short,int,long与byte数组之间的转换
- 格式:doc
- 大小:48.50 KB
- 文档页数:4

java中int与byte,以及long与byte之间的转换原⽂地址:/zgyulongfei/article/details/7738970public class Utilities {public static byte[] int2Bytes(int num) {byte[] byteNum = new byte[4];for (int ix = 0; ix < 4; ++ix) {int offset = 32 - (ix + 1) * 8;byteNum[ix] = (byte) ((num >> offset) & 0xff);}return byteNum;}public static int bytes2Int(byte[] byteNum) {int num = 0;for (int ix = 0; ix < 4; ++ix) {num <<= 8;num |= (byteNum[ix] & 0xff);}return num;}public static byte int2OneByte(int num) {return (byte) (num & 0x000000ff);}public static int oneByte2Int(byte byteNum) {return byteNum > 0 ? byteNum : (128 + (128 + byteNum));}public static byte[] long2Bytes(long num) {byte[] byteNum = new byte[8];for (int ix = 0; ix < 8; ++ix) {int offset = 64 - (ix + 1) * 8;byteNum[ix] = (byte) ((num >> offset) & 0xff);}return byteNum;}public static long bytes2Long(byte[] byteNum) {long num = 0;for (int ix = 0; ix < 8; ++ix) {num <<= 8;num |= (byteNum[ix] & 0xff);}return num;}public static void main(String[] args) {int num = 129;System.out.println("测试的int值为:" + num);byte[] int2bytes = Utilities.int2Bytes(num);System.out.printf("int转成bytes: ");for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {System.out.print(int2bytes[i] + " ");}System.out.println();int bytes2int = Utilities.bytes2Int(int2bytes);System.out.println("bytes转⾏成int: " + bytes2int);byte int2OneByte = Utilities.int2OneByte(num);System.out.println("int转⾏成one byte: " + int2OneByte);int oneByte2Int = Utilities.oneByte2Int(int2OneByte);System.out.println("one byte转⾏成int: " + oneByte2Int);System.out.println();long longNum = 100000;System.out.println("测试的long值为:" + longNum);byte[] long2Bytes = Utilities.long2Bytes(longNum);System.out.printf("long转⾏成bytes: ");for (int ix = 0; ix < long2Bytes.length; ++ix) {System.out.print(long2Bytes[ix] + " ");}System.out.println();long bytes2Long = Utilities.bytes2Long(long2Bytes); System.out.println("bytes转⾏成long: " + bytes2Long); }}测试的int值为:129int转成bytes: 0 0 0 -127bytes转⾏成int: 129int转⾏成one byte: -127one byte转⾏成int: 129测试的long值为:100000long转⾏成bytes: 0 0 0 0 0 1 -122 -96bytes转⾏成long: 100000。

javabyte数组与int,long,short,byte的转换实现⽅法实例如下:public class DataTypeChangeHelper {/*** 将⼀个单字节的byte转换成32位的int** @param b* byte* @return convert result*/public static int unsignedByteToInt(byte b) {return (int) b & 0xFF;}/*** 将⼀个单字节的Byte转换成⼗六进制的数** @param b* byte* @return convert result*/public static String byteToHex(byte b) {int i = b & 0xFF;return Integer.toHexString(i);}/*** 将⼀个4byte的数组转换成32位的int** @param buf* bytes buffer* @param byte[]中开始转换的位置* @return convert result*/public static long unsigned4BytesToInt(byte[] buf, int pos) {int firstByte = 0;int secondByte = 0;int thirdByte = 0;int fourthByte = 0;int index = pos;firstByte = (0x000000FF & ((int) buf[index]));secondByte = (0x000000FF & ((int) buf[index + 1]));thirdByte = (0x000000FF & ((int) buf[index + 2]));fourthByte = (0x000000FF & ((int) buf[index + 3]));index = index + 4;return ((long) (firstByte << 24 | secondByte << 16 | thirdByte << 8 | fourthByte)) & 0xFFFFFFFFL;}/*** 将16位的short转换成byte数组** @param s* short* @return byte[] 长度为2* */public static byte[] shortToByteArray(short s) {byte[] targets = new byte[2];for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {int offset = (targets.length - 1 - i) * 8;targets[i] = (byte) ((s >>> offset) & 0xff);}return targets;}/*** 将32位整数转换成长度为4的byte数组** @param s* int* @return byte[]* */public static byte[] intToByteArray(int s) {byte[] targets = new byte[2];for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {int offset = (targets.length - 1 - i) * 8;targets[i] = (byte) ((s >>> offset) & 0xff);}return targets;}/*** long to byte[]** @param s* long* @return byte[]* */public static byte[] longToByteArray(long s) {byte[] targets = new byte[2];for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {int offset = (targets.length - 1 - i) * 8;targets[i] = (byte) ((s >>> offset) & 0xff);}return targets;}/**32位int转byte[]*/public static byte[] int2byte(int res) {byte[] targets = new byte[4];targets[0] = (byte) (res & 0xff);// 最低位targets[1] = (byte) ((res >> 8) & 0xff);// 次低位targets[2] = (byte) ((res >> 16) & 0xff);// 次⾼位targets[3] = (byte) (res >>> 24);// 最⾼位,⽆符号右移。

Java中byte、byte数组与int、long的转换详解⼀、Java 中 byte 和 int 之间的转换源码://byte 与 int 的相互转换public static byte intToByte(int x) {return (byte) x;}public static int byteToInt(byte b) {//Java 总是把 byte 当做有符处理;我们可以通过将其和 0xFF 进⾏⼆进制与得到它的⽆符值return b & 0xFF;}测试代码://测试 int 转 byteint int0 = 234;byte byte0 = intToByte(int0);System.out.println("byte0=" + byte0);//byte0=-22//测试 byte 转 intint int1 = byteToInt(byte0);System.out.println("int1=" + int1);//int1=234⼆、Java 中 byte 数组和 int 之间的转换源码://byte 数组与 int 的相互转换public static int byteArrayToInt(byte[] b) {return b[3] & 0xFF |(b[2] & 0xFF) << 8 |(b[1] & 0xFF) << 16 |(b[0] & 0xFF) << 24;}public static byte[] intToByteArray(int a) {return new byte[] {(byte) ((a >> 24) & 0xFF),(byte) ((a >> 16) & 0xFF),(byte) ((a >> 8) & 0xFF),(byte) (a & 0xFF)};}测试代码://测试 int 转 byte 数组int int2 = 1417;byte[] bytesInt = intToByteArray(int2);System.out.println("bytesInt=" + bytesInt);//bytesInt=[B@de6ced//测试 byte 数组转 intint int3 = byteArrayToInt(bytesInt);System.out.println("int3=" + int3);//int3=1417三、Java 中 byte 数组和 long 之间的转换源码:private static ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(8);//byte 数组与 long 的相互转换public static byte[] longToBytes(long x) {buffer.putLong(0, x);return buffer.array();}public static long bytesToLong(byte[] bytes) {buffer.put(bytes, 0, bytes.length);buffer.flip();//need flipreturn buffer.getLong();}测试代码://测试 long 转 byte 数组long long1 = 2223;byte[] bytesLong = longToBytes(long1);System.out.println("bytes=" + bytesLong);//bytes=[B@c17164//测试 byte 数组转 longlong long2 = bytesToLong(bytesLong);System.out.println("long2=" + long2);//long2=2223四、整体⼯具类源码:import java.nio.ByteBuffer;public class Test {private static ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(8);public static void main(String[] args) {//测试 int 转 byteint int0 = 234;byte byte0 = intToByte(int0);System.out.println("byte0=" + byte0);//byte0=-22//测试 byte 转 intint int1 = byteToInt(byte0);System.out.println("int1=" + int1);//int1=234//测试 int 转 byte 数组int int2 = 1417;byte[] bytesInt = intToByteArray(int2);System.out.println("bytesInt=" + bytesInt);//bytesInt=[B@de6ced//测试 byte 数组转 intint int3 = byteArrayToInt(bytesInt);System.out.println("int3=" + int3);//int3=1417//测试 long 转 byte 数组long long1 = 2223;byte[] bytesLong = longToBytes(long1);System.out.println("bytes=" + bytesLong);//bytes=[B@c17164//测试 byte 数组转 longlong long2 = bytesToLong(bytesLong);System.out.println("long2=" + long2);//long2=2223}//byte 与 int 的相互转换public static byte intToByte(int x) {return (byte) x;}public static int byteToInt(byte b) {//Java 总是把 byte 当做有符处理;我们可以通过将其和 0xFF 进⾏⼆进制与得到它的⽆符值 return b & 0xFF;}//byte 数组与 int 的相互转换public static int byteArrayToInt(byte[] b) {return b[3] & 0xFF |(b[2] & 0xFF) << 8 |(b[1] & 0xFF) << 16 |(b[0] & 0xFF) << 24;}public static byte[] intToByteArray(int a) {return new byte[] {(byte) ((a >> 24) & 0xFF),(byte) ((a >> 16) & 0xFF),(byte) ((a >> 8) & 0xFF),(byte) (a & 0xFF)};}//byte 数组与 long 的相互转换public static byte[] longToBytes(long x) {buffer.putLong(0, x);return buffer.array();}public static long bytesToLong(byte[] bytes) {buffer.put(bytes, 0, bytes.length);buffer.flip();//need flipreturn buffer.getLong();}}运⾏测试结果:byte0=-22int1=234bytesInt=[B@de6cedint3=1417bytes=[B@c17164long2=2223总结以上就是这篇⽂章的全部内容了,希望本⽂的内容对⼤家的学习或者⼯作能带来⼀定的帮助,如果有疑问⼤家可以留⾔交流。

java基本数据类型之间的转换Java是一门强类型语言,变量需要明确指定其数据类型。
Java中含有8个基本数据类型,它们是boolean、byte、short、int、long、float、double和char。
在Java编程中,有时也需要对这些基本数据类型进行一些转换。
本文将围绕Java基本数据类型之间的转换展开。
一、自动类型转换Java中可以将一种数据类型的变量赋值给另一种数据类型的变量,这种转换称为自动类型转换。
自动类型转换是指从小类型到大类型的转换过程, Java在内部进行转换,无需开发人员进行显式的操作。
例如,将一个byte类型的变量赋值给int类型的变量:byte b = 10;int i = b;在这个过程中,Java自动将byte类型的变量b转换成int类型,并将其赋值给i。
二、强制类型转换有时需要对一个变量强制转换为另一种类型,这种转换称为强制类型转换。
强制类型转换是从大类型到小类型的转换过程,在进行强制类型转换时,需要在转换前使用小括号指定要转换的类型。
例如,将一个double类型的变量强制转换成int类型:double d = 10.5;int i = (int)d;在这个过程中,Java会将double类型的变量d转换成int类型,并将其赋值给i。
需要注意的是,在进行强制类型转换时,可能会出现数据精度丢失的情况。
三、字符类型转换在Java中,char类型可以被当做数字来处理,它与int类型可以互相转换。
在Java中,可以使用强制类型转换将字符类型转换成整型,例如:char c = 'a';int i = (int)c;在这个过程中,字符'a'会被转换成对应的ASCII码97。
四、字符串类型转换Java中的字符串类型与其他基本数据类型之间的转换需要借助于包装类。
Java中含有六个与基本数据类型对应的包装类,它们是Boolean、Byte、Short、Integer、Long、Float、Double和Character。

int类型转换byte类型计算机中,int类型占⽤4个字节,byte类型占⽤1个字节;当int类型强转为byte类型时,计算机会截取最后的⼋位(1个字节);由于计算机存储数据时,都是以补码的形式进⾏存储。
然⽽,我们通常看到的数却是计算机存储的补码先转换成反码,后转换成原码,再转换成⼗进制呈现的。
原码、反码与补码的关系:正数:原码 = 反码 = 补码负数:原码取反 = 反码(符号位不变);反码 + 1 = 补码(符号位上的进位舍弃)举例:int a = 128,转换成⼆进制形式是0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 1000 0000,由于正数的原码=反码=补码,因此计算机存储的是0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 1000 0000。
int a = -128,转换成⼆进制形式是1000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 1000 0000,由于负数的原码、反码与补码的转换关系是:原码取反=反码(符号位不变),反码+1=补码;反码:1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 0111 1111补码:1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1000 0000因此,在计算机中存储的是1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1000 0000int a = 128;byte b = (byte) a; // b=-128⾸先,由上述第⼀个例⼦得知,128在计算机中存储的补码形式为0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 1000 0000,此时强制转换成byte类型的数据时,计算机会⾃动截取最后的⼋位(1个字节)1000 0000,由补码最⾼位为1得知,转换后的数据是⼀个负数,根据负数补码求反码,我们可以得到该数的反码是1111 1111,根据负数反码求原码,可得到该数的原码是1000 0000。
![byte[]数组和int之间的转换](https://uimg.taocdn.com/fbee3500f08583d049649b6648d7c1c708a10bba.webp)
byte[]数组和int之间的转换这⾥简单记录下两种转换⽅式:第⼀种:1、int与byte[]之间的转换(类似的byte short,long型)[java]1. /**2. * 将int数值转换为占四个字节的byte数组,本⽅法适⽤于(低位在前,⾼位在后)的顺序。
和bytesToInt()配套使⽤3. * @param value4. * 要转换的int值5. * @return byte数组6. */7. public static byte[] intToBytes( int value )8. {9. byte[] src = new byte[4];10. src[3] = (byte) ((value>>24) & 0xFF);11. src[2] = (byte) ((value>>16) & 0xFF);12. src[1] = (byte) ((value>>8) & 0xFF);13. src[0] = (byte) (value & 0xFF);14. return src;15. }16. /**17. * 将int数值转换为占四个字节的byte数组,本⽅法适⽤于(⾼位在前,低位在后)的顺序。
和bytesToInt2()配套使⽤18. */19. public static byte[] intToBytes2(int value)20. {21. byte[] src = new byte[4];22. src[0] = (byte) ((value>>24) & 0xFF);23. src[1] = (byte) ((value>>16)& 0xFF);24. src[2] = (byte) ((value>>8)&0xFF);25. src[3] = (byte) (value & 0xFF);26. return src;27. }byte[]转int[java]1. /**2. * byte数组中取int数值,本⽅法适⽤于(低位在前,⾼位在后)的顺序,和和intToBytes()配套使⽤3. *4. * @param src5. * byte数组6. * @param offset7. * 从数组的第offset位开始8. * @return int数值9. */10. public static int bytesToInt(byte[] src, int offset) {11. int value;12. value = (int) ((src[offset] & 0xFF)13. | ((src[offset+1] & 0xFF)<<8)14. | ((src[offset+2] & 0xFF)<<16)15. | ((src[offset+3] & 0xFF)<<24));16. return value;17. }18.19. /**20. * byte数组中取int数值,本⽅法适⽤于(低位在后,⾼位在前)的顺序。
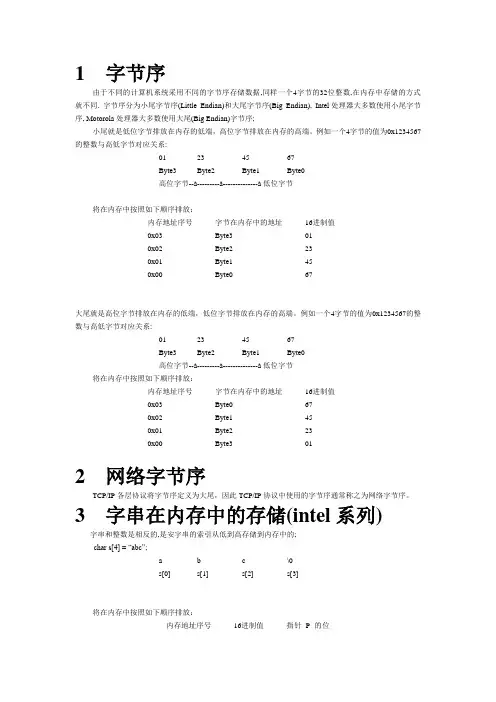
1字节序由于不同的计算机系统采用不同的字节序存储数据,同样一个4字节的32位整数,在内存中存储的方式就不同. 字节序分为小尾字节序(Little Endian)和大尾字节序(Big Endian), Intel处理器大多数使用小尾字节序, Motorola处理器大多数使用大尾(Big Endian)字节序;小尾就是低位字节排放在内存的低端,高位字节排放在内存的高端。
例如一个4字节的值为0x1234567的整数与高低字节对应关系:01234567Byte3Byte2Byte1Byte0高位字节--à---------à--------------à低位字节将在内存中按照如下顺序排放:内存地址序号字节在内存中的地址16进制值0x03Byte3010x02Byte2230x01Byte1450x00Byte067大尾就是高位字节排放在内存的低端,低位字节排放在内存的高端。
例如一个4字节的值为0x1234567的整数与高低字节对应关系:01234567Byte3Byte2Byte1Byte0高位字节--à---------à--------------à低位字节将在内存中按照如下顺序排放:内存地址序号字节在内存中的地址16进制值0x03Byte0670x02Byte1450x01Byte2230x00Byte3012网络字节序TCP/IP各层协议将字节序定义为大尾,因此TCP/IP协议中使用的字节序通常称之为网络字节序。
3字串在内存中的存储(intel系列)字串和整数是相反的,是安字串的索引从低到高存储到内存中的;char s[4] = “abc”;a b c\0s[0]s[1]s[2]s[3]将在内存中按照如下顺序排放:内存地址序号16进制值指针P的位置0xbffeadf7\0p+30xbffeadf6c p+20xbffeadf5b p+10xbffeadf4a pint main(void){char s[4] = "abc";char *p = s;printf("%02x, %02x, %02x, %02x\n", &s[0], &s[1], &s[2], &s[3]);printf("%02x, %02x, %02x, %02x\n", p, p+1, p+2, p+3);printf("%c, %c, %c, %c\n", s[0], s[1], s[2], s[3]);return 0;}输出结果:[netcool@HFINMSP2 demo]$ ./demo001bffeadf4, bffeadf5, bffeadf6, bffeadf7bffeadf4, bffeadf5, bffeadf6, bffeadf7a, b, c,4整数数组在内存中的存储(intel系列)同字串一样,但是数组里的每一个整数的存储是按照小尾字节序;5linux系统中的处理方法网络字节序作为一个标准字节序,如果系统并没有提供相关的转换函数,我们可以通过以下4个宏实现本地字节序和网络字节序的相互转换:htons():将16位无符号整数从本地字节序转换成网络字节序htonl():将32位无符号整数从本地字节序转换成网络字节序ntohs():将16位无符号整数从网络字节序转换成本地字节序ntohl():将32位无符号整数从网络字节序转换成本地字节序网络字节序与主机字节序不同的CPU有不同的字节序类型这些字节序是指整数在内存中保存的顺序这个叫做主机序最常见的有两种1.Little endian:将低序字节存储在起始地址2.Big endian:将高序字节存储在起始地址LE little-endian最符合人的思维的字节序地址低位存储值的低位地址高位存储值的高位怎么讲是最符合人的思维的字节序,是因为从人的第一观感来说低位值小,就应该放在内存地址小的地方,也即内存地址低位反之,高位值就应该放在内存地址大的地方,也即内存地址高位BE big-endian最直观的字节序地址低位存储值的高位地址高位存储值的低位为什么说直观,不要考虑对应关系只需要把内存地址从左到右按照由低到高的顺序写出把值按照通常的高位到低位的顺序写出两者对照,一个字节一个字节的填充进去例子:在内存中双字0x01020304(DWORD)的存储方式内存地址4000 4001 4002 4003LE 04 03 02 01BE 01 02 03 04例子:如果我们将0x1234abcd写入到以0x0000开始的内存中,则结果为big-endian little-endian0x0000 0x12 0xcd0x0001 0x23 0xab0x0002 0xab 0x340x0003 0xcd 0x12x86系列CPU都是little-endian的字节序.网络字节顺序是TCP/IP中规定好的一种数据表示格式,它与具体的CPU类型、操作系统等无关,从而可以保证数据在不同主机之间传输时能够被正确解释。

byte数组与byte数组转化摘要:一、引言二、byte数组与byte数组转化的概念1.byte数组2.byte数组转化三、byte数组与byte数组转化的方法1.字节数组转字符串2.字符串转字节数组四、byte数组与byte数组转化的应用场景1.网络传输2.文件存储五、总结正文:一、引言在计算机编程中,byte数组和byte数组转化是经常遇到的操作。
了解byte数组与byte数组转化的概念、方法和应用场景,对于编程工作非常有帮助。
二、byte数组与byte数组转化的概念1.byte数组byte数组,又称字节数组,是一种数据类型,用于存储一系列字节。
在Java、C#等编程语言中,它通常用于存储和处理二进制数据。
2.byte数组转化byte数组转化是指将byte数组与其他数据类型(如字符串、整数等)之间进行转换。
三、byte数组与byte数组转化的方法1.字节数组转字符串在Java中,可以使用`new String(byte[], charset)`方法将byte数组转换为字符串。
其中,`charset`表示字符集,如UTF-8、GBK等。
2.字符串转字节数组在Java中,可以使用`String.getBytes(charset)`方法将字符串转换为byte数组。
其中,`charset`表示字符集,如UTF-8、GBK等。
四、byte数组与byte数组转化的应用场景1.网络传输在网络传输过程中,数据通常以byte数组的形式进行传输。
因此,在处理网络数据时,需要将字符串、整数等数据类型转换为byte数组,以便进行传输。
2.文件存储在文件存储过程中,数据也需要以byte数组的形式进行存储。
例如,在将文本文件存储到磁盘时,需要将字符串转换为byte数组,然后将byte数组写入文件。
五、总结byte数组与byte数组转化是计算机编程中常见的操作。

java中long,int,short与byte数组之间的转换//long类型转成byte数组public static byte[] longToByte(long number) {long temp = number;byte[] b = new byte[8];for (int i = 0; i < b.length; i++) {b[i] = new Long(temp & 0xff).byteValue();// 将最低位保存在最低位temp = temp >> 8; // 向右移8位}return b;}//byte数组转成longpublic static long byteToLong(byte[] b) {long s = 0;long s0 = b[0] & 0xff;// 最低位long s1 = b[1] & 0xff;long s2 = b[2] & 0xff;long s3 = b[3] & 0xff;long s4 = b[4] & 0xff;// 最低位long s5 = b[5] & 0xff;long s6 = b[6] & 0xff;long s7 = b[7] & 0xff;// s0不变s1 <<= 8;s2 <<= 16;s3 <<= 24;s4 <<= 8 * 4;s5 <<= 8 * 5;s6 <<= 8 * 6;s7 <<= 8 * 7;s = s0 | s1 | s2 | s3 | s4 | s5 | s6 | s7;return s;}/*** 注释:int到字节数组的转换!** @param number* @return*/public static byte[] intToByte(int number) {int temp = number;byte[] b = new byte[4];for (int i = 0; i < b.length; i++) {b[i] = new Integer(temp & 0xff).byteValue();// 将最低位保存在最低位temp = temp >> 8; // 向右移8位}return b;}/*** 注释:字节数组到int的转换!** @param b* @return*/public static int byteToInt(byte[] b) {int s = 0;int s0 = b[0] & 0xff;// 最低位int s1 = b[1] & 0xff;int s2 = b[2] & 0xff;int s3 = b[3] & 0xff;s3 <<= 24;s2 <<= 16;s1 <<= 8;s = s0 | s1 | s2 | s3;return s;}/*** 注释:short到字节数组的转换!** @param s* @return*/public static byte[] shortToByte(short number) {int temp = number;byte[] b = new byte[2];for (int i = 0; i < b.length; i++) {b[i] = new Integer(temp & 0xff).byteValue();// 将最低位保存在最低位temp = temp >> 8; // 向右移8位}return b;}/*** 注释:字节数组到short的转换!** @param b* @return*/public static short byteToShort(byte[] b) { short s = 0;short s0 = (short) (b[0] & 0xff);// 最低位 short s1 = (short) (b[1] & 0xff); s1 <<= 8;s = (short) (s0 | s1);return s;}。
![byte[]到short、int、long的相互转换](https://uimg.taocdn.com/7d905e11a8114431b90dd8ad.webp)

int与byte数据之间的转换 在OutputStream中写⼊⼀个int类型,会截取其低8位,丢弃其⾼24位,因此,需要将基本类型先转换为字节流。
将int数字转换为字节流1/**2 * int转byte[]3 * 该⽅法将⼀个int类型的数据转换为byte[]形式,因为int为32bit,⽽byte为8bit所以在进⾏类型转换时,知会获取低8位,4 * 丢弃⾼24位。
通过位移的⽅式,将32bit的数据转换成4个8bit的数据。
注意 &0xff,在这当中,&0xff简单理解为⼀把剪⼑,5 * 将想要获取的8位数据截取出来。
6 * @param i ⼀个int数字7 * @return byte[]8*/9public static byte[] int2ByteArray(int i){10byte[] result=new byte[4];11 result[0]=(byte)((i >> 24)& 0xFF);12 result[1]=(byte)((i >> 16)& 0xFF);13 result[2]=(byte)((i >> 8)& 0xFF);14 result[3]=(byte)(i & 0xFF);15return result;16 }17/**18 * byte[]转int19 * 利⽤int2ByteArray⽅法,将⼀个int转为byte[],但在解析时,需要将数据还原。
同样使⽤移位的⽅式,将适当的位数进⾏还原,20 * 0xFF为16进制的数据,所以在其后每加上⼀位,就相当于⼆进制加上4位。
同时,使⽤|=号拼接数据,将其还原成最终的int数据21 * @param bytes byte类型数组22 * @return int数字23*/24public static int bytes2Int(byte[] bytes){25int num=bytes[3] & 0xFF;26 num |=((bytes[2] <<8)& 0xFF00);27 num |=((bytes[1] <<16)& 0xFF0000);28 num |=((bytes[0] <<24)& 0xFF0000);29return num;30 }。
JAVA中常用数据类型之间转换的方法在Java中,常见的数据类型转换包括基本数据类型之间的转换、引用数据类型之间的转换以及基本数据类型与引用数据类型之间的转换。
下面将依次介绍这些转换方法。
1.基本数据类型之间的转换:- 自动类型转换:当两个数据类型不完全相同时,较小范围的数据类型可以自动转换为较大范围的数据类型。
例如,byte可以自动转换为short、int、long、float或double,而short可以自动转换为int、long、float或double。
- 强制类型转换:当两个数据类型完全不相同时,需要使用强制类型转换进行转换。
强制类型转换需要使用括号将目标类型放在待转换的表达式前面。
例如,int可以强制转换为byte,即`(byte)a`,其中a为int 变量。
2.引用数据类型之间的转换:- 向上转型:子类对象可以自动转换为父类对象,这种转换被称为向上转型。
向上转型可以提高代码的可扩展性和复用性。
例如,Animal类的子类可以被赋值给Animal类型的引用变量。
- 向下转型:父类对象可以通过强制类型转换为子类对象,这种转换被称为向下转型。
向下转型在编译时是合法的,但在运行时可能会抛出ClassCastException异常。
因此,在进行向下转型时,需要先使用instanceof运算符检查对象是否是目标类型的实例。
例如,Animal类的引用变量可以转换为Cat类型的引用变量,即`(Cat)animal`,其中animal为Animal类型的引用变量。
3.基本数据类型与引用数据类型之间的转换:- 基本数据类型转换为引用数据类型:基本数据类型可以通过包装类(如Integer、Double、Boolean等)的构造函数或valueOf(方法来转换为对应的包装类对象。
例如,int可以转换为Integer,即`Integer.valueOf(a)`,其中a为int变量。
- 引用数据类型转换为基本数据类型:引用数据类型可以通过调用包装类的xxxValue(方法来获取对应的基本数据类型值。
2013-08-10 8个评论作者:在路上001收藏我要投稿在Java的网络编程中传输的经常是byte数组,但我们实际中使用的数据类型可能是任一种数据类型,这就需要在它们之间相互转换,转换的核心在于将其他类型的数据的每一位转换成byte类型的数据。
下面给出相关的转换代码1.short与byte数组的互转[java]/*** 转换short为byte** @param b* @param s 需要转换的short* @param index*/public static void putShort(byte b[], short s, int index) {b[index + 1] = (byte) (s >> 8);b[index + 0] = (byte) (s >> 0);}/*** 通过byte数组取到short** @param b* @param index 第几位开始取* @return*/public static short getShort(byte[] b, int index) {return (short) (((b[index + 1] << 8) | b[index + 0] & 0xff));}/*** 转换short为byte** @param b* @param s 需要转换的short* @param index*/public static void putShort(byte b[], short s, int index) {b[index + 1] = (byte) (s >> 8);b[index + 0] = (byte) (s >> 0);}/*** 通过byte数组取到short** @param b* @param index 第几位开始取* @return*/public static short getShort(byte[] b, int index) {return (short) (((b[index + 1] << 8) | b[index + 0] & 0xff));}2.int与byte数组的互转[java]/***将32位的int值放到4字节的byte数组* @param num* @return*/public static byte[] intToByteArray(int num) {byte[] result = new byte[4];result[0] = (byte)(num >>> 24);//取最高8位放到0下标result[1] = (byte)(num >>> 16);//取次高8为放到1下标result[2] = (byte)(num >>> 8); //取次低8位放到2下标result[3] = (byte)(num ); //取最低8位放到3下标return result;}/*** 将4字节的byte数组转成一个int值* @param b* @return*/public static int byteArrayToInt(byte[] b){byte[] a = new byte[4];int i = a.length - 1,j = b.length - 1;for (; i >= 0 ; i--,j--) {//从b的尾部(即int值的低位)开始copy数据if(j >= 0)a[i] = b[j];elsea[i] = 0;//如果b.length不足4,则将高位补0}int v0 = (a[0] & 0xff) << 24;//&0xff将byte值无差异转成int,避免Java自动类型提升后,会保留高位的符号位int v1 = (a[1] & 0xff) << 16;int v2 = (a[2] & 0xff) << 8;int v3 = (a[3] & 0xff) ;return v0 + v1 + v2 + v3;}/***将32位的int值放到4字节的byte数组* @param num* @return*/public static byte[] intToByteArray(int num) {byte[] result = new byte[4];result[0] = (byte)(num >>> 24);//取最高8位放到0下标result[1] = (byte)(num >>> 16);//取次高8为放到1下标result[2] = (byte)(num >>> 8); //取次低8位放到2下标result[3] = (byte)(num ); //取最低8位放到3下标return result;}/*** 将4字节的byte数组转成一个int值* @param b* @return*/public static int byteArrayToInt(byte[] b){byte[] a = new byte[4];int i = a.length - 1,j = b.length - 1;for (; i >= 0 ; i--,j--) {//从b的尾部(即int值的低位)开始copy数据if(j >= 0)a[i] = b[j];elsea[i] = 0;//如果b.length不足4,则将高位补0}int v0 = (a[0] & 0xff) << 24;//&0xff将byte值无差异转成int,避免Java自动类型提升后,会保留高位的符号位int v1 = (a[1] & 0xff) << 16;int v2 = (a[2] & 0xff) << 8;int v3 = (a[3] & 0xff) ;return v0 + v1 + v2 + v3;}3.long与byte数组的互转[java]/*** 将64位的long值放到8字节的byte数组* @param num* @return 返回转换后的byte数组*/public static byte[] longToByteArray(long num) {byte[] result = new byte[8];result[0] = (byte) (num >>> 56);// 取最高8位放到0下标result[1] = (byte) (num >>> 48);// 取最高8位放到0下标result[2] = (byte) (num >>> 40);// 取最高8位放到0下标result[3] = (byte) (num >>> 32);// 取最高8位放到0下标result[4] = (byte) (num >>> 24);// 取最高8位放到0下标result[5] = (byte) (num >>> 16);// 取次高8为放到1下标result[6] = (byte) (num >>> 8); // 取次低8位放到2下标result[7] = (byte) (num); // 取最低8位放到3下标return result;}/*** 将8字节的byte数组转成一个long值* @param byteArray* @return 转换后的long型数值*/public static long byteArrayToInt(byte[] byteArray) {byte[] a = new byte[8];int i = a.length - 1, j = byteArray.length - 1;for (; i >= 0; i--, j--) {// 从b的尾部(即int值的低位)开始copy数据if (j >= 0)a[i] = byteArray[j];elsea[i] = 0;// 如果b.length不足4,则将高位补0}// 注意此处和byte数组转换成int的区别在于,下面的转换中要将先将数组中的元素转换成long型再做移位操作,// 若直接做位移操作将得不到正确结果,因为Java默认操作数字时,若不加声明会将数字作为int型来对待,此处必须注意。
c#数据类型转换,BYTE,float,double,char类型间的转换方法2010年07月16日星期五13:00最近由于编程的需要,对C#的类型转换做了一些研究,其内容涉及C#的装箱/拆箱/别名、数值类型间相互转换、字符的ASCII码和Unicode码、数值字符串和数值之间的转换、字符串和字符数组/字节数组之间的转换、各种数值类型和字节数组之间的转换、十六进制数输出以及日期型数据的一些转换处理,在这里与大家分享――1.装箱、拆箱还是别名许多C#.NET的书上都有介绍int->Int32是一个装箱的过程,反之则是拆箱的过程。
许多其它变量类型也是如此,如:short<->Int16,long<->Int64等。
对于一般的程序员来说,大可不必去了解这一过程,因为这些装箱和拆箱的动作都是可以自动完成的,不需要写代码进行干预。
但是我们需要记住这些类型之间的关系,所以,我们使用“别名”来记忆它们之间的关系。
C#是全面向对象的语言,比Java的面向对象都还彻底――它把简单数据类型通过默认的装箱动作封装成了类。
Int32、Int16、Int64等就是相应的类名,而那些我们熟悉的、简单易记的名称,如int、short、long等,我们就可以把它称作是Int32、Int16、Int64等类型的别名。
那么除了这三种类型之外,还有哪些类有“别名”呢?常用的有如下一些:bool -> System.Boolean (布尔型,其值为true或者false)char->System.Char(字符型,占有两个字节,表示1个Unicode字符)byte->System.Byte(字节型,占1字节,表示8位正整数,范围0~255)sbyte -> System.SByte (带符号字节型,占1字节,表示8位整数,范围-128 ~ 127)ushort->System.UInt16(无符号短整型,占2字节,表示16位正整数,范围0 ~ 65,535)uint->System.UInt32(无符号整型,占4字节,表示32位正整数,范围0 ~ 4,294,967,295)ulong->System.UInt64(无符号长整型,占8字节,表示64位正整数,范围0 ~大约10的20次方)short -> System.Int16 (短整型,占2字节,表示16位整数,范围-32,768 ~ 32,767)int -> System.Int32 (整型,占4字节,表示32位整数,范围-2,147,483,648到2,147,483,647)long -> System.Int64 (长整型,占8字节,表示64位整数,范围大约-(10的19)次方到10的19次方)float -> System.Single (单精度浮点型,占4个字节)double -> System.Double (双精度浮点型,占8个字节)我们可以用下列代码做一个实验:private void TestAlias() {//this.textBox1是一个文本框,类型为System.Windows.Forms.TextBox//设计中已经将其Multiline属性设置为truebyte a = 1; char b = 'a'; short c = 1;int d = 2; long e = 3; uint f = 4; bool g = true;this.textBox1.Text = "";this.textBox1.AppendText("byte -> "+ a.GetType().FullName + "\n");this.textBox1.AppendText("char -> "+ b.GetType().FullName + "\n");this.textBox1.AppendText("short->"+c.GetType().FullName+"\n");this.textBox1.AppendText("int -> "+ d.GetType().FullName + "\n");this.textBox1.AppendText("long -> "+ e.GetType().FullName + "\n");this.textBox1.AppendText("uint -> "+ f.GetType().FullName + "\n");this.textBox1.AppendText("bool -> "+ g.GetType().FullName + "\n");}在窗体中新建一个按钮,并在它的单击事件中调用该TestAlias()函数,我们将看到运行结果如下:byte -> System.Bytechar -> System.Charshort -> System.Int16int -> System.Int32long -> System.Int64uint -> System.UInt32bool -> System.Boolean这足以说明各别名对应的类!2.数值类型之间的相互转换这里所说的数值类型包括byte, short, int, long, fload, double等,根据这个排列顺序,各种类型的值依次可以向后自动进行转换。
c语言不同数据类型间的混合运算转换规则+常见数据类型【C语言中不同数据类型间的混合运算转换规则+常见数据类型】在C语言中,数据类型是一种非常重要的概念。
在编写程序时,我们经常会涉及到不同类型数据的运算和转换。
本文将探讨C语言中不同数据类型间的混合运算转换规则,以及介绍常见的数据类型。
一、常见的数据类型1. 整型在C语言中,整型数据类型用于存储整数。
常见的整型数据类型包括int、short、long和long long。
这些数据类型在内存中占据的空间大小有所不同。
2. 浮点型浮点型数据类型用于存储带有小数点的数值。
常见的浮点型数据类型包括float、double和long double。
这些数据类型可以用来表示不同精度的浮点数。
3. 字符型字符型数据类型用于存储单个字符。
在C语言中,字符型数据类型用char表示。
4. 其他类型除了上述三种常见的数据类型之外,C语言还有一些其他类型,比如指针类型、数组类型、结构体类型等。
二、混合运算转换规则在C语言中,当不同类型的数据进行混合运算时,会涉及到数据类型的转换规则。
一般来说,C语言中的数据类型转换可以分为隐式转换和显式转换两种方式。
1. 隐式转换在C语言中,当不同类型的数据进行运算时,编译器会自动进行类型转换。
这种转换方式称为隐式转换。
隐式转换一般遵循以下规则:a. 如果参与运算的两个数据类型不同,系统会自动将宽度小的数据类型转换为宽度大的数据类型。
b. 如果参与运算的数据类型包括有符号数据类型和无符号数据类型,系统会自动将有符号数据类型转换为无符号数据类型。
c. 如果参与运算的数据类型包括整型和浮点型,系统会自动将整型转换为浮点型。
2. 显式转换除了隐式转换之外,C语言还支持显式转换。
在显式转换中,程序员可以通过强制类型转换的方式来改变数据类型。
在C语言中,使用强制类型转换可以通过类型名将需要转换的数据括在括号中,例如(int)x。
三、个人观点和理解在实际编程中,了解不同数据类型的转换规则是非常重要的。
byte数组与byte数组转化摘要:1.Byte 数组的概念和基本操作2.Byte 数组与其他数据类型的转换3.Byte 数组与字节数组的转换4.示例代码及注意事项正文:一、Byte 数组的概念和基本操作Byte 数组(字节数组)是Java 中一种数据类型,用于存储一组字节(byte)数据。
每个字节占用1 个字节空间,可以存储-128 到127 之间的整数。
Byte 数组可以进行各种基本操作,如创建、初始化、访问元素、修改元素值、遍历等。
二、Byte 数组与其他数据类型的转换1.Byte 数组转换为字符数组当Byte 数组存储的是ASCII 字符时,可以通过以下方法将其转换为字符数组:```javabyte[] byteArray = {72, 101, 108, 108, 111}; // Hellochar[] charArray = new char[byteArray.length];for (int i = 0; i < byteArray.length; i++) {charArray[i] = (char) byteArray[i];}```2.字符数组转换为Byte 数组当字符数组存储的是ASCII 字符时,可以通过以下方法将其转换为Byte 数组:```javachar[] charArray = {"H", "e", "l", "l", "o"};byte[] byteArray = new byte[charArray.length];for (int i = 0; i < charArray.length; i++) {byteArray[i] = (byte) charArray[i];}```3.Byte 数组转换为整数数组当Byte 数组存储的是有符号整数时,可以通过以下方法将其转换为整数数组:```javabyte[] byteArray = {72, 101, 108, 108, 111}; // -2, 1, -2, -2, 11int[] intArray = new int[byteArray.length];for (int i = 0; i < byteArray.length; i++) {intArray[i] = byteArray[i];}```4.整数数组转换为Byte 数组当整数数组存储的是有符号整数时,可以通过以下方法将其转换为Byte 数组:```javaint[] intArray = {72, 101, 108, 108, 111}; // -2, 1, -2, -2, 11byte[] byteArray = new byte[intArray.length];for (int i = 0; i < intArray.length; i++) {byteArray[i] = (byte) intArray[i];}```三、Byte 数组与字节数组的转换在Java 中,字节数组(byte[])和Byte 数组(Byte[])是相同的,因此它们之间的转换非常简单。
Java中byte、short、char、int、long运算时⾃动类型转化问题--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------★★⾃动(隐式、默认)类型转换与强制(显式)类型转换★★ 1) boolean类型不参与转换 2) 默认转换 A:从⼩到⼤ B:byte,short,char --» int --» long --» float --» double C:byte,short,char之间不相互转换,直接转成int类型参与运算。
3) 强制转换 A:从⼤到⼩ B:可能会有精度的损失,⼀般不建议这样使⽤。
C:格式: ⽬标数据类型变量名 = (⽬标数据类型) (被转换的数据);★★表达式的式值★★int a = 10;int b = 20;int c = (a = b); //赋值式本⾝也是表达式,所以它也有式值--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------⼤家都知道,在进⾏运算时,Java会隐式的⾃动进⾏类型转化。
那么有哪些情况会进⾏转化呢?总结如下:(⼀)算术运算符1) 单⽬运算符:+(取正)、-(取负)、 ++(⾃增1)、 --(⾃减1)a) +(取正)、-(取负) 当操作数是byte,short,char时,会⾃动转化为int类型;返回结果为int。
当操作数是int,long时,不转化,原来是啥类型,还是啥类型。
b) ++(⾃增1)、 --(⾃减1) 不管操作数是啥类型,不转化。
2) 双⽬运算符:+、 -、 *、 /、 %(取余) 当两个操作数中没有long类型时,两个操作数中⾮int类型会先⾃动转换为int类型,再参与运算,返回结果为int; 当两个操作数中含有long类型时,两个操作数中⾮long类型会⾃动转换为long类型,再参与运算,返回结果为long;(⼆)位运算符1) &(按位与)、|(按位或)、^(按位异或) 当两个操作数中没有long类型时,两个操作数中⾮int类型会先⾃动转换为int类型,再参与运算,返回结果为int; 当两个操作数中含有long类型时,两个操作数中⾮long类型会⾃动转换为long类型,再参与运算,返回结果为long;2) ~(按位⾮) 当操作数是byte,short,char时,会⾃动转化为int类型;返回结果为int。
1.2.package com.test;3.4.import java.nio.ByteBuffer;5.6.public class ByteUtil {7.8./**9. * @param args10. */11. public static void main(String[] args) {12. test2();13. }14. public static void test2()15. {16. short s = -20;17. byte[] b = new byte[2];18. putReverseBytesShort(b, s, 0);19. ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(2);20. buf.put(b);21. buf.flip();22. System.out.println(getReverseBytesShort(b, 0));23. System.out.println(Short.reverseBytes(buf.getShort()));24. System.out.println("***************************");25. int i = -40;26. b = new byte[4];27. putReverseBytesInt(b, i, 0);28. buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(4);29. buf.put(b);30. buf.flip();31. System.out.println(getReverseBytesInt(b, 0));32. System.out.println(Integer.reverseBytes(buf.getInt()));33. System.out.println("***************************");34. long l = -50;35. b = new byte[8];36. putReverseBytesLong(b, l, 0);37. buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(8);38. buf.put(b);39. buf.flip();40. System.out.println(getReverseBytesLong(b, 0));41. System.out.println(Long.reverseBytes(buf.getLong()));42. System.out.println("***************************");43. }44. public static void test1()45. {46. short s = -20;47. byte[] b = new byte[2];48. putShort(b, s, 0);49. ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(2);50. buf.put(b);51. buf.flip();52. System.out.println(getShort(b, 0));53. System.out.println(buf.getShort());54. System.out.println("***************************");55. int i = -40;56. b = new byte[4];57. putInt(b, i, 0);58. buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(4);59. buf.put(b);60. buf.flip();61. System.out.println(getInt(b, 0));62. System.out.println(buf.getInt());63. System.out.println("***************************");64. long l = -50;65. b = new byte[8];66. putLong(b, l, 0);67. buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(8);68. buf.put(b);69. buf.flip();70. System.out.println(getLong(b, 0));71. System.out.println(buf.getLong());72. System.out.println("***************************");73. }74. public static void putShort(byte b[], short s, int index){75. b[index] = (byte) (s >> 8);76. b[index + 1] = (byte) (s >> 0);77. }78. public static void putReverseBytesShort(byte b[], short s,int index) {79. b[index] = (byte) (s >> 0);80. b[index + 1] = (byte) (s >> 8);81. }82. public static short getShort(byte[] b, int index) {83. return (short) (((b[index] << 8) | b[index + 1] & 0xff));84. }85. public static short getReverseBytesShort(byte[] b, int index) {86. return (short) (((b[index+1] << 8) | b[index] & 0xff));87. }88.89. // ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////90. public static void putInt(byte[] bb, int x, int index) {91. bb[index + 0] = (byte) (x >> 24);92. bb[index + 1] = (byte) (x >> 16);93. bb[index + 2] = (byte) (x >> 8);94. bb[index + 3] = (byte) (x >> 0);95. }96. public static void putReverseBytesInt(byte[] bb, int x, intindex) {97. bb[index + 3] = (byte) (x >> 24);98. bb[index + 2] = (byte) (x >> 16);99. bb[index + 1] = (byte) (x >> 8);100. bb[index + 0] = (byte) (x >> 0);101. }102.103.public static int getInt(byte[] bb, int index) {104.return (int) ((((bb[index + 0] & 0xff) << 24) 105. | ((bb[index + 1] & 0xff) << 16)106. | ((bb[index + 2] & 0xff) << 8) | ((bb[ind ex + 3] & 0xff) << 0)));107. }108.public static int getReverseBytesInt(byte[] bb, int in dex) {109.return (int) ((((bb[index + 3] & 0xff) << 24) 110. | ((bb[index + 2] & 0xff) << 16)111. | ((bb[index + 1] & 0xff) << 8) | ((bb[ind ex + 0] & 0xff) << 0)));112. }113.114.// /////////////////////////////////////////////////// //////115.public static void putLong(byte[] bb, long x, int inde x) {116. bb[index + 0] = (byte) (x >> 56);117. bb[index + 1] = (byte) (x >> 48);118. bb[index + 2] = (byte) (x >> 40);119. bb[index + 3] = (byte) (x >> 32);120. bb[index + 4] = (byte) (x >> 24);121. bb[index + 5] = (byte) (x >> 16);122. bb[index + 6] = (byte) (x >> 8);123. bb[index + 7] = (byte) (x >> 0);124. }125.public static void putReverseBytesLong(byte[] bb, long x, int index) {126. bb[index + 7] = (byte) (x >> 56);127. bb[index + 6] = (byte) (x >> 48);128. bb[index + 5] = (byte) (x >> 40);129. bb[index + 4] = (byte) (x >> 32);130. bb[index + 3] = (byte) (x >> 24);131. bb[index + 2] = (byte) (x >> 16);132. bb[index + 1] = (byte) (x >> 8);133. bb[index + 0] = (byte) (x >> 0);134. }135.136.public static long getLong(byte[] bb, int index) { 137.return ((((long) bb[index + 0] & 0xff) << 56) 138. | (((long) bb[index + 1] & 0xff) << 48) 139. | (((long) bb[index + 2] & 0xff) << 40) 140. | (((long) bb[index + 3] & 0xff) << 32) 141. | (((long) bb[index + 4] & 0xff) << 24) 142. | (((long) bb[index + 5] & 0xff) << 16) 143. | (((long) bb[index + 6] & 0xff) << 8) | ( ((long) bb[index + 7] & 0xff) << 0));144. }145.public static long getReverseBytesLong(byte[] bb, int index) {146.return ((((long) bb[index + 7] & 0xff) << 56) 147. | (((long) bb[index + 6] & 0xff) << 48) 148. | (((long) bb[index + 5] & 0xff) << 40) 149. | (((long) bb[index + 4] & 0xff) << 32) 150. | (((long) bb[index + 3] & 0xff) << 24) 151. | (((long) bb[index + 2] & 0xff) << 16) 152. | (((long) bb[index + 1] & 0xff) << 8) | ( ((long) bb[index + 0] & 0xff) << 0));153. }154.}。