实验室玻璃仪器大全
- 格式:docx
- 大小:210.50 KB
- 文档页数:3


化学实验室常用玻璃仪器及使用1. 烧杯(Beaker):烧杯是一种常见的玻璃容器,形状为圆柱形,通常用于盛装液体、溶液和反应物等物质。
烧杯的使用方法是将待测物质或反应物置于烧杯内,可以加热、加入试剂进行反应、搅拌等操作。
2. 容量瓶(Volumetric Flask):容量瓶是一种用于精确配制溶液的玻璃器皿。
容量瓶的特点是瓶颈较细,足量线以上有一个标定容量,容易判读所配溶液的体积。
使用容量瓶时,应根据需要取相应的溶液量,然后用试剂瓶灌满至足量线,最后用准确定量的方法加入试剂。
3. 量筒(Graduated Cylinder):量筒是用于精确测量液体体积的玻璃仪器。
量筒的体积刻度是沿着筒壁延伸的,并标有刻度,通常以毫升为单位。
使用量筒时,将需要测量的液体缓缓倒入,然后以眼平行刻度线读取液面高度。
4. 试管(Test Tube):试管是一种较长而细的玻璃管,通常用于容纳少量试液进行试验、进行加热反应等。
试管一般可用火焰加热,在进行反应时可以加入试剂进行观察。
5. 滴定管(Burette):滴定管是一种用于定量投加试剂的玻璃仪器,通常用于酸碱滴定等试验中。
滴定管上设有刻度线,可以准确地读取所需投加的溶液体积。
使用滴定管时,先用洗涤液洗净滴定管,然后倒入所要滴定的溶液, tilting the burette to adjust the initial volume to zero or a certain value.6. 分液漏斗(Separatory Funnel):分液漏斗是一种用于将两种不溶液体分离的器皿。
分液漏斗通常呈漏斗状,底部有特殊的球形阀门,用于控制液体的流出速度。
使用分液漏斗时,将需要分离的液体倒入漏斗中,并轻轻摇晃,让两种液体充分接触、分离。
7. 转化瓶(Erlenmeyer Flask):转化瓶是一种具有锥形底部和长颈口的玻璃瓶,通常用于混合和放置试剂、反应产物等物质。
转化瓶的底部形状可以使液体充分搅拌,另外,其长颈口可以减少蒸发和液体的溢出。

常见化学实验室玻璃仪器Chemical laboratory glassware is a common tool used in scientific research and chemical experiments. With the help of these glassware instruments, chemists can carry out various operations with precision and accuracy. In this article, we will introduce the most commonly used chemical laboratory glassware and their functions.1. Erlenmeyer Flask (锥形瓶)The Erlenmeyer flask, also known as a conical flask, is a commonly used glassware instrument in chemical laboratories. It has a cone-shaped bottom and a narrow neck. The wide base of the flask provides stability during stirring and mixing, while the narrow neck allows for easy pouring and reduces thepossibility of spills.The Erlenmeyer flask can be used for a variety of purposes, such as holding, mixing, heating, andboiling liquids. It is ideal for use with solutions that need to be swirled or mixed, as its shape makesit easy to agitate the contents.2. Beaker (烧杯)A beaker is a cylindrical-shaped glassware instrument with a flat bottom and a spout for pouringliquids. It is commonly used in chemical experiments for measuring or mixing liquids.Beakers come in a range of sizes, from small to large volumes, and are often graduated for easy measurement. They are also often used for heating solutions on a hot plate.3. Test Tube (试管)A test tube is a small, thin glass tube used in chemical experiments. It is typically cylindrical in shape with a rounded bottom and an open top. Some test tubes come with a stopper or a cap to seal the contents.Test tubes are often used for holding and mixing small amounts of liquids, as well as for conducting small-scale experiments. They are ideal for heating small amounts of solutions in a water bath.4. Graduated Cylinder (量筒)A graduated cylinder is a cylindrical-shaped glassware instrument with a narrow neck and a flat base. It is mainly used for measuring liquids in chemical experiments.The cylinder is designed with markings along the side, allowing for precise measurement of the volume of liquid it contains. It is often used in conjunction with a pipette or burette for precise measurement of liquids.5. Burette (分液漏斗)A burette is a long and narrow glasswareinstrument that is used for delivering solution to a reaction mixture in a controlled and precise manner.It is often used in titration experiments.Burettes are typically long, thin, and graduated with markings indicating the volume of solution that has been dispensed. It is also equipped with astopcock at the bottom to control the flow of solution.6. Pipette (移液管)A pipette is a thin glass tube with a narrow, tapered tip used for measuring and transferringliquids in chemical experiments. It is also used when very precise and accurate measurements of fluid volume are required.There are two types of pipettes: volumetric and micropipette. Volumetric pipettes are used for measuring a precise volume of solution, while micropipettes are used for measuring very small volumes of liquids.7. Funnel (漏斗)A funnel is a glass cone-shaped instrument thatis used to channel liquids or fine-grained materials into a container with a small opening. It is commonly used in filtration experiments to transfer a liquid from one flask to another.Funnels are also used in decanting experiments, where a liquid is slowly poured off a precipitate, andin separating the different layers of immiscible liquids.8. Petri Dish (培养皿)A Petri dish is a small, shallow glassware instrument that is used for the culturing of microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi. It is often used in microbiology experiments.Petri dishes are made with a lid to prevent contamination of the culture media inside. They are also equipped with a flat bottom to help spread the culture media evenly.9. Watch Glass (蒸发皿)A watch glass is a circular-shaped glassware instrument with a flat bottom and a slightly curved top. It is mainly used for evaporation experiments and to hold small quantities of solids.Watch glasses are often used to cover evaporating dishes to prevent dust or other contaminants from entering or to heat small amounts of liquid over a Bunsen burner.10. Thermometer (温度计)A thermometer is a glassware instrument used for measuring the temperature of liquids or gases in chemical experiments. It is available in both analog and digital forms.Thermometers are typically made with a long, skinny glass bulb filled with a liquid, usuallymercury or alcohol. As the temperature increases, the liquid expands and rises in the thin, calibrated tube. The temperature is read off the scale marked on the glassware instrument.In conclusion, chemical laboratory glassware is an essential tool in scientific research and chemical experiments. Each instrument has its purpose and is designed for precision and accuracy. It is essential to use the appropriate glassware to ensure accurate and reliable results and to maintain the safety of the experimenters.。
实验室常用玻璃仪器[学习目标]1.了解化学实验常用仪器的类别。
2.了解化学实验常用玻璃仪器的规格、性能、用途。
3. 掌握常见玻璃仪器的使用、洗涤及干燥方法。
[学习内容]一、玻璃仪器分类化学实验常用的仪器中,大部分为玻璃制品和一些瓷质类仪器。
瓷质类仪器包括蒸发皿、布氏漏斗、瓷坩埚、瓷研钵等。
玻璃仪器种类很多,按用途大体可分为容器类、量器类和其他仪器类。
容器类包括试剂瓶、烧杯、烧瓶等。
根据它们能否受热又可分为可加热的仪器和不宜加热的仪器。
量器类有量筒、移液管、滴定管、容量瓶等。
量器类一律不能受热。
其他仪器包括具有特殊用途的玻璃仪器,如冷凝管、分液漏斗、干燥器、分馏柱、砂芯漏斗、标准磨口玻璃仪器等。
标准磨口玻璃仪器,是具有标准内磨口和外磨口的玻璃仪器。
标准磨口是根据国际通用技术标准制造的,国内已经普遍生产和使用。
使用时根据实验的需要选择合适的容量和口径。
相同编号的磨口仪器,它们的口径是统一的,连接是紧密的,使用时可以互换,用少量的仪器可以组装多种不同的实验装置,通常应用在有机化学实验中。
目前常用的是锥形标准磨口,其锥度为1:10,即锥体大端直径与锥体小端直径之差:磨面锥体的轴向长度为1:10。
根据需要,标准磨口制作成不同的大小。
通常以整数数字表示标准磨口的系列编号,这个数字是锥体大端直径(以mm为单位)最接近的整数。
常用标准磨口系列见表1-7。
表1-7常用标准磨口系列有时也用D/H两个数字表示标准磨口的规格,如14/23,即大端直径为14.5mm,锥体长度为23mm。
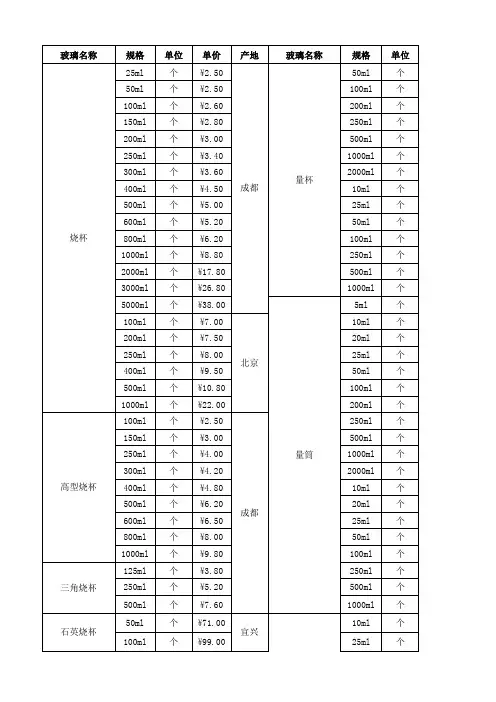
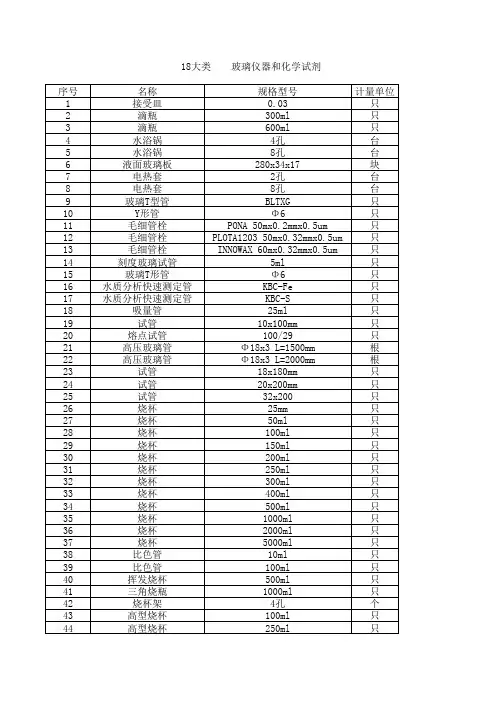
二、常用的玻璃仪器化学实验室常用的玻璃及其它简单仪器见图1-1图示烧杯试管碘量瓶容量瓶蒸发皿坩埚研钵蒸馏烧瓶洗气瓶干燥器冷凝管蒸馏头接头和塞子尾接管石棉网药匙漏斗架坩埚钳夹子铁架台试管夹泥三角点滴板水浴锅三脚架图1-1 化学实验室常见的玻璃等仪器三、玻璃仪器的洗涤1、洗涤液的选择洗涤玻璃仪器时,应根据实验要求、污物的性质及玷污程度,合理选用洗涤液。



实验室常用玻璃仪器的正确使用方法和注意事项!一、试管☆(一)主要作用:1、在常温或加热时,用作少量物质的反应容器;2、盛放少量固体或液体;3、用作收集少量气体。
(二)留意事项:1、应用拇、食、中三指握持试管上沿处,振荡时要腕动臂不动;2、作反应容器时液体不超过试管容积的1/2,加热时不超过1/3;3、加热前试管外面要擦干,加热时要用试管夹;4、加热液体时,管口不要对着人,并将试管倾斜与桌面成45°;5、加热固体时,管底应略高于管口。
二、锥形瓶☆(一)主要作用:1、加热液体;2、作气体发生的反应器;3、在蒸馏试验中作液体接收器。
(二)操作要领:1、盛液不能过多;2、滴定时,只需振荡不搅拌;3、加热时,需垫石棉网。
三、试剂瓶☆(一)主要作用:1、广口瓶用于存放固体药品,也可用来装配气体发生器;2、细口瓶用于存放液体药品。
(二)操作要领:1、不能加热、不能在瓶内配制溶液、磨口塞保持原配;2、酸性药品、具有氧化性的药品、有机溶剂要用玻璃塞,碱性试剂要用橡胶塞;3、对见光易变质的要用棕色瓶。
四、滴瓶☆(一)主要作用:试验时盛装需按滴数加入液体的容器,与胶头滴管配套使用(二)操作要领:1、使用时胶头在上,管口在下;2、滴管管口不能深化受滴容器;3、用过后应马上洗涤洁净并插在干净的试管内,未经洗涤的滴管严禁吸取别的试剂;4、滴瓶上的滴管必需与滴瓶配套使用。
五、量筒☆(一)主要作用:量筒是用于度量液体体积(二)操作要领:量筒倾斜握在手,先倒后滴把量瞅;平视凹液最低处,三线一齐为读数。
(三)留意事项:1、不能加热,不能用做反应容器;2、不能在其中溶解物质、稀释和混合液体。
六、烧杯☆(一)主要作用:1、常温或加热条件下大量物质的反应容器;2、配制溶液用。
(二)操作要领:1、反应液体不得超过烧杯容量的2/3;2、加热前将烧杯外壁擦干,烧杯底要垫石棉网;3、玻璃棒不断搅拌且勿触及杯壁。
七、酒精灯☆(一)主要作用:试验室加热用(二)操作要领:1、加入的酒精以灯的容积的1/2至2/3为宜,使用时用漏斗添加酒精;2、用火柴点燃,肯定不能用燃着的酒精灯去点另一酒精灯;3、熄灭时要用酒精灯灯盖盖灭,不行以用嘴吹灭。

---------------------------------------------------------------最新资料推荐------------------------------------------------------ 实验室常用玻璃仪器的基础知识实验室常用玻璃仪器的基础知识1/ 40使用玻璃仪器的原因? 玻璃仪器具有一系列可贵的性质,它有很高的化学稳定性、热稳定性,有很好的透明度、一定的机械强度和良好的绝缘性能。
? 玻璃原料来源方便,可以用多种方法按需要制成各种不同形状的产品。
---------------------------------------------------------------最新资料推荐------------------------------------------------------ 玻璃仪器常用的玻璃仪器玻璃仪器的洗涤洁净剂及其使用范围玻璃仪器的干燥与保存3/ 40常用玻璃仪器精密仪器非精密仪器---------------------------------------------------------------最新资料推荐------------------------------------------------------ 精密玻璃仪器?滴定管?移液管(单标线吸量管) ?分度吸量管 ?容量瓶 ?量筒、量杯5/ 40滴定管规格 : 容量 /mL 5 、 10 、 25 、 50 、100 无色,棕色,量出式分类:酸式,碱式(或聚四氟乙烯活塞) 主要用途 : 活塞要原配;漏水的不能使用;不能加热;不能长期存放碱液;碱式管不能放与橡皮作用的滴定液.---------------------------------------------------------------最新资料推荐------------------------------------------------------ 移液管(单标线吸量管)规格:滴定管容量25mL,储液瓶容量 1000mL,量出式主要用途 : 准确地移取一定量的液体使用注意事项 : 不能加热;上端和尖端不可磕破7/ 40分度吸量管规格:容量/mL 0.1、0.2、0.25、 0.5、1、2、5、10、25、50 类型:完全流出式不完全流出式主要用途:准确地移取各种不同量的液体使用注意事项:不能加热;上端和尖端不可磕破---------------------------------------------------------------最新资料推荐------------------------------------------------------ 移液管和刻度吸管的区别1.大肚移液管只能移一个体积的液体。

化学实验室常用玻璃仪器及使用1. 烧杯(Beaker):烧杯是一种常见的容器,形状为圆柱形,底部较宽。
它主要用于盛放液体、搅拌物质和进行少量的加热。
使用时,将待盛放的液体或溶液倒入烧杯中,可以通过刻度线判断体积,根据需要可以进行加热、搅拌等操作。
2. 烧瓶(Flask):烧瓶是一种颈部较长的容器,形状为圆底或扁底。
它主要用于制备溶液、蒸馏、回流等操作。
使用时,将待制备的溶液或反应物倒入烧瓶中,可以通过刻度线判断体积,根据需要可以连接其他器材进行蒸馏、回流等操作。
3. 试管(Test tube):试管是一种较小的圆筒形容器,通常用于小规模试验和储存少量物质。
使用时,将待操作物质倒入试管中,可以通过刻度线判断体积,可以通过加热、搅拌等操作进行实验。
4. 显微镜片(Microscope slide):显微镜片是一种长方形的平板,用于放置待观察的样品。
在化学实验中,显微镜片通常用于观察晶体结构、显微镜下的实验等。
使用时,将待观察的样品放在显微镜片上,通过显微镜放大观察。
5. 滴定管(Burette):滴定管是一种具有刻度的玻璃管,用于定量滴定,测量溶液的体积。
滴定管具有放置液体的储液器和滴液的流通管道,通过旋塞控制液体的流量和滴定过程。
使用时,打开旋塞,将待滴定的试剂滴入容器中,直到滴定终点出现颜色变化,记录滴定所用的体积,根据所需计算出待测溶液的浓度或反应物之间的摩尔比。
6. 双口胶头滴管(Dropping pipette):双口胶头滴管是一种玻璃仪器,通常用于降低溶液的浓度、调整pH值、标定浓度等。
使用时,将需要的试剂吸入滴管中,通过挤压滴管胶头使溶液缓慢地滴入反应容器。
除了上述常见的玻璃仪器,化学实验室中还有许多其他的玻璃仪器,如试剂瓶、漏斗、生物反应器、取样针等。
每一种仪器都有着特定的用途和使用方法。
在进行化学实验时,需要根据实验的目的和要求选择合适的玻璃仪器,并且要正确使用和操作,以确保实验的准确性和安全。
常用实验玻璃仪器名称和用途
1、烧杯:它是一种用于烧制和溶解的实验仪器,可以承受很高的
温度,具有耐腐蚀性,即使暴露在高浓度的强酸中,也不会发生腐蚀。
它的主要功能是将溶液加热到沸腾并将溶液过程中产生的残留物收集
起来。
2、分杯:分杯用于分离混合液中的溶质,并将分离出的溶质收集起来。
它可以分离成不同浓度的溶液,也可以收集沉淀物。
分杯的结构通常
以烧杯的形状为准,不同的分杯结构有不同的体积,以满足不同容量
的溶液收集需要。
3、圆底烧瓶:它是使用较多的实验仪器之一,通常用来收集溶质产生
的气体或液体,可知它的应用非常广泛,主要用于化学反应的称重,
液体的蒸发和除尘等实验。
圆底烧瓶一般都是由玻璃制成,可以抵抗
腐蚀,容量为250ml或500ml,有密封法兰和无密封法兰两种,其中密
封法兰可以用于精密分析或保持液体的气体质量等实验。
4、滴定管:它是一种容器形的玻璃仪器,用于滴定实验或校准实验。
它具有恒定的容积,在安装时,滴定管内和内表面会涂有标记,以保
证滴定时准确,滴定管的结构一般是圆柱形或椭圆形,其容量一般为
100ml 到1000ml 之间。
5、比重瓶:它是一种用于测定液体密度的实验仪器,它采用玻璃制成,长期在液体和气体中工作,具有良好的耐腐蚀性。
比重瓶通常有三部
分组成:数显表、表壳和比重瓶,这三部分的功能是在溶液中悬浮,
以测量它的密度。
比重瓶的容量一般为100ml,200ml,300ml,400ml,500ml等,可以用于测定各种液体或溶液的密度。
常用实验玻璃仪器名称和用途
1、烧杯:烧杯是常用的实验玻璃仪器,主要用于化学实验,通常用作混合物加热分解,精细提纯,或者将物质进行焓分析等;
2、滴定管:滴定管是带有标尺的玻璃管,在底部有一个滴定口,主要用于滴定解决方案中待测试物质的量,滴定管是实验室中最常见的装置;
3、化学隔板:也称为折面板,由折叠部分和桨叶部分组成,主要用于固定、保护试样,是常用的化学实验仪器;
4、烧瓶:是实验玻璃仪器中最普遍的设备之一,主要用于熔融、混合、引沸、收集液体、分离液体等,是制备有机溶液的常用设备;
5、分离漏斗:是实验玻璃玻璃仪器中的一种,具有膨胀沟口和分离室,用于分离或过滤混合物,并可以采用吸引瓶或灌装烧瓶进行收集;
6、容量瓶:容量瓶也是实验玻璃仪器中的一种,常用于含水量测定、液体蒸发、溶剂减量、浓度测定等操作;
7、带嘴烧杯:烧杯在实验中常用,它有厚壁、薄壁、带嘴、全底和半底五种类型。
带嘴烧杯是实验室中比较常用的装置,用于加热和蒸发升华分离液体;
8、蒸馏装置:蒸馏装置是一种实验仪器,由容器、口和管等组成,用于收集液体中高沸点物质,不同物质按沸点高低逐次收集。
9、安全端头装置:安全端头装置是由安全瓶、阀门和烧杯等组成的球形装置,主要用于多步实验,避免反应的过程中的压力变化,保护实验室内人员的安全。
化验室常用玻璃仪器一、常用玻璃仪器的主要用途、使用注意事项一览表二、玻璃仪器的洗涤方法1.洁净剂及其使用范围最常用的洁净剂有肥皂、合成洗涤剂(如洗衣粉)、洗液(清洁液)、有机溶剂等。
肥皂、合成洗涤剂等一般用于可以用毛刷直接刷洗的仪器,如烧瓶、烧杯、试剂瓶等非计量及非光学要求的玻璃仪器。
肥皂、合成洗涤剂也可用于滴定管、移液管、量瓶等计量玻璃仪器的洗涤,但不能用毛刷刷洗。
洗液多用于不能用毛刷刷洗的玻璃仪器,如滴定管、移液管、量瓶、比色管、玻璃垂熔漏斗、凯氏烧瓶等特殊要求与形状的玻璃仪器;也用于洗涤长久不用的玻璃仪器和毛刷刷不下的污垢。
2.洗液的配制及说明铬酸清洁液的配制:处方1 处方2重铬酸钾(钠) 10g 200g纯化水 10ml 100ml(或适量)浓硫酸 100ml 1500ml制法:称取处方量之重铬酸钾,于干燥研钵中研细,将此细粉加入盛有适量水的玻璃容器内,加热,搅拌使溶解,待冷后,将此玻璃容器放在冷水浴中,缓慢将浓硫酸断续加入,不断搅拌,勿使温度过高,容器内容物颜色渐变深,并注意冷却,直至加完混匀,即得。
(2(3(4(7)用铬酸清洁液洗涤仪器,是利用其与污物起化学反应的作用,将污物洗去,故要浸泡一定时间,一般放置过夜(根据情况);有时可加热一下,使有充分作用的机会。
3.洗涤玻璃仪器的方法与要求(1)一般的玻璃仪器(如烧瓶、烧杯等):先用自来水冲洗一下,然后用肥皂、洗衣粉用毛刷刷洗,再用自来水清洗,最后用纯化水冲洗3次(应顺壁冲洗并充分震荡,以提高冲洗效果)。
计量玻璃仪器(如滴定管、移液管、量瓶等):也可用肥皂、洗衣粉的洗涤,但不能用毛刷刷洗。
(2)精密或难洗的玻璃仪器(滴定管、移液管、量瓶、比色管、玻璃垂熔漏斗等):先用自来水冲洗后,沥干,再用铬酸清洁液处理一段时间(一般放置过夜),然后用自来水清洗,最后用纯化水冲洗3次。
(3)洗刷仪器时,应首先将手用肥皂洗净,免得手上的油污物沾附在仪器壁上,增加洗刷的困难。
实验室玻璃仪器的认识
实验室玻璃仪器是科学实验室中常见的实验器材,由玻璃材料制成。
玻璃仪器在实验室中用于各种实验操作,包括容器和器具。
以下是一些常见的实验室玻璃仪器及其功能:
1. 烧杯:用于加热、混合和储存液体试样。
2. 坩埚:用于加热和熔化固体样品,通常用于高温实验。
3. 试管:用于储存、混合和加热液体样品。
4. 烧瓶:用于将反应物加热至沸腾,并收集产生的气体。
5. 筒状测量瓶:用于准确测量液体体积。
6. 密度计:用于测量液体或固体样品的密度。
7. 滴定管:用于定量分析和滴定实验。
8. 片状玻璃器皿:如玻璃光滑板和角片,用于实验室中的观察和实验操作。
9. 过滤漏斗:用于分离固体和液体,通过滤纸或滤膜,将固体颗粒从液体中过滤出来。
10. 温度计:用于测量液体或气体的温度。
实验室玻璃仪器的选择和使用需要注意以下事项:
1. 应定期检查和维护实验室玻璃仪器,确保其完整和正常工作。
2. 玻璃仪器应该避免突然的温度变化,特别是在加热和冷却过程中,以免产生热应力导致破裂。
3. 玻璃仪器在使用前应清洗干净,以确保实验结果的准确性。
4. 使用玻璃仪器时要小心轻放,避免碰撞或摔落。
5. 如果玻璃仪器出现破损或裂纹,应立即停止使用,并进行修复或更换。
通过正确使用和维护实验室玻璃仪器,可以确保实验操作的安全性和准确性。
常用的玻璃量器进入我们的实验室后,容量的准确与否,直接影响分析结果的准确性。
为了获得准确的测量结果,用于定量分析的常用玻璃量器必须经过检定合格。
实验室玻璃仪器大全哪家好?您可以选择天长市华玻实验仪器厂,下面小编为您简单介绍,希望能给您带来一定程度上的帮助。
根据国际单位制(SI)规定容积的基本单位为立方米(m3),1升(l)=1dm。
(10qm。
)。
旧的定义,1升=1.000028dm3,相差甚微,可以忽略不计。
升是温度为3.980C时一千克水的体积,但这一温度过低,不合实际应用,一般用200C为标准温度以计算容量仪器的容积。
既然以200C为标准温度以计算玻璃仪器的容积,则校准与使用都应在200C下进行,这实际上是有困难的。
温度改变,仪器的容量以及溶液的体积都将发生改变。
仪器容量
的改变是由玻璃膨胀引起的,但玻璃的膨张系数极小,每差l0C只改变O.0026%,可以忽略。
液体体积则是由于密度的改变,改变较大。
如1升容量瓶,当温度升高50C,其体积改变可大于1m1,所以应进行换算。
容量瓶的校准:将待校准的容量瓶洗净晾干,准确称重后用放至室温的纯水用茎长可达刻度线下的漏斗加入,使不致润湿刻度线上瓶颈部分,慢慢加水至刻度线下,避免瓶壁有气泡,用一小玻管滴加至刻度线上缘,称重,计算其真实体积(200C)。
天长市华玻实验仪器厂(原天长市长城玻璃仪器制造厂)位于长江之滨的皖东明珠——天长市。
东临扬州与南京接壤。
本厂是国内专业制造高品质,复杂型玻璃仪器的厂家,已有18年生产经验,在国内及周边地区玻璃仪器行业具有影响力,本厂具有高仿进口产品的能
力,本厂为了达到进口质量和外观,不惜重金购买德国B2B全自动玻璃机床2台,高薪聘用高级工程师数名,这些技术人才,具有非标模具设计及开发的能力,制造工艺的创新,机床的操作技能及国外加工的理念。
另外我们对玻璃选材及厚度,清洗,包装,一些细节也十分苛刻。
由于质量过关和服务到位,一直为国内玻璃仪器制造商做贴牌生产,也为国外客户生产了大批优质玻璃仪器。