deleting one or two syllables without any change in meaning or part of speech. ominibus= busback-formation: to form a new word by removing the supposed suffix from a longer word already in a language.acronymy: to form a new word by joining the first letters of several words together.Acronym: the letters are pronounced as a single word. APEC, NASAInitialism: the letters are pronounced one by one. UFO, VOA。
morphology语言学定义【形态学morphology】是语法学的一个分支,研究单词的内部结构和构词规则。
形态学有两个分支:曲折形态学和词汇或派生形态学。
曲折形态学研究语法曲折和语法意义的形态学;派生形态学研究单词的构成和词义的表达。
morphology什么意思?1、词法:词法研究的对象是各种词的形式及其用法. 英语词类的形式变化有:名词和代词的数,格和性的形式变化;动词的人称、时态、语态、语气等形式变化;以及形容词和副词比较等级的形式变化。
2、句法(syntax)句法研究的对象是句子各个组成部分及其安排的规律,。
3、构词学:构词学(morphology)是语言学中的一门比较简单的学问,主要研究的是词的构成. 最近几年,电脑领域的某些词汇有了一些改变,某些词汇渐渐不被人们使用,新的词汇取而代之. 例如说,以前我们说「执行」一个程式,现在则说「跑」一个程式。
资料拓展:morphology.n.形态学,形态论;词法,词态学。
短语:soil morphology土壤形态学;土壤形态。
urban morphology城市形态;城市形态学。
例句:And morphology and performance of the coating has been examined. 并对镀层的表面形貌和性能进行了测定。
We also analyzed the effect of morphology on field emission properties.我们还分析了形貌对场发射性能的影响。
He also gave a very accurate description of the morphology of his cells.他给他所发现的.细胞的形态学特征进行了非常精细的描述。
They attain complex morphology, appearing as branched, tubular processes.它们达到复杂的形态,出现分枝,管状突起。
戴炜栋语言学-Chapter 3 Morphology●开放类和封闭类Open class and closed class●开放性词类(open class words):名词、动词、副词和形容词●封闭性词类(closed words):连词、介词、冠词、代词●词素Morphemes---the minimal units of the meaning●词素的定义the definition●词素morpheme--带着信息和功能的语言的最小单位 a morpheme can be definedas.a minimal unit of meaning.例如:reader是由read和er两个词素组成 boys是由boy和-s两个词素●注意:●词素既不是意义,也不是音阶,而是意义和音阶的组合;●词素通常是任意的,他们的声音和意义之间没有必然的联系;●如果想区分词素之间的区别,可以使用语素(morph);●区分独立词和复杂词的区别:前者为单一词素构成,后者包括两个及以上的词素●词素的分类●自由和黏着词素(Free and bound morphemes)●自由词素:可以独立成词的词素成为自由词素 can be a word by itself●黏着词素:必须依附于另一个词素must be attracted to another one●同质异形体(Allomorphs)The variant forms of a morpheme are called its allomorphs.●Analyzing word structures分析词的结构●root词根 The roots constitutes the core of the word and carries the major component ofits meaning.●The roots typically belongs to a lexical category and are always bound morphemes.●affixes词缀 Affixes do not belong to a lexical category and are always bound morphemes ●Derivational and inflectional morphemes派生词素和曲折词素●派生词素:-en, -ate, and -ic are thus called derivational morphemes●曲折词素:there are bound morphemes which are for the most part of purelygrammatical markers and signify such concepts as tense, number, case and so on.●Morphological rules of word formation构词的形态学规则●词的构成方式被称为形态学规则(morphological rules),这些规则决定了词素怎样组合成为词。
I. Decide whether each of the following statements is True or False:
1.Morphology studies the internal structure of words and the rules by which words are formed.
2.Words are the smallest meaningful units of language.
3.Just as a phoneme is the basic unit in the study of phonology, so is a morpheme the basic unit in the study of morphology.
4.The smallest meaningful units that can be used freely all by themselves are free morphemes.
5. Bound morphemes include two types: roots and affixes.
6.Inflectional morphemes manifest various grammatical relations or grammatical categories such as number, tense, degree, and case.
7.The existing form to which a derivational affix can be added is called a stem, which can be a bound root, a free morpheme, or a derived form itself.
8. Prefixes usually modify the part of speech of the original word, not the meaning of it.
9.There are rules that govern which affix can be added to what type of stem to form a new word. Therefore, words formed according to the morphological rules are acceptable words.
10.Phonetically, the stress of a compound always falls on the first element, while the second element receives secondary stress.
II.. There are four choices following each statement. Mark the choice that can best complete the statement:
1. The morpheme “vision” in the common word “television” is a(n) ______.
A. bound morpheme
B. bound form
C. inflectional morpheme
D. free morpheme 2.
2.The compound word “bookstore” is the place where books are sold. This indicates tha t the meaning of a compound __________.
A. is the sum total of the meaning of its components
B. can always be worked out by looking at the meanings of morphemes
C. is the same as the meaning of a free phrase.
D. None of the above.
3.The part of speech of the compounds is generally determined by the part of speech of __________.
A. the first element
B. the second element
C. either the first or the second element
D. both the first and the second elements.
4._______ are those that cannot be used independently but have to be combined with other morphemes, either free or bound, to form a word.
A. Free morphemes
B. Bound morphemes
C. Bound words
D. Words
5._________ is a branch of grammar which studies the internal structure of words and the rules by which words are formed.
A. Syntax
B.Grammar
C. Morphology
D. Morpheme
6. The meaning carried by the inflectional morpheme is _______.
A. lexical
B. morphemic
C. grammatical
D. semantic
7. Bound morphemes are those that ___________.
A. have to be used independently
B. can not be combined with other morphemes
C. can either be free or bound
D. have to be combined with other morphemes.
8. ____ modify the meaning of the stem, but usually do not change the part of speech of the original word.
A. Prefixes
B. Suffixes
C. Roots
D. Affixes
9. _________ are often thought to be the smallest meaningful units of language by the linguists.
A. Words
B. Morphemes
C. Phonemes
D. Sentences
10.“-s” in the word “books” is _______.
A. a derivative affix
B. a stem
C. an inflectional affix
D. a root IV. Define the following terms:
III.Answer the following questions
Discuss the types of morphemes with examples.。