汽车机械制动
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:5.78 MB
- 文档页数:123

摘要近年来,国内汽车市场发展迅速,而轿车则是汽车未来发展的方向。
然而随着汽车保有量的增加,所带来的一系列安全问题引起人们的注意,而汽车的制动系统则是汽车行驶的一个重要主动安全系统之一。
其性能的好坏直接影响着汽车的行驶安全,因此,高性能制动系统的研究开发,为安全行驶提供保障是我们要解决的主要问题。
另外,随着汽车市场竞争的加剧,如何缩短产品研发周期、提高生产效率、降低成本等,提高产品市场竞争力,已成为企业成功的关键。
本说明书是汽车制动系统的设计。
首先介绍了汽车制动系统的发展、结构、分类,并通过对鼓式制动器和盘式制动器的结构及优缺点进行分析。
最终确定方案采用液压双回路前盘后鼓式制动器。
除此之外,还介绍了前后制动器、制动主缸的设计计算,主要部件的参数选择及制动管路布置形式等的设计过程。
关键字:制动;鼓式制动器;盘式制动器;液压AbstractIn recent years, the domestic automobile market is growing rapidly, and the car is in the direction of the automotive future development. With the increase of car ownership, however, brought about by a series of security issues attract attention, the car's braking system is one of the vehicle driving is an important active safety systems. Whose performance directly affects the safety of car driving, high-performance braking system research and development, provide protection for safe driving we have to solve the problem. In addition, as the auto market competition intensifies, how to shorten the product development cycle, increase productivity, reduce costs, improve market competitiveness has become a key to business success.This manual is car braking system design. First introduced the development of automotive braking systems, structure, classification, and to analyze the structure and the advantages and disadvantages of drum brakes and disc brakes. Finalized program Qianpanhougu brake hydraulic double-loop. In addition, the front and rear brakes, brake master cylinder design calculations, the major components of the parameter selection and arrangement of the brake pipe of the design process.Key words: braking; brake drum; brake disc; hydroid pressure目录第1章绪论 (5)1.1 制动系统设计的意义 (5)1.2 制动系统研究现状 (5)1.3 本次制动系统应达到的目标 (6)1.4 本次制动系统设计要求 (6)第2章制动系统方案论证分析与选择 (7)2.1 制动器形式方案分析 (7)2.1.1 鼓式制动器 (7)2.1.2 盘式制动器 (10)2.2 制动驱动机构的结构形式选择 (11)2.2.1 简单制动系 (11)2.2.2 动力制动系 (12)2.2.3 伺服制动系 (14)2.3 液压分路系统的形式的选择 (14)2.3.1 II型回路 (15)2.3.2 X型回路 (15)2.3.3 其他类型回路 (15)2.4 液压制动主缸的设计方案 (16)第3章制动系统设计计算 (18)3.1 制动系统主要参数数值 (18)3.1.1 相关主要技术参数 (18)3.1.2 同步附着系数的分析 (19)3.2 制动器有关计算 (20)3.2.1 确定前后轴制动力矩分配系数β (20)3.2.2 制动器制动力矩的确定 (20)3.2.3 后轮制动器的结构参数与摩擦系数的选取 (21)3.2.4 前轮盘式制动器主要参数确定 (22)3.3 制动器制动因数计算 (23)3.3.1 前轮盘式制动效能因数 (23)3.3.2 后轮鼓式制动器效能因数 (23)3.4 制动器主要零部件的结构设计 (24)第4章液压制动驱动机构的设计计算 (28)4.1 后轮制动轮缸直径与工作容积的设计计算 (28)4.2 前轮盘式制动器液压驱动机构计算 (29)4.3 制动主缸与工作容积设计计算 (30)4.4 制动踏板力与踏板行程 (31)4.4.1 制动踏板力F (31)p4.4.2 制动踏板工作行程 (32)第5章制动性能分析 (33)5.1 制动性能评价指标 (33)5.2 制动效能 (33)5.3 制动效能的恒定性 (33)5.4 制动时汽车的方向稳定性 (33)5.5 制动器制动力分配曲线分析 (34)5.6 制动距离S (36)5.7 摩擦衬片(衬块)的磨损特性计算 (36)5.8 驻车制动计算 (39)第6章总论 (40)参考文献 (41)第1章绪论1.1制动系统设计的意义汽车是现代交通工具中用得最多,最普遍,也是最方便的交通运输工具。

汽车制动系统的分类
汽车制动系统可以分为机械制动系统和液压制动系统两类。
1.机械制动系统:机械制动系统包括脚踏制动和手刹制动。
脚踏制动是指通过踩踏刹车踏板,使刹车鼓或刹车盘与车轮(轮胎)摩擦,以达到减速或停车的目的;手刹制动是指通过拉手刹拉索,使左右后轮的制动鼓或制动盘与车轮摩擦,以固定车辆的位置。
2.液压制动系统:液压制动系统是目前主流的制动系统。
它包括主油缸、刹车油管、制动器和刹车片等部件。
踏下刹车踏板时,主油缸内的刹车油被压力推动流入刹车油管,再通过油管流入各个制动器,使制动器的刹车片与刹车盘或刹车鼓摩擦,从而使车辆减速或停车。
液压制动系统的优点在于刹车力度分配均匀,制动距离短,刹车稳定性高。



中国矿业大学China University of Mining and Technology科研训练题目:客车制动系统学院: 机电工程学院专业: 机械设计班级: 机自09-1班姓名: 翟宇佳学号: 03090895指导老师杨金勇老师一、汽车制动系统简介汽车制动系是用于使行驶中的汽车减速或停车,使下坡行驶的汽车的车速保持稳定以及使已停驶的汽车在原地(包括在斜坡上)驻留不动的机构。
汽车制动系直接影响着汽车行驶的安全性和停车的可靠性。
随着高速公路的迅速发展和车速的提高以及车流密度的日益增大,为了保证行车安全,停车可靠,汽车制动系的工作可靠性显得日益重要。
也只有制动性能良好,制动系工作可靠的汽车,才能充分发挥其动力性能。
汽车制动系至少应有行车制动装置和驻车制动装置。
行车制动装置用于使行驶中的汽车强制减速或停车,并使汽车在下段坡时保持适当的稳定车速。
驻车制动装置用于使汽车可靠而无时间限制地停住在一定位置甚至在斜坡上,它也有助于汽车在坡路上起步。
二、汽车制动系统的组成任何制动系统都有以下四个基本组成部分:1)功能装置:包括供给调节制动所需能量以及改善传能介质状态的各种零件,其中生产制动能量的部分称为制动能源。
2)控制装置:包括产生制动动作和控制动作和效果的各种部件,制动踏板机构即是最简单的一种控制装置。
3)传动装置:包括将制动能量传输到制动器的各个部件。
如制动主缸和制动轮缸。
4)制动器:产生阻碍车辆运动或运动趋势的力的部件,其中也包括辅助制动系中的缓速装置。
较为完善的制动系统还具有制动力调节装置,压力保护装置等。
三、汽车制动系统的类型1)按制动系统的功用分类(1)行车制动系统——使行驶中的汽车减低速度甚至停车的一套专门装置。
(2)驻车制动系统——使已停驶的汽车驻留原地不动的一套装置。
(3)第二制动系统——在行车制动系统失效的情况下保证汽车仍能实现减速或停车的一套装置。
(4)辅助制动系统——在汽车下长坡时用以稳定车速的一套装置。


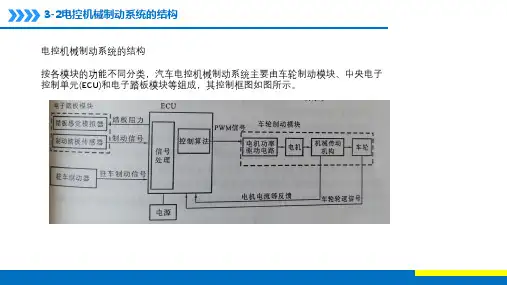
汽车电子机械制动系统的分析摘要:随着我国城市规模的不断扩大,交通行业作为人们日常出行的基本保障,成为了基础建设的重要组成部分。
我国乃至是世界范围内的汽车行业越来越多地受到了科学技术发展的影响。
另一个方面科学技术的发展在很大程度上带动了汽车行业的进一步繁荣。
电子机械制动系统是汽车中不可或缺的一个重要控制系统,该系统的性能稳定与否直接关系到车辆的运行安全性。
为此,在对该系统进行设计时,应当充分考虑车辆的安全运行需要,同时还要保证系统自身运行的可靠性。
关键词:汽车;电子机械;制动系统引言近几年,人们在线控技术上提出的要求越来越高,产生这种情况的原因主要是因为人们对于汽车安全上的需求。
当前线控技术和以往所使用的技术比较起来存在很大的差异,但是其自身具备的优势也有很多,其中比较明显的优势就是在电子机械制动技术在汽车上的使用。
首先,线控技术主要是运用电子制动踏板技术去提到以往使用的液压制动踏板系统,同时在使用线控技术的同时还避免了真空助力器的使用,这样的一种情况将以往汽车在制动过程中踏板经常会产生的抖动问题给予了很好的解决,也正是因为这样使得汽车制动的舒适性获得了快速合理的提高,这样的情况也令发动机在出现负载的时候其自身能够降低损耗率。
可以说这种线控技术的使用使得汽车整体的布置更加的简化,同时也在设置上也更加的趋于合理性,出了合理之外还符合当前国家对于汽车行业所提出的环保要求,避免了制动液对于当前环境造成的污染,降低了系统当前所需要负担成本。
1电子机械制动系统特点电子机械系统基于电子设备的控制功能,具有明显的优势。
首先,该系统中将电线作为管线连接,在传统制动系统上进行了优化,制动系统主要由电子元件构成,传统的管道、元件等,均更换为电子,其反应速度更强,安装起来也方便。
其次,电子机械制动系统具有环保特点,系统中无需应用制动液,但制动系统的摩擦减少,对元件的损坏也减少,系统的应用寿命更长,不易受到损坏。
最后,基于制动系统的完善应用,在设计中将数据系统与制动系统相连接,通过软件对制动系统进行控制,通过自动巡航系统的安装与应用,可实现系统的自动制动,保障汽车运行的安全性。

机械刹车原理
机械刹车原理是通过应用机械力将运动物体的动能转化成热能,从而使其减速或停止。
这种刹车机制通常由刹车盘、刹车盖、刹车片、刹车钳、弹簧和刹车操纵系统等多个部件组成。
工作原理是当驾驶员踩下刹车踏板时,刹车操纵系统会通过连杆等机构将机械力传递给刹车钳。
刹车钳内装有运动自由的活塞,当机械力传递到刹车钳上时,活塞会受力向刹车片施加压力。
刹车片由摩擦材料制成,通常是耐磨性能较好的金属或有机复合材料。
当刹车片受到压力时,它会与刹车盘接触并摩擦,从而产生摩擦力。
摩擦力的作用下,运动物体的动能会转化成热能,同时减速或停止。
为了保证刹车的效果和安全,机械刹车还需要一定的辅助部件。
其中,刹车盖用于保护刹车片和刹车盘免受外界物体的损害,同时也起到保护刹车系统润滑油的作用。
弹簧则常用于使刹车片在不施加力的情况下与刹车盘保持一定间隙,以避免摩擦带来的不必要的磨损。
刹车操纵系统则通过连杆等机构将驾驶员的操作转化为机械力,并传递给刹车钳。
总之,机械刹车原理是通过刹车片与刹车盘之间的摩擦力将机动物体的动能转化成热能,从而实现减速或停止的作用。
不同的车辆和机械设备在刹车原理上可能会有细微的差异,但基本的工作原理都是类似的。

汽车制动器的应用现状及发展趋势汽车制动器,这个小小的部件在我们的生活中扮演着举足轻重的角色。
它就像是我们驾驶汽车时的“刹车”,一旦出现问题,就会让我们的出行变得岌岌可危。
那么,汽车制动器的应用现状及发展趋势又是怎样的呢?接下来,就让我来给大家揭开这个神秘的面纱吧!我们来看看汽车制动器的应用现状。
随着科技的发展,汽车制动器已经从最初的机械式制动器逐渐发展到了电子式制动器。
现在的汽车制动器不仅能够提供强大的制动力,还具有很好的稳定性和可靠性。
而且,一些高端车型还配备了智能制动系统,可以根据路况自动调整制动力度,提高行车安全。
尽管汽车制动器的技术已经取得了很大的进步,但仍然存在一些问题。
比如,一些车主在使用过程中可能会发现制动器反应迟钝,需要很长时间才能停车。
这主要是由于制动器的摩擦片磨损严重导致的。
另外,有些车主在行驶过程中可能会遇到制动器失灵的情况,这时就需要紧急刹车,否则后果不堪设想。
这主要是因为制动器的液压系统出现故障所致。
那么,面对这些问题,汽车制动器的未来发展趋势又是怎样的呢?我认为,未来的汽车制动器将会朝着以下几个方向发展:1. 智能化:随着人工智能技术的不断发展,未来的汽车制动器将会具备更高的智能化水平。
例如,通过传感器实时监测车辆的速度、距离等信息,自动调整制动力度,提高行车安全。
还可以利用大数据技术分析驾驶员的驾驶习惯,为他们提供更加个性化的驾驶建议。
2. 环保化:随着全球气候变暖和环境污染问题日益严重,未来的汽车制动器将会更加注重环保性能。
例如,采用新型的制动材料,减少对环境的污染;或者研发电动制动系统,减少对化石能源的依赖。
3. 轻量化:为了提高汽车的燃油经济性和操控性能,未来的汽车制动器将会朝着轻量化的方向发展。
例如,采用新型的复合材料制作制动盘和刹车片,减轻重量;或者研发无需使用润滑油的磁悬浮制动系统,进一步降低摩擦损失。
4. 舒适化:为了让驾驶者在行驶过程中享受到更加舒适的体验,未来的汽车制动器将会注重人性化设计。
简述汽车制动原理
汽车制动原理是指通过产生摩擦阻力来减慢或停止车辆的运动。
在汽车制动系统中,主要涉及到的部件有制动盘、制动片、制动液、制动缸和制动踏板等。
汽车制动系统一般采用的是液压制动系统,即通过制动踏板的踩踏来产生液压力,将液压力传递给制动缸,再由制动缸传递给制动盘和制动片,从而实现制动效果。
当车辆需要制动时,驾驶员踩下制动踏板,将压力传递给主缸。
主缸中的制动液受到压力作用,将液压力传递到制动盘和制动片。
制动盘和制动片紧贴在一起,并产生摩擦力,阻止车辆的运动。
制动片通常是由摩擦材料制成,例如铸铁或陶瓷。
当制动片与制动盘接触时,摩擦会产生热量,这会导致制动片和制动盘的温度升高。
为了防止制动片过热造成损坏,汽车制动系统通常会通过通风孔或冷却系统来散热。
汽车制动系统还包括制动力分配系统,用于平衡车轮间的制动力分配,以确保车辆在制动时保持稳定。
制动系统还可能包括防抱死系统(ABS)和刹车辅助系统,用于提高制动效果和安全性能。
总的来说,汽车制动原理是通过利用摩擦力来减慢或停止车辆运动的一种技术。
通过制动盘、制动片、制动液、制动缸和制
动踏板等部件的相互配合,汽车制动系统可以提供良好的制动效果,并确保车辆在制动时的安全性能。
机械制动系统的制动力分析机械制动系统是一种常见的汽车制动系统,对于确保行车安全至关重要。
在当前科技发展迅猛的时代,电子和液压制动系统几乎代替了机械制动系统,但机械制动系统仍然广泛应用于一些特定领域,如古董车和自行车。
本文将对机械制动系统的制动力进行分析。
制动力是制动系统用于减速或停止运动物体的能力。
机械制动系统的制动力主要由摩擦力和传动比例两个因素决定。
首先,我们来看摩擦力对机械制动系统制动力的影响。
摩擦力是指两个物体之间相对移动时阻碍其运动的力。
在车辆制动中,摩擦力可以通过摩擦片与制动盘或制动鼓之间的接触来产生。
摩擦力的大小取决于接触面积、材料的摩擦系数以及所施加的力的大小。
接触面积越大,摩擦力越大;摩擦系数越大,摩擦力越大;施加的力越大,摩擦力也越大。
其次,传动比例对机械制动系统制动力的影响同样重要。
传动比例是指通过杠杆或其他机械装置将传动力转化为制动力的比例关系。
传动比例可以通过调整制动装置的设计来改变。
较大的传动比例意味着较小的输入力就能产生较大的制动力,而较小的传动比例则需要较大的输入力才能产生相同的制动力。
除了以上两个主要因素,还有一些其他因素也会影响机械制动系统的制动力。
摩擦片的磨损程度是一个重要因素,摩擦片磨损后与制动盘或制动鼓之间的接触面积减小,从而降低了制动力。
此外,制动系统的温度也会影响制动力。
当摩擦部件过热时,摩擦片与制动盘或制动鼓之间的摩擦系数会降低,从而减小了制动力。
总的来说,机械制动系统的制动力主要由摩擦力和传动比例决定。
通过调整接触面积、摩擦系数和施加的力,可以改变制动力的大小。
此外,摩擦片的磨损程度和制动系统的温度也会对制动力产生影响。
尽管机械制动系统在现代汽车中的应用越来越少,但在特定的领域中仍然具有重要的地位。
在古董车、老式自行车等古老的交通工具中,机械制动系统仍然是它们的制动方式。
研究和分析机械制动系统的制动力,不仅有助于改进和优化传统交通工具的制动性能,还有利于理解现代制动系统的原理和技术。
制动系统方案1. 引言制动系统是一辆汽车中非常重要的组成部分,它能够将汽车减速或停下来,确保驾驶员和乘客的安全。
本文档将介绍一个制动系统方案,包括其工作原理、主要组成部分以及相关的安全性和性能要求。
希望通过本文档,读者能够对制动系统有更深入的了解。
2. 工作原理制动系统的工作原理是通过利用摩擦力将车轮减速或停止。
当驾驶员踩下制动踏板时,制动系统将会传导驱动力到车轮上,使之减速。
制动系统通常分为两大类:机械制动和液压制动。
机械制动通过连接杠杆和线缆来传递力量,实现制动。
而液压制动则通过液压道路传递液体来完成制动。
3. 主要组成部分一个典型的制动系统包含以下几个主要组成部分:3.1 制动踏板制动踏板是驾驶员用于控制制动系统的部件。
驾驶员通过踩下制动踏板来施加制动力。
制动盘是固定在车轮上的金属盘。
当制动系统施加力量时,制动盘会与刹车片产生摩擦,减速车轮。
3.3 刹车片刹车片是制动系统中与制动盘接触的部件。
它们通常由耐磨材料制成,以便能够承受高温和摩擦力。
3.4 制动液制动液是液压制动系统中的介质。
它通过制动主缸和制动器之间的管道来传递力量。
制动液具有一定的粘度和耐高温性能,以确保制动系统正常运作。
3.5 制动主缸制动主缸是液压制动系统中的关键部件。
当驾驶员踩下制动踏板时,制动主缸会产生压力,将制动液推送到各个制动器中,实现制动效果。
3.6 制动器制动器是与车轮直接接触的部件,通过施加摩擦力将车轮减速或停止。
常见的制动器包括盘式刹车和鼓式刹车。
4. 安全性和性能要求制动系统是车辆上至关重要的系统之一,因此安全性和性能要求非常高。
以下是一些常见的安全性和性能要求:制动系统需要提供足够的制动力,以确保车辆能在短时间内减速或停下来,以避免碰撞。
制动力的大小通常取决于制动盘和刹车片的设计和材质。
4.2 反应时间制动系统需要快速响应驾驶员的踩踏操作,立即施加制动力。
因此,制动系统的设计和液压传动系统需要具有良好的灵敏性和机械传递效率。
行车制动系名词解释行车制动系统的意思就是:1、制动系统是使汽车的行驶速度可以强制降低的一系列专门装置;2、制动系统主要由供能装置、控制装置、传动装置和制动器4部分组成;3、制动系统的主要功用是使行驶中的汽车减速甚至停车、使下坡行驶的汽车速度保持稳定、使已停驶的汽车保持不动;发动机制动,是指通过发动机进行牵制车辆的速度,这点在下长坡时最有效。
驻车制动,也就是手刹或者自动挡中的停车挡,锁住传动轴或者后轮。
行车制动,指脚刹(脚制动)。
汽车制动系统就是通过一系列驱动机构施加到车轮制动盘或者制动鼓上的压力,达到使车轮减速和车辆停下来的目的,另外还有驻车机构目的是让车辆在停驶的时候保持原位置不动的机构。
就等于是刹车。
机械工程名词行车制动系(service braking system)是2013年公布的机械工程名词。
使行驶中的拖拉机平稳减速或停驶的制动系统。
行车制动系统使汽车的行驶速度可以强制降低的一系列专门装置。
制动系统主要由供能装置、控制装置、传动装置和制动器4部分组成。
制动系统的主要功用是使行驶中的汽车减速甚至停车、使下坡行驶的汽车速度保持稳定、使已停驶的汽车保持不动。
制动系统的功用分类如下:1、行车制动系——是由驾驶员用脚来操纵的,故又称脚制动系。
它的功用是使正在行驶中的汽车减速或在最短的距离内停车;2、驻车制动系——是由驾驶员用手来操纵的,故又称手制动系。
它的功用是使已经停在各种路面上的汽车驻留原地不动;3、第二制动系——在行车制动系失效的情况下,保证汽车仍能实现减速或停车的一套装置。
在许多国家的制动法规中规定,第二制动系也是汽车必须具备的;4、辅助制动系——经常在山区行驶的汽车以及某些特殊用途的汽车,为了提高行车的安全性和减轻行车制动系性能的衰退及制动器的磨损,用以在下坡时稳定车速。
行车制动系统是使汽车的行驶速度可以强制降低的一系列专门装置,简单的说就是踩刹车:1、制动系统主要由供能装置、控制装置、传动装置和制动器4部分组成;2、制动系统的主要功用是使行驶中的汽车减速甚至停车、使下坡行驶的汽车速度保持稳定、使已停驶的汽车保持不动;3、在行车过程中,一般都采用行车制动(脚刹),便于在前进的过程中减速停车;4、不单是使汽车保持不动。
Automobile Brake SystemThe braking system is the most important system in cars. If the brakes fail, the result can be disastrous. Brakes are actually energy conversion devices, which convert the kinetic energy (momentum) of the vehicle into thermal energy (heat).When stepping on the brakes, the driver commands a stopping force ten times as powerful as the force that puts the car in motion. The braking system can exert thousands of pounds of pressure on each of the four brakes.Two complete independent braking systems are used on the car. They are the service brake and the parking brake.The service brake acts to slow, stop, or hold the vehicle during normal driving. They are foot-operated by the driver depressing and releasing the brake pedal. The primary purpose of the brake is to hold the vehicle stationary while it is unattended. The parking brake is mechanically operated by when a separate parking brake foot pedalor hand lever is set.The brake system is composed of the following basic components: the “master cylinder” which is located under the hood, and is directly connected to the brake pedal, converts driver foot’s mechanical pressure into hydraulic pressure. Steel “brake lines” and flexible “brake hoses” connect the master cylinder to the “slave cylinders” located at each wheel. Brake fluid, specially designed to work in extreme conditions, fills the system. “Shoes” and “pads” are pushed by the slave cylinders to contact the “drums” and “rotors” thus causing drag, which (hopefully) slows the car.The typical brake system consists of disk brakes in front and either disk or drum brakes in the rear connected by a system of tubes and hoses that link the brake at each wheel to the master cylinder (Figure).Basically, all car brakes are friction brakes. When the driver applies the brake, the control device forces brake shoes, or pads, against the rotating brake drum or disks at wheel. Friction between the shoes or pads and the drums or disks then slows or stops the wheel so that the car is braked.In most modern brake systems (see Figure 15.1), there is a fluid-filled cylinder, called master cylinder, which contains two separate sections, there is a piston in each section and both pistons are connected to a brake pedal in the driver’s compartment. When the brake is pushed down, brake fluid is sent from the master cylinder to the wheels.At the wheels, the fluid pushes shoes, or pads, against revolving drums or disks. The friction between the stationary shoes, or pads, and the revolving drums or disks slows and stops them. This slows or stops the revolving wheels, which, in turn, slow or stop the car.The brake fluid reservoir is on top of the master cylinder. Most cars today have a transparent r reservoir so that you can see the level without opening the cover. The brake fluid level will drop slightly as the brake pads wear. This is a normal condition and no cause for concern. If the level drops noticeably over ashort period of time or goes down to about two thirds full, have your brakes checked as soon as possible. Keep the reservoir covered except for the amount of time you need to fill it and never leave a cam of brake fluid uncovered. Brake fluid must maintain a very high boiling point. Exposure to air will cause the fluid to absorb moisture which will lower that boiling point.The brake fluid travels from the master cylinder to the wheels through a series of steel tubes and reinforced rubber hoses. Rubber hoses are only used in places that require flexibility, such as at the front wheels, which move up and down as well as steer. The rest of the system uses non-corrosive seamless steel tubing with special fittings at all attachment points. If a steel line requires a repair, the best procedure is to replace the compete line. If this is not practical, a line can be repaired using special splice fittings that are made for brake system repair. You must never use copper tubing to repair a brake system. They are dangerous and illegal.Drum brakes, it consists of the brake drum, an expander, pull back springs, a stationary back plate, two shoes with friction linings, and anchor pins. The stationary back plate is secured to the flange of the axle housing or to the steering knuckle. The brake drum is mounted on the wheel hub. There is a clearance between the inner surface of the drum and the shoe lining. To apply brakes, the driver pushes pedal, the expander expands the shoes and presses them to the drum. Friction between the brake drum and the friction linings brakes the wheels and the vehicle stops. To releasebrakes, the driver release the pedal, the pull back spring retracts the shoes thus permitting free rotation of the wheels.Disk brakes, it has a metal disk instead of a drum. A flat shoe, or disk-brake pad, is located on each side of the disk. The shoes squeeze the rotatin g disk to stop the car. Fluid from the master cylinder forces the pistons to move in, toward the disk. This action pushes the friction pads tightly against the disk. The friction between the shoes and disk slows and stops it. This provides the braking action. Pistons are made of either plastic or metal. There are three general types of disk brakes. They are the floating-caliper type, the fixed-caliper type, and the sliding-caliper type. Floating-caliper and sliding-caliper disk brakes use a single piston. Fixed-caliper disk brakes have either two or four pistons.The brake system assemblies are actuated by mechanical, hydraulic or pneumatic devices. The mechanical leverage is used in the parking brakes fitted in all automobile. When the brake pedal is depressed, the rod pushes the piston of brake master cylinder which presses the fluid. The fluid flows through the pipelines to the power brake unit and then to the wheel cylinder. The fluid pressure expands the cylinder pistons thus pressing the shoes to the drum or disk. If the pedal is released, the piston returns to the initialposition, the pull back springs retract the shoes, the fluid is forced back to the master cylinder and braking ceases.The primary purpose of the parking brake is to hold the vehicle stationary while it is unattended. The parking brake is mechanically operated by the driver when a separate parking braking hand lever is set. The hand brake is normally used when the car has already stopped. A lever is pulled and the rear brakes are approached and locked in the “on” position. The car may now be left without fear of its rolling away. When the driver wants to move the car again, he must press a button before the lever can be released. The hand brake must also be able to stop the car in the event of the foot brake failing. For this reason, it is separate from the foot brake uses cable or rods instead of the hydraulic system.Anti-lock Brake SystemAnti-lock brake systems make braking safer and more convenient, Anti-lock brake systems modulate brake system hydraulic pressure to prevent the brakes from locking and the tires from skidding on slippery pavement or during a panic stop.Anti-lock brake systems have been used on aircraft for years, and some domestic car were offered with an early form of anti-lock braking in late 1990’s. Recently, several automakers have introduced more sophisticated anti-lock system. Investigations in Europe, where anti-lock brakin g systems have been available for a decade, have led one manufacture to state that the number of traffic accidents could be reduced by seven and a half percent if all cars had anti-lock brakes. So some sources predict that all cars will offer anti-lock brakes to improve the safety of the car.Anti-lock systems modulate brake application force several times per second to hold the tires at a controlled amount of slip。