公司理财第二章
- 格式:doc
- 大小:213.00 KB
- 文档页数:9



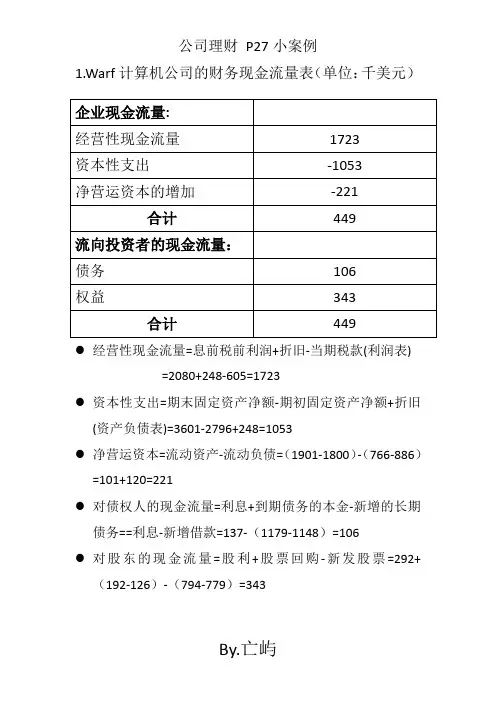
1.Warf计算机公司的财务现金流量表(单位:千美元)●经营性现金流量=息前税前利润+折旧-当期税款(利润表)=2080+248-605=1723●资本性支出=期末固定资产净额-期初固定资产净额+折旧(资产负债表)=3601-2796+248=1053●净营运资本=流动资产-流动负债=(1901-1800)-(766-886)=101+120=221●对债权人的现金流量=利息+到期债务的本金-新增的长期债务==利息-新增借款=137-(1179-1148)=106●对股东的现金流量=股利+股票回购-新发股票=292+(192-126)-(794-779)=343Warf计算机公司的会计现金流量表(单位:千美元)●经营活动产生的现金流量=净利润+折旧+递延税款+应收账款的变动+存货的变动+应付账款的变动+应计费用的变动+其他的变动=1167+248+171-(716-668)-(641-663)+(519-485)+(247-401)-(92-78)=1167+248+171-48+22+34-154-14=1426●投资活动产生的现金流量=长期资产原值的变动=429-1482=-1053●筹资活动产生的现金流量=长期债务变动+应付票据的变动-股票回购+发行新股-股利支付=(228-197)+0-66+15-292=-3122.哪一种现金流量表更准确的反映了公司的现金流量?●财务现金流量表。
●财务现金流量表上半部分包括三个部分的内容即经营活动产生的现金流量、资本性支出产生的现金流量与经营运资本增加产生的现金流量,它比较清楚的描述了公司经营活动的效果;●下半部分反映了企业现金流量的流向即现金主要流向了企业股东与债权者,可以反映出企业经营带给投资者的现金流,反映了企业的偿债能力和经营能力。
3.依据对前述问题的回答,对尼克的扩张计划作出评论。
●依据公司的财务现金流量,尼克的扩张计划是可行的●因为公司目前经营活动产生现金流的能力是很强的达到1723千美元,带给债权人和股权投资者的现金流量是106和343千美元,它的偿债能力和经营能力很强●因此可以通过证券市场进行权益性投资和银行的债务投资进行扩张。




第一章导论1. 公司目标:为所有者创造价值公司价值在于其产生现金流能力。
2. 财务管理的目标:最大化现有股票的每股现值。
3. 公司理财可以看做对一下几个问题进行研究:1. 资本预算:公司应该投资什么样的长期资产。
2. 资本结构:公司如何筹集所需要的资金。
3. 净运营资本管理:如何管理短期经营活动产生的现金流。
4. 公司制度的优点:有限责任,易于转让所有权,永续经营。
缺点:公司税对股东的双重课税。
第二章会计报表与现金流量资产 = 负债 + 所有者权益(非现金项目有折旧、递延税款)EBIT(经营性净利润) = 净销售额 - 产品成本 - 折旧EBITDA = EBIT + 折旧及摊销现金流量总额CF(A) = 经营性现金流量 - 资本性支出 - 净运营资本增加额 = CF(B) + CF(S)经营性现金流量OCF = 息税前利润 + 折旧 - 税资本性输出 = 固定资产增加额 + 折旧净运营资本 = 流动资产 - 流动负债第三章财务报表分析与财务模型1. 短期偿债能力指标(流动性指标)流动比率 = 流动资产/流动负债(一般情况大于一)速动比率 = (流动资产 - 存货)/流动负债(酸性实验比率)现金比率 = 现金/流动负债流动性比率是短期债权人关心的,越高越好;但对公司而言,高流动性比率意味着流动性好,或者现金等短期资产运用效率低下。
对于一家拥有强大借款能力的公司,看似较低的流动性比率可能并非坏的信号2. 长期偿债能力指标(财务杠杆指标)负债比率 = (总资产 - 总权益)/总资产 or (长期负债 + 流动负债)/总资产权益乘数 = 总资产/总权益 = 1 + 负债权益比利息倍数 = EBIT/利息现金对利息的保障倍数(Cash coverage radio) = EBITDA/利息3. 资产管理或资金周转指标存货周转率 = 产品销售成本/存货存货周转天数= 365天/存货周转率应收账款周转率 = (赊)销售额/应收账款总资产周转率 = 销售额/总资产 = 1/资本密集度4. 盈利性指标销售利润率 = 净利润/销售额资产收益率ROA = 净利润/总资产权益收益率ROE = 净利润/总权益5. 市场价值度量指标市盈率 = 每股价格/每股收益EPS 其中EPS = 净利润/发行股票数市值面值比 = 每股市场价值/每股账面价值企业价值EV = 公司市值 + 有息负债市值 - 现金EV乘数 = EV/EBITDA6. 杜邦恒等式ROE = 销售利润率(经营效率)x总资产周转率(资产运用效率)x权益乘数(财杠)ROA = 销售利润率x总资产周转率7. 销售百分比法假设项目随销售额变动而成比例变动,目的在于提出一个生成预测财务报表的快速实用方法。



第2章会计报表与现金流1.是非题:所有的资产在付出某种代价的情况下都具有流动性。
请解释。
答:正确。
所有资产都可以以某种价格转换为现金。
然而,当我们提到流动性资产的时候,一个附加的假设变得很重要,这个假设是资产可以以市场价值或接近市场价值的价格转换成现金。
2.为什么标准的利润表上列示的收入和成本不代表当期实际的现金流入和现金流出?答:财务会计里面的确认原则和匹配原则要求将收入和产生收入相关的费用在收入过程实际完成的时候就记录下来,而不必等到收到现金或支付账单的时候。
我们要注意到这种方式并不必然是正确的,主要取决于会计师的选择。
3.在会计现金流量表上,最后一栏表示什么?这个数字对于分析一家公司有何用处?答:最后一栏的数据显示了资产负债表上现金余额的变化。
既然如此,它对于分析一个公司来说并不是一个有用的数据。
4.财务现金流量表与会计现金流量表有何不同?哪个对于公司分析者更有用?答:主要的不同在于对利息费用的处理,会计现金流量表将利息视为经营现金流,而财务现金流量将其视为融资现金流。
会计现金流量的逻辑是,既然利息列支在利润表上,而利润表显示的是一定时期企业的经营状况,因此利息也就是经营性的现金流。
而事实上,利息是一种融资费用,是公司选择债务融资还是股权融资的结果,我们将在以后的章节中有更为详细的讲解。
相比两种现金流量表,财务现金流量表以其正确对待利息费用而成为分析公司业绩的更恰当的方法。
5.按照会计规定,一家公司的负债有可能超过资产,所有者权益为负,这种情况在市场价值上有没有可能发生?为什么?答:市场的价值不可能为负。
假设有一股股票,价格为负的20美元,这意味着如果你买入100股,你不仅得到了股票,而且还得到了一1200美元的现金支票,那么你会想买入多少股呢?更一般的情形是,根据公司破产和个人破产法,个人或公司的净资产不能为负,这意味着从市场价值的角度看,负债不可能超过资产。
6.为什么说在一个特定的期间资产的现金流量为负不一定不好?答:例如,对于一个正在迅速扩的成功企业来说,它的资本性支出将会很大,这可能会导致出现负的现金流。
1. The financial statement showing a firm's accounting value on a particular date is the:A. income statement.B.balance sheet.资产负债表反应公司在某一特定日期的账面价值C. statement of cash flows.D. tax reconciliation statement.E. shareholders' equity sheet.2. A current asset is:A. an item currently owned by the firm.B. an item that the firm expects to own within the next year.C. an item currently owned by the firm that will convert to cash within the next 12 months.在一年内能够变现的资产D. the amount of cash on hand the firm currently shows on its balance sheet.E. the market value of all items currently owned by the firm.3. The long-term debts of a firm are liabilities:A. that come due within the next 12 months.B.that do not come due for at least 12 months.偿还期限在一年以上C. owed to the firm's suppliers.D. owed to the firm's shareholders.E. the firm expects to incur within the next 12 months.4. Net working capital is defined as: 经营运资本A. total liabilities minus shareholders' equity.B. current liabilities minus shareholders' equity.C. fixed assets minus long-term liabilities.D. total assets minus total liabilities.E.current assets minus current liabilities.流动资产-流动负债5. A(n) ____ asset is one which can be quickly converted into cash without significant loss in value.A. currentB. fixedC. intangibleD. liquid速动资产E. long-term6. The financial statement summarizing a firm's accounting performance over a period of time is the:A. income statement.利润表反应公司一段时间内的经营成果B. balance sheet.C. statement of cash flows.D. tax reconciliation statement.E. shareholders' equity sheet. 7. Noncash items refer to: 非现金项目A. the credit sales of a firm.B. the accounts payable of a firm.C. the costs incurred for the purchase of intangible fixed assets.D. expenses charged against revenues that do not directly affect cash flow.与收入像配比的费用,并不影响现金流量E. all accounts on the balance sheet other than cash on hand.8. Your _____ tax rate is the amount of tax payable on the next taxable dollar you earn.A. deductibleB. residualC. totalD. averageE. marginal边际税率指多赚一美元需要多支付的税金9. Your _____ tax rate is the total taxes you pay divided by your taxable income.A. deductibleB. residualC. totalD.average平均税率E. marginal10. _____ refers to the cash flow that results from the firm's ongoing, normal business activities.A.Cash flow from operating activities经营活动现金流B. Capital spendingC. Net working capitalD. Cash flow from assetsE. Cash flow to creditors11. _____ refers to the changes in net capital assets.A. Operating cash flowB. Cash flow from investing投资活动产生的现金流C. Net working capitalD. Cash flow from assetsE. Cash flow to creditors12. _____ refers to the difference between a firm's current assets and its current liabilities.A. Operating cash flowB. Capital spending working capital净营运资本是流动资产与流动负债之差D. Cash flow from assetsE. Cash flow to creditors13. _____ is calculated by adding back noncash expenses to net income and adjusting for changes in current assets and liabilities. 非现金费用加净利润,根据流动资产和流动负债的变化做出调整A. Operating cash flowB. Capital spendingC. Net working capitalD.Cash flow from operation s经营活动产生的现金流E. Cash flow to creditors14. _____ refers to the firm's interest payments less any net new borrowing.A. Operating cash flowB. Capital spendingC. Net working capitalD. Cash flow from shareholdersE.Cash flow to creditors向债权人支付的现金流=支付的利息—净新借入额15. _____ refers to the firm's dividend payments less any net new equity raised.A. Operating cash flowB. Capital spendingC. Net working capitalD. Cash flow from creditorsE.Cash flow to stockholder s向股东支付的现金流=支付的股利—权益筹资净额16. Earnings per share is equal to: 每股收益A. net income divided by the total number of shares outstanding.净利润/流通在外的股数B. net income divided by the par value of the common stock.C. gross income multiplied by the par value of the common stock.D. operating income divided by the par value of the common stock.E. net income divided by total shareholders' equity.17. Dividends per share is equal to dividends paid: 每股股利A. divided by the par value of common stock.B.divided by the total number of shares outstanding.股利/流通在外的股数C. divided by total shareholders' equity.D. multiplied by the par value of the common stock.E. multiplied by the total number of shares outstanding.18. Which of the following are included in current assets?I. equipment设备II. Inventory存货III. accounts payable应付账款IV. cash 现金A. II and IV onlyB. I and III onlyC. I, II, and IV onlyD. III and IV onlyE. II, III, and IV only 19. Which of the following are included in current liabilities?I. note payable to a supplier in eighteen months应付票据II. debt payable to a mortgage company in nine months短期负债III. accounts payable to suppliers应付账款IV. loan payable to the bank in fourteen months 长期负债A. I and III onlyB. II and III onlyC. III and IV onlyD. II, III, and IV onlyE. I, II, and III only20. An increase in total assets:A. means that net working capital is also increasing.B. requires an investment in fixed assets.C. means that shareholders' equity must also increase.D.must be offset by an equal increase in liabilities and shareholders' equity.总资产的增加必定对应相应负债和所有者权益的增加E. can only occur when a firm has positive net income.21. Which one of the following assets is generally the most liquid?A. inventoryB. buildingsC.accounts receivable应收账款D. equipmentE. patents22. Which one of the following statements concerning liquidity is correct?A. If you sold an asset today, it was a liquid asset.B. If you can sell an asset next year at a price equal to its actual value, the asset is highly liquid.C. Trademarks and patents are highly liquid.D. The less liquidity a firm has, the lower the probability the firm will encounter financial difficulties.E.Balance sheet accounts are listed in order of decreasing liquidity.资产负债表账户是按流动性减弱排序的23. Liquidity is:A. a measure of the use of debt in a firm's capital structure.B. equal to current assets minus current liabilities.C. equal to the market value of a firm's total assets minus its current liabilities.D. v aluable to a firm even though liquid assets tend to be less profitable to own.在不引起价值大幅损失的前提下,资产变现的方便与快捷成度E. generally associated with intangible assets.24. Which of the following accounts are included in shareholders' equity?I. interest paid利息费用II. retained earnings留存收益III. capital surplus资本盈余IV. long-term debt 长期负债A. I and II onlyB. II and IV onlyC. I and IV onlyD. II and III onlyE. I and III only25. Book value: 账面价值A. is equivalent to market value for firms with fixed assets.B. is based on historical cost.基于历史成本C. generally tends to exceed market value when fixed assets are included.D. is more of a financial than an accounting valuation.E. is adjusted to market value whenever the market value exceeds the stated book value.26. When making financial decisions related to assets, you should:A. always consider market values.考虑市场价值B. place more emphasis on book values than on market values.C. rely primarily on the value of assets as shown on the balance sheet.D. place primary emphasis on historical costs.E. only consider market values if they are less than book values.27. As seen on an income statement:A. interest is deducted from income and increases the total taxes incurred.B. the tax rate is applied to the earnings before interest and taxes when the firm has both depreciation and interest expenses.C. depreciation is shown as an expense but does not affect the taxes payable.D. depreciation reduces both the pretax income and the net income.折旧会降低息税前利润和净利润E. interest expense is added to earnings before interest and taxes to get pretax income.28. The earnings per share will:A. increase as net income increases.B. increase as the number of shares outstanding increase.C. decrease as the total revenue of the firm increases.D. increase as the tax rate increases.E. decrease as the costs decrease. 29. Dividends per share: 每股股利A. increase as the net income increases as long as the number of shares outstanding remains constant.B. decrease as the number of shares outstanding decrease, all else constant.C. are inversely related to the earnings per share.D. are based upon the dividend requirements established by Generally Accepted Accounting Procedures.E. are equal to the amount of net income distributed to shareholders divided by the number of shares outstanding.30. Earnings per share 每股收益=净收入/流通在外股数A.will increase if net income increases and number of shares remains constant.不变B. will increase if net income decreases and number of shares remains constant.C. is number of shares divided by net income.D. is the amount of money that goes into retained earnings on a per share basis.E. None of the above.31. According to Generally Accepted Accounting Principles, costs are:A. recorded as incurred.B. recorded when paid.C. matched with revenues.资产应按成本计价D. matched with production levels.E. expensed as management desires.32. Depreciation:A. is a noncash expense that is recorded on the income statement.非现金项目B. increases the net fixed assets as shown on the balance sheet.C. reduces both the net fixed assets and the costs of a firm.D. is a non-cash expense which increases the net operating income.E. decreases net fixed assets, net income, and operating cash flows.33. When you are making a financial decision, the most relevant重要的,有意义的 tax rate is the _____ rate.A. averageB. fixedC. marginal边际税率D. totalE. variable34. An increase in which one of the following will cause the operating cash flow to increase?A. depreciation折旧B. changes in the amount of net fixed capitalC. net working capitalD. taxesE. costs35. A firm starts its year with a positive net working capital. During the year, the firm acquires more short-term debt than it does short-term assets. This means that:A. the ending net working capital will be negative.B. both accounts receivable and inventory decreased during the year.C. the beginning current assets were less than the beginning current liabilities.D. accounts payable increased and inventory decreased during the year.E. the ending net working capital can be positive, negative, or equal to zero.36. The cash flow to creditors includes the cash:A. received by the firm when payments are paid to suppliers.B. outflow of the firm when new debt is acquired.C. outflow when interest is paid on outstanding debt.D. inflow when accounts payable decreases.E. received when long-term debt is paid off.37. Cash flow to stockholders must be positive when:A. the dividends paid exceed(超过) the net new equity raised.B. the net sale of common stock exceeds the amount of dividends paid.C. no income is distributed but new shares of stock are sold.D. both the cash flow to assets and the cash flow to creditors are negative.E. both the cash flow to assets and the cash flow to creditors are positive.38. Which equality is the basis for the balance sheet?A. Fixed Assets = Stockholder's Equity + Current AssetsB. Assets = Liabilities + Stockholder's EquityC. Assets = Current Long-Term Debt + Retained EarningsD. Fixed Assets = Liabilities + Stockholder's EquityE. None of the above39. Assets are listed on the balance sheet in order of:A. decreasing liquidity.流动性减弱B. decreasing size.C. increasing size.D. relative life.E. None of the above. 40. Debt is a contractual obligation(契约责任) that:A. requires the payout of residual flows to the holders of these instruments.B. requires a repayment of a stated amount and interest over the period.支付固定利息C. allows the bondholders to sue the firm if it defaults不履行.当公司不履行债务时债权人可以请求偿还D. Both A and B.E. Both B and C.41. The carrying value or book value of assets:A. is determined under GAAP and is based on the cost of the asset.基于历史成本B. represents the true market value according to GAAP.C. is always the best measure of the company's value to an investor.D. is always higher than the replacement cost of the assets.E. None of the above.42. Under GAAP, a firm's assets are reported at:A. market value.B. liquidation value.C. intrinsic value.D. cost.E. None of the above.43. Which of the following statements concerning the income statement is true?A. It measures performance over a specific period of time.一段时间的经营成果B. It determines after-tax income of the firm.决定公司税后利润C. It includes deferred taxes.递延税D. It treats interest as an expense.把利息视做费用E. All of the above.44. According to generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP), revenue is recognized as income when:A. a contract is signed to perform a service or deliver a good.B. the transaction is complete and the goods or services are delivere d.实现收入C. payment is requested.D. income taxes are paid.E. All of the above.45. Which of the following is not included in the computation 估算 of operating cash flow?A. Earnings before interest and taxesB. Interest paid利息支付C. DepreciationD. Current taxesE. All of the above are included46. Net capital spending is equal to: 资本性支出=固定资产出售-固定资产取得A. net additions to net working capital.B. the net change in fixed assets.C. net income plus depreciation.D. total cash flow to stockholders less interest and dividends paid.E. the change in total assets.47. Cash flow to stockholders is defined as:A. interest payments.B. repurchases of equity less cash dividends paid plus new equity sold.C. cash flow from financing less cash flow to creditors.D. cash dividends plus repurchases of equity minus new equity financing.E. None of the above.48. Free cash flow is: 自由现金流A. without cost to the firm.B. net income plus taxes.C. an increase in net working capital.D. cash that the firm is free to distribute to creditors and stockholders.现金可以自由的分配给债权人和股东E. None of the above.49. The cash flow of the firm must be equal to:A. cash flow to stockholders minus cash flow to debtholders.B. cash flow to debtholders minus cash flow to stockholders.C. cash flow to governments plus cash flow to stockholders.D. cash flow to stockholders plus cash flow to debtholders.E. None of the above.50. Which of the following are all components 组成of the statement of cash flows?A. Cash flow from operating activities, cash flow from investing activities, and cash flow from financing activities经营活动,投资活动,筹资活动B. Cash flow from operating activities, cash flow from investing activities, and cash flow from divesting activitiesC. Cash flow from internal activities, cash flow from external activities, and cash flow from financing activitiesD. Cash flow from brokering activities, cash flow from profitable activities, and cash flow from non-profitable activitiesE. None of the above.51. One of the reasons why cash flow analysis is popular is because:A. cash flows are more subjective than net income.B. cash flows are hard to understand.C. it is easy to manipulate, or spin the cash flows.D. it is difficult to manipulate, or spin the cash flows.现金流很难编造和篡改E. None of the above. 52 A firm has $300 in inventory, $600 in fixed assets, $200 in accounts receivable, $100 in accounts payable, and $50 in cash. What is the amount of the current assets?A. $500B. $550C. $600D. $1,150E. $1,200Current assets = $300 + $200 + $50 = $55053. Total assets are $900, fixed assets are $600, long-term debt is $500, and short-term debt is $200. What is the amount of net working capital?A. $0B. $100C. $200D. $300E. $400Net working capital = $900 - $600 - $200 = $10054. Brad's Company has equipment with a book value of $500 that could be sold today at a 50% discount. Its inventory is valued at $400 and could be sold to a competitor for that amount. The firm has $50 in cash and customers owe it $300. What is the accounting value of its liquid assets?A. $50B. $350C. $700D. $750E. $1,000Liquid assets = $400 + $50 + $300 = $75055. Martha's Enterprises spent $2,400 to purchase equipment three years ago. This equipment is currently valued at $1,800 on today's balance sheet but could actually be sold for $2,000. Net working capital is $200 and long-term debt is $800. Assuming the equipment is the firm's only fixed asset, what is the book value of shareholders' equity?A. $200B. $800C. $1,200D. $1,400E. The answer cannot be determined from the information providedBook value of shareholders' equity = $1,800 + $200 - $800 = $1,20056. Art's Boutique has sales of $640,000 and costs of $480,000. Interest expense is $40,000 and depreciation is $60,000. The tax rate is 34%. What is the net income?A. $20,400B. $39,600C. $50,400D. $79,600E. $99,600Taxable income = $640,000 - $480,000 - $40,000 - $60,000 = $60,000; Tax = .34($60,000) = $20,400; Net income = $60,000 - $20,400 = $39,60057. Given the tax rates as shown, what is the average tax rate for a firm with taxable income of $126,500?A. 21.38%B. 23.88%C.25.76%应纳税额/应税所得D. 34.64%E. 39.00%Tax = .15($50,000) + .25($25,000) + .34($25,000)+ .39($126,500 - $100,000) = $32,585; Average tax rate = $32,585 ÷ $126,500 = .2576 = 25.76%58. The tax rates are as shown. Your firm currently has taxable income of $79,400. How much additional tax will you owe if you increase your taxable income by $21,000?A. $7,004B. $7,014C. $7,140D. $7,160E. $7,174Additional tax = .34($100,000 - $79,400) + .39($79,400 + $21,000 - $100,000) = $7,160 59. Your firm has net income of $198 on total sales of $1,200. Costs are $715 and depreciation is $145. The tax rate is 34%. The firm does not have interest expenses. What is the operating cash flow?A. $93B. $241C. $340D. $383E. $485Earnings before interest and taxes = $1,200 - $715 - $145 = $340; Tax = [$198 ÷ (1 - .34)] - $198 = $102; Operating cash flow = $340 + $145 - $102 = $383经营性现金流=息税前利润-折旧+所得税60. Teddy's Pillows has beginning net fixed assets of $480 and ending net fixed assets of $530. Assets valued at $300 were sold during the year. Depreciation was $40. What is the amount of capital spending?A. $10B. $50C. $90D. $260E. $390Net capital spending = $530 - $480 + $40 = $90资本性支出=期末固定资产净值-期初固定资产净值+折旧61. At the beginning of the year, a firm has current assets of $380 and current liabilities of $210. At the end of the year, the current assets are $410 and the current liabilities are $250. What is the change in net working capital?A. -$30B. -$10C. $0D. $10E. $30Change in net working capital = ($410 - $250) - ($380 - $210) = -$1062. At the beginning of the year, long-term debt of a firm is $280 and total debt is $340. At the end of the year, long-term debt is $260 and total debt is $350. The interest paid is $30. What is the amount of the cash flow to creditors?A. -$50B. -$20C. $20D. $30E. $50Cash flow to creditors = $30 - ($260 - $280) = $5063. Pete's Boats has beginning long-term debt of $180 andending long-term debt of $210. The beginning and ending total debt balances are $340 and $360, respectively. The interest paid is $20. What is the amount of the cash flow to creditors?A. -$10B. $0C. $10D. $40E. $50Cash flow to creditors = $20 - ($210 - $180) = -$1064. Peggy Grey's Cookies has net income of $360. The firm pays out 40% of the net income to its shareholders as dividends. During the year, the company sold $80 worth of common stock. What is the cash flow to stockholders?A. $64B. $136C. $144D. $224E. $296Cash flow to stockholders = .40($360) - $80 = $6465. Thompson's Jet Skis has operating cash flow of $218. Depreciation is $45 and interest paid is $35. A net total of $69 was paid on long-term debt. The firm spent $180 on fixed assets and increased net working capital by $38. What is the amount of the cash flow to stockholders?A. -$104B. -$28C. $28D. $114E. $142Cash flow of the firm = $218 - $38 - $180 = $0; Cash flow to creditors = $35 - (-$69) = $104; Cash flow to stockholders = $0 - $104 = -$10466. What is the change in the net working capital from 2007 to 2008?A. $1,235B. $1,035C. $1,335D. $3,405E. $4,740Change in net working capital = ($7,310 - $2,570) - ($6,225 - $2,820) = $1,33567. What is the amount of the non-cash expenses for 2008?A. $570B. $630C. $845D. $1,370E. $2,000The non-cash expense is depreciation in the amount of $1,370.68. What is the amount of the net capital spending for 2008?A. -$290B. $795C. $1,080D. $1,660E. $2,165Net capital spending = $10,670 - $10,960 + $1,370 = $1,08069. What is the operating cash flow for 2008?A. $845B. $1,930C. $2,215D. $2,845E. $3,060Operating cash flow = $1,930 + $1,370 - $455 = $2,84570. What is the cash flow of the firm for 2008?A. $430B. $485C. $1,340D. $2,590E. $3,100Operating cash flow = $1,930 + $1,370 - $455 = $2,845; Change in net working capital = ($7,310 - $2,570) - ($6,225 - $2,820) = $1,335; Net capital spending = $10,670 - $10,960 + $1,370 = $1,080; Cash flow of the firm = $2,845 - $1,335 - $1,080 = $43071. What is the amount of net new borrowing for 2008?A. -$225B. -$25C. $0D. $25E. $225Net new borrowing = $8,100 - $7,875 = $22572. What is the cash flow to creditors for 2008?A. -$405B. -$225C. $225D. $405E. $630Cash flow to creditors = $630 - ($8,100 - $7,875) = $40573. What is the net working capital for 2008?A. $345B. $405C. $805D. $812E. $1,005 Net working capital = $75 + $502 + $640 - $405 = $812 74. What is the change in net working capital from 2007 to 2008?A. -$93B. -$7C. $7D. $85E. $97Change in net working capital = ($75 + $502 + $640 - $405) - ($70 + $563 + $662 - $390) = -$9375. What is net capital spending for 2008?A. -$250B. -$57C. $0D. $57E. $477Net capital spending = $1,413 - $1,680 + $210 = -$5776. What is the operating cash flow for 2008?A. $143B. $297C. $325D. $353E. $367Earnings before interest and taxes = $785 - $460 - $210 = $115; Taxable income = $115 - $35 = $80; Taxes = .35($80) = $28; Operating cash flow = $115 + $210 - $28 = $29777. What is the cash flow of the firm for 2008?A. $50B. $247C. $297D. $447E. $517Cash flow of the firm = $297 - (-$93) - (-$57) = $447 (See problems 74 and 75)78. What is net new borrowing for 2008?A. -$70B. -$35C. $35D. $70E. $105Net new borrowing = $410 - $340 = $7079. What is the cash flow to creditors for 2008?A. -$170B. -$35C. $135D. $170E. $205Cash flow to creditors = $35 - ($410 - $340) = -$3580. What is the cash flow to stockholders for 2008?A. $408B. $417C. $452D. $482E. $503Cash flow to stockholders = $447 - (-$35) = $482 (See problems 77 and 79); or, Cash flow to stockholders = $17 - ($235 - $700) = $48281. What is the taxable income for 2008?A. $360B. $520C. $640D. $780E. $800Net income = $160 + $360 = $520; Taxable income = $520 (1 - .35) = $80082. What is the operating cash flow for 2008?A. $520B. $800C. $1,015D. $1,110E. $1,390Earnings before interest and taxes = $800 + $215 = $1,015 (See problem 81); Operating cash flow = $1,015 + $375 - ($800 - $520) = $1,110 (See problem 81)83. What are the sales for 2008?A. $4,225B. $4,385C. $4,600D. $4,815E. $5,000Sales = $1,015 + $375 + $3,210 = $4,600 (see problem 82) 84. Calculate net income based on the following information. Sales are $250, cost of goods sold is $160, depreciation expense is $35, interest paid is $20, and the tax rate is 34%.A. $11.90B. $23.10C. $35.00D. $36.30E. $46.20((Sales - COGS) - Depreciation - Interest) - Taxes = Net Income (($250 - $160) - $35 - $20) - $11.9 = $23.10。