springMVC 个人学习笔记
- 格式:docx
- 大小:1.79 MB
- 文档页数:25

spring MVC原理及配置springmvc原理及配置springmvc原理及配置1.springmvc详述:springmvc就是spring提供更多的一个强悍而有效率的web框架。
借助注释,springmvc提供更多了几乎就是pojo的研发模式,使控制器的研发和测试更加直观。
这些控制器通常不轻易处置命令,而是将其委托给spring上下文中的其他bean,通过spring的倚赖转化成功能,这些bean被转化成至控制器中。
springmvc主要由dispatcherservlet、处理器映射、处理器(控制器)、视图解析器、视图组成。
他的两个核心是两个核心:处理器映射:选择使用哪个控制器来处理请求视图解析器:选择结果应该如何渲染通过以上两点,springmvc确保了如何挑选掌控处置命令和如何挑选视图展现出输入之间的松耦合。
2.springmvc运行原理这里写图片描述(2)找寻处理器:由dispatcherservlet控制器查阅一个或多个handlermapping,找出处置命令的controller。
(3)调用处理器:dispatcherservlet将请求提交到controller。
(4)(5)调用业务处置和回到结果:controller调用业务逻辑处置后,回到modelandview。
3.springmvc接口解释(1)dispatcherservlet接口:spring提供的前端控制器,所有的请求都有经过它来统一分发。
在dispatcherservlet将请求分发给springcontroller 之前,需要借助于spring提供的handlermapping定位到具体的controller。
(2)handlermappingUSB:能够完成客户请求到controller映射。
(3)controller接口:须要为mammalian用户处置上述命令,因此同时实现controllerUSB时,必须确保线程安全并且可以器重。

SpringMVC源码总结(⼀)HandlerMapping和HandlerAdapter⼊门刚接触SpringMVC,对它的xml⽂件配置⼀直⽐较模模糊糊,最近花了⼀点时间稍微看了下源代码,再加上调试,开始逐渐理解它,⽹上的类似的内容有很多,写本⽂主要是⾃⼰加深⼀下理解。
本⽂适合⽤过SpringMVC的开发者,⾔归正传,⾸先搭建⼀个最简单的⼯程体验⼀下。
该⼯程是基于maven的,pom配置不再说明,所使⽤的spring版本4.0.5。
⾸先是web.xml⽂件配置,最简单的配置Java代码1. <!DOCTYPE web-app PUBLIC2. "-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Web Application 2.3//EN"3. "/dtd/web-app_2_3.dtd" >4.5. <web-app>6. <display-name>Archetype Created Web Application</display-name>7. <servlet>8. <servlet-name>mvc</servlet-name>9. <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>10. <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>11. </servlet>12.13. <servlet-mapping>14. <servlet-name>mvc</servlet-name>15. <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>16. </servlet-mapping>17. </web-app>然后是mvc-servlet.xml⽂件的配置,上⾯配置DispatcherServlet会默认加载[servlet-name]-servlet.xml⽂件。

spring mvc学习教程(一)-入门实例引言1.MVC:Model-View-Control框架性质的C层要完成的主要工作:封装web请求为一个数据对象、调用业务逻辑层来处理数据对象、返回处理数据结果及相应的视图给用户。
2.简要概述springmvcSpring C 层框架的核心是DispatcherServlet,它的作用是将请求分发给不同的后端处理器,也即使用了一种被称为Front Controller 的模式(后面对此模式有简要说明)。
Spring 的C 层框架使用了后端控制器来、映射处理器和视图解析器来共同完成C 层框架的主要工作。
并且spring 的C 层框架还真正地把业务层处理的数据结果和相应的视图拼成一个对象,即我们后面会经常用到的ModelAndView 对象。
一、入门实例1. 搭建环境在spring的官方API文档中,给出所有包的作用概述,现列举常用的包及相关作用:org.springframework.aop-3.0.5.RELEASE.jar:与Aop编程相关的包org.springframework.beans-3.0.5.RELEASE.jar:提供了简捷操作bean的接口org.springframework.context-3.0.5.RELEASE.jar:构建在beans包基础上,用来处理资源文件及国际化。
org.springframework.core-3.0.5.RELEASE.jar:spring核心包org.springframework.web-3.0.5.RELEASE.jar:web核心包,提供了web层接口org.springframework.web.servlet-3.0.5.RELEASE.jar:web 层的一个具体实包,DispatcherServlet也位于此包中。
后文全部在spring3.0 版本中进行,为了方便,建议在搭建环境中导入spring3.0 的所有jar 包(所有jar 包位于dist 目录下)。

Spring框架从创建伊始就致力于为复杂问题提供强大的、非侵入性的解决方案。
Spring 2.0当中为缩减XML配置文件数量引入定制命名空间功能,从此它便深深植根于核心Spring框架(aop、context、jee、jms、 lang、tx和util命名空间)、Spring Portfolio项目(例如Spring Security)和非Spring项目中(例如CXF)。
Spring 2.5推出了一整套注解,作为基于XML的配置的替换方案。
注解可用于Spring管理对象的自动发现、依赖注入、生命周期方法、Web层配置和单元/集成测试。
探索Spring 2.5中引入的注解技术系列文章由三部分组成,本文是其中的第二篇,它主要讲述了Web层中的注解支持。
最后一篇文章将着重介绍可用于集成和测试的其它特性。
这个系列文章的第一部分论述了Java注解(annotation)是如何代替XML来配置Spring管理对象和依赖注入的。
我们再用一个例子回顾一下:@Controllerpublic class ClinicController {private final Clinic clinic;@Autowiredpublic ClinicController(Clinic clinic) {this.clinic = clinic;}...@Controller表明ClinicController是Web层组件,@Autowired请求一个被依赖注入的Clinic实例。
这个例子只需要少量的XML语句就能使容器识别两个注解,并限定组件的扫描范围:<context:component-scanbase-package="org.springframework.samples.petclinic"/>这对Web层可谓是个福音,因为在这层Spring的XML配置文件已日益臃肿,甚至可能还不如层下的配置来得有用。

SpringMVC公开课笔记高浩阳2014-11-29目录1SpringMVC框架 (2)1.1SpringMVC框架 (2)1.2SpringMVC组件总结 (2)2开发SpringMVC的第一个程序 (3)2.1准备环境 (3)2.2开发SpringMVC的第一个程序 (3)2.2.1创建Java Web工程 (3)2.2.2向工程中填充SpringMVC的jar包 (3)2.2.3配置前端控制器 (4)2.2.4创建一个配置文件springmvc.xml(名称不固定) (7)2.2.5配置处理器映射器HandlerMapping (8)2.2.6配置处理器适配器HandlerAdapter (9)2.2.7配置视图解析器ViewResolver (12)2.2.8编写Handler (13)2.2.9在springmvc.xml中配置helloAction.java (16)2.2.10将工程部署到tomcat,启动tomcat (17)2.3小结: (18)3注解开发第一个例子 (19)3.1新建工程SpringMVCTest02 (19)3.2在springmvc.xml中配置 (20)3.3开发action (21)3.4配置action (22)3.5部署工程,运行Tomcat (24)4注解开发学生信息管理功能 (24)5SpringMVC特点 (33)6和Jquery easyui 整合完成数据列表 (33)1SpringMVC框架1.1SpringMVC框架1. 用户发起请求request(比如请求链接叫http://www.xxx/user.action)注册用户信息。
2. SpringMVC通过DispatcherServlet接受请求。
DispatcherServlet是一个前端控制器(想到struts2在web.xml配置一个filter前端控制器)相当于控制器Controller3. DispatcherServlet调用HandlerMapping(处理器映射器)根据user.action找到处理器(Handler)HandlerMapping负责分局user.action这个链接找到Handler,根据xml配置或注解配置找到Handler4. HandlerMapping将找到的Handler给DispatcherServlet前端控制器5. DispatcherServlet前端控制器调用HandlerAdapter(处理器适配器)去执行Handler处理器适配器负责执行Handler6. Handler将处理结果返回给HandlerAdapter(处理器适配器)处理结果就是ModelAndView(封装了模型数据和视图)7. DispatcherServlet调用视图解析器ViewResolver去解析视图8. 将View给用户相应1.2SpringMVC组件总结1. DispatcherServlet前端控制器(不需要程序员写)负责框架调度,相当于中央处理器基本controller控制器功能:接收用户request请求和给用户response响应2. HandlerMapping(处理器映射器)(不需要程序员写)负责根据action的连接找到Handler处理器(理解成写的action)3. HandlerAdapter(处理器适配器)(不需要程序员写)负责去执行Handler4. **Handler处理器需要程序员写理解成struts里边的action,需要程序员写action类,这个action类符合适配器的执行规则。

SpringBootActuator学习笔记spring boot ActuatorActuator概述Actuator指的是负责和移动装置的组件。
通过Actuator暴露的端点我们可以获取⼀个正在运⾏中的应⽤内部的状态导⼊依赖<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId></dependency>Actuator具备⼀些开箱即⽤的端⼝Endpoints id描述HTTP⽅法是否敏感信息auditevents显⽰当前应⽤程序的审计事件信息GET Yesbeans显⽰应⽤上下⽂中创建的所有Bean GET Yescaches显⽰可⽤缓存信息GET Yesconditions显⽰⾃动装配类的状态及及应⽤信息GET Yesconfigprops显⽰所有 @ConfigurationProperties 列表GET Yesenv显⽰ ConfigurableEnvironment 中的属性GET Yesflyway显⽰ Flyway 数据库迁移信息GET Yeshealth显⽰应⽤的健康信息(未认证只显⽰status,认证显⽰全部信息详情)GET Noinfo显⽰任意的应⽤信息(在资源⽂件写info.xxx即可)GET Noliquibase展⽰Liquibase 数据库迁移GET Yesmetrics提供应⽤运⾏状态的完整度量指标报告GET Yesmappings显⽰所有 @RequestMapping 路径集列表GET Yes scheduledtasks显⽰应⽤程序中的计划任务GET Yessessions允许从Spring会话⽀持的会话存储中检索和删除⽤户会话。

什么是SpringMVC?⼀、什么是SpringMVC?1.SpringMVC 是⼀种基于 Java 的实现 MVC 设计模型的请求驱动类型的轻量级 Web 框架,属于SpringFrameWork的后续产品,已经融合在Spring Web Flow 中。
2.SpringMVC = Spring +MVCspring mvc类似于struts的⼀个MVC开框架,其实都是属于spring,spring mvc需要有spring的架包作为⽀撑才能跑起来.spring是⼀个⼀站式的框架,提供了表现层(springmvc)到业务层(spring)再到数据层(springdata)的全套解决⽅案;spring的两⼤核⼼IOC(控制反转)和AOP(⾯向切⾯编程)更是给我们的程序解耦和代码的简介提供了⽀持。
Spring框架图:从Spring的结构图可以看出,springMVC位于spring web端的⼀个框架,是⼀种基于Java的实现了Web MVC设计模式的请求驱动类型的轻量级Web框架,即使⽤了MVC架构模式的思想,将web层进⾏职责解耦。
附:基于请求驱动指的就是使⽤请求-响应模型。
从名字上就可以窥探出,Spring>SpringMVC,那么事实上,spring和SpringMVC是⼀种⽗⼦关系。
SpringMVC是spring扩展出的⼀个应⽤于web端的框架。
在这⾥需要注意的⼀点,就是到底什么是⽗⼦容器关系:spring主要的作⽤是黏合其他模块组件,进⾏统⼀管理,springmvc则主要是负责web端。
那么,我们都知道,我们在应⽤spring的时候,可以使⽤注⼊。
这个时候,如果我们的web端是⽤的SpringMVC,这个时候,controller理论上是通过SpringMVC去注⼊,但是,使⽤spring注⼊,同样是可⾏的。
同理,service等层,使⽤SpringMVC配置的统⼀扫描装配也是可以的。

程序员实习日记程序员实习日记范文大全程序员实习日记一今天就简单聊聊上面的Struts+Spring+Hibernate吧。
Struts 代表:表示层;Spring代表:业务逻辑层;Hibernate则代表持久层。
他们是目前在Java Web编程开发中用得最多的框架,其实这样区分是为了适应软件开发过程中各个分工部门之间保持一致性的需要。
说得简单点就是大家都在一个模式下写代码,这样就能保证写出来的程序能被每一个人都能够读懂,而且有些基本的东西它可以自动帮你生成,不用你自己一个一个的敲了,达到了代码复用。
这样保证可读性的同时也提高了开发效率,从而降低了成本。
Struts这个框架其实就是Java MVC设计模式中(简称Model1与Model2)Model2的一个具体实现,Spring 则通过提供ICO(控制反转,也称依赖注入)实现了对对象甚至事务(如声明式事务)的集中管理,此外还引入了AOP(对向切面编程),当然也完全兼容其它框架。
Hibernate吗,就是一个实现对象与关系映射的中间件,大家知道,现在的主流数据库还是关系型的,但编程却已经采用了面向对象的思想,如何让编程人员能像操作对象一样,操纵数据库里的数据呢?Hibernate就是这样一种框架。
以前Java程序员与数据库打交道都是通过JDBC,还要写 SQL语句,不过Hibernate 彻底改变了这一切,它在JDBC之上又作了一次封装,从而实现了不用写SQL语句就可以实现操作数据库。
值得提醒的是,这三个框架都是轻量级的,没有侵入性或者侵入性很低,不像EJB这样的重量级框架,它们都能最大限度的.实现代码的可复用。
程序员实习日记二又是一个雨天,早上上班时间还下得很大,就没起床了。
直接电话向经理请了假,说是头痛下午再过去了,还好经理爽快的答应了,要不一去就会露馅现出原形的!上午上网,下载了三个网站源码,本想找个部署运行看下效果,结果一看,后台数据库全不一样:分别使用了三个不同的数据库(SQL Server2000、Oracle、Mysql),很是无奈。
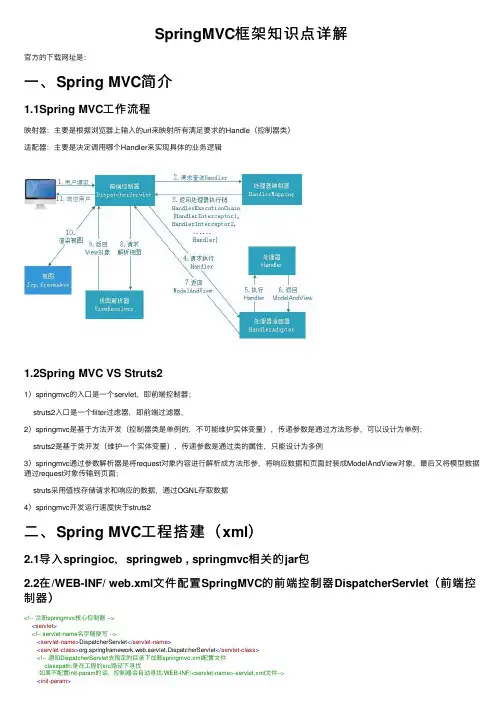
SpringMVC框架知识点详解官⽅的下载⽹址是:⼀、Spring MVC简介1.1Spring MVC⼯作流程映射器:主要是根据浏览器上输⼊的url来映射所有满⾜要求的Handle(控制器类)适配器:主要是决定调⽤哪个Handler来实现具体的业务逻辑1.2Spring MVC VS Struts21)springmvc的⼊⼝是⼀个servlet,即前端控制器;struts2⼊⼝是⼀个filter过虑器,即前端过滤器,2)springmvc是基于⽅法开发(控制器类是单例的,不可能维护实体变量),传递参数是通过⽅法形参,可以设计为单例;struts2是基于类开发(维护⼀个实体变量),传递参数是通过类的属性,只能设计为多例3)springmvc通过参数解析器是将request对象内容进⾏解析成⽅法形参,将响应数据和页⾯封装成ModelAndView对象,最后⼜将模型数据通过request对象传输到页⾯;struts采⽤值栈存储请求和响应的数据,通过OGNL存取数据4)springmvc开发运⾏速度快于struts2⼆、Spring MVC⼯程搭建(xml)2.1导⼊springioc,springweb , springmvc相关的jar包2.2在/WEB-INF/ web.xml⽂件配置SpringMVC的前端控制器DispatcherServlet(前端控制器)<!-- 注册springmvc核⼼控制器 --><servlet><!-- servlet-name名字随便写 --><servlet-name>DispatcherServlet</servlet-name><servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class><!-- 通知DispatcherServlet去指定的⽬录下加载springmvc.xml配置⽂件classpath:是在⼯程的src路径下寻找如果不配置init-param的话,控制器会⾃动寻找/WEB-INF/<servlet-name>-servlet.xml⽂件--><init-param><!-- 值是固定的,相当于键值对 --><param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name><param-value>classpath:springmvc.xml</param-value></init-param></servlet><servlet-mapping><servlet-name>DispatcherServlet</servlet-name><url-pattern>*.action</url-pattern>//拦截请求</servlet-mapping>注:在默认情况下:springmvc框架的配置⽂件必须叫<servlet-name>-servlet.xml且必须放在/WEB-INF/⽬录下,我们可以在web.xml⽂件中,为DispatcherServlet配置⼀个初始化参数,让它去我们指定的⽬录下加载springmvc.xml配置⽂件2.3配置springmvc.xml注:该配置⽂件的命名规则遵循web.xml⽂件中核⼼控制器配置。

SpringMVC之ModelAndView的⽤法(转)(⼀)使⽤ModelAndView类⽤来存储处理完后的结果数据,以及显⽰该数据的视图。
从名字上看ModelAndView中的Model代表模型,View代表视图,这个名字就很好地解释了该类的作⽤。
业务处理器调⽤模型层处理完⽤户请求后,把结果数据存储在该类的model属性中,把要返回的视图信息存储在该类的view属性中,然后让该ModelAndView返回该Spring MVC框架。
框架通过调⽤配置⽂件中定义的视图解析器,对该对象进⾏解析,最后把结果数据显⽰在指定的页⾯上。
具体作⽤:1、返回指定页⾯ModelAndView构造⽅法可以指定返回的页⾯名称,也可以通过setViewName()⽅法跳转到指定的页⾯ ,2、返回所需数值使⽤addObject()设置需要返回的值,addObject()有⼏个不同参数的⽅法,可以默认和指定返回对象的名字。
1、【其源码】:熟悉⼀个类的⽤法,最好从其源码⼊⼿。
public class ModelAndView {/** View instance or view name String */private Object view //该属性⽤来存储返回的视图信息/** Model Map */private ModelMap model;//<span style="color: rgb(0, 130, 0); font-family: Consolas, 'Courier New', Courier, mono, serif; line-height: 18px;">该属性⽤来存储处理后的结果数据</span> /*** Indicates whether or not this instance has been cleared with a call to {@link #clear()}.*/private boolean cleared = false;/*** Default constructor for bean-style usage: populating bean* properties instead of passing in constructor arguments.* @see #setView(View)* @see #setViewName(String)*/public ModelAndView() {}/*** Convenient constructor when there is no model data to expose.* Can also be used in conjunction with <code>addObject</code>.* @param viewName name of the View to render, to be resolved* by the DispatcherServlet's ViewResolver* @see #addObject*/public ModelAndView(String viewName) {this.view = viewName;}/*** Convenient constructor when there is no model data to expose.* Can also be used in conjunction with <code>addObject</code>.* @param view View object to render* @see #addObject*/public ModelAndView(View view) {this.view = view;}/*** Creates new ModelAndView given a view name and a model.* @param viewName name of the View to render, to be resolved* by the DispatcherServlet's ViewResolver* @param model Map of model names (Strings) to model objects* (Objects). Model entries may not be <code>null</code>, but the* model Map may be <code>null</code> if there is no model data.*/public ModelAndView(String viewName, Map<String, ?> model) {this.view = viewName;if (model != null) {getModelMap().addAllAttributes(model);}}/*** Creates new ModelAndView given a View object and a model.* <emphasis>Note: the supplied model data is copied into the internal* storage of this class. You should not consider to modify the supplied* Map after supplying it to this class</emphasis>* @param view View object to render* @param model Map of model names (Strings) to model objects* (Objects). Model entries may not be <code>null</code>, but the* model Map may be <code>null</code> if there is no model data.*/public ModelAndView(View view, Map<String, ?> model) {this.view = view;if (model != null) {getModelMap().addAllAttributes(model);}}/*** Convenient constructor to take a single model object.* @param viewName name of the View to render, to be resolved* by the DispatcherServlet's ViewResolver* @param modelName name of the single entry in the model* @param modelObject the single model object*/public ModelAndView(String viewName, String modelName, Object modelObject) { this.view = viewName;addObject(modelName, modelObject);}/*** Convenient constructor to take a single model object.* @param view View object to render* @param modelName name of the single entry in the model* @param modelObject the single model object*/public ModelAndView(View view, String modelName, Object modelObject) { this.view = view;addObject(modelName, modelObject);}/*** Set a view name for this ModelAndView, to be resolved by the* DispatcherServlet via a ViewResolver. Will override any* pre-existing view name or View.*/public void setViewName(String viewName) {this.view = viewName;}/*** Return the view name to be resolved by the DispatcherServlet* via a ViewResolver, or <code>null</code> if we are using a View object.*/public String getViewName() {return (this.view instanceof String ? (String) this.view : null);}/*** Set a View object for this ModelAndView. Will override any* pre-existing view name or View.*/public void setView(View view) {this.view = view;}/*** Return the View object, or <code>null</code> if we are using a view name* to be resolved by the DispatcherServlet via a ViewResolver.*/public View getView() {return (this.view instanceof View ? (View) this.view : null);}/*** Indicate whether or not this <code>ModelAndView</code> has a view, either* as a view name or as a direct {@link View} instance.*/public boolean hasView() {return (this.view != null);}/*** Return whether we use a view reference, i.e. <code>true</code>* if the view has been specified via a name to be resolved by the* DispatcherServlet via a ViewResolver.*/public boolean isReference() {return (this.view instanceof String);}/*** Return the model map. May return <code>null</code>.* Called by DispatcherServlet for evaluation of the model.*/protected Map<String, Object> getModelInternal() {return this.model;/*** Return the underlying <code>ModelMap</code> instance (never <code>null</code>). */public ModelMap getModelMap() {if (this.model == null) {this.model = new ModelMap();}return this.model;}/*** Return the model map. Never returns <code>null</code>.* To be called by application code for modifying the model.*/public Map<String, Object> getModel() {return getModelMap();}/*** Add an attribute to the model.* @param attributeName name of the object to add to the model* @param attributeValue object to add to the model (never <code>null</code>)* @see ModelMap#addAttribute(String, Object)* @see #getModelMap()*/public ModelAndView addObject(String attributeName, Object attributeValue) {getModelMap().addAttribute(attributeName, attributeValue);return this;}/*** Add an attribute to the model using parameter name generation.* @param attributeValue the object to add to the model (never <code>null</code>)* @see ModelMap#addAttribute(Object)* @see #getModelMap()*/public ModelAndView addObject(Object attributeValue) {getModelMap().addAttribute(attributeValue);return this;}/*** Add all attributes contained in the provided Map to the model.* @param modelMap a Map of attributeName -> attributeValue pairs* @see ModelMap#addAllAttributes(Map)* @see #getModelMap()*/public ModelAndView addAllObjects(Map<String, ?> modelMap) {getModelMap().addAllAttributes(modelMap);return this;}/*** Clear the state of this ModelAndView object.* The object will be empty afterwards.* <p>Can be used to suppress rendering of a given ModelAndView object* in the <code>postHandle</code> method of a HandlerInterceptor.* @see #isEmpty()* @see HandlerInterceptor#postHandle*/public void clear() {this.view = null;this.model = null;this.cleared = true;}/*** Return whether this ModelAndView object is empty,* i.e. whether it does not hold any view and does not contain a model.*/public boolean isEmpty() {return (this.view == null && CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.model));}/*** Return whether this ModelAndView object is empty as a result of a call to {@link #clear} * i.e. whether it does not hold any view and does not contain a model.* <p>Returns <code>false</code> if any additional state was added to the instance* <strong>after</strong> the call to {@link #clear}.* @see #clear()*/public boolean wasCleared() {return (this.cleared && isEmpty());}* Return diagnostic information about this model and view.*/@Overridepublic String toString() {StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("ModelAndView: ");if (isReference()) {sb.append("reference to view with name '").append(this.view).append("'");}else {sb.append("materialized View is [").append(this.view).append(']');}sb.append("; model is ").append(this.model);return sb.toString();}在源码中有7个构造函数,如何⽤?是⼀个重点。
SpringMVC学习笔记作者:胡晟源。
QQ:1312837781配置spring提示:1 Spring Tool Suit (STS)2 Hibernate Tools对于JUNO版本的Eclipse 可以在help->Eclipse Marketplace 输入插件的名字在列表中选择插件安装就可以了。
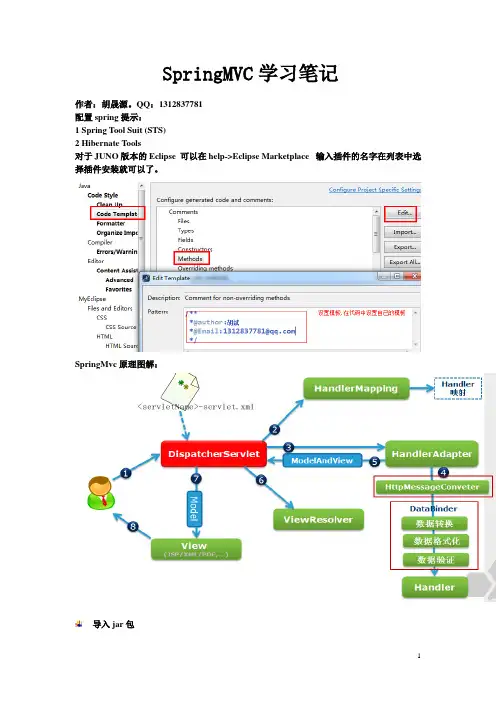
SpringMvc原理图解:导入jar包一:springmvc工作流程。
①.servlet容器初始化一个request请求②.DispatcherServlet分发器负责发送请求到映射器.③.despatcherServlet把请求交给处理器映射Mapping,mapping来寻找需要执行的control④.处理器映射把请求分发给控制器Controler。
⑤.Controler执行完毕后返回ModelAndView(视图解析器)⑥.把ModelAndView返回给dispatcherServlet核心分发器⑦.由于DespatcherServlet不参与具体的处理,所以把modelAndView交给视图解析器。
⑧.视图解析器解析成一个真正的视图,再发给view然后response。
ParameterizableViewController(参数控制器)①.在springmvc-servlet.xml里面加上配置②.通过参数控制器访问页面流程解析:也可以直接在参数控制器里定义name属性,直接通过name属性地址来访问。
如下:但要注意的是:配置文件里必须有BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping情况下,默认映射将会被覆盖;以name属性;来访问将会失败。
命令控制器③.在springmvc里面有如下配置。
④.使用简单url进行访问,参数被封装进javabean。
http://localhost:8080/mysm/comm.do?id=1&userName=zhangsan&password=123&age=13 命令控制器①.首先:springMVC有三个映射器,如果不定义映射Mapping,那么就会使默认:●<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping"></bean>也就是说:上面这个定义和不定义都是一样的。
springMVC详解以及注解说明基于注释(Annotation)的配置有越来越流行的趋势,Spring 2.5 顺应这种趋势,提供了完全基于注释配置Bean、装配Bean 的功能,您可以使用基于注释的Spring IoC 替换原来基于XML 的配置。
本文通过实例详细讲述了Spring 2.5 基于注释IoC 功能的使用。
概述注释配置相对于XML 配置具有很多的优势:∙ 它可以充分利用Java 的反射机制获取类结构信息,这些信息可以有效减少配置的工作。
如使用JPA 注释配置ORM 映射时,我们就不需要指定PO 的属性名、类型等信息,如果关系表字段和PO 属性名、类型都一致,您甚至无需编写任务属性映射信息——因为这些信息都可以通过Java 反射机制获取。
∙ 注释和Java 代码位于一个文件中,而XML 配置采用独立的配置文件,大多数配置信息在程序开发完成后都不会调整,如果配置信息和Java 代码放在一起,有助于增强程序的内聚性。
而采用独立的XML 配置文件,程序员在编写一个功能时,往往需要在程序文件和配置文件中不停切换,这种思维上的不连贯会降低开发效率。
因此在很多情况下,注释配置比XML 配置更受欢迎,注释配置有进一步流行的趋势。
Spring 2.5 的一大增强就是引入了很多注释类,现在您已经可以使用注释配置完成大部分XML 配置的功能。
在这篇文章里,我们将向您讲述使用注释进行Bean 定义和依赖注入的内容。
Spring2.5的注释Spring 2.5 提供了AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor、CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor、PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 和RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor这四个主要的关于Annotation 的BeanPostProcessor。
Springmvc拦截器实现原理解析概述SpringMVC的处理器拦截器类似于Servlet开发中的过滤器Filter,⽤于对处理器进⾏预处理和后处理。
开发者可以⾃⼰定义⼀些拦截器来实现特定的功能。
过滤器与拦截器的区别:拦截器是AOP思想的具体应⽤。
过滤器servlet规范中的⼀部分,任何java web⼯程都可以使⽤在url-pattern中配置了/*之后,可以对所有要访问的资源进⾏拦截拦截器拦截器是SpringMVC框架⾃⼰的,只有使⽤了SpringMVC框架的⼯程才能使⽤拦截器只会拦截访问的控制器⽅法,如果访问的是jsp/html/css/image/js是不会进⾏拦截的⾃定义拦截器那如何实现拦截器呢?想要⾃定义拦截器,必须实现 HandlerInterceptor 接⼝。
新建⼀个Moudule ,添加web⽀持配置web.xml 和 springmvc-servlet.xml ⽂件编写⼀个拦截器package com.xiaohua.interceptor;import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor;import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;public class MyInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {//在请求处理的⽅法之前执⾏//如果返回true执⾏下⼀个拦截器//如果返回false就不执⾏下⼀个拦截器public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, Object o) throws Exception {System.out.println("------------处理前------------");return true;}//在请求处理⽅法执⾏之后执⾏public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, Object o, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception { System.out.println("------------处理后------------");}//在dispatcherServlet处理后执⾏,做清理⼯作.public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, Object o, Exception e) throws Exception {System.out.println("------------清理------------");}}在springmvc的配置⽂件中配置拦截器<!--关于拦截器的配置--><mvc:interceptors><mvc:interceptor><!--/** 包括路径及其⼦路径--><!--/admin/* 拦截的是/admin/add等等这种 , /admin/add/user不会被拦截--><!--/admin/** 拦截的是/admin/下的所有--><mvc:mapping path="/**"/><!--bean配置的就是拦截器--><bean class="com.xiaohua.interceptor.MyInterceptor"/></mvc:interceptor></mvc:interceptors>编写⼀个Controller,接收请求package com.xiaohua.controller;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;//测试拦截器的控制器@Controllerpublic class InterceptorController {@RequestMapping("/interceptor")@ResponseBodypublic String testFunction() {System.out.println("控制器中的⽅法执⾏了");return "hello";}}前端 index.jsp<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/interceptor" rel="external nofollow" >拦截器测试</a>启动tomcat 测试⼀下!验证⽤户是否登陆(认证⽤户)实现思路有⼀个登陆页⾯,需要写⼀个controller访问页⾯。
详解springmvc常⽤5种注解⼀、组件型注解:1、@Component 在类定义之前添加@Component注解,他会被spring容器识别,并转为bean。
2、@Repository 对Dao实现类进⾏注解 (特殊的@Component)3、@Service ⽤于对业务逻辑层进⾏注解, (特殊的@Component)4、@Controller ⽤于控制层注解, (特殊的@Component)以上四种注解都是注解在类上的,被注解的类将被spring初始话为⼀个bean,然后统⼀管理。
⼆、请求和参数型注解:1、@RequestMapping:⽤于处理请求地址映射,可以作⽤于类和⽅法上。
●value:定义request请求的映射地址●method:定义地request址请求的⽅式,包括【GET, POST, HEAD, OPTIONS, PUT, PATCH, DELETE, TRACE.】默认接受get请求,如果请求⽅式和定义的⽅式不⼀样则请求⽆法成功。
●params:定义request请求中必须包含的参数值。
●headers:定义request请求中必须包含某些指定的请求头,如:RequestMapping(value = "/something", headers = "content-type=text/*")说明请求中必须要包含"text/html", "text/plain"这中类型的Content-type头,才是⼀个匹配的请求。
●consumes:定义请求提交内容的类型。
●produces:指定返回的内容类型,仅当request请求头中的(Accept)类型中包含该指定类型才返回@RequestMapping(value="/requestTest.do",params = {"name=sdf"},headers = {"Accept-Encoding=gzip, deflate, br"},method = RequestMethod.GET) public String getIndex(){System.out.println("请求成功");return "index";}上⾯代码表⽰请求的⽅式为GET请求,请求参数必须包含name=sdf这⼀参数,然后请求头中必须有 Accept-Encoding=gzip, deflate, br这个类型头。
springmvc期末考试题及答案Spring MVC期末考试题及答案一、选择题(每题2分,共20分)1. Spring MVC中的控制器(Controller)是什么?A. 一个服务类B. 一个数据访问对象C. 一个业务逻辑类D. 一个处理HTTP请求和响应的组件答案:D2. 在Spring MVC中,以下哪个注解用于映射请求到控制器方法?A. @ServiceB. @AutowiredC. @RequestMappingD. @Repository答案:C3. Spring MVC中的模型(Model)通常用于存储什么?A. HTTP请求数据B. HTTP响应数据C. 业务数据D. 控制器状态答案:C4. 在Spring MVC中,视图(View)的主要职责是什么?A. 处理业务逻辑B. 处理HTTP请求C. 渲染返回给客户端的数据D. 管理数据库连接答案:C5. Spring MVC中的DispatcherServlet的作用是什么?A. 处理数据库事务B. 处理HTTP请求和响应C. 管理Spring容器D. 调度控制器方法的执行答案:B6. 在Spring MVC中,以下哪个注解用于处理POST请求?A. @GetMappingB. @PostMappingC. @PutMappingD. @DeleteMapping答案:B7. Spring MVC中的异常处理器(Exception Handler)的作用是什么?A. 处理业务逻辑异常A. 处理控制器方法抛出的异常B. 处理数据库异常D. 处理Spring容器异常答案:A8. 在Spring MVC中,以下哪个注解用于将参数绑定到控制器方法的参数上?A. @RequestParamB. @PathVariableC. @RequestBodyD. @RequestHeader答案:A9. Spring MVC中的RESTful风格的URL设计通常遵循什么原则?A. 每个URL代表一个资源B. 使用GET请求获取资源C. 使用POST请求创建资源D. 所有以上答案:D10. 在Spring MVC中,以下哪个注解用于处理请求头?A. @RequestParamB. @RequestHeaderC. @RequestBodyD. @PathVariable答案:B二、填空题(每题2分,共20分)1. Spring MVC的入口是________。
springmvc知识点整理1.Springmvc架构2.Springmvc组件三⼤组件:处理器映射器,处理器适配器,视图解析器处理器映射器:注解式处理器映射器,对类中标记了@ResquestMapping的⽅法进⾏映射,根据@ResquestMapping定义的url匹配@ResquestMapping标记的⽅法,匹配成功返回HandlerMethod对象给前端控制器。
<!-- 配置处理器映射器 --><beanclass="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping" />处理器适配器:对标记@ResquestMapping的⽅法进⾏适配<!-- 配置处理器适配器 --><beanclass="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter" />解决办法:SpringMVC使⽤<mvc:annotation-driven>⾃动加载RequestMappingHandlerMapping和RequestMappingHandlerAdapter可以在springmvc.xml配置⽂件中使⽤<mvc:annotation-driven>替代注解处理器和适配器的配置。
<!-- 注解驱动 --><mvc:annotation-driven />视图解析器:视图解析器使⽤SpringMVC框架默认的InternalResourceViewResolver,这个视图解析器⽀持JSP视图解析。
<!-- 配置视图解析器 --><beanclass="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"><!-- 配置逻辑视图的前缀 --><property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/jsp/" /><!-- 配置逻辑视图的后缀 --><property name="suffix" value=".jsp" /></bean>最终jsp物理地址:前缀+逻辑视图名+后缀3.1简单参数的绑定(@RequestParam)当请求的参数名称和处理器形参名称⼀致时会将请求参数与形参进⾏绑定,若不⼀致,就需要@RequestParamvalue:参数名字,即⼊参的请求参数名字,如value=“itemId”表⽰请求的参数区中的名字为itemId的参数的值将传⼊required:是否必须,默认是true,表⽰请求中⼀定要有相应的参数,否则将报错TTP Status 400 - Required Integer parameter 'XXXX' is not presentdefaultValue:默认值,表⽰如果请求中没有同名参数时的默认值public String queryItemById(@RequestParam(value = "itemId", required = true, defaultValue = "1") Integer id,ModelMap modelMap) {}这⾥需要传⼊的是id,实际传⼊的是itemId,需要⽤@RequestParam转换⼀下3.2pojo参数绑定如果提交的参数很多,或者提交的表单中的内容很多的时候,可以使⽤简单类型接受数据,也可以使⽤pojo接收数据,但是pojo对象中的属性名和表单中input的name属性⼀致。
课程内容---…详细包括整合struts hibernate------------------------------------1.面向接口(抽象)编程的概念与好处2.IOC/DI的概念与好处a)inversion of controlb)dependency injection3.AOP的概念与好处4.Spring简介5.Spring应用IOC/DI(重要)a)xmlb)annotation6.Spring应用AOP(重要)a)xmlb)annotation7.Struts2.1.6 + Spring2.5.6 + Hibernate3.3.2整合(重要)a)opensessionInviewfilter(记住,解决什么问题,怎么解决)8.Spring JDBC面向接口编程…(面向抽象编程)1.场景:用户添加2.Spring_0100_AbstractOrientedProgramminga)不是AOP:Aspect Oriented Programming3.好处:灵活什么是IOC(DI),,,有什么好处1.把自己new的东西改为由容器提供a)初始化具体值b)装配<?xml version="1.0"?>-<beans><bean class="erDAOImpl" id="u"/>(class 是个类。
Id就等于构造了一个对象)<bean class="erService" id="userService"><property bean="u" name="userDAO"/> </bean>(把u这个对象注入到UserService这个类的一个userDAO的一个属性里)-</beans>2.好处:灵活装配Spring简介包括整合struts hibernate------------------------------------1.项目名称:Spring_0200_IOC_Introduction2.环境搭建a)只用IOCi.spring.jar , jarkata-commons/commons-loggin.jar3.IOC容器a)实例化具体beanb)动态装配4.AOP支持a)安全检查b)管理transactionSpring IOC配置与应用1.FAQ:不给提示:a)window – preferences – myeclipse – xml – xml catalogb)User Specified Entries – addi.Location: D:\share\0900_Spring\soft\spring-framework-2.5.6\dist\resources\spring-beans-2.5.xsdii.URI:file:///D:/share/0900_Spring/soft/spring-framework-2.5.6/dist/resources/spring-beans-2.5.xsd iii.Key Type: Schema Locationiv.Key: /schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd2.注入类型a)Spring_0300_IOC_Injection_Typeb)setter(重要)c)构造方法(可以忘记)d)接口注入(可以忘记)3.id vs. Name(可以把Id换成name,没什么区别!)a)Spring_0400_IOC_Id_Nameb)name可以用特殊字符4.简单属性的注入a)Spring_0500_IOC_SimplePropertyb)<property name=… value=….>在配置文件里直接赋值!(在此简单属性为int和string,会自动转换)5.<bean 中的scope属性a)Spring_0600_IOC_Bean_Scopeb)singleton 单例(无论去多少次都是同一个bean)c)proptotype 每次创建新的对象6.集合注入a)Spring_0700_IOC_Collectionsb)很少用,不重要!参考程序7.自动装配a)Spring_0800_IOC_AutoWireb)byNamec)byTyped)如果所有的bean都用同一种,可以使用beans的属性:default-autowire-<bean class="erDAOImpl" name="userDAO"><property name="daoId" value="1"/> </bean><bean class="erDAOImpl" name="userDAO2"><property name="daoId" value="2"/> </bean><bean class="erService"autowire="byType" scope="prototype" id="userService"></bean> </beans>(这里会报错,因为有两个userDAO和UserDAO2都是int类型!)(如果说byname则会显示第一个的内容“1”!,因为UserService类里面的userDAO属性与第一个的名字一样!)8.生命周期a)Spring_0900_IOC_Life_Cycleb)lazy-init (不重要)c)init-method与destroy-methd 不要和prototype一起用(了解)<bean class="erDAOImpl" id="u"></bean><bean class="erService" id="userService" scope="prototype"destroy-method="destroy" init-method="init"></bean></beans>9.Annotation第一步:a)修改xml文件,参考文档<context:annotation-config />b)默认按类型by typec)如果想用byName,使用@Qulifierd)写在private field(第三种注入形式)(不建议,破坏封装)e)如果写在set上,@qualifier需要写在参数上f)10.@Resource(重要)a)加入:j2ee/common-annotations.jarb)默认按名称,名称找不到,按类型c)可以指定特定名称d)推荐使用e)不足:如果没有源码,就无法运用annotation,只能使用xml11.@Component@Service @Controller @Repository(四个一样的功能!!)a)初始化的名字默认为类名首字母小写b)可以指定初始化bean的名字首先先加载ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); 即读beans.xml里面的内容,然后通过找从com.bjsxt开始“scan”含@component的类,找到之后就初始化对象,结果在其一个属相的set方法上找到一个源为“u”的一个bean,于是就加载那个bean!12.@Scope13.@PostConstruct = init-method;(在构造对象后执行此方法)@PreDestroy = destroy-method;(在容器销毁前执行此方法)什么是AOP1.面向切面编程Aspect-Oriented-Programminga)是对面向对象的思维方式的有力补充2.Spring_1400_AOP_Introduction3.好处:可以动态的添加和删除在切面上的逻辑而不影响原来的执行代码a)Filterb)Struts2的interceptor4.概念:a)JoinPoint 释意:切面与原方法交接点即切入点b)PointCut 释意:切入点集合是com.xyz.someapp.service.下面的任何类,任何方法,任何返回值的一个切入点的集合。
第一、二课所需jar包,本次使用版本是spring3.2.3Ps:spring的文件用上面的基本够了,但是整个过程可能需要很多的commons 软件,如fileupload,io,lang包SpringMVC demo案例1、加入相关jar包2、web.xml配置<servlet><servlet-name>springMVC</servlet-name><servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <!-- <init-param><param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name><param-value>classpath*:*/springMVC-*.xml</param-value></init-param> --><load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup></servlet><servlet-mapping><servlet-name>springMVC</servlet-name><url-pattern>/</url-pattern>这里一定要写成这样,如果写成 /* 输入地址总是No mapping found for HTTP request with URI</servlet-mapping>Ps:springMVC 也有个默认的xml配置文件,类似struts2的struts.xml该文件可以指定,即上面紫色注释掉部分。
默认路径是/WEB-INF/springMVC-servlet.xml3、springMVC-servlet.xml<?xml version="1.0"encoding="UTF-8"?><beans xmlns="/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xmlns:mvc="/schema/mvc"xmlns:context="/schema/context"xsi:schemaLocation="/schema/beans/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd /schema/mvc/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-3.0.xsd/schema/context/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd"><bean name="/helloword"class="com.wang.web.controller.HelloworldController"></bean><bean id="viewResolver"class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResource ViewResolver"><property name="prefix"value="/"></property><property name="suffix"value=".jsp"></property></bean></beans>4、编写controller该controller类似struts2的action,编写的controller 要实现org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.Controller接口第三课springMVC的传值通过modelandview 传值1、@Overridepublic ModelAndView handleRequest(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {returnnew ModelAndView("/hello","result","this is the result!");}页面上直接EL表达式显示值传递MAP第四课springMVC一个controller写多个方法1、Controller 类继承MultiActionController类publicclass MultiMethodController extends MultiActionController{public ModelAndView add(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response){returnnew ModelAndView("/multiAdd");}2、Xml配置文件<!-- 配置单controller 多个方法多请求处理控制器--><bean id="paramMethodResolver"class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.multiactio n.ParameterMethodNameResolver"><property name="paramName"value="method"></property><!—这里的methodurl使用 --> </bean><!--配置对应的controller --><bean name="/multiMethod"class="com.wang.web.controller.MultiMethodController"> <property name="methodNameResolver"ref="paramMethodResolver"/></bean>3、URL路径http://localhost:8080/springMVC/multiMethod?method=addps:controller 类中的方法都要是xxx(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response)第五课SpringMVC静态文件访问在现有的配置下在jsp 文件中<img src=”xx/xx/xx.png” />无法显示图片解决方法:在 springMVC的xml配置文件中加上<!-- 访问静态文件 --><mvc:resources location="/img/"mapping="/img/**"/>以后所有的静态文件,如js,css,html,video等均可以放置在一个统一的文件夹下。
可以配置多个原因:springMVC 的DispatcherServlet这个时候全部给过滤了。
同时也把所有的静态文件给拦截了。
<servlet-mapping><servlet-name>springMVC</servlet-name><url-pattern>/</url-pattern></servlet-mapping><bean id="viewResolver"class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.Interna lResourceViewResolver"><property name="prefix"value="/"></property><property name="suffix"value=".jsp"></property></bean>所以本质上urlhttp://localhost:8080/springMVC/img/img.jpg他会把img.jpg当成img.jpg.jsp另一种解决方法:<url-pattern>*.action</url-pattern>第六课(开始Annotation)springMVC注解启用spring xml 配置<mvc:annotation-driven/><context:component-scan base-package="com.wang"/><bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapt er"/><beanclass="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping"/> (该类已经废弃了,使用下面的代替)<beanclass="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingH andlerMapping"/><bean id="viewResolver"class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewR esolver"><property name="prefix"value="/"></property><property name="suffix"value=".jsp"></property></bean><mvc:resources location="/framework/"mapping="/framework/**"/>Ps:黄色部分是添加扫描和spring 的annotation所必须的。