英语学习:四种一般时态
- 格式:doc
- 大小:116.50 KB
- 文档页数:11

小学英语四种时态总结英语语法中的时态是非常重要的一部分,正确使用时态可以使语言表达更加准确和清晰。
在小学英语学习阶段,学生们需要掌握四种基本的时态,它们分别是一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时和现在进行时。
下面将对这四种时态进行总结和归纳,希望能够帮助学生们更好地理解和掌握这些时态的用法。
一、一般现在时。
一般现在时表示的是经常性或习惯性的动作,或者是客观事实。
在句子中,一般现在时的动词形式不随主语的变化而变化,即动词用原形。
例如:1. I play football every Sunday.(我每个星期天都踢足球。
)。
2. She likes singing.(她喜欢唱歌。
)。
3. The sun rises in the east.(太阳从东方升起。
)。
二、一般过去时。
一般过去时表示的是发生在过去的动作或状态。
在句子中,一般过去时的动词形式通常是动词的过去式。
例如:1. I watched a movie last night.(昨晚我看了一部电影。
)。
2. They played basketball yesterday.(他们昨天打篮球。
)。
3. She lived in London for ten years.(她在伦敦住了十年。
)。
三、一般将来时。
一般将来时表示将来某个时间要发生的动作或状态。
在句子中,一般将来时通常使用助动词“will”或“shall”加上动词的原形。
例如:1. I will go to the park tomorrow.(我明天要去公园。
)。
2. She shall visit her grandparents next week.(她下周要去看望她的祖父母。
)。
3. We will have a party on Friday.(我们星期五要举办派对。
)。
四、现在进行时。
现在进行时表示现在正在进行的动作,或者是现阶段正在发生的动作。
在句子中,现在进行时的动词形式是“be”动词的现在分词形式。
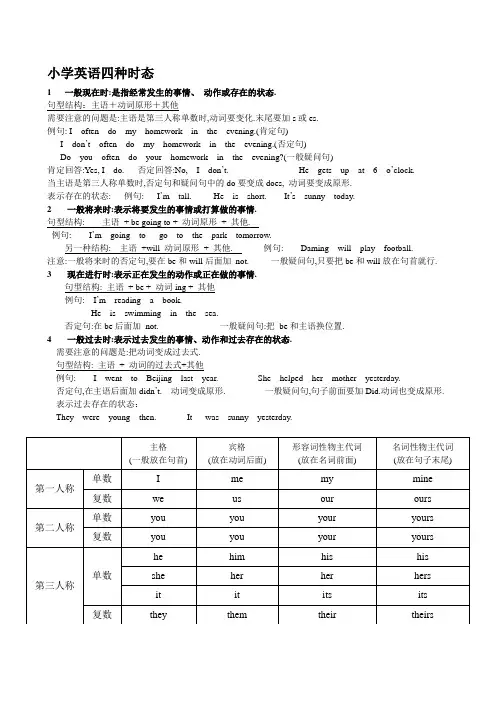
小学英语四种时态1一般现在时:是指经常发生的事情、动作或存在的状态.句型结构:主语+动词原形+其他需要注意的问题是:主语是第三人称单数时,动词要变化.末尾要加s或es.例句: I often do my homework in the evening.(肯定句)I don’t often do my homework in the evening.(否定句)Do you often do your homework in the evening?(一般疑问句)肯定回答:Yes, I do. 否定回答:No, I don’t. He gets up at 6 o’clock.当主语是第三人称单数时,否定句和疑问句中的do要变成does, 动词要变成原形.表示存在的状态: 例句: I’m tall. He is short. It’s sunny today.2一般将来时:表示将要发生的事情或打算做的事情.句型结构: 主语+ be going to + 动词原形+ 其他.例句: I’m going to go to the park tomorrow.另一种结构: 主语+will 动词原形+ 其他. 例句: Daming will play football.注意:一般将来时的否定句,要在be和will后面加not. 一般疑问句,只要把be和will放在句首就行. 3现在进行时:表示正在发生的动作或正在做的事情.句型结构: 主语+ be + 动词ing + 其他例句: I’m reading a book.He is swimming in the sea.否定句:在be后面加not. 一般疑问句:把be和主语换位置.4一般过去时:表示过去发生的事情、动作和过去存在的状态.需要注意的问题是:把动词变成过去式.句型结构: 主语+ 动词的过去式+其他例句: I went to Beijing last year. She helped her mother yesterday.否定句,在主语后面加didn’t. 动词变成原形. 一般疑问句,句子前面要加Did.动词也变成原形.表示过去存在的状态:They were young then. It was sunny yesterday.。

四大时态句型结构一、一般现在时: 经常或习惯性的动作(1) 含有be动词的句型肯定句——主语+be (am, is, are ) + 其他. eg: I am Chinese.否定句——主语+be not +其他. eg: I am not a boy.一般疑问句——Be+主语+其他. eg: Are you a girl?特殊疑问句——特殊疑问词+be (am, is, are )+主语+其他?eg:Why is your Mum so angry? What’s your name? How old are you? (2) 含有实意动词的句型肯定句——主语+动原+其他. (单三人称作主语时,动词要用相应的单三人称形式。
) eg: I (He) often get (gets) up early.否定句——主语+don't+动原+其他. (单三人称作主语时,don't变doesn't。
) eg: I (She) don’t (doesn’t) like him.一般疑问句——DO+主语+动原+其他. (单三作主语时,do变does)eg: Do (Does) you (she) like playing basketball?特殊疑问句——特殊疑问词+助动词(do或does)+主语+动词原形+其他?eg:Where do you study English? What do you do ?(3) 含有情态动词can的句型(只要遇见can,无论主语是什么人称,动词一律用原型。
)肯定句——主语+can+动原+其他. eg:I(She)can swim.否定句——主语+can't(can not)+动原+其他. eg: I (They) can't speak English.一般疑问句——Can+主语+动原+其他. eg: Can you (he) see the bird in the tree?特殊疑问句——特殊疑问词+情态动词(can)+主语+动词原形+其他?eg:What can I do for you?关键词: sometimes=at times有时,often经常, usually通常, always总是,every day每天, on Sunday afternoon在周日下午, five days a week一周五天, three times a month一个月三次…二、现在进行时: 正在发生的动作或存在的状态肯定句——主语+be+动词的现在分词(ing)+其他. eg: I am reading now.否定句——主语+be not+动词的现在分词(ing)+其他. eg: I am not working.一般疑问句——Be +主语+动词的现在分词(ing)+其他? eg: Are you sleeping?特殊疑问句——特殊疑问词+ be +主语+动词的现在分词(ing)+其他?eg:What are you doing?关键词:now现在, at the moment此刻, look, listen, keep quiet等提示语.三、一般将来时: 将要发生的动作(1)含有will的句型肯定句——主语+will+动词原型+其他. eg: I will call you later.否定句——主语+will not +动词原型+其他. eg: I will not go to the park.一般疑问句——Will +主语+动词原型+其他. Will you go shopping with her?特殊疑问句——特殊疑问词+will +主语+动词原形+其它?(will 可改为be going to ,疑问句中当主语是第一人称时will改为shall)(2)含有be going to 的句型肯定句——主语+be(am / is / are) + going to +动词原形+其它.否定句——主语+be(am / is / are)+not + going to +动词原形+其它.一般疑问句——Be(am / is / are) +主语+ going to +动词原形+其它?特殊疑问句——特殊疑问词+ be(am / is / are) +主语+ going to +动词原形+其它?关键词:tomorrow, next year明年, tonight今晚, this year今年, at the end of this term这学期期末, from now on从现在开始, soon一会儿马上, later后稍后,in three days三天之内, in the future未来…四、一般过去时: 过去发生的动作强调时间(1)含有be动词的句型肯定句——主语+be(was,were)+其他. eg: I was born on July.1st, 2000.否定句——主语+be(was,were) not+其他. eg: I was not born in 1999.一般疑问句—Be(was,were)+主语+其他? eg: Were you born in January?特殊疑问句—特殊疑问词+ be(was,were)+主语+其他. eg: When was he born?(2)含有实意动词过去式的句型肯定句——主语+动词的过去式+其他. eg: Lily went shopping yesterday.否定句——主语+did not+动原+其他. eg: He did not go to school today.一般疑问句——Did+主语+动原+其他? eg:Did she pass the test?特殊疑问句—特殊疑问词+did+主语+动原+其他. eg:Where did you go yesterday?关键词:yesterday昨天,last week上周, last year去年, 一段时间+ago如ten years ago十年前five hours ago五小时前, in +年/月,on+具体日期...Just now=a moment ago刚才,in the old days从前, long ago很久以前...。

英语四种时态+常见短语一、一般现在时 (Simple Present Tense)1. 描述现在经常或总是发生的事情,如:I go to work every day.2. 表达普遍真理或惯性动作,如:The sun rises in the east.3. 表达经常或通常的行为,如:He always eats breakfast at 7o'clock.常见短语:- every day(每天)- usually(通常)- always(总是)- often(经常)- sometimes(有时)- rarely(很少)- never(从不)二、一般过去时 (Simple Past Tense)1. 描述过去发生的事情,如:I watched a movie last night.2. 表达过去常常发生的动作,如:He often went fishing when he was young.3. 表达过去的惯,如:We lived in that house for many years.常见短语:- yesterday(昨天)- last night(昨晚)- a week ago(一周前)- in the past(在过去)- when I was young(在我年轻的时候)- for many years(多年来)- in those days(在那些日子里)三、一般将来时 (Simple Future Tense)1. 表达将来会发生的事情,如:I will visit my grandparents next week.2. 表示打算或计划做的事情,如:We are going to have a party on Saturday.3. 表达预测的事件,如:I think he will win the game.常见短语:- next week(下周)- in the future(在未来)- tomorrow(明天)- on Saturday(在星期六)- be going to(打算)- will(将)- I think(我认为)四、现在进行时 (Present Continuous Tense)1. 描述现在正在发生的事情,如:She is studying in the library right now.2. 表达将来安排好的事情,如:We are leaving for a vacation next month.3. 表示暂时的情况,如:He is living with his sister while his house is being renovated.常见短语:- right now(现在)- at the moment(此刻)- in the near future(不久的将来)- next month(下个月)- while(在...期间)- currently(目前)- at present(现在)以上是英语中四种常见的时态以及常见的短语,掌握这些时态和短语可以帮助你更准确地表达过去、现在和将来的事件和状态。
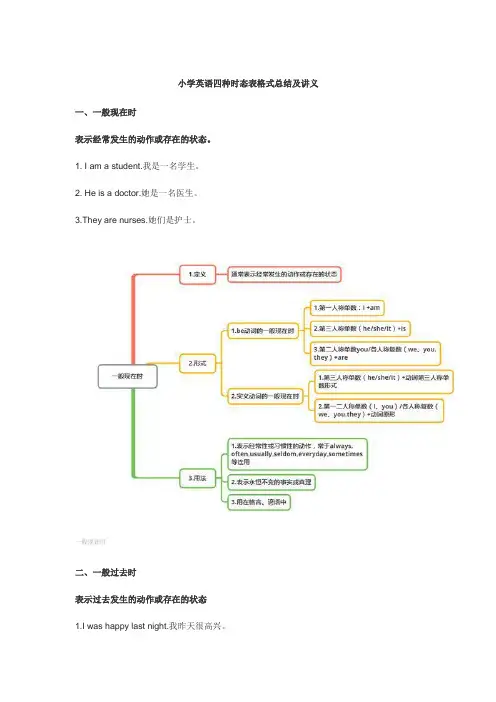
小学英语四种时态表格式总结及讲义一、一般现在时表示经常发生的动作或存在的状态。
1. I am a student.我是一名学生。
2. He is a doctor.她是一名医生。
3.They are nurses.她们是护士。
一般现在时二、一般过去时表示过去发生的动作或存在的状态1.I was happy last night.我昨天很高兴。
2.You were great in the exam.你考试考得不错。
3.We met a girl at the gate.在门口我们见到了一个女孩。
一般过去式时三、一般将来时通常表示现在还有发生,但即将发生的事情或动作。
1.I shall be there in 5 minutes.我五分钟后会到那里。
2.We will go to the park this night.我们今天晚上将去公园。
3.Ken is gonging to have a bath.Ken要去洗澡了。
一般将来时四、现在进行时表示正在进行或发生的动作1.I am eating now.我正在吃东西。
2.He is singing now.他正在唱歌。
3.They are playing now.他们正在玩。
4.We are writing a book this month.我们这个月正在写一本书。
现在进行时以上是小学阶段常见的四大时态,除了以上在使用时还需注意以下几点:1. I am=I'm he is=he's she is=she's it is=it's we are=we're you are=you'reI shall/I will=I'll you will=you'll she will=she'll it will=it'll2.表示将来时时只有第一人称(I/we)后面接shall,表示我(们)将要……,3.当征求某人意见时一般使用shall I/shall we。

小学英语四种时态知识点加练习一、一般现在时一. 意义:表示经常发生的事情,动作或存在的状态二. 构成及变化1.be动词的变化。
肯定句:主语+be(am,is,are)+其它。
如:I am a boy.我是一个男孩。
否定句:主语+ be + not +其它。
如:He is not a worker.他不是工人。
一般疑问句:Be +主语+其它。
如:-Are you a student? -Yes. I am. / No, I'm not.特殊疑问句:疑问词+一般疑问句。
如:Where is my bike?2. 行为动词的变化。
l、当主语为第一,二人称及复数时,助动词为do肯定句:主语+动词原形(+其它)。
如:We often play basketball after school.否定句:主语+ don't+动词原形(+其它)。
如:we don’t play basketball after school.一般疑问句:Do +主语+动词原形+其它?如:Do you often play basketball after school? Yes, we do. / No, we don't.特殊疑问句:疑问词+以do开头的一般疑问句?如:What do you often do after school ?2、当主语为第三人称单数时,助动词为does肯定句:主语+动词三单式(+其它)。
如:He swims well.否定句:主语+ doesn’t+动词原形(+其它)。
如:He doesn’t swim well..一般疑问句:Does +主语+动词原形+其它。
如:Does he swim well ?Yes, he does. / No, he doesn't.特殊疑问句:疑问词+以does开头的一般疑问句?如:How does your father go to work?三.第三人称单数的动词变化规则(只有在第三人称为主语的肯定句中,动词才用三单式)(1)多数动词直接加s: runs gets likes collets takes plays climbs…….(2)结尾是s, x, sh, ch, o,前为辅音字母, 结尾加es :watches teaches goes does washes crosses mixes brushes(3)动词末尾y前为辅音:将y改为i加es: study→studies fly→flies carry→carries cry→cries但在y前如果为元音则直接加s:buys says四.时间标志:always , usually , often , sometimes ,every…一般现在时练习题I.用下列单词的适当形式填空1.We often___________(play) in the playground.2.He _________(get) up at six o’clock.3.__________you _________(brush) your teeth every morning?4.What________________(do) he usually________________(do) after school?5.Danny ________________(study) English, Chinese, maths, science and Art at school.6.Mike sometimes __________(go) to the park with his sister.7.At eight at night, she __________(watch) TV with his parents.8.________ Mike________(read) English every day?9.How many lessons_________your classmates________(have) on Monday?10.What time_________his mother_________(do) the housework?II.改句子1.Do you often play football after school? (改为肯定句)2.I have many books.(改为否定句)3.Gao Shan’s sister likes playing table tennis (改为否定句)4.She lives in a small town near New York.(改为一般疑问句)5.I watch TV every day.(改为一般疑问句)6.We have four lessons.(改为否定句)7.Nancy doesn’t run fast (改为肯定句)二、现在进行时一、概念现在进行时表示说话时正在进行或发生的动作,也可表示当前一段时间内的活动或现阶段正在进行的动作。

英语四个时态的结构英语中有四个基本时态:一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时和现在进行时。
它们有不同的结构和用法,下面将详细介绍每个时态的结构。
一、一般现在时:1.肯定句结构:主语+动词原形/第三人称单数形式+其他例如:I play football every weekend.2. 否定句结构:主语 + do/does + not + 动词原形 + 其他例如:They do not like tomatoes.3. 疑问句结构:Do/Does + 主语 + 动词原形 + 其他?例如:Do you like ice cream?4. 特殊疑问句结构:特殊疑问词 + do/does + 主语 + 动词原形 + 其他?二、一般过去时:1.肯定句结构:主语+动词过去式+其他例如:She watched a movie last night.2. 否定句结构:主语 + did not + 动词原形 + 其他例如:He did not eat dinner yesterday.3. 疑问句结构:Did + 主语 + 动词原形 + 其他?例如:Did you go to the party?4. 特殊疑问句结构:特殊疑问词 + did + 主语 + 动词原形 + 其他?例如:When did you arrive?三、一般将来时:1. 肯定句结构:主语 + will + 动词原形 + 其他例如:I will visit my grandma next week.2. 否定句结构:主语 + will not + 动词原形 + 其他3. 疑问句结构:Will + 主语 + 动词原形 + 其他?例如:Will you go to the concert?4. 特殊疑问句结构:特殊疑问词 + will + 主语 + 动词原形 + 其他?例如:Where will you travel next summer?四、现在进行时:1. 肯定句结构:主语 + am/is/are + 动词-ing + 其他例如:She is watching TV now.2. 否定句结构:主语 + am/is/are + not + 动词-ing + 其他例如:They are not studying for the exam.3. 疑问句结构:Am/Is/Are + 主语 + 动词-ing + 其他?例如:Are you playing basketball?4. 特殊疑问句结构:特殊疑问词 + am/is/are + 主语 + 动词-ing + 其他?例如:What are you doing tonight?以上就是英语四个基本时态的结构和用法。

千里之行,始于足下。
小学四种英语时态的归纳总结小学英语时态的归纳总结在小学阶段学习英语,掌握四种基本的时态是非常重要的。
这四种时态分别是一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时和现在进行时。
以下是对这四种时态的归纳总结。
一、一般现在时(Simple Present Tense)1. 表示经常性的动作或状态。
例如:I play basketball every Saturday.2. 在陈述句中,主语和动词要一致。
例如:He likes to watch movies.3. 在否定句中,用do / does + not + 动词原形。
例如:She does not like vegetables.4. 在疑问句中,用do / does + 主语 + 动词原形?例如:Do you have any pets?5. 用于表示客观事实、经验等。
二、一般过去时(Simple Past Tense)1. 表示过去发生的动作或状态。
例如:I watched a movie yesterday.2. 在陈述句中,动词过去式的变化规则是直接加-ed。
例如:We played soccer last week.3. 在否定句中,用did + not + 动词原形。
例如:She did not go to school yesterday.4. 在疑问句中,用did + 主语 + 动词原形?例如:Did you finishyour homework?第1页/共3页锲而不舍,金石可镂。
三、一般将来时(Simple Future Tense)1. 表示将来发生的动作或状态。
例如:I will go to the park tomorrow.2. 在陈述句中,用will / shall + 动词原形。
例如:She will visither grandparents next week.3. 在否定句中,用will not / won't + 动词原形。

英语四种一般时态一般过去时态一般过去时态:表示过去某一时间所发生的动作或存在的状态。
谓语动词要用一般过去式。
经常与yesterday(昨天), last week(上周), last month(上个月), last year(去年), two months ago(两个月前), the day before yesterday(前天),in 1990 (在1990年), in those days (在那些日子里)等表示过去的时间状语连用。
如: I was born in 1990. (我出生在1990年)。
When did you go to the park? (你是什么时候去的公园)。
I went to the park last week. (我是上周去的公园)在上面的句子中第一句属于be动词的一般过去时态;第二句和第三句属于实义动词的一般过去时态。
1. Be 动词的一般过去时态在没有实义动词的句子中使用be动词, am is 的过去式为was; are的过去式为were.构成:肯定句:主语+was (were) +宾语如:I was late yesterday. (昨天我迟到了。
)否定句:主语+was (were) +not+宾语如:We weren't late yesterday. (我们昨天没迟到)疑问句:Was (Were) +主语+宾语如: Were you ill yesterday? (你昨天病了吗?)肯定回答: Yes, I was. (是的,我病了。
)否定句: No, I wasn't. (不,我没病。
)特殊疑问句:特殊疑问词+was (were) +主语+宾语如:When were you born? 你是什么时候出生的?2.实义动词的一般过去时态肯定句要使用动词的过去式,否定句和疑问句要使用助动词do和 does 的过去式 did.肯定句为:主语+动词过去式+宾语如: I went home at nine o'clock yesterday.(我昨天九点钟回的家。

四种时态的时间状语及用法一般现在时1.用法:1)表示经常性、习惯性的动作或状态2)表示事物或人物的特征、状态3)表示客观事实2.谓语动词:do/does(动词原形\动词第三人称单数形式)3.时间状语:always,usually, often,sometimes,never, at times(偶尔), oncea week,every…(every day,every morning, every year…) on Sundays,,on weekends注意:当主语是第三人称单数时,谓语动词要用第三人称单数形式一般过去时1.用法:1)表示在过去的时间发生的动作或存有的状态2)表示过去经常或反复发生的动作(能够和often,always等表示频率的时间副词连用)2.谓语动词:did(动词过去式)3.时间状语:yesterday, the day before yesterday(前天) ,two days ago, last week,in 2008附:常见动词及其过去式一般将来时1.用法:1)表示将来的时间要发生的动作或存有的状态2)表示打算、计划、决定要做某事2.谓语形式:will/shall+动词原形/be going to +动词原形3.时间状语:next week,this Sunday,next time,tomorrow,the day after tomorrow(后天),现在实行时1.用法:1)表示现在(说话瞬间)正在实行或发生的动作2)表示当前一段时间内的活动或现阶段正在实行的动作2.谓语形式:am/is/are+动词ing形式3.时间状语:now,these days(这几天)附:常见动词及其-ing形式。

英语的四大时态用法及结构英语中的时态共有四种,分别是一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时和现在完成时,它们各自有着不同的用法和结构。
一、一般现在时一般现在时表示现在的状态、经常发生的事情或普遍真理等,其结构为“主语+动词原形”。
例如:I go to school every day.(我每天去上学。
)Water boils at 100℃.(水沸腾的温度是100℃。
)二、一般过去时一般过去时表示过去发生的事情,其结构为“主语+动词过去式”。
例如:He played basketball yesterday.(昨天他打了篮球。
)They watched a movie last night.(昨晚他们看了一部电影。
)I visited my grandparents last summer vacation.(上个暑假我拜访了我的祖父母。
)三、一般将来时一般将来时表示将来要发生的事情或者预测的情况,其结构为“主语+ will/shall + 动词原形”。
例如:I will go to the library tomorrow.(我明天去图书馆。
)She shall visit her friends ne某t week.(下周她要去拜访她的朋友。
)The sky will be cloudy this afternoon.(今天下午天空将会是多云的。
)四、现在完成时现在完成时表示过去某个时间开始的某个动作一直持续到现在,或者过去某个时间开始的某个动作已经结束但对现在还有影响,其结构为“主语 + have/has + 动词过去分词”。
例如:I have been studying English for four years.(我已经学英语四年了。
)They have finished their homework.(他们已经完成了本次作业。
)She has lost her key.(她已经把钥匙丢失了。
小学英语四大时态语法知识点小学英语主要是如下的四大时态:一般现在时、现在进行时、一般过去时、一般将来时。
01一般现在时一、标志词always(总是)usually(通常)often(经常)sometimes(有时)never(从不)every(每一)二、基本用法1.表示事物或人物的特征、状态。
2.表示经常性、习惯性的动作。
3.表示客观现实。
三、构成1.be动词:主语+be动词(am isare)+其它.2.行为动词:主语+行为动词+其它。
四、句型肯定句:A. be 动词:be+主语+其它。
B. 行为动词:主语+动词(注意人称变化)+其它。
否定句:A.be动词:主语+be+not+其它。
B.行为动词:主语+助动词(do/does)+not+d动词原形+其它一般疑问句:A.be动词:be+主语+其它。
B.行为动词:助动词(Do/Does)+主语+动词原形+其他.特殊疑问词:疑问词+一般疑问句02现在进行时一、标志词now(现在), look(看),listen(听)二、基本用法表示现阶段正在进行的动作三、基本结构1.肯定句:主语+be动词+动词现在分词(ing)+其它。
2.否定句:主语+be动词+not+动词现在分词(ing)+其它。
3.一般疑问句:be动词+主语+现在分词(ing)+其它。
4.特殊疑问句:疑问词+一般疑问句。
03一般将来时一、标志词tomorrow(明天),soon(不久),will(将要=be going to)二、基本用法表示在在将来某个时间要发生的动作或存在的状态。
三、基本结构1.肯定句:主语+ be going to + 动词原形。
主语+will+动词原形。
2.否定句:主语+ be going to +动词原形。
主语+won’t + 动词原形3.一般疑问句:Be + 主语+ going to+动词原形Will + 主语+ 动词原形4.特殊疑问句:疑问词+一般疑问句04一般过去时一、标志词yesterday(昨天),ago(以前),before(在...之前)二、用法1.表示过去某个时间发生的动作或存在的状态,常和表示过去的时间状语连用。
时态小学阶段一共学了四种时态,分别是:一般现在时,一般将来时,现在进行时,一般过去时;1、一般现在时表示现在的习惯动作,即指现在经常发生的动作,一般现在时常用来表示现在时间里某种动作的经常性和习惯性;它常与表示程度或频度的词连用,如:often经常 , usually通常,一般 , sometimes有时 , always总是,一直 , never从不如:I often go to school on foot. My father works in a school. Mike watches TV every day.主语是第三人称单数时,势单力薄,需要一个帮手,在动词上给它加上丝丝s或es力吧英语动词的现在时与原形同形;但当主语是第三人称单数时,须在词尾加-s或 -es;Her mother works in a hospital. Amy often goes to school by bike. Mr. Liu teaches us English.加-es 的动词必须是以“sh , ch , o ”等字母结尾的;如:watches , teaches , goes , washes2、一般将来时表示在将来会发生的事或动作;它常与表示将来的时间连用,如:tomorrow , next week , next year , this morning , this afternoon , this evening, soon,注意☆ 一般将来时小学阶段主要学了两种结构:①be going to + 动词的原形 / 地点②will + 动词的原形例句:I’m going to go shopping this afternoon. You will see many birds in the sky. 3、现在进行时表示说话时正在进行的动作或现阶段一直在进行的动作;now listen look特征词主人正要干大事,要找比比be动词当保镖,保镖出门不简单,后面带着英英ing跟屁虫它的构成是:be的现在时形式am , is , are加动词的ing形式;如:What are you doing What are they doing They’re swimming. Look, Amy is reading an English book.☆注意☆ 动词的ing形式的构成规则:一般的直接在后面加上ing , 如doing , going , working , singing , eating② 以e 结尾的动词,要先去e再加ing ,如having , writing③ 双写最后一个字母的此类动词极少有:running , swimming , sitting , getting4、一般过去时主要用来表示在特定过去时间中一次完成的动作或一度存在的状态,也可表示过去的习惯动作;它与现在时间不发生关系,它表示的动作或状态都已成为过去,现已不复存在;它经常与表示过去的时间连用;如:I went to a park yesterday. I read a book last night. I watched TV yesterday evening.☆注意☆一般过去时主要体现在动词的形式要用过去式,动词的过去式的构成规则有:A、规则动词一般直接在动词的后面加ed ;如worked , learned , cleaned , visited②以e结尾的动词直接加d ;如lived , danced , used以辅音字母加y结尾的动词要改y为i再加ed 此类动词较少如study – studied carry – carried worry – worried play、stay除外④ 双写最后一个字母此类动词较少如stoppedB、不规则动词此类词并无规则,须熟记小学阶段要记住以下动词的原形和过去式:sing – sang , eat – ate , see – saw , have – had , do – did , go – went , take – took , buy – bought , get – got , read – read , fly –flew , am/is – was , are – were , say – said , leave – left , swim – swam , tell – told , draw – drew , come – came , lose –lost , find – found , drink – drank , hurt – hurt , feel – felt特征词ago, yesterday , last小学阶段不规则动词全表InfinitivePasttenseInfinitivePast tense1. am, is was2. keep k e pt3. are were4. let let5. become bec a me6. make ma d e7. begin beg a n 8. meet m e t9. bite b i t 10. put put11. blow bl e w 12. read read13. buy b ough t 14. ride r o de15. catch c augh t 16. run r a n17. come c a me 18. say s ai d19. cost cost 20. see s aw21. cut cut 22. sing s a ngd u g 24. sit s a td i d 26. sleep sle pt27. draw dr e w 28. speak sp o ke29. drink dr a nk 30. sweep sw e pt31. eat ate 32. take t oo kf e ll t augh t35. feed f e d 36. tell t o ldf e lt th ough t39. fly fl ew 40. throw thr e wforg o t underst oo d43. get g o t 44. give g a ve45. wake w o ke 46. go went47. wear w ore 48. growgr e w49. win w o n 50. have/has h a d51. write wr o te 52. knowkn e wsang 54. see sawgot flewsaid leftswam 60. lose lost found 62. hurt hurt一一般现在时用法专练:一、写出下列动词的第三人称单数drink________go_______stay________make________look_________have_______pass_______carry____come________watch______plant_______fly________study_______brush________do_________teach_______二、用括号内动词的适当形式填空;often________havedinner at home.and Tommy_______bein Class One.not watchTV on Monday.not goto the zoo on Sunday.likethe World Cupoften_______doon Saturdaysparents_______readnewspapers everydaygirl_______teachus English on Sundays.and I________takea walk together every evening.besome water in the bottle.likecooking.havethe same hobby.aunt_______lookafter her baby carefully.always_______doyour homework well.beill. I’m staying in bed.goto school from Monday to Friday.Tao_______donot like PE.child often_______watchTV in the evening.and SuYang_______haveeight lessons this term.20.-What day_______beit today-It’s Saturday.二现在进行时专项练习:一、写出下列动词的现在分词:play________ run__________ swim _________make__________go_________ like________write________ _ski___________read________ have_________ sing________ dance_________put_________ see________ buy _________ love____________live_______ take_________ come ________get_________stop_________ sit ________ begin________ shop___________二、用所给的动词的正确形式填空:boy __________________ drawa picture now.2. Listen .Some girls _______________ singin the classroom .3. My mother _________________ cook some nice foodnow.4. What _____ you ______ do now5. Look . They _______________ have an English lesson . ____________not ,water the flowers now.the girls ________________dance in the classroom .is our granddaughter doing She _________listen to music.9. It’s5o’clock now. We _____________havesupper nowwash clothes Yes ,she is .三将来时专项练习用所给词的适当形式填空;is a sunny day. We ____________ have a picnic this afternoon.2.My brother _______________ go to Shanghai next week.3.Tom often ______________go to school on foot. But today is rain. He ______________ go to school by bike.4.What do you usually do at weekends I usually __________ watch TV and ____________catch insects 5.It’s Friday today. What _____she _________ do this weekend She ______________ watch TV and _____________ catch insects.6.What ___________ d0 you do last Sunday I ____________ pick apples on a farm. What _______ do next Sunday I _________milk cows.7.Mary ____________ visit her grandparents tomorrow.8.Liu Tao ____________ fly kites in the playground yesterday.______________ give a puppet show next Monday. ________________ plan for my study now四过去时练习写出下列动词的过去式 is\am_________ fly_______ plant________ are ________drink_________ play_______ go________ make ________does_________ dance________ worry________ ask _____taste_________ eat__________ draw________ put ______throw________ kick_________ pass_______ do________。
英语四大时态变化规则英语语法中有四种主要的时态,它们包括:一般现在时(Simple Present)、一般过去时(Simple Past)、一般将来时(Simple Future)、和现在完成时(Present Perfect)。
下面是每种时态的变化规则:1. 一般现在时(Simple Present Tense):-陈述句:主语+ 动词原形(第三人称单数主语需要在动词后面加-s)。
例子:He works in an office.-否定句:主语+ 助动词"do" / "does" + not + 动词原形。
例子:They do not like coffee.-疑问句:助动词"do" / "does" + 主语+ 动词原形。
例子:Do you play the guitar?2. 一般过去时(Simple Past Tense):-陈述句:主语+ 动词过去式形式。
例子:She visited Paris last year.-否定句:主语+ 助动词"did" + not + 动词原形。
例子:I did not finish my homework.-疑问句:助动词"did" + 主语+ 动词原形。
例子:Did they arrive on time?3. 一般将来时(Simple Future Tense):-陈述句:主语+ 将来时标志词"will" + 动词原形。
例子:I will go to the store tomorrow.-否定句:主语+ 将来时标志词"will" + not + 动词原形。
例子:She will not attend the meeting.-疑问句:将来时标志词"will" + 主语+ 动词原形。
英语四个时态的定义英语四个时态的定义一、一般现在时(Present Simple)1.定义:一般现在时用来表示频繁的、习惯的动作;状态;存在;客观的真理;根据时间表、日历安排的动作;定期发生的动作等。
2.构成:动词原形(第三人称单数除外,要用动词的-s 或 -es 形式)3.使用的时间状语:often,usually,sometimes,never,every day,once a week,on Tuesday,in summer,at five o’clock,at night,in the morning,now,these days,in the 21st century 等二、一般过去时(Past Simple)1.定义:一般过去时用来表示已经发生的动作或状态,或曾经发生多次的动作,且已经结束。
2.构成:动词的过去式(第三人称单数除外,要用动词的-ed 和-en形式)3.使用的时间状语:yesterday,last year,ago,in 1988,on Tuesday,in my childhood等三、一般将来时(Future Simple)1.定义:一般将来时用来表示将要发生的动作或状态,或将来某一段时间内发生多次的动作。
2.构成:will(它是情态动词,后面接动词原形)或be going to()+动词原形be going to,表示“打算”,在口语中多用。
3.使用的时间状语:tomorrow,next month,next year,in 2020,in 30 minutes,soon,later,at last,after a while,in the future 等四、现在进行时(Present Continuous)1.定义:现在进行时是用来表示正在进行的动作或正在发生的状态,它强调动作正在进行(或发生)。
一般过去时态一般过去时态:表示过去某一时间所发生的动作或存在的状态。
谓语动词要用一般过去式。
经常与yesterday (昨天), last week(上周), last month(上个月), last year(去年), two months ago(两个月前), the day before yesterday(前天),in 1990 (在1990年), in those days (在那些日子里)等表示过去的时间状语连用。
如: I was born in 1990. (我出生在1990年)。
When did you go to the park? (你是什么时候去的公园)。
I went to the park last week. (我是上周去的公园)在上面的句子中第一句属于be动词的一般过去时态;第二句和第三句属于实义动词的一般过去时态。
1. Be 动词的一般过去时态在没有实义动词的句子中使用be动词, am is 的过去式为was; are的过去式为were.构成:肯定句:主语+was (were) +宾语如:I was late yesterday. (昨天我迟到了。
)否定句:主语+was (were) +not+宾语如:We weren't late yesterday. (我们昨天没迟到) 疑问句:Was (Were) +主语+宾语如: Were you ill yesterday? (你昨天病了吗?)肯定回答: Yes, I was. (是的,我病了。
)否定句: No, I wasn't. (不,我没病。
)特殊疑问句:特殊疑问词+was (were) +主语+宾语如:When were you born? 你是什么时候出生的?2.实义动词的一般过去时态肯定句要使用动词的过去式,否定句和疑问句要使用助动词do和 does 的过去式 did. 肯定句为:主语+动词过去式+宾语如: I went home at nine o'clock yesterday.(我昨天九点钟回的家。
小学常见的四种时态1.一般现在时:1)概念:经常、反复发生的动作或行为及现在的某种状况。
2)时间状语: always, usually, often, sometimes, every week (day, year, month …), once a week, etc.3)基本结构:①be动词;②行为动词4)否定形式:①am / is / are + not;②此时态的谓语动词若为行为动词,则在其前加don’t,如主语为第三人称单数,则用doesn’t,同时还原行为动词。
5)一般疑问句:①把be动词放于句首;②用助动词do提问,如主语为第三人称单数,则用does,同时,还原行为动词。
2.一般过去时:1)概念:过去某个时间里发生的动作或状态;过去习惯性、经常性的动作、行为。
2)时间状语:…ago, yesterday, the day before yesterday, last week (year, night, month …), in 1989, just now...3)基本结构:①be动词;②行为动词4)否定形式:①was / were + not;②在行为动词前加didn’t,同时还原行为动词。
5)一般疑问句:①was或were放于句首;②用助动词do的过去式did 提问,同时还原行为动词。
3.现在进行时:1)概念:表示现阶段或说话时正在进行的动作及行为。
2)时间状语:now, at this time, these days, listen, look, etc.3)基本结构:am / is / are + doing4)否定形式:am / is / are + not + doing.5)一般疑问句:把be动词放于句首。
4.一般将来时:1)概念:表示将要发生的动作或存在的状态及打算、计划或准备做某事。
2)时间状语:tomorrow, next day (week, month, year, Sunday, Saturday …), soon, etc.3)基本结构:①am / is / are going to + do;②will / shall + do ③ want to + do4)重点讲授一般将来时在对话中的使用。
四种一般时态导言当了解英文是由三种基本句型构成,识别它们的主要方法是动词。
掌握动词就成了学习的第二个难点。
要想掌握好时态,主要有以下三点:1.无论动词如何变化,我们都能识别它,并且熟练地应用它,这就要求我们熟记每种变化的构成。
2.它们的每种变化到底意味着什么?它们与中文的动词有什么区别?3.最关键的是,要了解什么是时态,其实时态的本质是一半时,一半态。
由于以上问题,在我们以往的教科书中非常混乱,中国人和英国人的思维方式有很大不同,以上问题就变得非常复杂,在整个学习中要注意上面提出的三个问题,当你能够回答并掌握以上三点时,你的英语就会产生一个极大的飞跃。
首先让我们从时入手,掌握英文中的时间概念并不难,请看下列时间轴。
过去←现在→将来过去将来─────→(即相对于过去的将来)▲一般时态所表示的时间概念从上面的图可以清楚地看出一般时态所使用的时间概念。
▲一般时态的构成▲主+系动词+表注:*注意该结构中的名词,它们能被定语修饰。
现在:is am are过去:was wereBe------将来:will be过去将来:Would beYou are rich.You are poor注口语:You are rich/you are not rich/are you rich/you were rich/you were not rich/ will you rich/ will you not rich / will you not be rich/ will you be rich/注:该结构中的状语可以置于句首或句尾。
is arewas wereThere be --- will beWould beThere is a wallet on the desk.注口语:there is(are\) a wallet on the deskthere is a wallet on the desk/ there is not a wallet on the desk/You are rich/you are not rich/are you rich/you were rich/you were not rich/ will you rich/ will you not rich / will you not be rich/ will you be rich/注:在该结构中主谓是不可缺少的部分,宾格有无取决于动词是及物还是不及物动词,状语根据需要而定。
▲一般现在时态DoThe students study English.The students do not study English.Do the students study English?DoesThe student studies English .The student does not study English.Does the student study English?注口语:▲一般过去时态DidThe students studied English.The students did not study English.Did the students study English?注口语:▲一般将来时态WillThe students will study English.The students will not study English.Will the students study English?注口语:▲一般过去将来时态的基本用法WouldThe students would study English.The students would not study English.Would the students study English?注口语:▲一般现在时态的基本用法1、表示客观事实或普遍真理●The earth moves around the sun.地球围绕太阳运行。
●Practice makes perfect.熟能生巧。
2、表示目前的情况及反复发生的动作,或习惯性的动作,常与频率副词连用。
如sometimes, often,always, usually, seldom(很少), 这种副词通常放在主语和动词之间。
注:如果表示一件事情,今天(明天、将来)如此,用一将来时。
●She seldom gets up before 6 in the morning.她早晨很少在6点以前起床。
●They often go for an outing on Sunday.星期天他们经常去郊游。
▲一般过去时态的基本用法一般过去时态表示过去的状态及发生的动作。
●I went to see a doctor yesterday。
昨天我去看病了。
●He was a pilot five years ago.五年前他是一个飞行员。
●He married a stewardess.他娶了个乘务员。
▲一般将来时态的基本用法在英语中,表示将来的动作或状态时,有多种形式。
这里介绍四种常用形式。
1. will, shallshall 用于第一人称,will用于其它人称。
在现代英语中,尤其在美国,在表示将来的时候,所有人称都使用will而shall只用于一些习惯用法。
●She will arrive in London on Friday.她将在星期五到伦敦。
●We will never forget you forever.我将永远不会忘记你。
●He often says he will be rich in the future.他常说他将来会富有。
2. to be (am, are, is ) going to do (be)该种形式用来表示将来时,尤其是在口语中用的较多,常常含有“打算”的含义。
●I am going to get up at five o’clock tomorrow morning.我明天早上打算五点起床。
●I’m going to have dinner at home this evening.今天晚上我打算在家吃晚饭。
shall, will(表示肯定)和to be going to的比较●He is going to see his teacher this afternoon.●He will see his teacher this afternoon.第一句只是一种打算,第二句在一定程度上已经决定了。
●I’m going to climb to the top.●I will climb to the top.第一句表达的是一种意向,第二句肯定程度比较大。
will和to be going to的区别有时并不十分明显,可以换用,但在有些情况下却不行。
●I will never forget you.╳I’m not going to forget you.第二句不对。
这里表示的不是一种打算而是一种不可能、决不会的意思。
3. be (is, am, are) to + 动词原形也是一种表示将来的形式,含有“计划”或“安排好了”的意思,是正式用语。
●Mary and my brother are to be married next year.玛丽和我的兄弟计划明年结婚。
be to + 动词原形与to be going to + 动词原形的比较●We are going to finish our paper the end of this month.我们打算本月底完成我们的论文。
●We are to finish our paper the end of this month.我们计划本月底完成我们的论文。
第一句to be going to do是表示打算。
第二句是计划,安排好了或必须完成的意思。
4. be (is, am, are) about to + 动词原形指马上就要发生的动作。
●Look! The plane is about to take off.看!飞机马上就要起飞了。
▲一般过去将来时态的基本用法过去将来时态实际上是过去时态与将来时态相加构成的时间概念。
在英语中表示过去将来状态或动作时有多种形式。
这里介绍四种常用形式。
1. would , shouldshould用于第一人称,would用于其他人称。
在现代英语中,尤其在美国,所有人称都用would.●I thought he would take the chance.我想他会抓住这个机会。
(相对于thought这个过去时态的将来)●I knew he would be a good teacher.我早知他会成为一个好老师。
(相对于knew这个过去时态的将来)●Last evening he said he would go to America.昨天晚上他说他要去美国。
(相对于昨天晚上的将来)从上面的三个例句可以看出:一般过去将来时态在使用时通常会给出一个过去的时间点。
should和would除表示过去将来以外,还可以作为情态动词用。
用法比较复杂,请同学们在今后的阅读中多加注意。
●Should I go on?我可以继续吗?(表示征求对方的同意,语气很客气)●You should give up smoking.你应该戒烟。
(表示应该,指一种义务或责任,但语气较客气)●Would you like to have dinner with me?你愿意和我共进晚餐吗?(表示请求对方做某事,语气很客气)2. to be ( was / were ) going to这种一般过去将来时态和我们上面讲的一般将来的用法是一样的。
只是立足于过去某一点谈将来的事情。
3. to be (was were) to +动词原形(用法可参考一般将来进行时态)4. be (was were) about to +动词原形(用法可参考一般将来时态)----------------------------------------------------●I am about to --- or I am going to --- die: eitherexpression is correct.----Dominique Bouhours, French grammarian, D.我将或者我即将——死去:两种表达方式都正确。
---法国语法学家伯阿沃斯. D.(遗言)●Oh, do not cry ---be good children and we willall meet in heaven(天堂).-----Andrew Jackson, American president哦,不要哭,要做乖孩子,我们都会在天堂见面的。