巴西汽车产品准入管理及技术法规简介
- 格式:doc
- 大小:28.50 KB
- 文档页数:2


RDC No.16: 2013年3月28本法规批准医疗器械以及体外诊断产品的良好作业规范的技术法规及其他条款巴西健康监督机构(ANVISA)的董事会执行1999年4月16日Decree 3.029批准的法规Article 11的子部分IV规定的职责,并考虑了Bylaws的Article 54的第1和3段以及Subsection II规定的条款,该法规根据Administrative Rule 354(2006年8月11日发表,并于2006年8月21日在巴西官方公报(DOU)再次发表)Exhibit I的规定批准的,;考虑了Act 6360(1976年9月23日)及其法规,Decree 79094(1977年1月5日);鉴于需要内在化Resolution MERCOSUL/GMC/RES 20/11,批准的“MERCOSUL Technical Regulation of Good Manufacturing Practices for Medical and in vitro Diagnostic Products医疗和体外诊断产品的良好生产规范的MERCOSUL技术法规(撤销Resolutions GMC 04/95、38/96、65/96和131/96)”;鉴于与医疗和体外诊断产品有关的良好生产规范的法规必须确保在巴西商品化的产品的质量、安全性和有效性;鉴于需要促使完善有关管理和控制医疗和体外诊断产品的国内体系;采纳董事会和执行总裁的以下法规,确定本法规的发表:Article 1:本法规批准“医疗和体外诊断产品的良好生产规范的技术法规”,在此附上的条款是本法规的一部分。
Sole Paragraph:本法规构成国家法律体系法规GMC MERCOSUL 20/2011“MERCOSUL Technical Regulation of Good Manufacturing Practices for Medical and in vitro Diagnostic Products医疗和体外诊断产品的良好生产规范的MERCOSUL技术法规(撤销Resolutions GMC 04/95、38/96、65/96和131/96)”。


巴西市场汽车能耗法规研究霍才仁【摘要】文章阐述了巴西能耗基准线(CE1/CE2/CE3)划定方法,不同基准线对应的IPI税减免幅度.巴西市场在售车型能耗计算方法,通过此方法来分析车辆能否到达巴西能耗要求.【期刊名称】《汽车实用技术》【年(卷),期】2017(000)009【总页数】4页(P75-78)【关键词】巴西能耗;能耗计算;能耗分级【作者】霍才仁【作者单位】安徽江淮汽车集团股份有限公司,安徽合肥 230601【正文语种】中文【中图分类】U461.99CLC NO.: U461.99 Document Code: B Article ID: 1671-7988 (2017)09-75-04 1.1 背景说明巴西政府于2012年10月3日实施第7.819号法令,内容提出技术创新与汽车产业链致密化激励项目即“汽车创新项目”,旨在推进汽车及其零部件在技术开发、创新、安全、环保、能源效率等层面的发展。
解读:(1)巴西政府鼓励主机厂采取新技术降低整车能耗,并通过划定的能耗基准线,来判定主机厂是否达标,判断主机厂是否满足享受创新项目资质,不达标无法享受30%IPI税减免,达标或者更优的可以享受进一步的IPI税减免(最高2%)。
(2)提高能源效率直观的理解就是进一步降低油耗和排放,由于巴西采用灵活燃料(市场销售E22和E100两种燃油,且两种燃油密度和热值均不相同,同时在售车型有搭载E22发动机和E100发动机的区别),相比于国内油品相对单一采用的计量单位L/100km,巴西无法直观从单一燃料油耗判断整车能耗水平,从而统一将判断基准转换成能量单位MJ/km。
(3)之前出口巴西车型均优先考虑动力性,油耗属于次要,由于新法规的实施,巴西经销商要求后续车型优先考虑经济性,动力性可以有所牺牲。
注:a.E100燃料为含7%水和93%乙醇的酒精,E22为含22%酒精和78%汽油的混合物;(百分比均表示体积)b.E22发动机只能燃烧E22的燃油,E100发动机可以燃烧E22和E100以任意比例混合的燃油。

巴西车辆市场导航巴西国家概况一、巴西国家概况一、巴西汽车工业二、二、巴西汽车工业巴西车辆准入制度三、巴西车辆准入制度三、巴西市场分析四、四、巴西市场分析中国汽车进入巴西市场的建议五、五、中国汽车进入巴西市场的建议巴西国家概况•巴西联邦共和国巴西联邦共和国(The Federative Republic of Brazil)(The Federative Republic of Brazil)(The Federative Republic of Brazil)是拉丁美洲是拉丁美洲最大的国家,最大的国家, 国土面积国土面积851.49851.49851.49万平方公里居世界第五,首都巴西利万平方公里居世界第五,首都巴西利亚,重要城市:圣保罗,里约热内卢。
•巴西人口数量巴西人口数量11亿86958695万万(2008(2008年年),位居世界第五。
其中白种人占,位居世界第五。
其中白种人占54.54. 0303%,黑白混血种人占%,黑白混血种人占%,黑白混血种人占39. 9439. 9439. 94%,黑种人占%,黑种人占%,黑种人占5. 395. 395. 39%,黄种人占%,黄种人占0.46%0.46%,印第安人约占,印第安人约占,印第安人约占0. 160. 160. 16%。
%。
•巴西货币名称为雷亚尔,和人民币汇率为巴西货币名称为雷亚尔,和人民币汇率为11:1.381.38,,20092009年年GDP GDP总量为总量为3143031430亿雷亚尔(亿雷亚尔(亿雷亚尔(11美元约合美元约合11.7777雷亚尔)雷亚尔)雷亚尔), , , 居世界第八。
居世界第八。
•巴西的官方语言为葡萄牙语。
巴西的官方语言为葡萄牙语。
717171%的居民信奉天主教。
%的居民信奉天主教。
•巴西人爱好足球,赛车等运动,治安状况不佳。
巴西汽车工业巴西汽车工业汽车品牌•世界汽车著名企业均在巴西投资设厂,其中包括戴姆勒、大众、福特、通用、菲亚特、本田、三菱、日产、丰田、标致、雷诺、沃尔沃等。


巴西汽车产品准入管理及技术法规简介巴西是拉丁美洲面积最大、人口最多的国家,位于南美洲的中心位置,除了智利和厄瓜多尔外,和南美洲的所有国家都接壤,巴西是南美共同市场(MERCOSUR)正式成员国(其它包括阿根廷、乌拉圭、巴拉圭、委内瑞拉,智利、玻利维亚、秘鲁、厄瓜多尔和哥伦比亚为其联系成员),因此巴西在南美洲对其它国家有较大的影响力,因此做好巴西市场,就能够辐射周边许多其它的南美国家。
近年来,包括汽车工业在内的巴西经济发展迅猛,与我国、印度、俄罗斯被国际社会并称为“金砖4国”。
在汽车工业方面,同我国相比,由于巴西从上世纪50年代开始,就采取宽松的外资引进政策,其汽车工业主要是国际跨国公司在巴西的工厂和车型,自主品牌的发展水平较低,这一点和亚洲泰国的情况比较类似。
因此我国企业在拓展巴西市场时,要考虑到起主要的竞争对手将是那些已不同程度本土化的国际汽车跨国公司。
虽然巴西对汽车产品建立了较完善的技术法规体系,但巴西市场的汽车产品管理体制仍然比较独特。
巴西市场另外一个特别需要注意的特点是,巴西政府一贯重视汽车环保和节能,在汽车新能源方面发展迅速,并已处于国际领先的地位,其中一是大力发展天然气车辆,主要是CNG车辆,二是大力发展使用生物燃料,主要是乙醇燃料,目前巴西已立法要求,所有的汽油必须混合25%的乙醇。
巴西近年还加紧研发生物柴油。
2008年开始生效的法律规定,对所有柴油掺加2%的生物柴油,2012年添加比例将提高到5%。
这主要是因为巴西具有丰富的天然气储量,巴西大部地区处于亚马逊河流域,土地广袤,大量的甘蔗种植和其它丰富的作物为乙醇的生产提供了源源不断、可再生的原材料。
巴西政府现不断地提高生物燃料的产能和产量,并不遗余力地推广汽车产品使用生物燃料,尤其是在乘用车和轻型车辆方面,为此在巴西的跨国公司也不断地对其产品进行不同程度的技术改造或改进,以适用巴西的新能源结构。
这一特点有可能发展成为巴西的汽车产品贸易壁垒,而且该壁垒是基于环境保护和节约不可再生能源,理由堂而煌之,因此我国企业对此要予以高度重视。
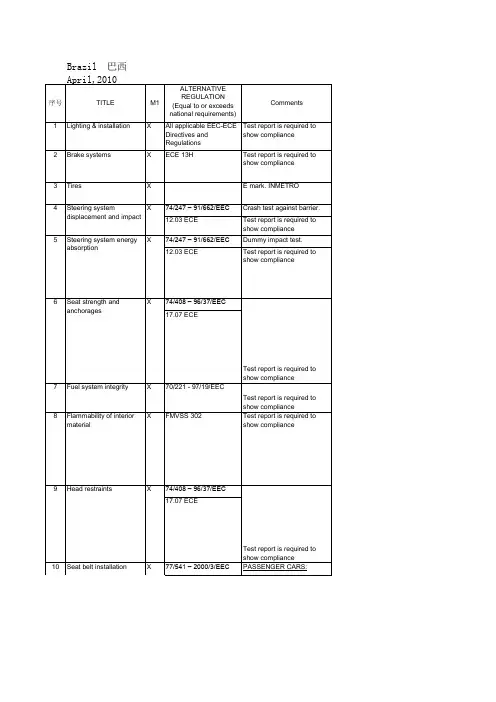

海湾六国汽车产品准入管理及技术法规简介来源:作者:浏览数:149 更新时间:2011-3-3 16:17:31海湾地区包括中东六国,即:阿联酋、巴林、沙特阿拉伯、阿曼、卡塔尔和科威特,该地区与世界其它地区不同,由于富含石油、天然气资源(据统计:海湾6国地区石油已探明储量达910亿吨,占全球的64.5%,其中沙特占25%,阿联酋9.5%,科威特9.1%),经济上十分富裕,对汽车产品的需求量一直很大,以海湾6国地区最大的国家和汽车消费市场----沙特阿拉伯(简称沙特)为例,沙特城市内交通主要依靠私人汽车,即使在大城市里,也只有少数几条公交线路,供收入较低的劳工乘坐;同时由于当地炎热气候以及阿拉伯民族独特的生活习惯,很少有人骑自行车或步行,所以一般家庭都拥有二至三辆私人汽车。
海湾6国尽管对汽车的需求量较大,但自身一直没有汽车工业,汽车一直依赖进口,因此对我国企业而言,该地区是十分重要的海外汽车市场,其现状和发展需要我们予以重点关注。
一、海湾地区是发展中国家(地区)唯一完善的共同体市场国际市场通常分为两大类别,即发达国家(地区)市场和发展中国家(地区)市场。
其中发达国家(地区)市场主要包括:-- 北美市场(美国、加拿大)-- 欧洲市场(欧洲联盟、俄罗斯等其他欧洲国家)-- 亚太市场(日本、韩国、澳大利亚、新西兰)-- 南非市场其它地区的市场,包括海湾6国地区的市场则划为到发展中国家(地区)市场。
发达国家(地区)市场的一个重要的特点是许多国家和地区已形成比较完善的共同体市场,这一点对企业进行国际市场和贸易的工作非常重要,所谓共同体市场就意味着在这个共同体内,所有的国家必须准循共同的法律法规和制度规则,企业进入这样的共同体市场就比较便利,只要经过一次准入认证和批准就可以进入该共同体内所有国家的市场。
这里最为典型、最国际影响最为深远的市场共同体为欧洲联盟。
北美的美国和加拿大尽管制定实施各自的汽车技术法规体系,但两者在技术内容上几乎相同,在对汽车产品的准入管理制度上都实施自我认证制度,再加上《北美自由贸易协定书》的相关规定,美国和加拿大也成为一个共同体市场,获得两者任一方的准入资格,进入其它一方的市场也很便利。

汽车产品认证制度和法规体系简介随着汽车工业的发展,为了保证人类健康和安全,动植物生命和健康,以及环境保护和公共安全,各国(地区)相继建立了符合本国实情的汽车产品认证制度,对汽车和挂车及部件、独立技术总成、系统进行认证。
认证的内容包括对产品的安全、环保、节能、防盗等性能进行型式试验;对产品生产企业的质量保证能力进行审查。
目前世界上主要有欧洲、美国、日本三种汽车产品认证制度,这三种认证制度,经过几十年的运行和不断完善,已相当成熟,为世界各国所参照或引用。
认证制度是依据相应法律建立的,并有配套的技术法规和管理法规做支撑。
1 美国汽车产品认证制度(自我认证强制召回)和法规体系1.1 认证制度1953年,美国在世界上首先颁发《联邦车辆法》,政府由此开始对车辆进行有法可依的管理。
美国汽车法规有联邦法规,也有州法规。
即按照联邦法规对汽车进行统一的认证。
它主要分为两个部分认证:安全认证(自我认证)和环境保护认证(强制认证)。
1.1.1 安全认证美国汽车业实行的是"自我认证",即汽车制造商按照联邦汽车法规的要求自己进行检查和验证。
如果企业认为产品符合法规要求,即可投入生产和销售。
因此说,"自我认证"体现了美国式的自由-汽车企业对自己的产品具有直接发言权。
美国政府主管部门的任务就是对产品进行抽查,以保证车辆的性能符合法规要求。
在美国,汽车安全的最高主管机关是隶属于运输部的国家公路交通安全署(NHTSA)。
为确保车辆符合联邦机动车安全法规的要求,NHTSA可随时在制造商不知情的情况下对市场中销售的车辆进行抽查,也有权调验厂家的鉴定实验数据和其他证据资料。
如果抽查发现车辆不符合安全法规要求,主管机关将向制造商通报,责令其在限期内修正,并要求制造商召回故障车辆,这就是所谓的强制召回。
同时,如果不符合法规的车辆造成了交通事故,厂家将面临高额惩罚性罚款。
在这种严厉的处罚背景下,汽车企业对产品设计和生产过程中的质量控制不敢有丝毫懈怠,而且对召回非常"热心",一旦发生车辆质量瑕疵,就主动召回,否则,被公路交通安全署查出,后果不堪设想。
汽车轮胎巴西INMETRO认证简介汽车轮胎INMETRO认证简介认证背景由巴西国家计量、标准化与⼯业质量局简( INMETRO )制定,由巴西发展、⼯业和商务部发布的NR. 7 规定对出⼝⾄巴西的轮胎(含乘⽤车胎,轻卡车胎,卡客车胎及其拖车轮胎,摩托车⾃⾏车轮胎)实施强制认证。
该法案规定从1997年1⽉1⽇起,所有出⼝轮胎⾄巴西的⼚家都必须通过巴西认证并在轮胎上打上INMETRO标识。
法规标准INMETRO Regulation # 5Passenger, Light Truck, Truck and Bus New Tires乘⽤车,轻轻卡车,卡客车轮胎INMETRO Regulation # 35Motorcycle, Scooter and Moped New Tires摩托车,踏板车和⼩型摩托车INMETRO Regulation # 342Bicycle New Tires for Adult Use⾃⾏车轮胎证书有效期4年。
每年必须接受⼯⼚审核,并且抽取初审的25%个家族进⾏抽样测试。
家族分类轮胎类型分类依据乘⽤车轮胎ü乘⽤车轮胎家族分类依据ü斜胶/⼦午线ü普通型/增强型ü⾼宽⽐: 85及以上;82和80/75/70/65/60;55/50及以下ü速度级别:L M N;P Q R;S T;U H;V 及以上轻卡车轮胎ü斜胶/⼦午线ü负荷指数:⼩于等于93;94-104;105-113;⼤于等于114ü有内胎/⽆内胎卡客车轮胎ü斜胶/⼦午线ü负荷指数:⼩于等于125;126-130;131-135;136-140;141-146;147-151;152-156;157-161;162-166;⼤于等于167ü有内胎/⽆内胎两三轮摩托车轮胎ü摩托车/机动脚ü斜胶/⼦午线ü普通型/增强型ü⾼宽⽐:⼤于等于75;⼩于75ü速度级别:⼩于等于N;P-T;S T;⼤于等于Uü⽤途:正常/特殊ü有内胎/⽆内胎认证条件1.企业具备本产品的⽣产能⼒2.企业质量管理体系依据ISO 9001进⾏运⾏3.企业实验中⼼,质量管理⼈员熟悉相关技术标准4.企业在巴西拥有法定代理⼈,⽤于产品的风险责任承担及处理客户投诉抱怨所需认证资料⽣产线与体系1.ISO9001或TS16949证书;2.最新的ISO年度审核报告及改进报告3.产品参数表和认证申请表4.公司质量管理⼿册Word版(有英⽂版请提供英⽂版,⽆英⽂版中⽂版也可);5.公司质量管理⼿册扫描件……………实验室资料需求清单1.实验室组织结构图;2.测试设备清单(仪器设备台帐,含名称,数量,出⼚编号,型号,精度,测量范围,⽣产⼚家,安装地点,上次校准⽇期,下次校准⽇期);3.测试设备校准证书及校准报告;4.…………认证流程。
巴西轻型车排放与燃油新法规概况巴西轻型车排放与燃油新法规概况东方汽车网 2011-06-10 15:51:57 作者:撰文/雷风梅来源: 文字大小:[大][中][小]巴西轻型车市场概况2003年,巴西出现了灵活燃料车,可以使用乙醇-汽油混合燃料(汽油中添加20%~25%无水乙醇组成的混合燃料),也可以使用水合乙醇,或这些燃料的任一比例的混合燃料。
灵活燃料车在巴西取得了很大成功,2009年巴西轻型车总产量的90%是灵活燃料车。
2009年巴西轻型车产量如图1所示。
2009年,巴西灵活燃料车队的车辆数达到850万辆,占轻型车车队车辆数的30%。
灵活燃料车的扩大应用,以及要求混合燃料中乙醇比例达到20%~25%的法规的影响,使得巴西乙醇消耗量超过了汽油。
乙醇价格更低,加之巴西市场认可乙醇燃料,灵活燃料车在巴西越来越普遍。
巴西轻型车使用CNG为燃料始于1992年。
1996年,巴西乘用车上开始允许使用CNG,但是直到1999年,乘用车车队才开始接受CNG乘用车。
大多数CNG车辆使用转换成套件,与原车辆相比,某些转换成套件技术水平较低,导致污染物排放水平更高。
现在,巴西的天然气车数量达150万辆,是世界天然气车辆数量排名第三的国家,排名第一、第二的国家是阿根廷和巴基斯坦。
2009年以来,由于乙醇价格低,CNG价格高的原因,巴西改造CNG车的数量有所下降。
巴西轻型车不允许使用柴油,柴油主要用于公共运输和货运。
巴西没有混合动力车。
巴西允许进口汽油车,但是由于汽油中的硫含量(600ppm)高,在不使用催化剂和燃油电子点火装置的情况下,汽油直喷模块不能正常使用。
巴西车辆认证与排放法规CONAMA是巴西制定车辆排放法规的部门,1986年开始的项目PROCONVE制定了巴西车辆排放限值。
遵照标准NBR 6601在底盘测功机上进行了试验,根据这一试验结果制定了这一限值。
这一标准与联邦试验程序FTP-75类似,包括3个阶段的排放试验,一个冷起动阶段、一个巡航阶段、10分钟休息之后的一个热起动阶段。
联邦公共服务国家计量、标准化和工业质量工业与对外贸易部-INMETRO法令371-2009,12月29日经巴西国家计量、标准化和工业质量协会(INMETRO)授权宣布,确认发布于1973年12月11日5966法案中第4章§3规定的, 发布于1999年12月20日9933法案中第3章标题1中规定的,以及由权威机构认可并发布的于007年12月28日6275法案中第18章V节规定的以下:家用和类似用途电器产品须进行强制安全认证, 强制性认证应由INMETRO认可的产品认证机构(OCP)进行。
第一条家用和类似用途电器产品认证要求可查询网址:.bn或以下地址:略第二条该通报来源于巴西国家计量、标准化和工业质量协会(INMETRO)8月7日发布的第228号部颁法令(征求意见稿)。
第三条2009年12月29日,巴西发布第371号法令,此次法规更新将把所有家用电器列入 INMETRO 强制认证名单,必须取得巴西政府认可的认证机构强制认证证书。
为了给生产厂家、进口商和分销商以过渡时间,法令将分为三个阶段实施:第四条·第一阶段:2011年7月1日,强制制造商生产的和进口商进口的产品必须符合 INMETRO 要求并取得认证。
·第二阶段:2012年7月1日,强制进口商和制造商在巴西所销售的产品必须符合 INMETRO 要求并取得认证。
第五条·第三阶段:2013年1月1日,强制巴西市场上所有销售的产品已经符合要求并取得认证。
* 最终约在2011年和2013年之间生效。
按法规要求,所有电气类产品必须按照法令列出的技术标准的要求进行检测。
所有根据强制认证项目进行检测的产品,必须标识强制性 INMETRO 标志,并且其相关公司还需在实施过程中建立“客户投诉服务中心”,以符合法规的维护要求。
此外,法规要求还将定期对厂家进行评估,保证其符合要求。
1 目的该法令对家用电器的合格评定规定了一定的要求,旨在保护消费者免受家用电器触电(电击)、短路和着火的危险。
巴西国内进口报关规则-概述说明以及解释1.引言1.1 概述巴西作为南美洲最大的经济体之一,其进口报关规则对于国内进口业务至关重要。
进口报关规则是指在巴西国内进口货物时需要遵守的相关法规和程序。
这些规则旨在确保进口商品的合法性、安全性和合规性,同时保护国内市场的利益。
巴西国内进口报关规则的实施涉及到许多方面,包括商品品类、报关文件、报关程序、税费缴纳等。
首先,根据巴西政府的规定,不同的商品被分为不同的品类,每一类商品都有对应的进口要求和限制。
在申请进口报关时,进口商需要提供详细的商品信息,以便相关部门对商品进行评估和审批。
其次,进口报关所需的文件非常重要。
进口商需要准备并提交一系列的文件,例如商业发票、运输文件、保险单以及其他相关证明文件。
同时,根据进口商品的特殊性质,还可能需要提供其他额外的文件,如卫生证明、质量和安全证明等。
进口报关的程序也是巴西国内进口业务中不可忽视的一环。
根据规定,进口商需要与海关部门进行密切合作,办理进口报关手续。
在实际操作中,进口商需要填写进口申报单、提供商品的详细描述和货值,同时缴纳相应的关税和其他清关费用。
最后,进口报关涉及到的税费缴纳也是一项重要工作。
根据巴西的税法,进口商品需要缴纳进口关税、增值税和其他相关费用。
这些费用的缴纳需要按照规定的税率和计算方法进行,进口商需要合理规划费用,以确保进口业务的经济效益和合规性。
总而言之,巴西国内进口报关规则对于国内进口业务具有重要的指导和规范作用。
进口商需要了解并遵守这些规则,确保进口商品的合法流通和顺利通关。
只有依法办理进口报关手续,才能在巴西市场上取得成功并获得可持续发展的机会。
1.2文章结构文章结构部分是用来介绍文章的整体结构和内容安排。
在这一部分,我们可以说明文章的各个章节和子章节的标题及其所代表的主要内容。
对于《巴西国内进口报关规则》这篇长文,我们可以编写如下内容:2. 正文正文部分是对巴西国内进口报关规则进行详细介绍和解析的主要部分。
巴西推进多种产品的技术和合格认证要求Chapter 1: Introduction- Background of Brazil's push for multiple product technologies and certifications- Importance of technology and certifications in global trade- Purpose and objectives of the paperChapter 2: Overview of Brazil's Product Certification System - Overview of Brazil's regulatory framework for product certification- Key features of Brazil's certification system- Comparison with certification systems in other countries Chapter 3: Technology Requirements for Different Products- Technological requirements for agricultural products- Technological requirements for industrial products- Technological requirements for services products- Impact of technology on product quality and competitiveness Chapter 4: Qualification and Certification Procedure- Procedure for obtaining certification for different products- Organizations responsible for issuing certifications- Standards and requirements for obtaining certifications- Costs and timeframes associated with certificationChapter 5: Challenges and Opportunities for Business- Challenges faced by businesses in the certification process- Benefits of certification and opportunities for businesses- Strategies for overcoming challenges and maximizing opportunitiesChapter 6: Conclusion- Summary of the key findings of the paper- Recommendations for businesses and policymakers- Future research directionsChapter 1: IntroductionIn recent years, Brazil has made a significant push towards developing multiple product technologies and certifications as it seeks to capitalize on the benefits of high-value exports. Product technologies and certifications play a crucial role in the global trade and are highly sought after by firms that deal with export-oriented trade. As Brazil aims to expand its export base, it recognizes the importance of ensuring that its products comply with international standards and regulations.The significance of technology and certifications in global trade cannot be understated. Firms that hold such certifications are better placed to compete in the global marketplace as they can demonstrate their commitment to quality and compliance with international standards. This is crucial as it assures buyers that the products they are purchasing are authentic and meet the required standards.The purpose of this paper is to provide an overview of Brazil's product certification system, with a specific focus on the technological requirements for different products, the qualification and certification procedure, the challenges and opportunities for businesses, and recommendations for policymakers. The objectives of the paper are as follows:1. To identify the key features of Brazil's certification system and compare it with other countries' certification systems.2. To evaluate the technological requirements for different products and their impact on product quality and competitiveness.3. To analyze the procedure for obtaining certification for different products, the organizations responsible for issuing certifications, and the associated costs and timeframes.4. To identify the challenges faced by businesses in the certification process and the benefits of certification and opportunities for businesses.5. To provide recommendations for businesses and policymakers and outline future research directions.The paper is structured as follows: Chapter 2 provides an overview of Brazil's product certification system, while Chapter 3 discusses the technological requirements for different products. Chapter 4 analyzes the qualification and certification procedure, while Chapter 5 identifies the challenges and opportunities for businesses. Chapter 6 concludes the paper by summarizing the key findings and outlining the recommendations and future research directions.Chapter 2: Overview of Brazil's Product Certification SystemBrazil has implemented a product certification system that aims to provide assurances to buyers that products meet international standards and regulations. The certification system applies to various sectors, including industrial, agricultural, and consumer goods.The National Institute of Metrology, Quality and Technology(Instituto Nacional de Metrologia, Qualidade e Tecnologia - INMETRO), is the government agency responsible for administering the certification system. INMETRO's mission is to ensure "the quality of goods and services, the protection of the environment and the health and safety of consumers through the use of standards, metrology, and conformity assessment practices."INMETRO has established a range of conformity assessment schemes to assess and verify products against technical regulations and standards. The schemes cover a wide range of products, including electrical equipment, automotive parts, construction materials, toys, and food products.The certification process varies depending on the type of product being certified. Generally, the certification process involves three stages: application, evaluation, and issuance of the certification. Product manufacturers or importers submit an application to a certification body, which initiates the evaluation process. After completing the evaluation process, the certification body will issue the certification if the product meets the required standards.The certification bodies are accredited by INMETRO and must follow strict guidelines to ensure the credibility and impartiality of their certification services. To become accredited, certification bodies must demonstrate compliance with ISO/IEC 17065:2012, a standard that sets requirements for the certification of products, processes, and services.In addition to the product certification process, Brazil has established a range of voluntary certification schemes to promotesustainable production practices and enhance product quality. These schemes include the Brazilian Organic Agricultural Certification, the Brazilian Forest Certification System, and the Brazilian Fair Trade Certification.The Brazilian Organic Agricultural Certification, for example, provides certification of products that are grown and processed without the use of chemical fertilizers, pesticides, or genetically modified organisms (GMOs). The certification scheme helps to promote sustainable agricultural practices and provides assurances to consumers that the products they are purchasing are organic and free from harmful chemicals.In summary, Brazil has established a robust product certification system that provides assurances to buyers that products meet international standards and regulations. The system is administered by INMETRO, which has established a range of conformity assessment schemes to assess and verify products against technical regulations and standards. The certification bodies are accredited by INMETRO, and the certification process involves application, evaluation, and issuance of the certification. Additionally, Brazil has established a range of voluntary certification schemes to promote sustainable production practices and productquality.Chapter 3: Benefits and Challenges of Brazil's Product Certification SystemBrazil's product certification system offers several benefits for both buyers and manufacturers. However, it also presents some challenges that need to be overcome to ensure the effectiveness of the system.Benefits1. Increased confidence for buyers: Buyers can have increased confidence in the quality and safety of products they purchase due to the rigorous certification process that the products undergo.2. Access to international markets: Certification to international standards can help manufacturers access international markets as it gives their products a competitive edge.3. Protection of health and safety: The system promotes the protection of health and safety of consumers by ensuring that products are safe for use and meet technical regulations.4. Promotes sustainable production practices: The voluntary certification schemes promote sustainable production practices and help to address environmental and social issues.5. Builds credibility: By going through the certification process, manufacturers can build credibility and establish trust with their customers, enhancing their brand reputation.Challenges1. Cost: The cost of product certification can be high, and this can pose a barrier to smaller manufacturers. The cost includes testing and evaluation fees and the cost of implementing any necessary changes to meet the required standards.2. Time-consuming: The certification process can be time-consuming, and this can delay the entry of products into the market.3. Lack of information: Some manufacturers may lack information on the standards and regulations that they need to comply with to have their products certified.4. Limited capacity: The certification bodies may not have enough capacity to handle the high number of applications for certification.5. Counterfeit products: The system may not be effective in curbing the sale of counterfeit products in the market.To overcome these challenges, there is a need for increased awareness and education on the product certification system's standards and regulations. The government can also offer incentives to manufacturers to encourage them to participate in the certification process. Additionally, certifying bodies can consider offering reduced fees to encourage participation by smaller manufacturers.To address limited capacity challenges, certifying bodies can consider increasing their workforce, and the government can provide support for the establishment of more certifying bodies. Additionally, technological advancements, such as automation in the certification process, can help reduce the cost and time required for certification.To tackle the sale of counterfeit products, there is a need for increased enforcement of existing intellectual property laws andregulations. The government can also work with manufacturers to raise awareness of the issue and encourage them to take proactive steps to protect their intellectual property rights.In conclusion, the benefits of Brazil's product certification system are numerous, and the system helps to enhance the quality and safety of products. However, it also presents some challenges that need to be addressed to ensure the system's effectiveness. Increased awareness, education, and incentives can encourage manufacturers to participate in the certification process, and technological advancements can help reduce the cost and time required for certification.Chapter 4: The Importance of Standards and Regulations in Product Certification in BrazilStandards and regulations play a crucial role in product certification in Brazil. They serve as guidelines that manufacturers must follow to ensure that their products are safe, reliable, and meet the required quality standards. This chapter explores the importance of standards and regulations in the product certification system in Brazil.1. Ensuring Quality and SafetyStandards and regulations are designed to ensure quality and safety in the production, distribution, and use of products. In Brazil, products that do not meet the required standards and regulations are not allowed to enter the market, or if they do, they are recalled or banned. This helps to prevent harm to consumers and protect their rights.2. Promoting Fair CompetitionStandards and regulations promote fair competition in the market by ensuring that all manufacturers comply with the same requirements. This eliminates the advantage that some manufacturers may have if they produce substandard products that are cheaper than those that meet the required standards. This ensures that customers have access to quality products that are safe for use.3. Facilitating TradeStandards and regulations facilitate trade by ensuring that products meet the required standards and regulations in the countries where they are sold. This promotes international trade and enables manufacturers to access new markets. Additionally, it increases the confidence of foreign buyers in the quality and safety of products from Brazil.4. Promoting InnovationStandards and regulations also promote innovation by encouraging manufacturers to develop new products that meet the required standards and regulations. This helps to address emerging needs and challenges in the market and promote the adoption of new technologies and production practices that are safe for use.5. Protecting the EnvironmentStandards and regulations promote environmentally sustainableproduction practices by requiring manufacturers to comply with environmental regulations. This minimizes the negative impact on the environment during the production, distribution, and disposal of products. It promotes the development and adoption of green technologies and sustainable practices that protect natural resources.In conclusion, standards and regulations play a critical role in the product certification system in Brazil. They ensure quality and safety in the production, distribution, and use of products, promote fair competition, facilitate trade, promote innovation, and protect the environment. They are important in ensuring that the product certification system is effective in promoting consumer protection, promoting sustainable and safe production practices, and enabling access to international markets. Therefore, manufacturers must comply with the required standards and regulations to ensure that their products meet the required quality and safetystandards.Chapter 5: The Challenges Faced by Product Certification in BrazilDespite the importance of product certification in Brazil, there are several challenges that the system faces. This chapter explores some of the major challenges faced by product certification in Brazil.1. Lack of Trust and AwarenessOne of the major challenges faced by product certification in Brazil is the lack of trust and awareness among consumers. Many consumers do not understand the importance of productcertification and may not be willing to pay extra for certified products. Additionally, there have been some cases of fraudulent certifications, which further erode consumer trust in the system.2. Limited ResourcesProduct certification requires significant resources, including skilled personnel, laboratories, and equipment. However, many certification bodies in Brazil face limited resources, which can affect the quality and speed of certification processes. This can lead to longer certification times, delayed product launches, and increased costs for manufacturers.3. Complex Regulatory FrameworkThe regulatory framework for product certification in Brazil is complex and can be difficult to navigate for manufacturers, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises. The certification process involves multiple agencies and regulations, which can be challenging to understand and comply with, leading to delays in certification.4. Fragmentation of the Certification SystemThe certification system in Brazil is fragmented, with multiple agencies responsible for different aspects of product certification. This can lead to duplication of efforts, conflicting requirements, and delays in certification. Additionally, there is no single database or platform for sharing certification information, making it difficult for manufacturers and consumers to access certification data.5. Protectionist TendenciesBrazil has been criticized for protectionist tendencies that can limit the access of foreign products to the domestic market. This can make it difficult for foreign manufacturers to obtain product certification and access the Brazilian market, leading to trade barriers and reduced competition.To overcome these challenges, several measures can be taken. First, greater efforts are needed to raise awareness about the importance of product certification among consumers, to increase trust in the system. Second, more resources need to be allocated to certification bodies to improve their capacity to certify products efficiently and effectively.Third, the regulatory framework for product certification needs to be simplified and streamlined to make it easier for manufacturersto navigate. Fourth, efforts should be made to integrate the certification system through a centralized database or platform, to improve access to certification information.Finally, Brazil needs to reduce protectionist tendencies and promote greater openness to foreign products, to improve access to the Brazilian market and promote healthy competition.In conclusion, product certification in Brazil faces several challenges, including lack of trust and awareness, limited resources, a complex regulatory framework, fragmentation of the certification system, and protectionist tendencies. Addressing these challengesis critical to promoting the role of certification in promoting consumer protection, facilitating trade, promoting innovation, and protecting the environment. By doing so, Brazil can improve the effectiveness and efficiency of its certification system and promote sustainable economic development.。
巴西汽车产品准入管理及技术法规简介
巴西是拉丁美洲面积最大、人口最多的国家,位于南美洲的中心位置,除了智利和厄瓜多尔外,和南美洲的所有国家都接壤,巴西是南美共同市场(MERCOSUR)正式成员国(其它包括阿根廷、乌拉圭、巴拉圭、委内瑞拉,智利、玻利维亚、秘鲁、厄瓜多尔和哥伦比亚为其联系成员),因此巴西在南美洲对其它国家有较大的影响力,因此做好巴西市场,就能够辐射周边许多其它的南美国家。
近年来,包括汽车工业在内的巴西经济发展迅猛,与我国、印度、俄罗斯被国际社会并称为“金砖4国”。
在汽车工业方面,同我国相比,由于巴西从上世纪50年代开始,就采取宽松的外资引进政策,其汽车工业主要是国际跨国公司在巴西的工厂和车型,自主品牌的发展水平较低,这一点和亚洲泰国的情况比较类似。
因此我国企业在拓展巴西市场时,要考虑到起主要的竞争对手将是那些已不同程度本土化的国际汽车跨国公司。
虽然巴西对汽车产品建立了较完善的技术法规体系,但巴西市场的汽车产品管理体制仍然比较独特。
巴西市场另外一个特别需要注意的特点是,巴西政府一贯重视汽车环保和节能,在汽车新能源方面发展迅速,并已处于国际领先的地位,其中一是大力发展天然气车辆,主要是CNG车辆,二是大力发展使用生物燃料,主要是乙醇燃料,目前巴西已立法要求,所有的汽油必须混合25%的乙醇。
巴西近年还加紧研发生物柴油。
2008年开始生效的法律规定,对所有柴油掺加2%的生物柴油,2012年添加比例将提高到5%。
这主要是因为巴西具有丰富的天然气储量,巴西大部地区处于亚马逊河流域,土地广袤,大量的甘蔗种植和其它丰富的作物为乙醇的生产提供了源源不断、可再生的原材料。
巴西政府现不断地提高生物燃料的产能和产量,并不遗余力地推广汽车产品使用生物燃料,尤其是在乘用车和轻型车辆方面,为此在巴西的跨国公司也不断地对其产品进行不同程度的技术改造或改进,以适用巴西的新能源结构。
这一特点有可能发展成为巴西的汽车产品贸易壁垒,而且该壁垒是基于环境保护和节约不可再生能源,理由堂而煌之,因此我国企业对此要予以高度重视。
巴西对汽车产品的市场准入管理体制,与发达国家的国际通行惯例不同,不是由一个主要的部门对包括汽车产品的各方面和全过程统一进行管理,而且也没有对汽车产品形成一套完备的认证批准体系。
在管理和在制订、实施汽车技术法规方面,有许多的部门涉及并参与其中。
1、巴西计量、标准化和工业质量国家研究院
该研究院简称为:Inmerto,,负责巴西汽车及国民经济中其它涉及安全环
保产品的管理,其中也包括汽车产品,但该部门没有象欧洲联盟、南非等国家和地区对汽车产品建立完整的认证批准制度,只对汽车产品建立了部分认证批准,2.巴西国家运输委员会
该机关隶属于巴西运输部,对汽车产品的管理权限非常大,尽管它没有对汽车产品按照国际惯例进行型式认证管理,但却对汽车产品的制造和使用发布了一系列的决议,实际上就相当于技术法规,在巴西市场的汽车产品不满足这些决议要求,实际上是无法上路运行的,也就相当于进不了它的市场。
3.其它的管理部门和机构
● 巴西涉及汽车产品标准和技术法规的部门还包括:
● 巴西技术标准协会,负责制定巴西国家标准;
● 巴西国家环境委员会,即上文提到的Conama;
● 巴西国家计量、标准化和工业质量委员会;
● 巴西国家石油局,负责制定燃油,尤其是新能源,诸如生物燃油方面的标
准和法规;
巴西的汽车技术法规,除了Inmerto政令和Conama决议外,大部分项目是以Contran决议的形式出现的。
此外,巴西和阿根廷相互以零关税进口车辆协议。
巴西严格禁止二手车的进口,禁止柴油轿车的进口。
巴西汽车市场的这些独特之处,值得我方预进军该国汽车市场的企业重点关注。